One-Parameter Residual Equations
|
|
|
- Alan Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 One-Parameter Residual Equations NFEM Ch 4 Slide 1
2 Total Force Residual Equation with One Control Parameter r(u, ) = 0 total force residual state vector staging parameter = single control parameter Derivatives with respect to will be often abbreviated with primes. For example u = u r = 2 r 2 = 1 = 0 NFEM Ch 4 Slide 2
3 Residual Derivatives Parametric representation of state and control as functions of pseudotime t : u = u(t) = (t) First two derivatives wrt t in matrix form:... r = K u q r = K u + K u q q in which K = r u, q = r = r NFEM Ch 4 Slide 3
4 Rate (Incremental) Equations These are obtained by setting residual derivatives to zero. First order incremental equation:... r = 0 or K u = q Second order incremental equation: r = 0 or K u + K u = q + q Both are systems of ordinary differential equations (ODE) in pseudotime t NFEM Ch 4 Slide 4
5 Incremental Velocity The first order rate equation introduced in last slide is... r = 0 or K u = q If K is nonsingular (a regular equilibrium point)... def. 1 u = K q = u' = v in which 1 v = u' = K q is called the incremental velocity NFEM Ch 4 Slide 5
6 Separable Residuals and Proportional Loading The balanced force residual form of r(u, ) = 0 is p(u) = f(u, ) If the external forces do not depend on the state p(u) = f( ) the residual is called separable. Furthermore if f is linear in, the loading is said to be proportional. NFEM Ch 4 Slide 6
7 Response Plots: Positive and NegativeTraversal Sense Response curve r = 0 (primary equilibrium path) u + Pseudo-time t increasing Pseudo-time t decreasing u t P t + Positive tangent vector Negative tangent vector u NFEM Ch 4 Slide 7
8 Response Visualization P(u, ) t + normal "hyperplane" at P P(u, ) t + positive tangent vector at P positive tangent vector at P equilibrium path r = 0 equilibrium path r = 0 u u Incremental flow Flow orthogonal envelope NFEM Ch 4 Slide 8
9 Example of Previous Lecture A E,A constant B A C' P = EA B θ θ u C k = β EA L k L 2L L NFEM Ch 4 Slide 9
10 Example Problem Response With a Compressible Initial Strain Load factor = P/EA Response using Green-Lagrange strain measure and e = β = 1 β = 1/10 β = 1/100, 1/1000 (indistinguishable at plot scale) Dimensionless displacement µ = u/l NFEM Ch 4 Slide 10
11 Load factor = P/EA Incremental Flow for Previous Response Dimensionless displacement µ = u/l Done by setting r(µ, ) = r c(a constant) value), solving for = (µ, r c), and plotting response curves for sample values of r shown on Figure c NFEM Ch 4 Slide 11
12 Incremental Flow Using Contour Plots r=µ*(β+(2*e0+µ^2)/sqrt[1+µ^2])-; r=simplify[r/.{β->1/10,e0->-0.2}]; ContourPlot[-r,{µ,-1,1},{,-0.25,.25},PlotPoints->101]; ContourPlot[-Sqrt[Abs[r]],{µ,-1,1},{,-0.25,.25},PlotPoints->101]; ContourPlot[-Sqrt[Abs[r]],{µ,-1,1},{,-0.25,.25},PlotPoints->301]; Does not require solving for (which may be inconvenient or impossible), but care must be taken to get reasonably good grading near r = 0, as well as sufficient plot resolution there NFEM Ch 4 Slide 12
13 Incremental Flow for Multiple DOF Problem r = 0 r = 0 u2 u2 u 1 u 1 NFEM Ch 4 Slide 13
14 Tangent Vector and Normal Hyperplane Normal.. hyperplane T v u + = 0 at P P t + + sense of increasing t P t + Equilibrium path r = 0 u 2 u 1 NFEM Ch 4 Slide 14
15 ArcLength Distance Normal hyperplane at P P s Q Positive tangent direction Equilibrium path r = 0 u 2 u 1 NFEM Ch 4 Slide 15
16 Unnormalized t = Tangent Vector [ ] u = [ ] v 1 P P Normal.. hyperplane T v u + = 0 at P t + + sense of increasing t r = 0 Normalized unit tangent vector with positive sense [ ] + v/f t u = 1/f in which u 1 t + Equilibrium path u 2 f = t =+ t 2 =+ 1 + v T v is a normalization factor NFEM Ch 4 Slide 16
17 ArcLength Distance and Orthogonal Flow Normal hyperplane at P The orthogonal hyperplane equation is (see Figure) P s Q Positive tangent direction where u = u u v T u + = 0 P = are increments from P. Dividing by s and t and passing to the limit we get v T.. u + = 0 as the differential equation for the orthogonal flow envelope P u 1 r = 0 Equilibrium path u 2 NFEM Ch 4 Slide 17
Residual Force Equations
 3 Residual Force Equations NFEM Ch 3 Slide 1 Total Force Residual Equation Vector form r(u,λ) = 0 r = total force residual vector u = state vector with displacement DOF Λ = array of control parameters
3 Residual Force Equations NFEM Ch 3 Slide 1 Total Force Residual Equation Vector form r(u,λ) = 0 r = total force residual vector u = state vector with displacement DOF Λ = array of control parameters
Overview of Solution Methods
 20 Overview of Solution Methods NFEM Ch 20 Slide 1 Nonlinear Structural Analysis is a Multilevel Continuation Process Stages Increments Iterations Individual stage Increments Iterations NFEM Ch 20 Slide
20 Overview of Solution Methods NFEM Ch 20 Slide 1 Nonlinear Structural Analysis is a Multilevel Continuation Process Stages Increments Iterations Individual stage Increments Iterations NFEM Ch 20 Slide
Nonlinear FEM. Critical Points. NFEM Ch 5 Slide 1
 5 Critical Points NFEM Ch 5 Slide Assumptions for this Chapter System is conservative: total residual is the gradient of a total potential energy function r(u,λ) = (u,λ) u Consequence: the tangent stiffness
5 Critical Points NFEM Ch 5 Slide Assumptions for this Chapter System is conservative: total residual is the gradient of a total potential energy function r(u,λ) = (u,λ) u Consequence: the tangent stiffness
PHYSICS 110A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS PROBLEM SET #5. (x). (g) Find the force of constraint which keeps the bead on the wire.
 PHYSICS 110A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS PROBLEM SET #5 [1] A bead of mass m slides frictionlessly along a wire curve z = x 2 /2b, where b > 0. The wire rotates with angular frequency ω about the ẑ axis. (a)
PHYSICS 110A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS PROBLEM SET #5 [1] A bead of mass m slides frictionlessly along a wire curve z = x 2 /2b, where b > 0. The wire rotates with angular frequency ω about the ẑ axis. (a)
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
Name: ID: Math 233 Exam 1. Page 1
 Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5
 Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Pseudo-Force Incremental Methods
 . 19 Pseudo-Force Incremental Methods 19 1 Chapter 19: PSEUDO-FORCE INCREMENTAL METHODS 19 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 19.1. Pseudo Force Formulation 19 3 19.2. Computing the Reference Stiffness and Internal
. 19 Pseudo-Force Incremental Methods 19 1 Chapter 19: PSEUDO-FORCE INCREMENTAL METHODS 19 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 19.1. Pseudo Force Formulation 19 3 19.2. Computing the Reference Stiffness and Internal
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity. Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess
 Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
Lecture 7. Pile Analysis
 Lecture 7 14.5 Release Pile Analysis 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 9, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Pile definition in Mechanical - There are a number of methods that can be used to analyze piled foundations in ANSYS
Lecture 7 14.5 Release Pile Analysis 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 9, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Pile definition in Mechanical - There are a number of methods that can be used to analyze piled foundations in ANSYS
2 Lecture Defining Optimization with Equality Constraints
 2 Lecture 2 2.1 Defining Optimization with Equality Constraints So far we have been concentrating on an arbitrary set. Because of this, we could of course incorporate constrains directly into the set.
2 Lecture 2 2.1 Defining Optimization with Equality Constraints So far we have been concentrating on an arbitrary set. Because of this, we could of course incorporate constrains directly into the set.
34 Imperfections 34 1
 34 Imperfections 34 1 Chapter 34: IMPERFECTIONS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 34.1 No Body is Perfect................... 34 3 34.2 Imperfection Sources................. 34 3 34.2.1 Physical Imperfections..............
34 Imperfections 34 1 Chapter 34: IMPERFECTIONS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 34.1 No Body is Perfect................... 34 3 34.2 Imperfection Sources................. 34 3 34.2.1 Physical Imperfections..............
Reciprocal of the initial shear stiffness of the interface K si under initial loading; reciprocal of the initial tangent modulus E i of the soil
 Appendix F Notation a b B C c C k C N C s C u C wt C θ D r D 1 D 2 D 10 D 30 Reciprocal of the initial shear stiffness of the interface K si under initial loading; reciprocal of the initial tangent modulus
Appendix F Notation a b B C c C k C N C s C u C wt C θ D r D 1 D 2 D 10 D 30 Reciprocal of the initial shear stiffness of the interface K si under initial loading; reciprocal of the initial tangent modulus
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC. Tutorial with Background and Exercises
 Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
ENGN2340 Final Project: Implementation of a Euler-Bernuolli Beam Element Michael Monn
 ENGN234 Final Project: Implementation of a Euler-Bernuolli Beam Element Michael Monn 12/11/13 Problem Definition and Shape Functions Although there exist many analytical solutions to the Euler-Bernuolli
ENGN234 Final Project: Implementation of a Euler-Bernuolli Beam Element Michael Monn 12/11/13 Problem Definition and Shape Functions Although there exist many analytical solutions to the Euler-Bernuolli
CSC 344 Algorithms and Complexity. Proof by Mathematical Induction
 CSC 344 Algorithms and Complexity Lecture #1 Review of Mathematical Induction Proof by Mathematical Induction Many results in mathematics are claimed true for every positive integer. Any of these results
CSC 344 Algorithms and Complexity Lecture #1 Review of Mathematical Induction Proof by Mathematical Induction Many results in mathematics are claimed true for every positive integer. Any of these results
Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures
 Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures Michael H. Scott Associate Professor School of Civil and Construction Engineering Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar April 8,
Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures Michael H. Scott Associate Professor School of Civil and Construction Engineering Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar April 8,
Course in. Geometric nonlinearity. Nonlinear FEM. Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Nonlinear FEM Geometric nonlinearity Nonlinear FEM Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity it continued
Course in Nonlinear FEM Geometric nonlinearity Nonlinear FEM Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity it continued
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 06
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 06 In the last lecture, we have seen a boundary value problem, using the formal
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 06 In the last lecture, we have seen a boundary value problem, using the formal
Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Today s Lecture Contents: Introduction Differential formulation
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Today s Lecture Contents: Introduction Differential formulation
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Free Vibration of Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) Systems
 Free Vibration of Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) Systems Procedure in solving structural dynamics problems 1. Abstraction/modeling Idealize the actual structure to a simplified version, depending on the
Free Vibration of Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) Systems Procedure in solving structural dynamics problems 1. Abstraction/modeling Idealize the actual structure to a simplified version, depending on the
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Continuation methods for non-linear analysis
 Continuation methods for non-linear analysis FR : Méthodes de pilotage du chargement Code_Aster, Salome-Meca course material GNU FDL licence (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) Outline Definition of
Continuation methods for non-linear analysis FR : Méthodes de pilotage du chargement Code_Aster, Salome-Meca course material GNU FDL licence (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) Outline Definition of
Nonlinear Bifurcation Analysis
 33 Nonlinear ifurcation Analysis 33 1 Chapter 33: NONLINEAR IFURCATION ANALYSIS TALE OF CONTENTS Page 33.1 Introduction..................... 33 3 33.2 ifurcation Analysis Levels............... 33 3 33.3
33 Nonlinear ifurcation Analysis 33 1 Chapter 33: NONLINEAR IFURCATION ANALYSIS TALE OF CONTENTS Page 33.1 Introduction..................... 33 3 33.2 ifurcation Analysis Levels............... 33 3 33.3
ME751 Advanced Computational Multibody Dynamics
 ME751 Advanced Computational Multibody Dynamics November 2, 2016 Antonio Recuero University of Wisconsin-Madison Quotes of the Day The methods which I set forth do not require either constructions or geometrical
ME751 Advanced Computational Multibody Dynamics November 2, 2016 Antonio Recuero University of Wisconsin-Madison Quotes of the Day The methods which I set forth do not require either constructions or geometrical
CS Tutorial 5 - Differential Geometry I - Surfaces
 236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering
 Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
Unit Speed Curves. Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if
 Unit Speed Curves Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if The reason that we like unit speed curves that the parameter t is equal to arc length; i.e. the value of t tells us how far along
Unit Speed Curves Recall that a curve Α is said to be a unit speed curve if The reason that we like unit speed curves that the parameter t is equal to arc length; i.e. the value of t tells us how far along
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Overview of Solution Methods
 20 Overview of Solution Methods 20 1 Chapter 20: OVERVIEW OF SOLUTION METHODS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 20.1 Introduction..................... 20 3 20.2 Solution Framework.................. 20 3 20.2.1 Stages,
20 Overview of Solution Methods 20 1 Chapter 20: OVERVIEW OF SOLUTION METHODS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 20.1 Introduction..................... 20 3 20.2 Solution Framework.................. 20 3 20.2.1 Stages,
Nonconservative Loading: Overview
 35 Nonconservative Loading: Overview 35 Chapter 35: NONCONSERVATIVE LOADING: OVERVIEW TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 35. Introduction..................... 35 3 35.2 Sources...................... 35 3 35.3 Three
35 Nonconservative Loading: Overview 35 Chapter 35: NONCONSERVATIVE LOADING: OVERVIEW TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 35. Introduction..................... 35 3 35.2 Sources...................... 35 3 35.3 Three
The integrating factor method (Sect. 1.1)
 The integrating factor method (Sect. 1.1) Overview of differential equations. Linear Ordinary Differential Equations. The integrating factor method. Constant coefficients. The Initial Value Problem. Overview
The integrating factor method (Sect. 1.1) Overview of differential equations. Linear Ordinary Differential Equations. The integrating factor method. Constant coefficients. The Initial Value Problem. Overview
Newton Method: General Control and Variants
 23 Newton Method: General Control and Variants 23 1 Chapter 23: NEWTON METHOD: GENERAL CONTROL AND VARIANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 23.1 Introduction..................... 23 3 23.2 Newton Iteration as Dynamical
23 Newton Method: General Control and Variants 23 1 Chapter 23: NEWTON METHOD: GENERAL CONTROL AND VARIANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 23.1 Introduction..................... 23 3 23.2 Newton Iteration as Dynamical
MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FUNCTIONS OF SINGLE & SEVERAL VARIABLES
 MATHEMATICS-I MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FUNCTIONS OF SINGLE & SEVERAL VARIABLES I YEAR B.TECH By Y. Prabhaker Reddy Asst. Professor of Mathematics Guru Nanak Engineering College Ibrahimpatnam, Hyderabad. Name
MATHEMATICS-I MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FUNCTIONS OF SINGLE & SEVERAL VARIABLES I YEAR B.TECH By Y. Prabhaker Reddy Asst. Professor of Mathematics Guru Nanak Engineering College Ibrahimpatnam, Hyderabad. Name
MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor
 MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor 1) For a static uniaxial bar problem at isothermal (Θ const.) conditions, state principle of energy conservation (first law of thermodynamics). On the basis of
MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor 1) For a static uniaxial bar problem at isothermal (Θ const.) conditions, state principle of energy conservation (first law of thermodynamics). On the basis of
Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates
 Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates * S.N.Patel 1) 1) Dept. of Civi Engineering, BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus, Pilani-333031, (Raj), India 1) shuvendu@pilani.bits-pilani.ac.in
Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates * S.N.Patel 1) 1) Dept. of Civi Engineering, BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus, Pilani-333031, (Raj), India 1) shuvendu@pilani.bits-pilani.ac.in
Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures
 Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Topics presented Types of nonlinearities Materially nonlinear only Geometrically nonlinear analysis Deformation-dependent
Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Topics presented Types of nonlinearities Materially nonlinear only Geometrically nonlinear analysis Deformation-dependent
31.1.1Partial derivatives
 Module 11 : Partial derivatives, Chain rules, Implicit differentiation, Gradient, Directional derivatives Lecture 31 : Partial derivatives [Section 31.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following
Module 11 : Partial derivatives, Chain rules, Implicit differentiation, Gradient, Directional derivatives Lecture 31 : Partial derivatives [Section 31.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following
Drilling in tempered glass modelling and experiments
 Drilling in tempered glass modelling and experiments Jens H. NIELSEN* * Department of Civil Engineering, Technical University of Denmark jhn@byg.dtu.dk Abstract The present paper reports experimentally
Drilling in tempered glass modelling and experiments Jens H. NIELSEN* * Department of Civil Engineering, Technical University of Denmark jhn@byg.dtu.dk Abstract The present paper reports experimentally
Mechanics of Structures (CE130N) Lab 3
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY CE 130N, Spring 2009 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Prof. S. Govindjee and Dr. T. Koyama Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Lab 3 1
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY CE 130N, Spring 2009 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Prof. S. Govindjee and Dr. T. Koyama Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Lab 3 1
Homework Exercises for Chapter 10 TL Bar Elements: Truss Analysis
 Solutions to Exercises omework Exercises for Chapter TL Bar Elements: Truss Analysis Note: not all solutions fully worked out. EXECISE. The strain measures (engineering strain versus GL strain) are different.
Solutions to Exercises omework Exercises for Chapter TL Bar Elements: Truss Analysis Note: not all solutions fully worked out. EXECISE. The strain measures (engineering strain versus GL strain) are different.
Course Summary Math 211
 Course Summary Math 211 table of contents I. Functions of several variables. II. R n. III. Derivatives. IV. Taylor s Theorem. V. Differential Geometry. VI. Applications. 1. Best affine approximations.
Course Summary Math 211 table of contents I. Functions of several variables. II. R n. III. Derivatives. IV. Taylor s Theorem. V. Differential Geometry. VI. Applications. 1. Best affine approximations.
The Finite Element Method II
 [ 1 The Finite Element Method II Non-Linear finite element Use of Constitutive Relations Xinghong LIU Phd student 02.11.2007 [ 2 Finite element equilibrium equations: kinematic variables Displacement Strain-displacement
[ 1 The Finite Element Method II Non-Linear finite element Use of Constitutive Relations Xinghong LIU Phd student 02.11.2007 [ 2 Finite element equilibrium equations: kinematic variables Displacement Strain-displacement
The Four Fundamental Subspaces
 The Four Fundamental Subspaces Introduction Each m n matrix has, associated with it, four subspaces, two in R m and two in R n To understand their relationships is one of the most basic questions in linear
The Four Fundamental Subspaces Introduction Each m n matrix has, associated with it, four subspaces, two in R m and two in R n To understand their relationships is one of the most basic questions in linear
PHYSICS 200A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTION SET #2
 PHYSICS 200A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTION SET #2 [1] [José and Saletan problem 3.11] Consider a three-dimensional one-particle system whose potential energy in cylindrical polar coordinates {ρ,φ,z} is
PHYSICS 200A : CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTION SET #2 [1] [José and Saletan problem 3.11] Consider a three-dimensional one-particle system whose potential energy in cylindrical polar coordinates {ρ,φ,z} is
MAE 323: Chapter 6. Structural Models
 Common element types for structural analyis: oplane stress/strain, Axisymmetric obeam, truss,spring oplate/shell elements o3d solid ospecial: Usually used for contact or other constraints What you need
Common element types for structural analyis: oplane stress/strain, Axisymmetric obeam, truss,spring oplate/shell elements o3d solid ospecial: Usually used for contact or other constraints What you need
Lecture 9. Systems of Two First Order Linear ODEs
 Math 245 - Mathematics of Physics and Engineering I Lecture 9. Systems of Two First Order Linear ODEs January 30, 2012 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 245, Lecture 9 January 30, 2012 1 / 15 Agenda General Form
Math 245 - Mathematics of Physics and Engineering I Lecture 9. Systems of Two First Order Linear ODEs January 30, 2012 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 245, Lecture 9 January 30, 2012 1 / 15 Agenda General Form
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 28, 2015
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions
 Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Reflections and Rotations in R 3
 Reflections and Rotations in R 3 P. J. Ryan May 29, 21 Rotations as Compositions of Reflections Recall that the reflection in the hyperplane H through the origin in R n is given by f(x) = x 2 ξ, x ξ (1)
Reflections and Rotations in R 3 P. J. Ryan May 29, 21 Rotations as Compositions of Reflections Recall that the reflection in the hyperplane H through the origin in R n is given by f(x) = x 2 ξ, x ξ (1)
Additional Problem (HW 10)
 1 Housekeeping - Three more lectures left including today: Nov. 20 st, Nov. 27 th, Dec. 4 th - Final Eam on Dec. 11 th at 4:30p (Eploratory Planetary 206) 2 Additional Problem (HW 10) z h y O Choose origin
1 Housekeeping - Three more lectures left including today: Nov. 20 st, Nov. 27 th, Dec. 4 th - Final Eam on Dec. 11 th at 4:30p (Eploratory Planetary 206) 2 Additional Problem (HW 10) z h y O Choose origin
An example of panel solution in the elastic-plastic regime
 An example of panel solution in the elastic-plastic regime Piotr Mika May, 2014 2013-05-08 1. Example solution of the panel with ABAQUS program The purpose is to analyze the elastic-plastic panel. The
An example of panel solution in the elastic-plastic regime Piotr Mika May, 2014 2013-05-08 1. Example solution of the panel with ABAQUS program The purpose is to analyze the elastic-plastic panel. The
LECTURE 12 FRICTION, STRINGS & SPRINGS. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 12 FRICTION, STRINGS & SPRINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 12 2! Reading chapter 6-1 to 6-4! Friction " Static friction " Kinetic friction! Strings! Pulleys! Springs Origin of friction 3!!
LECTURE 12 FRICTION, STRINGS & SPRINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 12 2! Reading chapter 6-1 to 6-4! Friction " Static friction " Kinetic friction! Strings! Pulleys! Springs Origin of friction 3!!
EE2007: Engineering Mathematics II Vector Calculus
 EE2007: Engineering Mathematics II Vector Calculus Ling KV School of EEE, NTU ekvling@ntu.edu.sg Rm: S2-B2b-22 Ver 1.1: Ling KV, October 22, 2006 Ver 1.0: Ling KV, Jul 2005 EE2007/Ling KV/Aug 2006 EE2007:
EE2007: Engineering Mathematics II Vector Calculus Ling KV School of EEE, NTU ekvling@ntu.edu.sg Rm: S2-B2b-22 Ver 1.1: Ling KV, October 22, 2006 Ver 1.0: Ling KV, Jul 2005 EE2007/Ling KV/Aug 2006 EE2007:
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS. Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016
 AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
MATHEMATICS XII. Topic. Revision of Derivatives Presented By. Avtar Singh Lecturer Paramjit Singh Sidhu June 19,2009
 MATHEMATICS XII 1 Topic Revision of Derivatives Presented By Avtar Singh Lecturer Paramjit Singh Sidhu June 19,2009 19 June 2009 Punjab EDUSAT Society (PES) 1 Continuity 2 Def. In simple words, a function
MATHEMATICS XII 1 Topic Revision of Derivatives Presented By Avtar Singh Lecturer Paramjit Singh Sidhu June 19,2009 19 June 2009 Punjab EDUSAT Society (PES) 1 Continuity 2 Def. In simple words, a function
PILE SOIL INTERACTION MOMENT AREA METHOD
 Pile IGC Soil 2009, Interaction Moment Guntur, INDIA Area Method PILE SOIL INTERACTION MOMENT AREA METHOD D.M. Dewaikar Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay, Mumbai 400 076, India. E-mail:
Pile IGC Soil 2009, Interaction Moment Guntur, INDIA Area Method PILE SOIL INTERACTION MOMENT AREA METHOD D.M. Dewaikar Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay, Mumbai 400 076, India. E-mail:
Ch 3.7: Mechanical & Electrical Vibrations
 Ch 3.7: Mechanical & Electrical Vibrations Two important areas of application for second order linear equations with constant coefficients are in modeling mechanical and electrical oscillations. We will
Ch 3.7: Mechanical & Electrical Vibrations Two important areas of application for second order linear equations with constant coefficients are in modeling mechanical and electrical oscillations. We will
Unforced Oscillations
 Unforced Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law Newton s Second Law Method of Force Competition Visualization of Harmonic Motion Phase-Amplitude Conversion The Simple Pendulum and The Linearized
Unforced Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law Newton s Second Law Method of Force Competition Visualization of Harmonic Motion Phase-Amplitude Conversion The Simple Pendulum and The Linearized
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Non-Linear Dynamics Part I
 The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Non-Linear Dynamics Part I Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 5/Part A - 23 November,
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Non-Linear Dynamics Part I Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 5/Part A - 23 November,
Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments)
 Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments) by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Ductile
Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments) by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Ductile
More Examples Of Generalized Coordinates
 Slides of ecture 8 Today s Class: Review Of Homework From ecture 7 Hamilton s Principle More Examples Of Generalized Coordinates Calculating Generalized Forces Via Virtual Work /3/98 /home/djsegal/unm/vibcourse/slides/ecture8.frm
Slides of ecture 8 Today s Class: Review Of Homework From ecture 7 Hamilton s Principle More Examples Of Generalized Coordinates Calculating Generalized Forces Via Virtual Work /3/98 /home/djsegal/unm/vibcourse/slides/ecture8.frm
Chapter 2. Preview. Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically
 Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS
 NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5
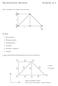 Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Econ Slides from Lecture 8
 Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 8 Joel Sobel September 1, 2010 Computational Facts 1. det AB = det BA = det A det B 2. If D is a diagonal matrix, then det D is equal to the product of its
Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 8 Joel Sobel September 1, 2010 Computational Facts 1. det AB = det BA = det A det B 2. If D is a diagonal matrix, then det D is equal to the product of its
Response Surface Methods
 Response Surface Methods 3.12.2014 Goals of Today s Lecture See how a sequence of experiments can be performed to optimize a response variable. Understand the difference between first-order and second-order
Response Surface Methods 3.12.2014 Goals of Today s Lecture See how a sequence of experiments can be performed to optimize a response variable. Understand the difference between first-order and second-order
Chapter 0. Preliminaries. 0.1 Things you should already know
 Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a
 Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a Some slides are due to Christopher Bishop Limitations of K-means Hard assignments of data points to clusters small shift of a
Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a Some slides are due to Christopher Bishop Limitations of K-means Hard assignments of data points to clusters small shift of a
BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS IN RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
 1 BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS IN RECTANGULAR COORDINATES 1.1 Separable Partial Differential Equations 1. Classical PDEs and Boundary-Value Problems 1.3 Heat Equation 1.4 Wave Equation 1.5 Laplace s Equation
1 BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS IN RECTANGULAR COORDINATES 1.1 Separable Partial Differential Equations 1. Classical PDEs and Boundary-Value Problems 1.3 Heat Equation 1.4 Wave Equation 1.5 Laplace s Equation
Second-Order ODE and the Calculus of Variations
 Chapter 3 Second-Order ODE and the Calculus of Variations 3.1. Tangent Vectors and the Tangent Bundle Let σ : I R n be a C 1 curve in R n and suppose that σ(t 0 )=p and σ (t 0 )=v. Up until this point
Chapter 3 Second-Order ODE and the Calculus of Variations 3.1. Tangent Vectors and the Tangent Bundle Let σ : I R n be a C 1 curve in R n and suppose that σ(t 0 )=p and σ (t 0 )=v. Up until this point
Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th
 Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th jacques@ucsdedu Key words: Systems of equations, Implicit differentiation Know how to do implicit differentiation, how to use implicit and inverse function theorems 131
Lecture 13 - Wednesday April 29th jacques@ucsdedu Key words: Systems of equations, Implicit differentiation Know how to do implicit differentiation, how to use implicit and inverse function theorems 131
Lecture 6 Friction. Friction Phenomena Types of Friction
 Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Introduction to Optimization Techniques. Nonlinear Optimization in Function Spaces
 Introduction to Optimization Techniques Nonlinear Optimization in Function Spaces X : T : Gateaux and Fréchet Differentials Gateaux and Fréchet Differentials a vector space, Y : a normed space transformation
Introduction to Optimization Techniques Nonlinear Optimization in Function Spaces X : T : Gateaux and Fréchet Differentials Gateaux and Fréchet Differentials a vector space, Y : a normed space transformation
Department of Architecture & Civil Engineering
 MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
Linear Algebra. Paul Yiu. 6D: 2-planes in R 4. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Fall 2011
 Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing
 Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
MATH 100 Introduction to the Profession
 MATH 100 Introduction to the Profession Differential Equations in MATLAB Greg Fasshauer Department of Applied Mathematics Illinois Institute of Technology Fall 2012 fasshauer@iit.edu MATH 100 ITP 1 What
MATH 100 Introduction to the Profession Differential Equations in MATLAB Greg Fasshauer Department of Applied Mathematics Illinois Institute of Technology Fall 2012 fasshauer@iit.edu MATH 100 ITP 1 What
Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression
 Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression Dan Sheldon September 23, 2014 Topics Multivariate linear regression Model Cost function Normal equations Gradient descent Features Book Data 10 8 Weight (lbs.)
Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression Dan Sheldon September 23, 2014 Topics Multivariate linear regression Model Cost function Normal equations Gradient descent Features Book Data 10 8 Weight (lbs.)
The Plane Stress Problem
 14 The Plane Stress Problem IFEM Ch 14 Slide 1 Plate in Plane Stress Thickness dimension or transverse dimension z Top surface Inplane dimensions: in, plane IFEM Ch 14 Slide 2 Mathematical Idealization
14 The Plane Stress Problem IFEM Ch 14 Slide 1 Plate in Plane Stress Thickness dimension or transverse dimension z Top surface Inplane dimensions: in, plane IFEM Ch 14 Slide 2 Mathematical Idealization
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1
 Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary
 GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn 2016 Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary To learn today The lecture should give you overview of how non-linear problems in Finite Element Method
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn 2016 Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary To learn today The lecture should give you overview of how non-linear problems in Finite Element Method
Rotational Motion. Lecture 17. Chapter 10. Physics I Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 17 Chapter 10 Physics I 04.0.014 otational Motion Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov013/physics1spring.html
Lecture 17 Chapter 10 Physics I 04.0.014 otational Motion Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov013/physics1spring.html
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS
 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
An example solution of a panel in the elastic-plastic regime
 An example solution of a panel in the elastic-plastic regime Piotr Mika May, 2013 1. Example solution of the panel with ABAQUS program The purpose is to analyze an elastic-plastic panel. The elastic solution
An example solution of a panel in the elastic-plastic regime Piotr Mika May, 2013 1. Example solution of the panel with ABAQUS program The purpose is to analyze an elastic-plastic panel. The elastic solution
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II
 STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
Nonlinear Modeling for Health Care Applications Ashutosh Srivastava Marc Horner, Ph.D. ANSYS, Inc.
 Nonlinear Modeling for Health Care Applications Ashutosh Srivastava Marc Horner, Ph.D. ANSYS, Inc. 2 Motivation 12 Motivation Linear analysis works well for only small number of applications. The majority
Nonlinear Modeling for Health Care Applications Ashutosh Srivastava Marc Horner, Ph.D. ANSYS, Inc. 2 Motivation 12 Motivation Linear analysis works well for only small number of applications. The majority
Topic 5: Finite Element Method
 Topic 5: Finite Element Method 1 Finite Element Method (1) Main problem of classical variational methods (Ritz method etc.) difficult (op impossible) definition of approximation function ϕ for non-trivial
Topic 5: Finite Element Method 1 Finite Element Method (1) Main problem of classical variational methods (Ritz method etc.) difficult (op impossible) definition of approximation function ϕ for non-trivial
Multiple Regression. Dr. Frank Wood. Frank Wood, Linear Regression Models Lecture 12, Slide 1
 Multiple Regression Dr. Frank Wood Frank Wood, fwood@stat.columbia.edu Linear Regression Models Lecture 12, Slide 1 Review: Matrix Regression Estimation We can solve this equation (if the inverse of X
Multiple Regression Dr. Frank Wood Frank Wood, fwood@stat.columbia.edu Linear Regression Models Lecture 12, Slide 1 Review: Matrix Regression Estimation We can solve this equation (if the inverse of X
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Estimation of the Residual Stiffness of Fire-Damaged Concrete Members
 Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.22, no.3, pp.261-273, 2011 Estimation of the Residual Stiffness of Fire-Damaged Concrete Members J.M. Zhu 1, X.C. Wang 1, D. Wei 2, Y.H. Liu 2 and B.Y. Xu 2 Abstract:
Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.22, no.3, pp.261-273, 2011 Estimation of the Residual Stiffness of Fire-Damaged Concrete Members J.M. Zhu 1, X.C. Wang 1, D. Wei 2, Y.H. Liu 2 and B.Y. Xu 2 Abstract:
Soil strength. the strength depends on the applied stress. water pressures are required
 Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Chapter 2: Deflections of Structures
 Chapter 2: Deflections of Structures Fig. 4.1. (Fig. 2.1.) ASTU, Dept. of C Eng., Prepared by: Melkamu E. Page 1 (2.1) (4.1) (2.2) Fig.4.2 Fig.2.2 ASTU, Dept. of C Eng., Prepared by: Melkamu E. Page 2
Chapter 2: Deflections of Structures Fig. 4.1. (Fig. 2.1.) ASTU, Dept. of C Eng., Prepared by: Melkamu E. Page 1 (2.1) (4.1) (2.2) Fig.4.2 Fig.2.2 ASTU, Dept. of C Eng., Prepared by: Melkamu E. Page 2
Vectors in Physics. Topics to review:
 Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
ME185 Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
 Fall, 0 ME85 Introduction to Continuum Mechanics The attached pages contain four previous midterm exams for this course. Each midterm consists of two pages. As you may notice, many of the problems are
Fall, 0 ME85 Introduction to Continuum Mechanics The attached pages contain four previous midterm exams for this course. Each midterm consists of two pages. As you may notice, many of the problems are
Lecture XXVI. Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopkins University November 5, 2003
 Lecture XXVI Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopins University morris@jhu.edu November 5, 2003 Lecture XXVI: Oscillations Oscillations are periodic motions. There are many examples of
Lecture XXVI Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopins University morris@jhu.edu November 5, 2003 Lecture XXVI: Oscillations Oscillations are periodic motions. There are many examples of
Advanced Dynamics. - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations. Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich
 Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
