Diffusion wave and signal transduction in biological live cells. Department of Physics, School of Physics, Beijing Institute of
|
|
|
- Kathleen Stevenson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diffusion wave and signal transduction in biological live cells Tian You Fan 1 and Lei Fan 1 Department of Physics, School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing , China Department of Biology, School of Life Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing , China tyfan@bit.edu.cn; tyfan006@yahoo.com.cn Abstract Transduction of mechanical stimuli into biochemical signals is a fundamental subject for cell physics. In the experiments of FRET signal in cells a wave propagation in nanoscope was observed. We here develop a diffusion wave concept and try to give an explanation to the experimental observation. The theoretical prediction is in good agreement to result of the experiment. Mechanical effects of environment influence many essential processes of gene expression, cell survival and growth etc [1], among them the transduction of mechanical stimuli into biochemical signals is a fundamental subject for cell physics. However the mechanism on the transduction remains unsolved mystery so far [-7]. Combination of fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET), 1
2 genetically encoded biosensor and laser-tweezer [8-11] makes a revolutionary progress of our understanding on the transduction above mentioned in the recent two decades. This experimental technology enables the imaging and quantification of spatio-temporal characterization of mechanotransduction to biochemical signals in live cells. Wang et al. [9] carried out a systematical study by using fluorescent resonance energy transfer and developed a genetically encoded biosensor approach. They observed a series of signal transduction events at the cell membrane, in which the long-range wave propagation with speed U ( ) nm / s along the cell membrane is especially interesting. They further measured the wave length in a certain extent, this provides the most important information for theoretical analysis. Na et al. [] summarized the relevant studies up to 008 and developed the stress-induced Src activation, and analyzed some mechanism on the transduction, e.g. stress effect, interaction between integrins and cytoskeleton, deformation of mircotubules, effect of stiffness of substrates, conformational changes or unfolding of membrane-bound proteins, and diffusion of the proteins, and so on. There is no possibility to explore all aspects concerning the mechanism, it is difficult even if revealing each among them. In this note we focus on the dynamic process explored by Wang et al. [9], and suggest a
3 physical-mathematical model to explain the long-range wave propagation. Experiment [9] is carried out in a fibronectin-integrin-cytoskeleton-cell memebrane of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEs), this is a complex of proteins. A local mechanical stimulation is implemented by the laser-tweezer traction (The experimental detail can be referred to Wang et al. [9]). This aroused a motion of the protein complex, and led to a kind of wave propagation of Src activation with new feature. This new feature should reflect the dynamic nature of interaction between proteins and cell membrane. Due to the unclearness of mechanism of the wave propagation, the following study has to undertake some phenomenological analyses. One-dimensional analysis. Relative to slow wave propagation, the dimensional of cell body ( 1m1m 1m ) is quite large, we approximately assume that the cell membrane is a large plane for a certain time interval, we take the plane is xy plane. Furthermore, for simplicity we consider the one-dimensional case first. If the protein concentration of a cell is denoted by C( x, t ), then the equation of motion of the membrane-bound proteins is C t C D x (1) in which D represents diffusion coefficient of the membrane-bound proteins, x the spatial coordinate, t the time. 3
4 The local mechanical stimulation f ( x, t ) (induced by external force F( x, t ), or displacement u( x, t ), or stress ( xt, ) ) is not, in general, a periodic function, but which may be expanded by a Fourier series as follows n n n f ( x, t) Ane no i( xk t ) in which each Fourier component is a periodic function. For simplicity, we consider a periodic mechanical stimulation. Equation (1) is diffusion equation, for the periodic stimulation, it can have a wave propagation solution for long-range wave propagation such as C( x, t) i( kxt ) C0e () the wave is propagating along the cytoplasm membrane, in which C 0 is a constant, k the wave number, the circular frequency (or angular frequency), i 1, respectively, and the wave speed U is unknown at moment. Substituting () into (1) yields k 1 D (3) This is a new relation dispersion relation between and k, in which the wave number is connected to diffusion coefficient D, this is quite different from those based on traditional wave theory. The wave described by () and (3) may be viewed as diffusion wave. According to the well-known wave law one can find the wave speed as 4
5 U (4) k and substituting (3) into (4), we determine the wave speed as follows U 4kD 8 D (5) where is the wave length and there is relation between the wave length and the wave number k as below k (6) Formula (5) is also a new result, in which the wave speed depends upon not only quantity concerning wave (e.g. wave length) but also diffusion coefficient. With the above theoretical results, we can analysis on experimental phenomena. As reported in Ref [9], the observed values of wave length for the signal propagation are nm. In the following calculation one can take an average value, e.g. 500nm Furthermore we analyze the proteins are membrane-bound membrane proteins of cells, the diffusion coefficient of the proteins of cell membrane is in the order of magnitude (refer to Fan and Fan [1]) 9 13 D cm / s As an average value we take an average value, e.g. 10 D (3 5) 10 cm / s Substituting above data into (5), one finds that the wave propagation speed of PRET signal is in the range 5
6 U ( ) nm / s which is in good agreement to the experimental measurement value U ( ) nm / s that was measured by Wang et al. [9]. This has examined the efficiency of our physical-mathematical model. Two- and three-dimensional analysis. For simplicity only the one-dimensional analysis is discussed in the above section. However the two- and three-dimensional analyses have no difficulty and are given in the following. For two- and three-dimensional cases the equation of motion (1) will be replaced by t C D C in which C( r, t) represents the concentration of proteins of a cell, and (7) x y for two-dimensional case, and x y z for three-dimensional case, respectively. The wave solution of equation (7) is C( x, t) C e i( t) 0 kr (8) where C 0 is a constant, 1 i, k ( k, k, k ) x y z the wave vector, r ( x, y, z) the radius vector, and kxx kyy kr for two-dimensional case, and kr kx x k y y kzz for three-dimensional case, respectively. Furthermore the dispersion relation is similar to (3), i.e., 1 k kx k y kz k (9) D 6
7 The wave velocity formula is also similar to (4), i.e., U k (10) but here the wave velocity U is a vector rather than a scalar. According to (10) any wave velocity components can be evaluated. Up to now we have not found the experimental data concerning the two- and three-dimensional wave propagation in the mechanical activation in cells, the further calculation cannot be offered yet. Although the present study is phenomenological, the solution especially the new dispersion relation (3) are very simple and effective, which can serve a mathematical basis to explain the long-range wave propagation induced by external force stimulation to the living cells. Furthermore there is another example in physics (the phason dynamics of quasicrystals) supporting the diffusion wave theory, we will report the relevant results elsewhere. Acknowledgement The first author thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China for financial support. We also thank Dr. S. Chien of the University of California at San Diego and Dr. Y. Wang of University of Illinois at Urban for their helps, so that the figures of Ref [9] with high resolution are available. 7
8 [1] E B Singer, K D Puri, R Alon, M B Lawrences, U H von Andrian and H A Springer, Nature, 349, 66(1996). [] S Na, D Collin, F Chowdhury, B Tay, M Ouyan, Y Wang and N Wang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 105, 666(008). [3] D E Ingber and H Tensegrity, J. Cell. Sci., 116, 1397(003). [4] D P Felsenfeld, P L Schwarzberg, A Venegas, R Tse and M P Sheetz, Nature Cell Biol. 1, 00(1999). [5] D R Critchley, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1, 133(000). [6] M E Chicurel, R H Singer, C J Meyer and D E Ingber, Nature 39, 730 (1998). [7] E G Arias-Salgado, S. Lizano, S Sarker, J S Brugge, M. H. Ginsberg and S J Shattil, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 1398(003). [8] M Puig-de-Moreles, E Millet, B Fabry, D Navajas, N Wang, J P Butler and J J Fredberg, Am J. Physiol. 87, C643(004) [9] Y Wang, E L Botvinck, Y Zhaol, Berns M W, Usami S, Tsien R Y and S Chien, Nature 434, 1040(005). [10] Y Sawada, M Tamada, B J Dubin-Thaler, O Chemiavskaya, R Sakai, S Tanaka and M P Sheetz, Cell 17, 1015(006). [11] C P Johnson, H Y Tang, C Carag, D W Speicher and D E Discher, Science 317, 663(007). [1] L Fan and T Y Fan, Modern Physics Letters B 4, 1533(010). 8
6 Mechanotransduction
 6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Biol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 June 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Biol. 2009 September 15; 19(17): R745 R748. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.034. The mechanical cell Shang-You Tee 1, Andreas Bausch
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Biol. 2009 September 15; 19(17): R745 R748. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.034. The mechanical cell Shang-You Tee 1, Andreas Bausch
Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer
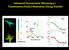 Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer 3.0 Pax 2.5 2.0 1200 800 400 GFP- Pax GFP-Pax + FATmCherry FAT FAT 1.5 Lifetime (ns) 0 1500 2000 2500 3000 Average lifetime
Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy I: Fluorescence (Foster) Resonance Energy Transfer 3.0 Pax 2.5 2.0 1200 800 400 GFP- Pax GFP-Pax + FATmCherry FAT FAT 1.5 Lifetime (ns) 0 1500 2000 2500 3000 Average lifetime
LIMIT CYCLE OSCILLATORS
 MCB 137 EXCITABLE & OSCILLATORY SYSTEMS WINTER 2008 LIMIT CYCLE OSCILLATORS The Fitzhugh-Nagumo Equations The best example of an excitable phenomenon is the firing of a nerve: according to the Hodgkin
MCB 137 EXCITABLE & OSCILLATORY SYSTEMS WINTER 2008 LIMIT CYCLE OSCILLATORS The Fitzhugh-Nagumo Equations The best example of an excitable phenomenon is the firing of a nerve: according to the Hodgkin
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION
 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 328 (2005) Long-distance propagation of forces in a cell
 Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 328 (2005) 1133 1138 BBRC www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Long-distance propagation of forces in a cell Ning Wang a, *, Zhigang Suo b a Physiology Program,
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 328 (2005) 1133 1138 BBRC www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Long-distance propagation of forces in a cell Ning Wang a, *, Zhigang Suo b a Physiology Program,
Dynamics of cell size and force during spreading
 1 Supplementary Information Dynamics of cell size and force during spreading Yifat Brill-Karniely 1, Noam Nisenholz 1, Kavitha Rajendran 2, Quynh Dang 2, Ramaswamy Krishnan 2, and Assaf Zemel 1,* Figure
1 Supplementary Information Dynamics of cell size and force during spreading Yifat Brill-Karniely 1, Noam Nisenholz 1, Kavitha Rajendran 2, Quynh Dang 2, Ramaswamy Krishnan 2, and Assaf Zemel 1,* Figure
Website: Selected readings Topics Introduction to Cell Biology Analysis of Cell Mechanics Cell
 Session 1 Website: http://faculty.washington.edu/nsniadec/me599/w13/ Selected readings Topics Introduction to Cell Biology Analysis of Cell Mechanics Cell Mechanics Modeling Measuring Cell Forces Mechanotransduction
Session 1 Website: http://faculty.washington.edu/nsniadec/me599/w13/ Selected readings Topics Introduction to Cell Biology Analysis of Cell Mechanics Cell Mechanics Modeling Measuring Cell Forces Mechanotransduction
Modelling spatio-temporal interactions within the cell
 Modelling cellular spatio-temporal interactions 157 Modelling spatio-temporal interactions within the cell PADMINI RANGAMANI* and RAVI IYENGAR Department of Pharmacology and Biological Chemistry, Mount
Modelling cellular spatio-temporal interactions 157 Modelling spatio-temporal interactions within the cell PADMINI RANGAMANI* and RAVI IYENGAR Department of Pharmacology and Biological Chemistry, Mount
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Fragility and mechanosensing in a thermalized cytoskeleton model with forced protein unfolding
 Fragility and mechanosensing in a thermalized cytoskeleton model with forced protein unfolding Brenton D. Hoffman,* Gladys Massiera, and John C. Crocker Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Fragility and mechanosensing in a thermalized cytoskeleton model with forced protein unfolding Brenton D. Hoffman,* Gladys Massiera, and John C. Crocker Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP.
![FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP. FRET 1 FRET CFP YFP. , resonance energy transfer, FRET), , CFP, (green fluorescent protein, GFP) ). GFP ]. GFP GFP, YFP. , GFP , CFP.](/thumbs/92/108070919.jpg) 980 Prog Biochem Biophys FRET 2 3 33 (, 510631) FRET 2,, 2,, 2 (fluorescence resonance energy transfer, FRET),, 2, ( FRET), 2, Q6 ( ) GFP CFP YFP : CFP : ( fluorescence YFP, resonance energy transfer,
980 Prog Biochem Biophys FRET 2 3 33 (, 510631) FRET 2,, 2,, 2 (fluorescence resonance energy transfer, FRET),, 2, ( FRET), 2, Q6 ( ) GFP CFP YFP : CFP : ( fluorescence YFP, resonance energy transfer,
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Quantitative Analysis of Forces in Cells
 Quantitative Analysis of Forces in Cells Anders Carlsson Washington University in St Louis Basic properties of forces in cells Measurement methods and magnitudes of particular types of forces: Polymerization
Quantitative Analysis of Forces in Cells Anders Carlsson Washington University in St Louis Basic properties of forces in cells Measurement methods and magnitudes of particular types of forces: Polymerization
Effective stochastic dynamics on a protein folding energy landscape
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 125, 054910 2006 Effective stochastic dynamics on a protein folding energy landscape Sichun Yang, a José N. Onuchic, b and Herbert Levine c Center for Theoretical Biological
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 125, 054910 2006 Effective stochastic dynamics on a protein folding energy landscape Sichun Yang, a José N. Onuchic, b and Herbert Levine c Center for Theoretical Biological
return in class, or Rm B
 Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Optical Tweezers. The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research
 Optical Tweezers The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research Student: Nikki Barron Class: Modern Physics/ Biophysics laboratory Advisor: Grant Allen Instructor: David Kleinfeld Date: June 15, 2012 Introduction
Optical Tweezers The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research Student: Nikki Barron Class: Modern Physics/ Biophysics laboratory Advisor: Grant Allen Instructor: David Kleinfeld Date: June 15, 2012 Introduction
SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes
 1/ 223 SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes Jane Hillston LFCS, School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Scotland 7th March 2013 Outline 2/ 223 1 Introduction
1/ 223 SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes Jane Hillston LFCS, School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Scotland 7th March 2013 Outline 2/ 223 1 Introduction
Transport of single molecules along the periodic parallel lattices with coupling
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 124 204901 2006 Transport of single molecules along the periodic parallel lattices with coupling Evgeny B. Stukalin The James Franck Institute The University of Chicago
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 124 204901 2006 Transport of single molecules along the periodic parallel lattices with coupling Evgeny B. Stukalin The James Franck Institute The University of Chicago
Homotopy Analysis Method for Nonlinear Differential Equations with Fractional Orders
 Homotopy Analysis Method for Nonlinear Differential Equations with Fractional Orders Yin-Ping Liu and Zhi-Bin Li Department of Computer Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai, 200062, China Reprint
Homotopy Analysis Method for Nonlinear Differential Equations with Fractional Orders Yin-Ping Liu and Zhi-Bin Li Department of Computer Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai, 200062, China Reprint
Supporting information. Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via
 Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics of a Membrane-Bulk Coupling Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 455 459 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 3, March 15, 2009 Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 455 459 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 3, March 15, 2009 Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS WAVES IN THE OCEANS. Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany
 WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
AXISYMMETRIC ELASTICITY PROBLEM OF CUBIC QUASICRYSTAL *
 Volume 9, Number April, 9-963//9/9- CHINESE PHYSICS c Chin. Phys. Soc. AXISYMMETRIC ELASTICITY PROBLEM OF CUBIC QUASICRYSTAL * Zhou Wang-min and Fan Tian-you Research Center of Materials Science, Beijing
Volume 9, Number April, 9-963//9/9- CHINESE PHYSICS c Chin. Phys. Soc. AXISYMMETRIC ELASTICITY PROBLEM OF CUBIC QUASICRYSTAL * Zhou Wang-min and Fan Tian-you Research Center of Materials Science, Beijing
A Quantitative Model of Cellular Elasticity Based on Tensegrity
 A Quantitative Model of Cellular Elasticity Based on Tensegrity Dimitrije Stamenović Mark F. Coughlin Department of Biomedical Engineering, Boston University, Boston, MA 02215 A tensegrity structure composed
A Quantitative Model of Cellular Elasticity Based on Tensegrity Dimitrije Stamenović Mark F. Coughlin Department of Biomedical Engineering, Boston University, Boston, MA 02215 A tensegrity structure composed
Single molecule force spectroscopy reveals a highly compliant helical
 Supplementary Information Single molecule force spectroscopy reveals a highly compliant helical folding for the 30 nm chromatin fiber Maarten Kruithof, Fan-Tso Chien, Andrew Routh, Colin Logie, Daniela
Supplementary Information Single molecule force spectroscopy reveals a highly compliant helical folding for the 30 nm chromatin fiber Maarten Kruithof, Fan-Tso Chien, Andrew Routh, Colin Logie, Daniela
CIV-E1060 Engineering Computation and Simulation Examination, December 12, 2017 / Niiranen
 CIV-E16 Engineering Computation and Simulation Examination, December 12, 217 / Niiranen This examination consists of 3 problems rated by the standard scale 1...6. Problem 1 Let us consider a long and tall
CIV-E16 Engineering Computation and Simulation Examination, December 12, 217 / Niiranen This examination consists of 3 problems rated by the standard scale 1...6. Problem 1 Let us consider a long and tall
Lecture 8: Temporal programs and the global structure of transcription networks. Chap 5 of Alon. 5.1 Introduction
 Lecture 8: Temporal programs and the global structure of transcription networks Chap 5 of Alon 5. Introduction We will see in this chapter that sensory transcription networks are largely made of just four
Lecture 8: Temporal programs and the global structure of transcription networks Chap 5 of Alon 5. Introduction We will see in this chapter that sensory transcription networks are largely made of just four
Jkjcj + C2 - Co)2, (1)
 ON THEORETICAL SHAPES OF BILIPID VESICLES UNDER CONDITIONS OF INCREASING MEMBRANE AREA JON C. LUKE, Department o Mathematical Sciences, Indiana University- Purdue University At Indianapolis, Indianapolis,
ON THEORETICAL SHAPES OF BILIPID VESICLES UNDER CONDITIONS OF INCREASING MEMBRANE AREA JON C. LUKE, Department o Mathematical Sciences, Indiana University- Purdue University At Indianapolis, Indianapolis,
Untangling the Mechanics of Entangled Biopolymers
 Untangling the Mechanics of Entangled Biopolymers Rae M. Robertson-Anderson Physics Department University of San Diego students/postdocs: Cole Chapman, PhD Tobias Falzone, PhD Stephanie Gorczyca, USD 16
Untangling the Mechanics of Entangled Biopolymers Rae M. Robertson-Anderson Physics Department University of San Diego students/postdocs: Cole Chapman, PhD Tobias Falzone, PhD Stephanie Gorczyca, USD 16
6 Models of cytoskeletal mechanics based on tensegrity
 6 Models of cytoskeletal mechanics based on tensegrity Dimitrije Stamenović ABSTRACT: Cell shape is an important determinant of cell function and it provides a regulatory mechanism to the cell. The idea
6 Models of cytoskeletal mechanics based on tensegrity Dimitrije Stamenović ABSTRACT: Cell shape is an important determinant of cell function and it provides a regulatory mechanism to the cell. The idea
Models of cytoskeletal mechanics of adherent cells
 Original paper Biomechan Model Mechanobiol 1 (2002) 95 108 Ó Springer-Verlag 2002 DOI 10.1007/s10237-002-0009-9 Models of cytoskeletal mechanics of adherent cells D. Stamenović, D. E. Ingber Abstract Adherent
Original paper Biomechan Model Mechanobiol 1 (2002) 95 108 Ó Springer-Verlag 2002 DOI 10.1007/s10237-002-0009-9 Models of cytoskeletal mechanics of adherent cells D. Stamenović, D. E. Ingber Abstract Adherent
A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF AN ADHERENT EUKARYOTIC CELL
 JG European McGarry Cells and and PJ Prendergast Materials Vol. 7. 2004 (pages 27-34) DOI: 10.22203/eCM.v007a03 Finite element model of ISSN an adherent 1473-2262 cell A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT
JG European McGarry Cells and and PJ Prendergast Materials Vol. 7. 2004 (pages 27-34) DOI: 10.22203/eCM.v007a03 Finite element model of ISSN an adherent 1473-2262 cell A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT
Supplemental Information. Spatio-temporal mapping of variation potentials in leaves of Helianthus annuus L. seedlings in
 Supplemental Information Spatio-temporal mapping of variation potentials in leaves of Helianthus annuus L. seedlings in situ using multi-electrode array Dong-Jie Zhao 1, Zhong-Yi Wang 1, Lan Huang 1*,
Supplemental Information Spatio-temporal mapping of variation potentials in leaves of Helianthus annuus L. seedlings in situ using multi-electrode array Dong-Jie Zhao 1, Zhong-Yi Wang 1, Lan Huang 1*,
Macromolecular Crowding
 Macromolecular Crowding Keng-Hwee Chiam Mathematical and Theoretical Biology Group Goodsell (1994) Macromolecular Crowding, Oct. 15, 2003 p.1/33 Outline What: introduction, definition Why: implications
Macromolecular Crowding Keng-Hwee Chiam Mathematical and Theoretical Biology Group Goodsell (1994) Macromolecular Crowding, Oct. 15, 2003 p.1/33 Outline What: introduction, definition Why: implications
Grouping of amino acids and recognition of protein structurally conserved regions by reduced alphabets of amino acids
 Science in China Series C: Life Sciences 2007 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Grouping of amino acids and recognition of protein structurally conserved regions by reduced alphabets of amino acids
Science in China Series C: Life Sciences 2007 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Grouping of amino acids and recognition of protein structurally conserved regions by reduced alphabets of amino acids
COMPLEX EFFECTS OF MOLECULAR TOPOLOGY, LENGTH AND CONCENTRATION ON MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN ENTANGLED DNA BLENDS
 COMPLEX EFFECTS OF MOLECULAR TOPOLOGY, LENGTH AND CONCENTRATION ON MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN ENTANGLED DNA BLENDS Students Cole E. Chapman Kent Lee Dean Henze Collaborators Doug Smith (UCSD) Sachin Shanbhag
COMPLEX EFFECTS OF MOLECULAR TOPOLOGY, LENGTH AND CONCENTRATION ON MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN ENTANGLED DNA BLENDS Students Cole E. Chapman Kent Lee Dean Henze Collaborators Doug Smith (UCSD) Sachin Shanbhag
Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch
 Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Some Generalizations of Logistic Model
 Review Communications Biomath Communications 4 (2017) Biomath Communications www.biomathforum.org/biomath/index.php/conference Some Generalizations of Logistic Model Gurgen Dallakyan Aygestan 8, Yerevan
Review Communications Biomath Communications 4 (2017) Biomath Communications www.biomathforum.org/biomath/index.php/conference Some Generalizations of Logistic Model Gurgen Dallakyan Aygestan 8, Yerevan
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease
 Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Size Scaling and Nondiffusive Features of Electron Heat Transport in Multi-Scale Turbulence
 Size Scaling and Nondiffusive Features of Electron Heat Transport in Multi-Scale Turbulence Z. Lin 1, Y. Xiao 1, W. J. Deng 1, I. Holod 1, C. Kamath, S. Klasky 3, Z. X. Wang 1, and H. S. Zhang 4,1 1 University
Size Scaling and Nondiffusive Features of Electron Heat Transport in Multi-Scale Turbulence Z. Lin 1, Y. Xiao 1, W. J. Deng 1, I. Holod 1, C. Kamath, S. Klasky 3, Z. X. Wang 1, and H. S. Zhang 4,1 1 University
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization
 Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
2018. Nonlinear free vibration analysis of nanobeams under magnetic field based on nonlocal elasticity theory
 2018. Nonlinear free vibration analysis of nanobeams under magnetic field based on nonlocal elasticity theory Tai-Ping Chang National Kaohsiung First University of Science and Technology, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
2018. Nonlinear free vibration analysis of nanobeams under magnetic field based on nonlocal elasticity theory Tai-Ping Chang National Kaohsiung First University of Science and Technology, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Elasticity of the human red blood cell skeleton
 Biorheology 40 (2003) 247 251 247 IOS Press Elasticity of the human red blood cell skeleton G. Lenormand, S. Hénon, A. Richert, J. Siméon and F. Gallet Laboratoire de Biorhéologie et d Hydrodynamique Physico-Chimique,
Biorheology 40 (2003) 247 251 247 IOS Press Elasticity of the human red blood cell skeleton G. Lenormand, S. Hénon, A. Richert, J. Siméon and F. Gallet Laboratoire de Biorhéologie et d Hydrodynamique Physico-Chimique,
Anatoly B. Kolomeisky. Department of Chemistry CAN WE UNDERSTAND THE COMPLEX DYNAMICS OF MOTOR PROTEINS USING SIMPLE STOCHASTIC MODELS?
 Anatoly B. Kolomeisky Department of Chemistry CAN WE UNDERSTAND THE COMPLEX DYNAMICS OF MOTOR PROTEINS USING SIMPLE STOCHASTIC MODELS? Motor Proteins Enzymes that convert the chemical energy into mechanical
Anatoly B. Kolomeisky Department of Chemistry CAN WE UNDERSTAND THE COMPLEX DYNAMICS OF MOTOR PROTEINS USING SIMPLE STOCHASTIC MODELS? Motor Proteins Enzymes that convert the chemical energy into mechanical
Protein Folding In Vitro*
 Protein Folding In Vitro* Biochemistry 412 February 29, 2008 [*Note: includes computational (in silico) studies] Fersht & Daggett (2002) Cell 108, 573. Some folding-related facts about proteins: Many small,
Protein Folding In Vitro* Biochemistry 412 February 29, 2008 [*Note: includes computational (in silico) studies] Fersht & Daggett (2002) Cell 108, 573. Some folding-related facts about proteins: Many small,
Membrane-bound Turing patterns
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 72, 061912 2005 Membrane-bound Turing patterns Herbert Levine and Wouter-Jan Rappel Center for Theoretical Biological Physics, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 72, 061912 2005 Membrane-bound Turing patterns Herbert Levine and Wouter-Jan Rappel Center for Theoretical Biological Physics, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive,
Monte Carlo Study of Planar Rotator Model with Weak Dzyaloshinsky Moriya Interaction
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 46 (2006) pp. 663 667 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 46, No. 4, October 15, 2006 Monte Carlo Study of Planar Rotator Model with Weak Dzyaloshinsky Moriya
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 46 (2006) pp. 663 667 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 46, No. 4, October 15, 2006 Monte Carlo Study of Planar Rotator Model with Weak Dzyaloshinsky Moriya
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
Laser. emission W FL
 W Laser Laser emission W FL Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison between fluorescence and laser emission spectra. The fluorescence has broad spectrum whereas the laser has very narrow spectrum. W FL and
W Laser Laser emission W FL Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison between fluorescence and laser emission spectra. The fluorescence has broad spectrum whereas the laser has very narrow spectrum. W FL and
MATHEMATICAL MODELS - Vol. III - Mathematical Modeling and the Human Genome - Hilary S. Booth MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND THE HUMAN GENOME
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND THE HUMAN GENOME Hilary S. Booth Australian National University, Australia Keywords: Human genome, DNA, bioinformatics, sequence analysis, evolution. Contents 1. Introduction:
MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND THE HUMAN GENOME Hilary S. Booth Australian National University, Australia Keywords: Human genome, DNA, bioinformatics, sequence analysis, evolution. Contents 1. Introduction:
What Is a Soliton? by Peter S. Lomdahl. Solitons in Biology
 What Is a Soliton? by Peter S. Lomdahl A bout thirty years ago a remarkable discovery was made here in Los Alamos. Enrico Fermi, John Pasta, and Stan Ulam were calculating the flow of energy in a onedimensional
What Is a Soliton? by Peter S. Lomdahl A bout thirty years ago a remarkable discovery was made here in Los Alamos. Enrico Fermi, John Pasta, and Stan Ulam were calculating the flow of energy in a onedimensional
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Mar 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Mar 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Mar 2001](/thumbs/88/114574654.jpg) Modeling two-state cooperativity in protein folding Ke Fan, Jun Wang, and Wei Wang arxiv:cond-mat/0103385v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Mar 2001 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructure and Department
Modeling two-state cooperativity in protein folding Ke Fan, Jun Wang, and Wei Wang arxiv:cond-mat/0103385v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Mar 2001 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructure and Department
Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems
 Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems Marina Ruths Department of Chemistry, UMass Lowell What can force measurements tell us about a system? Depending on the technique, we might
Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems Marina Ruths Department of Chemistry, UMass Lowell What can force measurements tell us about a system? Depending on the technique, we might
Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
 American Journal of Modern Physics 7; 6(5: 9-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmp doi:.68/j.ajmp.765.3 ISSN: 36-8867 (Print; ISSN: 36-889 (Online Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
American Journal of Modern Physics 7; 6(5: 9-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmp doi:.68/j.ajmp.765.3 ISSN: 36-8867 (Print; ISSN: 36-889 (Online Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
Properties of Life. Levels of Organization. Levels of Organization. Levels of Organization. Levels of Organization. The Science of Biology.
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
Supplementary Material
 1 2 3 Topological defects in confined populations of spindle-shaped cells by G. Duclos et al. Supplementary Material 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Supplementary Note 1: Characteristic time associated with the
1 2 3 Topological defects in confined populations of spindle-shaped cells by G. Duclos et al. Supplementary Material 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Supplementary Note 1: Characteristic time associated with the
Fura22. Ca 2 +, Study on Transmembrane Behaviors of Ca 2 + to Escherichia coli Cells with Fura22 Fluorescence Probe
 2004 62 4, 445 448 ACTA CHIMICA SINICA Vol 62, 2004 No 4, 445 448 Fura22 Ca 2 + Ξ, a, b b b a Ξ ( a 430072) ( b 430072) Fura22/ AM, Ca 2 + HB101, CaCl 2, Ca 2 +, ; Ca 2 +, Ca 2 +, Ca 2 +, Fura22/ AM, Study
2004 62 4, 445 448 ACTA CHIMICA SINICA Vol 62, 2004 No 4, 445 448 Fura22 Ca 2 + Ξ, a, b b b a Ξ ( a 430072) ( b 430072) Fura22/ AM, Ca 2 + HB101, CaCl 2, Ca 2 +, ; Ca 2 +, Ca 2 +, Ca 2 +, Fura22/ AM, Study
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
CEMB summer school. Intro to cell and tissue mechanics July 10, 2017 Paul Janmey
 CEMB summer school. Intro to cell and tissue mechanics July 10, 2017 Paul Janmey janmey@mail.med.upenn.edu Soft Stiff Motivation Soft tissues have well-defined and controlled elastic moduli Cells in vitro
CEMB summer school. Intro to cell and tissue mechanics July 10, 2017 Paul Janmey janmey@mail.med.upenn.edu Soft Stiff Motivation Soft tissues have well-defined and controlled elastic moduli Cells in vitro
Formation and breakage of noncovalent protein protein interactions
 Dynamics of unbinding of cell adhesion molecules: Transition from catch to slip bonds V. Barsegov and D. Thirumalai Institute for Physical Science and Technology and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Dynamics of unbinding of cell adhesion molecules: Transition from catch to slip bonds V. Barsegov and D. Thirumalai Institute for Physical Science and Technology and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
The architecture of transcription elongation A crystal structure explains how transcription factors enhance elongation and pausing
 The architecture of transcription elongation A crystal structure explains how transcription factors enhance elongation and pausing By Thomas Fouqueau and Finn Werner The molecular machines that carry out
The architecture of transcription elongation A crystal structure explains how transcription factors enhance elongation and pausing By Thomas Fouqueau and Finn Werner The molecular machines that carry out
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of spatially symmetric traveling waves. (a) Infusing flows and the positioning of a stationary standing wave.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of spatially symmetric traveling waves. (a) Infusing flows and the positioning of a stationary standing wave. The relative differences between the side flows shifts the
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of spatially symmetric traveling waves. (a) Infusing flows and the positioning of a stationary standing wave. The relative differences between the side flows shifts the
Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal
 Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal Tsung-Tsong Wu* Zin-Chen Hsu and Zi-ui Huang Institute of Applied
Band gaps and the electromechanical coupling coefficient of a surface acoustic wave in a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal Tsung-Tsong Wu* Zin-Chen Hsu and Zi-ui Huang Institute of Applied
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit Cell
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
six lectures on systems biology
 six lectures on systems biology jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 3 5 april 2011 part 2 seminar room, department of genetics a rather provisional syllabus
six lectures on systems biology jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 3 5 april 2011 part 2 seminar room, department of genetics a rather provisional syllabus
Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity. We ll start with optics. The one-dimensional wave equation. What is a wave? Optional optics texts: f(x)
 We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution.
 The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
Law of Gravity and Gravitational Radiation
 Law of Gravity and Gravitational Radiation Tian Ma, Shouhong Wang Supported in part by NSF and ONR http://www.indiana.edu/ fluid Blog: https://physicalprinciples.wordpress.com I. Laws of Gravity, Dark
Law of Gravity and Gravitational Radiation Tian Ma, Shouhong Wang Supported in part by NSF and ONR http://www.indiana.edu/ fluid Blog: https://physicalprinciples.wordpress.com I. Laws of Gravity, Dark
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Protein folding. Today s Outline
 Protein folding Today s Outline Review of previous sessions Thermodynamics of folding and unfolding Determinants of folding Techniques for measuring folding The folding process The folding problem: Prediction
Protein folding Today s Outline Review of previous sessions Thermodynamics of folding and unfolding Determinants of folding Techniques for measuring folding The folding process The folding problem: Prediction
Introduction ODEs and Linear Systems
 BENG 221 Mathematical Methods in Bioengineering ODEs and Linear Systems Gert Cauwenberghs Department of Bioengineering UC San Diego 1.1 Course Objectives 1. Acquire methods for quantitative analysis and
BENG 221 Mathematical Methods in Bioengineering ODEs and Linear Systems Gert Cauwenberghs Department of Bioengineering UC San Diego 1.1 Course Objectives 1. Acquire methods for quantitative analysis and
Theoretical analysis on the effect of divergent section with laminar boundary layer of sonic nozzles
 6th International Flow Measurement Conference, FOMEKO 03 4-6th September 03, Paris Theoretical analysis on the effect of divergent section with laminar boundary layer of sonic nozzles Hongbing Ding, Chao
6th International Flow Measurement Conference, FOMEKO 03 4-6th September 03, Paris Theoretical analysis on the effect of divergent section with laminar boundary layer of sonic nozzles Hongbing Ding, Chao
Local Measurements of Viscoelastic Parameters of Adherent Cell Surfaces by Magnetic Bead Microrheometry
 2038 Biophysical Journal Volume 75 October 1998 2038 2049 Local Measurements of Viscoelastic Parameters of Adherent Cell Surfaces by Magnetic Bead Microrheometry Andreas R. Bausch,* Florian Ziemann,* Alexei
2038 Biophysical Journal Volume 75 October 1998 2038 2049 Local Measurements of Viscoelastic Parameters of Adherent Cell Surfaces by Magnetic Bead Microrheometry Andreas R. Bausch,* Florian Ziemann,* Alexei
What Can Physics Say About Life Itself?
 What Can Physics Say About Life Itself? Science at the Interface of Physics and Biology Michael Manhart Department of Physics and Astronomy BioMaPS Institute for Quantitative Biology Source: UIUC, Wikimedia
What Can Physics Say About Life Itself? Science at the Interface of Physics and Biology Michael Manhart Department of Physics and Astronomy BioMaPS Institute for Quantitative Biology Source: UIUC, Wikimedia
Tailorable stimulated Brillouin scattering in nanoscale silicon waveguides.
 Tailorable stimulated Brillouin scattering in nanoscale silicon waveguides. Heedeuk Shin 1, Wenjun Qiu 2, Robert Jarecki 1, Jonathan A. Cox 1, Roy H. Olsson III 1, Andrew Starbuck 1, Zheng Wang 3, and
Tailorable stimulated Brillouin scattering in nanoscale silicon waveguides. Heedeuk Shin 1, Wenjun Qiu 2, Robert Jarecki 1, Jonathan A. Cox 1, Roy H. Olsson III 1, Andrew Starbuck 1, Zheng Wang 3, and
2. Waves and the Wave Equation
 2. Waves and the Wave Equation What is a wave? Forward vs. backward propagating waves The one-dimensional wave equation Phase velocity Reminders about complex numbers The complex amplitude of a wave What
2. Waves and the Wave Equation What is a wave? Forward vs. backward propagating waves The one-dimensional wave equation Phase velocity Reminders about complex numbers The complex amplitude of a wave What
Propagation of Plane Waves in Micro-stretch Elastic Solid in Special Case
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 973-768 Volume 3, Number 6 (7), pp. 43-5 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Propagation of Plane Waves in Micro-stretch Elastic
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 973-768 Volume 3, Number 6 (7), pp. 43-5 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Propagation of Plane Waves in Micro-stretch Elastic
A Model for Integrin Binding in Cells
 A Model for Integrin Binding in Cells By: Kara Huyett Advisor: Doctor Stolarska 31 st of August, 2015 Cell movement, and cell crawling in particular, has implications in various biological phenomena. For
A Model for Integrin Binding in Cells By: Kara Huyett Advisor: Doctor Stolarska 31 st of August, 2015 Cell movement, and cell crawling in particular, has implications in various biological phenomena. For
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10 Temporal Programs and the Global Structure The single-input module (SIM) network motif The network motifs we have studied so far all had a defined number of nodes.
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10 Temporal Programs and the Global Structure The single-input module (SIM) network motif The network motifs we have studied so far all had a defined number of nodes.
THE subject of the analysis is system composed by
 MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
From Molecular Cell Engineering to Biologically Inspired Engineering
 Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (Ó 2008) DOI: 10.1007/s12195-008-0006-x From Molecular Cell Engineering to Biologically Inspired Engineering DONALD E. INGBER Departments of Pathology and Surgery,
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (Ó 2008) DOI: 10.1007/s12195-008-0006-x From Molecular Cell Engineering to Biologically Inspired Engineering DONALD E. INGBER Departments of Pathology and Surgery,
Advanced ensemble modelling of flexible macromolecules using X- ray solution scattering
 Supporting information IUCrJ Volume 2 (2015) Supporting information for article: Advanced ensemble modelling of flexible macromolecules using X- ray solution scattering Giancarlo Tria, Haydyn D. T. Mertens,
Supporting information IUCrJ Volume 2 (2015) Supporting information for article: Advanced ensemble modelling of flexible macromolecules using X- ray solution scattering Giancarlo Tria, Haydyn D. T. Mertens,
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9 The Feed-Forward Loop Network Motif Subgraphs in random networks We have discussed the simplest network motif, self-regulation, a pattern with one node We now consider
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9 The Feed-Forward Loop Network Motif Subgraphs in random networks We have discussed the simplest network motif, self-regulation, a pattern with one node We now consider
Fluorescence Imaging of Signaling Networks
 Fluorescence Imaging of Signaling Networks Mary N. Teruel and Tobias Meyer Department of Molecular Pharmacology 269 Campus Drive, Room 3230 Stanford University School of Medicine Stanford, CA 94305 Tobias.meyer@stanford.edu
Fluorescence Imaging of Signaling Networks Mary N. Teruel and Tobias Meyer Department of Molecular Pharmacology 269 Campus Drive, Room 3230 Stanford University School of Medicine Stanford, CA 94305 Tobias.meyer@stanford.edu
Evolutionary Games and Computer Simulations
 Evolutionary Games and Computer Simulations Bernardo A. Huberman and Natalie S. Glance Dynamics of Computation Group Xerox Palo Alto Research Center Palo Alto, CA 94304 Abstract The prisoner s dilemma
Evolutionary Games and Computer Simulations Bernardo A. Huberman and Natalie S. Glance Dynamics of Computation Group Xerox Palo Alto Research Center Palo Alto, CA 94304 Abstract The prisoner s dilemma
Particles with opposite charges (positives and negatives) attract each other, while particles with the same charge repel each other.
 III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
A A A A B B1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
Scaling of erosion from laboratory experiments to temporal and spatial extent of a repository
 VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Scaling of erosion from laboratory experiments to temporal and spatial extent of a repository Clay Colloids in Aqueous Systems 3-4 February 2016, Berlin, Germany
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Scaling of erosion from laboratory experiments to temporal and spatial extent of a repository Clay Colloids in Aqueous Systems 3-4 February 2016, Berlin, Germany
PREREQUISITE CHECKLIST
 PREREQUISITE CHECKLIST UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY SCHOOL OF OPTOMETRY ADMISSIONS AND STUDENT AFFAIRS OFFICE Name: Date: Email: Status (complete, in progress, or planned) Prerequisite Course Requirements
PREREQUISITE CHECKLIST UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY SCHOOL OF OPTOMETRY ADMISSIONS AND STUDENT AFFAIRS OFFICE Name: Date: Email: Status (complete, in progress, or planned) Prerequisite Course Requirements
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Reply to the 'Comment on Intracellular stresses in patterned cell assemblies ' by D. Tambe et al., Soft Matter, 2014, 10, DOI: 10.
 Reply to the 'Comment on Intracellular stresses in patterned cell assemblies ' by D. Tambe et al., Soft Matter, 2014, 10, DOI: 10.1039/C4SM00597J Journal: Soft Matter Manuscript ID: SM-CMT-05-2014-001066.R2
Reply to the 'Comment on Intracellular stresses in patterned cell assemblies ' by D. Tambe et al., Soft Matter, 2014, 10, DOI: 10.1039/C4SM00597J Journal: Soft Matter Manuscript ID: SM-CMT-05-2014-001066.R2
Supplemental materials: The role of filopodia in the recognition of nanotopographies
 Supplemental materials: The role of filopodia in the recognition of nanotopographies Authors and affiliations: Jörg Albuschies and Viola Vogel* Department of Health Sciences and Technology ETH Zurich CH-8093
Supplemental materials: The role of filopodia in the recognition of nanotopographies Authors and affiliations: Jörg Albuschies and Viola Vogel* Department of Health Sciences and Technology ETH Zurich CH-8093
Propagation of Mechanical Stress through the Actin Cytoskeleton toward Focal Adhesions: Model and Experiment
 1470 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 February 2008 1470 1482 Propagation of Mechanical Stress through the Actin Cytoskeleton toward Focal Adhesions: Model and Experiment Raja Paul,* Patrick Heil, yz Joachim
1470 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 February 2008 1470 1482 Propagation of Mechanical Stress through the Actin Cytoskeleton toward Focal Adhesions: Model and Experiment Raja Paul,* Patrick Heil, yz Joachim
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation
 A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation Federico Felizzi and Dagmar Iber 1 D-BSSE, ETH Zurich, Mattenstrasse 26, CH-4058 Basel, Switzerland 1 Author for correspondance, Dagmar.Iber@bsse.ethz.ch
A Monte Carlo study of ligand-dependent integrin signal initiation Federico Felizzi and Dagmar Iber 1 D-BSSE, ETH Zurich, Mattenstrasse 26, CH-4058 Basel, Switzerland 1 Author for correspondance, Dagmar.Iber@bsse.ethz.ch
Sound Propagation through Media. Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON
 Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON Energy in Biological systems: 1 Photon = 400 pn.nm 1 ATP = 100 pn.nm 1 Ion moving across
Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON Energy in Biological systems: 1 Photon = 400 pn.nm 1 ATP = 100 pn.nm 1 Ion moving across
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 7 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 7 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 7 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/102608433.jpg) Role of self-loop in cell-cycle network of budding yeast Shu-ichi Kinoshita a, Hiroaki S. Yamada b a Department of Mathematical Engineering, Faculty of Engeneering, Musashino University, -- Ariake Koutou-ku,
Role of self-loop in cell-cycle network of budding yeast Shu-ichi Kinoshita a, Hiroaki S. Yamada b a Department of Mathematical Engineering, Faculty of Engeneering, Musashino University, -- Ariake Koutou-ku,
