1 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM
|
|
|
- Rudolph Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM Chapter 8 Homework Due: 9:00am on Wednesday October Note: To understand how points are awarded read your instructor's Grading Policy [Return to Standard Assignment View] Normal Force and Centripetal Force Ranking Task A roller-coaster track has six semicircular "dips" with different radii of curvature The same roller-coaster cart rides through each dip at a different speed For the different values given for the radius of curvature and speed rank the magnitude of the force of the roller-coaster track on the cart at the bottom of each dip Hint A1 Newton s 2nd law Newton s 2nd law is valid for any motion whether the motion is along a straight line or a circular path The net force acting on the cart must be equal to the product of its mass and acceleration and since the cart is moving along a circular path its acceleration (toward the center of the circular path) is given by Hint A2 Determine the net force on the cart Defining up as the positive direction which of the following expressions describes the net force acting on the cart in the vertical direction while it's at the bottom of the dip? The variables and are the magnitudes of the forces Substituting the expression for the net force on the cart and the centripetal acceleration of the cart into Newton's 2nd law Keep in mind that the same cart passes through the six different dips along the track so the mass in the expression doesn't vary Rank from largest to smallest To rank items as equivalent overlap them View Velocity of a Roller Coaster Ranking Task Six roller-coaster carts pass over the same semicircular "bump" The mass of each cart (including passenger) and the normal force of the track on the cart at the top of each bump are given in the figures
2 2 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM Rank the speeds of the different carts as each passes over the top of the bump Hint A1 Newton's 2nd law Newton's 2nd law is valid for any motion whether the motion is along a straight line or a circular path The net force acting on the cart must be equal to the product of its mass and acceleration and since the cart is moving along a circular path its acceleration (toward the center of the circular path) has magnitude Hint A2 Determine the net force on the cart Defining the down direction (toward the center of the circular path) as positive which of the following expressions describes the component of the net force acting on the cart in the vertical direction? Taking the expressions for the net force on the cart and the centripetal acceleration of the cart and substituting into Newton's 2nd law Since the radius is the same for every cart we can ignore and write But is simply so or Rank from largest to smallest To rank items as equivalent overlap them View Taking the expressions for the net force on the cart and the centripetal acceleration of the cart and substituting into Newton's 2nd law Since the radius is the same for every cart we can ignore and write But is simply so or
3 Therefore larger implies smaller A Ride on the Ferris Wheel A woman rides on a Ferris wheel of radius 16 that maintains the same speed throughout its motion To better understand physics she takes along a digital bathroom scale (with memory) and sits on it When she gets off the ride she uploads the scale readings to a computer and creates a graph of scale reading versus time Note that the graph has a minimum value of 510 and a maximum value of 666 What is the woman's mass? Hint A1 The woman is moving in a circle with constant speed To maintain this motion she must experience a net acceleration (called centripetal acceleration) directed toward the center of the Ferris wheel Draw and analyze the woman's free-body diagram at a wisely chosen point on the circular path and use Newton's 2nd law to determine her mass Hint A2 Find the extreme points on the circular path The bathroom scale does not record the woman s weight If it did the reading would not vary as she rides the Ferris wheel Instead the scale records the normal force acting on the woman which can vary as she moves along the circular path and experiences different accelerations This normal force is sometimes referred to as an apparent weight because it mimics the feelings of being heavier or lighter As the woman travels along the circular path her apparent weight fluctuates between a maximum value and a minimum value At what location (A - D) will the apparent weight be a maximum? Where will it be a minimum? Hint A21 Analyze the free-body diagram Draw a free-body diagram for the woman Assume that the y direction points vertically upward Which of the following statements are true for every point on the circle traveled by the woman? Check all that apply The woman's weight points in the y direction The woman's weight points in the y direction The magnitude of the woman's weight is constant The normal force points in the y direction The normal force points in the y direction The magnitude of the normal force is constant Hint A22 Analyze the acceleration At all times during the woman's motion she experiences a net acceleration (called centripetal acceleration) directed toward the center of the Ferris wheel At what location (A - D) will the acceleration be in only the vertical direction? Check all that apply 3 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM
4 4 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM A B C D Hint A23 Applying Newton's 2nd law Since the normal force and weight are the only forces acting on the woman in the vertical (y) direction where and are the magnitudes of the normal force and the weight respectively Apply what you know about the acceleration of the woman in the y direction at certain points along the circular path to determine when will be a maximum or minimum Enter the letters that correspond to the correct positions separated by a comma CA Answer Requested You can read the value of the woman's apparent weight from the graph at either of these locations Pick one of these locations and apply Newton's 2nd law to the woman at that point to solve for her mass Hint A3 Find the acceleration of the woman What is the acceleration of the woman? Hint A31 You can use the information from the problem statement and the graph to determine the woman's speed This can be used to find her centripetal acceleration: Hint A32 What is the speed Find the woman's speed of the woman? Hint A321 Determining the speed Since the Ferris wheel turns at constant speed the distance the woman travels during some time interval is given by where is the speed and is the time For a complete cycle the distance traveled is the circumference of the Ferris wheel and the time required is one period Thus for a Ferris wheel of radius Hint A322 Find the period The easiest way to determine the speed of the woman is to calculate the distance she travels during one complete cycle of motion and divide this by the time that it takes to complete this cycle The time for a complete cycle is called the period What is the period of the Ferris wheel? Express your answer in seconds = 22 Answer Requested Express your answer in meters per second = 457 Express your answer in meters per second squared = 131 Hint A4 The weight Mass and weight of the woman is the force of gravity that acts on her Her mass is related to the number and type of atoms that comprise her The two quantities are related by Express your answer in kilograms = 60 Problem 830 A 500 g ball swings in a vertical circle at the end of a 15-m-long string When the ball is at the bottom of the circle the tension in the string is 15 N What is the speed of the ball at that point?
5 5 of 5 10/4/2009 8:45 PM 550 Mass on Turntable A small metal cylinder rests on a circular turntable that is rotating at a constant speed as illustrated in the diagram The small metal cylinder has a mass of from the center of the turntable the coefficient of static friction between the cylinder and the turntable is 0080 and the cylinder is located Take the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity to be 981 What is the maximum speed that the cylinder can move along its circular path without slipping off the turntable? Hint A1 Hint A2 Hint A3 Hint A4 Centripetal acceleration Determine the force causing acceleration Find the maximum possible friction force Newton's 2nd law Express your answer numerically in meters per second to two significant figures = 034 At the Test Track You want to test the grip of the tires on your new race car You decide to take the race car to a small test track to experimentally determine the coefficient of friction The racetrack consists of a flat circular road with a radius of 45 The applet shows the result of driving the car around the track at various speeds What is Hint A1 Hint A2 Hint A3 the coefficient of static friction between the tires and the track? Use the applet to find the speed Find an expression for Express your answer to two significant figures = 091 Score Summary: Your score on this assignment is 1274% You received 343 out of a possible total of 35 points plus 103 points of extra credit
Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion
 1 Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion 2016 07 20 www.njctl.org 2 Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency and Rotational Velocity Kinematics of
1 Algebra Based Physics Uniform Circular Motion 2016 07 20 www.njctl.org 2 Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency and Rotational Velocity Kinematics of
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW
 Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT CIRCULAR MOTION MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 65 TOTAL / 95 NAME: 1. An object travels along a path at constant speed. There is a constant
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT CIRCULAR MOTION MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 65 TOTAL / 95 NAME: 1. An object travels along a path at constant speed. There is a constant
Uniform Circular Motion. Uniform Circular Motion
 Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion An object that moves at uniform speed in a circle of constant radius is said to be in uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform
Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion An object that moves at uniform speed in a circle of constant radius is said to be in uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform
AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2 600 rev/min is equivalent
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP C - Webreview ch 7 (part I) Rotation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2 600 rev/min is equivalent
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes. Name
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
Period: Date: Review - UCM & Energy. Page 1. Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below. The diagram shows the top view of a -kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below. The diagram shows the top view of a -kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a
B) v `2. C) `2v. D) 2v. E) 4v. A) 2p 25. B) p C) 2p. D) 4p. E) 4p 2 25
 1. 3. A ball attached to a string is whirled around a horizontal circle of radius r with a tangential velocity v. If the radius is changed to 2r and the magnitude of the centripetal force is doubled the
1. 3. A ball attached to a string is whirled around a horizontal circle of radius r with a tangential velocity v. If the radius is changed to 2r and the magnitude of the centripetal force is doubled the
TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB
 TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB 1. A car traveling at 20 m/s rounds a curve so that its centripetal acceleration
TYPICAL NUMERIC QUESTIONS FOR PHYSICS I REGULAR QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM CUTNELL AND JOHNSON CIRCULAR MOTION CONTENT STANDARD IB 1. A car traveling at 20 m/s rounds a curve so that its centripetal acceleration
1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of
 1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of friction.] A) Its vertical speed remains the same, and its horizontal
1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of friction.] A) Its vertical speed remains the same, and its horizontal
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM
 1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
Proficient. a. The gravitational field caused by a. The student is able to approximate a numerical value of the
 Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Introductory Physics PHYS101
 Introductory Physics PHYS101 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Office Hours Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu TRF 9:30-11:00am
Introductory Physics PHYS101 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Office Hours Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu TRF 9:30-11:00am
AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW
 Basics 1D Mot. 2D Mot. Forces Energy Moment. Rotation Circ/Grav SHM Waves Circuits AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW AP Exam Knowledge & Skills (What skills are needed to achieve the desired
Basics 1D Mot. 2D Mot. Forces Energy Moment. Rotation Circ/Grav SHM Waves Circuits AP Unit 8: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravity HW AP Exam Knowledge & Skills (What skills are needed to achieve the desired
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion
 Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? F actual = Centripetal Force F fictitious = Centrifugal Force Center FLEEing Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? Center
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? F actual = Centripetal Force F fictitious = Centrifugal Force Center FLEEing Centrifugal Force is Fictitious? Center
Extra Circular Motion Questions
 Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
Lecture 6. Circular Motion. Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2. Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF
 Lecture 6 Circular Motion Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2 Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF 6.1 6.4 Angular position If an object moves in a circle of radius r, then after travelling a distance s
Lecture 6 Circular Motion Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2 Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF 6.1 6.4 Angular position If an object moves in a circle of radius r, then after travelling a distance s
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Circular Motion.
 1 Circular Motion www.njctl.org 2 Topics of Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Kinematics of UCM Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency, and Rotational Velocity Dynamics of UCM Vertical
1 Circular Motion www.njctl.org 2 Topics of Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Kinematics of UCM Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency, and Rotational Velocity Dynamics of UCM Vertical
Circular Orbits. Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 Circular Orbits The figure shows a perfectly smooth, spherical, airless planet with one tower of height h. A projectile is launched parallel to the ground with speed v 0. If v 0 is very small, as in trajectory
Circular Orbits The figure shows a perfectly smooth, spherical, airless planet with one tower of height h. A projectile is launched parallel to the ground with speed v 0. If v 0 is very small, as in trajectory
Circular Motion Test Review
 Circular Motion Test Review Name: Date: 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration is equal to zero. B) No,
Circular Motion Test Review Name: Date: 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration is equal to zero. B) No,
Circular Motion PreTest
 Circular Motion PreTest Date: 06/03/2008 Version #: 0 Name: 1. In a series of test runs, a car travels around the same circular track at different velocities. Which graph best shows the relationship between
Circular Motion PreTest Date: 06/03/2008 Version #: 0 Name: 1. In a series of test runs, a car travels around the same circular track at different velocities. Which graph best shows the relationship between
Name Period Date A) B) C) D)
 Example Problems 9.2 E1. A car rounds a curve of constant radius at a constant speed. Which diagram best represents the directions of both the car s velocity and acceleration? Explain: A) B) C) D) E2.
Example Problems 9.2 E1. A car rounds a curve of constant radius at a constant speed. Which diagram best represents the directions of both the car s velocity and acceleration? Explain: A) B) C) D) E2.
Physics 8, Fall 2017, Homework #6. Due at start of class on Friday, October 20, 2017
 Physics 8, Fall 2017, Homework #6. Due at start of class on Friday, October 20, 2017 Problems marked with (*) must include your own drawing or graph representing the problem and at least one complete sentence
Physics 8, Fall 2017, Homework #6. Due at start of class on Friday, October 20, 2017 Problems marked with (*) must include your own drawing or graph representing the problem and at least one complete sentence
Multiple Choice Portion
 Unit 5: Circular Motion and Gravitation Please Note that the gravitational potential energy questions are located in Unit 4 (Energy etc.) Multiple Choice Portion 1. What is the centripetal acceleration
Unit 5: Circular Motion and Gravitation Please Note that the gravitational potential energy questions are located in Unit 4 (Energy etc.) Multiple Choice Portion 1. What is the centripetal acceleration
(1) +0.2 m/s (2) +0.4 m/s (3) +0.6 m/s (4) +1 m/s (5) +0.8 m/s
 77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation In the game of tetherball, the struck ball whirls around a pole. In what direction does the net force on the ball point? 1) Tetherball 1) toward the top of the pole
Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation In the game of tetherball, the struck ball whirls around a pole. In what direction does the net force on the ball point? 1) Tetherball 1) toward the top of the pole
1 A car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. Which of the following statements is true?
 Slide 1 / 30 1 car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. Which of the following statements is true? The car s velocity is constant The car s acceleration is constant The
Slide 1 / 30 1 car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. Which of the following statements is true? The car s velocity is constant The car s acceleration is constant The
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
UCM-Circular Motion. Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram below.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram The diagram shows the top view of a 65-kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a horizontal
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information and diagram The diagram shows the top view of a 65-kilogram student at point A on an amusement park ride. The ride spins the student in a horizontal
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Physics A - PHY 2048C
 Physics A - PHY 2048C Dynamics of 10/18/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapters 8.1-8.7 in the textbook? 2 In uniform circular motion, which
Physics A - PHY 2048C Dynamics of 10/18/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapters 8.1-8.7 in the textbook? 2 In uniform circular motion, which
Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions
 Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions A 2.10 m rope attaches a tire to an overhanging tree limb. A girl swinging on the tire has a tangential speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the
Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration Questions A 2.10 m rope attaches a tire to an overhanging tree limb. A girl swinging on the tire has a tangential speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 MECHANICS: CIRCULAR MOTION QUESTIONS CIRCULAR MOTION (2016;1) Alice is in a car on a ride at a theme park. The car travels along a circular track that is banked, as shown in the diagram. On the diagram,
MECHANICS: CIRCULAR MOTION QUESTIONS CIRCULAR MOTION (2016;1) Alice is in a car on a ride at a theme park. The car travels along a circular track that is banked, as shown in the diagram. On the diagram,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation
 Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation Conceptual Questions 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration
Chapter 5 Review : Circular Motion; Gravitation Conceptual Questions 1) Is it possible for an object moving with a constant speed to accelerate? Explain. A) No, if the speed is constant then the acceleration
Crash Course: Uniform Circular Motion. Our next test will be the week of Nov 27 Dec 1 and will cover projectiles and circular motion.
 Curriculum Outcomes Circular Motion (8 hours) describe uniform circular motion using algebraic and vector analysis (325 12) explain quantitatively circular motion using Newton s laws (325 13) Crash Course:
Curriculum Outcomes Circular Motion (8 hours) describe uniform circular motion using algebraic and vector analysis (325 12) explain quantitatively circular motion using Newton s laws (325 13) Crash Course:
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014
 Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Circular Motion. Unit 7
 Circular Motion Unit 7 Do Now You drive a car that follows a circular path with the radius r = 100 m. Find the distance travelled if you made one complete circle. C 2 R 2(3.14)(100) 6.28(100) 628m Uniform
Circular Motion Unit 7 Do Now You drive a car that follows a circular path with the radius r = 100 m. Find the distance travelled if you made one complete circle. C 2 R 2(3.14)(100) 6.28(100) 628m Uniform
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Newton s Laws including friction, resistive forces, and centripetal force).
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Newton s Laws including friction, resistive forces, and centripetal force). 1981M1. A block of mass m, acted on by a force of magnitude F directed horizontally to the
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Newton s Laws including friction, resistive forces, and centripetal force). 1981M1. A block of mass m, acted on by a force of magnitude F directed horizontally to the
https://njctl.org/courses/science/ap-physics-c-mechanics/attachments/summerassignment-3/
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
Circular Motion. 2 types of Acceleration. Centripetal Force and Acceleration. In a circle. Constant Velocity vs. Constant Speed.
 Circular Motion What does it mean to accelerate Centripetal Force and Acceleration Constant Velocity vs. Constant Speed. 2 types of Acceleration In a circle Direction of acceleration / velocity top view
Circular Motion What does it mean to accelerate Centripetal Force and Acceleration Constant Velocity vs. Constant Speed. 2 types of Acceleration In a circle Direction of acceleration / velocity top view
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 11, 2017
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 11, 2017 HW5 due Friday. It s really Friday this week! Homework study/help sessions (optional): Bill will be in DRL 2C6 Wednesdays from 4 6pm (today). Grace will be in DRL
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 11, 2017 HW5 due Friday. It s really Friday this week! Homework study/help sessions (optional): Bill will be in DRL 2C6 Wednesdays from 4 6pm (today). Grace will be in DRL
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Phys101 Second Major-162 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1
 Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body that can move over a frictionless floor. One force is 20 N, acting due east, and the other
Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body that can move over a frictionless floor. One force is 20 N, acting due east, and the other
Multiple Choice (A) (B) (C) (D)
 Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions are: (A) (B) (C) (D) 2.
Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions are: (A) (B) (C) (D) 2.
66 Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II
 Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II 1 A brick slides on a horizontal surface Which of the following will increase the magnitude of the frictional force on it? A Putting a second brick on top B Decreasing the
Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II 1 A brick slides on a horizontal surface Which of the following will increase the magnitude of the frictional force on it? A Putting a second brick on top B Decreasing the
AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion
 AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion Q1 1999B1. (REDUCED 9 mins) The Sojourner rover vehicle shown in the sketch above was used to explore the surface of Mars as part of the
AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion Q1 1999B1. (REDUCED 9 mins) The Sojourner rover vehicle shown in the sketch above was used to explore the surface of Mars as part of the
Family Name (Please print Given Name(s) Student Number Tutorial Group in BLOCK LETTERS) as on student card Code (eg. R3C,etc)
 Family Name (Please print Given Name(s) Student Number Tutorial Group in BLOCK LETTERS) as on student card Code (eg. R3C,etc) PHY131H1S Mid-Term Test version 1 Tuesday, February 24, 2009 Duration: 80 minutes
Family Name (Please print Given Name(s) Student Number Tutorial Group in BLOCK LETTERS) as on student card Code (eg. R3C,etc) PHY131H1S Mid-Term Test version 1 Tuesday, February 24, 2009 Duration: 80 minutes
1 Page. Uniform Circular Motion Introduction. Earlier we defined acceleration as being the change in velocity with time:
 Uniform Circular Motion Introduction Earlier we defined acceleration as being the change in velocity with time: a=δv/t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleration:
Uniform Circular Motion Introduction Earlier we defined acceleration as being the change in velocity with time: a=δv/t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleration:
Physics Circular Motion Problems. Science and Mathematics Education Research Group
 F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Circular Motion Problems Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
F FA ACULTY C U L T Y OF O F EDUCATION E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Physics Circular Motion Problems Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
Physics 101. Hour Exam I Spring Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
Physics 207 Lecture 10. Lecture 10. Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion
 Lecture 10 Goals: Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion Assignment: HW5, (Chapters 8 & 9, due 3/4, Wednesday) For Tuesday: Finish reading Chapter 8, start Chapter 9. Physics 207: Lecture
Lecture 10 Goals: Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion Assignment: HW5, (Chapters 8 & 9, due 3/4, Wednesday) For Tuesday: Finish reading Chapter 8, start Chapter 9. Physics 207: Lecture
1. In which situation is an object undergoing centripetal acceleration? (C) a car accelerating on a drag strip (D) a hockey puck gliding on ice
 Physics 3204 Assignment 2.1 UCM DUE: Thursday Nov 24, 2017 Name: Part A. Multiple Choice: Select the best possible answer. Place the answer on the answer sheet. 1. In which situation is an object undergoing
Physics 3204 Assignment 2.1 UCM DUE: Thursday Nov 24, 2017 Name: Part A. Multiple Choice: Select the best possible answer. Place the answer on the answer sheet. 1. In which situation is an object undergoing
Unless otherwise specified, use g = 9.80 m/s2
 Phy 111 Exam 2 March 10, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phy 111 Exam 2 March 10, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Welcome back to Physics 211. Physics 211 Spring 2014 Lecture ask a physicist
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Forces in Circular Motion Impulse Physics 211 Spring 2014 Lecture 07-1 1 ask a physicist My question is on sonoluminescence, which is supposed to be when a sound
Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Forces in Circular Motion Impulse Physics 211 Spring 2014 Lecture 07-1 1 ask a physicist My question is on sonoluminescence, which is supposed to be when a sound
Chapter 8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane
 Chapter 8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane Chapter Goal: To learn how to solve problems about motion in a plane. Slide 8-2 Chapter 8 Preview Slide 8-3 Chapter 8 Preview Slide 8-4 Chapter 8 Preview Slide
Chapter 8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane Chapter Goal: To learn how to solve problems about motion in a plane. Slide 8-2 Chapter 8 Preview Slide 8-3 Chapter 8 Preview Slide 8-4 Chapter 8 Preview Slide
Upon collision, the clay and steel block stick together and move to the right with a speed of
 1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box?
 1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
Section Vertical Circular Motion
 Section 11.3 Vertical Circular Motion When a ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle, the ball is accelerating because A. the speed is changing. B. the direction is changing. C. the speed
Section 11.3 Vertical Circular Motion When a ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle, the ball is accelerating because A. the speed is changing. B. the direction is changing. C. the speed
MAKING MEASUREMENTS. I walk at a rate of paces per...or...my pace =
 MAKING MEASUREMENTS TIME: The times that are required to work out the problems can be measured using a digital watch with a stopwatch mode or a watch with a second hand. When measuring the period of a
MAKING MEASUREMENTS TIME: The times that are required to work out the problems can be measured using a digital watch with a stopwatch mode or a watch with a second hand. When measuring the period of a
Hint 1. The direction of acceleration can be determined from Newton's second law
 Chapter 5 [ Edit ] Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Chapter 5 Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 2, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Chapter 5 [ Edit ] Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Chapter 5 Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 2, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits and Gravity
 Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits and Gravity Topics: The kinematics of uniform circular motion The dynamics of uniform circular motion Circular orbits of satellites Newton s law of gravity Sample question:
Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits and Gravity Topics: The kinematics of uniform circular motion The dynamics of uniform circular motion Circular orbits of satellites Newton s law of gravity Sample question:
PHYSICS. Chapter 8 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 8 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to solve problems about motion
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 8 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to solve problems about motion
Physics 23 Exam 2 March 3, 2009
 Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Basic Physics 29:008 Spring 2005 Exam I
 Exam I solutions Name: Date: 1. Two cars are moving around a circular track at the same constant speed. If car 1 is at the inner edge of the track and car 2 is at the outer edge, then A) the acceleration
Exam I solutions Name: Date: 1. Two cars are moving around a circular track at the same constant speed. If car 1 is at the inner edge of the track and car 2 is at the outer edge, then A) the acceleration
Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane
 8.1 Dynamics in 2 Dimensions p. 210-212 Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane 8.2 Velocity and Acceleration in uniform circular motion (a review of sec. 4.6) p. 212-214 8.3 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
8.1 Dynamics in 2 Dimensions p. 210-212 Chapter 8: Dynamics in a plane 8.2 Velocity and Acceleration in uniform circular motion (a review of sec. 4.6) p. 212-214 8.3 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
Circular Motion CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION. tf-t,
 Circular Motion Ill SECTION OBJECTIVES Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. Solve problems involving centripetal force. Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular
Circular Motion Ill SECTION OBJECTIVES Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. Solve problems involving centripetal force. Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 9
 Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 9 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Circular Motion q 3.4 Motion in a Circle q 5.4 Dynamics of Circular Motion If it weren t for the spinning, all the galaxies would collapse
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 9 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Circular Motion q 3.4 Motion in a Circle q 5.4 Dynamics of Circular Motion If it weren t for the spinning, all the galaxies would collapse
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts
 Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
Preparing for Six Flags Physics Concepts uniform means constant, unchanging At a uniform speed, the distance traveled is given by Distance = speed x time At uniform velocity, the displacement is given
ω = k/m x = A cos (ωt + ϕ 0 ) L = I ω a x = ω 2 x P = F v P = de sys J = F dt = p w = m g F G = Gm 1m 2 D = 1 2 CρAv2 a r = v2
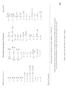 PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
Physics 20 Amusement Park WEM
 Physics 20 Amusement Park Physics @ WEM Page 1 of 6 Group Members: Mindbender Rollercoaster Materials Needed: Stopwatch Maximum Height: 41.5 m First Hill Drop: 38.7 m Radius of the 1 st Loop: 7.177 m Height
Physics 20 Amusement Park Physics @ WEM Page 1 of 6 Group Members: Mindbender Rollercoaster Materials Needed: Stopwatch Maximum Height: 41.5 m First Hill Drop: 38.7 m Radius of the 1 st Loop: 7.177 m Height
Chapter 4 Circular Motion and Gravitation Planetary Data Homework # 26
 Planetary Data Homework # 26 PLANETARY DATA Mean Distance Mass from Sun Radius Period Planet (kg) (m) (m) (days) Sun 1.99 x 10 30 6.970 x 10 8 Mercury 3.30 x 10 23 5.791 x 10 10 2.439 x 10 6 87.97 Venus
Planetary Data Homework # 26 PLANETARY DATA Mean Distance Mass from Sun Radius Period Planet (kg) (m) (m) (days) Sun 1.99 x 10 30 6.970 x 10 8 Mercury 3.30 x 10 23 5.791 x 10 10 2.439 x 10 6 87.97 Venus
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
= mgcos" w. = mgsin! Text: Chapter 5: All sections of Chapter 5. Chapter 6: All sections of Chapter 6. Questions (p ) 1, 3, 7, 8, 10, 12
 Unit 3: Newtonʼs Laws NAME: Text: Chapter 5: All sections of Chapter 5. Chapter 6: All sections of Chapter 6. Questions (p. 106-7) 1, 3, 7, 8, 10, 12 Problems (p. 108-15) #1: 3, 4, 5, 7, 10, 12 #2: 19,
Unit 3: Newtonʼs Laws NAME: Text: Chapter 5: All sections of Chapter 5. Chapter 6: All sections of Chapter 6. Questions (p. 106-7) 1, 3, 7, 8, 10, 12 Problems (p. 108-15) #1: 3, 4, 5, 7, 10, 12 #2: 19,
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead. Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity
 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 EXAM #1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 29, 2010
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
Circular Motion 1
 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Circular Motion 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Circular Motion 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Circular Motion Dynamics Concept Questions
 Circular Motion Dynamics Concept Questions Problem 1: A puck of mass m is moving in a circle at constant speed on a frictionless table as shown above. The puck is connected by a string to a suspended bob,
Circular Motion Dynamics Concept Questions Problem 1: A puck of mass m is moving in a circle at constant speed on a frictionless table as shown above. The puck is connected by a string to a suspended bob,
ΣF=ma SECOND LAW. Make a freebody diagram for EVERY problem!
 PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions
 1992 Q1 AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of a 0.80-meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown
1992 Q1 AP* Circular & Gravitation Free Response Questions A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of a 0.80-meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown
Circular Velocity and Centripetal Acceleration
 1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
1. An object is spun around in circular motion such that it completes 100 cycles in 25 s. a. What is the period of its rotation? [0.25 s] b. If the radius is 0.3 m what is the velocity? [7.54 m/s] c. Draw
Exam 2 Phys Fall 2002 Version A. Name ID Section
 Closed book exam - Calculators are allowed. Only the official formula sheet downloaded from the course web page can be used. You are allowed to write notes on the back of the formula sheet. Use the scantron
Closed book exam - Calculators are allowed. Only the official formula sheet downloaded from the course web page can be used. You are allowed to write notes on the back of the formula sheet. Use the scantron
Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1
 Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1 Next Reading Assignment: W04D2 Young and Freedman: 3.4; 5.4-5.5 Experiment 2: Circular Motion 2 Concept Question: Coastal Highway A sports car drives along the coastal highway
Circular Motion 8.01 W04D1 Next Reading Assignment: W04D2 Young and Freedman: 3.4; 5.4-5.5 Experiment 2: Circular Motion 2 Concept Question: Coastal Highway A sports car drives along the coastal highway
Contents. Objectives IAI motion w/o force motion with force F=ma third law work and energy circular motion Final Exam mechanics questions Recap IAI
 Physics 121 for Majors Section 1 IAI Review 4 Review for IAI and Final Exam Exam Details In the Testing Center Friday - Wednesday Wed. is a late day with a $5 fee Hours: 8 am 9 pm Friday 10 am 3 pm Saturday
Physics 121 for Majors Section 1 IAI Review 4 Review for IAI and Final Exam Exam Details In the Testing Center Friday - Wednesday Wed. is a late day with a $5 fee Hours: 8 am 9 pm Friday 10 am 3 pm Saturday
Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 (2 weeks!
 Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 ( weeks!) Physics 101:
Exam I Physics 101: Lecture 08 Centripetal Acceleration and Circular Motion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zyf5wsmxrai Today s lecture will cover Chapter 5 Exam I is Monday, Oct. 7 ( weeks!) Physics 101:
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
6. Find the centripetal acceleration of the car in m/s 2 a b c d e. 32.0
 PHYSICS 5 TEST 2 REVIEW 1. A car slows down as it travels from point A to B as it approaches an S curve shown to the right. It then travels at constant speed through the turn from point B to C. Select
PHYSICS 5 TEST 2 REVIEW 1. A car slows down as it travels from point A to B as it approaches an S curve shown to the right. It then travels at constant speed through the turn from point B to C. Select
A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane.
![A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane.](/thumbs/78/77486004.jpg) T6 [200 marks] 1. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a horizontal plane. The resultant force acting on the mass is A. zero.
T6 [200 marks] 1. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a horizontal plane. The resultant force acting on the mass is A. zero.
Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #1 Fall 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #1 Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning each
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) EXAM #1 Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning each
Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems
 Problem 1: Double Star System Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems Consider a double star system under the influence of gravitational force between the stars. Star 1 has mass m 1
Problem 1: Double Star System Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems Consider a double star system under the influence of gravitational force between the stars. Star 1 has mass m 1
PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion
 PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions
PSI AP Physics B Circular Motion Multiple Choice 1. A ball is fastened to a string and is swung in a vertical circle. When the ball is at the highest point of the circle its velocity and acceleration directions
Cutnell/Johnson Physics
 Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Interactive Lecture Questions 5.1.1. An airplane flying at 115 m/s due east makes a gradual turn
Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Interactive Lecture Questions 5.1.1. An airplane flying at 115 m/s due east makes a gradual turn
EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK
 Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
Grades 9 12 EDUCATION DAY WORKBOOK It is with great thanks for their knowledge and expertise that the individuals who devised this book are recognized. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Time: Solve problems using a
closed book & notes calculator permitted
 midterm 2 page 1 of 5 closed book & notes calculator permitted score 48 minutes potentially useful equations x = vt cos Ô= adj hyp F =ma v = v o +at sin Ô= opp hyp f k =µ k N x = 1 2 (v o+v) t tan Ô= opp
midterm 2 page 1 of 5 closed book & notes calculator permitted score 48 minutes potentially useful equations x = vt cos Ô= adj hyp F =ma v = v o +at sin Ô= opp hyp f k =µ k N x = 1 2 (v o+v) t tan Ô= opp
SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 10 Spring 009 George A. WIllaims SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format. A data sheet is provided. No solutions for the following problems:
Physics 10 Spring 009 George A. WIllaims SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format. A data sheet is provided. No solutions for the following problems:
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
