2017 Drill Team Patten Drill Team Riders
|
|
|
- Juliana Cobb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Updated /0/0 0 Drill Team Patten A few things to know about the pattern:.it is not drawn to scale. The horses represented in these drawings do not understand the concept of even spacing..it is subject to change - it is a work in progress..remember to use your imagination not all steps are included.please follow your position and me (heidimckenzie@gmail.com) with mistakes 0 Drill Team Riders. Mark. Rachel. Lynne. Heather. Paul. Jerry. Sara. Marney. Heidi 0.Katie. Peg.Bonnie M.Aoife.Loree.Sam.Betty.Beatriz.Janis.Erica 0.Bonnie S.Brendan.Ariel Alt Lori Alt Lousia Alt Dottie page
2 Entry Column of Butterfly Heart Turn Snake Around Figure, column of Figure, column of Lace the Boot Passing Lines Loop di Loop Interdigitating Lines Swinging Gate Spoke Wheel Great Circle Giant Pinwheel Rank and File X-Factor Chevron Exit to Rail Do Si Do Out to rail for Salute Exit Lines Passing Ribbon Candy Circle Celtic Knot page
3 Entry Column of 0 0 spacing page
4 Butterfly Heart Turn aims for and leads group until center continues to follow aims for and leads group until center, then takes the lead aims for and follows aims for 0 0 spacing page
5 0 Snake Around 0 spacing page
6 0 0 Snake Around page
7 0 0 Fig., col of Meet your partner here page
8 Fig., col of Col of order & - R & - L & 0 - R & - L & - R & - L & - R & - L & - R 0 & - L 0 0 Large, even spacing Keep the size of the circles the same page
9 0 Fig., col of Col of order & - R & - L & 0 - R & - L & - R & - L & - R & - L & - R 0 & - L & - R 0 Large, even spacing Keep the size of the circles the same page
10 Fig. Pairs A: & B: & I G E C: & 0 D: & E: & F: & G: & H: & K A C B I: & J: 0 & K: & J D H F I G K I G K E A B C D B C D E A F J F H J H page 0
11 Fig. K I B K I B G C D E F D E F G C H A H J A J B K D B K D I E F G H F G H I E J C J A C A page
12 Fig. D B F D B F K G H I J H I J K G A E A C E C F D B H F D H I J K A J K A B I C G E C G E page
13 A B Fig., col of Order of pairings A & B C & D E & F H F G & H I & J 0 D J I 0 C G E page
14 G H C D A B I J E F Fig. J J H F C D H A B I C D G E J A B G H C D I G F E I A B E F page
15 I J A B B E F G H C D Fig. G G H H A B C D E F E F I J A A B E F H G D C I J I J C D page
16 Exiting Figure E F A B 0 J I H G 0 C D page
17 0 A B Exiting Figure E F Stand at I J Stand at follows follows Stand at 0 C D G H Stand at Large, even spacing page
18 Lace the Boot 0 0 page
19 Lace the Boot 0 0 page
20 Lace the Boot 0 0 page 0
21 0 Lace the Boot Everyone should be on the same side at the same time. 0 page
22 0 Lace the Boot 0 page
23 0 0 Exiting Lace the Boot follows and follow follows Outside for passing lines Turn left behind, cutting in if necessary page
24 0 Exiting Lace the Boot 0 Catch up to nose to tail page
25 Passing Lines 0 0 Nose to tail page
26 0 Passing Lines 0 Nose to tail page
27 Loop di Loop 0 0 Nose to tail page
28 Loop di Loop 0 0 Nose to tail - pass through center page
29 0 0 Loop di Loop Nose to tail page
30 0 Loop di Loop 0 Nose to tail - pass through center page 0
31 Interdigitating Lines 0 0 page
32 0 Interdigitating lines & lead across to center center 0 side to side page
33 0 0 Interdigitating lines & are the center horses; they should stay about apart Each line has an inside and outside horse. Everyone should stay even between the two riders. Outside Inside spacing between riders in same line page
34 Interdigitating Lines Each line has an inside and outside horse. Everyone should stay even between the two riders. Outside Inside 0 0 page
35 0 Interdigitating Lines 0 page
36 Interdigitating Lines 0 0 side to side page
37 0 0 Interdigitating Lines page
38 Interdigitating Lines 0 0 side to side page
39 0 End of Interdigitating Lines aims for. aims for. 0 aims for. aims for. page
40 0 Swinging gates Bring spacing to between riders aims for. aims for. 0 Everyone should get to the rail at the same time and spread out evenly between their outside and inside horse aims for. aims for. page 0
41 0 0 To the rail before Lines Passing spacing page
42 0 0 Lines Passing Turn wide at the corner spacing page
43 Passing Lines on Diagonal 0 0 spacing page
44 0 Inside up Inside horse move ahead at corner 0 Nose to tail page
45 0 Beginning of Ribbon Candy 0 Nose to tail spacing page
46 0 Ribbon Candy 0 page
47 Ribbon Candy 0 0 page
48 Ribbon Candy 0 0 page
49 Ribbon Candy into Circle 0 0 page
50 Circle 0 0 page 0
51 0 Circle 0 Spread out to spacing page
52 Great Circle 0 0 Spread out to spacing page
53 Celtic Knot 0 0 page
54 Celtic Knot 0 0 page
55 0 Celtic Knot 0 page
56 0 Celtic Knot 0 page
57 Celtic Knot 0 0 page
58 Spoke Wheel 0 0 Catch up nose to tail page
59 Spoke Wheel 0 0 page
60 -Spoke Wheel Quarter turn behind the group ahead Inside horses stay away from flags 0 0 page 0
61 -Spoke Wheel into Outside Rotation & Stay up with the outside horse, and in with the horse on your inside. 0 0 page
62 0 Outside Rotation of spokes & 0 page
63 Outside Rotation of spokes & 0 0 page
64 Outside Rotation & (cont) 0 0 page
65 Outside Rotations completed 0 0 page
66 0 Out to Great Circle 0 page
67 0 Great Circle 0 Even spacing page
68 0 0 Close Call page
69 0 Passing Lines in pairs 0 Nose to tail Stay in towards the horse on your right the inside page
70 Giant Pinwheel 0 0 page 0
71 0 Giant Pinwheel 0 page
72 After / turns - Exiting Giant Pinwheel As pairs, & lead out to the rail, turning left, followed by: & & 0 & & 0 0 As pairs, & lead out to the rail, turning left, followed by: & & & & 0 & About spacing page
73 Entering Rank & File 0 0 page
74 Rank & File Leg yield out on whistle Outside lines move Inside lines move Outside lines, be careful not to go to far out 0 0 side to side front to back page
75 Rank & File 0 0 side to side front to back page
76 Rank & File 0 0 side to side front to back page
77 Salute, then out to rail Leaders should get to rail at the same 0 0 page
78 0 Out to the rail 0 page
79 0 Passing Lines 0 page
80 X-Factor Meet in middle 0 0 spacing page 0
81 0 X-Factor 0 side to side page
82 0 X-Factor 0 Meet in middle page
83 X-Factor 0 0 page
84 0 X-Factor 0 page
85 X-Factor 0 0 page
86 X-Factor 0 0 page
87 0 X-Factor 0 page
88 0 X-Factor 0 page
89 0 X-Factor 0 page
90 X-Factor 0 0 page 0
91 0 Chevron 0 Wedge nose to hip Side to side spacing - leave enough room to pass page
92 0 0 Chevron page
93 0 0 X-Factor Chevron page
94 0 0 Chevron There should be separate wedges - lead horses should stay back feet from the group ahead of them. page
95 Chevron & continue forward then turn to follow 0 0 page
96 Chevron into Do-si-do This side should be slightly ahead of other side 0 0 page
97 Do-si-do 0 0 spacing page
98 0 0 Do-si-do spacing page
99 0 0 Do-si-do spacing page
100 0 Do-si-do 0 spacing page 00
101 Exit Do-si-do 0 0 spacing page 0
102 Salute the crowd 0 0 spacing page 0
103 0 Exit 0 page 0
104 Exit 0 0 page 0
105 Exit 0 0 Medium trot to allow everyone to catch up Nose to tail page 0
106 Exit 0 0 Nose to tail page 0
107 How did they do that? Exit 0 0 Nose to tail page 0
108 How did they do that? Exit 0 0 Nose to tail page 0
109 How did they do that? Exit 0 Arrive in line a the same time as partner 0 Nose to tail page 0
110 0 0 Are they ever going to leave? Exit follows follows page 0
111 0 0 Are they ever going to leave? Exit follows follows page
112 0 Are they ever going to leave? Exit 0 follows follows page
113 Final Exit 0 0 Exit out the gate page
2009 Drill Team Pattern - Draft Version
 00 Drill Team Pattern - Draft Version A few things to know about the pattern:. It is not drawn to scale. It is subject to change - it is a work in progress.. At all times, stay 0 feet off the rail. Remember
00 Drill Team Pattern - Draft Version A few things to know about the pattern:. It is not drawn to scale. It is subject to change - it is a work in progress.. At all times, stay 0 feet off the rail. Remember
2010 Draft Drill Team Pattern
 0 Draft Drill Team Pattern A few things to know about the pattern:. It is not drawn to scale. It is subject to change - it is a work in progress.. At all times, stay 0 feet off the rail. Remember to use
0 Draft Drill Team Pattern A few things to know about the pattern:. It is not drawn to scale. It is subject to change - it is a work in progress.. At all times, stay 0 feet off the rail. Remember to use
Introduction to Playground Circuits
 Introduction to Playground Circuits These playground circuits are designed to help kids get active while still making sure that they are having fun. These circuits will encourage kids to engage in physical
Introduction to Playground Circuits These playground circuits are designed to help kids get active while still making sure that they are having fun. These circuits will encourage kids to engage in physical
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere
 AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 1: Stellarium and The Celestial Sphere Name: Student number (SUID): Lab section: Group Members: 1 Introduction Following the prelab, you should be now acquainted
Section 29: What s an Inverse?
 Section 29: What s an Inverse? Our investigations in the last section showed that all of the matrix operations had an identity element. The identity element for addition is, for obvious reasons, called
Section 29: What s an Inverse? Our investigations in the last section showed that all of the matrix operations had an identity element. The identity element for addition is, for obvious reasons, called
Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses
 Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
LASER TEAM ANTI-BULLYING PROGRAM STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS
 LASER TEAM ANTI-BULLYING PROGRAM STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS Dear Assembly Coordinator and Teachers, The following pages contain a review of the sign language used, student worksheet masters
LASER TEAM ANTI-BULLYING PROGRAM STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS Dear Assembly Coordinator and Teachers, The following pages contain a review of the sign language used, student worksheet masters
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall Nov. 4/5 Solution Set - The Pythagorean Theorem
 1 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 014 - Nov. 4/5 Solution Set - The Pythagorean Theorem 1. Let a and b be the lengths
1 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 014 - Nov. 4/5 Solution Set - The Pythagorean Theorem 1. Let a and b be the lengths
Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations
 Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations Question 1 One revolution is equal to one circumference: C = r = 6 = 1, which is approximately 37.68 inches. Multiply that by 100 to get 3,768
Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations Question 1 One revolution is equal to one circumference: C = r = 6 = 1, which is approximately 37.68 inches. Multiply that by 100 to get 3,768
Magnets and Potential Energy
 efinitions of Energy Magnets and Potential Energy 1 Potential energy (PE), also known as stored energy, is the energy stored within a physical system. Since energy can be defined as the ability to do work
efinitions of Energy Magnets and Potential Energy 1 Potential energy (PE), also known as stored energy, is the energy stored within a physical system. Since energy can be defined as the ability to do work
In this section we want to learn how to solve equations containing radicals, like 5 x 4 = 9. In order to do this we need the following property.
 .7 Solving Radical Equations In this section we want to learn how to solve equations containing radicals, like. In order to do this we need the following property. n-th Power Property n n If a b, then
.7 Solving Radical Equations In this section we want to learn how to solve equations containing radicals, like. In order to do this we need the following property. n-th Power Property n n If a b, then
MATH-G Circles Task Cards Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-G Circles Task Cards Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:YL6VSY 1 Chords MA and TH intersect forming segments with the measures shown. What is the value of x? A 40 B 5 C 20 D 8
MATH-G Circles Task Cards Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:YL6VSY 1 Chords MA and TH intersect forming segments with the measures shown. What is the value of x? A 40 B 5 C 20 D 8
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
PHYS208 RECITATIONS PROBLEMS: Week 2. Electric fields
 Electric fields Prob.#1 Prob.#2 Prob.#3 Prob.#4 Prob.#5 Total Your Name: Your UIN: Your section# These are the problems that you and a team of other 2-3 students will be asked to solve during the recitation
Electric fields Prob.#1 Prob.#2 Prob.#3 Prob.#4 Prob.#5 Total Your Name: Your UIN: Your section# These are the problems that you and a team of other 2-3 students will be asked to solve during the recitation
Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA
 Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA Observations and measurements on board Your sensations and the spring accelerometer 1) For the two positions indicated by the arrows, note down changes to how heavy
Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA Observations and measurements on board Your sensations and the spring accelerometer 1) For the two positions indicated by the arrows, note down changes to how heavy
PHY221 Lab 2 - Experiencing Acceleration: Motion with constant acceleration; Logger Pro fits to displacement-time graphs
 Page 1 PHY221 Lab 2 - Experiencing Acceleration: Motion with constant acceleration; Logger Pro fits to displacement-time graphs Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names You will return this handout to
Page 1 PHY221 Lab 2 - Experiencing Acceleration: Motion with constant acceleration; Logger Pro fits to displacement-time graphs Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names You will return this handout to
Sun, Moon, and Stars. The Stars
 The Sun The Moon Sun, Moon, and Stars The Stars VOCABULARY *The sun is the star that rises in the morning, crosses the sky, and sets at night. *The cardinal directions are the four main points on a compass:
The Sun The Moon Sun, Moon, and Stars The Stars VOCABULARY *The sun is the star that rises in the morning, crosses the sky, and sets at night. *The cardinal directions are the four main points on a compass:
Phys 2B Final Exam Name:
 Phys 2B Final Exam Name: Multiple Choice (3 points each) 1. Two capacitors initially uncharged are connected in series to a battery, as shown. What is the charge on the top plate of C 1? a. 81 μc b. 18
Phys 2B Final Exam Name: Multiple Choice (3 points each) 1. Two capacitors initially uncharged are connected in series to a battery, as shown. What is the charge on the top plate of C 1? a. 81 μc b. 18
a C = 1.4) If the mass of a rider is 65 kg, then what is the rider s centripetal force?
 Ferris Wheel Select Ferris Wheel. After the animation pops up press the Play button. 1.1) Use the stopwatch to measure the period of motion for the Ferris wheel. What is its period? T = 1.2) Calculate
Ferris Wheel Select Ferris Wheel. After the animation pops up press the Play button. 1.1) Use the stopwatch to measure the period of motion for the Ferris wheel. What is its period? T = 1.2) Calculate
Select activities then select grade level. Click on Search.
 Dear Fifth Grader, Your math packet was created to give you practice with applying your skills. Remember use what you know to figure things out and to come up with a strategy to solve. Please be sure to
Dear Fifth Grader, Your math packet was created to give you practice with applying your skills. Remember use what you know to figure things out and to come up with a strategy to solve. Please be sure to
L I T T L E L I O N C H A L L E N G E
 L I T T L E L I O N C H A L L E N G E Dear Teacher: We are excited to have you and your students participate in Little Lion Challenge Day this year! Little Lion Challenge Day is February 11th and it is
L I T T L E L I O N C H A L L E N G E Dear Teacher: We are excited to have you and your students participate in Little Lion Challenge Day this year! Little Lion Challenge Day is February 11th and it is
(1) Recall the different isomers mentioned in this tutorial.
 DAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Conformational Analysis Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Isomers that differ by rotation about a single bond are called: Question #01 (A) Stereoisomers (B) Constitutional
DAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Conformational Analysis Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Isomers that differ by rotation about a single bond are called: Question #01 (A) Stereoisomers (B) Constitutional
BSCS Science: An Inquiry Approach Level 3
 BSCS Science: An Inquiry Approach Level 3 First edition, 2010 by BSCS Unit 5 Overview 5415 Mark Dabling Blvd. Colorado Springs, CO 80919 719.531.5550 www.bscs.org Unit Overview Nanoscience and nanotechnology
BSCS Science: An Inquiry Approach Level 3 First edition, 2010 by BSCS Unit 5 Overview 5415 Mark Dabling Blvd. Colorado Springs, CO 80919 719.531.5550 www.bscs.org Unit Overview Nanoscience and nanotechnology
AP Physics Daily Problem #31
 AP Physics Daily Problem #31 A 10kg mass is whirled around on the end of a 3m long cord. The speed of the mass is 7m/s. Ignore gravitational forces. 3.0m 7.0m/s Draw a free body diagram of the mass. (hint:
AP Physics Daily Problem #31 A 10kg mass is whirled around on the end of a 3m long cord. The speed of the mass is 7m/s. Ignore gravitational forces. 3.0m 7.0m/s Draw a free body diagram of the mass. (hint:
Lesson 12: Solving Equations
 Exploratory Exercises 1. Alonzo was correct when he said the following equations had the same solution set. Discuss with your partner why Alonzo was correct. (xx 1)(xx + 3) = 17 + xx (xx 1)(xx + 3) = xx
Exploratory Exercises 1. Alonzo was correct when he said the following equations had the same solution set. Discuss with your partner why Alonzo was correct. (xx 1)(xx + 3) = 17 + xx (xx 1)(xx + 3) = xx
6 Hour Radar Observer (Unlimited) Recertification Class INFORMATION & REVIEW PACKAGE
 6 Hour Radar Observer (Unlimited) Recertification Class INFORMATION & REVIEW PACKAGE Course requirements Instructions Plotting review Practice problems/answers Course Requirements Objective: Demonstrate
6 Hour Radar Observer (Unlimited) Recertification Class INFORMATION & REVIEW PACKAGE Course requirements Instructions Plotting review Practice problems/answers Course Requirements Objective: Demonstrate
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion
 Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures
 II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
EXPERIMENT 7: ANGULAR KINEMATICS AND TORQUE (V_3)
 TA name Lab section Date TA Initials (on completion) Name UW Student ID # Lab Partner(s) EXPERIMENT 7: ANGULAR KINEMATICS AND TORQUE (V_3) 121 Textbook Reference: Knight, Chapter 13.1-3, 6. SYNOPSIS In
TA name Lab section Date TA Initials (on completion) Name UW Student ID # Lab Partner(s) EXPERIMENT 7: ANGULAR KINEMATICS AND TORQUE (V_3) 121 Textbook Reference: Knight, Chapter 13.1-3, 6. SYNOPSIS In
Percentile: Formula: To find the percentile rank of a score, x, out of a set of n scores, where x is included:
 AP Statistics Chapter 2 Notes 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Percentile: The pth percentile of a distribution is the value with p percent of the observations (If your test score places you in
AP Statistics Chapter 2 Notes 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Percentile: The pth percentile of a distribution is the value with p percent of the observations (If your test score places you in
PHY 111L Activity 2 Introduction to Kinematics
 PHY 111L Activity 2 Introduction to Kinematics Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce the relationship between position, velocity, and acceleration 2. Investigate
PHY 111L Activity 2 Introduction to Kinematics Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce the relationship between position, velocity, and acceleration 2. Investigate
Q25: Record the wavelength of each colored line according to the scale given.
 C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
DUPLICATION PROHIBITED by copyright holder
 C o n t e n t s Preface to the Paperback Edition ix Foreword by George H. Morris xi I n t r o d u c t i o n The Basics Behind the Basics xv Part I Basic Flat Work C H A P T E R O N E Why Flat Work? 3 A
C o n t e n t s Preface to the Paperback Edition ix Foreword by George H. Morris xi I n t r o d u c t i o n The Basics Behind the Basics xv Part I Basic Flat Work C H A P T E R O N E Why Flat Work? 3 A
Shenandoah University. (PowerPoint) LESSON PLAN *
 Shenandoah University (PowerPoint) LESSON PLAN * NAME DATE 10/28/04 TIME REQUIRED 90 minutes SUBJECT Algebra I GRADE 6-9 OBJECTIVES AND PURPOSE (for each objective, show connection to SOL for your subject
Shenandoah University (PowerPoint) LESSON PLAN * NAME DATE 10/28/04 TIME REQUIRED 90 minutes SUBJECT Algebra I GRADE 6-9 OBJECTIVES AND PURPOSE (for each objective, show connection to SOL for your subject
Question 2 (12 marks)
 PHYS 1131 Test 1, 2005 Question 1 (23 marks) a) Investigators at the scene of an accident see that a car has left black rubber marks ("skid marks") that are L = 22 m long on a flat section of road. The
PHYS 1131 Test 1, 2005 Question 1 (23 marks) a) Investigators at the scene of an accident see that a car has left black rubber marks ("skid marks") that are L = 22 m long on a flat section of road. The
THE GREAT SUN-EARTH-MOON LINE-UP
 NAME DATE PARTNERS THE GREAT SUN-EARTH-MOON LINE-UP Activity 1: Where Do Lunar Phases Come From? The phases of the moon have fascinated people for thousands of years. They have appeared in myths, art,
NAME DATE PARTNERS THE GREAT SUN-EARTH-MOON LINE-UP Activity 1: Where Do Lunar Phases Come From? The phases of the moon have fascinated people for thousands of years. They have appeared in myths, art,
CHUNG-ANG UNIVERSITY Linear Algebra Spring Solutions to Computer Project #2
 CHUNG-ANG UNIVERSITY Linear Algebra Spring 2014 s to Computer Project #2 Problem 2.1 Find the adjacency matrix for the following graph (all edges are bidirectional). P5 From the given bidirectional graph
CHUNG-ANG UNIVERSITY Linear Algebra Spring 2014 s to Computer Project #2 Problem 2.1 Find the adjacency matrix for the following graph (all edges are bidirectional). P5 From the given bidirectional graph
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment
 N a m e : _ AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Concepts and Connections of Math in Physics: Review This assignment is designed to refresh the student with an understanding of conceptual math problems that
N a m e : _ AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Concepts and Connections of Math in Physics: Review This assignment is designed to refresh the student with an understanding of conceptual math problems that
The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates.
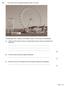 Q1. The London Eye is the largest observation wheel in the world. The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates. (a) Explain how the wheel can move at a steady
Q1. The London Eye is the largest observation wheel in the world. The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates. (a) Explain how the wheel can move at a steady
REVIEW SET MIDTERM 1
 Physics 010 Fall 01 Orest Symko REVIEW SET MIDTERM 1 1. On April 15, 1991, Dr. Rudolph completed the Boston Marathon (6 miles, 385 yards) in a time of 3 hours, minutes, 30 seconds. Later in the summer
Physics 010 Fall 01 Orest Symko REVIEW SET MIDTERM 1 1. On April 15, 1991, Dr. Rudolph completed the Boston Marathon (6 miles, 385 yards) in a time of 3 hours, minutes, 30 seconds. Later in the summer
Lesson 9. Exit Ticket Sample Solutions ( )= ( ) The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79
 Exit Ticket Sample Solutions 1. Find the arc length of. ( )= ()() ( )=. ( ) = The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79 1. and are points on the circle of radius, and the
Exit Ticket Sample Solutions 1. Find the arc length of. ( )= ()() ( )=. ( ) = The arc length of is (. ) or.. Homework Problem Set Sample Solutions S.79 1. and are points on the circle of radius, and the
Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class.
 b Lab Physics 211 Lab 10 Torque What You Need To Know: Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class. F (a) (b) FIGURE 1 Forces acting on an object
b Lab Physics 211 Lab 10 Torque What You Need To Know: Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class. F (a) (b) FIGURE 1 Forces acting on an object
Circular Velocity and Centripetal Acceleration
 1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead. Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity
 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
MODEL 1: Molecule Shapes Simulation (http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/molecule- shapes)
 Molecule Shapes MODEL 1: Molecule Shapes Simulation (http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/molecule- shapes) PART I: ELECTRON DOMAINS 1. Explore the Model screen of the simulation. As you explore, answer
Molecule Shapes MODEL 1: Molecule Shapes Simulation (http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/molecule- shapes) PART I: ELECTRON DOMAINS 1. Explore the Model screen of the simulation. As you explore, answer
Self-Directed Course: Transitional Math Module 4: Algebra
 Lesson #1: Solving for the Unknown with no Coefficients During this unit, we will be dealing with several terms: Variable a letter that is used to represent an unknown number Coefficient a number placed
Lesson #1: Solving for the Unknown with no Coefficients During this unit, we will be dealing with several terms: Variable a letter that is used to represent an unknown number Coefficient a number placed
Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum
 b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: The Physics Today we will deal with two physical concepts: impulse and momentum. For both, it turns out to be harder to say what they
b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: The Physics Today we will deal with two physical concepts: impulse and momentum. For both, it turns out to be harder to say what they
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running
Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running
EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK
 Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
Did you read chapter 7? Housekeeping. Special Relativity Postulates. Famous quotes from Einstein. Symmetry. (Special Principle of Relativity) 5/9/2007
 Housekeeping Vocab quiz: Do Due Exam versus Vocab Quiz Did you read chapter 7? a) Yes b) No c) We have a book? 1 2 Famous quotes from Einstein "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not
Housekeeping Vocab quiz: Do Due Exam versus Vocab Quiz Did you read chapter 7? a) Yes b) No c) We have a book? 1 2 Famous quotes from Einstein "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not
TEACHER Worksheet: Phases of the Moon and Tides
 TEACHER Worksheet: Phases of the Moon and Tides Subject: Physics & Astronomy Grades levels: 6-8 Description: Data pattern recognition exercise where students compare the two daily datasets (for one month)
TEACHER Worksheet: Phases of the Moon and Tides Subject: Physics & Astronomy Grades levels: 6-8 Description: Data pattern recognition exercise where students compare the two daily datasets (for one month)
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Coulomb s Law. 1 Equipment. 2 Introduction
 Coulomb s Law 1 Equipment conducting ball on mono filament 2 conducting balls on plastic rods housing with mirror and scale vinyl strips (white) wool pads (black) acetate strips (clear) cotton pads (white)
Coulomb s Law 1 Equipment conducting ball on mono filament 2 conducting balls on plastic rods housing with mirror and scale vinyl strips (white) wool pads (black) acetate strips (clear) cotton pads (white)
Animal Trivia. When a dolphin is sick or injured, it makes a distress call to other dolphins, who help bring it to the surface so it can breathe.
 Animal Trivia When a dolphin is sick or injured, it makes a distress call to other dolphins, who help bring it to the surface so it can breathe. A queen ant can live up to 25 years of age. A hippopotamus
Animal Trivia When a dolphin is sick or injured, it makes a distress call to other dolphins, who help bring it to the surface so it can breathe. A queen ant can live up to 25 years of age. A hippopotamus
FORCES & MOTION STUDY GUIDE. 1. What does it mean when forces are balanced on an object? (Exploration F)
 FORCES & MOTION STUDY GUIDE 1. What does it mean when forces are balanced on an object? (Exploration F) 2. How do unbalanced forces affect the motion of an object? (Exploration G and Idea Questions) 3.
FORCES & MOTION STUDY GUIDE 1. What does it mean when forces are balanced on an object? (Exploration F) 2. How do unbalanced forces affect the motion of an object? (Exploration G and Idea Questions) 3.
BELLWORK feet
 BELLWORK 1 A hot air balloon is being held in place by two people holding ropes and standing 35 feet apart. The angle formed between the ground and the rope held by each person is 40. Determine the length
BELLWORK 1 A hot air balloon is being held in place by two people holding ropes and standing 35 feet apart. The angle formed between the ground and the rope held by each person is 40. Determine the length
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses
 Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Daily Science 03/30/2017
 Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
A SIMPLE MODEL OF A CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR FOR QUADRUPED GAITS
 A SIMPLE MODEL OF A CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR FOR QUADRUPED GAITS JEFFREY MARSH Humankind s long association with four-legged animals, wild as well as domesticated, has produced a rich vocabulary of words
A SIMPLE MODEL OF A CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR FOR QUADRUPED GAITS JEFFREY MARSH Humankind s long association with four-legged animals, wild as well as domesticated, has produced a rich vocabulary of words
Reading Question 24.1
 Reading Question 24.1 A compass in a magnetic field will line up A. With the north pole pointing in the direction of the magnetic field. B. With the north pole pointing opposite the direction of the magnetic
Reading Question 24.1 A compass in a magnetic field will line up A. With the north pole pointing in the direction of the magnetic field. B. With the north pole pointing opposite the direction of the magnetic
Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic
 Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic A is a quantity that has magnitude but no direction. You can have signed scalar quantities as well. A is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic A is a quantity that has magnitude but no direction. You can have signed scalar quantities as well. A is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Student Book SERIES. Measurement. Name
 Student Book Name ontents Series Topic 1 Length (pp. 1 12) l language of length l measure with informal units l choose an appropriate unit to measure l compare and order lengths l centimetres l metres
Student Book Name ontents Series Topic 1 Length (pp. 1 12) l language of length l measure with informal units l choose an appropriate unit to measure l compare and order lengths l centimetres l metres
PHYSICS Principles and Problems. Chapter 2: Representing Motion
 PHYSICS Principles and Problems Chapter 2: Representing Motion CHAPTER 2 Representing Motion BIG IDEA You can use displacement and velocity to describe an object s motion. CHAPTER 2 Table Of Contents Section
PHYSICS Principles and Problems Chapter 2: Representing Motion CHAPTER 2 Representing Motion BIG IDEA You can use displacement and velocity to describe an object s motion. CHAPTER 2 Table Of Contents Section
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 4335/03 4437/08 London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry 4335 Paper 3 Science (Double Award) 4437 Paper
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 4335/03 4437/08 London Examinations IGCSE Chemistry 4335 Paper 3 Science (Double Award) 4437 Paper
Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 24/25, 2015 Variables in Real Life: Kinematics Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 24/25, 2015 Variables in Real Life: Kinematics Solutions The Science of
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles February 24/25, 2015 Variables in Real Life: Kinematics Solutions The Science of
What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year?
 LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
Introductory Physics PHYS101
 Introductory Physics PHYS101 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Office Hours Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu TRF 9:30-11:00am
Introductory Physics PHYS101 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Office Hours Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu TRF 9:30-11:00am
TIME: 45 minutes. LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st SUMMARY:
 LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
Mixtures. Part 2 Add 50 ml of water (one full syringe) to each cup. Stir and observe. Write your observations on the opposite page.
 Mixtures Part 1 Prepare three cups. Put 1 level spoon (5 ml) of each solid material in each cup. Observe the three solid materials. Fill in the property chart below. Color Texture Particle shape Particle
Mixtures Part 1 Prepare three cups. Put 1 level spoon (5 ml) of each solid material in each cup. Observe the three solid materials. Fill in the property chart below. Color Texture Particle shape Particle
Warmup 2/(The length of the third side of this triangle, rounded to the nearest whole number)
 Created by Max Robinson Warmup 2/(The length of the third side of this triangle, rounded to the nearest whole number) x 5 28 ***Get a calculator. Yellow or blue doesn t matter*** 1) Estimate how many feet
Created by Max Robinson Warmup 2/(The length of the third side of this triangle, rounded to the nearest whole number) x 5 28 ***Get a calculator. Yellow or blue doesn t matter*** 1) Estimate how many feet
Greenwich Public Schools Science Objectives and Grade Level Concepts. Grade One. Force and Motion
 Greenwich Public Schools Science Objectives and Grade Level Concepts Grade One Force and Motion CSDE Science Curriculum Standard 1.1: The sun appears to move across the sky in the same way every day, but
Greenwich Public Schools Science Objectives and Grade Level Concepts Grade One Force and Motion CSDE Science Curriculum Standard 1.1: The sun appears to move across the sky in the same way every day, but
Discovery Quest K-1. Chaperone Guide
 Discovery Quest K-1 Chaperone Guide Chaperone: Partner this guide with the K-1 Discovery Quest Worksheet. This guide will help you lead students through the natural history exhibits of the Pink Palace
Discovery Quest K-1 Chaperone Guide Chaperone: Partner this guide with the K-1 Discovery Quest Worksheet. This guide will help you lead students through the natural history exhibits of the Pink Palace
LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions, designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. A charged particle is moving with a constant velocity
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions, designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. A charged particle is moving with a constant velocity
Sticky Tape Lab Name: Block: Date:
 Name: Block: Date: Part I Preparing the Setup 1. Cut two ~15 cm pieces of paper and foil. Tape one piece of paper and foil to the ruler so it can swing freely. Set the other two pieces to the side. 2.
Name: Block: Date: Part I Preparing the Setup 1. Cut two ~15 cm pieces of paper and foil. Tape one piece of paper and foil to the ruler so it can swing freely. Set the other two pieces to the side. 2.
Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory. Nov 1 Hour One: Conservation Laws: Momentum and Collision Theory. Reading: YF
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory Available on-line October 29; Due: November 9 at 4:00 p.m. Please write
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory Available on-line October 29; Due: November 9 at 4:00 p.m. Please write
Uniform circular motion: Review
 Announcements: 1 st test at Lockett #6 (6:00PM, Feb 3 rd ) Formula sheet will be provided No other materials is needed Practice exam and answers are on the web Uniform circular motion: Review As you go
Announcements: 1 st test at Lockett #6 (6:00PM, Feb 3 rd ) Formula sheet will be provided No other materials is needed Practice exam and answers are on the web Uniform circular motion: Review As you go
Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 14/15/16, Estimation
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Introduction Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 14/15/16, 2017 Estimation Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing If you ever find yourself without
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Introduction Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 14/15/16, 2017 Estimation Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing If you ever find yourself without
Motion II. Goals and Introduction
 Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
AP Physics II Summer Packet
 Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
https://njctl.org/courses/science/ap-physics-c-mechanics/attachments/summerassignment-3/
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
Case 1:03-cv EGS Document Filed 03/20/09 Page 1 of 19
 Case 1:03-cv-02006-EGS Document 482-6 Filed 03/20/09 Page 1 of 19 Case 1:03-cv-02006-EGS Document 482-6 Filed 03/20/09 Page 2 of 19 1 2 On behalf of the Plaintiffs: 3 BY: KATHERINE ANNE MEYER, ESQ. 3 Meyer
Case 1:03-cv-02006-EGS Document 482-6 Filed 03/20/09 Page 1 of 19 Case 1:03-cv-02006-EGS Document 482-6 Filed 03/20/09 Page 2 of 19 1 2 On behalf of the Plaintiffs: 3 BY: KATHERINE ANNE MEYER, ESQ. 3 Meyer
DISPLACEMENT AND DISTANCE They re similar but not the same.
 1.2 DISPLCEMENT VS DISTNCE (Guided Notes) Page 328-331 in Text. Section 11.1 Learning Objectives: What is distance? What is displacement? What is the difference between distance and displacement? 1.2 Distinguish
1.2 DISPLCEMENT VS DISTNCE (Guided Notes) Page 328-331 in Text. Section 11.1 Learning Objectives: What is distance? What is displacement? What is the difference between distance and displacement? 1.2 Distinguish
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II
 Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Suggestions for Use. To help complete the graphic organizer (and motivate students) have them go to each website listed to learn more.
 Suggestions for Use Read the first page titled "Everything You Wanted to Know About Protists together as a class. You could have students read in partners or popcorn read --this is where one students reads
Suggestions for Use Read the first page titled "Everything You Wanted to Know About Protists together as a class. You could have students read in partners or popcorn read --this is where one students reads
Varsity Meet 3 January 8, 2014 Round 1: Similarity and Pythagorean Theorem
 Round 1: Similarity and Pythagorean Theorem 1. A baseball diamond is a square 90 feet on each side. The right fielder picks up the ball 30 feet behind first base (at point R) and throws it to the third
Round 1: Similarity and Pythagorean Theorem 1. A baseball diamond is a square 90 feet on each side. The right fielder picks up the ball 30 feet behind first base (at point R) and throws it to the third
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2018 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbiz Homework 7
 EECS 6B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 28 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbiz Homework 7 This homework is due on Thursday, March 22, 28, at :59AM (NOON). Self-grades are due on Monday,
EECS 6B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 28 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbiz Homework 7 This homework is due on Thursday, March 22, 28, at :59AM (NOON). Self-grades are due on Monday,
Waves ~ Learning Guide
 Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
a) An object decreasing speed then increasing speed in the opposite direction.
 Putting it all Together 10.1 Practice Use the kinematics equations to solve the following problems: a) You throw a marble up at the speed of 10 m/s. What is its maximum height? b) You drop a marble from
Putting it all Together 10.1 Practice Use the kinematics equations to solve the following problems: a) You throw a marble up at the speed of 10 m/s. What is its maximum height? b) You drop a marble from
Preptests 55 Answers and Explanations (By Ivy Global) Section 4 Logic Games
 Section 4 Logic Games Questions 1 6 There aren t too many deductions we can make in this game, and it s best to just note how the rules interact and save your time for answering the questions. 1. Type
Section 4 Logic Games Questions 1 6 There aren t too many deductions we can make in this game, and it s best to just note how the rules interact and save your time for answering the questions. 1. Type
GRAPHS AND STATISTICS Central Tendency and Dispersion Common Core Standards
 B Graphs and Statistics, Lesson 2, Central Tendency and Dispersion (r. 2018) GRAPHS AND STATISTICS Central Tendency and Dispersion Common Core Standards Next Generation Standards S-ID.A.2 Use statistics
B Graphs and Statistics, Lesson 2, Central Tendency and Dispersion (r. 2018) GRAPHS AND STATISTICS Central Tendency and Dispersion Common Core Standards Next Generation Standards S-ID.A.2 Use statistics
Lesson 3: Locating Plots on the Ground
 Review and Introduction Lesson 3: Locating Plots on the Ground So far, you have identified individual stands in the forest, learned about plot sampling, and marked locations on a map of where your inventory
Review and Introduction Lesson 3: Locating Plots on the Ground So far, you have identified individual stands in the forest, learned about plot sampling, and marked locations on a map of where your inventory
Roller Coaster Physics: Energy and Forces
 Roller : Energy and Forces Carnegie Mellon University jzink@andrew.cmu.edu 98-186: Spring 2015 Outline Energy, and how to design with it Forces, and how to design with them Example Design in No Limits
Roller : Energy and Forces Carnegie Mellon University jzink@andrew.cmu.edu 98-186: Spring 2015 Outline Energy, and how to design with it Forces, and how to design with them Example Design in No Limits
Course Updates. Reminders: 1) Quiz today. 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, ) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web page)
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phy272-pr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Quiz today 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, 22.30 3) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phy272-pr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Quiz today 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, 22.30 3) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web
ACTIVITY 2: Motion with a Continuous Force
 CHAPTER 2 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 2: Motion with a Continuous Force Purpose In Activity 1 you saw the effect that quick pushes had on the motion of a cart. This is like the situation in many sports,
CHAPTER 2 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 2: Motion with a Continuous Force Purpose In Activity 1 you saw the effect that quick pushes had on the motion of a cart. This is like the situation in many sports,
Projects in Geometry for High School Students
 Projects in Geometry for High School Students Goal: Our goal in more detail will be expressed on the next page. Our journey will force us to understand plane and three-dimensional geometry. We will take
Projects in Geometry for High School Students Goal: Our goal in more detail will be expressed on the next page. Our journey will force us to understand plane and three-dimensional geometry. We will take
Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models
 5 th Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models Investigation 1: Motion and Variables Name: Big Question: How does investigating a pendulum help you understand how scientists use math to do their work?
5 th Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models Investigation 1: Motion and Variables Name: Big Question: How does investigating a pendulum help you understand how scientists use math to do their work?
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
9/27/12. Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces. Motion and Position. Motion. Distance. Relative Motion
 9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
