Experiences with the Coulter Counter in Bacteriology1
|
|
|
- Dustin Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experiences with the Coulter Counter in Bacteriology1 ELLEN M. SWANTON, WILLIAM A. CTJRBY, AND HOWARD E. LIND Sias Laboratories, Brooks Hospital, Brookline, Massachusetts Received for publication May 24, 1962 ABSTRACT SWANTON, ELLEN M. (Brooks Hospital, Brookline, Mass.), WILLIAM A. CURBY, AND HOWARD E. LIND. Experiences with the Coulter Counter in bacteriology. Appl. Microbiol. 10: Viable and killed suspensions of Staphylococcus aureus SM, Escherichia coli, and Serratia marcescens, as well as polystyrene spheres, 0.81 and 2.85 A in diameter, were counted electronically with a model A Coulter Counter. Simultaneous counts by standard bacteriological methods and microscopy were done for purposes of control and comparison with the data from the Coulter Counter. Results indicated: (i) electrical characteristics of different bacterial populations are different; (ii) electronic counts were consistent for species used; (iii) live S. aureus exhibits a denser pattern of thick bright pulses on the cathode-ray tube than does live E. coli; (iv) killed bacteria resemble inert particles in pulse pattern; and (v) some viable bacteria do not react independently of current flow, as do inert particles and killed bacteria. The object of this study was to determine the reliability as well as the limitations of an electronic counting system, the Coulter Counter, in enumerating bacteria in suspension in a fluid medium. Previous studies by Kubitschek (1958) and Lark and Lark (1960) cited the utility of the Coulter Counter in measuring the volumes of bacterial cells and volume ratios of bacterial populations and mixtures of bacteria and spores. As yet, reports with data on actual numbers of bacteria in a given population have not appeared in the literature. (During the completion of this study, such a work was published: Toennies, G., L. Iszard, N. B. Rogers, and G. D. Shockman Cell multiplication studied with an electronic counter. J. Bacteriol. 82: ) The assembled Coulter Counter includes an aspirator pump, a mercury manometer stand with aperture tube and microscope, and a unit containing the electronic components: the pulse-amplifying system, the oscilloscope, and the decade counter. Particles suspended in a 0.900% solution of sodium chloride (equivalent conductance, 97.5 mhos/cm at 22 C) are counted and sized while flowing through an aperture immersed in the sus- 1 Presented before the Laboratory Section of the American Public Health Association on Wednesday November 15, 1961, at Detroit, Mich. pension. As a particle passes through the aperture, it changes the resistance between two electrodes located on either side of the aperture. The resulting voltage pulse, proportional to the size of the particle, is amplified and counted. These pulses are visible on an oscilloscope screen. An adjustable threshold circuit permits counting of particles which reach and exceed the threshold level chosen. Counts taken at various levels provide data for plotting the range of sizes of particles in suspension. For this study, a model A Coulter Counter calibrated to count the particles in a 0.05-ml volume and equipped with an aperture tube 30 A in diameter was used. MATERIALS AND METHODS Preparation of inert material. Polystyrene spheres, 2.85 and 0.81,u in diameter, were used. They were supplied by J. W. Vanderhoff of Dow Chemical Co., Midland, Mich. and Difco Laboratories, Inc., Detroit, Mich. Prior to diluting the spheres, stock samples were placed in a shaker for 10 to 20 min to enhance even distribution and as an aid in breaking clumps. Appropriate dilutions were made in commercially prepared 0.900% saline (Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, Ill.). Coulter Counter dilutions were made in 100-ml amounts. Simultaneously, dilutions were made in sterile water for visual counts. Before counting, all samples were shaken mechanically for at least 10 min. Preparation of organisms. Staphylococcus aureus SM, Serratia marcescens, and Escherichia coli were selected for counting on the basis of size, shape, safety, and ease of handling. Initial inocula into Brain Heart Infusion Broth were from Brain Heart Infusion Agar slants. Cultures were incubated at 37 C for varying lengths of time during the growth period. To prepare the organisms for counting, the broth cultures were centrifuged at 1,500 X g for 25 min, and the supernatant fluid was discarded. This procedure was repeated for two % saline washes and the organisms were suspended in 10 ml of saline. Serial dilutions from 102 to 106 were made for standard plate counts and from 102 to 104 in duplicate 100-ml amounts for electronic counting. That dilution was selected which would yield counts ranging between 6 X 103 and 6 X 104 particles per ml per sec. One set of each dilution was incubated in a 56 C water bath for up to 2 hr to kill the bacteria. Killing was checked by plating in NIH Agar Medium. Specimens were shaken in the same way as the latex spheres. 480
2 1962] USE OF THE COULTER COUNTER 481 Analysis of counting procedures. The determination of total solids content (densitometric analysis) for the latex spheres (Difco) was made after appropriate dilution, as another check of the inert particle count. To examine visually and to count both latex spheres and the bacteria by microscopy, preparations of appropriate dilutions were used. Ten lambda samples were dropped and spread onto a 1-cm2 area and allowed to dry. The bacterial slides were heat-fixed and gram-stained. The latex spheres were examined unstained using phasecontrast microscopy. The dry-count method was not satisfactory for counting organisms in all phases of growth and was therefore discarded. Latex spheres were also counted in a hemacytometer. The lack of reliability of the hemacytometer counts concurs with that reported by Mattern, Brackett, and Olson (1957). Since differences were found to occur in the comparison of predicted counts with those obtained from the optical dry count, a counting method was developed which gave a measure of the population distribution of particles in the suspension to be evaluated by the electronic counter. The method is similar to that described in the optical dry method except that the counts are made of all particles in a field of a hanging drop. The assumption that, for motile organisms, the number leaving a random field will equal the number entering the field of count seems to be valid from consideration of data thus far obtained. The depth of focus for the microscope system used for counting particles in this study was 24 IA. Making the assumption that a hanging drop will assume a cross-sectional lower edge approximating a catenary, it was calculated that a 2-lambda drop having a diameter of 3 mm for its upper surface, using a Simpson's rule integration, would contain 844 field per drop. By use of drops of 2-lambda and optically measuring their upper diameter to be sure that drops 3-mm in diameter alone were counted, the standard error of the arithmetic mean was found to be i 7.7 particles about a field mean of 13.6 for 8 to 20 field samples. All electronic counts were made on a model A Coulter Counter set for maximal gain. Checks were made to determine the circuit characteristics of the counter following the procedures indicated by the manufacturer (Coulter Electronics Inc., Chicago, Ill.). For each specimen, the method of preparation for electronic counting was the same. Particles studied were less than 1,A in diameter and a 30-,u orifice was used with aperture current settings of 4, 5, and 6. Background noise was kept below 100 for all counts quoted, and threshold settings of less than three were not used. Counts were recorded from the lowest possible threshold above the noise level (threshold setting 4) and increased in increments of 1 unit to the threshold level where the counts dropped markedly (threshold setting 15). Any fall-off in count as a function of time was noted; however, none was seen in the case of particles less than 1,A diameter. The count distribution obtained with the Coulter Counter was compared with the results obtained by the other counting methods. Because of the size and shape of the particle studied, the data relating to the electronic counter are given with no corrections made for coincidence. Bacterial populations were also counted by standard plate methods. Depending upon the age of the culture, dilutions of from 103 to 106 were plated in NIH Agar Medium. After incubation at 37 C, the counts were made with the aid of a Quebec Colony Counter. Size and shape of organisms were determined with the aid of a calibrated ocular disc. RESULTS The results of our preliminary investigations are summed up in tables comparing counts from different procedures and TABLE 1. Comparison of counting methods and results from inert latex beads* Counting method Total Particle count per ml pgut Optical dry 3.18 X 10' 1.78 X 109 Optical wet 3.29 X X 109 Densitometric X 109 Coulter electronic (un X 109 corrected) * Latex spheres (0.81,u) follow a normal frequency distribution with respect to number of spheres in groups (1, 2, 3, 4, and more than 4) in the population. t For inert spheres, the pgu (pulse-generating units) count varies from the Coulter count by 4% for the same fluid medium. TABLE 2. Comparison of counting methods and results from Staphylococcus aureus SM* Counting method Particle count per ml Total pgut Optical wet 5.9 X X 109 Standard plate 1.6 X 109 Coulter electronic (uncorrected) 0.9 X 109 * S. aureus (4-hr culture, 0.8,u) does not follow a normal frequency distribution with respect to grouping (1, 2, 3, and 4 organisms per grouip) in the population. t Pulse-generating units. TABLE 3. Comparison of counting methods and results from Serratia marcescens* Counting method Particle count per ml Total pgut Optical wet 1.8 X X 109 Standard plate 2.2 X 109 Coulter electronic (uncorrected) 0.9 X 109 * S. marcescens (4-hr culture, 0.5 X 1.0 A) follows a normal frequency distribution with respect to the grouping (1, 2, 3, and 4 organisms per group) in the population. t Pulse-generating units.
3 482 SWANTON, CURBY, AND LIND [VOL. 10 figures showing displayed pulses from inert particles and representative microorganisms. Table 1 shows results from counts of inert latex beads. Particle count (total) represents the total number of single spheres enumerated; pulse generating unit (pgu) count is the number of spheres counted either singly or as clumps. The latter count should agree with the Coulter count. This relationship between optical wet pgu and Coulter counts was observed consistently when using inert particles. For each counting procedure, results obtained from at least ten independent experiments varied within the following limits: the mean variation for the Coulter count was :1: 1 %; for the plate count, ±t5 %; for the optical wet count, 4t7 %. The number of spheres in groups of 1, 2, 3, 4, and greater than 4 was counted and plotted on normal probability paper as an index for complete mixing in the case of latex particles and to determine the degree of deviation from a chance distribution of particle aggregates existing in the actively growing microorganism populations. Table 2 shows a comparison of counting methods and results for S. aureus SM. A 4-hr culture was used for these data. The pgu count from the wet count does not agree with the Coulter count as closely as did the count with inert latex beads. The difference, however, is consistent with this organism. The differential is felt to be due to the effect of electric and surface characteristics peculiar to this organism. The closer agreement observed between standard plate count and Coulter count was encouraging. FIG. 1. Comparison of cathode-ray tube display obtained with inert latex particles (top), 1,u in diameter, and heat-killed (70 C, 1 hr) Staphylococcus aureus (bottom).
4 USE OF THE COULTER COUNTER 483 With S. marcescenrs (Table 3), one is not dealing with a sphere but a cylinder. Again, the variations between the Coulter count and the optical count, as well as the standard plate count, are consistent with this species. In addition to the counting characteristics, we observed that the pulses displayed on the cathode-ray tube of the counter were unique in some respects with regard to the condition, type, and viability of the particulate material being counted. After heat-killing (70 C for 1 to 1.25 hr), the pulse pattern displayed by any microorganism tested was seen to be similar to that obtained with inert particles of the same size and concentration. Further, viable populations, populations mixed with live and dead organisms, and nonviable populations display different pulse patterns. Figures 1 through 3 show representative patterns photographed using a camera synchronized to record one sweep of the electron beam on the Coulter Counter cathode-ray tube. Figure 1 compares the cathode-ray tube display obtained with inert latex particles and killed S. aureus. From Fig. 2, a comparison of oscilloscope tracings obtained from a 4-hr culture of S. aureus and E. coli may be made. Figure 3 demonstrates the oscilloscope pattern obtained with the same samples but incubated for 18 hr. For similar population densities, live S. aureus usually exhibited a denser pattern on the cathode-ray tube than did E. coli. Electrical properties, cellular elasticity, as well as the morphology of the organism, may be among the FIG. 2. Comparison of oscilloscope tracings from 4-hr cultures of Staphylococcus aureus (top) and Escherichia coli (bottom). In both cultures, organisms were 1,u in diameter in 1O4 dilutions.
5 484 SWANTON, CURBY, AND LIND [VOL. 10 factors contributing to this effect. At this time we have no further definitive information on this phenomenon. It seems that the patterns displayed are consistent for the species tested. Whether this will hold true among given species of each genus is still to be determined. DISCUSSION It appears that the use of the Coulter Counter in the analysis of dynamic bacteriology is appropriate and worthwhile. The necessity for the analysis of natural phenomena without changing the established equilibrium in a definite fluid environment suggests that an electronic counter may well be the instrument of choice. However, background noise arising from the circuitry, from the current generated at the aperture, and outside interference, must be taken into consideration. Because the electric and surface characteristics of individual species of organisms may be different, a profile must be made for each organism under study. Such data should be obtained before attempting to assay quantitatively from body fluids. Certain factors affect the motility of the organisms, their shape, electrical characteristics, conductive mass, and surface properties. We have seen changes in pulse pattern occur with changes in aperture-current setting when studying live S. aureus, but not with inert particles or with heat-killed S. aureus. This suggests that some viable bacteria do not react independently of current flow across the aperture of FIG. 3. Oscilloscope pattern from Staphylococcus aureus (top) and Escherichia coli (bottom) cultures of Fig. 2 after 18-hr incubation period. S. aureus, 1,u diameter, 104 dilution; E. coli, 1 X 0.6 u diameters, 104 dilution.
6 1962] USE OF THE COULTER COUNTER 485 an electronic counter, whereas inert latex particles and heat-killed cells show a reaction which is independent of current. This observation indicates that a technique may be developed to assess the viability of part of whole bacterial populations. These preliminary results show that: (i) the Coulter Counter is reliable within definite limits in the counting of a bacterial population, (ii) the Coulter Counter may indicate the degree of viability of a part of a whole bacterial population, and (iii) electrical characteristics of different bacterial populations are different. LITERATURE CITED KUBITSCHEK, H. W Electronic counting and sizing of bacteria. Nature 182: LARK, K. G., AND C. LARK Changes during the division cycle in bacterial cell wall synthesis, volume, and ability to concentrate amino acids. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta 43: MATTERN, C. F., F. S. BRACKETT, AND B. J. OLSON Determination of number and size particles by electronic gating: Blood cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 10: COULTER ELECTRONICS COMPANY. Theory of the Coulter Counter. Chicago.
Microbiology. Definition of a Microorganism. Microorganisms in the Lab. The Study of Microorganisms
 Microbiology The Study of Microorganisms Definition of a Microorganism Derived from the Greek: Mikros, «small» and Organismos, organism Microscopic organism which is single celled (unicellular) or a mass
Microbiology The Study of Microorganisms Definition of a Microorganism Derived from the Greek: Mikros, «small» and Organismos, organism Microscopic organism which is single celled (unicellular) or a mass
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique
 Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
THE JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE
 THE JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE OF THE UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO Issued quarterly by the Agricultural Expenment Station of the University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez Campus, for the publication of articles and
THE JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE OF THE UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO Issued quarterly by the Agricultural Expenment Station of the University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez Campus, for the publication of articles and
Bacterial Gram Staining
 PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Coulter Counters. range can be selectively counted. overlap appreciably, they can then be counted. and threshold settings can be chosen so
 APPUED MICROBILOGY, JUlY 1973, p. 9-13 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Differential Counting in Mixed Cultures with Coulter Counters J. F. DRAKE AND
APPUED MICROBILOGY, JUlY 1973, p. 9-13 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Differential Counting in Mixed Cultures with Coulter Counters J. F. DRAKE AND
Relationship Between Atmospheric Temperature
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1970, p. 245-249 Copyright ( 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 19, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Relationship Between Atmospheric Temperature and Survival of Airborne Bacteria
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1970, p. 245-249 Copyright ( 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 19, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Relationship Between Atmospheric Temperature and Survival of Airborne Bacteria
Killing of Bacillus Spores by High-Intensity Ultraviolet Light
 Killing of Bacillus Spores by High-Intensity Ultraviolet Light STUDY ON EFFECTS OF PULSED LIGHT Abraham L. Sonenshein, PhD Professor and Deputy Chair Department of Molecular Biology and Microbiology Tufts
Killing of Bacillus Spores by High-Intensity Ultraviolet Light STUDY ON EFFECTS OF PULSED LIGHT Abraham L. Sonenshein, PhD Professor and Deputy Chair Department of Molecular Biology and Microbiology Tufts
Comparative Bacteriology Analysis: Source, cultivation, and preparation of bacterial samples:
 Silver Hydrosol Info Home Articles Comparative Bacteriology Analysis: Particulate vs. Ionic Silver December 22, 2004 Andrew Martin, B.S. John W. Roberts, Ph.D. Natural-Immunogenics Corp Purpose Claims
Silver Hydrosol Info Home Articles Comparative Bacteriology Analysis: Particulate vs. Ionic Silver December 22, 2004 Andrew Martin, B.S. John W. Roberts, Ph.D. Natural-Immunogenics Corp Purpose Claims
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS & METHODS
 Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Evaluation of the efficiency of Mxxxx as a barrier against microrganisms crossing
 Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
Application of Micro-Flow Imaging (MFI TM ) to The Analysis of Particles in Parenteral Fluids. October 2006 Ottawa, Canada
 Application of Micro-Flow Imaging (MFI TM ) to The Analysis of Particles in Parenteral Fluids October 26 Ottawa, Canada Summary The introduction of a growing number of targeted protein-based drug formulations
Application of Micro-Flow Imaging (MFI TM ) to The Analysis of Particles in Parenteral Fluids October 26 Ottawa, Canada Summary The introduction of a growing number of targeted protein-based drug formulations
CYTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN AGING BACTERIAL CULTURES
 CYTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN AGING BACTERIAL CULTURES B. R. CHATTERJEE AND ROBERT P. WILLIAMS Department of Microbiology, Baylor University College of Medicine, Houston, Texas Received for publication March
CYTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN AGING BACTERIAL CULTURES B. R. CHATTERJEE AND ROBERT P. WILLIAMS Department of Microbiology, Baylor University College of Medicine, Houston, Texas Received for publication March
BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015
 BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015 Week of May 18 th Introduction to the Microbiology Laboratory: Become familiar with the laboratory and its safety features Review safety rules
BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015 Week of May 18 th Introduction to the Microbiology Laboratory: Become familiar with the laboratory and its safety features Review safety rules
Bacterial Aerosol Samplers
 1959] BACTERIAL AEROSOL SAMPLERS. II 349 II. Bacterial Aerosol Samplers RETTGER, L. F. 1910 A new and improved method of enumerating air bacteria. J. Med. Research, 22, 461-468. ROSEBURY, T. 1947 Experimental
1959] BACTERIAL AEROSOL SAMPLERS. II 349 II. Bacterial Aerosol Samplers RETTGER, L. F. 1910 A new and improved method of enumerating air bacteria. J. Med. Research, 22, 461-468. ROSEBURY, T. 1947 Experimental
Electrical Sensing Zone Particle Analyzer for Measuring Germination of Fungal Spores in the Presence of Other Particles'
 APPUED MicRoBImoLY, July 1967, p. 935-639 Vol. 15, No. 4 Copyright 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed bi U.S.A. Electrical Sensing Zone Particle Analyzer for Measuring Germination of Fungal
APPUED MicRoBImoLY, July 1967, p. 935-639 Vol. 15, No. 4 Copyright 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed bi U.S.A. Electrical Sensing Zone Particle Analyzer for Measuring Germination of Fungal
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Hedderich, R., Müller, R., Greulich, Y., Bannert, N., Holland, G., Kaiser, P., Reissbrodt, R. Mechanical damage to Gram-negative bacteria by surface plating with the Drigalski-spatula
Originally published as: Hedderich, R., Müller, R., Greulich, Y., Bannert, N., Holland, G., Kaiser, P., Reissbrodt, R. Mechanical damage to Gram-negative bacteria by surface plating with the Drigalski-spatula
Ultraviolet Bactericidal Irradiation of Ice
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 463-467 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Ultraviolet Bactericidal Irradiation of Ice P. A. LADANYI AND S. M. MORRISON
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 463-467 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Ultraviolet Bactericidal Irradiation of Ice P. A. LADANYI AND S. M. MORRISON
Tentative Identification of Methanogenic Bacteria by Fluorescence Microscopy
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 713-717 Copyright (C 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 33, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Tentative Identification of Methanogenic Bacteria by Fluorescence
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 713-717 Copyright (C 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 33, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Tentative Identification of Methanogenic Bacteria by Fluorescence
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD
 MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
Statistical Study of the Spot-Plate Technique for Viable-Cell Counts
 Statistical Study of the Spot-Plate Technique for Viable-Cell Counts A. F. GAUDY, JR., F. ABU-NIAAJ,' AND E. T. GAUDY 0 Bio-engineering Laboratories, School of Civil Engineering, and Microbiology Department,
Statistical Study of the Spot-Plate Technique for Viable-Cell Counts A. F. GAUDY, JR., F. ABU-NIAAJ,' AND E. T. GAUDY 0 Bio-engineering Laboratories, School of Civil Engineering, and Microbiology Department,
Electron Microscopic Studies on Mode of Action of Polymyxin
 JOURNAL OF BACrERIOLOGY, Jan. 1969, p. 448452 Vol. 97, No. I Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Printed In U.S.A. Electron Microscopic Studies on Mode of Action of Polymyxin M. KOIKE, K.
JOURNAL OF BACrERIOLOGY, Jan. 1969, p. 448452 Vol. 97, No. I Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Printed In U.S.A. Electron Microscopic Studies on Mode of Action of Polymyxin M. KOIKE, K.
Pharmaceutical Microbiology Forum Newsletter Vol. 12 (4) Page 3 of 14 (NCIMB 8545, CIP NBRC. Salmonella enterica ssp typhimurium
 Page 3 of 14 Continued from page 2 Table 2. Absence of Specified Details Media Growth Promotion Organisms for Trypticase Soy Staphylococcus aureus Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Salmonella Staphylococcus
Page 3 of 14 Continued from page 2 Table 2. Absence of Specified Details Media Growth Promotion Organisms for Trypticase Soy Staphylococcus aureus Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Salmonella Staphylococcus
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA FLOW CHART UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
 ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM DIFFERENTIATION'
 RELATONSHP OF CELL WALL STANNG TO GRAM DFFERENTATON' J. W. BARTHOLOMEW AND HAROLD FNKELSTEN Department of Bacteriology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California Received for publication
RELATONSHP OF CELL WALL STANNG TO GRAM DFFERENTATON' J. W. BARTHOLOMEW AND HAROLD FNKELSTEN Department of Bacteriology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California Received for publication
Coolidge-type molybdenum-target x-ray tube, the x-rays being
 THE EFFECT OF CERTAIN X-RAYS ON THE ELECTRO- PHORETIC MOBILITY OF ESCHERICHIA COLI1 MARGARET E. SMITH AND MARTIN W. LISSE Department of Agricultural and Biological Chemistry AND WHEELER P. DAVEY Department
THE EFFECT OF CERTAIN X-RAYS ON THE ELECTRO- PHORETIC MOBILITY OF ESCHERICHIA COLI1 MARGARET E. SMITH AND MARTIN W. LISSE Department of Agricultural and Biological Chemistry AND WHEELER P. DAVEY Department
Thermal Injury and Recovery of Salmonella typhimurium and Its Effect on
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1969, p. 332-336 Copyright @ 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Thermal Injury and Recovery of Salmonella typhimurium and Its Effect on
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1969, p. 332-336 Copyright @ 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Thermal Injury and Recovery of Salmonella typhimurium and Its Effect on
Disruption of Bacterial Cells by a Synthetic Zeolite
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1968, p. 1269-1275 Copyright @ 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 9 Printed in U.S.A. Disruption of Bacterial Cells by a Synthetic Zeolite GEORGE WISTREICH,
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1968, p. 1269-1275 Copyright @ 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 9 Printed in U.S.A. Disruption of Bacterial Cells by a Synthetic Zeolite GEORGE WISTREICH,
Particle size analysis -Chapter 3
 Particle size analysis -Chapter 3 Importance of PSA Size and hence surface area of particles affect: The rate of drug dissolution and release from dosage forms Flow properties of granules and powders.
Particle size analysis -Chapter 3 Importance of PSA Size and hence surface area of particles affect: The rate of drug dissolution and release from dosage forms Flow properties of granules and powders.
Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation. and Elimination of Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
The impact of spore aggregation on viable and total counts of Bacillus subtilis
 The impact of spore aggregation on viable and total counts of Bacillus subtilis Nikos Mavroudis and Catherine Bowe Food Engineering and Separation of Actives, FoESA, laboratory Department of Applied Sciences,
The impact of spore aggregation on viable and total counts of Bacillus subtilis Nikos Mavroudis and Catherine Bowe Food Engineering and Separation of Actives, FoESA, laboratory Department of Applied Sciences,
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
of the work reported here was to define the point in the developmental process at which the curing salts act to prevent outgrowth.
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1968, p. 406-411 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Sodium Nitrite, Sodium Chloride, and Sodium Nitrate on Germination
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1968, p. 406-411 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Sodium Nitrite, Sodium Chloride, and Sodium Nitrate on Germination
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE 5/14/18
 THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
Kinetics of Escherchia coli Destruction by Microwave Irradiation
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 92-924 99-224/92/392-5$2./ Copyright X) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 3 Kinetics of Escherchia coli Destruction by Microwave
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 92-924 99-224/92/392-5$2./ Copyright X) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 3 Kinetics of Escherchia coli Destruction by Microwave
Fundamentals of Particle Counting
 Fundamentals of Particle Counting 1 Particle Counting: Remains the most significant technique for determining the cleanliness level of a fluid Useful as a tool for qualification and monitoring cleanroom
Fundamentals of Particle Counting 1 Particle Counting: Remains the most significant technique for determining the cleanliness level of a fluid Useful as a tool for qualification and monitoring cleanroom
Morphology and Ultrastructure of Staphylococcal L Colonies: Light, Scanning,
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb. 1973, p. 1049-1053 Copyright ( 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 113, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Morphology and Ultrastructure of Staphylococcal L Colonies: Light,
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb. 1973, p. 1049-1053 Copyright ( 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 113, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Morphology and Ultrastructure of Staphylococcal L Colonies: Light,
Biosynthesis of Prodigiosin by White Strains of Serratia
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 476-480 0095-1137/83/030476-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Biosynthesis of Prodigiosin by White Strains of Serratia
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 476-480 0095-1137/83/030476-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Biosynthesis of Prodigiosin by White Strains of Serratia
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria
 Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Technical Paper 3 Verifying Particle Counter Calibration: Size Verification
 Technical Paper 3 Verifying Particle Counter Calibration: Size Verification By D. John Hunt, Pacific Scientific Instruments. Originally printed in Pollution Equipment News Publication, June 1996. Volume
Technical Paper 3 Verifying Particle Counter Calibration: Size Verification By D. John Hunt, Pacific Scientific Instruments. Originally printed in Pollution Equipment News Publication, June 1996. Volume
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques
 Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON
 TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-prescottsmicrobiology-9th-edition-by-willey-sherwood-woolverton/
TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-prescottsmicrobiology-9th-edition-by-willey-sherwood-woolverton/
(Jennison, 1937). This lack of agreement may be overcome, at
 EVALUATION OF THE ERRORS INVOLVED IN ESTIMATING BACTERIAL NUMBERS BY THE PLATING METHOD' MARSHALL W. JENNISON AND GEORGE P. WADSWORTH Department of Biology and Public Health, and Department of Mathematics,
EVALUATION OF THE ERRORS INVOLVED IN ESTIMATING BACTERIAL NUMBERS BY THE PLATING METHOD' MARSHALL W. JENNISON AND GEORGE P. WADSWORTH Department of Biology and Public Health, and Department of Mathematics,
NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells
 NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells Catalog Number: 30029 (100-500 assays) Contact Information Address: Biotium, Inc. 3423 Investment Blvd. Suite 8 Hayward, CA 94545 USA Telephone: (510)
NucView TM 488 Caspase-3 Assay Kit for Live Cells Catalog Number: 30029 (100-500 assays) Contact Information Address: Biotium, Inc. 3423 Investment Blvd. Suite 8 Hayward, CA 94545 USA Telephone: (510)
ENTEROBACTER CLOACAE OUTER MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY TO CEFTIZOXIME (FK 749) AND FIVE OTHER NEW CEPHALOSPORIN DERIVATIVES
 VOL. XXXIII NO. 3 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 317 ENTEROBACTER CLOACAE OUTER MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY TO CEFTIZOXIME (FK 749) AND FIVE OTHER NEW CEPHALOSPORIN DERIVATIVES HITOSHI Kojo, YASUTAKA SHIGI and MINORU
VOL. XXXIII NO. 3 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 317 ENTEROBACTER CLOACAE OUTER MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY TO CEFTIZOXIME (FK 749) AND FIVE OTHER NEW CEPHALOSPORIN DERIVATIVES HITOSHI Kojo, YASUTAKA SHIGI and MINORU
Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections
 327 BIRCH-ANDERSEN, A. (1955). J. gen. Microbial. 13, 327429 Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections BY A. BIRCH-ANDERSEN Statens Seruminstitut,
327 BIRCH-ANDERSEN, A. (1955). J. gen. Microbial. 13, 327429 Reconstruction of the Nuclear Sites of Salmonella typhimurium from Electron Micrographs of Serial Sections BY A. BIRCH-ANDERSEN Statens Seruminstitut,
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 209 Supporting information Na 2 S promoted reduction of azides in water: Synthesis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 209 Supporting information Na 2 S promoted reduction of azides in water: Synthesis
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Determination of particle size distributions Electrical sensing zone method
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13319 First edition 2000-04-01 Determination of particle size distributions Electrical sensing zone method Détermination des répartitions granulométriques Méthodes de la zone
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13319 First edition 2000-04-01 Determination of particle size distributions Electrical sensing zone method Détermination des répartitions granulométriques Méthodes de la zone
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification. ~10 um. Red Blood Cells = mm 1500 um. Width of penny
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types
Resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to Carbenicillin
 J. gen. Microbiol. (1969, 58, 301-305 Printed in Great Britain 301 Resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to Carbenicillin By H. C. NEU AND H. S,WARZ Department of Medicine, College
J. gen. Microbiol. (1969, 58, 301-305 Printed in Great Britain 301 Resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to Carbenicillin By H. C. NEU AND H. S,WARZ Department of Medicine, College
Photobleaching resistant polymer supported hexanuclear molybdenum. iodide cluster for photocatalytic oxygenations and photodynamic
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Photobleaching resistant polymer supported hexanuclear
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Photobleaching resistant polymer supported hexanuclear
washed cells of Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol.
 SELECTIVE INHIBITION OF PROLINE-INDUCED PIGMENTATION IN WASHED CELLS OF SERRATIA MARCESCENS' JOHN L. BLIZZARD2 AND G. E. PETERSON Department of Biology, University of Houston, Houston, Texas Received for
SELECTIVE INHIBITION OF PROLINE-INDUCED PIGMENTATION IN WASHED CELLS OF SERRATIA MARCESCENS' JOHN L. BLIZZARD2 AND G. E. PETERSON Department of Biology, University of Houston, Houston, Texas Received for
A Selective Medium for Bacillus anthracis
 56 R~ORRIS, E. J. (955). J. gen. Microbiol. 3, 566 A Selective Medium for Bacillus anthracis BY E. J. MORRIS Microbiological Research Department, Ministry of Supply, Porton, Wiltshire SUMMARY: A medium
56 R~ORRIS, E. J. (955). J. gen. Microbiol. 3, 566 A Selective Medium for Bacillus anthracis BY E. J. MORRIS Microbiological Research Department, Ministry of Supply, Porton, Wiltshire SUMMARY: A medium
Vol. 14, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Preservation of Serratia marcescens by High-Vacuum Lyophilization
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, July, 1966 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Preservation of Serratia marcescens by High-Vacuum Lyophilization ROBERT R. DEWALD1 Physical
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, July, 1966 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Preservation of Serratia marcescens by High-Vacuum Lyophilization ROBERT R. DEWALD1 Physical
Removal of Escherichia coli in Wastewater by Activated Sludge
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1977, p. 315-319 Copyright C 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 34, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Removal of Escherichia coli in Wastewater by Activated
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1977, p. 315-319 Copyright C 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 34, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Removal of Escherichia coli in Wastewater by Activated
Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries
 Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries Total Holographic Characterization (THC) Comparison of THC to other technologies Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Scanning Electron Microscopy
Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries Total Holographic Characterization (THC) Comparison of THC to other technologies Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Scanning Electron Microscopy
NNIN Nanotechnology Education
 NNIN Nanotechnology Education Name: Date: Class: Nanoparticle (circle one): Au Ag Group role (circle one): nanoparticle synthesis dilution Exposure conditions (circle two): a b c d e f Student Worksheet
NNIN Nanotechnology Education Name: Date: Class: Nanoparticle (circle one): Au Ag Group role (circle one): nanoparticle synthesis dilution Exposure conditions (circle two): a b c d e f Student Worksheet
UNCLASSIFIED ADL DEFENSE DOCUMENTATION CENTER FOR SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION CAMERON STATION ALEXANDRIA. VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED
 UNCLASSIFIED ADL 4 5 2981 DEFENSE DOCUMENTATION CENTER FOR SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION CAMERON STATION ALEXANDRIA. VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When goverment or other drawings, specifications
UNCLASSIFIED ADL 4 5 2981 DEFENSE DOCUMENTATION CENTER FOR SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION CAMERON STATION ALEXANDRIA. VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When goverment or other drawings, specifications
Effect of Microwaves on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1967, p. 1371-1375 Copyright 1967 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 15, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Microaves on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis SAMUEL A. GOLDBLITH
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1967, p. 1371-1375 Copyright 1967 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 15, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Microaves on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis SAMUEL A. GOLDBLITH
Cell Shape coccus bacillus spirillum vibrio
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
Standard Operating Procedure. Immunology
 Standard Operating Procedure Immunology SOP Ref No SOP title SOP-IU010 PCA Category Laboratory Version 1.0 Page 1 of 12 PCA Introduction The enumeration of fresh or frozen-thawed PBMC (peripheral blood
Standard Operating Procedure Immunology SOP Ref No SOP title SOP-IU010 PCA Category Laboratory Version 1.0 Page 1 of 12 PCA Introduction The enumeration of fresh or frozen-thawed PBMC (peripheral blood
Inactivation of Bacillus cereus Spores by High Hydrostatic Pressure at Different Temperatures
 599 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 66, No. 4, 2003, Pages 599 603 Copyright q, International Association for Food Protection Inactivation of Bacillus cereus Spores by High Hydrostatic Pressure at Different
599 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 66, No. 4, 2003, Pages 599 603 Copyright q, International Association for Food Protection Inactivation of Bacillus cereus Spores by High Hydrostatic Pressure at Different
Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp.
 Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp. March 11, 213 Prof Steve Forsythe Pathogen Research Centre, School of Science and Technology Nottingham Trent University Clifton
Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp. March 11, 213 Prof Steve Forsythe Pathogen Research Centre, School of Science and Technology Nottingham Trent University Clifton
The Prokaryotes & Viruses
 The Prokaryotes & Viruses Lab Exercise Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae 2 Activity.3 Viruses 3 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria
The Prokaryotes & Viruses Lab Exercise Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae 2 Activity.3 Viruses 3 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria
BIT TM Detailed Technical Discussion
 National Security Solutions BIT TM Detailed Technical Discussion Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizer that is used for high-level disinfection and sterilization. It produces reactive hydroxyl free radicals
National Security Solutions BIT TM Detailed Technical Discussion Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizer that is used for high-level disinfection and sterilization. It produces reactive hydroxyl free radicals
EFFECT OF ph AND AMMONIUM IONS ON THE PERMEABILITY
 EFFECT OF ph AND AMMONIUM IONS ON THE PERMEABILITY OF BACILLUS PASTEURII W. R. WILEY AND J. L. STOKES Department of Bacteriology and Public Health, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington ABSTRACT
EFFECT OF ph AND AMMONIUM IONS ON THE PERMEABILITY OF BACILLUS PASTEURII W. R. WILEY AND J. L. STOKES Department of Bacteriology and Public Health, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington ABSTRACT
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
The Coulter Principle for Outlier Detection in Highly Concentrated Solutions
 The Coulter Principle for Outlier Detection in Highly Concentrated Solutions Particle Characterization Application Note Abstract This application note will benefit chemical and material manufacturers concerned
The Coulter Principle for Outlier Detection in Highly Concentrated Solutions Particle Characterization Application Note Abstract This application note will benefit chemical and material manufacturers concerned
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
The Elzone II Particle Count and Size Analyzer
 The Elzone II 5390 Particle Count and Size Analyzer Elzone II Overview of Basic Theory Operates using the Electrical Sensing Zone (ESZ) Principle, also known as the Coulter Principle. First commercially
The Elzone II 5390 Particle Count and Size Analyzer Elzone II Overview of Basic Theory Operates using the Electrical Sensing Zone (ESZ) Principle, also known as the Coulter Principle. First commercially
Effect of Coliform and Proteus Bacteria on Growth
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan., 19 Copyright @ 19 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Coliform and Proteus Bacteria on Growth of Staphylococcus aureus1 J. V. DiGIACINTO2
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Jan., 19 Copyright @ 19 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Coliform and Proteus Bacteria on Growth of Staphylococcus aureus1 J. V. DiGIACINTO2
Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 m
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Required Materials: immersion oil microscopes Kim-wipes prepared microscope slides
 Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Center for Cell Imaging Department of Cell Biology
 Center for Cell Imaging Department of Cell Biology Contents Preparation of Colloidal Gold Conjugates Coupling the Protein A to the Gold Particles Purification of the protein A-gold. Storage Influence of
Center for Cell Imaging Department of Cell Biology Contents Preparation of Colloidal Gold Conjugates Coupling the Protein A to the Gold Particles Purification of the protein A-gold. Storage Influence of
Sporulation of Bacillus stearothermophilus
 APPLm MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1967, p. 975-979 Vol. 15, No. 5 Copyright i 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Sporulation of Bacillus stearothermophilus P. J. THOMPSON AND 0. A. THAMES,
APPLm MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1967, p. 975-979 Vol. 15, No. 5 Copyright i 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Sporulation of Bacillus stearothermophilus P. J. THOMPSON AND 0. A. THAMES,
Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN
 Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN Introduction The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is a staining technique allowing different types of microorganisms (usually bacteria)
Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN Introduction The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is a staining technique allowing different types of microorganisms (usually bacteria)
Microstructure of Colonies of Rod-Shaped Bacteria
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1971, p. 515-525 Copyright 0 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 108, No. I Printed in U.S.A. Microstructure of Colonies of Rod-Shaped Bacteria D. B. DRUCKER AND D.
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1971, p. 515-525 Copyright 0 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 108, No. I Printed in U.S.A. Microstructure of Colonies of Rod-Shaped Bacteria D. B. DRUCKER AND D.
Rapid Aerobic Count. Interpretation Guide. 3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Rapid Aerobic Count Plate
 3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Rapid Aerobic Count Plate Rapid Aerobic Count Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Rapid Aerobic Count Plate is a sample-ready culture medium system which contains nutrients,
3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Rapid Aerobic Count Plate Rapid Aerobic Count Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Rapid Aerobic Count Plate is a sample-ready culture medium system which contains nutrients,
The Effect of Static Magnetic Field on E. coli, S. aureus and B. subtilis Viability
 The Effect of Static Magnetic Field on E. coli, S. aureus and B. subtilis Viability Khaled A. Al-Khaza'leh 1* Abdullah T. Al-fawwaz 2 1. Department of Physics, Al-albayt University, PO box 130040, Mafraq,
The Effect of Static Magnetic Field on E. coli, S. aureus and B. subtilis Viability Khaled A. Al-Khaza'leh 1* Abdullah T. Al-fawwaz 2 1. Department of Physics, Al-albayt University, PO box 130040, Mafraq,
Effect of Several Environmental Conditions on the "Thermal Death Rate" of Endospores of Aerobic, Thermophilic Bacteria
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov., 1965 Copyright 1965 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Several Environmental Conditions on the "Thermal Death Rate" of Endospores of
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Nov., 1965 Copyright 1965 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Several Environmental Conditions on the "Thermal Death Rate" of Endospores of
SUSPENSION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Strebel (1900), Aschkinass and Caspari (1901), Crooks (1903), and Pfeiffer and
 THE EFFECT OF RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS UPON A SUSPENSION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI CLARENCE F. SCHMIDT Research Department, Continental Can Company, Chicago, Illinois Received for publication February 4, 1948
THE EFFECT OF RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS UPON A SUSPENSION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI CLARENCE F. SCHMIDT Research Department, Continental Can Company, Chicago, Illinois Received for publication February 4, 1948
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10
 Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10 Principle and Purpose THE GRAM STAIN The Gram stain is perhaps the most useful test conducted in the clinical microbiology laboratory. It was first developed
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10 Principle and Purpose THE GRAM STAIN The Gram stain is perhaps the most useful test conducted in the clinical microbiology laboratory. It was first developed
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017
 GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017 1. A student offering Microbiology programme will be offered two theory papers of core course MI 101 and
GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017 1. A student offering Microbiology programme will be offered two theory papers of core course MI 101 and
Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system
 I. Abstract. Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system Project Investigator(s): Jorge M. Fonseca 1, Sadhana Ravishankar
I. Abstract. Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system Project Investigator(s): Jorge M. Fonseca 1, Sadhana Ravishankar
Formaldehyde Fluorescent Detection Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Formaldehyde Fluorescent Detection Kit For detection in human urine and tissue culture media Cat. No. KT-723 For Research Use Only. Not for Use
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Formaldehyde Fluorescent Detection Kit For detection in human urine and tissue culture media Cat. No. KT-723 For Research Use Only. Not for Use
Module 2. Measurement Systems. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Measurement Systems Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 8 Measurement of Level, Humidity and ph Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will
Module 2 Measurement Systems Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 8 Measurement of Level, Humidity and ph Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang
 Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
ICP-OES DETERMINATION OF IRON. Introduction:
 ICP-OES DETERMINATION OF IRON. Introduction: Silver impregnated cloth has bene used in bandages and dressings to help kill bacteria associated with a wound. Cloth samples are to anaysed for silver and
ICP-OES DETERMINATION OF IRON. Introduction: Silver impregnated cloth has bene used in bandages and dressings to help kill bacteria associated with a wound. Cloth samples are to anaysed for silver and
Acta Medica Okayama. Selective staining of cytoplasmic membrane and nuclear apparatus of bacteria. Yasuhiro Kanemasa FEBRUARY 1962
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 16, Issue 1 1962 Article 5 FEBRUARY 1962 Selective staining of cytoplasmic membrane and nuclear apparatus of bacteria Yasuhiro Kanemasa Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 16, Issue 1 1962 Article 5 FEBRUARY 1962 Selective staining of cytoplasmic membrane and nuclear apparatus of bacteria Yasuhiro Kanemasa Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA
Effect of static electric field treatment on multiple antibiotic-resistant pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
 Antimicrobial J Microbiol Immunol effects of Infect electric fields 25;38:394-398 Effect of static electric field treatment on multiple antibiotic-resistant pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
Antimicrobial J Microbiol Immunol effects of Infect electric fields 25;38:394-398 Effect of static electric field treatment on multiple antibiotic-resistant pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain. Mgr. Tomáš Kastl
 Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain Mgr. Tomáš Kastl MARKS TO NOTICE Morphology of colonies and cells - strructure - size - surface - shape - profile - special organels
Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain Mgr. Tomáš Kastl MARKS TO NOTICE Morphology of colonies and cells - strructure - size - surface - shape - profile - special organels
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supplementary Information
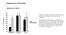 Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Component Product # Product # Cell Lysis Reagent 100 ml 500 ml Product Insert 1 1
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cell Lysis Reagent Product # 18800 (100 ml) Product # 18801 (500
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cell Lysis Reagent Product # 18800 (100 ml) Product # 18801 (500
surface of each plate and spread evenly with a sterile glass rod. Inoculated media were incubated The stock cultures of the C. perfringens strains
 STUDIES OF THE L-FORMS OF CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS I. RELATIONSHIP OF COLONY MORPHOLOGY AND REVERSIBILITY TOSHIO KAWATOMARI Department of Bacteriology, 406th Medical General Laboratory, APO 343, San Francisco,
STUDIES OF THE L-FORMS OF CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS I. RELATIONSHIP OF COLONY MORPHOLOGY AND REVERSIBILITY TOSHIO KAWATOMARI Department of Bacteriology, 406th Medical General Laboratory, APO 343, San Francisco,
Performance Evaluation of Various ATP Detecting Units
 Silliker, Inc., Food Science Center Report RPN: 13922 December 11, 2009 Revised January 21, 2010 Performance Evaluation of Various ATP Detecting Units Prepared for: Steven Nason 941 Avenida Acaso Camarillo,
Silliker, Inc., Food Science Center Report RPN: 13922 December 11, 2009 Revised January 21, 2010 Performance Evaluation of Various ATP Detecting Units Prepared for: Steven Nason 941 Avenida Acaso Camarillo,
(inner dense substance) of the identical bacteria later photographed in the electron
 ON THE MICROSCOPIC METHODS OF MEASURING THE DIMENSIONS OF THE BACTERIAL CELL GEORGES KNAYSI Laboratory of Bacteriology, College of Agriculture, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York Received for publication
ON THE MICROSCOPIC METHODS OF MEASURING THE DIMENSIONS OF THE BACTERIAL CELL GEORGES KNAYSI Laboratory of Bacteriology, College of Agriculture, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York Received for publication
Lysozyme Lysis of Gram-Negative Bacteria without Production of Spheroplasts
 J. gen. Microbial. (1964), 35, 313-317 With 1 plate Printed in Great Britain 313 Lysozyme Lysis of Gram-Negative Bacteria without Production of Spheroplasts BY J. G. VOSS Research Division, Miami Valley
J. gen. Microbial. (1964), 35, 313-317 With 1 plate Printed in Great Britain 313 Lysozyme Lysis of Gram-Negative Bacteria without Production of Spheroplasts BY J. G. VOSS Research Division, Miami Valley
