The Prokaryotes & Viruses
|
|
|
- Valerie Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Prokaryotes & Viruses Lab Exercise Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae 2 Activity.3 Viruses 3 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria 3 Resutls Section 6 Objectives - Know the principal characteristics of the Prokaryotes - Identify three basic shapes of bacteria - Understand the Gram staining technique - Identify Gram + and Gram bacteria Introduction The Prokaryotes include all organisms which lack a nucleus. This characteristic is termed prokaryotic. Many scientists now divide these organisms into two Domains: the Bacteria and the Archaea. The Archaea is a very ancient group which is thought to resemble the first organisms on earth. These organisms are frequently found in very harsh environments. There are several phylogenetic groups within the Bacteria. However, with one exception, we will not be concerned with the characteristics of these separate groups. Rather we will only be concerned with more general characteristics of these organisms. The one group which we will specifically identify are the blue-green algae, the Cyanobacteria. In the Diversity Section of the BiologyOne DVD, select The Prokaryotes simulation. 1
2 Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae This simulation illustrates some of the basic features of prokaryotic organisms. Review these to be familiar with the characteristics of these organisms. For the Eubacteria, one of the more important features used to distinguish these organisms is their shape. Three general bacterial shapes are termed coccus, bacillus, and spirillus. There are also variations based on these shapes. Because of the small size of bacteria, these shapes can only be determined under high magnification with light microscopes. The Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes. The combination of photosynthetic pigments found in these organisms frequently makes them blue-green in appearance, thus the common name, the Blue-Green Algae. In The Prokaryotic simulation on the BiologyOne DVD, examine micrographs of the four species of blue-green algae shown. Make your own diagram of these species in the Results Section. Coccus (pl: cocci) - This is a spherical or round shape. Bacteria with this general shape may be found singly, in pairs (diplococcus), in long chains (streptococcus), or in clusters (staphylococcus). Bacillus (pl: bacilli) - This is a rod shape. Bacteria with the bacillus shape may also be found singly, in pairs (diplobacillus) or in long chains (streptobacillus). Spirillum (pl: spirilla) - These bacteria have a spiral or corkscrew shape. Turning of the corkscrew shaped cell allows motility. Bacterial Shapes In the Prokaryotic tutorial on the BiologyOne DVD, after reviewing the material concerning the general structure of bacteria, examine the micrographs of the cell shapes found in bacteria. Label the illustration of the bacterial cell in the Results Section. Coccus Bacillus Spirillum 2
3 Activity.3 Viruses Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria While viruses are not prokaryotes, usually not considered to be living organisms at all, viruses are often discussed with the prokaryotes. Perhaps because of their small size and tendency to cause disease. This simulation follows this tradition and illustrates some of the characteristics of viral particles. After review these features, label the diagram of a viral particle in the Results Section. An important method to classify bacteria is by observing their ability to complex with various chemicals (stains). This represents differences in bacterial morphology and physiology. One of the most commonly used stains for bacterial classification is the Gram Stain. This staining procedure will distinguish between two morphological types of bacteria, those with a thick, uniform cell wall and those with a thinner, bilayered cell wall. In this simulation you will follow the Gram staining procedure to determine the Gram staining characteristics for several species of bacteria. When you start this simulation you will see a shelf with the supplies you will need to complete this simulation (see diagram below). For most of these, clicking on the item will pull it off the shelf so you can use it. Clicking on the item again will place it back on the shelf. Just as in an actual laboratory setting, it is important to follow these directions in order or you will not obtain the desired results. Simulation Screen for Gram Staining click on item to pull from shelf 1. To begin, click on the Bunsen burner to bring it off the shelf. Then click on the container of inoculating loops. click on stains to remove from shelf move loop into tube for sample to view, move slide to scope slide arrow to select bacteria 3
4 You can click on and drag the loop which appears. Clicking on the loop container again will put away the loop. Drag the loop over to the Bunsen burner so its end enters the flame. This sterilizes the end of the loop. You can put the burner away at this point. 2. Click on the rack of culture vials. You have ten different cultures to select from. In each vial, the bacteria are growing on media called agar. Move the arrow under the culture you would like to begin with. When you release the arrow, the culture vial will be removed from the rack and opened so you can collect a sample of the bacteria. Select a culture, then move the loop so that its tip slowly enters the vial and collects a sample of the bacteria. Slowly remove the loop. Click on the culture vials to put them back on the shelf. You now have the bacteria on the end of the loop. 3. Click on the container with the forceps. Once you have forceps on the screen, click on it and drag it up to the box of slides on the shelf. You will pick up a microscope slide on the end of the forceps. Move this to the middle area of the screen. 4. Move the loop so that its tip contacts the slide. This will transfer the bacteria from the loop to the surface of the slide. You can put the loop away now by clicking on its container. (In an actual lab you should flame the loop before storing the inoculating loop.) Solution 1 is crystal violet stain. Dip the slide into this jar. If you were doing this procedure live, you would leave the slide in the solution for one minute. You do not have to time any of the steps in the simulation. Dip the slide into solution 2. This is water to wash off excess crystal violet stain. Dip the slide into solution 3. This contains Gram s iodine. If the cell is a Gram + bacterium, the iodine will react with the crystal violet causing it to adhere to the cell wall. The slide would remain in the iodine for one minute in the actual procedure. Dip the slide into solution 4. This is water to wash off excess iodine. Dip the slide into solution 5. This is alcohol. This solution will remove any crystal violet stain which has not reacted to adhere to the cell wall. The slide should remain in the alcohol for 10 to 30 seconds. Dip the slide into solution 6. This is water to remove excess alcohol. Dip the slide into solution 7. This is safranin stain. It will stain any bacteria which did not retain the crystal violet. This allows you to see these bacteria. The slide should be stained in safranin for 30 seconds. 5. You need to fix the bacteria to the glass of the slide to prevent them from washing off during the staining process. To do this, pull down the Bunsen burner and pass the slide through the flame several times. When completed, put the burner away. 6. You are now ready to stain the bacteria. Click on the stain tray to bring the stains off the shelf. When you do this the forceps and slide will change orientation for staining. The Gram Stain procedure requires that you pass the slide and bacteria through eight different solutions in order. In the simulation you do this by dipping the slide slowly into the solution until the tip of the forceps is about at the level of the top of the stain jar. Dip the slide into solution 8. This is water to remove the excess safranin stain. Once you ve removed the slide from solution 8 you can put the staining jars away by clicking on them. The slide and forceps will return to a side view. 7. You are now ready to view your results. If you were using a real slide and microscope you would probably want to place a cover slip on the slide. The simulation skips this step. Move the slide over to the microscope image in the lower left corner. When the slide is placed on the microscope stage, the screen will change to view your results. 4
5 8. For the bacteria you selected, record the bacteria s name, identify its shape and whether the bacteria is Gram + or Gram - in the Results Section. Repeat this experiment for at least three different bacteria. Before you finish, be sure you have observed at least one Gram + and one Gram - bacteria. 5
6 Lab Exercise Name Results Section Activity.1 Prokaryotic Cell Structure
7 Activity.2 Blue-Green Algae object object object object 7
8 Activity.3 Viruses surface proteins (found in some viruses) lipid envelope (found in some viruses)
9 Activity.4 Gram Staining of Bacteria 9
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD
 MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
MICROBIOLOGY LAB #1 SAFETY RULES & GRAM STAIN METHOD Precaution processes are extremely important when working with cultures in the lab for the safety of the microbiologist from getting diseases from bacteria
Exercise VI. Differential Staining: The Gram Stain
 Exercise VI Differential Staining: The Gram Stain The Gram stain, discovered by Dr. Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is the most useful differential stain used to aid in identifying bacteria. It divides bacterial
Exercise VI Differential Staining: The Gram Stain The Gram stain, discovered by Dr. Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is the most useful differential stain used to aid in identifying bacteria. It divides bacterial
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Required Materials: immersion oil microscopes Kim-wipes prepared microscope slides
 Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Microbiology CA/IA Lab Microscopic Examination of Microbes September 10 Objectives: 1. learn how to use a microscope to examine microbes 2. learn to recognize the characteristics of different microbes
Microbiology. Definition of a Microorganism. Microorganisms in the Lab. The Study of Microorganisms
 Microbiology The Study of Microorganisms Definition of a Microorganism Derived from the Greek: Mikros, «small» and Organismos, organism Microscopic organism which is single celled (unicellular) or a mass
Microbiology The Study of Microorganisms Definition of a Microorganism Derived from the Greek: Mikros, «small» and Organismos, organism Microscopic organism which is single celled (unicellular) or a mass
THE GRAM STAIN OBJECTIVE/RATIONALE KEY POINTS
 THE GRAM STAIN OBJECTIVE/RATIONALE One of the first procedures preformed by the medical microbiologist for the identification of bacteria is the Gram Stain. The student will learn the procedure for performing
THE GRAM STAIN OBJECTIVE/RATIONALE One of the first procedures preformed by the medical microbiologist for the identification of bacteria is the Gram Stain. The student will learn the procedure for performing
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 4. Discuss how microscopy has revealed the structure
Bacterial Gram Staining
 PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR021 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Bacterial Gram Staining Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 202) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique
 Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
Shape, Arrangement, and Size. Cocci (s., coccus) bacillus (pl., bacilli) 9/21/2013
 Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
Cell Structure. Lab Exercise 6. Contents. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Cell Structure Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Cellular Structures 2 Activity.2 Matching Exercise 2 Activity.3 Identify Organelles 2 Resutls Section 3 Objectives - Identify
Lab Exercise Cell Structure Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Cellular Structures 2 Activity.2 Matching Exercise 2 Activity.3 Identify Organelles 2 Resutls Section 3 Objectives - Identify
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
Microbiology and Protista Lab
 Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN
 Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN Introduction The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is a staining technique allowing different types of microorganisms (usually bacteria)
Exercise 6-B STAINING OF MICROORGANISMS GRAM STAIN Introduction The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is a staining technique allowing different types of microorganisms (usually bacteria)
Cellular Basis of Microbiology
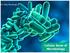 Presentation Subtitle Dr. Gary Mumaugh Cellular Basis of Microbiology Microorganism: Structure Structure of Prokaryotic Cell Structure of Eukaryotic Cell Microorganism: Varieties of Shapes Microorganism:
Presentation Subtitle Dr. Gary Mumaugh Cellular Basis of Microbiology Microorganism: Structure Structure of Prokaryotic Cell Structure of Eukaryotic Cell Microorganism: Varieties of Shapes Microorganism:
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour
 MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
EXERCISE CHAPTER. Marine Bacteria INTRODUCTION. Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION. & Bartlett Learning,
 EXERCISE CHAPTER 4 Marine Bacteria INTRODUCTION Jones & Bartlett To most of Learning, us, the ecological LLC roles of large divisions or Jones phyla of & life Bartlett forms seem Learning, rather obvious.
EXERCISE CHAPTER 4 Marine Bacteria INTRODUCTION Jones & Bartlett To most of Learning, us, the ecological LLC roles of large divisions or Jones phyla of & life Bartlett forms seem Learning, rather obvious.
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Kingdom Monera. These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class.
 Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Cell Shape coccus bacillus spirillum vibrio
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
Enzymes. Lab Exercise 7. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Enzymes Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Optimal ph 3 Activity.2 Optimal Temperature 4 Activity.3 Reaction Rates 4 Resutls Section 5 Objectives - Appreciate the sensitivity
Lab Exercise Enzymes Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Optimal ph 3 Activity.2 Optimal Temperature 4 Activity.3 Reaction Rates 4 Resutls Section 5 Objectives - Appreciate the sensitivity
MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
LABORATORY 7 ENDOSPORE STAIN AND BACTERIAL MOTILITY
 LABORATORY 7 ENDOSPORE STAIN AND BACTERIAL MOTILITY A. Endospore Stain B. Bacterial Motility A. ENDOSPORE STAIN DISCUSSION A few genera of bacteria, such as Bacillus and Clostridium have the ability to
LABORATORY 7 ENDOSPORE STAIN AND BACTERIAL MOTILITY A. Endospore Stain B. Bacterial Motility A. ENDOSPORE STAIN DISCUSSION A few genera of bacteria, such as Bacillus and Clostridium have the ability to
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Microbial Diversity. Yuzhen Ye I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University
 Microbial Diversity Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University Contents Microbial diversity Morphological, structural,
Microbial Diversity Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) I609 Bioinformatics Seminar I (Spring 2010) School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University Contents Microbial diversity Morphological, structural,
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote
 Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses 19.1 Bacteria Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2 Groups of Prokaryotes Prokaryote has no nucleus, bacteria Eukaryote has nucleus, plants, animals, fungi Archaebacteria Cell
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses 19.1 Bacteria Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2 Groups of Prokaryotes Prokaryote has no nucleus, bacteria Eukaryote has nucleus, plants, animals, fungi Archaebacteria Cell
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
TER 26. Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny. Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains. Nitrogen cycle
 Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification. ~10 um. Red Blood Cells = mm 1500 um. Width of penny
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10
 Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10 Principle and Purpose THE GRAM STAIN The Gram stain is perhaps the most useful test conducted in the clinical microbiology laboratory. It was first developed
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 10 Principle and Purpose THE GRAM STAIN The Gram stain is perhaps the most useful test conducted in the clinical microbiology laboratory. It was first developed
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
Take-Home Quiz I. Summer 2005 Semester
 General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name, you must enter your Patron ID Number (NOT
General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name, you must enter your Patron ID Number (NOT
EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS
 EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous exercise you studied the ultrastructure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells with the help of electron
EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous exercise you studied the ultrastructure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells with the help of electron
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses. Name Class Date
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 3. Observing Organisms Through a Microscope
 Chapter 3 Observing Organisms Through a Microscope Units of Measurement Used n Microbiology Table 3.1 mm Figure 3.2 Figure 3.1 - Overview Compound Light microscopy Have ocular and objective lenses Calculate
Chapter 3 Observing Organisms Through a Microscope Units of Measurement Used n Microbiology Table 3.1 mm Figure 3.2 Figure 3.1 - Overview Compound Light microscopy Have ocular and objective lenses Calculate
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
Mouth animalcules (bacteria)
 Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
 CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTRODUCTION. Gram Stain
 INTRODUCTION In microbiology, organisms are so small that additional techniques are often required for proper viewing under the microscope. Cytological stains, or dyes that stain cells or cellular features,
INTRODUCTION In microbiology, organisms are so small that additional techniques are often required for proper viewing under the microscope. Cytological stains, or dyes that stain cells or cellular features,
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques
 Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
CELL LAB OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION: CELL UNIT. After completing this lab you should be able to:
 AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
Subject: Staining-Bacterial Cell Structure Lecture Number: 3 Done by: Joud Baki Corrected by: Issa Deir
 Subject: Staining-Bacterial Cell Structure Lecture Number: 3 Done by: Joud Baki Corrected by: Issa Deir 0 Principles of staining: - Revision: Stains can be either simple or differential Gram stains are
Subject: Staining-Bacterial Cell Structure Lecture Number: 3 Done by: Joud Baki Corrected by: Issa Deir 0 Principles of staining: - Revision: Stains can be either simple or differential Gram stains are
Introduction to microbiology
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
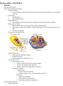 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria. Prepared by. Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood
 Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3
 MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms
 Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
MICR2208 Lecture 3: Prokaryotic Structure and Function 1
 MICR2208 Lecture 3: Prokaryotic Structure and Function 1 Diversity of Prokaryotes Size Not all prokaryotes are similar in size as they all differ, however, most of the prokaryotes cannot be seen from the
MICR2208 Lecture 3: Prokaryotic Structure and Function 1 Diversity of Prokaryotes Size Not all prokaryotes are similar in size as they all differ, however, most of the prokaryotes cannot be seen from the
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Directed Reading A. Section: Bacteria CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA. bacteria? a. cocci b. spirilla c. flagella d. bacilli.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Bacteria 1 Which of the following is true of bacteria? a All bacteria are the same size b Most bacteria can be seen without a microscope c There are fewer bacteria
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Bacteria 1 Which of the following is true of bacteria? a All bacteria are the same size b Most bacteria can be seen without a microscope c There are fewer bacteria
19-1 Notes Bacteria. Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope
 19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Eukaryotic Cells. Figure 1: A mitochondrion
 Eukaryotic Cells Figure 1: A mitochondrion How do cells accomplish all their functions in such a tiny, crowded package? Eukaryotic cells those that make up cattails and apple trees, mushrooms and dust
Eukaryotic Cells Figure 1: A mitochondrion How do cells accomplish all their functions in such a tiny, crowded package? Eukaryotic cells those that make up cattails and apple trees, mushrooms and dust
Kharkov National Medical University. Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich
 Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Bacteriology تركي محمد الداود مكتب 2 ب 45
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Bacteriology د. تركي محمد الداود مكتب 2 ب 45 Occurrence & distribution of bacteria - They live everywhere. They occur in water (fresh and salty), in soil
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Bacteriology د. تركي محمد الداود مكتب 2 ب 45 Occurrence & distribution of bacteria - They live everywhere. They occur in water (fresh and salty), in soil
Introduction to Bacteria
 Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA FLOW CHART UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
 ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells?
 Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology
 Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
BIOLOGY. Bacteria and Archaea
 27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
Red Layer Microbial Observatory Biology In-Lab Workshop Photosynthetic Microbes from Local Rivers & Beyond
 Red Layer Microbial Observatory Biology 507 - In-Lab Workshop Photosynthetic Microbes from Local Rivers & Beyond Schedule of Activities Session One 1. Microbial Diversity & the RLMO Program 2. Photosynthetic
Red Layer Microbial Observatory Biology 507 - In-Lab Workshop Photosynthetic Microbes from Local Rivers & Beyond Schedule of Activities Session One 1. Microbial Diversity & the RLMO Program 2. Photosynthetic
Ch 2 Part 2. The Microscope
 Ch 2 Part 2 The Microscope SLOs for Microscopic Analysis of Microorganisms Convert among the different units of the metric system. List and describe three elements of good microscopy. Differentiate between
Ch 2 Part 2 The Microscope SLOs for Microscopic Analysis of Microorganisms Convert among the different units of the metric system. List and describe three elements of good microscopy. Differentiate between
Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some
Bacteria Found on Frequently Used Surfaces on Campus
 Introduction: Bacteria Found on Frequently Used Surfaces on Campus Humans come into contact with a multitude of different surfaces on a daily basis. When we touch these surfaces, we simultaneously come
Introduction: Bacteria Found on Frequently Used Surfaces on Campus Humans come into contact with a multitude of different surfaces on a daily basis. When we touch these surfaces, we simultaneously come
Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista
 Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista Refer to the AP Biology book, Helms Labs 22 and be sure to site other resources used complete this lab in your lab journal. Be
Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista Refer to the AP Biology book, Helms Labs 22 and be sure to site other resources used complete this lab in your lab journal. Be
Creating a Dichotomous Key
 Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON
 TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-prescottsmicrobiology-9th-edition-by-willey-sherwood-woolverton/
TEST BANK FOR PRESCOTTS MICROBIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY WILLEY SHERWOOD WOOLVERTON Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-prescottsmicrobiology-9th-edition-by-willey-sherwood-woolverton/
Announcements KEY CONCEPTS
 What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Ch 10. Classification of Microorganisms
 Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain. Mgr. Tomáš Kastl
 Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain Mgr. Tomáš Kastl MARKS TO NOTICE Morphology of colonies and cells - strructure - size - surface - shape - profile - special organels
Microscopic and macroscopic observation of microorganisms & Gram stain Mgr. Tomáš Kastl MARKS TO NOTICE Morphology of colonies and cells - strructure - size - surface - shape - profile - special organels
Investigating Cells Lab. 1. What major differences do you expect to see between bacterial cells and plant/animal
 Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
