Unit 5 Selected Answers
|
|
|
- Russell Job Cobb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ) Find the zeros of the function means to find the -value(s) that make the function f() = 0. (answers will var) ) The -intercepts (answers will var) ) # & tpe: real root (rational) zeros: = ) # & tpe: no real roots zeros: none ) # & tpe: real roots (rational) zeros: = 0 or = ) solutions: = or = check: f() = () + () = 0 f( ) = ( ) + ( ) = 0 both solutions create a zero 7) solutions: = 0 or = check: f(0) = (0) + (0) = 0 f() = () + () = 0 both solutions create a zero ) 9) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A solutions: = or = check: f( ) = ( ) + ( ) 0 = 0 f() = () + () 0 = 0 0) solutions:. or. ) solutions:.7or =.0 ) solutions: 0.9 or. ) solutions:. or. 0.(.) (.) 0 0.(.) (.) 0 ) solutions:. or. (.) +(.) (.) +(.) ) solutions:. or. (.) (.) 0 (.) (.) 0 ) 7) solutions: = or = ) solutions: = or = 9) solutions: = or = check: f( ) = ( ) + ( ) + = 0 f() = () + () + = 0 solutions: = 0 or = solutions: = or = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
2 0) solutions: = 0 or = ) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A (continued) ) a) () f() = + + =, = (7) f() = =, = () f() = + + =, = b) (9) f() = + = 0, = (0) f() = (½) + = 0, = () f() = + = 0, = c) If one function is a multiple of another function, then the will have the same solutions. (answers will var) ) a) b) feet; the point (, ) is the verte of the graph of the equation. c) 0 feet; this is the -intercept of the graph of the equation (that is greater than zero). (answers will var) solutions: = 0 or = ) a) Peter is correct. The -intercept gives the time (t) when = 0, which is where the ball has a height of 0 on the ground. (eplanations will var) b) Pablo s ball hit the ground first. It took. seconds for it to hit the ground. c) Peter s ball hit the ground second. It took. seconds for it to hit the ground. ) a) h(t) = t + t +. b). feet c) After 0. seconds and then again after.0 seconds. d) After.09 seconds. SECTION.B ) e). feet is the maimum that the football ever gets into the air. f). seconds is when the ball hits the ground (the -intercept). ) Verte: (.,.0). The verte reveals how long it takes (. seconds) for the ball to reach the maimum height (.0 ft). (eplanations will var) ) t = das, which is the -coordinate of the verte. ) a). sections is the maimum speed (the -coordinate of the verte of the graph) b) 9 km/h (the -coordinate of the verte of the graph) ) c). seconds (the -coordinate of the -intercept of the graph. ) a) 0 is half the perimeter, so one length plus one width equals 0 feet of fencing. (eplanations will var) b) A(L) = L(0 L) A(L) = L + 0L c) (L, A(L)) = (, ) when the length is, the width is 0 L =. So, Area = L W ft ft ft Area of the tomato patch is square feet. d) The tomato patch is a square shape (ft ft). Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
3 7) a) According to #d, Sharon should make a square with her 0 feet of fencing. So, 0 = 0 feet on each side. b) A(L) = L(0 L) A(L) = L + 0L calc the ma, shows a verte at (0, 00) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.B (continued) 7 c) (L, A(L)) = (0, 00) when the length is 0, the width is 0 L = 0. So, Area = L W 0 ft 0 ft = 00 ft The area of the fenced pla area is 00 square feet. ) Yes! The maimum height of the orange is 9 feet (which is the -coordinate of the verte of the graph). Jim can grab the orange either on the wa up for the orange or on its wa down (eplanations will var). 9) At approimatel miles per hour will the car be able to stop for a sign 0 feet awa. 0) a). feet b).79 seconds ) ( + ) ) ( ) ) 7(a + ) ) (z ) ) b(b + ) ) r( r) 7) t(9t + ) ) n(n ) 9) h(h + ) 0) 9( ) ) a(a + ) ) d(d ) ) ( + 7)( + ) ) ( + )( + ) or ( + ) ) ( + )( + ) SECTION.A ) ( + )( ) 7) ( )( ) or ( ) ) ( )( + ) 9) ( + )( ) 0) ( )( + ) ) ( )( ) or ( ) ) ( )( ) ) ( + )( ) ) ( + )( + ) ) (a )(a + ) ) ( )( + ) 7) ( )( + ) ) = ( + )( + ) 9) = ( + 7)( 7) 0) The -intercepts have a -coordinate of zero. Setting = 0 and solving for gives the solution(s), which are the -intercept(s). (answers will var) ) (, 0) and (0, 0) ) (, 0) and ( 0, 0) ) a) an arrow should be drawn to the location that the graph of the height of the ball in relationship to time touches the -ais. ) b) = 0 means the place where the ball hits the ground (where the height is zero). ) = or = 9 ) = (double root) ) = or = ) = or = ) = or = ) = 0 or = 7) = 0 or = SECTION.B ) = or = 9 9) = or = 0) = (double root) ) = or = ) = or = ) = or = ) = or = ) = or = ) = or = 7) = or = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
4 ) The legs of the triangle have lengths of units and units. ) The legs of the triangle have lengths of units and units. ) The value of is 0 (side lengths are 9 units and units). Unit Selected Answers SECTION.C ) The value of is (side lengths are 0 units and units). ) The two numbers that satisf the situation are and. ) The dimensions are feet b feet. 7) The two positive numbers are and. ) The two negative integers are and. 9) ( = ) You can frame a ft ft square picture. ) a) b) c) 0 d) e) 0 f) ) a) 9 ) a) ) b) b) + c) 0 7 d) e) f) + ) a) b) 0 c) d) e) 0 f) ) a) + 7 SECTION.D b) + c) + d) + 0 e) f) + ) a) 9 + b) c) 7 d) 7 + e) 7 f) 7 7) a) es, this -value is a solution b) no ( = + ) is not a solution to the equation. c) es, ( = ) is a solution to the equation. ) a) a + 9) b) + c) 7 d) ? = ? = ? + = ? + = ? + = ? = 0? = 0? = 0 0 = 0 Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
5 Unit Selected Answers ) = or = ( = ± ) ) = or = ( = ± ) ) = or = ( = ± ) ) = or = 7 ) = 7 or = ) = or = ) The error occurs when Omar tried to add to both sides before he takes the square root of both sides. The correct solutions are = or = 0 ) Yes, both of the values given are solutions. ) Yes, both of the values given are solutions. ) Yes, both of the values given are solutions. ) No, neither value given is a solution. SECTION.E 7) It takes seconds to reach the ground. ) A sign should be posted stating the maimum speed is km per hour. SECTION.F ) Both answers are correct. The balloon could have hit a foot tall student on the wa up after 0. seconds, or it could have hit the student on its descending path after. seconds. 9) The other leg of the triangle And created is 9 feet long. 7) = ± ) = ± 9) = ± 0) = or = ) = ± ) = ) = or = ) = ± ) t.seconds ) 9.7 miles (eplanations will var) ) a) b) c) i d) e) i f) i g) i h) i i) 0i 7 j) i k) i 0 l) 0i ) a) 9 + i b) i SECTION.G ) c) + i d) + i e) 9 i f) 9i ) a) b) c) i d) 0i e) i f) ) (all answers in # ma var) a) () in method, Kasem never used the definition on i = to rewrite either radical. Method uses the definition correctl. () method used the product propert of radicals incorrectl; onl if a and b are both nonnegative with an even inde, is a b = a b. Method uses the product propert of radicals correctl. b) () both methods combine 9 = instead of simplifing each separatel. () both methods used the fact that = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
6 ) c) () from line to line, multiplication was done in a different order b commutative propert for multiplication. () method simplified the radicals and 9 ; method multiplied them together. d) () both used the definition of i = whenever there was a. () both used the fact that i = ) a) b) 0 c) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.G ) a) i b) 9 + i c) 0i d) i e) 0 + 0i f) + i 0 7) a) + 0i b) i c) 7 0i ) a) + i b) i 7 c) 7i 9) a) Yes () += = (continued) b) Yes (+) (+)+0= = 9) c) Yes ( i ) ( i ) ( i ) ( i ) i + = + + = ( ) ( ) ( ) i i + = 0) a) + i ) b) + i c) 7i d) i ( ) =? + i + i + = 9 + i + i? ( + i ) + = 9 + i +? 9 i + = i? + i = i? + i = + i i =? = ) i ) i ) i ) 0i ) i ) i 7) ) 9 9) 0) ) i 0i ) + i ) 0 + i ) Yes () += = ) Yes SECTION.H (+) = 7 7= 7 ) Yes () +=7 7=7 7) Yes ( +)+ = = ) =± 9) =± 0) =± ) = ± ). seconds. The balloon lands on the ground after approimatel. seconds. ( 0.9 does not work when verified) (#-, verification of solutions should be shown b student.) ) =± ) = 7 ) =± ) =± 7) s 7.07inches; The length of one side of the square is approimatel 7.07 inches. ) =±. With these solutions being imaginar, it reinforces the reason wh the graph does not cross the -ais. There are no real solutions, there are two comple solutions. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
7 ) = 7 or = ) = 0 or = ) = or = ) From line to line, the person forgot to add to both sides of the equation. ) = or = 0 ) = or = ) = 7 ± ) = 9 ± ) = ± ) ) ± = 7 ± 7 = ) = ± 7) 7 ± 7 = Unit Selected Answers SECTION.I 7) = or = 9 ) = or = 9) = 0) =7 or = ) = The two numbers that satisf the conditions are and. ) SECTION.J ± = ± 9) = 0) When > 0, there will be real solutions. When = 0 there will be real solution. ) =. ; The width of the pool is meters and the length is 9 meters. ) = The length of each side of the original garden is ards and the area of the garden is square ards. ) = The ball was in the air for seconds when it reached a height of feet in the air. ) t = ; The arrow will strike the ground after seconds. ) a) h ( ) = ; The bottle rocket is feet high after seconds. b) t. or t.7 ; The rocket will be at 00 feet in the air at two different times. Once on the wa up and once on the wa down during its flight. ) = ± i ) = 7 ± i ) = ± i ) = ± i ) = ± i ) ± i = 7) = ± i ) ± i = 0 ± i 9) = 0) 0. ; Emma hits the golf ball approimatel 0. ards. ) SECTION.K = or = ; At eactl ½ second and ½ seconds, the tape measure is at eactl 7 feet above the ground. Gail can catch the tape measure anwhere between ½ second and ½ seconds after Veronica tosses the tool. ) When < 0 there will be imaginar solutions for a quadratic equation. ) Creates the quadratic formula: a b c + + = 0 a b c = a a b c + + = 0 a a b c + = a a b b c b + + = + a a a a b b ac + = a a a b b ac + = a a + = a a b b ac b b ac b b ac + = or + = + a a a a b b ac b b a = or = + a a a b b ac = ± a a ± = b b ac a a c Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 7 ~
8 ) If the quadratic equation does not factor, the roots are either irrational or imaginar. (Answers will var) ) a: b: c: = or = solve b factoring? Yes, b ac (9) is a perfect square number. ) a: b: 7 c: 9 7 ± = solve b factoring? No, b ac () is not a perfect square number. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.L ) a: b: c: ± 9 = 0 solve b factoring? No, b ac (9) is not a perfect square number. ) a: b: c: = ± solve b factoring? No, b ac () is not a perfect square number ) a: 9 b: c: ± = 7) a: b: c: ± 7 = ). seconds 9) a) seconds b) seconds ) i ) ) i ) = or = ) = ± i ) = 7) ± i = ) = ± i 9) = or = )» Use a graphing utilit to find real zeros.» Factor and use the zero product propert.» Square root propert» Complete the square» Quadratic formula SECTION.M 0) Error on line, need to divide both terms of the numerator b the denominator value of ; = ± i ) = ± 7 ) = ± i ) = 0 ) a). seconds SECTION.N ) Graph: The solutions are the -intercepts of =, = ) b) Since t = 0 means time when object is initiall thrown, positive time means time after the throw was started. Negative time implies time before the object was thrown, which doesn t make sense here. (Answers will var) c) The object was at a height of feet after 0.7 seconds and again at.7 seconds. Factor: + = 0 ( ) ( ) = or = Quadratic Formula: ± = ± = = or = solutions: = or = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
9 ) method:: The factoring method is the fastest and ields rational solutions with fewer possibilities of careless errors. (eplanations ma var) ) Graph: The solutions are the - intercepts of ±.7 Square Root: =0 = =± Quadratic Formula: 0 ± = ± = = ± solutions: = ± method: The square root method. There is no linear term (the term). The b-value is equal to zero. (Answers will var) ) a) Graphing calculator (but it can t be used to find comple/imaginar solutions) b) Completing the Square and Quadratic Formula c) Factoring or Square Root propert ) Factoring it s a trinomial that factors nicel. (method and eplanation ma var) = or = Unit Selected Answers SECTION.N (continued) ) Factoring it is a binomial with a common factor. (method and eplanation ma var) = 0 or = 000 7) Factoring it is a trinomial with a leading coefficient of. (method and eplanation ma var) = 9 or = ) There are two scenarios for this situation: () Numbers and 9 () Numbers and 9 9) width: 7 in. length: 0 in. 0) Suzie needs 0 feet of fencing. ) Mike needs 0 feet of fencing. ) Solutions: = ± Methods included here ma var Method : Factoring + = 0 ( ) ( ) Method : Square Root Propert + = = = 9 continued Wh? Using square roots has a less chance for careless sign error. Also, we have been using square roots to solve longer than using factoring to solve. (methods ma var) ) Solutions: = ; so the width is m and length is m Method :Complete the Square + 0 = 7 ( ) = = 900 ( ) + = 900 continued Note that is etraneous. Method : Factoring + 0 = 7 ( ) = 0 ( ) ( ) + = 0 continued ) Wh? Complete the Square was more efficient since was a whole number, and the square root propert is well engrained. Factoring might have taken longer to find integers with a product of 7. (answers/methods ma var) ± i ) = ; solutions should be verified ± 9 ) = ; solutions should be verified ) = 7) ( ) +( )+9=0 0=0 i = ± 9 9 +=0 0=0 and 9 +=0 0=0 ) a) The ball was in the air sec. b) The ball reaches the ma height at. seconds. c) The ma height is 00 feet. d) Graph a second line at = 0 and use calculate intersect to get the -coordinate that creates a function value of 0. The ball is at 0 feet again at approimatel.0 seconds. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 9 ~
10 () () (answers will var) Square Root Propert: Eq n #: ( ) = Solution(s): = ± + = and = = = Factoring: Eq n #: = 0 Solution(s): = or = () () =0 0=0 and ( ) ( ) =0 0=0 Factoring: Eq n #: + = 0 Solution(s): = ± =0 0=0 and + =0 0=0 Quadratic Formula: Eq n #: + 7 = 0 Solution(s): = or = +7 =0 0=0 And ( ) +7( ) =0 0=0 ) In the quadratic formula, b ± b ac =, the a discriminant is the value of the epression b ac that is under the radical. This number is used to determine the number and tpe of solutions of a quadratic equation. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.O Graphing: Eq n #: h t = t + t + 7 ( ) Solution(s): t.00 It took approimatel seconds for the rock to hit the ground. (.00) +(.00)+7=0 0=0 SECTION.A ) discriminant: number of solutions: tpe: imaginar ) discriminant: number of solutions: tpe: real, rational ) discriminant: 0 number of solutions: tpe: real, rational ) a) = 7 or = b) graph: c) The intersection points of the graphs in part b) are the solutions for in part a). 9=(7 ) 9=9 and 9=( ) 9=9 7) a) The. feet is how far the hose s nozzle is above the ground where the water begins to shoot out. b). feet c) No. At 7.9 feet from the nozzle, the stream would hit the top of the foot fence. However, at the foot distance, the water height is lower, reaching onl.9 feet high. ) (answers will var) Xmin: 0 Xma: 0 Ymin: 00 Yma: 000 ) discriminant: 7 number of solutions: tpe: real, irrational ) discriminant: 0 number of solutions: tpe: real, rational 7) discriminant: number of solutions: tpe: imaginar Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 0 ~
11 ) discriminant: number of solutions: tpe: real, rational 9) discriminant: 7 number of solutions: tpe: imaginar 0) the second line of work, the negative must be in parentheses ( ) ( ) ( ) discriminant: # of solutions tpe: real, rational Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A (continued) ) a) 0000 = b) = 0 c) 90. d) Yes, the discriminant > 0, which ields two real solutions. Onl the positive solution would pertain to this stor. ) d = 977. Yes, the discriminant is greater than zero and ields two real solutions. ) d = 0,000. No, since discriminant < 0 there are no real solutions. ) a) b) c) real, rational d) = or = e) f) (, 9) g) minimum h) (0, ) i) all real numbers j) 9 ) a) Not a solution b) Solution ) a) Solution b) Not a solution ) a) Not a solution b) Not a solution SECTION.B ) a) b) c) real, rational d) =± e) f) (0, 9) g) maimum h) (0, 9) i) all reals j) 9 SECTION.A ) (test points ma var) Use (0, 0) Is 0? No, so points outside the parabola are solutions. ) D ) discriminant = solutions, real, irrational ) discriminant = 0 solution, real, rational ) discriminant = imaginar solutions 7) a) negative discriminant b) zero discriminant c) positive discriminant ) Discriminant is a positive perfect square number real, rational solutions Possible equation: ( ) ( 7) = = + 0 (Answers ma var) ) (test points ma var) Use (0, 0) Is 0? Yes, so points outside the parabola are solutions. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
12 ) (test points ma var) Use (0, 0) Is 0>? No, so graph outside the parabola. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A 7) (continued) 0) ) 7) < ) 9) > 0) C ) A ) F ) E ) B ) D ) ) ) ) ) Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
13 ) a) When < or > b) << c) graph Unit Selected Answers SECTION.B ) < or > Function values are MORE than 0 above -ais 9) 0 > 0 < or > 0 Function values are MORE than 0 above -ais ) a) << b) < or > c) graph ) 0 or Function values are MORE than 0 above -ais 0) + 7 < 0 <<9 Function values are LESS than 0 below -ais ) Answers will var, but -intercepts and concavit must match. Eample: 7) << - Function values are LESS than 0 below -ais - ) or Function values are MORE than 0 above -ais ) Answers will var, but -intercepts and concavit must match. Eample: ) ) < < Function values are LESS than 0 below -ais Function values are LESS than 0 below -ais Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
14 ) $0<<$00 (line is dashed) -intercepts are 0, 00 and verte is at (0, 00) ) seconds -intercepts are at and, verte is at (, ) Unit Selected Answers SECTION. B (continued) ) a) 0.0 ft and. ft. The -intercepts are at.0 and. and the verte is at (.,.7) b) No. From feet awa, the height of the ball would be 9. feet, so the ball would go over the top of the net. Also, from the graph and algebraic solution inequalities above, is not in the correct ranges (eplanations ma var). ) inches. Values in the range are etraneous. -intercepts are at and, the verte is at (0, -90) 7) Driver s age is between. ears and 70 ears (inclusive on 70). ) Answers will var a) There is no -term, such as = or if it is in verte form, like ( ) + = 0 b) If it is unfactorable and a = and b is even c) a, b, c are all integers and are fairl small numbers d) If it is unfactorable and a, b, and c are larger numbers and/or decimals. ) Answers ma var Suggest A, J and K for square root method Suggest B, F and I for factoring Suggest C, D, and E for completing the square Suggest G, H and L for quadratic formula Unit Review Material ) a) =± b) =± c) = or = ) a) = 0± b) =± c) = or = ) a) = or = b) = or = c) = ) a) = ± b) = ± c) = or = 7) a) = ± b) = or = c) = ± d) = 7± ) t = seconds 9). seconds 0) a) Disc. is negative. There are two imaginar solutions. b) Disc. is zero. There is one real, rational solution. c) Disc. is positive. There are two real solutions. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
15 ) a) Disc. is. There are two imaginar solutions. b) Disc. is. There are two irrational solutions. c) Disc. is 0. There is one real, rational solution. ) B ) << Unit Selected Answers Unit Review Material (continued) ) Algebraicall find the -intercepts. Sketch the graph of a parabola that has these -intercepts and opens up if a > 0 or down if a < 0. Also determine dashed or solid line. Identif the -values for which the graph lies below the -ais (#a) or above (or on) the -ais (#b). For or include the -intercepts in the solution. ) a) << Function values less than 0 (below -ais) b) or Function values are 0 (on or above the -ais) ) Graph B 7) or Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
16 . a) <.9, >. b).9 < <. c) (.9,.) Relative Ma (., 0.7) Relative Min These occur at turning points d) (, 0), (0, 0), (, 0) e) (0, 0) f) none. a) i) ii) iii) iv) b) If a is positive, the ends have a positive slope If a is negative, the ends have a negative slope c) The all either look like or. Some have more of a squiggle in the middle, with relative maimums and minimums. The differ in the number of times each graph crosses the -ais (answers ma var).. a) The are all using different windows, so the are seeing different portions of the graph. (answers ma var) b) Meng s is the best because ou can see all the ke features: ma, min, intercepts, end behavior. (answers ma var). Sign: Positive Domain:R Range: R Rel Min: appro. (0.,.) Rel Ma: (., ) Increasing: <. and > 0. Decreasing:. < < 0. -int(s): ( 7, 0), (, 0), (, 0) -int: appro. (0,.). Sign: Negative Domain:R Range: R Rel Min: appro. (.,.) Rel Ma: (0, ) Increasing:. < < 0 Decreasing: <. and > 0 -int(s): (, 0), (, 0), (, 0) -int: appro. (0, ) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A. Sign: Positive Domain:R Range: R Rel Min: appro. none Rel Ma: none Increasing: R Decreasing: none -int(s): (0, 0) -int: appro. (0, 0) 7. Table # # # # = (,0) (0,0) (,0) (,0) (7,0) (,0) = (0,-.) (0,0) (0,) Ma (., ) (,) None Min (., 7) (,0) None Inc <.<<. > None Dec <. Dec. over << >. entire dom. Continued # # # (, 0) (0,0) (., 0) (, 0) (9, 0) (0,0) (0, ) (0,.7) None (., 7) (., 9.) None (., 0.9) (.,.) Inc. over entire dom. None >. <..<<..<<. <. >.. Eplanations will var. a) Yes if before ear 99 the number of acres was less than 7,0 and declining each previous ear, then the end behavior would be ( ) b. Yes if sometime after 99 the number of bales was > 900 thousand and increasing each succeeding ear, the end behavior would then be ( ). Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
17 . c) Yes if before the ear 99 the ield per acre was <. thousand and decreasing each previous ear, the end behavior would then be ( ). Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A (continued) 9. Answers will var but will all be of the form =. 0. Answers will var but will all be of the form =.. Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: (.9,.0) Rel Ma: (.9, 7.0) Inc: <.9 and >.9 Dec:.9 < <.9 -int(s):(.9, 0),(0., 0),(., 0) -int(s): (0, ). Sign: Negative End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: none Rel Ma: none Inc: none Dec: R -int(s): (0., 0) -int(s): (0, ). Eplanations ma var. a determines the end behavior. If a > 0 the end behavior is ( ) and if a < 0 the end behavior is ( ). d is the -intercept.. Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: (.0,.) Rel Ma: (.0,.0) Inc: <.0 and >.0 Dec:.0 < <.0 -int(s): (, 0), (, 0), (, 0) -int(s): (0,.) SECTION.B. Sign: negative End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: (.,.) Rel Ma: (.,.) Inc:. < <. Dec: <. and >. -int(s): (, 0), ( 7, 0), (, 0) -int(s): (0,.). Eplanations ma var. The -intercepts occur at m, n, and p. The -intercept is ( )( )( ). a determines the end behavior. If a > 0 the end behavior is ( ), and if a < 0 the end behavior is ( ). 7. Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: none Rel Ma: none Inc: R Dec: none -int(s): (., 0) -int(s): (0, ). Sign: Negative End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel Min: none Rel Ma: none Inc: none Dec: R -int(s): (., 0) -int(s): (0, 0.) 9. Eplanations ma var. k moves the graph up and down; h moves the graph left and right. a stretches the graph. If a is negative, the graph alwas slopes down. If a is positive the graph alwas slopes up. There will be no maimum or minimum values. 0) Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range:. Rel. Min. (.9,.), (.,.9) Rel. Ma. (0, ) Inc:.9<<0,>. Dec: <.9,0<<. -int: (., 0), (, 0) -int: (0, ) Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 7 ~
18 ) Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range: R Rel. Min. ( 0.,.0), (.,.) Rel. Ma. (., 7.), (., 0.7) Inc: <., 0.<<.,>. Dec:.<< 0.,.<<. -int: (., 0), (.7, 0), (., 0) -int: (0, ) ) Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range: Rel. Min: (, ) Rel. Ma: None Inc: > Dec: < -int: (0., 0), (., 0) -int: (0,.) ) Sign: Positive End: ( ) Domain: R Range:.9 Rel. Min: (.,.), (.9,.9) Rel. Ma: (, 0) Inc:. < <, >.9 Dec: <., < <.9 -int: (, 0), (, 0), (, 0) -int: (0,.) ) Eplanations ma var. Even degree: end behavior is either ( ) or ( ). Odd degree: end behavior is either ( ) or ( ). ) a) 7.9 million ft when t =, since 990 is ears after 97. b) Increasing. Eplanations ma var, but graph is alwas increasing on this interval. c) No. When 0 < t <, S increases each ear. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.B (continued) ) d) Domain: 0 where t is the number of ears since 97. Range: S is the retail space (in millions of ft ) over that time period. ) a) Domain: 0, Number of ears from 90 to 00. Range: $7.70 $0.99, monthl rate for cable TV in that time period. b) In the ear 00, the maimum rate was $.0 (.,.0). After that, the rates decrease over time Not the case! For 0 this model would ield a rate of $ per month! c) 0, cable TV rates were alwas increasing from 90 to 00. d) When t >., indicating the rates started declining in the ear 00. e) ()=$. 7) Eplanations ma var a) L() = 0.7 in. H() =. in. 0.7 < normal height <. b) No. After a certain age, a heifer does not get an taller. c). mo. < age <. mo. Draw a horizontal line = and use Calc. Intersect on both curves L(.) = and H(.) =. d) At the point of inflection, the increasing height starts to level off before the graph starts to increase again. This occurs when the height is near ", so probable age would be 0 mo. < age <. mo. ) Eplanations ma var a) Domain: 0 < < Width > 0 and > 0 < Range: 0 < V < 9.07 Volume > 0, and within given domain the ma. volume is 9.07 b) 9 in within the acceptable domain 0 < <. The ma volume occurs at (., 9.07) c) Approimatel. in 9) Eplanations ma var. a) -int. = 0. The roller coaster is 0 ft. above ground before it starts a certain portion of the track. b) Yes. (0, ) => after 0 seconds the roller coaster reaches its maimum height of feet. c) Yes. (0, 0) => After 0 seconds the roller coaster returns to a height of 0 feet. d) No. The height never equals 0 after the coaster begins rolling. e) H() =.. After seconds the roller coaster has reached a height of. feet above the ground. f) At t = 0 seconds and at t =. seconds. The roller coaster s height of feet is obtained twice during the ride once on the wa up and once again on its wa down. At t = 77 the height is again feet, but the roller coaster ride lasts 0 seconds. 77 seconds is not part of the domain. g) After 0 seconds the height of the coaster is continuall increasing to. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
19 Unit Selected Answers SECTION.B 0) a) mg b) das c) Domain: 0 after das the drug is completel out of the patient s bloodstream ( = 0) Range: 0 (). mg is the original amount of the drug in the patient s bloodstream which lessens each hour afterwards. (Eplanations for 0c ma var) SECTION.A ) C ) A ) B ) B ) A ) B 7) a) True b) False: +9 = c) False: ( ) = ) True: Using the power of a power rule, =. B the commutative propert of multiplication, ab = ba. 9) False: using power of a power rule ( ) = = 0) ) 0 ) ) 9 ) ) ) Jamal added and, which are not like terms. The correct answer is 9 Precious also added unlike terms and. She had a second error when she added + to get. Those eponents don t combine. The correct answer is + +. Kiarra used the distributive propert incorrectl. ( + 7)= +7. The correct answer is +7 ) Eplanations ma var Thao used the product propert of powers incorrectl. He multiplied and to get. It should be. Similarl, he multiplied and to get. It should be. The correct answer is + + Louis mied up the +/ smbols when combining 7 and to get 0 instead of. The correct answer is +. SECTION.B ) 7 + ) + ) 0 7 ) ) 7 7) 9+ ) ) + 0) 7 + ) a + 7b ) + z ) p q ) 7 + ) + + SECTION.C Monique didn t distribute the over the last two terms. The correct answer is +. ) 0 + ) ) ) +7 ) + 7) ) +0+ 9) ) + 0 ) = +9 7) + ) + 9) + 0) ) 0 meters ) ()=0. +7+,0 ) +0 ) ++ ) a) b) c) d) 7 e) ) + + ) = int. = ) =9 +9 -int. = 9 ) = int. = ) = + + -int. = ) = ++ -int. = 7) = +7 -int. = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 9 ~
20 ) Eplanations ma var a) The end behavior is determined b looking at the degree (the highest eponent, which should be the first term) and the leading coefficient. b) The -intercept is the constant, or last term in standard form. 9) Eplanations ma var a) 7.; In 99 the average amount of bananas (in pounds) eaten per person in the US was 7.. b) Increasing pounds of bananas consumed per person from 99 to 99, then decreasing from 99 to 000. ) + 7 Yes, ( + 9) is a factor. ) No, ( ) is not a factor. ) + + No, ( + ) is not a factor. ) 9 + No, ( ) is not a factor. ) + Yes, ( ) is a factor. ) No, ( + ) is not a factor. 7) Yes, ( ) is a factor. ) No, ( ) is not a factor. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.C 0) a) ( ) b) $,79,90,000 c) -intercept ) Width = feet Length = 0 feet ) a) (continued) R t = 0.7t +.t +.7t ( ) R t = , 000 b) (0)=$ 0,000 c) Yes; negative number for revenue means the costs were higher than the sales (which was $0) (eplanations ma var) ) = 0 ) 0 + ) 0 7 ) = + SECTION.D 9) + Yes, ( ) is a factor. 0) #7 and #9; the divisor is a factor of the dividend. ) Lisa is correct, ecept to write the quotient: + + Maut is missing a place holder for the linear () term. The correct quotient for his problem: Craig is used for the outside value and should have used a value of (the value that creates a zero value for the divisor. The correct quotient for his problem: 7) ( n ) n = n + 0 n = ( n 7 + 0) n = n n = = ) a) b) c) 7 d) 9) ) + + ) Eplanations ma var. The number of bags of various flavored chips times the price per bag gives the amount of mone collected from the sales. ) ( ) is the length of the rectangular garden. ) ( ) + is the base of the triangle. ) ( ) is the width of the mural. ) a) ( + ) b) B is the divisor, located in the denominator of the remainder fraction. c) A = + ) One eample would be ( + ) ( ) 7) One eample would be: ( + ) ( ) Snthetic division can onl be used when the divisor is a binomial with degree, like ( c) Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 0 ~
21 ) a) There are distinct linear factors, which ield -intercepts at, 0, 0, and, 0. ( ) ( ) ( ) b) There is one duplicate linear factor which gives a double root at = (but onl one -intercept here) and the other linear factor ields the -intercept at, 0. ( ) c) There are distinct linear factors which ield -intercepts at, 0 (, 0 ), and ( 0, 0 ) ) zero, root, solution ) algebraicall: set the function equal to zero (0) and solve for. ) a) Real zeros: = 0,, Factors: ( + 0) ( + ) ( ) Possible equation: = b) Real zeros: = (double root), ( ) ( ) ( ) Factors: ( + ) ( + ) ( ) Possible equation: = + + c) Real zeros: = 7,, ( ) ( ) ( ) Factors: ( + 7) ( + ) ( ) Unit Selected Answers SECTION.E graphicall: look for the -intercept(s) and/or use a graphing calculator to calculate the zeros. ) No; there is a remainder value different than zero. ) No; there is a remainder of. If ( ) was a factor, there would be a zero value for a remainder. ) Yes; because the remainder is zero, this means that ( + ) is a factor of the polnomial, which means = is a zero (or solution). 7) No; the remainder is (not zero) so = is not a zero. ) k = 9) k = 0 f = + 0) ( ) ( ) ( ) SECTION.A ) a) (, 0 ),(, 0 ), (, 0 ) b) (.79, 0 ), (.7, 0 ), (.9, 0) c) ( 0., 0 ), (., 0 ), ( 9, 0 ) d) (, 0) ) a) = b) =.09, 0.9, or c) =,, or d) =, or P = + ) ( ) ) a) = ( )( + ) ( + ) b) = ( + ) ( ) ( ) c) = ( + ) ( ) d) = ( + ) ( + )( ) ) a) = ( ) ( + ) ( + ) b) = ( + ) ( ) ( ) c) = ( 9 + ) ( )( + ) d) = ( + ) ( + ) ( ) e) = ( ) ( + ) ( + ) f) = ( + ) ( ) ( + ) ) a) Height: ( 0) Width: ( + ) b) length: ( + ) height: ( + ) ) Height: feet Width: feet Length: 0 feet ) Height:. feet Width:. feet Length:. feet ) The will need to sell 0 cars 7) = 0 meters or = meters Possible equation: = ( + 7) ( + ) ( ) SECTION.B ) a) Yes; Jebediah knows he -values (solutions) where = Jebediah can find the -intercepts =. = 0 (solutions) where the b) Yes; both are effectivel = value equals zero. solving a sstem of two Kalani = Kalani knows she can look equivalent equations b ) =,, at the intersection(s) of her graphing. ) =,., graphs to find the Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
22 ) = ) a) =.07,.9, or 7.7 b) =.7, 0.77, or.9 c) =.97 d) = 7.7,.0 or.9 ) a) =.07 or. b) =., 0.77, or.0 c) =., 0, 0.79 or.7 d) =.9,.,.0 or 7.0 7) There are situations that demonstrate there are a total of solutions: real solution, comple solutions (show a graph) real solutions ( of these being a double root), 0 comple solutions (show a graph) real solutions, 0 comple(show a graph) ) a) ± =, b) =, ± i c) = 0,, ± ) a) =,± b) =, ± c) = 0,, ± i ) a) =,, b) =, ± 7 c) =,, ± Unit Selected Answers ) a) Graph: b) In the ear 99 (.7 ears after 99). c) The average number of pounds equals. pounds three different times: When. ear 99 When.7 ear 997 When. ear 000 9) a).% b) % c) 7% 0) a) arrests; it is the -intercept b). ears after, so in the ear 00 c) In the ear 00 d) About ears after 990, so in the ear 0; this is represented b the -intercept SECTION.C ) a) ± 7 =, b) =, ± i c) ± i =, ) a) ± =, b) =,,± i 7 c) = (double root), ± ) a) =,, 0.7 b) =,.,0 c) =, ± i d) =, 0, 7 e) =,, f) =, ± i ) a) In the ear 0 and again in the ear 0 b) 9. million; this is a relative maimum for time after 970. c) When = 0. ears after 970, which is in the ear 07 ) 99 ) a) (, ),(, ), (, ) b) method : using the graphing method as shown here, the solutions are the -coordinates of the point(s) of intersection, so =,, method : solve this algebraicall. Using substitution, set the two epressions equal to each other: ( ) ( ) ( ) Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~ + = + + = = 0 =, =, = = 7) A cubic function alwas has solutions: Either real and imaginar solutions (show graph with -intercept) distinct real solutions (with one of them being a double root creating three solutions in total) (show graph with curve that crosses over the -ais and one section that has a verte that touches the -ais). real solutions (all different) (show graph with curve crossing over the -ais three distinct times).
23 ) a) Standard Form b) It is the -intercept c) ) a) d) Rel min: (., 0.) Rel ma: ( 0.7,.0) Domain: all real numbers b) Range: all real numbers Inc. int.: < 0.7, >. Decr. int.: 0.7 < <. Zero(s): (, 0 ), (, 0 ), (, 0) = + 7 = + 0 ) a) Intercept form or Factored form b) It brings forward the information for finding the -intercept c) Unit Selected Answers Unit Review Material d) Rel min: (.,.) Rel ma: ( 0., 0. ) Domain: all real numbers Range: all real numbers Inc. int.:. < < 0. Decr. int.: <., > 0. Zero(s): ( 0, 0 ), (, 0 ), (, 0) -intercept: ( 0, 0 ) ) a) It is similar to the verte form of a quadratic function, but this is a cubic function. b) It provides information about the inflection point. c) d) Rel min: none Rel ma: none Domain: all real numbers Range: all real numbers Inc. int.: < <, or R Decr. int.: none -intercept: (, 0) -intercept: ( 0,. ) ) a) + + b) 0 + c) + + d) e) f) + g) ) a) During month # b) 00 coats c) 0 coats d) >. e) 0 < <. f) no 70 7) a) f ( ) = ( + ) ( ) ( 7) b) f ( ) = ( ) ( ) ( + ) ) a) =,, b) =,, c) = 0,, d) =,, [(a) (d) the procedure for finding the rational zeros ma var.] 9) a) =,, b) =,, 0) ) a) b) ± i =,, ± i =,, ± =,, Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
24 . a) From the store, drive South on Aspen St Turn Right on Elm St Turn Left on Acorn St Go past one stop sign and turn Right/West on Hw 7 Travel mi to our home b) I drew a picture of the route TO the store and then followed it backwards. c) Reverse. a) b) c) ()= () d) ()= + e) An inverse function is the reverse process of a function; it undoes what a function does.. a) Pairs of Skates Additional Pa $0 0 $00 $0 $ $ $ b) The etra pa P() is times the # skate pairs sharpened. c) The number of pairs of skates N() is the etra pa. d) P() = ; If he sharpens pairs of skates, he will make $ additional pa. e) N() = ; If he made $ additional pa, he must have sharpened pairs of skates. f) The give the same results, backward. Unit 7 Selected Answers SECTION 7.A g) i) P() N() ii) The are reversed.. a) b) f() f - () c) - - d) No Each input () does not have eactl one output (). [e. (0, ) and (0, 0.)]. a) {(, ), ( 9, 9), (, 0), (, ), (0, 9)} b) Yes Each input () has onl one output ().. a) {(, ),(7, ),(, 0),(7, )} b) No the input 7 has two different outputs ( and ) 7. a) 0 g - () b) c) Yes Each input () has onl one output (). = = Yes the inputs () and outputs () are reversed. = = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
25 Yes the inputs () and outputs () are reversed. 0. a) 770 pounds b) It would tell us how much mone (in US dollars) we Unit 7 Selected Answers brought with us, given we received a known amount of British pounds. c) =. d) $9.. -Choose points on the graph. -Reverse the coordinates (, ) (, ) -Graph the new coordinates a) Values lower than would make a negative in the b) The smallest result would be 0, and then adding gives a minimum value of, so cannot be less than. c) Think about (guess/check) what #s can t work for and then #s that won t be results for. (see a) and b)) d) There are no points graphed with an -value before ; there are no points graphed with a -value less than. e) There are error s before = and no -values below =.. a) Equation Domain: > 7 Range: < Eplanation: an -value lower than 7 would make a neg. under the ; the greatest result is 0, and then subtracting gives a ma value of, so cannot be greater than. b) Graph Domain: > Range: > 7 Eplanation: There are no points graphed with an -value before ; there are no points graphed with a -value below 7. SECTION 7.B. c) Table of values Domain: > Range: > Eplanation: There are error s before = and no -values less than.. Milo is correct Basra appears to be thinking about the range.. [B]. [C]. [A] 7. Increasing Domain: > 0 Range: > -int: none -int: (0, ) Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~ Decreasing Domain: > Range: < -int: (, 0) -int: (0, ) Decreasing Domain: >
26 0. Range: < -int: none -int: (0, ). Unit 7 Selected Answers. Shifted Left and Down. Flipped Shifted Right and Up. Graph Number Beginning Point (0,0) (-,0) (, -) (-,) -intercept (0,0) (-,0) -intercept (0,0) (0,.) None (0,.) Inc./Dec. Dec. Inc. Inc. Dec. Domain > 0 > - > > - Range < 0 > 0 > - < Increasing Domain: > 0 Range: > 0 -int: (0,0) -int: (0,0). Increasing Domain: > Range: > -int: none -int: none. Domain: > Range: > 7. Domain: > Range: <. Answers ma var a) b) 70 c) 9 Increasing Domain: > Range: > -int: (, 0) -int: (0, 0.7). a) No ou can an number (pos or neg). b) No since can be anthing and could be anthing, adding could lead to an #. c) (, ) d) The -coordinate is the result of setting what is under the radical equal to zero and then solving for ; the -coordinate is the value of the constant added/subtracted outside the. e) Increasing it is a positive. SECTION 7.C. a) Increasing Domain: Range: Point of Inflection: (, ) b) Decreasing Domain: Range: Point of Inflection: (, ). Neither should be (, 0) Arturo didn t set what is under the radical equal to zero and then solving for. Kira has the and switched Decreasing Domain: Range: Point of Inflection: (0, 0) - - Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
27 Increasing Domain: R Range: R Point of Inflection: (, ) Increasing Domain: R Range: R Point of Inflection: (0, ) Unit 7 Selected Answers Decreasing Domain: R Range: R Point of Inflection: (, ) Decreasing Domain: R Range: R Point of Inflection: (, ) [C]. [A]. [B]. a) Answers will var: Graph: Identif where the curve changes from a hill to a bowl. Table: Look for a set of three -values that are the same distance apart; the inflection point is the middle of these three. Equation: The -coord. is calculated b setting what is under the radical equal to zero and then solving for ; the -coordinate is the number added/subtracted outside the. b) Answers will var: Graph: Look left to right to see if it is going uphill or downhill Table: Look to see if -values increase or decrease (as -values increase.) Equation: Look for the sign on the number in front of the ; positive is increasing, negative is decreasing.. Increasing, (7, ). Decreasing, ( 9, 0). Shifted Left, Down 7. Flipped; Shifted Right, Up Increasing Domain: R Range: R Point of Inflection: (, ) - -. Graph Number Point of Inflect. (-,) (-,) (,0) (0,-) -intercept (0,.) (0,) (0,.) (0,-) Inc/Decreasing Dec. Inc. Dec. Inc. 9. Answers will var: a) = ++ b) = c) = +9 Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 7 ~
28 . [A]. [C]. [A]. [B]. [A]. [C] 7. a) False: should= b) True c) False: should= d) True e) False: should= f) False: should=. Katiana ( ) = = 9. a) b) c) 0 d) an real number ecept 0 0. Sarah made an error when simplifing the denominator in Line : the eponent should have gone to the p and d, not the q. The denominator should simplif to and a final answer of p q Unit 7 Selected Answers SECTION 7.A. Trell also made an error in Line : should simplif to (not ). The final answer should be.. Answers will var: -Simplif: ( ) to So: -Simplif s in numerator: = So: -Reduce numbers: = -Simplif s: = -Simplif s: = = -Final Answer:. Yes Variable parts match so the are like terms = k p c p 9 r 9b z 9. [H]. [B]. [D]. [E]. [G]. [A] 7. [F]. [C] 9. [C] 0. [B]. No Eponent is NOT neg, so eponent should not be moved to denominator. Ans = 7. Yes. Yes. No. Ans =. Yes. Never:. Alwas. Alwas. Never: = 7. Sometimes. Sometime 7. Sometimes is not real. Yes SECTION 7.B 7. No: =. [D] 9. [C] 0.. () / or / /. ( ) fg = f g ; ( ). b. ( ) + c ; cannot be simplified since there is no power of a sum eponent propert. SECTION 7.C # - #7: Since the radical on the left side of the equation has an even root, the answer must be greater than or equal to zero. However, the right side of the equation has a variable to an odd power, which could be d people.,770mm. True: / = / 7. False: = is not real either a positive or a negative answer.. Alwas /. h Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
29 Unit 7 Selected Answers. [A], [C], and [D] require absolute value smbols around one of the variables... in.. ft. 0. cm. cm 7. cm. 0..% ANSWER KEY = b Quiz grade: /0 Incorrect: (,,,, 7,, 9, 0). Neither Jerome nor Cambria have correct answers: ( ) SECTION 7.D = ( ) which is not a real number. ( ) =,79,7,7.? =.? =. no number possible to replace the question mark.? =.? = 7.? = z a / 9 k... / Over trillion ears. a) Intersection at (, ); = b) Intersections at (, 0) and (, ); = or = c) Intersections at (, ) and (, ); = or = d) No intersections; No Real Solutions e) Intersection at (, ); = f) Intersection at (., ); =. SECTION 7.A. a) = b) = c) =0.07 or =.9 d) =. e) = f) = or = g) = or = h) No Real Solution i) = ft. 9. million km. a). km/hr b) 0.0 km. a).9 sec b).0 ft 7. No If the graphing calculator ields decimal solutions that do not terminate or repeat, the solutions (irrational) can be found algebraicall.. = 9; Yes, one intersection on graph at = 9. = ; Yes, one intersection on graph at =. = ; NO, graphs do not intersect so NO REAL SOLUTION. = or = ; Yes, two ints on graph at = and = SECTION 7.B. = 7 or = -; No, onl one intersection at = 7 so = is etraneous.. = ; Yes, one intersection on graph at = 7. = 0; Yes, one intersection on graph at = 0. = or = ; Yes, two ints on graph at = and = 9. For problem #, when =, the check ields =. This is a false sentence therefore the value of is not a solution to the equation. For problem #, when =, the check ields =. This is a false sentence therefore the value of is not a solution to the equation. Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 9 ~
30 0. a) Graphicall: The graphs do not intersect for the etraneous -value. b) Algebraicall: A solution comes out of the work but doesn t check so is not a true solution.. Serge did the problem correctl. Jerem needed to subtract BEFORE squaring both sides. Ind did the problem correctl. Latishia did the work correctl but did not check for etraneous solutions; = is Unit 7 Selected Answers etraneous. Sango squared ( ) incorrectl; ( ) = ( ) ( ) not. =. n = 77. No real solution. No real solution 7. = 7. = 9. = 0. =. r =. No real solution. =. = ±. d = ±. b = 0 7. = : Answers ma var. graphicall 9. algebraicall 0. graphicall. algebraicall. algebraicall. algebraicall. Answers will var: +=. h 0.. a) f = 0 gallons/min b) p = 0,000 lbs/in 7. t. ; It would take. hours.. =. mi. a) Domain: > 0 Range: > 0 b) c) Unit 7 - Review Domain: > 0 Range: > e) Domain: > 0 Range: < Domain: > Range: > 0 d) Domain: > Range: > Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page 0 ~ f) Domain: > Range: <
31 . Answers ma var:. a) + Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (0, 0) b) Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (, 0) c) Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (0, ) d) Unit 7 Selected Answers Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (, ) e) Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (0, 0) f) Domain: Range: Inflection Point: (, ) i /.. 7. a. 9. ft 0. 0,7 people. =. = or =. = 7. = or = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
32 . Opens: Up Ais: = Verte: (, ). Opens: Down Ais: = Verte: (, ). Opens: Up Ais: = Verte: (, ). Opens: Down Ais: = Verte: (, ). Opens: Down Ais: = Verte: (, ). Opens: Up Ais: = Verte: (, ) Domain: = R Range: > Domain: = R Range: > Unit Selected Answers SECTION.A Domain: = R Range: > Domain: = R Range: < Domain: = R Range: <. 0 - Domain: = R Range: <. Domain: = R Range : > Verte: (, 0) Opens: Up Domain: = R Range: > 0 Steepness: m = ± Verte: (, 0) Opens: Up Domain: = R Range: > 0 Steepness: m = ±. Both have a in the absolute value bars with the. 7. # has the multiplier of inside the absolute values bars; # has the multiplier outside the absolute value bars.. When the is on the inside, it influences the -coordinate of the verte b dividing the b a factor of. 9. [equation B] 0. [D]. = +, > =, < Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
33 .. Unit Selected Answers SECTION.B Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
34 .. Unit Selected Answers. [B] and [D]. Answers ma var. a. b. > c. 7. [C]. [B] 9. [A] 0. [D] Domain: = R Range: = R Domain: = R Range: > 0. Graphical Solution SECTION.A. Graphical Solution. Graphical Solution Algebraic Solution = = Algebraic Solution = = Algebraic Solution < <. Graphical Solution 0. Graphical Solution 0. Graphical Solution Algebraic Solution = = Algebraic Solution = = Algebraic Solution < or > Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
35 7. Graphical Solution Unit Selected Answers 9. Graphical Solution {all REAL numbers} 7. < <. a) Answers will var:,.,.,.9,. b) Algebraic Solution < or > 0 Algebraic Solution < < c). < <. d) 0.. Graphical Solution 0. 0 < < 9. a) Answers will var: 0,,, 7, 7 b) Algebraic Solution < < 0. > 9 or <.. < <. < < c) < or > 7 d) > 0. a) Answers will var:,,.,, b) c) < < d)... < or > 0 Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
36 Unit Selected Answers. a) Up b) (, ) c) = d) ±. Unit - Review. = = 0 9. > or < < < a) 0 < < 70 b) 0 0. a) 7.7 < <. b) <0.. a) Down b) (, ) c) = - d) ± Answers ma var: = Answers ma var: = = = Answers Intermediate Algebra (B) ~ page ~
Unit 4 Practice Problem ANSWERS
 Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
CHAPTER 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
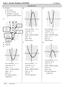
Algebra II Notes Unit Five: Quadratic Functions. Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technology.
 Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
3.1 Graph Quadratic Functions
 3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
d. 2x 3 7x 2 5x 2 2x 2 3x 1 x 2x 3 3x 2 1x 2 4x 2 6x 2 3. a. x 5 x x 2 5x 5 5x 25 b. x 4 2x 2x 2 8x 3 3x 12 c. x 6 x x 2 6x 6 6x 36
 Vertices: (.8, 5.), (.37, 3.563), (.6, 0.980), (5.373, 6.66), (.8, 7.88), (.95,.) Graph the equation for an value of P (the second graph shows the circle with P 5) and imagine increasing the value of P,
Vertices: (.8, 5.), (.37, 3.563), (.6, 0.980), (5.373, 6.66), (.8, 7.88), (.95,.) Graph the equation for an value of P (the second graph shows the circle with P 5) and imagine increasing the value of P,
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Study Guide and Intervention
 6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
y = f(x + 4) a) Example: A repeating X by using two linear equations y = ±x. b) Example: y = f(x - 3). The translation is
 Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Course 15 Numbers and Their Properties
 Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
For Thought. 3.1 Exercises 142 CHAPTER 3 POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. 1. False, the range of y = x 2 is [0, ).
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
Copyrighted by Gabriel Tang B.Ed., B.Sc. Page 1.
 Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions -: Points and Lines Sstem of Linear Equations: - two or more linear equations on the same coordinate grid. Solution of
Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions -: Points and Lines Sstem of Linear Equations: - two or more linear equations on the same coordinate grid. Solution of
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
Math 121. Practice Questions Chapters 2 and 3 Fall Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint.
 Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Unit 3 NOTES Honors Common Core Math 2 1. Day 1: Properties of Exponents
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards. An equation that contains an absolute value expression
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Advanced Algebra 2 Final Review Packet KG Page 1 of Find the slope of the line passing through (3, -1) and (6, 4).
 Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
Algebra II Notes Unit Six: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6.2 The student will simplify polynomial expressions.
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences
 Lesson 7.1 Polnomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identif the degree of each polnomial. a. 1 b. 0. 1. 3. 3 c. 0 16 0. Determine which of the epressions are polnomials. For each polnomial, state its
Lesson 7.1 Polnomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identif the degree of each polnomial. a. 1 b. 0. 1. 3. 3 c. 0 16 0. Determine which of the epressions are polnomials. For each polnomial, state its
CHAPTER 3 Polynomial Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS. A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts. Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra
 COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra [A teacher prepared compilation of the 7 Algebraic concepts deemed
COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra [A teacher prepared compilation of the 7 Algebraic concepts deemed
Algebra 2 Unit 2 Practice
 Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
MATH 152 COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 0//0 MATH COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions Be sure to write out all our work, because method is as important as getting the correct answer. The answers to
0//0 MATH COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions Be sure to write out all our work, because method is as important as getting the correct answer. The answers to
Math Analysis Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Name Period Date. Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (50 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit!
 Name Period Date Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (0 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit! ) Evaluate the algebraic epression for the given value or values of the variable(s).
Name Period Date Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (0 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit! ) Evaluate the algebraic epression for the given value or values of the variable(s).
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
Graphing Calculator Computations 2
 Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
Ch 5 Alg 2 L2 Note Sheet Key Do Activity 1 on your Ch 5 Activity Sheet.
 Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus
 Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
x Radical Sign: Radicand: the number beneath the radical sign
 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing.
Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing.
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f(x) = x Example 1
 TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
One of your primary goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan.
 PROBLEM SOLVING One of our primar goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan. Step Step Step Step Understand the problem. Read the problem
PROBLEM SOLVING One of our primar goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan. Step Step Step Step Understand the problem. Read the problem
Honors Pre-Calculus. Multiple Choice 1. An expression is given. Evaluate it at the given value
 Honors Pre-Calculus Multiple Choice. An epression is given. Evaluate it at the given value, (A) (B) 9 (C) 9 (D) (E). Simplif the epression. (A) + (B) (C) (D) (E) 7. Simplif the epression. (A) (B) (C) (D)
Honors Pre-Calculus Multiple Choice. An epression is given. Evaluate it at the given value, (A) (B) 9 (C) 9 (D) (E). Simplif the epression. (A) + (B) (C) (D) (E) 7. Simplif the epression. (A) (B) (C) (D)
6.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing Algebra 2
 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
2.1 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial
 2. Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Georgia Performance Standard(s) MM3Ab, MM3Ac, MM3Ad Your Notes Goal p Evaluate and graph polnomial functions. VOCABULARY Polnomial Polnomial function Degree of
2. Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Georgia Performance Standard(s) MM3Ab, MM3Ac, MM3Ad Your Notes Goal p Evaluate and graph polnomial functions. VOCABULARY Polnomial Polnomial function Degree of
MATH 110: FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
Chapter 8 Vocabulary Check
 28 CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations and Functions d. What is the level of methane emissions for that ear? (Use our rounded answer from part (c).) (Round this answer to 2 decimals places.) Use a graphing calculator
28 CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations and Functions d. What is the level of methane emissions for that ear? (Use our rounded answer from part (c).) (Round this answer to 2 decimals places.) Use a graphing calculator
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question
 Midterm Review 0 Precalculu Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question ) A graph of a function g is shown below. Find g(0). (-, ) (-, 0) - -
Midterm Review 0 Precalculu Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question ) A graph of a function g is shown below. Find g(0). (-, ) (-, 0) - -
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 0390) Final Exam Oct 2009
 Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Math Intermediate Algebra
 Math 095 - Intermediate Algebra Final Eam Review Objective 1: Determine whether a relation is a function. Given a graphical, tabular, or algebraic representation for a function, evaluate the function and
Math 095 - Intermediate Algebra Final Eam Review Objective 1: Determine whether a relation is a function. Given a graphical, tabular, or algebraic representation for a function, evaluate the function and
Unit 2 Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring
 Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Polynomial Functions. INVESTMENTS Many grandparents invest in the stock market for
 4-1 BJECTIVES Determine roots of polnomial equations. Appl the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Polnomial Functions INVESTMENTS Man grandparents invest in the stock market for their grandchildren s college
4-1 BJECTIVES Determine roots of polnomial equations. Appl the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Polnomial Functions INVESTMENTS Man grandparents invest in the stock market for their grandchildren s college
College Algebra ~ Review for Test 2 Sections
 College Algebra ~ Review for Test Sections. -. Find a point-slope form for the equation of the line satisfing the conditions. ) a) Slope -, passing through (7, ) b) Passing through (-, -8) and (-, ) Write
College Algebra ~ Review for Test Sections. -. Find a point-slope form for the equation of the line satisfing the conditions. ) a) Slope -, passing through (7, ) b) Passing through (-, -8) and (-, ) Write
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM
 Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
Northwest High School s Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2
 Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing
 www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
Lecture Guide. Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra. Stephen Toner. Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition. Miller, O'Neill, & Hyde. Victor Valley College
 Lecture Guide Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra to accompan Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition Miller, O'Neill, & Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Last updated: 11/24/10 0 1.1 Sets of Numbers
Lecture Guide Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra to accompan Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition Miller, O'Neill, & Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Last updated: 11/24/10 0 1.1 Sets of Numbers
MATH 115: Final Exam Review. Can you find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (1.1)
 MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
Polynomials and Polynomial Functions
 Unit 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objectives: SWBAT identify polynomial functions SWBAT evaluate polynomial functions. SWBAT find the end behaviors of polynomial
Unit 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objectives: SWBAT identify polynomial functions SWBAT evaluate polynomial functions. SWBAT find the end behaviors of polynomial
 Eam Name algebra final eam review147 aam032020181t4highschool www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation.
Eam Name algebra final eam review147 aam032020181t4highschool www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation.
Intermediate Algebra 100A Final Exam Review Fall 2007
 1 Basic Concepts 1. Sets and Other Basic Concepts Words/Concepts to Know: roster form, set builder notation, union, intersection, real numbers, natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers,
1 Basic Concepts 1. Sets and Other Basic Concepts Words/Concepts to Know: roster form, set builder notation, union, intersection, real numbers, natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers,
Mathematics 2201 Midterm Exam Review
 Mathematics 0 Midterm Eam Review Chapter : Radicals Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Chapter 7: Quadratic Equations. Evaluate: 6 8 (A) (B) (C) (D). Epress as an entire radical. (A) (B) (C) (D). What is the
Mathematics 0 Midterm Eam Review Chapter : Radicals Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Chapter 7: Quadratic Equations. Evaluate: 6 8 (A) (B) (C) (D). Epress as an entire radical. (A) (B) (C) (D). What is the
6 p p } 5. x 26 x 5 x 3 5 x Product of powers property x4 y x 3 y 2 6
 Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Mth Quadratic functions and quadratic equations
 Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
ALGEBRA 2 NY STATE COMMON CORE
 ALGEBRA NY STATE COMMON CORE Kingston High School 017-018 emathinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 1571, 015 Table of Contents U n i t 1 - Foundations of Algebra... 1 U n i t - Linear Functions, Equations, and their
ALGEBRA NY STATE COMMON CORE Kingston High School 017-018 emathinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 1571, 015 Table of Contents U n i t 1 - Foundations of Algebra... 1 U n i t - Linear Functions, Equations, and their
Unit 10 - Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
H.Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet
 H.Algebra Summer Review Packet 1 Correlation of Algebra Summer Packet with Algebra 1 Objectives A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Use the commutative, associative,
H.Algebra Summer Review Packet 1 Correlation of Algebra Summer Packet with Algebra 1 Objectives A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Use the commutative, associative,
3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities
 3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities Quadratic Functions: Quadratic functions are polnomial functions of the form also be written in the form f ( ) a( h) k. f ( ) a b c. A quadratic function ma Verte
3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities Quadratic Functions: Quadratic functions are polnomial functions of the form also be written in the form f ( ) a( h) k. f ( ) a b c. A quadratic function ma Verte
Coached Instruction Supplement
 Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 8 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 8 679NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 8 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 8 679NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
5. Determine the discriminant for each and describe the nature of the roots.
 4. Quadratic Equations Notes Day 1 1. Solve by factoring: a. 3 16 1 b. 3 c. 8 0 d. 9 18 0. Quadratic Formula: The roots of a quadratic equation of the form A + B + C = 0 with a 0 are given by the following
4. Quadratic Equations Notes Day 1 1. Solve by factoring: a. 3 16 1 b. 3 c. 8 0 d. 9 18 0. Quadratic Formula: The roots of a quadratic equation of the form A + B + C = 0 with a 0 are given by the following
College Algebra ~ Review for Test 2 Sections
 College Algebra ~ Review for Test Sections. -. Use the given graphs of = a + b to solve the inequalit. Write the solution set in interval notation. ) - + 9 8 7 6 (, ) - - - - 6 7 8 - Solve the inequalit
College Algebra ~ Review for Test Sections. -. Use the given graphs of = a + b to solve the inequalit. Write the solution set in interval notation. ) - + 9 8 7 6 (, ) - - - - 6 7 8 - Solve the inequalit
Algebra 2 Honors Summer Packet 2018
 Algebra Honors Summer Packet 018 Solving Linear Equations with Fractional Coefficients For these problems, ou should be able to: A) determine the LCD when given two or more fractions B) solve a linear
Algebra Honors Summer Packet 018 Solving Linear Equations with Fractional Coefficients For these problems, ou should be able to: A) determine the LCD when given two or more fractions B) solve a linear
review math0410 (1-174) and math 0320 ( ) aafinm mg
 Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
Law of Sines, Law of Cosines, Heron s Formula:
 PreAP Math Analsis nd Semester Review Law of Sines, Law of Cosines, Heron s Formula:. Determine how man solutions the triangle has and eplain our reasoning. (FIND YOUR FLOW CHART) a. A = 4, a = 4 ards,
PreAP Math Analsis nd Semester Review Law of Sines, Law of Cosines, Heron s Formula:. Determine how man solutions the triangle has and eplain our reasoning. (FIND YOUR FLOW CHART) a. A = 4, a = 4 ards,
SEE the Big Idea. Quonset Hut (p. 218) Zebra Mussels (p. 203) Ruins of Caesarea (p. 195) Basketball (p. 178) Electric Vehicles (p.
 Polnomial Functions.1 Graphing Polnomial Functions. Adding, Subtracting, and Multipling Polnomials.3 Dividing Polnomials. Factoring Polnomials.5 Solving Polnomial Equations. The Fundamental Theorem of
Polnomial Functions.1 Graphing Polnomial Functions. Adding, Subtracting, and Multipling Polnomials.3 Dividing Polnomials. Factoring Polnomials.5 Solving Polnomial Equations. The Fundamental Theorem of
Characteristics of Quadratic Functions
 . Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Essential Question What tpe of smmetr does the graph of f() = a( h) + k have and how can ou describe this smmetr? Parabolas and Smmetr Work with a partner. a. Complete
. Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Essential Question What tpe of smmetr does the graph of f() = a( h) + k have and how can ou describe this smmetr? Parabolas and Smmetr Work with a partner. a. Complete
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
Visit us at: for a wealth of information about college mathematics placement testing!
 North Carolina Early Mathematics Placement Testing Program, 9--4. Multiply: A. 9 B. C. 9 9 9 D. 9 E. 9 Solution and Answer to Question # will be provided net Monday, 9-8-4 North Carolina Early Mathematics
North Carolina Early Mathematics Placement Testing Program, 9--4. Multiply: A. 9 B. C. 9 9 9 D. 9 E. 9 Solution and Answer to Question # will be provided net Monday, 9-8-4 North Carolina Early Mathematics
a 2 x y 1 x 1 y SOL AII.1a
 SOL AII.a The student, given rational, radical, or polnomial epressions, will a) add, subtract, multipl, divide, and simplif rational algebraic epressions; Hints and Notes Rules for fractions: ) Alwas
SOL AII.a The student, given rational, radical, or polnomial epressions, will a) add, subtract, multipl, divide, and simplif rational algebraic epressions; Hints and Notes Rules for fractions: ) Alwas
LESSON #1 - BASIC ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #1 - BASIC ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarif concepts and remove ambiguit from the analsis of problems. To achieve
1 LESSON #1 - BASIC ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarif concepts and remove ambiguit from the analsis of problems. To achieve
C H A P T E R 3 Polynomial Functions
 C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
Rational Equations. You can use a rational function to model the intensity of sound.
 UNIT Rational Equations You can use a rational function to model the intensit of sound. Copright 009, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
UNIT Rational Equations You can use a rational function to model the intensit of sound. Copright 009, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
CHAPTER 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
x 2 20x x 10 0 x 10 2x 2 5x 12 2 x x x x Lesson 6.1 Activity (p. 323) 1. 7; 2. a. b. c. d.
 CHAPTER Think & Discuss (p. ). about seconds Speed (ft/sec) Shuttle Speed After Launch Time (sec). A quadratic function would be a good model because the data lies on a curve... ± ± or Skill Review (p.
CHAPTER Think & Discuss (p. ). about seconds Speed (ft/sec) Shuttle Speed After Launch Time (sec). A quadratic function would be a good model because the data lies on a curve... ± ± or Skill Review (p.
4Cubic. polynomials UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 4Cubic polnomials 4.1 Kick off with CAS 4. Polnomials 4.3 The remainder and factor theorems 4.4 Graphs of cubic polnomials 4.5 Equations of cubic polnomials 4.6 Cubic models and applications 4.7 Review
4Cubic polnomials 4.1 Kick off with CAS 4. Polnomials 4.3 The remainder and factor theorems 4.4 Graphs of cubic polnomials 4.5 Equations of cubic polnomials 4.6 Cubic models and applications 4.7 Review
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions. Quadratic functions are of the form.
 3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
a 2 x y 1 y SOL AII.1a
 SOL AII.a The student, given rational, radical, or polnomial epressions, will a) add, subtract, multipl, divide, and simplif rational algebraic epressions; Hints and Notes Rules for fractions: ) Alwas
SOL AII.a The student, given rational, radical, or polnomial epressions, will a) add, subtract, multipl, divide, and simplif rational algebraic epressions; Hints and Notes Rules for fractions: ) Alwas
Honors Algebra 2 ~ Spring 2014 Name 1 Unit 3: Quadratic Functions and Equations
 Honors Algebra ~ Spring Name Unit : Quadratic Functions and Equations NC Objectives Covered:. Define and compute with comple numbers. Operate with algebraic epressions (polnomial, rational, comple fractions)
Honors Algebra ~ Spring Name Unit : Quadratic Functions and Equations NC Objectives Covered:. Define and compute with comple numbers. Operate with algebraic epressions (polnomial, rational, comple fractions)
9 (0, 3) and solve equations to earn full credit.
 Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Algebra I Practice Questions ? 1. Which is equivalent to (A) (B) (C) (D) 2. Which is equivalent to 6 8? (A) 4 3
 1. Which is equivalent to 64 100? 10 50 8 10 8 100. Which is equivalent to 6 8? 4 8 1 4. Which is equivalent to 7 6? 4 4 4. Which is equivalent to 4? 8 6 Page 1 of 0 11 Practice Questions 6 1 5. Which
1. Which is equivalent to 64 100? 10 50 8 10 8 100. Which is equivalent to 6 8? 4 8 1 4. Which is equivalent to 7 6? 4 4 4. Which is equivalent to 4? 8 6 Page 1 of 0 11 Practice Questions 6 1 5. Which
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
Cubic and quartic functions
 3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
Summer Math Packet (revised 2017)
 Summer Math Packet (revised 07) In preparation for Honors Math III, we have prepared a packet of concepts that students should know how to do as these concepts have been taught in previous math classes.
Summer Math Packet (revised 07) In preparation for Honors Math III, we have prepared a packet of concepts that students should know how to do as these concepts have been taught in previous math classes.
Factoring Polynomials
 5. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS 2A.7.D 2A.7.E Factoring Polnomials Essential Question How can ou factor a polnomial? Factoring Polnomials Work with a partner. Match each polnomial equation with
5. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS 2A.7.D 2A.7.E Factoring Polnomials Essential Question How can ou factor a polnomial? Factoring Polnomials Work with a partner. Match each polnomial equation with
review for math TSI 182 practice aafm m
 Eam TSI 182 Name review for math TSI 182 practice 01704041700aafm042430m www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif.
Eam TSI 182 Name review for math TSI 182 practice 01704041700aafm042430m www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif.
P.4 Lines in the Plane
 28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
Nonlinear Systems. No solution One solution Two solutions. Solve the system by graphing. Check your answer.
 8-10 Nonlinear Sstems CC.9-1.A.REI.7 Solve a simple sstem consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables algebraicall and graphicall. Objective Solve sstems of equations in two
8-10 Nonlinear Sstems CC.9-1.A.REI.7 Solve a simple sstem consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables algebraicall and graphicall. Objective Solve sstems of equations in two
CHAPTER 3 Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
Secondary Mathematics 2 Table of Contents
 Secondar Mathematics Table of Contents Unit 1: Etending the Number Sstem Cluster 1: Etending Properties of Eponents (N.RN.1 and N.RN.)... 3 Cluster : Using Properties of Rational and Irrational Numbers
Secondar Mathematics Table of Contents Unit 1: Etending the Number Sstem Cluster 1: Etending Properties of Eponents (N.RN.1 and N.RN.)... 3 Cluster : Using Properties of Rational and Irrational Numbers
LESSON #11 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Math 0312: Intermediate Algebra Name
 FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Math 0312: Intermediate Algebra Name 1) Find the SUM of the solutions of the equation. 82 + 0 = 16 Use the quadratic formula to solve the equation. (All solutions are real numbers.)
FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Math 0312: Intermediate Algebra Name 1) Find the SUM of the solutions of the equation. 82 + 0 = 16 Use the quadratic formula to solve the equation. (All solutions are real numbers.)
Review of Exponent Rules
 Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
