Vibrationdata FEA Matlab GUI Package User Guide Revision A
|
|
|
- Estella Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vibrationdata FEA Matlab GUI Package User Guide Revision A By Tom Irvine tom@vibrationdata.com March 25, 2014 Introduction Matlab Script: vibrationdata_fea_preprocessor.zip vibrationdata_fea_preprocessor.m is the main script. The remaining scripts are supporting functions. The user is responsible for consistent units. The package allows for nodes and elements in a 3D space. There are three translational and three rotational degrees-of-freedom per node. The available elements are dof springs, point masses and rigid links. Additional elements will be included in future revisions, such as beams, plates, gap springs, etc. This package began as a preprocessor, but it will solve for the normal modes. Forced response and enforced acceleration will added in future revisions, both for frequency and time domain analyses. Static analysis and buckling are also on the to-do list. The scripts have some error-detection capability, but further checks are needed. The data may be input manually or through an input file as shown in the following example. Examples Examples are given in the appendices. 1
2 References 1. T. Irvine, Two-degree-of-freedom System Subjected to a Half-sine Pulse Force, Revision A, Vibrationdata, T. Irvine, Sample Lateral Natural Frequency Calculations for a Space Vehicle/Dispenser Analysis, Vibrationdata, T. Irvine, Assembly of Subsystem Matrices, Revision B, Vibrationdata,
3 APPENDIX A Example Consider the two-degree-of-freedom system in Figure A-1 with the mass and stiffness values shown in Table A-1. k 3 m2 x 2 k 2 m1 x 1 k 1 Figure A-1. Two-degree-of-freedom System, Springs & Masses Table A-1. Parameters Variable Value Unit m lbf sec^2/in m lbf sec^2/in k 1 400,000 lbf/in k 2 300,000 lbf/in k 3 100,000 lbf/in The equations of motion for this system are given in Reference 1. 3
4 The data could be added manually into the vibrationdata_fea_preprocessor script. Or it could be imported via a file. The input file could either be an ASCII text or Excel file. Here is the input file and its format. The row order is unimportant. Lower case must be used for the identifying text labels. Underscores must be used where there are two or more words in the label. Node Node Node Node point_mass point_mass dof_spring_property dof_spring_property dof_spring_property dof_spring_element dof_spring_element dof_spring_element The node format is: node Node number X coord Y coord Z coord TX TY TZ RX RY RZ TX, TY & TZ are the translational constraints in the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. RX, RY & RZ are the rotational constraints about the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. A constraint value of 1 means fixed. A value of 0 indicates free. 4
5 The point_mass format is: point_mass Node number mass JX JY JZ JX, JY & JZ are the polar moments of inertia about the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. The dof_spring_property format is: dof_spring_property Spring Property Number KX KY KZ K theta X K theta Y K theta Z KX, KY & KZ are the translational stiffness values in the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. The dimension is [force/length]. K theta X, K theta Y & K theta Z are the rotational stiffness values about the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. The dimension is [force/radian]. The stiffness values may be set to zero is the corresponding dofs are to be constrained. The axes are global. The dof_spring_element format is: dof_spring_element Spring Property Number Node 1 Node 2 5
6 Figure A-2. Two-degree-of-freedom System, Finite Element Model The blue lines are the dof springs. The red circles are point masses. The numbers are node numbers. The nodal coordinate spacing is somewhat arbitrary for this example since neither the stiffness nor point mass depends on length. 6
7 The normal modes results from vibrationdata_fea_preprocessor are: mass = stiffness = Natural Frequencies n f(hz) ModeShapes
8 APPENDIX B Example The three-degree-of-freedom system in Figure B-1 is taken from Reference 2. It is a real-world problem from a launch vehicle/dispenser analysis. This example will demonstrate the use of rigid link elements, although the analysis could have been performed without the links. x 2 x 3 m2 m3 k 2 k 3 m1 x 1 k 1 Figure B-1. Three-degree-of-freedom System, Springs & Masses Table B-1. Parameters Variable Value Unit m kg m Kg m Kg k e+08 N/m k e+07 N/m 8
9 Here is the model file. node node node node node node point_mass point_mass point_mass dof_spring_property E dof_spring_property dof_spring_element dof_spring_element dof_spring_element rigid_link rigid_link The rigid_link format is: rigid_link Primary Node Secondary Node TX TY TZ RX RY RZ TX, TY & TZ are the translational links in the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. RX, RY & RZ are the rotational links about the X, Y & Z-axes, respectively. A constraint value of 1 means connected. A value of 0 indicates disconnected. 9
10 Figure B-2. Three-degree-of-freedom System, Finite Element Model The blue lines are the dof springs. The black lines are rigid links. The red circles are point masses. The numbers are node numbers. Again, the nodal coordinate spacing is somewhat arbitrary for this example since neither the stiffness nor point mass depends on length. 10
11 The normal modes results from vibrationdata_fea_preprocessor are: mass = stiffness = Natural Frequencies n f(hz) ModeShapes =
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
CRAIG-BAMPTON METHOD FOR A TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM Revision C
 CRAIG-BAMPON MEHOD FOR A WO COMPONEN SYSEM Revision C By om Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com May, 03 Introduction he Craig-Bampton method is method for reducing the size of a finite element model, particularly
CRAIG-BAMPON MEHOD FOR A WO COMPONEN SYSEM Revision C By om Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com May, 03 Introduction he Craig-Bampton method is method for reducing the size of a finite element model, particularly
SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C
 SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com November 19, 2010 Introduction This report gives a method for determining the response of
SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com November 19, 2010 Introduction This report gives a method for determining the response of
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I B To Irvine Eail: to@vibrationdata.co Deceber, 5 Introduction The effective odal ass provides a ethod for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I B To Irvine Eail: to@vibrationdata.co Deceber, 5 Introduction The effective odal ass provides a ethod for judging the significance of a vibration
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F
 MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A. By Tom Irvine February 25, 2008
 TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
Quintic beam closed form matrices (revised 2/21, 2/23/12) General elastic beam with an elastic foundation
 General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
Direct Fatigue Damage Spectrum Calculation for a Shock Response Spectrum
 Direct Fatigue Damage Spectrum Calculation for a Shock Response Spectrum By Tom Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com June 25, 2014 Introduction A fatigue damage spectrum (FDS) was calculated for a number
Direct Fatigue Damage Spectrum Calculation for a Shock Response Spectrum By Tom Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com June 25, 2014 Introduction A fatigue damage spectrum (FDS) was calculated for a number
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine May 24, 2010
 SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
General elastic beam with an elastic foundation
 General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
General elastic beam with an elastic foundation Figure 1 shows a beam-column on an elastic foundation. The beam is connected to a continuous series of foundation springs. The other end of the foundation
Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms
 Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms Introduction SPACAR Mechanical Automation (WA) Room: HR Z 2.29 Phone: (053) 489 2557 Email: R.G.K.M.Aarts@utwente.nl Info: http://www.wa.ctw.utwente.nl/lectures/113173/
Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms Introduction SPACAR Mechanical Automation (WA) Room: HR Z 2.29 Phone: (053) 489 2557 Email: R.G.K.M.Aarts@utwente.nl Info: http://www.wa.ctw.utwente.nl/lectures/113173/
Program System for Machine Dynamics. Abstract. Version 5.0 November 2017
 Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Random Vibration Analysis in FEMAP An Introduction to the Hows and Whys
 Random Vibration Analysis in FEMAP An Introduction to the Hows and Whys Adrian Jensen, PE Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer Kyle Hamilton Staff Mechanical Engineer Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4
Random Vibration Analysis in FEMAP An Introduction to the Hows and Whys Adrian Jensen, PE Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer Kyle Hamilton Staff Mechanical Engineer Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4
k 21 k 22 k 23 k 24 k 31 k 32 k 33 k 34 k 41 k 42 k 43 k 44
 CE 6 ab Beam Analysis by the Direct Stiffness Method Beam Element Stiffness Matrix in ocal Coordinates Consider an inclined bending member of moment of inertia I and modulus of elasticity E subjected shear
CE 6 ab Beam Analysis by the Direct Stiffness Method Beam Element Stiffness Matrix in ocal Coordinates Consider an inclined bending member of moment of inertia I and modulus of elasticity E subjected shear
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic. FEMAP & NX Nastran
 Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Optimized PSD Envelope for Nonstationary Vibration Revision A
 ACCEL (G) Optimized PSD Envelope for Nonstationary Vibration Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com July, 014 10 FLIGHT ACCELEROMETER DATA - SUBORBITAL LAUNCH VEHICLE 5 0-5 -10-5 0 5 10
ACCEL (G) Optimized PSD Envelope for Nonstationary Vibration Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tom@vibrationdata.com July, 014 10 FLIGHT ACCELEROMETER DATA - SUBORBITAL LAUNCH VEHICLE 5 0-5 -10-5 0 5 10
Numerical simulation of surface ship hull beam whipping response due to submitted underwater explosion
 Numerical simulation of surface ship hull beam whipping response due to submitted underwater explosion Presenter / Ssu-Chieh Tsai Supervisor / Pr. Hervé Le Sourne 1 March 2017, Rostock 1 Motivation UNDEX
Numerical simulation of surface ship hull beam whipping response due to submitted underwater explosion Presenter / Ssu-Chieh Tsai Supervisor / Pr. Hervé Le Sourne 1 March 2017, Rostock 1 Motivation UNDEX
Workshop 8. Lateral Buckling
 Workshop 8 Lateral Buckling cross section A transversely loaded member that is bent about its major axis may buckle sideways if its compression flange is not laterally supported. The reason buckling occurs
Workshop 8 Lateral Buckling cross section A transversely loaded member that is bent about its major axis may buckle sideways if its compression flange is not laterally supported. The reason buckling occurs
NATURAL FREQUENCIES OF A HONEYCOMB SANDWICH PLATE Revision F. A diagram of a honeycomb plate cross-section is shown in Figure 1.
 NATURAL FREQUENCIES OF A HONEYCOMB SANDWICH PLATE Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 5, 008 Bending Stiffness of a Honeycomb Sandwich Plate A diagram of a honeycomb plate cross-section
NATURAL FREQUENCIES OF A HONEYCOMB SANDWICH PLATE Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 5, 008 Bending Stiffness of a Honeycomb Sandwich Plate A diagram of a honeycomb plate cross-section
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser
 Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
FEM Validation. 12th January David Schmid Teamleader Structural Analysis
 FEM Validation 12th January 2012 David Schmid Teamleader Structural Analysis FEM Validation and Verification Each FE model which is used to substantiate flight material must be verified Depending on the
FEM Validation 12th January 2012 David Schmid Teamleader Structural Analysis FEM Validation and Verification Each FE model which is used to substantiate flight material must be verified Depending on the
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (SI Units)
 WORKSHOP 6 Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometrical representation of a cantilever beam. Use this geometry model to define an MSC/NASTRAN analysis model comprised
WORKSHOP 6 Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometrical representation of a cantilever beam. Use this geometry model to define an MSC/NASTRAN analysis model comprised
A Case Study of Modal Mass Acceleration Curve Loads vs. Sine Loads
 A Case Study of Modal Mass Acceleration Curve Loads vs. Sine Loads Ramses Mourhatch Bing-Chung Chen Walter Tsuha Peyman Mohasseb Chia-Yen Peng Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
A Case Study of Modal Mass Acceleration Curve Loads vs. Sine Loads Ramses Mourhatch Bing-Chung Chen Walter Tsuha Peyman Mohasseb Chia-Yen Peng Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5
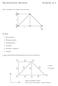 Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
Methods of Analysis. Force or Flexibility Method
 INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
Software Verification
 POGAM NAME: EVISION NO.: 0 EXAMPLE 6-005 LINK DAMPE ELEMENT UNDE HAMONIC LOADING POBLEM DESCIPTION In this single degree of freedom example a spring-mass-damper system is subjected to a harmonic load.
POGAM NAME: EVISION NO.: 0 EXAMPLE 6-005 LINK DAMPE ELEMENT UNDE HAMONIC LOADING POBLEM DESCIPTION In this single degree of freedom example a spring-mass-damper system is subjected to a harmonic load.
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011
 EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
FEA A Guide to Good Practice. What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice
 FEA A Guide to Good Practice What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice 1. Background Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has transformed design procedures for engineers. Allowing more
FEA A Guide to Good Practice What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice 1. Background Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has transformed design procedures for engineers. Allowing more
Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (CBAR Problem)
 WORKSHOP 17 Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (CBAR Problem) Objectives: Create a geometrical representation of a cantilever beam. Use this geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran analysis model
WORKSHOP 17 Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam (CBAR Problem) Objectives: Create a geometrical representation of a cantilever beam. Use this geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran analysis model
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Multi-Degree-of-Freedom System Response to Multipoint Base Excitation
 lti-degree-of-freeo Syste Response to ltipoint Base Ecitation By o Irvine Eail: to@vibrationata.co October 6, Introction, J Figre. ( - ( + Figre. he free-boy iagra is given in Figre. he syste has a CG
lti-degree-of-freeo Syste Response to ltipoint Base Ecitation By o Irvine Eail: to@vibrationata.co October 6, Introction, J Figre. ( - ( + Figre. he free-boy iagra is given in Figre. he syste has a CG
Static Equilibrium. University of Arizona J. H. Burge
 Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
SHOCK AND VIBRATION RESPONSE SPECTRA COURSE Unit 6B. Notes on the Fourier Transform Magnitude
 SHOCK AND VIBRATION RESPONSE SPECTRA COURSE Unit 6B. Notes on the Fourier Transform Magnitude By Tom Irvine Introduction Fourier transforms, which were introduced in Unit 6A, have a number of potential
SHOCK AND VIBRATION RESPONSE SPECTRA COURSE Unit 6B. Notes on the Fourier Transform Magnitude By Tom Irvine Introduction Fourier transforms, which were introduced in Unit 6A, have a number of potential
4 Finite Element Method for Trusses
 4 Finite Element Method for Trusses To solve the system of linear equations that arises in IPM, it is necessary to assemble the geometric matrix B a. For the sake of simplicity, the applied force vector
4 Finite Element Method for Trusses To solve the system of linear equations that arises in IPM, it is necessary to assemble the geometric matrix B a. For the sake of simplicity, the applied force vector
OpenSees Navigator. OpenSees Navigator
 Andreas Schellenberg & Tony Yang University of California at Berkeley Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center Introduction: MATLAB based Graphical User Interface Create 2D/3D structural models for
Andreas Schellenberg & Tony Yang University of California at Berkeley Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center Introduction: MATLAB based Graphical User Interface Create 2D/3D structural models for
#SEU16. FEA in Solid Edge and FEMAP Mark Sherman
 FEA in Solid Edge and FEMAP Mark Sherman Realize innovation. FEMAP Continuous development with the same core team! Since 1985 there have been more than 35 releases of FEMAP with only one major architecture
FEA in Solid Edge and FEMAP Mark Sherman Realize innovation. FEMAP Continuous development with the same core team! Since 1985 there have been more than 35 releases of FEMAP with only one major architecture
APPENDIX 4.8.B GSMT IMAGE QUALITY DEGRADATION DUE TO WIND LOAD
 APPENDIX 4.8.B GSMT IMAGE QUALITY DEGRADATION DUE TO WIND LOAD Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office, December 2001. GSMT Image Quality Degradation due to Wind Load NIO-TNT-003 Issue 1.B 05-Dec-2001
APPENDIX 4.8.B GSMT IMAGE QUALITY DEGRADATION DUE TO WIND LOAD Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office, December 2001. GSMT Image Quality Degradation due to Wind Load NIO-TNT-003 Issue 1.B 05-Dec-2001
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Using MATLAB and. Abaqus. Finite Element Analysis. Introduction to. Amar Khennane. Taylor & Francis Croup. Taylor & Francis Croup,
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using MATLAB and Abaqus Amar Khennane Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using MATLAB and Abaqus Amar Khennane Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Module - 01 Lecture - 13
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
FEA CODE WITH MATLAB. Finite Element Analysis of an Arch ME 5657 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD. Submitted by: ALPAY BURAK DEMIRYUREK
 FEA CODE WITH MATAB Finite Element Analysis of an Arch ME 5657 FINITE EEMENT METHOD Submitted by: APAY BURAK DEMIRYUREK This report summarizes the finite element analysis of an arch-beam with using matlab.
FEA CODE WITH MATAB Finite Element Analysis of an Arch ME 5657 FINITE EEMENT METHOD Submitted by: APAY BURAK DEMIRYUREK This report summarizes the finite element analysis of an arch-beam with using matlab.
10. Applications of 1-D Hermite elements
 10. Applications of 1-D Hermite elements... 1 10.1 Introduction... 1 10.2 General case fourth-order beam equation... 3 10.3 Integral form... 5 10.4 Element Arrays... 7 10.5 C1 Element models... 8 10.6
10. Applications of 1-D Hermite elements... 1 10.1 Introduction... 1 10.2 General case fourth-order beam equation... 3 10.3 Integral form... 5 10.4 Element Arrays... 7 10.5 C1 Element models... 8 10.6
BECAS - an Open-Source Cross Section Analysis Tool
 BECAS - an Open-Source Cross Section Analysis Tool José P. Blasques and Robert D. Bitsche Presented at DTU Wind Energy stand at the EWEA 2012 conference, Copenhagen, 16.4.2012 BECAS-DTUWind@dtu.dk Motivation
BECAS - an Open-Source Cross Section Analysis Tool José P. Blasques and Robert D. Bitsche Presented at DTU Wind Energy stand at the EWEA 2012 conference, Copenhagen, 16.4.2012 BECAS-DTUWind@dtu.dk Motivation
Estimation of Rotational FRFs via Cancellation Methods
 Estimation of Rotational FRFs via Cancellation Methods Nomenclature ij ( l, k ) ij M. Reza shory, Semnan university, Iran Email: mashoori@semnan.ac.ir exact ccelerance measured accelerance when two mechanical
Estimation of Rotational FRFs via Cancellation Methods Nomenclature ij ( l, k ) ij M. Reza shory, Semnan university, Iran Email: mashoori@semnan.ac.ir exact ccelerance measured accelerance when two mechanical
Solve the problem. Determine the center and radius of the circle. Use the given information about a circle to find its equation.
 Math1314-TestReview2-Spring2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Is the point (-5, -3) on the circle defined
Math1314-TestReview2-Spring2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Is the point (-5, -3) on the circle defined
Final Exam April 30, 2013
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-203 Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book No additional data is attached
9210-203 Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book No additional data is attached
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT
 APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
EFFECTIVITY PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE 24/07/14 24/07/14
 173 ROCHEFORT FAX: (33) 5 46 87 4 12 EFFECTIVITY PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 24/7/14 24/7/14 24/7/14 24/7/14
173 ROCHEFORT FAX: (33) 5 46 87 4 12 EFFECTIVITY PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE PAGE DATE ISSUE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 24/7/14 24/7/14 24/7/14 24/7/14
Homogeneous Transformations
 Purpose: Homogeneous Transformations The purpose of this chapter is to introduce you to the Homogeneous Transformation. This simple 4 x 4 transformation is used in the geometry engines of CAD systems and
Purpose: Homogeneous Transformations The purpose of this chapter is to introduce you to the Homogeneous Transformation. This simple 4 x 4 transformation is used in the geometry engines of CAD systems and
COMPONENT MODE SYNTHESIS, FIXED-INTERFACE MODEL Revision A
 COMPONEN MODE SYNHESS, FXED-NERFACE MODEL Revision A By o rvine Eail: toirvine@aol.co February, ntroduction Coponent ode synthesis is a ethod for analyzing the dynaic behavior of a syste consisting of
COMPONEN MODE SYNHESS, FXED-NERFACE MODEL Revision A By o rvine Eail: toirvine@aol.co February, ntroduction Coponent ode synthesis is a ethod for analyzing the dynaic behavior of a syste consisting of
ME101 (Division III) webpage
 ME101 (Division III) webpage Lecture Slides available on http://www.iitg.ernet.in/kd/me101.htm Also available on: http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~kd/me101.htm Equivalent Systems: Resultants Equilibrium Equilibrium
ME101 (Division III) webpage Lecture Slides available on http://www.iitg.ernet.in/kd/me101.htm Also available on: http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~kd/me101.htm Equivalent Systems: Resultants Equilibrium Equilibrium
Finite Element Method
 Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered in this course one dimensional
Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered in this course one dimensional
Dynamic Loads CE 543. Examples. Harmonic Loads
 CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
The Spring Pendulum. Nick Whitman. May 16, 2000
 The Spring Pendulum Nick Whitman May 16, 2 Abstract The spring pendulum is analyzed in three dimensions using differential equations and the Ode45 solver in Matlab. Newton s second law is used to write
The Spring Pendulum Nick Whitman May 16, 2 Abstract The spring pendulum is analyzed in three dimensions using differential equations and the Ode45 solver in Matlab. Newton s second law is used to write
3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN
 3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN MSC/NASTRAN is a general purpose finite element analysis program used in the field of static, dynamic, nonlinear, thermal, and optimization and is a FORTRAN program containing
3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN MSC/NASTRAN is a general purpose finite element analysis program used in the field of static, dynamic, nonlinear, thermal, and optimization and is a FORTRAN program containing
BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS
 CIMS 4 Fourth International Conference on Coupled Instabilities in Metal Structures Rome, Italy, 27-29 September, 24 BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS S. ÁDÁNY,
CIMS 4 Fourth International Conference on Coupled Instabilities in Metal Structures Rome, Italy, 27-29 September, 24 BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS S. ÁDÁNY,
Coding isothermal Reynolds equation in Matlab and comparing with analytical solution for the OOOO boundary condition
 Mechanics of Microsystems : Micro/nano Mechanics (NE 211) Course Project Coding isothermal Reynolds equation in Matlab and comparing with analytical solution for the OOOO boundary condition More S. K.
Mechanics of Microsystems : Micro/nano Mechanics (NE 211) Course Project Coding isothermal Reynolds equation in Matlab and comparing with analytical solution for the OOOO boundary condition More S. K.
Part D: Frames and Plates
 Part D: Frames and Plates Plane Frames and Thin Plates A Beam with General Boundary Conditions The Stiffness Method Thin Plates Initial Imperfections The Ritz and Finite Element Approaches A Beam with
Part D: Frames and Plates Plane Frames and Thin Plates A Beam with General Boundary Conditions The Stiffness Method Thin Plates Initial Imperfections The Ritz and Finite Element Approaches A Beam with
CAEFEM v9.5 Information
 CAEFEM v9.5 Information Concurrent Analysis Corporation, 50 Via Ricardo, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 USA Tel. (805) 375 1060, Fax (805) 375 1061 email: info@caefem.com or support@caefem.com Web: http://www.caefem.com
CAEFEM v9.5 Information Concurrent Analysis Corporation, 50 Via Ricardo, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 USA Tel. (805) 375 1060, Fax (805) 375 1061 email: info@caefem.com or support@caefem.com Web: http://www.caefem.com
Engineering Mechanics: Statics. Chapter 7: Virtual Work
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 7: Virtual Work Introduction Previous chapters-- FBD & zero-force and zero-moment equations -- Suitable when equilibrium position is known For bodies composed of
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 7: Virtual Work Introduction Previous chapters-- FBD & zero-force and zero-moment equations -- Suitable when equilibrium position is known For bodies composed of
Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000
 26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
Leaf Spring (Material, Contact, geometric nonlinearity)
 00 Summary Summary Nonlinear Static Analysis - Unit: N, mm - Geometric model: Leaf Spring.x_t Leaf Spring (Material, Contact, geometric nonlinearity) Nonlinear Material configuration - Stress - Strain
00 Summary Summary Nonlinear Static Analysis - Unit: N, mm - Geometric model: Leaf Spring.x_t Leaf Spring (Material, Contact, geometric nonlinearity) Nonlinear Material configuration - Stress - Strain
Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan
 Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan Instant download and all chapters Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan https://testbandata.com/download/solution-manual-first-course-finite-elementmethod-5th-edition-logan/
Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan Instant download and all chapters Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan https://testbandata.com/download/solution-manual-first-course-finite-elementmethod-5th-edition-logan/
Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
Effect of Mass Matrix Formulation Schemes on Dynamics of Structures
 Effect of Mass Matrix Formulation Schemes on Dynamics of Structures Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Sudeep Bosu Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR,
Effect of Mass Matrix Formulation Schemes on Dynamics of Structures Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Sudeep Bosu Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR,
Computational Stiffness Method
 Computational Stiffness Method Hand calculations are central in the classical stiffness method. In that approach, the stiffness matrix is established column-by-column by setting the degrees of freedom
Computational Stiffness Method Hand calculations are central in the classical stiffness method. In that approach, the stiffness matrix is established column-by-column by setting the degrees of freedom
Project Engineer: Wesley Kinkler Project Number: 4.14 Submission Date: 11/15/2003. TAMUK Truss Company Trusses Made Simple
 Submission Date: 11/15/2003 TAMUK Truss Company Trusses Made Simple Table of Contents Introduction..3 Proposal.3 Solution..5 Hand Calculations 5 TRUSS2D 7 NENastran 7 Comparison of Results... 8 Data Analysis.10
Submission Date: 11/15/2003 TAMUK Truss Company Trusses Made Simple Table of Contents Introduction..3 Proposal.3 Solution..5 Hand Calculations 5 TRUSS2D 7 NENastran 7 Comparison of Results... 8 Data Analysis.10
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian
 Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Multi-Point Constraints
 Multi-Point Constraints Multi-Point Constraints Multi-Point Constraints Single point constraint examples Multi-Point constraint examples linear, homogeneous linear, non-homogeneous linear, homogeneous
Multi-Point Constraints Multi-Point Constraints Multi-Point Constraints Single point constraint examples Multi-Point constraint examples linear, homogeneous linear, non-homogeneous linear, homogeneous
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
Experimental Modal Analysis of a Flat Plate Subjected To Vibration
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2016 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-6, pp-30-37 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2016 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-6, pp-30-37 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
Adams-to-Nastran. Jose L Ortiz, PhD. Adams User Meeting Munich - May 19, 2011
 Adams-to-Nastran Jose L Ortiz, PhD. Adams User Meeting Munich - May 19, 2011 Agenda Overview Manual and Scripted Translation Theoretical Background Implementation Details Example Q&A 5/26/2011 2 Agenda
Adams-to-Nastran Jose L Ortiz, PhD. Adams User Meeting Munich - May 19, 2011 Agenda Overview Manual and Scripted Translation Theoretical Background Implementation Details Example Q&A 5/26/2011 2 Agenda
Modal Transient Analysis of a Beam with Enforced Motion via a Ramp Invariant Digital Recursive Filtering Relationship
 oal ransient Analysis of a Beam ith Enforce otion via a Ramp nvariant Digital Recrsive iltering Relationship By om rvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com December, Variables f f ass matrix Stiness matrix Applie
oal ransient Analysis of a Beam ith Enforce otion via a Ramp nvariant Digital Recrsive iltering Relationship By om rvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com December, Variables f f ass matrix Stiness matrix Applie
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
Lecture Outline Chapter 11. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 11 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static
Lecture Outline Chapter 11 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static
M.S Comprehensive Examination Analysis
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2014 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... M.S Comprehensive
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2014 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... M.S Comprehensive
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Lecture 8: Assembly of beam elements.
 ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks.
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks.
To initiate a dynamic analysis in FormWorks, the Analysis Mode in the JOB CONTROL tab of DEFINE JOB window has to be set to one of the two Dynamic
 Dynamic Analysis with VecTor2 This bulletin describes the dynamic analysis facilities within VecTor2. Details of VecTor2 and FormWorks can be found in the VecTor2 and FormWorks Manual (Vecchio and Wong,
Dynamic Analysis with VecTor2 This bulletin describes the dynamic analysis facilities within VecTor2. Details of VecTor2 and FormWorks can be found in the VecTor2 and FormWorks Manual (Vecchio and Wong,
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Module - 01 Lecture - 11
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 01 Lecture - 11 Last class, what we did is, we looked at a method called superposition
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 01 Lecture - 11 Last class, what we did is, we looked at a method called superposition
Laboratory 4 Topic: Buckling
 Laboratory 4 Topic: Buckling Objectives: To record the load-deflection response of a clamped-clamped column. To identify, from the recorded response, the collapse load of the column. Introduction: Buckling
Laboratory 4 Topic: Buckling Objectives: To record the load-deflection response of a clamped-clamped column. To identify, from the recorded response, the collapse load of the column. Introduction: Buckling
DOWNLOAD OR READ : WAVE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : WAVE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 wave finite element method wave finite element method pdf wave finite element method A wave-based numerical approach is proposed
DOWNLOAD OR READ : WAVE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 wave finite element method wave finite element method pdf wave finite element method A wave-based numerical approach is proposed
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010126-00-E October 24th, 2001 Integration of mechanical
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010126-00-E October 24th, 2001 Integration of mechanical
EQUIVALENT STATIC LOADS FOR RANDOM VIBRATION Revision M
 EQUIVALENT STATIC LOADS FOR RANDOM VIBRATION Revision M By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com October 8, 010 The following approach in the main text is intended primarily for single-degree-of-freedom
EQUIVALENT STATIC LOADS FOR RANDOM VIBRATION Revision M By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com October 8, 010 The following approach in the main text is intended primarily for single-degree-of-freedom
EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY
 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free diagram. APPLICATIONS A 200 kg platform is suspended off an oil rig. How do we
EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free diagram. APPLICATIONS A 200 kg platform is suspended off an oil rig. How do we
F R. + F 3x. + F 2y. = (F 1x. j + F 3x. i + F 2y. i F 3y. i + F 1y. j F 2x. ) i + (F 1y. ) j. F 2x. F 3y. = (F ) i + (F ) j. ) j
 General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments of trough type folded plate roofs using ANSYS
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4 pp-22-28 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4 pp-22-28 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments
Software Verification
 EXAMPLE 6-003 LINK GAP ELEMENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example uses a single-bay, single-story rigid frame to test the gap link element. This link element carries compression loads only; it has zero stiffness
EXAMPLE 6-003 LINK GAP ELEMENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example uses a single-bay, single-story rigid frame to test the gap link element. This link element carries compression loads only; it has zero stiffness
Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17
 4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17 Trevor Dutton, Arup Solihull,
4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17 Trevor Dutton, Arup Solihull,
Critical Speed Analysis of Offset Jeffcott Rotor Using English and Metric Units
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Critical Speed Analysis of Offset Jeffcott Rotor Using English and Metric Units E. J. Gunter,PhD Fellow ASME February,2004 RODYN Vibration Inc. 1932 Arlington
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Critical Speed Analysis of Offset Jeffcott Rotor Using English and Metric Units E. J. Gunter,PhD Fellow ASME February,2004 RODYN Vibration Inc. 1932 Arlington
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
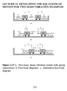 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
3. Numerical integration
 3. Numerical integration... 3. One-dimensional quadratures... 3. Two- and three-dimensional quadratures... 3.3 Exact Integrals for Straight Sided Triangles... 5 3.4 Reduced and Selected Integration...
3. Numerical integration... 3. One-dimensional quadratures... 3. Two- and three-dimensional quadratures... 3.3 Exact Integrals for Straight Sided Triangles... 5 3.4 Reduced and Selected Integration...
 University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
Chapter 4 Analysis of a cantilever
 Chapter 4 Analysis of a cantilever Before a complex structure is studied performing a seismic analysis, the behaviour of simpler ones should be fully understood. To achieve this knowledge we will start
Chapter 4 Analysis of a cantilever Before a complex structure is studied performing a seismic analysis, the behaviour of simpler ones should be fully understood. To achieve this knowledge we will start
