x Radical Sign: Radicand: the number beneath the radical sign
|
|
|
- Paul Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing. Square Root: Radical Sign: Radicand: the number beneath the radical sign Positive (Principal) Square Root: 9 3 Negative Square Root: 9 3 Review: Simplifing Square Roots A square root is simplified if the radicand has no perfect square factor (other than 1) and there is no radical in the denominator of a fraction. E: Simplif the square root 7. Method 1 Step One: Find the largest perfect square that is a factor of Step Two: Rewrite 7 as a product using 36 as a factor. 36 Step Three: Rewrite as the product of two radicals. 36 Step Four: Evaluate the square root of the perfect square. 6 Method Step One: Rewrite 7 as a product of prime factors Step Two: Find the square root of each pair of factors. 3 3 E: Simplif the epression We must rationalize the denominator b multipling b 1. 8 Now simplif the radical and the fraction Quadratic Equation: an equation that can be written in the standard form a b c 0, a 0 Page 1 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
2 Solving a Quadratic Equation b Finding Square Roots: to use this method, the quadratic equation must be of the form a c 0, b 0 E: Solve the equation 16. Step One: Find the square root of both sides Step Two: Solve for. (Note that there are two solutions.) 4, 4 This can also be written 4 E: Solve the equation 4 4. Step One: Isolate the squared epression Step Two: Find the square root of both sides. 0 0 Step Three: Solve for. (Note that there is one solution.) 0 E: Solve the equation 3. Step One: Isolate the squared epression. 3 1 Step Two: Find the square root of both sides is not a real number Step Three: Solve for. (Note that there is no solution.) This equation has no real solution. E: Solve the equation Step One: Isolate the squared epression Page of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
3 Step Two: Find the square root of both sides Step Three: Solve for the variable. 6 or 6 E: Solve the equation Step One: Isolate the squared epression. Step Two: Find the square root of both sides Step Three: Solve for the variable. 5 or 5 E: Solve the equation n Step One: Isolate the squared epression. n 5 81 Step Two: Find the square root of both sides. Step Three: Solve for the variable. n 5 81 n 5 9 n 59 n5 9 n 14 n 4 n 7 n E: Solve the equation a, Step One: Isolate the squared epression. a 8 8 Step Two: Find the square root of both sides. a 8 8 a 8 7 Page 3 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
4 Step Three: Solve for the variable. a8 7 a8 7 a 8 7 a 8 7 a 8 7 Note: The ( plus or minus ) smbol is used to write both solutions in a shorter wa. In set notation, the solutions would be written 8 7,8 7. Real-Life Application: Free Fall On Earth, the equation for the height (h) of an object for t seconds after it is dropped can be modeled b the function h 16t h0, where h0 is the initial height of the object. E: A ball is dropped from a height of 81 ft. How long will it take for the ball to hit the ground? Use the free-fall function. h 16t h0 h0 81, h 0 Initial height is 81 ft. The ball will hit the ground when its height is 0 ft. Solve for t. 016t 81 16t t 16 9 t t, 4 4 Solution: Since time is positive, the onl feasible answer is seconds You Tr: Solve the equation QOD: Wh do some quadratic equations have two, one, or no real solution? Page 4 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
5 Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): 1. Solve the equation A. B. C. D , 5 5, 4 4 Sample Nevada High School Proficienc Eam Questions (taken from 009 released version H): An equation is shown below What is the solution set of the equation? A 5 B 5,5 C 5 D 1.5,1.5 Page 5 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
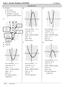
6 Sllabus Objectives: 9. The student will compare characteristics of a given famil of quadratic functions. 9.3 The student will determine the domain and range of quadratic equations algebraicall and graphicall. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form Parabola: the U-shaped graph of a quadratic function a b c, when a 0 Verte: the highest or lowest point on a quadratic function (maimum or minimum) Ais of Smmetr: the vertical line that passes through the verte of a quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Verte Ais of Smmetr Domain and Range: Domain of a Quadratic Function: all real numbers Range of a Quadratic Function: If the parabola opens up, then the range is all values of greater than or equal to the - coordinate of the verte. If the parabola opens down, then the range is all values of less than or equal to the - coordinate of the verte. Page 6 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
7 Graphing a Parabola E: Graph the quadratic function. Step One: Make a table of values (t-chart) Step Two: Plot the points on a coordinate grid and connect to draw the parabola Note: The verte is 0,0, and the ais of smmetr is 0. E: Graph the parabola Step One: Make a table of values (t-chart) Step Two: Plot the points on a coordinate grid and connect to draw the parabola Note: The verte is 0,0, and the ais of smmetr is Comparing and : The verte is 0,0, and the ais of smmetr is 0 for both graphs. When a is positive, the parabola opens up; when a is negative, the parabola opens down. Page 7 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
8 Activit: Transformations with and. Use the graphing calculator to graph the quadratic functions. Describe the effect on the graphs of and dotted line.). (Note: In the calculator graphs shown, or is graphed as a 1. Compare to Verte: Same 0,0 Opens narrower than. 1 3 Compare to Verte: Same 0,0 Opens wider than 3. 3 Compare to Verte: Up 3 0,3 Opens the same as 4. 4 Compare to Verte: Down 4 0, 4 Opens the same as Conclusions (sample): For quadratic functions of the form a c a 1 Opens down Narrower than 1a 0 Opens down Wider than 0a 1 Opens up Wider than a 1 Opens up Narrower than c 0 Verte moves down c units c 0 Verte moves up c units Page 8 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
9 Standard Form of a Quadratic Function: a b c Verte: the -coordinate of the verte is b Ais of Smmetr: a b a Graphing a Quadratic Function in Standard Form E: Graph the quadratic function and range State the verte, ais of smmetr, domain, Step One: Find the -coordinate of the verte. a 1, b Step Two: Make a table of values. When choosing -values, use the verte, a few values to the left of the verte, and a few values to the right of the verte coordinate of verte: Note: When calculating the -coordinate of points to the right and left of the verte, notice the smmetr. Step Three: Plot the points from the table and draw the parabola. 10 Verte: 3, 10 Ais of Smmetr: Domain: all real numbers -10 Range: 10 Page 9 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
10 E: Graph the quadratic function 1 1. State the verte and ais of smmetr. 3 Step One: Find the -coordinate of the verte. 1 a, b Step Two: Make a table of values. When choosing -values, use the verte, a few values to the left of the verte, and a few values to the right of the verte. (Note: Because of the fraction, ou ma want to choose values that will guarantee whole numbers for the -coordinates.) Step Three: Plot the points from the table and draw the parabola Verte: 3, 4 Ais of Smmetr: 3-10 E: Graph the quadratic function Step One: Find the -coordinate of the verte. a, b Step Two: Make a table of values. When choosing -values, use the verte, a few values to the left of the verte, and a few values to the right of the verte coordinate of verte: Note: When calculating the -coordinate of points to the right and left of the verte, notice the smmetr. Step Three: Plot the points from the table and draw the parabola Verte:, 18 Ais of Smmetr: Page 10 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
11 Using a Quadratic Model E: A basketball s path can be modeled b , where represents time (in seconds) and represents the height of the basketball (in feet). What is the maimum height that the basketball reaches? Graph the function and find the maimum (in the Calc menu). The maimum is the verte. The maimum height of the basketball is the -coordinate of the verte, which is approimatel 9.5ft. You Tr: Find the verte and ais of smmetr for the following quadratic function. Determine if the parabola will open up or down. Then graph the parabola. QOD: How man points does it take to determine a unique parabola? Page 11 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
12 Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): 1. Which of the following is the graph of 6? A. B. C. D. Page 1 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
13 . Which equation best represents the following graph? A. B. C. D Which of the following are true statements about the graph of 8 4? I. Opens Up II. Opens Down III. Ais of smmetr = 4 IV. Ais of smmetr = 4 B. I and III onl C. I and IV onl D. II and III onl E. II and IV onl Page 13 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
14 4. Find the verte of the parabola: A. 6, 7 B. 3, 11 C. 3, 61 D. 6, What is the domain and range of the function below? 4 shown in the graph A. Domain: all real numbers Range: all real numbers B. Domain: Range: 4.5 C. Domain: all real numbers Range: 4.5 D. Domain: Range: all real numbers Page 14 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
15 Sample Nevada High School Proficienc Eam Questions (taken from 009 released version H): A painter is designing a mural. The mural will be shaped like a rectangle. The length of the mural will be 3 times the width of the mural. Which graph shows the relationship between the width of the mural () and the area of the mural ()? Page 15 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
16 Sllabus Objectives: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing. 9.5 The student will graph quadratic equations and find possible solutions to those equations using coordinate geometr. Solving a Quadratic Equation b Graphing Step One: Write the equation in the form a b c 0. Step Two: Graph the function a b c. Step Three: Find the zero(s) or root(s) of the function. These are the solution(s) to the equation. Note: The words -intercept, zero, root, and solution can be used interchangeabl for the above value. E: Solve the equation 1 8 b graphing. Then check b solving algebraicall. Step One: Write the equation in the form a b c Step Two: Graph the function a b c. 1 8 Verte: b 0 0 a Step Three: Find the -intercept(s) of the function. 0, 8 The zeros are at 4 and 4, so the solutions are 4, Solve algebraicall: Page 16 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
17 E: Solve the equation 3 b graphing. Step One: Write the equation in the form 3 0 a b c Step Two: Graph the function a b c. 3 5 Verte: b 3 3 a , Step Three: Find the -intercept(s) of the function. The zeros are at 1 and, so the solutions are 1, E: Solve the equation 4 4 b graphing. -10 Step One: Write the equation in the form 0. a b c 44 0 Step Two: Graph the function 4 4 a b c. 10 Verte: b 4 4 a , Step Three: Find the -intercept(s) of the function. The root is at, so the solution is Check: Page 17 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
18 E: Solve the equation 3 0 graphicall. Step One: Write the equation in the form 0. a b c 3 0 Step Two: Graph the function 3 Verte: b a a b c. 0,3 Step Three: Find the -intercept(s) of the function. There is no zero, so this equation has no real solution Using a Graphing Calculator to Solve Quadratic Equations E: Approimate the solution(s) of 1 4 using a graphing calculator. Step One: Write the equation in the form a b c Step Two: Graph the function a b c. 4 1 Step Three: Find the zero(s) of the function. 4.36,0.36 You Tr: Solve the quadratic equation 6 3 graphicall. Then check our answer algebraicall. QOD: How can ou tell from the graph of a quadratic function if the equation has one, two, or no solution? Page 18 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
19 Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): The graph of 1 has how man -intercepts? A. 1 B. C. 1 D. 0 Sample Nevada High School Proficienc Eam Questions (taken from 009 released version H): Fiona is designing a skateboard park. One skating area in the park will be shaped like the parabola that is described b the equation below A sketch of Fiona s design for the skating area is shown below. What is the distance across the top of the skating area? A 1 units B 14 units C 15 units D 18 units Page 19 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
20 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing. Review: Factoring Quadratic Trinomials into Two Binomials (Using the ac method or splitting the middle term.) Factoring, 1 a b c a E: Factor 7 1. Find two integers such that their product is 1 and their sum is 7. 4 and 3 Write the two binomials as a product. 4 3 Factoring, 1 a b c a E: Factor 7 3. Step One: Multipl a c. 3 6 Step Two: Find two integers such that their product is a c 6 and their sum is b 7. 6 and 1 Step Three: Rewrite ( split ) the middle term as a sum of two terms using the numbers from Step Two Step Four: Factor b grouping. Group the first terms and last terms and factor out the GCF from each pair Step Five: If Step Four was done correctl, there should be a common binomial factor. Factor this binomial out and write what remains from each term as the second binomial factor. 1 3 E: Factor 5 7. Step One: Multipl a c Step Two: Find two integers such that their product is a c 10 and their sum is b 7. and 5 Step Three: Rewrite ( split ) the middle term as a sum of two terms using the numbers from Step Two. Page 0 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
21 5 5 Step Four: Factor b grouping. Group the first terms and last terms and factor out the GCF from each pair Step Five: If Step Four was done correctl, there should be a common binomial factor. Factor this binomial out and write what remains from each term as the second binomial factor. 5 1 Recall: Special Factoring Patterns Difference of Two Squares: a b aba b Perfect Square Trinomial: a abb ab a abb ab Zero Product Propert: If the product of two factors is 0, then one or both of the factors must equal 0. E: Solve the equation using the zero product propert. Since one or both of the factors must equal 0, we will solve the two equations 30 and Solutions: 1, 3 Solving a Quadratic Equation b Factoring E: Solve the equation 5 6 b factoring. Step One: Write the equation in standard form Step Two: Factor the quadratic. 3 0 Step Three: Set each factor equal to zero and solve. Note: Check this answer b graphing on the calculator , 3 Page 1 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
22 E: Solve the equation 4 8. Step One: Write the equation in standard form. Step Two: Factor the quadratic using the ac method a c 4 b 5 8 and Step Three: Set each factor equal to zero and solve. The solutions can be written in set notation: , 3 E: Solve the equation Step One: Write the equation in standard form Step Two: Factor the quadratic Note: Step Three: Set each factor equal to zero and solve. The solution can be written in set notation: Zero(s) of Quadratic Functions: the -value(s) where the function intersects the -ais To find the zero(s), factor the quadratic and set each factor equal to 0. Note: We can graph quadratic functions b plotting the zeros. The verte is halfwa between the zeros. E: Find the zero(s) of the quadratic function Step One: Factor the quadratic polnomial. 3and graph the parabola Page of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
23 Step Two: Set each factor equal to 0 and solve. Step Three: Find the coordinates of the verte. Step Four: Plot the points and sketch the parabola You Tr: Solve the quadratic equation 5t 5 4t 6 b factoring. QOD: What must be true about a quadratic equation before ou can solve it using the zero product propert? Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): 1. What is the solution set for the following equation? A. { 9, 1} B. { 9, 1} C. { 1, 9} D. {1, 9}. Which of the following equations has roots of 7 and 4? A B C D Page 3 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
24 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing. Review: Factoring a Perfect Square Trinomial a abb ab a abb ab Completing the Square: writing an epression of the form to factor it as a binomial squared b as a perfect square trinomial in order To complete the square of b, we must add b. Teacher Note: Algebra Tiles work well to illustrate completing the square. See Page 79 for an activit. E: Find the value of c such that 10 c is a perfect square trinomial. b 10, therefore we must add Note: 10 5 c to complete the square. Solving a Quadratic Equation b Completing the Square E: Solve 87 0 b completing the square. Step One: Rewrite to make the lead coefficient 1. Step Two: Take the constant term to the other side. b Step Three: Complete the square (add to both sides) Step Four: Factor the perfect square trinomial Step Five: Take the square roots of both sides Step Si: Solve for the variable The solution set is 7, 1. Check our answer b factoring. E: Solve 14 0 b completing the square. Page 4 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
25 Step One: Rewrite to make the lead coefficient 1. Step Two: Take the constant term to the other side. b Step Three: Complete the square (add to both sides) Step Four: Factor the perfect square trinomial Step Five: Take the square roots of both sides. Step Si: Solve for the variable. The solution set is 3 11, E: Solve 3 0 b completing the square. Step One: Rewrite to make the lead coefficient 1. Step Two: Take the constant term to the other side. b Step Three: Complete the square (add Step Four: Factor the perfect square trinomial. Step Five: Take the square roots of both sides. Step Si: Solve for the variable The solutions are. to both sides) Page 5 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
26 You Tr: Solve b completing the square QOD: Describe wh adding b to b makes it a perfect square trinomial. Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): What are the roots (solutions) of A. 1 3, 1 3 B. 1 5, ? C. D , , Page 6 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
27 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing. Deriving the Quadratic Formula b Completing the Square Solve the quadratic equation a b c 0 b completing the square. Step One: Rewrite so that the lead coefficient is 1. a b c 0 a a a a b c 0 a a Step Two: Take the constant term to the other side. b c a a b Step Three: Complete the square (add to both sides). b b c b a a a a b b 4acb a 4a 4a b b 4ac Step Four: Factor the perfect square trinomial. a 4a b b 4ac a 4a Step Five: Take the square roots of both sides. b b 4ac a 4a b b 4ac b b 4ac a a a a Step Si: Solve for the variable. b b 4ac b b 4ac a a The Quadratic Formula: To solve a quadratic equation in the form b b 4ac. a a b c 0, use the formula Note: To help memorize the quadratic formula, sing it to the tune of the song Pop Goes the Weasel. Page 7 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
28 E: Solve the quadratic equation 8 1 using the quadratic formula. Step One: Rewrite in standard form (if necessar) Step Two: Identif a, b, and c. a 1, b8, c 1 Step Three: Substitute the values into the quadratic formula. b b 4ac a Step Four: Simplif The solution set is 4 15,4 15 E: Solve the quadratic equation using the quadratic formula. Step One: Rewrite in standard form (if necessar) Step Two: Identif a, b, and c. a 6, b5, c 1 Step Three: Substitute the values into the quadratic formula. Step Four: Simplif. The solution set is 1 1, 6 b b 4ac a E: Solve the quadratic equation using the quadratic formula. Step One: Rewrite in standard form (if necessar) Step Two: Identif a, b, and c. a 9, b1, c 4 Page 8 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
29 b b 4ac a Step Three: Substitute the values into the quadratic formula Step Four: Simplif The solution set is 3. E: Solve the quadratic equation 3 0 using the quadratic formula. Step One: Rewrite in standard form (if necessar). 3 0 Step Two: Identif a, b, and c. a, b, c 3 Step Three: Substitute the values into the quadratic formula. b b 4ac a Step Four: Simplif. 4 4 There is no real solution to the quadratic equation because 0 is not a real number. You Tr: Solve the equation 6 3 using the quadratic formula. QOD: Write a conjecture about how the radicand in the quadratic formula relates to the number of solutions that a quadratic equation has. Page 9 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
30 Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): 1. What are the roots (solutions) of A. 1 3, 1 3 B. 1 5, ? C. D , ,. Which of the following is the correct use of the quadratic formula to find the solutions of the equation 7 5? A. B. C. D , , , , Page 30 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
31 Sllabus Objective: 9.6 The student will solve practical problems involving quadratic equations with a variet of methods, including discrete methods (with and without technolog). Discriminant: the discriminant of the quadratic equation 0 is a b c b 4ac Note: The discriminant is the radicand of the quadratic formula! Determining the Number of Real Solutions of a Quadratic Equation Using the Discriminant Teacher Note: Students should have come up with this in the QOD. If If If b b b 4ac 0, then there are no real solutions. 4ac 0, then there is one solution. 4ac 0, then there are two real solutions. E: Determine the number of real solutions that the equations have Rewrite the equation in standard form a 3, b1, c 1 Find the discriminant. b ac Determine the number of real solution(s). b 4ac 11 0, so there are no real solutions.. 45 Rewrite the equation in standard form a 1, b5, c 4 Find the discriminant. b ac Determine the number of real solution(s). b 4ac 41 0, so there are two real solutions Rewrite the equation in standard form. a 9, b1, c Find the discriminant. b ac Determine the number of real solution(s). b 4ac 0, so there is one real solution. Page 31 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
32 Determining the Number of -Intercepts of a Quadratic Function Using the Discriminant Because the -intercepts of a b c are the same as the zeros of the equation a b c 0, we can use the discriminant to determine the number of -intercepts that a quadratic function has. E: Sketch the graph of a quadratic function with a negative discriminant. Because the discriminant, b 4ac 0, the function will have no -intercept. 10 A sample answer is shown in the graph. Note: An parabola which does not intersect the -ais is an acceptable answer. Application Problem E: A baton twirler tosses a baton into the air. The baton leaves the twirler s hand 6 feet above the ground and has an initial vertical velocit of 45 feet per second. This can be modeled b the equation h 16t 45t 6, where h is the height (in feet) and t is the time (in seconds). The twirler wants her baton to reach at least 40 feet. Will the baton reach that height? Substitute h 1. Write in standard form t 45t t 45t 34 a 16, b45, c 34 Find the discriminant. b ac Since the discriminant is less than 0, this equation has no real solution. Therefore, the baton could not reach 40 feet. How high will the baton reach? Graph the function h t t Find the maimum (verte). The baton will reach approimatel ft. You Tr: Find values for c so that the equation will have no real solution, one real solution, and two real solutions. 3c 0 QOD: Write a quadratic equation which can be factored. Find its discriminant. Teacher Note: Have students share their answers to the QOD and allow students to make a conjecture for how to determine if a quadratic polnomial is factorable using the discriminant. (It must be a perfect square.) Page 3 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
33 Sample CCSD Common Eam Practice Question(s): The graph of 1 has how man -intercepts? A. 1 B. C. 1 D. 0 Page 33 of 33 McDougal Littell: 9.1, , , 1.4
Algebra II Notes Unit Five: Quadratic Functions. Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technology.
 Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
Algebra Notes Quadratic Functions and Equations Unit 08
 Note: This Unit contains concepts that are separated for teacher use, but which must be integrated by the completion of the unit so students can make sense of choosing appropriate methods for solving quadratic
Note: This Unit contains concepts that are separated for teacher use, but which must be integrated by the completion of the unit so students can make sense of choosing appropriate methods for solving quadratic
Solve Quadratic Equations
 Skill: solve quadratic equations by factoring. Solve Quadratic Equations A.SSE.A. Interpret the structure of epressions. Use the structure of an epression to identify ways to rewrite it. For eample, see
Skill: solve quadratic equations by factoring. Solve Quadratic Equations A.SSE.A. Interpret the structure of epressions. Use the structure of an epression to identify ways to rewrite it. For eample, see
Algebra II Notes Unit Six: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6.2 The student will simplify polynomial expressions.
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART TWO
 Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART TWO PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multiply polynomials students should be able to factor polynomials students should be able
Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART TWO PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multiply polynomials students should be able to factor polynomials students should be able
Study Guide and Intervention
 6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
Unit 10 - Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
= x. Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit Graphing Quadratic Functions. Math Background
 Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Unit 2 Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring
 Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Chapter 9 Notes Alg. 1H 9-A1 (Lesson 9-3) Solving Quadratic Equations by Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square
 Chapter Notes Alg. H -A (Lesson -) Solving Quadratic Equations b Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square p. *Calculator Find the Square Root: take the square root of. E: Solve b finding square
Chapter Notes Alg. H -A (Lesson -) Solving Quadratic Equations b Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square p. *Calculator Find the Square Root: take the square root of. E: Solve b finding square
Section 5.5 Complex Numbers
 Name: Period: Section 5.5 Comple Numbers Objective(s): Perform operations with comple numbers. Essential Question: Tell whether the statement is true or false, and justify your answer. Every comple number
Name: Period: Section 5.5 Comple Numbers Objective(s): Perform operations with comple numbers. Essential Question: Tell whether the statement is true or false, and justify your answer. Every comple number
f(x) = 2x 2 + 2x - 4
 4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
x (vertex is halfway between the x-intercepts)
 Big Idea: A quadratic equation in the form a b c 0 has a related function f ( ) a b c. The zeros of the function are the -intercepts of its graph. These -values are the solutions or roots of the related
Big Idea: A quadratic equation in the form a b c 0 has a related function f ( ) a b c. The zeros of the function are the -intercepts of its graph. These -values are the solutions or roots of the related
Quadratic Function. Parabola. Parent quadratic function. Vertex. Axis of Symmetry
 Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations
 Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations Part 1 Name: Period: Date Name of Lesson Notes Tuesda 4/4 Wednesda 4/5 Thursda 4/6 Frida 4/7 Monda 4/10 Tuesda 4/11 Wednesda 4/12 Thursda 4/13 Frida 4/14 Da 1- Quadratic
Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations Part 1 Name: Period: Date Name of Lesson Notes Tuesda 4/4 Wednesda 4/5 Thursda 4/6 Frida 4/7 Monda 4/10 Tuesda 4/11 Wednesda 4/12 Thursda 4/13 Frida 4/14 Da 1- Quadratic
Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART ONE
 Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART ONE PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multiply polynomials students should be able to factor polynomials students should be able
Unit 11 - Solving Quadratic Functions PART ONE PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multiply polynomials students should be able to factor polynomials students should be able
Algebra 2 Semester Exam Review
 Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
3.1 Graph Quadratic Functions
 3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY REVIEW EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES
 Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Math 030 Review for Final Exam Revised Fall 2010 RH/ DM 1
 Math 00 Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 010 RH/ DM 1 1. Solve the equations: (-1) (7) (-) (-1) () 1 1 1 1 f. 1 g. h. 1 11 i. 9. Solve the following equations for the given variable: 1 Solve for. D ab
Math 00 Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 010 RH/ DM 1 1. Solve the equations: (-1) (7) (-) (-1) () 1 1 1 1 f. 1 g. h. 1 11 i. 9. Solve the following equations for the given variable: 1 Solve for. D ab
Algebra Final Exam Review Packet
 Algebra 1 00 Final Eam Review Packet UNIT 1 EXPONENTS / RADICALS Eponents Degree of a monomial: Add the degrees of all the in the monomial together. o Eample - Find the degree of 5 7 yz Degree of a polynomial:
Algebra 1 00 Final Eam Review Packet UNIT 1 EXPONENTS / RADICALS Eponents Degree of a monomial: Add the degrees of all the in the monomial together. o Eample - Find the degree of 5 7 yz Degree of a polynomial:
+ = + + = x = + = + = 36x
 Ch 5 Alg L Homework Worksheets Computation Worksheet #1: You should be able to do these without a calculator! A) Addition (Subtraction = add the opposite of) B) Multiplication (Division = multipl b the
Ch 5 Alg L Homework Worksheets Computation Worksheet #1: You should be able to do these without a calculator! A) Addition (Subtraction = add the opposite of) B) Multiplication (Division = multipl b the
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
Final Exam Review Part 2 #1 Page 1 / 21
 Final Eam Review Part #1 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Spring 017 Master ( Master Templates) Student Name/ID: v 1. Solve for, where is a real number. v v + 1 + =. Solve for, where is a real number. +
Final Eam Review Part #1 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Spring 017 Master ( Master Templates) Student Name/ID: v 1. Solve for, where is a real number. v v + 1 + =. Solve for, where is a real number. +
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
Nonlinear Systems. No solution One solution Two solutions. Solve the system by graphing. Check your answer.
 8-10 Nonlinear Sstems CC.9-1.A.REI.7 Solve a simple sstem consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables algebraicall and graphicall. Objective Solve sstems of equations in two
8-10 Nonlinear Sstems CC.9-1.A.REI.7 Solve a simple sstem consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables algebraicall and graphicall. Objective Solve sstems of equations in two
QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW
 Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
Ch 5 Alg 2 L2 Note Sheet Key Do Activity 1 on your Ch 5 Activity Sheet.
 Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
Mth Quadratic functions and quadratic equations
 Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
Mth 0 - Quadratic functions and quadratic equations Name Find the product. 1) 8a3(2a3 + 2 + 12a) 2) ( + 4)( + 6) 3) (3p - 1)(9p2 + 3p + 1) 4) (32 + 4-4)(2-3 + 3) ) (4a - 7)2 Factor completel. 6) 92-4 7)
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula
 Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring 04 Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula Write the quadratic formula. The NUMBER of REAL and COMPLEX SOLUTIONS to a quadratic equation ( a b
Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring 04 Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula Write the quadratic formula. The NUMBER of REAL and COMPLEX SOLUTIONS to a quadratic equation ( a b
Keira Godwin. Time Allotment: 13 days. Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to:
 Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Graphing Calculator Computations 2
 Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Algebra 1 Skills Needed to be Successful in Algebra 2
 Algebra 1 Skills Needed to be Successful in Algebra A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed
Algebra 1 Skills Needed to be Successful in Algebra A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed
math FALL developmental mathematics sullivan 1e
 TSIpractice eam review 1 131 180 plus 34 TSI questions for elementar and intermediate algebra m0300004301 aaa Name www.alvarezmathhelp.com math0300004301 FALL 01 100 interactmath developmental mathematics
TSIpractice eam review 1 131 180 plus 34 TSI questions for elementar and intermediate algebra m0300004301 aaa Name www.alvarezmathhelp.com math0300004301 FALL 01 100 interactmath developmental mathematics
MAT 1033C -- Martin-Gay Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1, 8.2, 8.5, 8.6) Practice for the Exam
 MAT 33C -- Martin-Ga Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1 8. 8. 8.6) Practice for the Eam Name Date Da/Time: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
MAT 33C -- Martin-Ga Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1 8. 8. 8.6) Practice for the Eam Name Date Da/Time: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Algebra I Notes Unit Eleven: Polynomials
 Syllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will add, subtract, multiply, and factor polynomials connecting the arithmetic and algebraic processes. Teacher Note: A nice way to illustrate operations with polynomials
Syllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will add, subtract, multiply, and factor polynomials connecting the arithmetic and algebraic processes. Teacher Note: A nice way to illustrate operations with polynomials
2 nd Semester Final Exam Review Block Date
 Algebra 1B Name nd Semester Final Eam Review Block Date Calculator NOT Allowed Graph each function. 1 (10-1) 1. (10-1). (10-1) 3. (10-1) 4. 3 Graph each function. Identif the verte, ais of smmetr, and
Algebra 1B Name nd Semester Final Eam Review Block Date Calculator NOT Allowed Graph each function. 1 (10-1) 1. (10-1). (10-1) 3. (10-1) 4. 3 Graph each function. Identif the verte, ais of smmetr, and
Using Intercept Form
 8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
Algebra I Quadratics Practice Questions
 1. Which is equivalent to 64 100? 10 50 8 10 8 100. Which is equivalent to 6 8? 4 8 1 4. Which is equivalent to 7 6? 4 4 4. Which is equivalent to 4? 8 6 From CCSD CSE S Page 1 of 6 1 5. Which is equivalent
1. Which is equivalent to 64 100? 10 50 8 10 8 100. Which is equivalent to 6 8? 4 8 1 4. Which is equivalent to 7 6? 4 4 4. Which is equivalent to 4? 8 6 From CCSD CSE S Page 1 of 6 1 5. Which is equivalent
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences
 Lesson 7.1 Polnomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identif the degree of each polnomial. a. 1 b. 0. 1. 3. 3 c. 0 16 0. Determine which of the epressions are polnomials. For each polnomial, state its
Lesson 7.1 Polnomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identif the degree of each polnomial. a. 1 b. 0. 1. 3. 3 c. 0 16 0. Determine which of the epressions are polnomials. For each polnomial, state its
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
2 nd Semester Final Exam Review Block Date
 Algebra 1B Name nd Semester Final Eam Review Block Date Calculator NOT Allowed Graph each function. Identif the verte and ais of smmetr. 1 (10-1) 1. (10-1). 3 (10-) 3. 4 7 (10-) 4. 3 6 4 (10-1) 5. Predict
Algebra 1B Name nd Semester Final Eam Review Block Date Calculator NOT Allowed Graph each function. Identif the verte and ais of smmetr. 1 (10-1) 1. (10-1). 3 (10-) 3. 4 7 (10-) 4. 3 6 4 (10-1) 5. Predict
MATH 0312 FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS
 MATH 012 FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Name The items on this review are representative of the items that ou might see on our course final eam. No formul sheets are allowed and calculators are not allowed on
MATH 012 FINAL EXAM REVIEW ITEMS Name The items on this review are representative of the items that ou might see on our course final eam. No formul sheets are allowed and calculators are not allowed on
Algebra II Unit #2 4.6 NOTES: Solving Quadratic Equations (More Methods) Block:
 Algebra II Unit # Name: 4.6 NOTES: Solving Quadratic Equations (More Methods) Block: (A) Background Skills - Simplifying Radicals To simplify a radical that is not a perfect square: 50 8 300 7 7 98 (B)
Algebra II Unit # Name: 4.6 NOTES: Solving Quadratic Equations (More Methods) Block: (A) Background Skills - Simplifying Radicals To simplify a radical that is not a perfect square: 50 8 300 7 7 98 (B)
review math0410 (1-174) and math 0320 ( ) aafinm mg
 Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Algebra 2 Honors Summer Packet 2018
 Algebra Honors Summer Packet 018 Solving Linear Equations with Fractional Coefficients For these problems, ou should be able to: A) determine the LCD when given two or more fractions B) solve a linear
Algebra Honors Summer Packet 018 Solving Linear Equations with Fractional Coefficients For these problems, ou should be able to: A) determine the LCD when given two or more fractions B) solve a linear
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 3.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Define each term in our own words.. quadratic function. vertical motion Problem
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Define each term in our own words.. quadratic function. vertical motion Problem
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Exam
 MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
Name Class Date. Solving by Graphing and Algebraically
 Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
4 B. 4 D. 4 F. 3. How can you use the graph of a quadratic equation to determine the number of real solutions of the equation?
 3.1 Solving Quadratic Equations COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSA-SSE.A. HSA-REI.B.b HSF-IF.C.8a Essential Question Essential Question How can ou use the graph of a quadratic equation to determine the
3.1 Solving Quadratic Equations COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSA-SSE.A. HSA-REI.B.b HSF-IF.C.8a Essential Question Essential Question How can ou use the graph of a quadratic equation to determine the
Algebra 2 Unit 2 Practice
 Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards. An equation that contains an absolute value expression
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Lesson Goals. Unit 4 Polynomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) Family of Quadratic Functions. Parabolas
 Unit 4 Polnomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) William (Bill) Finch Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Graph and analze the graphs of quadratic functions. Solve
Unit 4 Polnomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) William (Bill) Finch Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Graph and analze the graphs of quadratic functions. Solve
Solving Quadratic Equations
 9 Solving Quadratic Equations 9. Properties of Radicals 9. Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing 9. Solving Quadratic Equations Using Square Roots 9. Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square
9 Solving Quadratic Equations 9. Properties of Radicals 9. Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing 9. Solving Quadratic Equations Using Square Roots 9. Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the linear equation. 1. = 5. = + 3 3. 1 = + 3. = + Evaluate the epression when =. 5. + 8. + 3 7. 3 8. 5 + 8 9. 8 10. 5 + 3 11. + + 1. 3 + +
Name Date Chapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the linear equation. 1. = 5. = + 3 3. 1 = + 3. = + Evaluate the epression when =. 5. + 8. + 3 7. 3 8. 5 + 8 9. 8 10. 5 + 3 11. + + 1. 3 + +
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Unit 4 Practice Problem ANSWERS
 Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
MATH 115: Final Exam Review. Can you find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (1.1)
 MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
H.Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet
 H.Algebra Summer Review Packet 1 Correlation of Algebra Summer Packet with Algebra 1 Objectives A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Use the commutative, associative,
H.Algebra Summer Review Packet 1 Correlation of Algebra Summer Packet with Algebra 1 Objectives A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Use the commutative, associative,
Graph the linear system and estimate the solution. Then check the solution algebraically.
 (Chapters and ) A. Linear Sstems (pp. 6 0). Solve a Sstem b Graphing Vocabular Solution For a sstem of linear equations in two variables, an ordered pair (x, ) that satisfies each equation. Consistent
(Chapters and ) A. Linear Sstems (pp. 6 0). Solve a Sstem b Graphing Vocabular Solution For a sstem of linear equations in two variables, an ordered pair (x, ) that satisfies each equation. Consistent
Final Exam Review Part 2 #4
 Final Eam Review Part # Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 01 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for, where is a real number. + = 8. Solve for, where is a real number. 9 1 = 3. Solve
Final Eam Review Part # Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 01 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for, where is a real number. + = 8. Solve for, where is a real number. 9 1 = 3. Solve
Final Exam Review Part 2 #4
 Final Eam Review Part # Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 01 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for, where is a real number. + =. Solve for, where is a real number. 9 1 = 3. Solve for,
Final Eam Review Part # Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 01 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for, where is a real number. + =. Solve for, where is a real number. 9 1 = 3. Solve for,
12x y (4) 2x y (4) 5x y is the same as
 Name: Unit #6 Review Quadratic Algebra Date: 1. When 6 is multiplied b the result is 0 1 () 9 1 () 9 1 () 1 0. When is multiplied b the result is 10 6 1 () 7 1 () 7 () 10 6. Written without negative eponents
Name: Unit #6 Review Quadratic Algebra Date: 1. When 6 is multiplied b the result is 0 1 () 9 1 () 9 1 () 1 0. When is multiplied b the result is 10 6 1 () 7 1 () 7 () 10 6. Written without negative eponents
Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math
 Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed to simplif
Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed to simplif
Objectives To solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula To find the number of solutions of a quadratic equation
 9-6 The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant Content Standards A.REI..a Use the method of completing the square to transform an quadratic equation in into an equation of the form ( p) 5 q... Derive the
9-6 The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant Content Standards A.REI..a Use the method of completing the square to transform an quadratic equation in into an equation of the form ( p) 5 q... Derive the
National 5 Mathematics
 St Andrew s Academ Mathematics Department National 5 Mathematics UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT PREPARATION St Andrew's Academ Maths Dept 016-17 1 Practice Unit Assessment 4A for National 5 1. Simplif, giving our answer
St Andrew s Academ Mathematics Department National 5 Mathematics UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT PREPARATION St Andrew's Academ Maths Dept 016-17 1 Practice Unit Assessment 4A for National 5 1. Simplif, giving our answer
Fair Game Review. Chapter 9. Find the square root(s) ± Find the side length of the square. 7. Simplify Simplify 63.
 Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 1.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Give an eample of each term.. quadratic function 9 0. vertical motion equation s
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Give an eample of each term.. quadratic function 9 0. vertical motion equation s
Algebra 2 CPA Summer Assignment 2018
 Algebra CPA Summer Assignment 018 This assignment is designed for ou to practice topics learned in Algebra 1 that will be relevant in the Algebra CPA curriculum. This review is especiall important as ou
Algebra CPA Summer Assignment 018 This assignment is designed for ou to practice topics learned in Algebra 1 that will be relevant in the Algebra CPA curriculum. This review is especiall important as ou
PreCalculus. Ocean Township High School Mathematics Department
 PreCalculus Summer Assignment Name Period Date Ocean Township High School Mathematics Department These are important topics from previous courses that ou must be comfortable doing before ou can be successful
PreCalculus Summer Assignment Name Period Date Ocean Township High School Mathematics Department These are important topics from previous courses that ou must be comfortable doing before ou can be successful
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. 3Quadratics. Chapter 3. Objectives
 Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
Quadratic Functions. Key Terms. Slide 1 / 200. Slide 2 / 200. Slide 3 / 200. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Table of Contents Key Terms Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic Equations
Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Table of Contents Key Terms Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic Equations
Quadratic Functions. Key Terms. Slide 2 / 200. Slide 1 / 200. Slide 3 / 200. Slide 4 / 200. Slide 6 / 200. Slide 5 / 200.
 Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Slide 2 / 200 Table of Contents Key Terms Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic
Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Slide 2 / 200 Table of Contents Key Terms Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic
Slide 1 / 200. Quadratic Functions
 Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Key Terms Slide 2 / 200 Table of Contents Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic
Slide 1 / 200 Quadratic Functions Key Terms Slide 2 / 200 Table of Contents Identify Quadratic Functions Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Solve Quadratic
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f(x) = x Example 1
 TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
Math 121. Practice Questions Chapters 2 and 3 Fall Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint.
 Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY
 APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY Constructed Response # Objective Sllabus Objective NV State Standard 1 Graph a polnomial function. 1.1.7.1 Analze graphs of polnomial functions
APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY Constructed Response # Objective Sllabus Objective NV State Standard 1 Graph a polnomial function. 1.1.7.1 Analze graphs of polnomial functions
indicates that a student should be able to complete this item without a calculator.
 HONORS ALGEBRA A Semester Eam Review The semester A eamination for Honors Algebra will consist of two parts. Part 1 will be selected response on which a calculator is NOT allowed. Part will be grid-in
HONORS ALGEBRA A Semester Eam Review The semester A eamination for Honors Algebra will consist of two parts. Part 1 will be selected response on which a calculator is NOT allowed. Part will be grid-in
Find the distance between the pair of points. 2) (7, -7) and (3, -5) A) 12 3 units B) 2 5 units C) 6 units D) 12 units B) 8 C) 63 2
 Sample Departmental Final - Math 9 Write the first five terms of the sequence whose general term is given. 1) a n = n 2 - n 0, 2,, 12, 20 B) 2,, 12, 20, 30 C) 0, 3, 8, 1, 2 D) 1,, 9, 1, 2 Find the distance
Sample Departmental Final - Math 9 Write the first five terms of the sequence whose general term is given. 1) a n = n 2 - n 0, 2,, 12, 20 B) 2,, 12, 20, 30 C) 0, 3, 8, 1, 2 D) 1,, 9, 1, 2 Find the distance
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Rev Name Date. Solve each of the following equations for y by isolating the square and using the square root property.
 Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Rev 8-8-3 Name Date TI-8 GC 3 Using GC to Graph Parabolae that are Not Functions of Objectives: Recall the square root propert Practice solving a quadratic equation f Graph the two parts of a hizontal
Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions
 19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Midterm Practice Exam Answer Key
 G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Midterm Practice Eam Answer Key G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s Midterm Practice Eam Answer Key Name:
G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Midterm Practice Eam Answer Key G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s Midterm Practice Eam Answer Key Name:
review for math TSI 55 practice aafm m
 Eam TSI Name review for math TSI practice 01704041700aafm042430m www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the
Eam TSI Name review for math TSI practice 01704041700aafm042430m www.alvarezmathhelp.com MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the
MATH College Algebra Review for Test 2
 MATH 4 - College Algebra Review for Test Sections. and.. For f (x) = x + 4x + 5, give (a) the x-intercept(s), (b) the -intercept, (c) both coordinates of the vertex, and (d) the equation of the axis of
MATH 4 - College Algebra Review for Test Sections. and.. For f (x) = x + 4x + 5, give (a) the x-intercept(s), (b) the -intercept, (c) both coordinates of the vertex, and (d) the equation of the axis of
The American School of Marrakesh. Algebra 2 Algebra 2 Summer Preparation Packet
 The American School of Marrakesh Algebra Algebra Summer Preparation Packet Summer 016 Algebra Summer Preparation Packet This summer packet contains eciting math problems designed to ensure our readiness
The American School of Marrakesh Algebra Algebra Summer Preparation Packet Summer 016 Algebra Summer Preparation Packet This summer packet contains eciting math problems designed to ensure our readiness
Chapter 6 Resource Masters
 Chapter 6 Resource Masters Consumable Workbooks Man of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Stud Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-07-8809-X
Chapter 6 Resource Masters Consumable Workbooks Man of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Stud Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-07-8809-X
Northwest High School s Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2
 Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
Northwest High School s Algebra /Honors Algebra Summer Review Packet 0 DUE Frida, September, 0 Student Name This packet has been designed to help ou review various mathematical topics that will be necessar
MATH College Algebra Review for Test 2
 MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 2 Sections 3. and 3.2. For f (x) = x 2 + 4x + 5, give (a) the x-intercept(s), (b) the -intercept, (c) both coordinates of the vertex, and (d) the equation of the
MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 2 Sections 3. and 3.2. For f (x) = x 2 + 4x + 5, give (a) the x-intercept(s), (b) the -intercept, (c) both coordinates of the vertex, and (d) the equation of the
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 3.5
 Overview of Section.5 Introduction Sstems of linear equations were solved in Algebra using substitution, elimination, and graphing. These same techniques are applied to nonlinear sstems in this lesson.
Overview of Section.5 Introduction Sstems of linear equations were solved in Algebra using substitution, elimination, and graphing. These same techniques are applied to nonlinear sstems in this lesson.
MATH 91 Final Study Package Name
 MATH 91 Final Stud Package Name Solve the sstem b the substitution method. If there is no solution or an infinite number of solutions, so state. Use set notation to epress the solution set. 1) - = 1 1)
MATH 91 Final Stud Package Name Solve the sstem b the substitution method. If there is no solution or an infinite number of solutions, so state. Use set notation to epress the solution set. 1) - = 1 1)
Applied Algebra II Semester 2 Practice Exam A DRAFT. 6. Let f ( x) = 2x A. 47 B. 92 C. 139 D. 407
 Applied Algebra II Semester Practice Eam A. Find the solution set of { + 0, 0} { + i 0, i 0} { + i, i } { +, } + = 9.. Let f ( ) = and ( ) 0 g =. Which epression is equivalent to f g? ( ) ( ). What is
Applied Algebra II Semester Practice Eam A. Find the solution set of { + 0, 0} { + i 0, i 0} { + i, i } { +, } + = 9.. Let f ( ) = and ( ) 0 g =. Which epression is equivalent to f g? ( ) ( ). What is
