a C = 1.4) If the mass of a rider is 65 kg, then what is the rider s centripetal force?
|
|
|
- Erik Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ferris Wheel Select Ferris Wheel. After the animation pops up press the Play button. 1.1) Use the stopwatch to measure the period of motion for the Ferris wheel. What is its period? T = 1.2) Calculate it s tangential velocity: v = 1.3) Calculate its centripetal acceleration: a C = 1.4) If the mass of a rider is 65 kg, then what is the rider s centripetal force? F C = 1.5) The term centripetal force is a generic term. If you were to talk about gravity, you would know that only mass exerts a gravitational force. But a centripetal force can be exerted by many different things. What is supplying the centripetal force to keep the rider going in a circle at the bottom of the motion?
2 The Anti-Gravity Ride go to Select, Anti-Gravity Machine, from the menu. Press the, Play, button when the animation opens up. 2.1) Use the stopwatch to measure the period of motion for the ride s wheel. What is its period? T = 2.2) Calculate it s tangential velocity: v = 2.3) Calculate its centripetal acceleration: a C = 2.4) If the mass of a rider is 55 kg, the what is the rider s centripetal force? F C = 2.5) The term centripetal force is a generic term. If you were to talk about gravity, you would know that only mass exerts a gravitational force. But a centripetal force can be exerted by many different things. What is supplying the centripetal force to keep the rider going in a circle?
3 Loop Design Select, Loops (Design), from the menu. Click on LOOP A from the menu screen. The meter on the right of the animation shows the g s felt on the seat of the rider. This is called a force factor. It describes the amount of weight felt by a rider. 2 g s is twice the normal weight. Press the play button and watch the g s felt meter. Keep in mind the ranges. For ever animation the coaster s velocity is the same LOOP A 6.1) Where in the motion does the rider feel 1 g? 6.2) How many g s does the rider feel as he enters the loop at the bottom? 6.3) How many g s does the rider feel as he passes through the top of the loop? 6.4) Is this loop safe or unsafe for its passengers? 6.5) Explain 6.6) Look at the formulae on the left of the screen. Given that the speed of the coaster cannot be changed, how can the loop physically be altered to reduce the g s felt by the rider AT THE BOTTOM OF THE LOOP? LOOP B Click on LOOP B at the bottom of the animation. Click on play to see what happens. 6.7) How many g s does the rider feel as he enters the loop at the bottom? 6.8) How many g s does the rider feel as he passes through the top of the loop? 6.9) Why does the rider behave this way at the top of the loop?
4 Loop Design 6.10) Look at the formulae on the left of the screen. Given that the speed of the coaster cannot be changed, how can the loop physically be altered to increase the g s felt by the rider AT THE TOP OF THE LOOP? LOOP C Click on LOOP C at the bottom of the animation. Click on play to see what happens. 6.11) What is the name of this loop? 6.12) Does this loop design solve problems with the small and large loop? 6.13) Explain LOOP D Click on LOOP D at the bottom of the animation. Click on play to see what happens. 6.14) What is the name of this loop s shape? 6.15) Compare LOOP C and LOOP D, Which is a better solution to the problems with small and large loops (A & B)? 6.16) Explain
5 Scrambler Select, The Scrambler, from the menu. Press the, Play, button when the animation opens up. The Scrambler s motion is a complex circular motion. When rider is the farthest away from the center, point B, the rider is moving with a speed equal to the tangential velocities about the minor axis AND the major axis. The rider s radius is equal to the distance between his/herself, at point B, and the center. When the rider is closest to the center, point C, the rider experiences a velocity that is the difference between the major and minor axis. The rider s radius is equal to the minor arm s length. 3.1) What is the period of motion when the MINOR arm is the radius? T = 3.2) What is the tangential velocity when the MINOR arm is the radius? v = 3.3) What is the period of motion when the MAJOR arm is the radius? (Point B) T = 3.4) What is the tangential velocity when the MAJOR arm is the radius? v = 3.5) What is the centripetal acceleration in g s at point A? (When the major arm is the axis.) a C =
Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion
 1 Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion 2016 07 20 www.njctl.org 2 Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency and Rotational Velocity Kinematics of
1 Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion 2016 07 20 www.njctl.org 2 Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency and Rotational Velocity Kinematics of
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 7
 1 A grindstone increases in angular speed from 4.00 rad/sec to 12.00 rad/sec in 4.00 seconds. Through what angle does it turn during that time if the angular acceleration is constant? a 8.00 rad b 12.0
1 A grindstone increases in angular speed from 4.00 rad/sec to 12.00 rad/sec in 4.00 seconds. Through what angle does it turn during that time if the angular acceleration is constant? a 8.00 rad b 12.0
Circular Velocity and Centripetal Acceleration
 1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 MECHANICS: CIRCULAR MOTION QUESTIONS CIRCULAR MOTION (2016;1) Alice is in a car on a ride at a theme park. The car travels along a circular track that is banked, as shown in the diagram. On the diagram,
MECHANICS: CIRCULAR MOTION QUESTIONS CIRCULAR MOTION (2016;1) Alice is in a car on a ride at a theme park. The car travels along a circular track that is banked, as shown in the diagram. On the diagram,
Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Preview. Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1. Section 1 Circular Motion. Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA
 Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA Observations and measurements on board Your sensations and the spring accelerometer 1) For the two positions indicated by the arrows, note down changes to how heavy
Drop towers: DISCOVERY and COLUMBIA Observations and measurements on board Your sensations and the spring accelerometer 1) For the two positions indicated by the arrows, note down changes to how heavy
Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation Exam-Style Questions 1 a) Calculate the angular velocity of a person standing on the Earth s surface at sea level. b) The summit of Mount Everest is 8848m above
Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation Exam-Style Questions 1 a) Calculate the angular velocity of a person standing on the Earth s surface at sea level. b) The summit of Mount Everest is 8848m above
Physics Circular Motion Problems. Science and Mathematics Education Research Group
 F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Circular Motion Problems Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Circular Motion Problems Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
MAKING MEASUREMENTS. I walk at a rate of paces per...or...my pace =
 MAKING MEASUREMENTS TIME: The times that are required to work out the problems can be measured using a digital watch with a stopwatch mode or a watch with a second hand. When measuring the period of a
MAKING MEASUREMENTS TIME: The times that are required to work out the problems can be measured using a digital watch with a stopwatch mode or a watch with a second hand. When measuring the period of a
Circular motion minutes. 62 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor Page 1 of 22. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks:
 Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Chapter 5. A rock is twirled on a string at a constant speed. The direction of its acceleration at point P is A) B) P C) D)
 A 1500 kg car travels at a constant speed of 22 m/s around a circular track which has a radius of 80 m. Which statement is true concerning this car? A) The velocity of the car is changing. B) The car is
A 1500 kg car travels at a constant speed of 22 m/s around a circular track which has a radius of 80 m. Which statement is true concerning this car? A) The velocity of the car is changing. B) The car is
Preview. Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1. Section 1 Circular Motion. Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Page 2. Q1.A satellite X is in a circular orbit of radius r about the centre of a spherical planet of mass
 Q1. satellite X is in a circular orbit of radius r about the centre of a spherical planet of mass M. Which line, to, in the table gives correct expressions for the centripetal acceleration a and the speed
Q1. satellite X is in a circular orbit of radius r about the centre of a spherical planet of mass M. Which line, to, in the table gives correct expressions for the centripetal acceleration a and the speed
Circular Motion CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION. tf-t,
 Circular Motion Ill SECTION OBJECTIVES Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. Solve problems involving centripetal force. Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular
Circular Motion Ill SECTION OBJECTIVES Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. Solve problems involving centripetal force. Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular
Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30
 Name: Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30 A. True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite
Name: Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30 A. True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite
1D-04 Radial Acceleration & Tangential Velocity
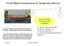 1D-04 Radial Acceleration & Tangential Velocity Once the string is cut, where is the ball going? AT ANY INSTANT, THE VELOCITY VECTOR OF THE BALL IS DIRECTED ALONG THE TANGENT. AT THE INSTANT WHEN THE BLADE
1D-04 Radial Acceleration & Tangential Velocity Once the string is cut, where is the ball going? AT ANY INSTANT, THE VELOCITY VECTOR OF THE BALL IS DIRECTED ALONG THE TANGENT. AT THE INSTANT WHEN THE BLADE
Uniform Circular Motion. Uniform Circular Motion
 Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion An object that moves at uniform speed in a circle of constant radius is said to be in uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform
Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion An object that moves at uniform speed in a circle of constant radius is said to be in uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform
1 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM
 http://sessionmasteringphysicscom/myct/assignmentprint?assignmentid= 1 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM Chapter 8 Homework Due: 9:00am on Wednesday October 7 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded read
http://sessionmasteringphysicscom/myct/assignmentprint?assignmentid= 1 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM Chapter 8 Homework Due: 9:00am on Wednesday October 7 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded read
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK
 Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
Linear vs. Rotational Motion
 Linear vs. Rotational Motion Every term in a linear equation has a similar term in the analogous rotational equation. Displacements: s = r θ v t ω Speeds: v t = ω r Accelerations: a t = α r Every point
Linear vs. Rotational Motion Every term in a linear equation has a similar term in the analogous rotational equation. Displacements: s = r θ v t ω Speeds: v t = ω r Accelerations: a t = α r Every point
AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2 600 rev/min is equivalent
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2 600 rev/min is equivalent
Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation In the game of tetherball, the struck ball whirls around a pole. In what direction does the net force on the ball point? 1) Tetherball 1) toward the top of the pole
Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation In the game of tetherball, the struck ball whirls around a pole. In what direction does the net force on the ball point? 1) Tetherball 1) toward the top of the pole
Section Vertical Circular Motion
 Section 11.3 Vertical Circular Motion When a ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle, the ball is accelerating because A. the speed is changing. B. the direction is changing. C. the speed
Section 11.3 Vertical Circular Motion When a ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle, the ball is accelerating because A. the speed is changing. B. the direction is changing. C. the speed
Centripetal force keeps an Rotation and Revolution
 Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. Which moves faster on a merry-go-round, a horse near the outside rail or one near the inside rail? While a hamster rotates its cage about an axis,
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. Which moves faster on a merry-go-round, a horse near the outside rail or one near the inside rail? While a hamster rotates its cage about an axis,
An object moving in a circle with radius at speed is said to be undergoing.
 Circular Motion Study Guide North Allegheny High School Mr. Neff An object moving in a circle with radius at speed is said to be undergoing. In this case, the object is because it is constantly changing
Circular Motion Study Guide North Allegheny High School Mr. Neff An object moving in a circle with radius at speed is said to be undergoing. In this case, the object is because it is constantly changing
SPH4U Sample Test Dynamics
 1of14 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the gravitational force
1of14 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the gravitational force
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes. Name
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
PH201 Chapter 6 Solutions
 PH201 Chapter 6 Solutions 6.2. Set Up: Since the stone travels in a circular path, its acceleration is directed toward the center of the circle. The only horizontal force on the stone is the tension of
PH201 Chapter 6 Solutions 6.2. Set Up: Since the stone travels in a circular path, its acceleration is directed toward the center of the circle. The only horizontal force on the stone is the tension of
Angle recap. Angular position: Angular displacement: s. Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration:
 Angle recap Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Today s lecture
Angle recap Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Today s lecture
The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates.
 Q1. The London Eye is the largest observation wheel in the world. The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates. (a) Explain how the wheel can move at a steady
Q1. The London Eye is the largest observation wheel in the world. The passengers ride in capsules. Each capsule moves in a circular path and accelerates. (a) Explain how the wheel can move at a steady
Lab/Demo 4 Circular Motion and Energy PHYS 1800
 Lab/Demo 4 Circular Motion and Energy PHYS 1800 Objectives: Demonstrate the dependence of centripetal force on mass, velocity and radius. Learn to use these dependencies to predict circular motion Demonstrate
Lab/Demo 4 Circular Motion and Energy PHYS 1800 Objectives: Demonstrate the dependence of centripetal force on mass, velocity and radius. Learn to use these dependencies to predict circular motion Demonstrate
Physics 211 Week 4. Work and Kinetic Energy: Block on Incline (Solutions)
 Physics 211 Week 4 Work and Kinetic Energy: Block on Incline (Solutions) A block of mass 3 kg is moved up an incline that makes an angle of 37 o with the horizontal under the action of a constant horizontal
Physics 211 Week 4 Work and Kinetic Energy: Block on Incline (Solutions) A block of mass 3 kg is moved up an incline that makes an angle of 37 o with the horizontal under the action of a constant horizontal
Introduction. 2. Collect student money before arriving at the park and present one check for the entire group.
 Amusement Park Physics Introduction Notes to Teachers: 1. Copy and hand out a packet to each student. 2. Collect student money before arriving at the park and present one check for the entire group. 3.
Amusement Park Physics Introduction Notes to Teachers: 1. Copy and hand out a packet to each student. 2. Collect student money before arriving at the park and present one check for the entire group. 3.
Roller Coaster Design Project Lab 3: Coaster Physics Part 2
 Roller Coaster Design Project Lab 3: Coaster Physics Part 2 Introduction The focus of today's lab is on the understanding how various features influence the movement and energy loss of the ball. Loops
Roller Coaster Design Project Lab 3: Coaster Physics Part 2 Introduction The focus of today's lab is on the understanding how various features influence the movement and energy loss of the ball. Loops
Uniform Circular Motion
 Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Traveling with a constant speed in a circular path Even though the speed is constant, the acceleration is non-zero The acceleration responsible
Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Traveling with a constant speed in a circular path Even though the speed is constant, the acceleration is non-zero The acceleration responsible
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
B) v `2. C) `2v. D) 2v. E) 4v. A) 2p 25. B) p C) 2p. D) 4p. E) 4p 2 25
 1. 3. A ball attached to a string is whirled around a horizontal circle of radius r with a tangential velocity v. If the radius is changed to 2r and the magnitude of the centripetal force is doubled the
1. 3. A ball attached to a string is whirled around a horizontal circle of radius r with a tangential velocity v. If the radius is changed to 2r and the magnitude of the centripetal force is doubled the
DP Physics Torque Simulation
 DP Physics Torque Simulation Name Go to Phet Simulation: ( http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=torque ) Part I: Torque 1. Click the tab at the top that says torque 2. Set the force equal
DP Physics Torque Simulation Name Go to Phet Simulation: ( http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=torque ) Part I: Torque 1. Click the tab at the top that says torque 2. Set the force equal
Why Doesn t the Moon Hit us? In analysis of this question, we ll look at the following things: i. How do we get the acceleration due to gravity out
 Why Doesn t the oon Hit us? In analysis of this question, we ll look at the following things: i. How do we get the acceleration due to gravity out of the equation for the force of gravity? ii. How does
Why Doesn t the oon Hit us? In analysis of this question, we ll look at the following things: i. How do we get the acceleration due to gravity out of the equation for the force of gravity? ii. How does
Speed and Velocity. Circular and Satellite Motion
 Name: Speed and Velocity Read from Lesson 1 of the Circular and Satellite Motion chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/circles/u6l1a.html MOP Connection: Circular Motion
Name: Speed and Velocity Read from Lesson 1 of the Circular and Satellite Motion chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/circles/u6l1a.html MOP Connection: Circular Motion
AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW
 Basics 1D Mot. 2D Mot. Forces Energy Moment. Rotation Circ/Grav SHM Waves Circuits AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW AP Exam Knowledge & Skills (What skills are needed to achieve the desired
Basics 1D Mot. 2D Mot. Forces Energy Moment. Rotation Circ/Grav SHM Waves Circuits AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW AP Exam Knowledge & Skills (What skills are needed to achieve the desired
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW
 Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Circular Motion Test Review
 Circular Motion Test Review Name: Date: 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration is equal to zero. B) No,
Circular Motion Test Review Name: Date: 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration is equal to zero. B) No,
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes
 Formulas: a C = v 2 /r a = a C + a T F = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 Chapter 5 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Constants: G = 6.67 10-11 N-m 2 /kg 2. Main Ideas: 1. Uniform circular motion 2. Nonuniform circular
Formulas: a C = v 2 /r a = a C + a T F = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 Chapter 5 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Constants: G = 6.67 10-11 N-m 2 /kg 2. Main Ideas: 1. Uniform circular motion 2. Nonuniform circular
Quest Chapter 09. Eliminate the obviously wrong answers. Consider what is changing: speed, velocity, some part of velocity? Choose carefully.
 1 A dragster maintains a speedometer reading of 100 km/h and passes through a curve with a constant radius. Which statement is true? 1. The dragster rounded the curve at a changing speed of 100 km/h. 2.
1 A dragster maintains a speedometer reading of 100 km/h and passes through a curve with a constant radius. Which statement is true? 1. The dragster rounded the curve at a changing speed of 100 km/h. 2.
Name Period Date A) B) C) D)
 Example Problems 9.2 E1. A car rounds a curve of constant radius at a constant speed. Which diagram best represents the directions of both the car s velocity and acceleration? Explain: A) B) C) D) E2.
Example Problems 9.2 E1. A car rounds a curve of constant radius at a constant speed. Which diagram best represents the directions of both the car s velocity and acceleration? Explain: A) B) C) D) E2.
Chapter 7. Preview. Objectives Tangential Speed Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force Describing a Rotating System. Section 1 Circular Motion
 Section 1 Circular Motion Preview Objectives Tangential Speed Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force Describing a Rotating System Section 1 Circular Motion Objectives Solve problems involving centripetal
Section 1 Circular Motion Preview Objectives Tangential Speed Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force Describing a Rotating System Section 1 Circular Motion Objectives Solve problems involving centripetal
AP Physics Daily Problem #31
 AP Physics Daily Problem #31 A 10kg mass is whirled around on the end of a 3m long cord. The speed of the mass is 7m/s. Ignore gravitational forces. 3.0m 7.0m/s Draw a free body diagram of the mass. (hint:
AP Physics Daily Problem #31 A 10kg mass is whirled around on the end of a 3m long cord. The speed of the mass is 7m/s. Ignore gravitational forces. 3.0m 7.0m/s Draw a free body diagram of the mass. (hint:
AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation
 AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation Name: 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation Name: 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
Circular Motion and Gravitation. Centripetal Acceleration
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Centripetal Acceleration Recall linear acceleration 3. Going around a curve, at constant speed 1. Speeding up vi vi Δv a ac ac vi ac 2. Slowing down v velocity and acceleration
Circular Motion and Gravitation Centripetal Acceleration Recall linear acceleration 3. Going around a curve, at constant speed 1. Speeding up vi vi Δv a ac ac vi ac 2. Slowing down v velocity and acceleration
TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB
 TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB 1. A car traveling at 20 m/s rounds a curve so that its centripetal acceleration
TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB 1. A car traveling at 20 m/s rounds a curve so that its centripetal acceleration
Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1
 Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1 An object of mass m is released from rest at a height h above the surface of a table. The object slides along the inside of the loop-the-loop track consisting
Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1 An object of mass m is released from rest at a height h above the surface of a table. The object slides along the inside of the loop-the-loop track consisting
Circular Motion Concept Questions
 Circular Motion Concept Questions Question 1 A bead is given a small push at the top of a hoop (position A) and is constrained to slide around a frictionless circular wire (in a vertical plane). Circle
Circular Motion Concept Questions Question 1 A bead is given a small push at the top of a hoop (position A) and is constrained to slide around a frictionless circular wire (in a vertical plane). Circle
Section Study Guide. Teacher Notes and Answers. Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Section Study Guide Teacher Notes and Answers CIRCULAR MOTION 1. a. yes b. The car has a non-zero acceleration because the direction of motion is changing. c. The direction of centripetal acceleration
Section Study Guide Teacher Notes and Answers CIRCULAR MOTION 1. a. yes b. The car has a non-zero acceleration because the direction of motion is changing. c. The direction of centripetal acceleration
UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY
 Conceptual Questions UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY 1) D_What type of linear acceleration does an object moving with constant linear speed (st) in a circular path experience? A) free fall C) linear acceleration
Conceptual Questions UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY 1) D_What type of linear acceleration does an object moving with constant linear speed (st) in a circular path experience? A) free fall C) linear acceleration
Chapter 6: Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6: Circular Motion and Gravitation Goals for Chapter 6 To understand the dynamics of circular motion. To study the unique application of circular motion as it applies to Newton's
Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6: Circular Motion and Gravitation Goals for Chapter 6 To understand the dynamics of circular motion. To study the unique application of circular motion as it applies to Newton's
Circular Motion PreTest
 Circular Motion PreTest Date: 06/03/2008 Version #: 0 Name: 1. In a series of test runs, a car travels around the same circular track at different velocities. Which graph best shows the relationship between
Circular Motion PreTest Date: 06/03/2008 Version #: 0 Name: 1. In a series of test runs, a car travels around the same circular track at different velocities. Which graph best shows the relationship between
Multiple Choice Portion
 Unit 5: Circular Motion and Gravitation Please Note that the gravitational potential energy questions are located in Unit 4 (Energy etc.) Multiple Choice Portion 1. What is the centripetal acceleration
Unit 5: Circular Motion and Gravitation Please Note that the gravitational potential energy questions are located in Unit 4 (Energy etc.) Multiple Choice Portion 1. What is the centripetal acceleration
Period: Date: Review - UCM & Energy. Page 1. Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below. The diagram shows the top view of a -kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below. The diagram shows the top view of a -kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a
Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion Vocabulary: acceleration, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, Newton s first law, Newton s second law, uniform circular motion, vector,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Uniform Circular Motion Vocabulary: acceleration, centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, Newton s first law, Newton s second law, uniform circular motion, vector,
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test Provincial Questions
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test Provincial Questions 1. A 1 200 kg car is traveling at 25 m s on a horizontal surface in a circular path of radius 85 m. What is the net force acting on this
Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test Provincial Questions 1. A 1 200 kg car is traveling at 25 m s on a horizontal surface in a circular path of radius 85 m. What is the net force acting on this
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT CIRCULAR MOTION MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 65 TOTAL / 95 NAME: 1. An object travels along a path at constant speed. There is a constant
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT CIRCULAR MOTION MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 65 TOTAL / 95 NAME: 1. An object travels along a path at constant speed. There is a constant
Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book
 Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Define rotation and revolution 2) Calculate the rotational speed of an object 3) Calculate the centripetal acceleration
Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Define rotation and revolution 2) Calculate the rotational speed of an object 3) Calculate the centripetal acceleration
Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work
 Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work This Exploration allows you to discover how work causes changes in kinetic energy. Restart. Drag "handy" to the front and/or the back of
Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work This Exploration allows you to discover how work causes changes in kinetic energy. Restart. Drag "handy" to the front and/or the back of
ASTRONAUT PUSHES SPACECRAFT
 ASTRONAUT PUSHES SPACECRAFT F = 40 N m a = 80 kg m s = 15000 kg a s = F/m s = 40N/15000 kg = 0.0027 m/s 2 a a = -F/m a = -40N/80kg = -0.5 m/s 2 If t push = 0.5 s, then v s = a s t push =.0014 m/s, and
ASTRONAUT PUSHES SPACECRAFT F = 40 N m a = 80 kg m s = 15000 kg a s = F/m s = 40N/15000 kg = 0.0027 m/s 2 a a = -F/m a = -40N/80kg = -0.5 m/s 2 If t push = 0.5 s, then v s = a s t push =.0014 m/s, and
Cutnell/Johnson Physics
 Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Interactive Lecture Questions 5.1.1. An airplane flying at 115 m/s due east makes a gradual turn
Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Interactive Lecture Questions 5.1.1. An airplane flying at 115 m/s due east makes a gradual turn
Potential and Kinetic Energy: Roller Coasters Student Advanced Version
 Potential and Kinetic Energy: Roller Coasters Student Advanced Version Key Concepts: Energy is the ability of a system or object to perform work. It exists in various forms. Potential energy is the energy
Potential and Kinetic Energy: Roller Coasters Student Advanced Version Key Concepts: Energy is the ability of a system or object to perform work. It exists in various forms. Potential energy is the energy
CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION
 CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Uniform Circular Motion What holds an object in a circular path? A force. String Friction Gravity What happens when the force is diminished? Object flies off in
CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Uniform Circular Motion What holds an object in a circular path? A force. String Friction Gravity What happens when the force is diminished? Object flies off in
The Force of Gravity exists between any two masses! Always attractive do you feel the attraction? Slide 6-35
 The Force of Gravity exists between any two masses! Always attractive do you feel the attraction? Slide 6-35 Summary Newton s law of gravity describes the gravitational force between A. the earth and the
The Force of Gravity exists between any two masses! Always attractive do you feel the attraction? Slide 6-35 Summary Newton s law of gravity describes the gravitational force between A. the earth and the
Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 (2 weeks!
 Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 ( weeks!) Physics 101:
Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 ( weeks!) Physics 101:
1. In which situation is an object undergoing centripetal acceleration? (C) a car accelerating on a drag strip (D) a hockey puck gliding on ice
 Physics 3204 Assignment 2.1 UCM DUE: Thursday Nov 24, 2017 Name: Part A. Multiple Choice: Select the best possible answer. Place the answer on the answer sheet. 1. In which situation is an object undergoing
Physics 3204 Assignment 2.1 UCM DUE: Thursday Nov 24, 2017 Name: Part A. Multiple Choice: Select the best possible answer. Place the answer on the answer sheet. 1. In which situation is an object undergoing
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead. Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity
 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
II. Universal Gravitation - Newton 4th Law
 Periodic Motion I. Circular Motion - kinematics & centripetal acceleration - dynamics & centripetal force - centrifugal force II. Universal Gravitation - Newton s 4 th Law - force fields & orbits III.
Periodic Motion I. Circular Motion - kinematics & centripetal acceleration - dynamics & centripetal force - centrifugal force II. Universal Gravitation - Newton s 4 th Law - force fields & orbits III.
Vocabulary. Centripetal Force. Centripetal Acceleration. Rotate. Revolve. Linear Speed. Angular Speed. Center of Gravity. 1 Page
 Vocabulary Term Centripetal Force Definition Centripetal Acceleration Rotate Revolve Linear Speed Angular Speed Center of Gravity 1 Page Force Relationships 1. FORCE AND MASS a. An object swung in a uniform
Vocabulary Term Centripetal Force Definition Centripetal Acceleration Rotate Revolve Linear Speed Angular Speed Center of Gravity 1 Page Force Relationships 1. FORCE AND MASS a. An object swung in a uniform
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY
 Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
Circular Motion (Chapter 5)
 Circular Motion (Chapter 5) So far we have focused on linear motion or motion under gravity (free-fall). Question: What happens when a ball is twirled around on a string at constant speed? Ans: Its velocity
Circular Motion (Chapter 5) So far we have focused on linear motion or motion under gravity (free-fall). Question: What happens when a ball is twirled around on a string at constant speed? Ans: Its velocity
PHY 309 K. Solutions for the second mid-term test (3/25/2014).
 PHY 309 K. Solutions for the second mid-term test (3/25/2014). Problem #1: (a) Forces on the top block: T Forces on the top block m g N bot f bot T string force, N bot normal force from the bottom block,
PHY 309 K. Solutions for the second mid-term test (3/25/2014). Problem #1: (a) Forces on the top block: T Forces on the top block m g N bot f bot T string force, N bot normal force from the bottom block,
Proficient. a. The gravitational field caused by a. The student is able to approximate a numerical value of the
 Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion
 Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Physics 101: Lecture 8, Pg 1 Circular Motion Act B A
Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Physics 101: Lecture 8, Pg 1 Circular Motion Act B A
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 06: CENTRIPETAL FORCES & GRAVITATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION In Uniform Circular Motion, an object moves with constant speed in a circular path. v,t = a,c = a,c = v,t 2 / r r = When an object completes one lap ( or ),
!! www.clutchprep.com UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION In Uniform Circular Motion, an object moves with constant speed in a circular path. v,t = a,c = a,c = v,t 2 / r r = When an object completes one lap ( or ),
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD.
 SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET/JEE Date : 13/05/2017 TEST ID: 120517 Time : 02:00:00 Hrs. PHYSICS, Chem Marks : 360 Phy : Circular Motion, Gravitation, Che : Halogen Derivatives Of Alkanes Single Correct
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET/JEE Date : 13/05/2017 TEST ID: 120517 Time : 02:00:00 Hrs. PHYSICS, Chem Marks : 360 Phy : Circular Motion, Gravitation, Che : Halogen Derivatives Of Alkanes Single Correct
A N D. c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N F O R C E S
 F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation
 Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation Conceptual Questions 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration
Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation Conceptual Questions 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration
Rotational Motion Examples:
 Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Part 1: Relationship of Radius and Time Period. PHY Lab 10: Circular Motion
 Circular Motion The wind goes towards the south, and turns towards the north; it turns about continually, and the wind returns again to its circuits. Ecclesiastes 1:6 Introduction Most have been on a Ferris
Circular Motion The wind goes towards the south, and turns towards the north; it turns about continually, and the wind returns again to its circuits. Ecclesiastes 1:6 Introduction Most have been on a Ferris
Solutions to Exam #1
 SBCC 2017Summer2 P 101 Solutions to Exam 01 2017Jul11A Page 1 of 9 Solutions to Exam #1 1. Which of the following natural sciences most directly involves and applies physics? a) Botany (plant biology)
SBCC 2017Summer2 P 101 Solutions to Exam 01 2017Jul11A Page 1 of 9 Solutions to Exam #1 1. Which of the following natural sciences most directly involves and applies physics? a) Botany (plant biology)
Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions
 Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions A 2.10 m rope attaches a tire to an overhanging tree limb. A girl swinging on the tire has a tangential speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the
Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions A 2.10 m rope attaches a tire to an overhanging tree limb. A girl swinging on the tire has a tangential speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the
Chapter 7 & 8 Prep Test: Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Chapter 7 & 8 Prep Test: Circular Motion and Gravitation Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A monkey rides a tricycle in a circular path with
Chapter 7 & 8 Prep Test: Circular Motion and Gravitation Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A monkey rides a tricycle in a circular path with
Chapter 5.1 Variation Direct Variation, Inverse Variation and Joint Variation
 1 Chapter 5.1 Variation Direct Variation, Inverse Variation and Joint Variation Sometimes the equation that relates two or more variables can be described in words by the idea of variation. There are three
1 Chapter 5.1 Variation Direct Variation, Inverse Variation and Joint Variation Sometimes the equation that relates two or more variables can be described in words by the idea of variation. There are three
Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1
 Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1 Next Reading Assignment: W04D2 Young and Freedman: 3.4; 5.4-5.5 Experiment 2: Circular Motion 2 Concept Question: Coastal Highway A sports car drives along the coastal highway
Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1 Next Reading Assignment: W04D2 Young and Freedman: 3.4; 5.4-5.5 Experiment 2: Circular Motion 2 Concept Question: Coastal Highway A sports car drives along the coastal highway
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Circular Motion & Gravitation MC Question Database
 (Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
(Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
Centripetal force. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/13/14
 Centripetal force Objecties Describe and analyze the motion of objects moing in circular motion. Apply Newton s second law to circular motion problems. Interpret free-body force diagrams. 1. A race car
Centripetal force Objecties Describe and analyze the motion of objects moing in circular motion. Apply Newton s second law to circular motion problems. Interpret free-body force diagrams. 1. A race car
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts
 Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Upon collision, the clay and steel block stick together and move to the right with a speed of
 1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion
 Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? F actual = Centripetal Force F fictitious = Centrifugal Force Center FLEEing Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? Center
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? F actual = Centripetal Force F fictitious = Centrifugal Force Center FLEEing Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? Center
PES Physics 1 Practice Questions Exam 2. Name: Score: /...
 Practice Questions Exam /page PES 0 003 - Physics Practice Questions Exam Name: Score: /... Instructions Time allowed for this is exam is hour 5 minutes... multiple choice (... points)... written problems
Practice Questions Exam /page PES 0 003 - Physics Practice Questions Exam Name: Score: /... Instructions Time allowed for this is exam is hour 5 minutes... multiple choice (... points)... written problems
