Differential Equation of Motion of the Particle. with Helical Structure and Spin 2. the Form Like Schrodinger s
|
|
|
- Tamsin Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 5, 11, no. 13, Diffeential Equation of Motion of te Patile wit Helial Stutue and Spin Has te Fom Like Sodinge s Cen Sen nian Dept. of Pys., (National) Hua Qiao Univ. Quanzou, Fujian, P.. Cina ensennian@gmail.om Abstat. Eletomagneti adiations ae obviously waves. Potoeleti effet aused A. Einstein to postulate tat ligt of fequenyν itself onsists of individual quanta of enegy = ν. Follow Einstein dietly, we ty to teat a tin beam of onial wave tain wit enegy ν as a poton to see if tee is anyting inteesting. We fist pove teoetially tat su a tain must be oveed by a membane of pefet efletion and zeo est mass as lateal bounday. Ten we pove tat tee is a pai of symmetial spials of maximum stess Σ E tat divides te membane into equal pats wit same amount of diffeent ages. One te field being stengtened stongly and te onditions of mass and age satisfied, te membane will beak into two ±aged patiles of spin /. Cages and mass distibution inside ae poved to be of elial symmety. Ten we pove tat te spin of tis lass of patiles ae geneally onsisted of two pats: owing to su spial stutue s tanslational motion plus exta self-otation. Just beause of tis speial stutue, we pove at last tat diffeential equation of motion patile s inne system satisfied looks like Sodinge equation altoug intepetation fo te wave funtion is diffeent. Keywods: Membane, O-planes, ±aged spial-alves, un-foming ±eleton. max
2 61 Cen Sen nian pit, spin, spial stutue, otating on O-planes, intinsi fequeny, exta self-otation, wave funtion, mass density, elial symmety, Sodinge equation I. Intodution Eletomagneti adiations ae obviously waves. Potoeleti effet aused A. Einstein to postulate tat ligt of fequenyν itself onsists of individual quanta of enegy = ν. In te demonstation of quantum eletodynamis, E. Femi (1) and ten. P. Feynman () onneted te aveage enegy density ( = ν ) of eletomagneti wave wit te pobability (=1) of finding a poton tee to be a basi. To follow A. Einstein s idea dietly, it is natual to teat a tin beam of a monoomati speial eletomagneti wave fom = angle Ω and lengt L aving enegy ν as a poton. Tat is, wit solid ε A μ H S ( ) ( ) 1 t t d π π ds = ν L os + T os T (1) Wee, is te speial distant fom te ente of wave sufae to te inne and bounday iumfeenes and L equals to multiple wavelengt. Te speial aea of te ing toug point on sufae is ds = π sinϕ dϕ. angle tat suspends at = ϕ = is te plane. Hee we teat E s, H s magnitudes A, H disegad of te dietion of on wave sufae, just beause tat a poton wave tain must be symmeti wit its longitudinal axis. And ten, we depend on a seies of logial infeenes to see if tee is anyting inteesting we will ave? Ae tey wot to be fute studied teoetially and deteted by expeiments?
3 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 611 II. A poton wave tain must be oveed by a membane of pefet efletion and zeo est mass as lateal bounday. As well known, if tey ae fa enoug fom vaying dipole U, vetos E and H ae tansvese, mutually pependiula, in pase, and its magnitude (3) : E = μ H ε U&& ( t ) sin θ Aoding to equation (), E = H = wenθ =. It leads to tat etain poton waves wit te bounday tangent to te line of θ = will ave E = H = at tangent points. Beause of te symmety of a poton and te identity between potons, we an affim tat any poton wave tain as got E = H = along its iula bounday, despite of te distibution funtion of A ( ) and H ( ) ae ontinued o disete ee. Fo onveniene in late illustation, we name te geometial plane (te synonym of te tin laye) as obsevation (O)-plane if a plane wave passes toug it pependiulaly. Of ouse, fo a speial wave O-plane is efe to speial and oinides wit te speial wave sufae. We often use tangential to epesent te dietion tangent o paallel to te wave sufae. Now a speial poton wave tain emitted fom = an be expessed as () A( ) E = (,, t ' ) t' os π ( ) ( 1 ', t, f ) (3) T Sine te aea of speial ile of adius on wave sufae is Ω = Φ π sinϕ dϕ = 4π sin Φ, wee 1 Ω Φ = = sin (onstan 4π and = ϕ. Ten and E ( ) just ae funtions ofϕ, disegad of te adial Φ oodinate. Expession (3) satisfies diffeential wave equation. Sine A( ) is always an even funtion and equal to at bounday = be expanded in Fouie seies as follow:, it an
4 61 Cen Sen nian A ( ) = j = 1 b j-1 let j = 1 os π ( j 1) 4 b j-1 os π ( j 1) Λ ( Λ = 4, ) (4) Te wave funtion (3) will make a stationay vibation on te O-plane loated at. Its funtion is o A( ) E(, o, = o o t os π T let E (, = L A ( ) = ( p o, t T ) (5) Hea we ave osen te zeo point oft so as initial pase of osine funtion equal to zeo. Instead equation (4) into (5), we ave 1 E (, = o j = 1 b j-1 os π ( Λ j 1 let E+ ( V + E ( + V t 1 ) + T o j = 1 b j-1 os π ( Λ j 1 + T t ) Λ (Λ j-1 = ( j 1), Λ = 4o, V Λ =, o, T L t T ) (6) Fo any dietion of on te O-plane (tin laye), E+ ( V is te sum of all taveling waves to te igt. And E ( + V is te one to te left. Tey move towad ea ote and eflet pefetly at te bounday points wit 18 pase loss (wee E = H = ) Te identity of equations (5) and (6) means wen a poton wave passes -plane at timet, te enegy exited in te tin laye an be teated as stoage eite in type of stationay vibation, o in type of te distibution of infinite pais of tansvesal taveling waves along te O-plane at same time. Tey ae matematially equivalent. An inteesting question is wete te tansvesal taveling o
5 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 613 eletomagneti waves eally exist ove te O-plane (te spae tat tin laye oupied)? Te answe is etainly positive. As a matte of fat, fo evey moment t, E of all points at same laye ae paallel and vaying synonially. Tey will exite adiation along all dietions inlude te tangential dietions of te laye. Te mutual tangential adiations, ten mutual Poynting vetos (S= E H) and mutual adiation pessues Q aoss te intefae of any two adjaent pats in te same laye ae eally existed. Equation (6) means tat te esultant tansvesal taveling waves and enegy flow ae adial in te tin laye. Te adiation intensity fom a vaying E is anisotopi even along wave sufae, equation (). If a poton wave is linea polaized, te oeffiients in equation (6) must be diffeent in diffeent -dietion. So te poton waves just emitted fom vaying dipole must be equal mixtues of igt and left iula polaized. A poton must be etain sot of iula polaized and te oeffiients of equation (6) must 1 π be te statistial mean values in te alf peiod ( Emax sinθ dθ Emax π = ). It π makes te oeffiients same along any -dietion on same wave sufae. Fo eq. (1), sine A ( ) (π sinϕdϕ) = π A ( ) sin ( Φ ) d( Φ ) (7) And te limits of tis integal ae Φ, so te total aveage enegy ove any wave sufae wit unit tikness ae equal and independent of. A poton s enegy is estited witin te solid angle Ω subtended at te point soue = despite of ow lage te aea of wave sufaes duing popagation. It means tat no adiation enegy an un out pependiulaly aoss a poton s lateal bounday sufae. On te ote and, outwad tangential adiations fom te egion ( β, β f ) along te iumfeene of O-planes ae always existed. Te outwad Poynting vetos pependiula to te lateal sufae S (, θ, = E (, θ, H (, θ,, ( θ π, p L ) ae geneally diffeent to zeo ove wole bounday. Fo simplify of notation, we use (, θ,...) to epesent
6 614 Cen Sen nian (, θ,...) wee p β fo small enoug β f ee and in te following. Sine eletomagneti adiation an not be efleted fom vauum. Teefoe, we ome to a vey impotant onlusion: Te lateal bounday of a poton wave tain must be oveed by a membane of pefet efletion and zeo est mass. Tis mateial must be dietly tansfeed fom te enegy of soue mateial. By te way if unelated to tis atile, as an impotant oollay, it was pointed out in one of ou last papes (4) tat vaying field is not te suffiient ondition fo te podution of a poton. It is just a neessay ondition. Anote one is tat te soue an povide te enegy to be membane, altoug its enegy is supposed to be so small in ompae wit poton s field enegies. It seems to be te eason of wy te eleton of atom in gound state is stable, sine tee is not any available lowe state pemit im to loate so as no exta enegy of eleton an povide te neessay membane no matte ow small it is. All esultant tansvesal waves on O-planes ae adial, equation (6). Any beam of te tansvesal taveling wave E+ ( V and E ( + V ) is seto-like. Letδθ be te angle of te seto. Ten on te same seto, te enegy flow passes toug te aea i δθ δ equal to te one toug k δθ δ. Tat is S (, θ, δθ δ = S (, θ, δθ δ ( p p p ) (8) i i k A ( ) ε ε Sine lim S = E =, let i =, k and A = A( ), μ μ ten equation (8) gives te elation between magnitudes A of and as follow k i k A ( ) = A ( < < ) Wee A ( ) = ( = ) (9) A is a onstant disegad of. Te late bounday ondition as been disussed at te beginning of tis pape. Equation (9) is te distibution funtion
7 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 615 of A( ) on any wave sufae. To substitute equation (9) into (3), we ave te wave funtion of a poton emmited fom te point soue = A t E(, = osπ ( ) ( p, T L t t t + T, f ) E(,, = (1) Equation (1) efes to tat su a poton s eation pobability wit ote patile at wave s ente is fa geate tan ote pats of it. On te ote and, te time ate of ange of momentum at bounday is S (, θ,. It will ause te existene of entifugal pessue of same amount (, θ, fom all points of te ove membane. Q mem Q mem (, θ, = S (, θ, ( π θ π, + L ) (11) Combining equations (11) wit (8), we ave te equilibium equation between two opposite sufaes Q outwad δθ δ and δθ δ in te same seto spae (, θ, δθ δ = (, θ, δθ δ Q mem ( p p, θ π, L ) (1) III. Fou impotant meanial and eletomagneti popeties of te membane Figue 1 is a sket map of te distibution of E( ) on a wave sufae,. Let θ be te angle of adius fom absissaof. Momentum s ate of ange at te S (, θ ) bounday makes te iula tension pe unit lengt of wave tain T (, θ ) in te membane. Tat is
8 616 Cen Sen nian ε T (, θ ) = S(, θ ) = A os θ (13) μ Te maximum appens at points A and F, Φ ε TF (,,) = TA(, π ) = Tmax = A. Tis elation is valid fo ote A μ and F points of evey wave laye. Conneting all tese points A and F espetively tey fom two paallel spials, A- spial and F- spial (igt-anded o left-anded double tead) on te lateal sufae of te iula polaized wave tain. Figue 1 Te mateial of membane must be vey easy to ange its sape duing popagation, so we suppose it is a liquid-like mateial aving almost onstant volume. Te aea of membane s oss-setion π δ = π Γ is onstant. So te tikness δ = Γ (14) let Let Σ max be te maximum nomal stess on te oss-setion. Sine Tmax = Σ max δ and equation (13), it gives ε Φ Σ max = A = A (15) Γ μ Γ μ ε
9 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 617 Fo a poton of iula polaized wit givenν, tee ae fou impotant popeties of its membane: (i) Te maximum stess Σ max is onstant, eq.(15) tat always appened along A-spial and F-spial on te poton s lateal sufae despite of te magnitude of and. Te eletomagneti wave tain plus ove membane fom an independent stutue. Unde geneal iumstanes, te poton tain will always keep its integity unless tee is a vey stong extenal effet, fo example, ty to stop te tain and geatly inease te density of its E-H field aound A,F and makes Σ max bigge tan ultimate tensile stengt (unknown but must exis and beak te membane. (ii) Sine sufae density of age σ on te inne side of te membane equals to D = ε E ), so, fo te uppe spial-alf. Fig 1, te absolute value of σ θ is n ( n σ θ A = ε sinθ ( θ π ) (16) Te age densityσ θ of any point foms an equal-magnitude spial on te inne side of te membane. Tis is to say tat ages inside distibute wit elial symmety about its longitudinally ental axis. Te total negative age in uppe spial-alf is L π θ = q = d A σθ dθ = ε L = ε ΦA L (17) Te lowe alf as same amount of positive age. Like te Σ max, quantity q in te ±aged spial-alves always exists and keeps unanged despite of te magnitude of and. (iii) Te inease of wave sufaes magnitude as poton moves fowad will ause te iumfeenes of membane beome longe and longe. Witin d θ egion, wen te adius of membane ineases fom to + d, te inement
10 618 Cen Sen nian of iumfeene is d dθ. Te wok down in te δ -laye of te wave tain against tension fom oiginal nuleus dimension to final is δ W π = δ 4 π Φ T (, θ ) d dθ = ε A δ ln μ Fo a poton, te wok an be down against te tension is etainly (18) finite, ln and ten te adius of poton wave sufaes must be uppe bounded if a poton annot self blast. A poton wave tain will at last beomes exatly (not appoximately) ylindial wit adius max. Tis will make te poton tat ame fom te end of ou univese ten billion yeas ago still aving a finite max wave sufae. γ (iv) As well-known te intinsi fequeny ν γ ( = ) of te iula polaized poton is exatly te otation fequeny of E,H on diffeent O-planes wit diffeent initial pases aused by tanslational motion of poton s E,H fields. Su otations on te O-planes make poton s spin and equal to. As pats of a poton, it is evident tatν γ and ae also te fequeny and spin of te pai of ±aged spial-alves. Te pites of te pai and te poton ae equal. Tese popeties ae owing to te tanslational motion of a elial stutue of fields o of enegy densities and ages at speed. Fo simply of illustation in te following we always use otating on O-planes to expess su speial kind of otation. IV Extenal podution and ages distibute inside aged and anti-aged patiles. If te enegy of a poton equal to te double of etain ±aged patile s m p and q in eq.(17) equals to te amount of tis patile s age, su as leptons and adons (wit spin ), ten unde appopiate onditions, tat is te fields E, H of poton ineased stongly and beak te membane, extenal podution of su pai may appen.
11 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 619 As a possible ase, if a poton losely skims ove a eavy nulei and te supeposition of fields make etain pats of membane s neigboood ( max ) E Σ oveload and lage tan its ultimate tensile stengt, it will be possible to ave te membane quikly and ten entiely split along A-spial and F-spial. Te pai of ±aged spial-alves of te poton will beome two independent aged spial-pats (no longe a poton but two un-foming ±patiles) altoug tey ae still supeimposed tempoaily befoe axial depatue ompleted. Te late is beause of opposite magneti fields te otating ±ages podued. In tis poess: (a) Split of membane makes edistibution of its ±ages. Eleti attation will ause two eleti flows along diffeent membane s iumfeenes and at last stop evenly at two ends A and F. Te poton s E, H field (wo podues te ages in membane, not te evese) still exists at all points inside. Te oiginal field dietions ae diffeent on diffeent O-planes, so te distibution of enegy density on any O-planes must ave dietional popety, otewise its spin will vanis and beak te onsevation law of angula momentum. As a matte of fat, two aged points (positive o negative) loated at te ends of te diamete AF (X-axis) will etainly effet te distibution of enegy density and make tem aving simila axial symmety on any O-plane. Te ages distibution on any un-foming ±patile s sufae looks like symmeti double elix. Connetion of te points of equal enegy density among all neigboing O-planes foms equal-magnitude spial in it. Te distibution of ages and mass ae all of elial symmety. (b) Te iumfeene of any laye s membane afte split will ontat and eovey to its oiginal lengt. And in te meantime, attation between ±ages on opposite ±patiles sufaes will geatly soten its diamete. Te esult is tat te lage -adius un-foming ±patile beome te small ones wit oiginal nuleus adius (o even smalle). Sine supeposition of fields and adial ontation of oss-setions do not ange te lengt of its longitudinal pit and tey still move wit speed befoe axial sepaation by magneti epulsion begins, so otating fequeny of te small pais on O-planes still equals toν γ (= /pit. Te spin must be onseved in tis poess. So te moment of inetias (=spin/ πν γ ) of te small pai and of te big pai ae equal, despite of te
12 6 Cen Sen nian magnitude of all laye s adius (even if tey ae not equal). Evey small un-foming ±patile as spin. ( In te poess of axial sepaation of te small un-foming ±patile, tey must still move at speed. epulsion foe along adial dietion between te aged spial itself will step by step expand patile s diamete to inease its moment of inetia and deease te otating fequeny of dq ( d O-planes until tey ae totally sepaated. me also) on te Te pai podution of eleton and positon is a eal example. Let ν eal( expess te final otating fequeny of dq on O-planes wile te small un-foming ±eletons ae totally sepaated but tempoaily still at speed. In tis poess, te spin must be onseved. So ν eal( is te neessay and suffiient fequeny fo te fee un-foming ±eleton to guaantee its spin. Aoding to te onsevation law of enegy, ea un-foming ±eleton podued must ave enegy e 1 e = ν γ let = ν (19) We name ν as intinsi fequeny of te un-foming eleton. Does ν eal( equal to ν? Tee ae just two types of expession to indiate a ting s total enegy tat is Einstein s = ν and = m oespondent to zeo and none zeo est mass espetively. ν eal( as enegy dimension. If ν eal ν e, it means tee must be appened an exta gain o loss of enegy ± δν duing tis miosopi poess. So, if diffeent type of enegy tansfe does not appen in tis poess of pai podution, we will ave ν = () eal( = ν e e Intinsi fequeny ν ( = ) is eally te neessay and suffiient fequeny
13 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 61 fo te un-foming eleton otating on O-planes to guaantee its spin. Tis is te pysial meaning of tis intinsi fequeny. At last, duing eletomagneti enegy tansfes to mateial ( m ), un-foming eleton beomes a fee eleton and speed deeases tov. Sine vaiation of longitudinal veloity fom tov do not affet te adial distibution of mass on oss-setions; do not affet its moment of inetia, if we suppose eleton is made up by isotopi mateial. Ten te atioν ( ) : e will keep unanged. Above assetion will be still available fo ±eleton not only fo un-foming one. O in ote wods, te pysial meaning of eleton s intinsi fequeny e ν ( = ) is tat te intinsi fequeny is eally te neessay and suffiient fequeny otated on O-planes to guaantee its spin. On te ote and, ν eal( also efes to tat te ν eal( time of equals to. = ν (1) Wee is te pit of un-foming eleton just sepaated but still at speed. Fo te un-foming eleton just totally sepaated, sine ν pit is e ( = 1 ν γ, te e γ () ( ) = Tis lengtening effet of un-foming eleton s pit an be explained as self longitudinal epulsion of evey aged spial itself. Besides, onsevation law makes te momentum of ea un-foming eleton to 1 be pγ. O p = () 1 = γ. (3) Wen an un-foming eleton anges to a fee eleton, field enegy beomes mass ( m ) and speed deeases tov. Aoding to speial elativity, te
14 6 Cen Sen nian momentum of eleton is o p ν (1) let V = mev = V = =. (4) p Compaing eq. (5) wit eq. (3), V ) and (1) = ( = = Te ( ) (5) V V ave same dimension and same fom of elation wit momentum p and lim =. We an easonably asset tat V is te pit of eleton duing speedv. It is times of. Wy? V Aoding to onsevation of enegy fom un-foming eleton to eleton m = = p and Einstein s enegy-momentum elation e e p m =, 4 e m ten = m, te appeaane of m ineases its pit fom to. Above esults ae all available at least fo ±aged patiles wit spin and even te neutal patiles if it an be modeled as double ±aged spials of same pit inside. We ave notied tat e = ν ) and p = (In geneal symbol, tat is = ν and p = ) ae just a logial esult ee, not a postulate. Tey eflet te featues of patile s spial stutue. Tey epesent diffeent pysial meaning as tey used to be.
15 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 63 V. Fomation of spin and te equation of motion of aged patile s inne system Let a aged patile moves wit V in dietion of Z-axis and te oodinate of fist dq 1 be x = 1, y =, z = at t =. Let T be te peiod of dq 1 yling on te O-planes duing te ages tanslational motion is of speedv. Ten we ave te elation = VTe (. Te equation of motion of igt-anded spial age dq1 is z t x = q os π ( ) (6) T z t y = q sin π ( ) ( = V Te ( ) (7) T ( J V z ). Wee J is te total numbe of pites in te eleton, q - te adius of aged spial-alves. Teat X-, Y- as omplex plane pependiula to te dietion of motion and ewite (6),(7) in omplex fom t z i π ( ) Te ( = q e (8) On te ote and, te pysial meaning of eleton s intinsi fequeny sows tat spin of magnitude always demands eleton s otating fequeny on O-planes equals to ν (o yling peiod equals to te intinsi peiod Te ( ( = 1/ ν ) disegad te tanslational veloity is ov. So te yling peiod of dq, dm on O-planes must be T ) not T. Te eleton must posses an exta self-otation about Z-axis to meet te demand ifv <. Tat is t z must t z π ( ν extat + ) = π ( ) ( = VTe ( ) (9) T T Sine = Te (, eq. (5), te exta self-otation fequeny ν exta sould be V
16 64 Cen Sen nian V V ν exta = ( 1 ) ν ( ν = ν ) (3) If V, ν, eleton just moves tanslational fo keeping spin. On exta te ontay, if V, aged patiles spin totally depend on aged patile s self-otation wit fequeny ν about Z-axis. Geneally speaking, te eleton s spin onsists of two pats: iula motion of all dq on O-planes aused by its tanslational motion of speed V and V te exta self-otation ν exta = ( 1 ) ν about symmeti axis. Te otation estits te adius of eleton. Linea speed at its sufae must be small ten ligt. Combine te spial stutue of ages inside wit te exta self-otation unde te demand of spin, age dq s equation of motion must be t z i π ( ) Te ( ) = q e ( = Te ( ) (31) V Matematially speaking, te spin ould be ealized if te patile (witout exta self-otation) simply moves tanslational wit pase veloity V. Tis is te pysial meaning of pase veloity. It is te exta self-otation tat made te appaently supeluminal effet of tis veloity. Sine age inside te patile distibutes wit elial symmety about its longitudinally ental axis, te distibution of mass density also ave same symmety as we mentioned above. So, veto ( = q = x + y ) in equations (31) an be also used to expess te motion of any mass density s spial ( ). Let Ψ ( x, y, z, be te equation of motion of eleton s mass density, te following elation olds
17 Diffeential equation of motion of patile 65 t z i π ( ) Te ( ) e ( Ψ ( x, y, z, = Ae ( A = x + y ) (3) Aoding to equation () and (5), we an ewite equation (3) into genealized omplex fom and neglet te subsipt of and p : i ( t xp yp zp ) x y z Ψ( x, y, z, = A e (33) Te diffeential fom of tis wave funtion is of te fom like Sodinge equation. Hee we aive at su a onlusion tat te spial distibution inside plus te demand of spin makes tis kind of aged patiles aving eq. (33) as tei equations of motion and satisfy te diffeential equations of te fom like Sodinge s (and Dia s also). Teefoe at least fo tis lass of ±aged patiles of spin, it seems we may simultaneously intepet te solutions of Sodinge equation as te equation of motion of su patile s inne system. Fo example, it seems we may teat te eleton loud as te moving figue of eleton s mass density distibution aound te nuleus et. VI. Conlusion Base on Maxwell teoy and Einstein quanta postulate, we ave deived te diffeential equation of motion of te patile tat possesses elial stutue and spin /. It as te fom like Sodinge s, altoug te intepetation of wave funtion is somewat diffeent. It gives us anote way to undestand geat Sodinge equation if we do not ejet te idea tat patile as its dimension and inne system. Unde tis pemise, te wave funtion may use to indiate te spae-time distibution of te patile s mass and ages. To aept te idea tat patile as its inne system not just point will elp us to undestand wee and ow does mass and ±ages ome fom in te pai podution. And also elp us to undestand te meanism of te fomation of spin / in su patiles. Te poton and te ±aged patiles poton podued obey simila fom of equations γ = ν γ, p γ = and e = ν ), p γ = espetively just beause tey ave simila stutue of elial symmety about te longitudinally ental
18 66 Cen Sen nian axis. A poton wave tain as elial symmety of field E, H and te patiles ave same symmety of ages and mass distibution. Intinsi fequenies ν γ and ν of tem epesent te neessay and suffiient fequenies of fields o of mass (inlude dq ) on te O-planes to guaantee tei spin and / espetively. and V ) epesent te pit of te poton s and aged patile s stutues. γ Tey ae also te wave lengts of tanslational motion. An impotant diffeene between tem is tat tose patiles wit non-zeo est mass ave self-otation in geneal in ompensating itself to guaantee te spin. As to te explanation of absoption by atom and Compton s effet and te diffation beavio, inlude ow a poton tain an pass toug a pinole o slit wit smalle aea ave been disussed in te fome pape (4). By te way, if tee ae somewat diffeent statements in ou diffeent papes about same ting, please take tis pape s. Aknowledgement: Speial tanks to my wife, Pei Min. He saifie as given me mu time to omplete my favoite jobs. efeenes (1) Enio Femi, Quantum Teoy of adiation, evs. Moden Pys., 4, 87 (193). ().P.Feynman, Quantum Eletodynamis, W.A.Benjamin,In. (1961) (3) iad Fitzpatik, Maxwell s Equations and te Piniples of Eletomagnetism, Infinity Siene Pess (7). (4) Cen Sen Nian, Poton, aged patile and anti-aged patile, Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 3, 9, no. 9-1, (5) Cen Sen Nian, Te fomation of spin in ±aged patiles and diffeent intepetation fo te wave funtion, Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 4, 1, no. 9-1, eeived: Apil, 11
Photon, Charged Particle and Anti-charged Particle
 Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 3, 9, no. 11, 41-419 Poton, Caged Patile and Anti-aged Patile Cen Sen nian Dept. of Pys., (National) Hua Qiao Univ. Quanzou, Fujian, P.. Cina ensennian@yaoo.om.n Abstat: Based
Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 3, 9, no. 11, 41-419 Poton, Caged Patile and Anti-aged Patile Cen Sen nian Dept. of Pys., (National) Hua Qiao Univ. Quanzou, Fujian, P.. Cina ensennian@yaoo.om.n Abstat: Based
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Physics Courseware Electromagnetism
 Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
Gravitational Equivalent Frequency, the Planck Length and Matter Waves
 Gaitational Equialent Fequeny, te Plank Lengt and Matte Waes by Roge Ellman Abstat Analysis of gaitation and of matte waes disloses a geate signifiane tan eetofoe eognized fo te fequeny, wae, osillation
Gaitational Equialent Fequeny, te Plank Lengt and Matte Waes by Roge Ellman Abstat Analysis of gaitation and of matte waes disloses a geate signifiane tan eetofoe eognized fo te fequeny, wae, osillation
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Tutorial on Strehl ratio, wavefront power series expansion, Zernike polynomials expansion in small aberrated optical systems By Sheng Yuan
 Tutoial on Stel atio, wavefont powe seies expansion, Zenike polynomials expansion in small abeated optical systems By Seng Yuan. Stel Ratio Te wave abeation function, (x,y, is defined as te distance, in
Tutoial on Stel atio, wavefont powe seies expansion, Zenike polynomials expansion in small abeated optical systems By Seng Yuan. Stel Ratio Te wave abeation function, (x,y, is defined as te distance, in
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
Classical Approach to the Theory of Elementary Particles
 Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Ion-sound waves (electrostatic low frequency waves)
 OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
Mass Transfer. Dispersion. Lecture 13, , Dr. K. Wegner
 Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Determine the Stress Calculating Mode of Sliding Failure of Soil Mass under the Push-Extend Multi-under-Reamed Pile
 Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Thermal-Fluids I. Chapter 17 Steady heat conduction. Dr. Primal Fernando Ph: (850)
 emal-fluids I Capte 7 Steady eat conduction D. Pimal Fenando pimal@eng.fsu.edu P: (850 40-633 Steady eat conduction Hee we conside one dimensional steady eat conduction. We conside eat tansfe in a plane
emal-fluids I Capte 7 Steady eat conduction D. Pimal Fenando pimal@eng.fsu.edu P: (850 40-633 Steady eat conduction Hee we conside one dimensional steady eat conduction. We conside eat tansfe in a plane
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
CHAPTER 25 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
 CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Reflectance spectra for Si
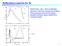 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
2. Equation of generalized Dynamics. Let rectangular right hand coordinate triple is fixed in three-dimensional Euclidian space.
 Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD
 Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustausch)
 Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
An analytic calculation method on air gap flux in permanent magnet. brushless DC motor with ironless rotor
 Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Improved Preisach -DOK Modeling on the Henkel Plot of A Longitudinal Barium Ferrite
 Poeedings of te 01 nd Intenational Confeene on Compute and Infomation Appliation (ICCIA 01) Impoved Peisa -DOK odeling on te Henkel Plot of A Longitudinal Baium Feite Zao Jing, Xue Fang, Han Ning Depatment
Poeedings of te 01 nd Intenational Confeene on Compute and Infomation Appliation (ICCIA 01) Impoved Peisa -DOK odeling on te Henkel Plot of A Longitudinal Baium Feite Zao Jing, Xue Fang, Han Ning Depatment
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
8 Separation of Variables in Other Coordinate Systems
 8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
Simulation thus allows us to check the efficacy of our screening tools.
 all 2004 ICE opis: Poess Contol by esign 0.492 Letue Notes 2: Simulating te Sowe Poess te sowe poess is simple enoug tat we an simulate its opeation Ove te past deade ou tools fo simulating poesses ave
all 2004 ICE opis: Poess Contol by esign 0.492 Letue Notes 2: Simulating te Sowe Poess te sowe poess is simple enoug tat we an simulate its opeation Ove te past deade ou tools fo simulating poesses ave
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Electric Potential and Energy
 Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 lectomagnetism Physics 15b Lectue #20 Dielectics lectic Dipoles Pucell 10.1 10.6 What We Did Last Time Plane wave solutions of Maxwell s equations = 0 sin(k ωt) B = B 0 sin(k ωt) ω = kc, 0 = B, 0 ˆk =
lectomagnetism Physics 15b Lectue #20 Dielectics lectic Dipoles Pucell 10.1 10.6 What We Did Last Time Plane wave solutions of Maxwell s equations = 0 sin(k ωt) B = B 0 sin(k ωt) ω = kc, 0 = B, 0 ˆk =
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B. Calculations for Sample Cross-Section 2
 SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
Mass- and light-horizons, black holes' radii, the Schwartzschild metric and the Kerr metric
 006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
Recitation PHYS 131. must be one-half of T 2
 Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
Reitation PHYS 131 Ch. 5: FOC 1, 3, 7, 10, 15. Pobles 4, 17, 3, 5, 36, 47 & 59. Ch 5: FOC Questions 1, 3, 7, 10 & 15. 1. () The eloity of a has a onstant agnitude (speed) and dietion. Sine its eloity is
Black Body Radiation and Radiometric Parameters:
 Black Body Radiation and Radiometic Paametes: All mateials absob and emit adiation to some extent. A blackbody is an idealization of how mateials emit and absob adiation. It can be used as a efeence fo
Black Body Radiation and Radiometic Paametes: All mateials absob and emit adiation to some extent. A blackbody is an idealization of how mateials emit and absob adiation. It can be used as a efeence fo
Chapter 7-8 Rotational Motion
 Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Three dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compressors
 1 Thee dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compessos 2 The ealie assumption on blade flow theoies that the flow inside the axial flow compesso annulus is two dimensional means that adial movement of
1 Thee dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compessos 2 The ealie assumption on blade flow theoies that the flow inside the axial flow compesso annulus is two dimensional means that adial movement of
Transmission Line Analysis of Beam Deflection in a BPM Stripline Kicker
 UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
Chapter 22 The Electric Field II: Continuous Charge Distributions
 Chapte The lectic Field II: Continuous Chage Distibutions A ing of adius a has a chage distibution on it that vaies as l(q) l sin q, as shown in Figue -9. (a) What is the diection of the electic field
Chapte The lectic Field II: Continuous Chage Distibutions A ing of adius a has a chage distibution on it that vaies as l(q) l sin q, as shown in Figue -9. (a) What is the diection of the electic field
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Problem Set 5: Universal Law of Gravitation; Circular Planetary Orbits
 Poblem Set 5: Univesal Law of Gavitation; Cicula Planetay Obits Design Engineeing Callenge: Te Big Dig.007 Contest Evaluation of Scoing Concepts: Spinne vs. Plowe PROMBLEM 1: Daw a fee-body-diagam of a
Poblem Set 5: Univesal Law of Gavitation; Cicula Planetay Obits Design Engineeing Callenge: Te Big Dig.007 Contest Evaluation of Scoing Concepts: Spinne vs. Plowe PROMBLEM 1: Daw a fee-body-diagam of a
A Constructive Model of Gravitation
 A Constuctive Model of Gavitation agubans P. Sing agu.sing@veizon.net Abstact Tis pape poposes a pysical model in wic gavitational inteaction between masses is mediated by tei mass-momentum fields. A mass
A Constuctive Model of Gavitation agubans P. Sing agu.sing@veizon.net Abstact Tis pape poposes a pysical model in wic gavitational inteaction between masses is mediated by tei mass-momentum fields. A mass
Section 26 The Laws of Rotational Motion
 Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Today in Astronomy 142: the Milky Way s disk
 Today in Astonomy 14: the Milky Way s disk Moe on stas as a gas: stella elaxation time, equilibium Diffeential otation of the stas in the disk The local standad of est Rotation cuves and the distibution
Today in Astonomy 14: the Milky Way s disk Moe on stas as a gas: stella elaxation time, equilibium Diffeential otation of the stas in the disk The local standad of est Rotation cuves and the distibution
The electrified interface.
 Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Chapter 22: Electric Fields. 22-1: What is physics? General physics II (22102) Dr. Iyad SAADEDDIN. 22-2: The Electric Field (E)
 Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
( ) Make-up Tests. From Last Time. Electric Field Flux. o The Electric Field Flux through a bit of area is
 Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
The Kerr-metric, mass- and light-horizons, and black holes' radii.
 006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Physics 121 Hour Exam #5 Solution
 Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
Chem 453/544 Fall /08/03. Exam #1 Solutions
 Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Study of the Endface Friction of the Revolving Vane Mechanism
 Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Welcome to Physics 272
 Welcome to Physics 7 Bob Mose mose@phys.hawaii.edu http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~mose/physics7.html To do: Sign into Masteing Physics phys-7 webpage Registe i-clickes (you i-clicke ID to you name on class-list)
Welcome to Physics 7 Bob Mose mose@phys.hawaii.edu http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~mose/physics7.html To do: Sign into Masteing Physics phys-7 webpage Registe i-clickes (you i-clicke ID to you name on class-list)
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
c n ψ n (r)e ient/ h (2) where E n = 1 mc 2 α 2 Z 2 ψ(r) = c n ψ n (r) = c n = ψn(r)ψ(r)d 3 x e 2r/a0 1 πa e 3r/a0 r 2 dr c 1 2 = 2 9 /3 6 = 0.
 Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Problem Solutions
 Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Lecture 2 - Thermodynamics Overview
 2.625 - Electochemical Systems Fall 2013 Lectue 2 - Themodynamics Oveview D.Yang Shao-Hon Reading: Chapte 1 & 2 of Newman, Chapte 1 & 2 of Bad & Faulkne, Chaptes 9 & 10 of Physical Chemisty I. Lectue Topics:
2.625 - Electochemical Systems Fall 2013 Lectue 2 - Themodynamics Oveview D.Yang Shao-Hon Reading: Chapte 1 & 2 of Newman, Chapte 1 & 2 of Bad & Faulkne, Chaptes 9 & 10 of Physical Chemisty I. Lectue Topics:
E(r,t) = e 3. r 3. (b) Show that the transverse current, J t,is 3n(n e 3 ) e 3
 Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
Introduction to Nuclear Forces
 Intoduction to Nuclea Foces One of the main poblems of nuclea physics is to find out the natue of nuclea foces. Nuclea foces diffe fom all othe known types of foces. They cannot be of electical oigin since
Intoduction to Nuclea Foces One of the main poblems of nuclea physics is to find out the natue of nuclea foces. Nuclea foces diffe fom all othe known types of foces. They cannot be of electical oigin since
$ i. !((( dv vol. Physics 8.02 Quiz One Equations Fall q 1 q 2 r 2 C = 2 C! V 2 = Q 2 2C F = 4!" or. r ˆ = points from source q to observer
 Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
But for simplicity, we ll define significant as the time it takes a star to lose all memory of its original trajectory, i.e.,
 Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
A Relativistic BCS Theory of S-Wave Superconductivity
 A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam)
 (Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
Nuclear models: Shell model
 Lectue 3 Nuclea models: Shell model WS0/3: Intoduction to Nuclea and Paticle Physics,, Pat I Nuclea models Nuclea models Models with stong inteaction between the nucleons Liquid dop model α-paticle model
Lectue 3 Nuclea models: Shell model WS0/3: Intoduction to Nuclea and Paticle Physics,, Pat I Nuclea models Nuclea models Models with stong inteaction between the nucleons Liquid dop model α-paticle model
A near-perfect invisibility cloak constructed with homogeneous materials
 A nea-pefet invisibility loak onstuted with homogeneous mateials Wei Li, Jianguo Guan, * Zhigang Sun, Wei Wang, and Qingjie Zhang 1 State Key Lab of Advaned Tehnology fo Mateials Synthesis and Poessing,
A nea-pefet invisibility loak onstuted with homogeneous mateials Wei Li, Jianguo Guan, * Zhigang Sun, Wei Wang, and Qingjie Zhang 1 State Key Lab of Advaned Tehnology fo Mateials Synthesis and Poessing,
Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Errors in Waveguide Samples for the Nicolson-Ross-Weir Permittivity Technique
 Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Algebra-based Physics II
 lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
The second law of thermodynamics - II.
 Januay 21, 2013 The second law of themodynamics - II. Asaf Pe e 1 1. The Schottky defect At absolute zeo tempeatue, the atoms of a solid ae odeed completely egulaly on a cystal lattice. As the tempeatue
Januay 21, 2013 The second law of themodynamics - II. Asaf Pe e 1 1. The Schottky defect At absolute zeo tempeatue, the atoms of a solid ae odeed completely egulaly on a cystal lattice. As the tempeatue
