IMPROVING CENTRIFUGAL PUMP BY ADDING VORTEX ROTOR
|
|
|
- Rosemary Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
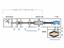
1 Poboljšanje centrifugalne pumpe dodavanjem vrtložnog rotora IMPROVING CENTRIFUGAL PUMP BY ADDING VORTEX ROTOR Tihomir Mihalić, Srđan Medić, Živko Kondić ISSN (Print), ISSN (Online) UDC/UDK : ]: Original scientific paper The improvements of the characteristics of centrifugal pump were investigated in this work experimentally and with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis of the influence of adding vortex rotor to centrifugal one. The idea behind that improvement is in creating the so-called coherent structures of eddies and turbulence in the peripheral area of the vortex rotor mounted at the back side of centrifugal rotor. Research on the energy transformations in the centrifugal vortex pump in this work was carried out using control volume method for simulations of the flow in the centrifugal and the centrifugal vortex pump, and also by taking measurements of relevant parameters that describe the performance of pumps at their physical models. The measurement results were used as experimental validation and verification of numerical simulations; in contrast, flow visualization derived from the numerical simulation was used to interpret measurements. In deriving that experimental procedure, special care was taken with the flow measurements. The reason for this is in the fact that the flow measurements had the biggest influence on the overall measurement uncertainty. However, flow measurements were the most demanding with regard to experiment design and in taking the measurement readings. This experimental - CFD research made it possible to undertake an assessment of vortex rotor contribution on the head of centrifugal vortex pump. The influence of the vortex rotor on the efficiency of the centrifugal vortex pump was studied in contrast to the efficiency of a centrifugal pump with the same geometry. An analysis of the structure of flow was conducted in order to better understand the energy transformations that are the result of interaction between vortex rotor and the flow from the channels of centrifugal part of centrifugal vortex rotor. Keywords: centrifugal vortex pump, computational fluid dynamics, energy transformation, flow measurement, pump performances, unsteady flow Poboljšanje centrifugalne pumpe dodavanjem vrtložnog rotora Izvorni znanstveni članak Poboljšanja karakteristika centrifugalne pumpe istraživana su u ovom radu primjenom eksperimenta i računalne dinamike fluida (CFD). Istraživan je utjecaj dodavanja vrtložnog na centrifugalni rotor. Pokretačka zamisao ovog načina poboljšanja je u stvaranju tzv. tokova koherentnih struktura i turbulencije na vanjskom promjeru vrtložnog rotora koji je pričvršćen na stražnjoj strani centrifugalnog rotora. Proučavanje energetskih transformacija u ovom radu provedeno je primjenom numeričke metode kontrolnih volumena za simuliranje strujanja u centrifugalnom i centrifugalno vrtložnom stupnju te mjerenjem relevantnih parametara na njihovim fizikalnim modelima. Rezultati mjerenja korišteni su za validaciju i verifikaciju numeričkih simulacija dok su vizualizacije strujanja proizišle iz računalne dinamike fluida poslužile za interpretaciju eksperimentalnih rezultata. Pri dizajniranju eksperimenta posebna pažnja pridala se mjerenju protoka, zato što je mjerenje protoka imalo najveći utjecajni faktor na ukupnu nesigurnost provedenih eksperimenata. Pri tome je organiziranje mjerenja protoka bilo najzahtjevnije. Ovo eksperimentalno-numeričko istraživanje omogućilo je procjenjivanje utjecaja vrtložnog rotora na visinu dobave centrifugalno vrtložne pumpe te na njenu iskoristivost u usporedbi sa sličnom centrifugalnom pumpom. Analiza struktura strujanja dala je bolje razumijevanje mehanizama energetskih pretvorbi koje su rezultat interakcija vrtložnog rotora i strujanja fluida koje dolazi s centrifugalnih lopatica. Ključne riječi: centrifugalno vrtložna pumpa, energetska pretvorba, karakteristike pumpe, mjerenje protoka, nestacionarno strujanje, računalna dinamika fluida 1 Introduction Any improvements of the pump performances can provide financial and energy savings and by that have a positive impact on the environment. One way of improving the characteristics of centrifugal pumps is by adding a vortex rotor to the centrifugal rotor by which energy of induced vortices at the vortex rim is added to the fluid energy gained in centrifugal rotor Fig. 1, as demonstrated in [1, 2, 3] and [4]. Fig. 1 shows one stage of the centrifugal vortex pump with major components. On the periphery of the disc of the centrifugal rotor on the stator side, the vortex rim (rotor) is installed. There is a gap between the stator cover and vortex radial vanes that, together with the gap between centrifugal vanes and the stator, entrance forms a peripheral-lateral annular vortex chamber. The resulting additional kinetic energy of coherent structures induced at the vortex rim transforms to the head H 4, which is added to the bulk head (pressure) obtained in the centrifugal rotor of the centrifugal vortex pump H cen as shown in Eq. (1): H = Hcen + H4. (1) Mere physical simulations (experiments) do not provide all the necessary information about the structure of the energy conversions. Therefore, the use of the joined method, computer simulations (CFD) together with experiment, can provide insight into the structure of flows and the quantification of parameters, which helps in understanding the processes of energy conversions [5, 6, 7]. Figure 1 Centrifugal vortex pump stage Tehnički vjesnik 20, 2(2013),
2 Improving centrifugal pump by adding vortex rotor The numerical simulations of unsteady flow in centrifugal pumps and centrifugal vortex pumps were conducted using the control volume method. The objectives of this research were to clarify the mechanisms of energy conversion in a centrifugal vortex pump and to confirm the positive impact of a vortex rim on the pump characteristics. To do that it was necessary to research the flow structures occurring in the vortex chamber and the interaction of this flow with vortex rotor. 2 Experimental models The rotor and stator, formed from transparent plexiglass, are also embedded in a transparent casing of plexiglass to enable flow visualization, both in the passages of the rotor and the stator and in the zone of special interest for research, i.e. the chamber between the rotor and the stator, where the vortex rim is located (Fig. 2). 2.1 Preparing the flow for taking measurements Fig. 4, shows the measurement section of the centrifugal vortex and centrifugal test pump stages, [9]. Fluid from the pump stage is conducted by front collector through 14 connectors, and evenly distributed on the outer diameter of the front collector. The collector is designed in such a manner as to introduce as few instabilities to the flow as possible in order to not affect the measurement results. The fluid is conducted from the front collector with 14 tubes that allowed fluid to go around the electric motor without changing its hydrostatic energy and to simultaneously smooth the flow. These 14 tubes then merge at the back collector. 3 Numerical models Between physical and numerical models, geometric, kinematic and dynamic conditions for similar work were satisfied. A simplification of geometries was conducted only in areas that do not affect the flow in the stator and rotor. Figure 2 Centrifugal and centrifugal vortex pump stage made of Plexiglas for experimental research The experimental assembly [8] was made in accordance with the following standards: ISO , 4:2003 and ISO / TR 15377:2007. Figure 3 Pump stage housing The housing of the researched pump stages (centrifugal or centrifugal vortex) is designed to allow very fast exchange between pump stages (Fig. 3). Furthermore, the housing provides all the necessary seal between the rotor zone and the suction zone, between the front plate of the rotor and the housing, between the stator and the housing. Figure 5 Structured mesh of the stator (left) and the rotor (right) In the used CFD model, the rotor rotates unrestrained, and is connected to the rest of the domain with a sliding mesh boundary condition. The output tube is connected with the output from the stator with the interface boundary condition because there the flow is less demanding for mesh quality. The entire continuum is meshed with control volumes with the largest volume edge of 0,3 mm. Of the total number of control volumes, 85 % of them were hexahedral control volumes, Fig. 5. The research was conducted at the rotor angular speed n = /min, time step was s. The selected time step showed rapid convergence solutions. For the working fluid, water of standard properties at 25 C was used. Turbulence was modelled using a hybrid detached eddy simulations (DES SST) model, [10] and [11]. At the entrance to the domain, a pressure-inlet boundary condition was used, while at the exit from the domain, an outlet-vent boundary condition was used, because it allows adjustment of the loss coefficient at the exit, [12]. The boundary condition outlet vent is defined by pressure loss (attenuation) that is proportional to dynamic pressure: 1 p = kl ρ v 2. 2 Figure 4 Measurement section 306 (2) Loss coefficient kl in the boundary condition outlet vent (2) is a number, and the whole simulation was Technical Gazette 20, 2(2013),
3 conducted varying it; kl = 0 (fully open valve), 2, 5, 10, 20, 60, 300 (fully closed valve), [13]. 4 Research results Fig. 6 shows the Q-H characteristics of a centrifugal and a hybrid centrifugal vortex pump stage. It is evident that the characteristics of the centrifugal vortex pump smoothly follow the characteristics of centrifugal pump from the maximum flow to the flow 105 m3/day (1,22 l/s). After the flow 105 m3/day (1,22 l/s), the characteristics of the centrifugal vortex pump continue to rise steeply as a characteristic of vortex pumps in [14], in contrast to the characteristics of centrifugal pump, which grows slower than the characteristics of the centrifugal vortex pump to its maximum at flow rate of 65 m³/day (0,75 l/s), and then begins to decline steeply. This form of performance curve (falling steeply after its maximum) represents the instability of the pump, because the pump can generate two different flow rates at a given head, left and right from the maximum Q-H characteristic curve, [15]. Figure 6 Q-H characteristics of centrifugal vortex and centrifugal pump stage Adding a vortex rotor to the centrifugal pump stage provided a rising pump Q-H characteristic, which ensures the stability of its operation. This confirmed one of the positive roles of the vortex rim in the centrifugal vortex pump stage. Poboljšanje centrifugalne pumpe dodavanjem vrtložnog rotora The swirl effect achieved by vortex rim increased the magnitude of the head of the plain centrifugal pump stage for a maximum of 23,13 % (average increase of 11,64 %). Figure 7 Contribution of the energy fluxes from the vortex rim to the increase of head H 4.2 Characteristic of vortex part of the centrifugal vortex pump Fig. 8 shows the head of vortex part of centrifugal vortex pump calculated with CFD simulation of the researched centrifugal vortex pump by taking out centrifugal rotor. As evident from the figure, the vortex rotor produced a maximum of 0,63 m of head working alone, while operating in synergy with the centrifugal rotor; it generated a maximum of 1,306 m of head as can be seen from Fig. 9. Therefore, the vortex rotor in synergy with the centrifugal rotor generates a double head, as opposed to working alone. The reason for this is in the fact that when it works in synergy with the centrifugal rotor, it affects the secondary stream which already gained a certain amount of energy in the centrifugal rotor (Fig. 9). 4.1 Quantification of the amount of the head generated by vortex rotor The contribution of eddy processes on the amount of the head and the corresponding increase in pressure depends on the flow rate, and the given flow rate depends on the magnitude of the axial component of absolute velocity of the fluid from the discharge of centrifugal rotor to the entrance in the diffuser channels. The lower the flow rate and the smaller the axial velocity component are, the greater the number of the vortex rim passages participating in the momentum change between the fluid contained in these passages, at that instant of time, and the main stream of the fluid from the centrifugal rotor to the diffuser, [16]. Fig. 7 clearly shows that the vortex rim in the centrifugal vortex pump stage begins to increase the amount of the head from the flow rate 105 m³/day (1,22 l/s) to the zero flow. This property is very convenient, because if there is a higher demand on the pump, so as to overcome the greater resistance, the vortex rim is increasingly helping the pump. Figure 8 Head of vortex part of the centrifugal vortex pump Figure 9 Main and secondary fluid flow Tehnički vjesnik 20, 2(2013),
4 Improving centrifugal pump by adding vortex rotor From Fig. 8 it can be seen that when a vortex rotor is working alone, it creates a steep drop-down characteristic with a small flow. When working alone vortex rotor consumes 33,66 W of power, while the maximum power brought to centrifugal vortex pump stage is 108,25 W. 4.3 Comparison of the centrifugal vortex and centrifugal pump efficiency Fig. 10 shows a comparison of efficiency curves of the centrifugal vortex and centrifugal pump stage researched in this work. It can be assumed that both curves show a greater efficiency than would be present with the utilization of actual pumps. The reason for this is that the numerical models do not take into account friction losses due to wall roughness, and losses due to fluid flow through clearances [17]. However we assumed that the numerical models of real pump geometry will calculate efficiency curves with the realistic trends and mutual correlations. Figure 10 Efficiency curves of centrifugal vortex and centrifugal pump A comparison of the efficiency curves (Fig. 10) shows that at high flow rates (low loss coefficient k L = 0 to 10) centrifugal pump obtained greater efficiency than centrifugal vortex pump. That was expected as we conducted flow analysis. The vortex rotor at high flow rates does not get enough fluid from the main flow (coming from the centrifugal rotor, Fig. 9) so it does not increase the head (Fig. 6), while at the same time it contributes significantly to the increase of entropy. In that working range, the vortex rotor only creates turbulence, and its kinetic energy is converted into losses. Thus, in this working range the vortex rotor is "parasitic part" in the centrifugal vortex pump, [14]. In contrast, at low flow rates (high loss coefficient k L = 10 to 300) the efficiency of the centrifugal vortex pump is greater than that of the centrifugal pump. In this working range, the vortex rotor grips sufficient amount of fluid from the main stream and contributes to increasing the level of head (Fig. 6). Its kinetic energy is not transferred entirely to the creation of fluid turbulence, but a part of its kinetic energy is used to create a coherent flow structure and to accelerate the flow of secondary stream, [18]. It is also evident from Figure 10 that the best efficiency point of the centrifugal vortex pump is shifted to the left (to the smaller flow rates, and higher head) in comparison to the centrifugal pump. 5 Conclusion This work has proven and quantified the benefits of the centrifugal vortex pump stage in relation to the centrifugal one. The method used was based on the unsteady CFD experiments and experiments on physical models. This method has been validated and verified and thus is a valuable tool for flow simulation and performance determination in various turbo machines. Detailed measurements on the physical models of the power consumed to drive the centrifugal and the centrifugal vortex pump stage resulted in a more accurate quantification of energy balance. This led to prove that the kinetic energy of coherent vortex structures created by the vortex rim is added to the fluid flowing from the passages of the centrifugal rotor and thus increases the total energy of the fluid before entering the stator. Furthermore, this extra energy is added to the main fluid stream by the longitudinal vortices generated by the edges of the vortex rim due to a change of kinetic energy of eddies and by the radial vortices detached from vortex rim vanes. Centrifugal vortex pumps generate an increased head for a maximum of 23,13 % (average increase of 11,64 %) compared to the centrifugal pumps with the same geometry operating at the same angular velocity. Furthermore, the vortex rim of the centrifugal vortex pump increases the amount of the head for working range from 0 to 57 % of maximum flow. At higher flow rates, it does not affect the level of head. Also this research has shown that adding vortex rotor to the centrifugal one improves the character of Q-H characteristics which become steeply sloping as opposed to the characteristics of centrifugal pump. That increases pump stability disabling it of running in "pumping" mode. It has been found that vortex rotor head is 210 % higher when operating in synergy with centrifugal impeller than when acting alone. The efficiency of the centrifugal vortex pump is increased for the working regime 0 to 0,57 Q max, while at the higher flow rates, efficiency is actually lower than that of the centrifugal pump. It can be concluded that at higher flow rates centrifugal vortex pump wastes driving energy on spinning vortex rim. At lower flow rates the contribution of vortex rotor to the head is significant while it does not consume additional driving energy. This suggested that there must be some mechanism that recovers a part of the energy that otherwise is lost in centrifugal pumps. This mechanism is explained by the coherent structures which act as an energy bridge between the main fluid flow and the kinetic energy of the vortex rotor. Preliminary research also demonstrated a great superiority of the centrifugal vortex pump for cavitation resistance. However this must be a topic of another detail study. 6 References [1] Mihajlovič, P. O.; Jurevič, M. I.; Borisovič, K. P.; Isaakovič, R. A.; Pavlovič, T. I. New rotary-vortex pumps for crude oil production in the complicated conditions, 1 th 308 Technical Gazette 20, 2(2013),
5 Poboljšanje centrifugalne pumpe dodavanjem vrtložnog rotora International conference of technical sciences, Russia, Voronež, [2] Isaakovič, R. A.; Vasiljevič, G. N. High-head, economical modification of multistage centrifugal pump for oil production, 2 nd International conference of technical sciences, Russia, Voronež, [3] Karakulov, S. T.; Meljnikov, D. J.; Pereljmman, M. O.; Dengaev, A. V. Ways of increasing efficiency of oil exploitation from oil wells, 3 rd International conference of technical sciences, Russia, Voronež, [4] Melzi, E. Vortex impeller for centrifugal fluid-dynamic pumps, European Patent Application EP A2, Italy, [5] Navratil, P.; Balate, J. Simulation of Control of Multi- Variable Control Loop: Steam Turbine. // International Journal of Simulation Modelling, 10, 2(2011) pp [6] Tic, V.; Lovrec, D. Design of Modern Hydraulic Tank Using Fluid Flow Simulation. // International Journal of Simulation Modelling, 11, 2(2012), pp [7] Santhakumar, M.; Asokan, T. Investigations on the Dynamic Station Keeping of an Underactuated Autonomous Underwater Robot. // International Journal of Simulation Modelling, 10, 3(2011), pp [8] Franjić, K. Measurements in mechanics of fluid. Engineering handbook IP1, Školska knjiga, Zagreb, 1996, pp [9] Goldstein, R. J. Fluid mechanics measurements, 2 nd edition, Taylor & Francis, USA, [10] Spalart, P. R. Detached-eddy simulation. // Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 41, 1(2009), pp [11] Travin, A.; Shur, M.; Strelets, M.; Spalart P. R. Physical and Numerical Upgrades in the Detached-Eddy Simulation of Complex Turbulent Flows, Advances in LES of Complex Flows, Kluwer Academic Publishers, (2002), pp [12] Launder, B. E.; Spalding, D. B. Lectures in Mathematical Models of Turbulence, Academic Press, London, [13] Fluent Inc: Fluent 12 user guide, Fluent Inc. [14] Mihalić, T.; Guzović, Z.; Sviderek, S. Improving centrifugal pump by adding vortex rotor. // Journal of Energy Technology - JET, 4, 2(2011), pp [15] Feng, J.; Benra, F. K.; Dohmen, H. J. Comparison of Periodic Flow Fields in a Radial Pump among CFD, PIV and LDV Results. // International Journal of Rotating Machinery, 2009, Article ID , 10 pages, ISBN X. [16] Dochterman, R. W. Centrifugal-vortex pump, General Electric Company, United States Patent 3,936,240, USA, [17] Lobanoff, V. S.; Ross, R. R. Centrifugal pumps Design & Application, 2nd edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, USA, [18] Matijašević, B.; Sviderek, S.; Mihalić, T. Numerical Investigation of the Flow instabilities in Centrifugal Fan. // WSEAS Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Agios Nicolaos, Greece, Doc. dr.sc. Živko Kondić, dipl. ing. Varaždin University of Applied Sciences J. Križanića 33/6, Varaždin, Croatia zkondic@velv.hr Authors addresses Dr. sc. Tihomir Mihalić, dipl. ing. University of Zagreb Faculty of Mechanical engineering and Naval Architecture Ivana Lučića 5, Zagreb, Croatia tihomir.mihalic1@zg.htnet.hr Dr. sc. Srđan Medić, dipl. ing. Karlovac University of Applied Sciences Trg J. J. Strossmayera 9, Karlovac, Croatia smedic@vuka.hr Tehnički vjesnik 20, 2(2013),
CFD FLOW ANALYSIS IN CENTRIFUGAL VORTEX PUMP
 CFD FLOW ANALYSIS IN CENTRIFUGAL VORTEX PUMP 1 INTRODUCTION One way of improving the characteristics of centrifugal pumps is by adding a vortex rotor to the centrifugal rotor by which energy of induced
CFD FLOW ANALYSIS IN CENTRIFUGAL VORTEX PUMP 1 INTRODUCTION One way of improving the characteristics of centrifugal pumps is by adding a vortex rotor to the centrifugal rotor by which energy of induced
Numerical investigation of the flow instabilities in centrifugal fan
 Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS International Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Elounda, Greece, August 21-23, 26 (pp282-288) Numerical investigation of the flow instabilities in centrifugal
Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS International Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, Elounda, Greece, August 21-23, 26 (pp282-288) Numerical investigation of the flow instabilities in centrifugal
(Refer Slide Time: 4:41)
 Fluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-30. Basic Principle and Energy Transfer in Centrifugal Compressor Part
Fluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department Of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute Of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-30. Basic Principle and Energy Transfer in Centrifugal Compressor Part
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Centrifugal Compressor Part I Good morning
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Centrifugal Compressor Part I Good morning
Contents. 2 Basic Components Aerofoils Force Generation Performance Parameters xvii
 Contents 1 Working Principles... 1 1.1 Definition of a Turbomachine... 1 1.2 Examples of Axial Turbomachines... 2 1.2.1 Axial Hydraulic Turbine... 2 1.2.2 Axial Pump... 4 1.3 Mean Line Analysis... 5 1.4
Contents 1 Working Principles... 1 1.1 Definition of a Turbomachine... 1 1.2 Examples of Axial Turbomachines... 2 1.2.1 Axial Hydraulic Turbine... 2 1.2.2 Axial Pump... 4 1.3 Mean Line Analysis... 5 1.4
9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook.
 Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook. Basics (pressure head, efficiency, working point, stability) Pumps
Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook. Basics (pressure head, efficiency, working point, stability) Pumps
Introduction to Turbomachinery
 1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
mywbut.com Hydraulic Turbines
 Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
Theory of turbo machine Effect of Blade Configuration on Characteristics of Centrifugal machines. Unit 2 (Potters & Wiggert Sec
 Theory of turbo machine Effect of Blade Configuration on Characteristics of Centrifugal machines Unit (Potters & Wiggert Sec. 1..1, &-607) Expression relating Q, H, P developed by Rotary machines Rotary
Theory of turbo machine Effect of Blade Configuration on Characteristics of Centrifugal machines Unit (Potters & Wiggert Sec. 1..1, &-607) Expression relating Q, H, P developed by Rotary machines Rotary
FLOW PATTERN STUDY OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP USING CFD METHODS CONCENTRATING ON VOLUTE TONGUE ROLE
 FLOW PATTERN STUDY OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP USING CFD METHODS CONCENTRATING ON VOLUTE TONGUE ROLE N. Pourmahmoud and S. Majid Taleby Faculty of Engineering, Urmia University, Urmia, Iran E-Mail: majid.taleby@gmail.com
FLOW PATTERN STUDY OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP USING CFD METHODS CONCENTRATING ON VOLUTE TONGUE ROLE N. Pourmahmoud and S. Majid Taleby Faculty of Engineering, Urmia University, Urmia, Iran E-Mail: majid.taleby@gmail.com
DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
 DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP 1 CH.YADAGIRI, 2 P.VIJAYANAND 1 Pg Scholar, Department of MECH, Holymary Institute of Technology, Ranga Reddy, Telangana, India. 2 Assistant Professor, Department
DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP 1 CH.YADAGIRI, 2 P.VIJAYANAND 1 Pg Scholar, Department of MECH, Holymary Institute of Technology, Ranga Reddy, Telangana, India. 2 Assistant Professor, Department
Numerical Study of Pressure and Velocity Distribution Analysis of Centrifugal Pump
 International Journal of Thermal Technologies, Vol.1, No.1 (Dec. 2011) Research Article Numerical Study of Pressure and Velocity Distribution Analysis of Centrifugal Pump Munish Gupta 1, Satish Kumar 2,
International Journal of Thermal Technologies, Vol.1, No.1 (Dec. 2011) Research Article Numerical Study of Pressure and Velocity Distribution Analysis of Centrifugal Pump Munish Gupta 1, Satish Kumar 2,
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S
 CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S Pupmps are devices for supplying energy or head to a flowing liquid in order to overcome head losses due to friction and also if necessary, to raise liquid
CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S Pupmps are devices for supplying energy or head to a flowing liquid in order to overcome head losses due to friction and also if necessary, to raise liquid
Numerical Prediction Of Torque On Guide Vanes In A Reversible Pump-Turbine
 Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) ISSN: 3159 Vol. 2 Issue 6, June - 215 Numerical Prediction Of Torque On Guide Vanes In A Reversible Pump-Turbine Turbine and pump
Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) ISSN: 3159 Vol. 2 Issue 6, June - 215 Numerical Prediction Of Torque On Guide Vanes In A Reversible Pump-Turbine Turbine and pump
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow in a Centrifugal Pump Stage
 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow in a Centrifugal Pump Stage FRIEDRICH-KARL BENRA, HANS JOSEF DOHMEN Faculty of Engineering Sciences Department of Mechanical Engineering, Turbomachinery
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow in a Centrifugal Pump Stage FRIEDRICH-KARL BENRA, HANS JOSEF DOHMEN Faculty of Engineering Sciences Department of Mechanical Engineering, Turbomachinery
Numerical Simulation of a Complete Francis Turbine including unsteady rotor/stator interactions
 Numerical Simulation of a Complete Francis Turbine including unsteady rotor/stator interactions Ruprecht, A., Heitele, M., Helmrich, T. Institute for Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery University
Numerical Simulation of a Complete Francis Turbine including unsteady rotor/stator interactions Ruprecht, A., Heitele, M., Helmrich, T. Institute for Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery University
Keywords - Gas Turbine, Exhaust Diffuser, Annular Diffuser, CFD, Numerical Simulations.
 Numerical Investigations of PGT10 Gas Turbine Exhaust Diffuser Using Hexahedral Dominant Grid Vaddin Chetan, D V Satish, Dr. Prakash S Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering, VVCE, Mysore, Department
Numerical Investigations of PGT10 Gas Turbine Exhaust Diffuser Using Hexahedral Dominant Grid Vaddin Chetan, D V Satish, Dr. Prakash S Kulkarni Department of Mechanical Engineering, VVCE, Mysore, Department
In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines
 Lect- 35 1 In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines Radial turbines Lect-35 Development of radial flow turbines
Lect- 35 1 In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines Radial turbines Lect-35 Development of radial flow turbines
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
MODELLING OF SINGLE-PHASE FLOW IN THE STATOR CHANNELS OF SUBMERSIBLE AERATOR
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 21, 2014, No. 5, p. 289 298 289 MODELLING OF SINGLE-PHASE FLOW IN THE STATOR CHANNELS OF SUBMERSIBLE AERATOR Martin Bílek*, Jaroslav Štigler* The paper deals with the design
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 21, 2014, No. 5, p. 289 298 289 MODELLING OF SINGLE-PHASE FLOW IN THE STATOR CHANNELS OF SUBMERSIBLE AERATOR Martin Bílek*, Jaroslav Štigler* The paper deals with the design
1917. Numerical simulation and experimental research of flow-induced noise for centrifugal pumps
 1917. Numerical simulation and experimental research of flow-induced noise for centrifugal pumps Xiao-ping Rui 1, Yang Zhao 2 1 College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,
1917. Numerical simulation and experimental research of flow-induced noise for centrifugal pumps Xiao-ping Rui 1, Yang Zhao 2 1 College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,
INVESTIGATION OF SWIRLING FLOW IN DIFFUSERS INSTALLED AT THE EXIT OF AN AXIAL-FLOW PUMP
 TASK QUARTERLY 5 No 4 (2001), 603 610 INVESTIGATION OF SWIRLING FLOW IN DIFFUSERS INSTALLED AT THE EXIT OF AN AXIAL-FLOW PUMP ALEXEY N. KOCHEVSKY Department of Fluid Mechanics, Sumy State University, Rimsky-Korsakov
TASK QUARTERLY 5 No 4 (2001), 603 610 INVESTIGATION OF SWIRLING FLOW IN DIFFUSERS INSTALLED AT THE EXIT OF AN AXIAL-FLOW PUMP ALEXEY N. KOCHEVSKY Department of Fluid Mechanics, Sumy State University, Rimsky-Korsakov
Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump To cite this article: E M Kraeva 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump To cite this article: E M Kraeva 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
STUDY ON TIP LEAKAGE VORTEX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRESS TRANSPORT k-ω TURBULENCE MODEL
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
Performance Investigation of High Pressure Ratio Centrifugal Compressor using CFD
 International Journal of Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Performance Investigation of High Pressure Ratio Centrifugal Compressor using CFD Manjunath DC a, Rajesh b, Dr.V.M.Kulkarni c a PG student, Department
International Journal of Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Performance Investigation of High Pressure Ratio Centrifugal Compressor using CFD Manjunath DC a, Rajesh b, Dr.V.M.Kulkarni c a PG student, Department
Numerical simulation of pressure pulsations in Francis turbines
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Numerical simulation of pressure pulsations in Francis turbines To cite this article: M V Magnoli and R Schilling 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Numerical simulation of pressure pulsations in Francis turbines To cite this article: M V Magnoli and R Schilling 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
Flow behaviour analysis of reversible pumpturbine in "S" characteristic operating zone
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Flow behaviour analysis of reversible pumpturbine in "S" characteristic operating zone To cite this article: S Q Zhang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Flow behaviour analysis of reversible pumpturbine in "S" characteristic operating zone To cite this article: S Q Zhang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.:
EVALUATION OF FOUR TURBULENCE MODELS IN THE INTERACTION OF MULTI BURNERS SWIRLING FLOWS
 EVALUATION OF FOUR TURBULENCE MODELS IN THE INTERACTION OF MULTI BURNERS SWIRLING FLOWS A Aroussi, S Kucukgokoglan, S.J.Pickering, M.Menacer School of Mechanical, Materials, Manufacturing Engineering and
EVALUATION OF FOUR TURBULENCE MODELS IN THE INTERACTION OF MULTI BURNERS SWIRLING FLOWS A Aroussi, S Kucukgokoglan, S.J.Pickering, M.Menacer School of Mechanical, Materials, Manufacturing Engineering and
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION IMPELLER OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
 Proceedings of the Fortieth National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power December 12-14, 2013, NIT Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh, India FMFP2013_141 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION
Proceedings of the Fortieth National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power December 12-14, 2013, NIT Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh, India FMFP2013_141 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION
VACUUM PUMPING METHODS
 VACUUM PUMPING METHODS VACUUM PUMPS (METHODS) Positive Displacement Vacuum Gas Transfer Vacuum Kinetic Vacuum Entrapment Vacuum Adsorption Reciprocating Displacement Rotary Drag Fluid Entrainment Ion Transfer
VACUUM PUMPING METHODS VACUUM PUMPS (METHODS) Positive Displacement Vacuum Gas Transfer Vacuum Kinetic Vacuum Entrapment Vacuum Adsorption Reciprocating Displacement Rotary Drag Fluid Entrainment Ion Transfer
Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal pump
 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
Transactions of the VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, Mechanical Series. article No. 1887
 Transactions of the VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, Mechanical Series No. 2, 2011, vol. LVII article No. 1887 Lukáš ZAVADIL *, Sylva DRÁBKOVÁ ** DETERMINATION OF PUMP PERFORMANCE USING NUMERICAL MODELLING
Transactions of the VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, Mechanical Series No. 2, 2011, vol. LVII article No. 1887 Lukáš ZAVADIL *, Sylva DRÁBKOVÁ ** DETERMINATION OF PUMP PERFORMANCE USING NUMERICAL MODELLING
Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis To cite this article: Q W Liang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis To cite this article: Q W Liang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
The effect of geometric parameters on the head loss factor in headers
 Fluid Structure Interaction V 355 The effect of geometric parameters on the head loss factor in headers A. Mansourpour & S. Shayamehr Mechanical Engineering Department, Azad University of Karaj, Iran Abstract
Fluid Structure Interaction V 355 The effect of geometric parameters on the head loss factor in headers A. Mansourpour & S. Shayamehr Mechanical Engineering Department, Azad University of Karaj, Iran Abstract
STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS A SIMPLIFIED APPROACH
 Proceedings of the First Middle East Turbomachinery Symposium February 13-16, 2011, Doha, Qatar STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS A SIMPLIFIED APPROACH Urs Baumann Head of Calculation and Development MAN Diesel
Proceedings of the First Middle East Turbomachinery Symposium February 13-16, 2011, Doha, Qatar STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS A SIMPLIFIED APPROACH Urs Baumann Head of Calculation and Development MAN Diesel
Performance characteristics of turbo blower in a refuse collecting system according to operation conditions
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Numerical Study of the Semi-Open Centrifugal Pump Impeller Side Clearance A. Farid Ayad *, H. M. Abdalla,A. S. Abo El-Azm Egyptian Armed Forces, Egypt
 16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 24 Axial Flow Compressor Part I Good morning
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 24 Axial Flow Compressor Part I Good morning
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS. CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids
 CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
COURSE CODE : 3072 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : FLUID MECHANICS COURSE CODE : 307 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIOD 1 Properties of Fluids 0 Fluid Friction and Flow
COURSE TITLE : FLUID MECHANICS COURSE CODE : 307 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIOD 1 Properties of Fluids 0 Fluid Friction and Flow
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
THERMAL ANALYSIS OF SECOND STAGE GAS TURBINE ROTOR BLADE
 Polymers Research Journal ISSN: 195-50 Volume 6, Number 01 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. THERMAL ANALYSIS OF SECOND STAGE GAS TURBINE ROTOR BLADE E. Poursaeidi, M. Mohammadi and S. S. Khamesi University
Polymers Research Journal ISSN: 195-50 Volume 6, Number 01 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. THERMAL ANALYSIS OF SECOND STAGE GAS TURBINE ROTOR BLADE E. Poursaeidi, M. Mohammadi and S. S. Khamesi University
Research on energy conversion mechanism of a screw centrifugal pump under the water
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Research on energy conversion mechanism of a screw centrifugal pump under the water To cite this article: H Quan et al 213 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Research on energy conversion mechanism of a screw centrifugal pump under the water To cite this article: H Quan et al 213 IOP Conf.
Flow analysis in centrifugal compressor vaneless diffusers
 348 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research J SCI IND RES VOL 67 MAY 2008 Vol. 67, May 2008, pp. 348-354 Flow analysis in centrifugal compressor vaneless diffusers Ozturk Tatar, Adnan Ozturk and Ali
348 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research J SCI IND RES VOL 67 MAY 2008 Vol. 67, May 2008, pp. 348-354 Flow analysis in centrifugal compressor vaneless diffusers Ozturk Tatar, Adnan Ozturk and Ali
The influence of disc friction losses and labyrinth losses on efficiency of high head Francis turbine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The influence of disc friction losses and labyrinth losses on efficiency of high head Francis turbine To cite this article: D eli and H Ondráka 2015 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The influence of disc friction losses and labyrinth losses on efficiency of high head Francis turbine To cite this article: D eli and H Ondráka 2015 J.
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel
 CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER
 EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
Prof. Dr.-Ing. F.-K. Benra. ISE batchelor course
 University Duisburg-Essen Campus Duisburg Faculty of engineering Science Department of Mechanical Engineering Examination: Fluid Machines Examiner: Prof. Dr.-Ing. F.-K. Benra Date of examination: 06.03.2006
University Duisburg-Essen Campus Duisburg Faculty of engineering Science Department of Mechanical Engineering Examination: Fluid Machines Examiner: Prof. Dr.-Ing. F.-K. Benra Date of examination: 06.03.2006
Journal of Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology
 J. Mechatron. Electr. Power Veh. Technol 06 (2015) 39 8 Journal of Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology e-issn:2088-6985 p-issn: 2087-3379 www.mevjournal.com GEOMETRY ANALYSIS AND EFFECT
J. Mechatron. Electr. Power Veh. Technol 06 (2015) 39 8 Journal of Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology e-issn:2088-6985 p-issn: 2087-3379 www.mevjournal.com GEOMETRY ANALYSIS AND EFFECT
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook. THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 Fluid Flow
 Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance
 Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance Andrey Sherbina 1, Ivan Klimov 2 and Leonid Moroz 3 SoftInWay Inc., 1500 District Avenue, Burlington, MA, 01803,
Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance Andrey Sherbina 1, Ivan Klimov 2 and Leonid Moroz 3 SoftInWay Inc., 1500 District Avenue, Burlington, MA, 01803,
Centrifugal Machines Table of Contents
 NLNG Course 017 Table of Contents 1 Introduction and Basic Principles... 1.1 Hydraulic Machines... 1.... 1.3 Pump Geometry... 1.4 Pump Blade Geometry...3 1.5 Diffusers...5 1.6 Pump Losses...6 1.7 Example
NLNG Course 017 Table of Contents 1 Introduction and Basic Principles... 1.1 Hydraulic Machines... 1.... 1.3 Pump Geometry... 1.4 Pump Blade Geometry...3 1.5 Diffusers...5 1.6 Pump Losses...6 1.7 Example
CFD Analysis of Centrifugal Pump in Sewerage System
 CFD Analysis of Centrifugal Pump in Sewerage System J. Beston 1, G. Gopi 1, S. Gopi 1, M. Karthika 1, Dr. S. V. Suresh Babu 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering,
CFD Analysis of Centrifugal Pump in Sewerage System J. Beston 1, G. Gopi 1, S. Gopi 1, M. Karthika 1, Dr. S. V. Suresh Babu 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
 DRAFT Proceedings of ASME IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Conference & Exposition Chicago, Illinois Nov. 5-10, 2006 IMECE2006-14867 DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
DRAFT Proceedings of ASME IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Conference & Exposition Chicago, Illinois Nov. 5-10, 2006 IMECE2006-14867 DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
Contents. 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines Overview of Turbomachinery Nomenclature...9
 Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
MASS, MOMENTUM, AND ENERGY EQUATIONS
 MASS, MOMENTUM, AND ENERGY EQUATIONS This chapter deals with four equations commonly used in fluid mechanics: the mass, Bernoulli, Momentum and energy equations. The mass equation is an expression of the
MASS, MOMENTUM, AND ENERGY EQUATIONS This chapter deals with four equations commonly used in fluid mechanics: the mass, Bernoulli, Momentum and energy equations. The mass equation is an expression of the
Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer
 Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer Joel de Almeida Mendes E-mail: joeldealmeidamendes@hotmail.com Abstract This work presents the application of a CFD code Fluent to simulate the
Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer Joel de Almeida Mendes E-mail: joeldealmeidamendes@hotmail.com Abstract This work presents the application of a CFD code Fluent to simulate the
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy
 Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy Martin Böhle 1, Annika Fleder 1, Matthias Mohr 1 * SYMPOSIA ON ROTATING MACHINERY ISROMAC 16 International Symposium on Transport Phenomena
Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy Martin Böhle 1, Annika Fleder 1, Matthias Mohr 1 * SYMPOSIA ON ROTATING MACHINERY ISROMAC 16 International Symposium on Transport Phenomena
Steady state operation simulation of the Francis- 99 turbine by means of advanced turbulence models
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Steady state operation simulation of the Francis- 99 turbine by means of advanced turbulence models To cite this article: A Gavrilov et al 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Steady state operation simulation of the Francis- 99 turbine by means of advanced turbulence models To cite this article: A Gavrilov et al 2017 J.
Rotordynamic Forces from Dischargeto-Suction Leakage Flows in Centrifugal Pumps : Effects of Geometry*
 Rotordynamic Forces from Dischargeto-Suction Leakage Flows in Centrifugal Pumps : Effects of Geometry* Robert V. UY**, Brian L. BIRCUMSHAW** and Christopher E. BRENNEN* * The rotordynamic forces generated
Rotordynamic Forces from Dischargeto-Suction Leakage Flows in Centrifugal Pumps : Effects of Geometry* Robert V. UY**, Brian L. BIRCUMSHAW** and Christopher E. BRENNEN* * The rotordynamic forces generated
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Available Online at:
 A COMPUTER PROGRAMMED DESIGN OPTIMISATION AND ANALYSIS OF COMPRESSOR IMPELLER G. Naga Malleshwar Rao 1, Dr. S.L.V. Prasad 2, Dr. S. Sudhakarbabu 3 1, 2 Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Shri Shirdi
A COMPUTER PROGRAMMED DESIGN OPTIMISATION AND ANALYSIS OF COMPRESSOR IMPELLER G. Naga Malleshwar Rao 1, Dr. S.L.V. Prasad 2, Dr. S. Sudhakarbabu 3 1, 2 Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Shri Shirdi
Lect 22. Radial Flow Turbines. Prof. Bhaskar Roy, Prof. A M Pradeep, Department of Aerospace, IIT Bombay
 Lecture Lect Radial Flow Turbines Lect Radial inflow turbines, which look similar to centrifugal compressor, are considered suitable for application in small aircraft engines. In many applications a radial
Lecture Lect Radial Flow Turbines Lect Radial inflow turbines, which look similar to centrifugal compressor, are considered suitable for application in small aircraft engines. In many applications a radial
Aerodynamics of Centrifugal Turbine Cascades
 ASME ORC 2013 2nd International Seminar on ORC Power Systems October 7th-8th, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Aerodynamics of Centrifugal Turbine Cascades G. Persico, M. Pini, V. Dossena, and P. Gaetani Laboratorio
ASME ORC 2013 2nd International Seminar on ORC Power Systems October 7th-8th, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Aerodynamics of Centrifugal Turbine Cascades G. Persico, M. Pini, V. Dossena, and P. Gaetani Laboratorio
Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around the Runner Blade)
 Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 415 424, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474629 Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around
Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 415 424, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474629 Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around
PERFORMANCE OF A CENTRAL-TYPE JET PUMP II- EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON WATER FLOW
 Eighth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC8 24, Alexandria, Egypt PERFORMANCE OF A CENTRAL-TYPE JET PUMP II- EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON WATER FLOW ABSTRACT EL-Otla, F. M. *, EL-Sawaf, I. A. * and
Eighth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC8 24, Alexandria, Egypt PERFORMANCE OF A CENTRAL-TYPE JET PUMP II- EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON WATER FLOW ABSTRACT EL-Otla, F. M. *, EL-Sawaf, I. A. * and
Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
A SIMPLE ACOUSTIC MODEL TO SIMULATE THE BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY SOUND PRESSURE GENERATED IN THE VOLUTE OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
 A SIMPLE ACOUSTIC MODEL TO SIMULATE THE BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY SOUND PRESSURE GENERATED IN THE VOLUTE OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS PACS REFERENCE: 43.28.Ra Parrondo Gayo, Jorge; Pérez Castillo, Javier; Fernández
A SIMPLE ACOUSTIC MODEL TO SIMULATE THE BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY SOUND PRESSURE GENERATED IN THE VOLUTE OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS PACS REFERENCE: 43.28.Ra Parrondo Gayo, Jorge; Pérez Castillo, Javier; Fernández
Radial Compressors. Damian Vogt Course MJ2429. Nomenclature
 Turbomachinery Lecture Notes 1 007-10-04 Radial Compressors Damian Vogt Course MJ49 Nomenclature Subscripts Symbol Denotation Unit c Absolute velocity m/s h Enthalpy J/kg m& Mass flow rate kg/s r Radius
Turbomachinery Lecture Notes 1 007-10-04 Radial Compressors Damian Vogt Course MJ49 Nomenclature Subscripts Symbol Denotation Unit c Absolute velocity m/s h Enthalpy J/kg m& Mass flow rate kg/s r Radius
FLUID CHARACTERISTICS OF ROTARY WING HEAT METER WITH SINGLE-CHANNEL *
 101 2008,20(1):101-107 FLUID CHARACTERISTICS OF ROTARY WING HEAT METER WITH SINGLE-CHANNEL * Du Guang-sheng, Liu Zheng-gang, LI Li, LIU Yong-hui, MA Yong-kun, MENG Liang School of Energy and Power Engineering,Shandong
101 2008,20(1):101-107 FLUID CHARACTERISTICS OF ROTARY WING HEAT METER WITH SINGLE-CHANNEL * Du Guang-sheng, Liu Zheng-gang, LI Li, LIU Yong-hui, MA Yong-kun, MENG Liang School of Energy and Power Engineering,Shandong
Optimizing Centrifugal Pump Performance by Different Blade Configuration Patterns
 American Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering 2018; 3(1): 1-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmie doi: 10.11648/j.ajmie.20180301.11 ISSN: 2575-6079 (Print); ISSN: 2575-6060 (Online)
American Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering 2018; 3(1): 1-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmie doi: 10.11648/j.ajmie.20180301.11 ISSN: 2575-6079 (Print); ISSN: 2575-6060 (Online)
Numerical Analysis of Partial Admission in Axial Turbines. Narmin Baagherzadeh Hushmandi
 Numerical Analysis of Partial Admission in Axial Turbines Narmin Baagherzadeh Hushmandi Doctoral Thesis 2010 II Doctoral Thesis Report / Narmin B. Hushmandi 2009 ABSTRACT Numerical analysis of partial
Numerical Analysis of Partial Admission in Axial Turbines Narmin Baagherzadeh Hushmandi Doctoral Thesis 2010 II Doctoral Thesis Report / Narmin B. Hushmandi 2009 ABSTRACT Numerical analysis of partial
Comparative Analysis of Heat Transfer and Friction Characteristics in a Corrugated Tube
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Comparative
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 216 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Comparative
CHAPTER THREE FLUID MECHANICS
 CHAPTER THREE FLUID MECHANICS 3.1. Measurement of Pressure Drop for Flow through Different Geometries 3.. Determination of Operating Characteristics of a Centrifugal Pump 3.3. Energy Losses in Pipes under
CHAPTER THREE FLUID MECHANICS 3.1. Measurement of Pressure Drop for Flow through Different Geometries 3.. Determination of Operating Characteristics of a Centrifugal Pump 3.3. Energy Losses in Pipes under
Development of the Floating Centrifugal Pump by Use of Non Contact Magnetic Drive and Its Performance
 Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 337 344, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474421 Development of the Floating Centrifugal Pump by Use of
Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 337 344, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474421 Development of the Floating Centrifugal Pump by Use of
Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj. Mr. YVS. Karthick AIR WALK PUBLICATIONS
 Fluid Machinery As per Revised Syllabus of Leading Universities including APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj Professors School of Mechanical Engineering Sathyabama
Fluid Machinery As per Revised Syllabus of Leading Universities including APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj Professors School of Mechanical Engineering Sathyabama
A Numerical study of effect of Return Channel Vanes Shroud Wall Divergence Angle on the Cross-over System Performance in Centrifugal Compressors
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Numerical study of effect of Return Channel Vanes Shroud Wall Divergence Angle on the Cross-over System Performance in Centrifugal Compressors * K.Srinivasa Reddy *, M Sai
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Numerical study of effect of Return Channel Vanes Shroud Wall Divergence Angle on the Cross-over System Performance in Centrifugal Compressors * K.Srinivasa Reddy *, M Sai
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CVNG 1001: Mechanics of Fluids
 INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Machines A hydromachine is a device used either for extracting energy from a fluid or to add energy to a fluid. There are many types of hydromachines and Figure 1 below illustrates
INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Machines A hydromachine is a device used either for extracting energy from a fluid or to add energy to a fluid. There are many types of hydromachines and Figure 1 below illustrates
A two-dimensional design method for the hydraulic turbine runner and its preliminary validation
 A two-dimensional design method for the hydraulic turbine runner and its preliminary validation Zbigniew Krzemianowski 1 *, Adam Adamkowski 1, Marzena Banaszek 2 ISROMAC 2016 International Symposium on
A two-dimensional design method for the hydraulic turbine runner and its preliminary validation Zbigniew Krzemianowski 1 *, Adam Adamkowski 1, Marzena Banaszek 2 ISROMAC 2016 International Symposium on
Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 53)
 Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 5) Q. Choose the crect answer (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) A hydraulic turbine rotates at N rpm operating under a net head H and having a discharge Q while developing
Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 5) Q. Choose the crect answer (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) A hydraulic turbine rotates at N rpm operating under a net head H and having a discharge Q while developing
Contents. Microfluidics - Jens Ducrée Physics: Laminar and Turbulent Flow 1
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Applications of Harmonic Balance Method in Periodic Flows Gregor Cvijetić and Inno Gatin
 Applications of Harmonic Balance Method in Periodic Flows Gregor Cvijetić and Inno Gatin Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Zagreb 10000, Croatia, gregor.cvijetic@gmail.com The Harmonic
Applications of Harmonic Balance Method in Periodic Flows Gregor Cvijetić and Inno Gatin Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Zagreb 10000, Croatia, gregor.cvijetic@gmail.com The Harmonic
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve
 Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Chapter 7 The Energy Equation
 Chapter 7 The Energy Equation 7.1 Energy, Work, and Power When matter has energy, the matter can be used to do work. A fluid can have several forms of energy. For example a fluid jet has kinetic energy,
Chapter 7 The Energy Equation 7.1 Energy, Work, and Power When matter has energy, the matter can be used to do work. A fluid can have several forms of energy. For example a fluid jet has kinetic energy,
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 23
 M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 23 Today, we will: Discuss diffusers and do an example problem Begin discussing pumps, and how they are analyzed in pipe flow systems D. Diffusers 1. Introduction.
M E 320 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 23 Today, we will: Discuss diffusers and do an example problem Begin discussing pumps, and how they are analyzed in pipe flow systems D. Diffusers 1. Introduction.
Effective Modes of Axial Balancing of Centrifugal Pump Rotor
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 39 (2012 ) 111 118 XIIIth International Scientific and Engineering Conference HERVICON-2011 Effective Modes of Axial Balancing of Centrifugal
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 39 (2012 ) 111 118 XIIIth International Scientific and Engineering Conference HERVICON-2011 Effective Modes of Axial Balancing of Centrifugal
WALL ROUGHNESS EFFECTS ON SHOCK BOUNDARY LAYER INTERACTION FLOWS
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
Effect of Geometric Configuration on Performance of Uniflow Cyclone
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-67X, p-issn: 2278-X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 1 (January 215), PP.63-69 Effect of Geometric Configuration on Performance
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-67X, p-issn: 2278-X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 1 (January 215), PP.63-69 Effect of Geometric Configuration on Performance
Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
Steady and unsteady flow inside a centrifugal pump for two different impellers
 International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2014; 3(2): 65-76 Published online March 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20140302.15 Steady and unsteady
International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2014; 3(2): 65-76 Published online March 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijepe) doi: 10.11648/j.ijepe.20140302.15 Steady and unsteady
EFFECT OF FORCED ROTATING VANELESS DIFFUSERS ON CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE PERFORMANCE
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 6, No. 5 (2011) 558-574 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EFFECT OF FORCED ROTATING VANELESS DIFFUSERS ON CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE PERFORMANCE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 6, No. 5 (2011) 558-574 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EFFECT OF FORCED ROTATING VANELESS DIFFUSERS ON CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR STAGE PERFORMANCE
ENERGY TRANSFER BETWEEN FLUID AND ROTOR. Dr. Ir. Harinaldi, M.Eng Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering University of Indonesia
 ENERGY TRANSFER BETWEEN FLUID AND ROTOR Dr. Ir. Harinaldi, M.Eng Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering University of Indonesia Basic Laws and Equations Continuity Equation m m ρ mass
ENERGY TRANSFER BETWEEN FLUID AND ROTOR Dr. Ir. Harinaldi, M.Eng Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering University of Indonesia Basic Laws and Equations Continuity Equation m m ρ mass
A NEW METHOD FOR PREDICITING THE PERFORAMNCE MAP OF A SINGLE STAGE OF A CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR
 Proceedings of the 1st Global Power and Propulsion Forum GPPF 2017 Jan 16-18, 2014, Zurich, Switzerland www.pps.global GPPF-2017-119 A NEW METHOD FOR PREDICITING THE PERFORAMNCE MAP OF A SINGLE STAGE OF
Proceedings of the 1st Global Power and Propulsion Forum GPPF 2017 Jan 16-18, 2014, Zurich, Switzerland www.pps.global GPPF-2017-119 A NEW METHOD FOR PREDICITING THE PERFORAMNCE MAP OF A SINGLE STAGE OF
