|
|
|
- Imogene Wade
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 ople are co-authors if there edge to each of them. derived from the five largest PH, HEP TH, HEP PH, place a time-stamp on each h paper, and for each perission to the arxiv. The the period from April 1992 the graphs (category GR thors, 13,454 papers) and largest graph, with 57,381 pers) and 133,170 edges. It of the other categories also uthors per paper. s we observe similar pheve densification exponents lack of space we present s only for ASTRO PH, the s 1(d) and 2(d) show the me, and a densification exthe effective diameter over rk datasets. Following the ic, we expected the underould detect the differences Effective diameter Effective diameter Full graph Post 95 subgraph Post 95 subgraph, no past Time [years] (a) arxiv citation graph Time [years] (c) Patents Full graph Post 85 subgraph Post 85 subgraph, no past Effective diameter Effective diameter Full graph Post 95 subgraph Post 95 subgraph, no past Time [years] (b) Affiliation network Size of the graph [number of nodes] (d) AS Figure 3: The effective diameter over time. the result of subsequent papers acting as bridges by citing earlier papers from disparate areas. Note that for other Linear fit diameter has the following interpretation: Since all the links out of a node are frozen at the moment it joins the graph, the decreasing distance between pairs of nodes appears to be
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 Probability mass function of a Zipf random variable; differing α values 0.9 α = α = probability of k k
22 Probability 10 0 mass function of a Zipf random variable; differing α values α =2.0 α = probability of k k
23
24
25 2.0 PDF of a Pareto random variable; differing α values α =2.0 α = probability of x x
26 10 1 PDF of a Pareto random variable; differing α values α =2.0 α = probability of x x
27
28
29
30
31 14 The structure and function of complex networks (a) collaborations in mathematics (b) citations (c) World Wide Web (d) Internet (e) power grid (f) protein interactions 1 10 FIG. 6 Cumulative degree distributions for six different networks. The horizontal axis for each panel is vertex degree k (or indegree for the citation and Web networks, which are directed) and the vertical axis is the cumulative probability distribution of degrees, i.e., the fraction of vertices that have degree greater than or equal to k. The networks shown are: (a) the collaboration network of mathematicians [182]; (b) citations between 1981 and 1997 to all papers cataloged by the Institute for Scientific Information [351]; (c) a 300 million vertex subset of the World Wide Web, circa 1999 [74]; (d) the Internet at the level of
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 12: Generalized Random Graphs
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 12: Generalized Random Graphs 1 Outline Small-world model Growing random networks Power-law degree distributions: Rich-Get-Richer effects Models: Uniform attachment model
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 12: Generalized Random Graphs 1 Outline Small-world model Growing random networks Power-law degree distributions: Rich-Get-Richer effects Models: Uniform attachment model
arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.soc-ph] 28 Jan 2007
![arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.soc-ph] 28 Jan 2007 arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.soc-ph] 28 Jan 2007](/thumbs/87/96771501.jpg) arxiv:physics/0603229v3 [physics.soc-ph] 28 Jan 2007 Graph Evolution: Densification and Shrinking Diameters Jure Leskovec School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA Jon Kleinberg
arxiv:physics/0603229v3 [physics.soc-ph] 28 Jan 2007 Graph Evolution: Densification and Shrinking Diameters Jure Leskovec School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA Jon Kleinberg
CS224W: Analysis of Networks Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Analysis of Networks Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu 10/30/17 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis, http://cs224w.stanford.edu 2
CS224W: Analysis of Networks Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu 10/30/17 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis, http://cs224w.stanford.edu 2
Power laws. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Power laws Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Power laws Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
LAPLACIAN MATRIX AND APPLICATIONS
 LAPLACIAN MATRIX AND APPLICATIONS Alice Nanyanzi Supervisors: Dr. Franck Kalala Mutombo & Dr. Simukai Utete alicenanyanzi@aims.ac.za August 24, 2017 1 Complex systems & Complex Networks 2 Networks Overview
LAPLACIAN MATRIX AND APPLICATIONS Alice Nanyanzi Supervisors: Dr. Franck Kalala Mutombo & Dr. Simukai Utete alicenanyanzi@aims.ac.za August 24, 2017 1 Complex systems & Complex Networks 2 Networks Overview
CMU SCS. Large Graph Mining. Christos Faloutsos CMU
 Large Graph Mining Christos Faloutsos CMU Thank you! Hillol Kargupta NGDM 2007 C. Faloutsos 2 Outline Problem definition / Motivation Static & dynamic laws; generators Tools: CenterPiece graphs; fraud
Large Graph Mining Christos Faloutsos CMU Thank you! Hillol Kargupta NGDM 2007 C. Faloutsos 2 Outline Problem definition / Motivation Static & dynamic laws; generators Tools: CenterPiece graphs; fraud
Power Laws & Rich Get Richer
 Power Laws & Rich Get Richer CMSC 498J: Social Media Computing Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2015 Hadi Amiri hadi@umd.edu Lecture Topics Popularity as a Network Phenomenon
Power Laws & Rich Get Richer CMSC 498J: Social Media Computing Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2015 Hadi Amiri hadi@umd.edu Lecture Topics Popularity as a Network Phenomenon
Assortativity and Mixing. Outline. Definition. General mixing. Definition. Assortativity by degree. Contagion. References. Contagion.
 Outline Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, 2009 Prof Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics University of Vermont Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Outline Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, 2009 Prof Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics University of Vermont Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure and Their Graph Theoretic Properties
 Advances in Pure Mathematics, 2016, 6, 409-419 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/apm.2016.66028 Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure
Advances in Pure Mathematics, 2016, 6, 409-419 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/apm.2016.66028 Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure
Lecture notes for /12.586, Modeling Environmental Complexity. D. H. Rothman, MIT October 20, 2014
 Lecture notes for 12.086/12.586, Modeling Environmental Complexity D. H. Rothman, MIT October 20, 2014 Contents 1 Random and scale-free networks 1 1.1 Food webs............................. 1 1.2 Random
Lecture notes for 12.086/12.586, Modeling Environmental Complexity D. H. Rothman, MIT October 20, 2014 Contents 1 Random and scale-free networks 1 1.1 Food webs............................. 1 1.2 Random
Small-world structure of earthquake network
 Small-world structure of earthquake network Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Small-world structure of earthquake network Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
1 The preferential attachment mechanism
 Inference, Models and Simulation for Complex Systems CSCI 7-1 Lecture 14 2 October 211 Prof. Aaron Clauset 1 The preferential attachment mechanism This mechanism goes by many other names and has been reinvented
Inference, Models and Simulation for Complex Systems CSCI 7-1 Lecture 14 2 October 211 Prof. Aaron Clauset 1 The preferential attachment mechanism This mechanism goes by many other names and has been reinvented
Data mining in large graphs
 Data mining in large graphs Christos Faloutsos University www.cs.cmu.edu/~christos ALLADIN 2003 C. Faloutsos 1 Outline Introduction - motivation Patterns & Power laws Scalability & Fast algorithms Fractals,
Data mining in large graphs Christos Faloutsos University www.cs.cmu.edu/~christos ALLADIN 2003 C. Faloutsos 1 Outline Introduction - motivation Patterns & Power laws Scalability & Fast algorithms Fractals,
THEORY OF SEARCH ENGINES. CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1 2. RANKING OF PAGES 2 3. TWO EXAMPLES 4 4. CONCLUSION 5 References 5
 THEORY OF SEARCH ENGINES K. K. NAMBIAR ABSTRACT. Four different stochastic matrices, useful for ranking the pages of the Web are defined. The theory is illustrated with examples. Keywords Search engines,
THEORY OF SEARCH ENGINES K. K. NAMBIAR ABSTRACT. Four different stochastic matrices, useful for ranking the pages of the Web are defined. The theory is illustrated with examples. Keywords Search engines,
1 Complex Networks - A Brief Overview
 Power-law Degree Distributions 1 Complex Networks - A Brief Overview Complex networks occur in many social, technological and scientific settings. Examples of complex networks include World Wide Web, Internet,
Power-law Degree Distributions 1 Complex Networks - A Brief Overview Complex networks occur in many social, technological and scientific settings. Examples of complex networks include World Wide Web, Internet,
Quantitative Metrics: II
 Network Observational Methods and Topics Quantitative Metrics: II Degree correlation Exploring whether the sign of degree correlation can be predicted from network type or similarity to regular structures,
Network Observational Methods and Topics Quantitative Metrics: II Degree correlation Exploring whether the sign of degree correlation can be predicted from network type or similarity to regular structures,
Complex-Network Modelling and Inference
 Complex-Network Modelling and Inference Lecture 12: Random Graphs: preferential-attachment models Matthew Roughan http://www.maths.adelaide.edu.au/matthew.roughan/notes/
Complex-Network Modelling and Inference Lecture 12: Random Graphs: preferential-attachment models Matthew Roughan http://www.maths.adelaide.edu.au/matthew.roughan/notes/
Analysis & Generative Model for Trust Networks
 Analysis & Generative Model for Trust Networks Pranav Dandekar Management Science & Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 ppd@stanford.edu ABSTRACT Trust Networks are a specific kind of social
Analysis & Generative Model for Trust Networks Pranav Dandekar Management Science & Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 ppd@stanford.edu ABSTRACT Trust Networks are a specific kind of social
The Mathematics of Scientific Research: Scientometrics, Citation Metrics, and Impact Factors
 Wayne State University Library Scholarly Publications Wayne State University Libraries 1-1-2016 The Mathematics of Scientific Research: Scientometrics, Citation Metrics, and Impact Factors Clayton Hayes
Wayne State University Library Scholarly Publications Wayne State University Libraries 1-1-2016 The Mathematics of Scientific Research: Scientometrics, Citation Metrics, and Impact Factors Clayton Hayes
Induced Cycle Decomposition of Graphs
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 2015, no. 84, 4165-4169 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2015.5269 Induced Cycle Decomposition of Graphs Rosalio G. Artes, Jr. Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 2015, no. 84, 4165-4169 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2015.5269 Induced Cycle Decomposition of Graphs Rosalio G. Artes, Jr. Department
Sampling. Everything Data CompSci Spring 2014
 Sampling Everything Data CompSci 290.01 Spring 2014 2 Announcements (Thu. Mar 26) Homework #11 will be posted by noon tomorrow. 3 Outline Simple Random Sampling Means & Proportions Importance Sampling
Sampling Everything Data CompSci 290.01 Spring 2014 2 Announcements (Thu. Mar 26) Homework #11 will be posted by noon tomorrow. 3 Outline Simple Random Sampling Means & Proportions Importance Sampling
Scale-free network of earthquakes
 Scale-free network of earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Scale-free network of earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Get acquainted with the computer program, The Quadratic Transformer. When you're satisfied that you understand how it works, try the tasks below.
 Weaving a Parabola Web with the Quadratic Transformer In this activity, you explore how the graph of a quadratic function and its symbolic expression relate to each other. You start with a set of four
Weaving a Parabola Web with the Quadratic Transformer In this activity, you explore how the graph of a quadratic function and its symbolic expression relate to each other. You start with a set of four
Motivation Data mining: ~ find patterns (rules, outliers) Problem#1: How do real graphs look like? Problem#2: How do they evolve? Problem#3: How to ge
 Graph Mining: Laws, Generators and Tools Christos Faloutsos CMU Thank you! Sharad Mehrotra UCI 2007 C. Faloutsos 2 Outline Problem definition / Motivation Static & dynamic laws; generators Tools: CenterPiece
Graph Mining: Laws, Generators and Tools Christos Faloutsos CMU Thank you! Sharad Mehrotra UCI 2007 C. Faloutsos 2 Outline Problem definition / Motivation Static & dynamic laws; generators Tools: CenterPiece
Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, Prof. Peter Dodds
 Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, 2009 Prof. Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics University of Vermont Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
Complex Networks, Course 303A, Spring, 2009 Prof. Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics University of Vermont Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
Introducing the New SciFinder. Veli Pekka Hyttinen Regional Marketing Manager, Central and Eastern Europe Jasna April 1, 2014
 Introducing the New SciFinder Veli Pekka Hyttinen Regional Marketing Manager, Central and Eastern Europe Jasna April 1, 2014 Hyttinen, CAS 1 ( 20 ) Jasna, April 1, 2014 Chemical Abstracts Service A non
Introducing the New SciFinder Veli Pekka Hyttinen Regional Marketing Manager, Central and Eastern Europe Jasna April 1, 2014 Hyttinen, CAS 1 ( 20 ) Jasna, April 1, 2014 Chemical Abstracts Service A non
Topology and Evolution of Technology Innovation Networks
 Topology and Evolution of Technology Innovation Networks Sergi Valverde Ricard V. Solé Mark Bedau Norman Packard SFI WORKING PAPER: 2006-12-054 SFI Working Papers contain accounts of scientific work of
Topology and Evolution of Technology Innovation Networks Sergi Valverde Ricard V. Solé Mark Bedau Norman Packard SFI WORKING PAPER: 2006-12-054 SFI Working Papers contain accounts of scientific work of
Agata Fronczak, Piotr Fronczak and Janusz A. Hołyst. Information-theoretic approach to random networks: fluctuations and responses
 Creen Meeting in Karlsruhe, June 2004 Agata Fronczak, Piotr Fronczak and Janusz A. Hołyst Faculty of Physics, Warsaw University of Technology Information-theoretic approach to random networks: fluctuations
Creen Meeting in Karlsruhe, June 2004 Agata Fronczak, Piotr Fronczak and Janusz A. Hołyst Faculty of Physics, Warsaw University of Technology Information-theoretic approach to random networks: fluctuations
Properties of Continuous Probability Distributions The graph of a continuous probability distribution is a curve. Probability is represented by area
 Properties of Continuous Probability Distributions The graph of a continuous probability distribution is a curve. Probability is represented by area under the curve. The curve is called the probability
Properties of Continuous Probability Distributions The graph of a continuous probability distribution is a curve. Probability is represented by area under the curve. The curve is called the probability
Monochromatic and Rainbow Colorings
 Chapter 11 Monochromatic and Rainbow Colorings There are instances in which we will be interested in edge colorings of graphs that do not require adjacent edges to be assigned distinct colors Of course,
Chapter 11 Monochromatic and Rainbow Colorings There are instances in which we will be interested in edge colorings of graphs that do not require adjacent edges to be assigned distinct colors Of course,
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T0 INTRODUCING PARABOLAS 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) QUADRATIC FUNCTION = a statement containing different kinds of variables where one variable lacks a visible exponent and
FOM 11 T0 INTRODUCING PARABOLAS 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) QUADRATIC FUNCTION = a statement containing different kinds of variables where one variable lacks a visible exponent and
Induced Cycles of Fixed Length
 Induced Cycles of Fixed Length Terry McKee Wright State University Dayton, Ohio USA terry.mckee@wright.edu Cycles in Graphs Vanderbilt University 31 May 2012 Overview 1. Investigating the fine structure
Induced Cycles of Fixed Length Terry McKee Wright State University Dayton, Ohio USA terry.mckee@wright.edu Cycles in Graphs Vanderbilt University 31 May 2012 Overview 1. Investigating the fine structure
Chapter 3: Propositional Calculus: Deductive Systems. September 19, 2008
 Chapter 3: Propositional Calculus: Deductive Systems September 19, 2008 Outline 1 3.1 Deductive (Proof) System 2 3.2 Gentzen System G 3 3.3 Hilbert System H 4 3.4 Soundness and Completeness; Consistency
Chapter 3: Propositional Calculus: Deductive Systems September 19, 2008 Outline 1 3.1 Deductive (Proof) System 2 3.2 Gentzen System G 3 3.3 Hilbert System H 4 3.4 Soundness and Completeness; Consistency
 0.20 N=000 N=5000 0.30 0.5 0.25 P 0.0 P 0.20 0.5 0.05 0.0 0.05 0.00 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8.0 n r 0.00 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8.0 n r 0.4 N=0000 0.6 0.5 N=50000 P 0.3 0.2 0. P 0.4 0.3 0.2 0. 0.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
0.20 N=000 N=5000 0.30 0.5 0.25 P 0.0 P 0.20 0.5 0.05 0.0 0.05 0.00 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8.0 n r 0.00 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8.0 n r 0.4 N=0000 0.6 0.5 N=50000 P 0.3 0.2 0. P 0.4 0.3 0.2 0. 0.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Erzsébet Ravasz Advisor: Albert-László Barabási
 Hierarchical Networks Erzsébet Ravasz Advisor: Albert-László Barabási Introduction to networks How to model complex networks? Clustering and hierarchy Hierarchical organization of cellular metabolism The
Hierarchical Networks Erzsébet Ravasz Advisor: Albert-László Barabási Introduction to networks How to model complex networks? Clustering and hierarchy Hierarchical organization of cellular metabolism The
The Probabilistic Method
 The Probabilistic Method In Graph Theory Ehssan Khanmohammadi Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University February 25, 2010 What do we mean by the probabilistic method? Why use this method?
The Probabilistic Method In Graph Theory Ehssan Khanmohammadi Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University February 25, 2010 What do we mean by the probabilistic method? Why use this method?
Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks
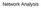 Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Hyperbolic metric spaces and their applications to large complex real world networks II
 Hyperbolic metric spaces Hyperbolic metric spaces and their applications to large complex real world networks II Gabriel H. Tucci Bell Laboratories Alcatel-Lucent May 17, 2010 Tucci Hyperbolic metric spaces
Hyperbolic metric spaces Hyperbolic metric spaces and their applications to large complex real world networks II Gabriel H. Tucci Bell Laboratories Alcatel-Lucent May 17, 2010 Tucci Hyperbolic metric spaces
Navigating between patents, papers, abstracts and databases using public sources and tools
 Navigating between patents, papers, abstracts and databases using public sources and tools Christopher Southan 1 and Sean Ekins 2 TW2Informatics, Göteborg, Sweden, Collaborative Drug Discovery, North Carolina,
Navigating between patents, papers, abstracts and databases using public sources and tools Christopher Southan 1 and Sean Ekins 2 TW2Informatics, Göteborg, Sweden, Collaborative Drug Discovery, North Carolina,
Mining Newsgroups Using Networks Arising From Social Behavior by Rakesh Agrawal et al. Presented by Will Lee
 Mining Newsgroups Using Networks Arising From Social Behavior by Rakesh Agrawal et al. Presented by Will Lee wwlee1@uiuc.edu September 28, 2004 Motivation IR on newsgroups is challenging due to lack of
Mining Newsgroups Using Networks Arising From Social Behavior by Rakesh Agrawal et al. Presented by Will Lee wwlee1@uiuc.edu September 28, 2004 Motivation IR on newsgroups is challenging due to lack of
Alternative Methods for Obtaining. Optimization Bounds. AFOSR Program Review, April Carnegie Mellon University. Grant FA
 Alternative Methods for Obtaining Optimization Bounds J. N. Hooker Carnegie Mellon University AFOSR Program Review, April 2012 Grant FA9550-11-1-0180 Integrating OR and CP/AI Early support by AFOSR First
Alternative Methods for Obtaining Optimization Bounds J. N. Hooker Carnegie Mellon University AFOSR Program Review, April 2012 Grant FA9550-11-1-0180 Integrating OR and CP/AI Early support by AFOSR First
Network Analysis and Modeling
 lecture 0: what are networks and how do we talk about them? 2017 Aaron Clauset 003 052 002 001 Aaron Clauset @aaronclauset Assistant Professor of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder External
lecture 0: what are networks and how do we talk about them? 2017 Aaron Clauset 003 052 002 001 Aaron Clauset @aaronclauset Assistant Professor of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder External
An Interlacing Approach for Bounding the Sum of Laplacian Eigenvalues of Graphs
 An Interlacing Approach for Bounding the Sum of Laplacian Eigenvalues of Graphs Tilburg University joint work with M.A. Fiol, W.H. Haemers and G. Perarnau Laplacian matrix Eigenvalue interlacing Two cases
An Interlacing Approach for Bounding the Sum of Laplacian Eigenvalues of Graphs Tilburg University joint work with M.A. Fiol, W.H. Haemers and G. Perarnau Laplacian matrix Eigenvalue interlacing Two cases
Networks as vectors of their motif frequencies and 2-norm distance as a measure of similarity
 Networks as vectors of their motif frequencies and 2-norm distance as a measure of similarity CS322 Project Writeup Semih Salihoglu Stanford University 353 Serra Street Stanford, CA semih@stanford.edu
Networks as vectors of their motif frequencies and 2-norm distance as a measure of similarity CS322 Project Writeup Semih Salihoglu Stanford University 353 Serra Street Stanford, CA semih@stanford.edu
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds
 MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
Dynamic Programming on Trees. Example: Independent Set on T = (V, E) rooted at r V.
 Dynamic Programming on Trees Example: Independent Set on T = (V, E) rooted at r V. For v V let T v denote the subtree rooted at v. Let f + (v) be the size of a maximum independent set for T v that contains
Dynamic Programming on Trees Example: Independent Set on T = (V, E) rooted at r V. For v V let T v denote the subtree rooted at v. Let f + (v) be the size of a maximum independent set for T v that contains
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Alan Frieze Charalampos (Babis) E. Tsourakakis WAW June 12 WAW '12 1
 Alan Frieze af1p@random.math.cmu.edu Charalampos (Babis) E. Tsourakakis ctsourak@math.cmu.edu WAW 2012 22 June 12 WAW '12 1 Introduction Degree Distribution Diameter Highest Degrees Eigenvalues Open Problems
Alan Frieze af1p@random.math.cmu.edu Charalampos (Babis) E. Tsourakakis ctsourak@math.cmu.edu WAW 2012 22 June 12 WAW '12 1 Introduction Degree Distribution Diameter Highest Degrees Eigenvalues Open Problems
Network models: dynamical growth and small world
 Network models: dynamical growth and small world Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics
Network models: dynamical growth and small world Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics
Prerequisite: Qualification by assessment process or completion of Mathematics 1050 or one year of high school algebra with a grade of "C" or higher.
 Reviewed by: D. Jones Reviewed by: B. Jean Reviewed by: M. Martinez Text update: Spring 2017 Date reviewed: February 2014 C&GE Approved: March 10, 2014 Board Approved: April 9, 2014 Mathematics (MATH)
Reviewed by: D. Jones Reviewed by: B. Jean Reviewed by: M. Martinez Text update: Spring 2017 Date reviewed: February 2014 C&GE Approved: March 10, 2014 Board Approved: April 9, 2014 Mathematics (MATH)
Intelligent Data Analysis. PageRank. School of Computer Science University of Birmingham
 Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
A necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of a spanning tree with specified vertices having large degrees
 A necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of a spanning tree with specified vertices having large degrees Yoshimi Egawa Department of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo University of
A necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of a spanning tree with specified vertices having large degrees Yoshimi Egawa Department of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo University of
Network Observational Methods and. Quantitative Metrics: II
 Network Observational Methods and Whitney topics Quantitative Metrics: II Community structure (some done already in Constraints - I) The Zachary Karate club story Degree correlation Calculating degree
Network Observational Methods and Whitney topics Quantitative Metrics: II Community structure (some done already in Constraints - I) The Zachary Karate club story Degree correlation Calculating degree
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 6 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 6 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 6 Dec 2007](/thumbs/79/79835373.jpg) DRAFT VERSION MAY 28, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 THE IMPORTANCE OF BEING FIRST: POSITION DEPENDENT CITATION RATES ON ARXIV:ASTRO-PH J. P. DIETRICH ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
DRAFT VERSION MAY 28, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 THE IMPORTANCE OF BEING FIRST: POSITION DEPENDENT CITATION RATES ON ARXIV:ASTRO-PH J. P. DIETRICH ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
Overview of Network Theory
 Overview of Network Theory MAE 298, Spring 2009, Lecture 1 Prof. Raissa D Souza University of California, Davis Example social networks (Immunology; viral marketing; aliances/policy) M. E. J. Newman The
Overview of Network Theory MAE 298, Spring 2009, Lecture 1 Prof. Raissa D Souza University of California, Davis Example social networks (Immunology; viral marketing; aliances/policy) M. E. J. Newman The
Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map
 Subject Area Mathematics Senior High Course Name Advanced Algebra 2A (Prentice Hall Mathematics) Date April 2010 The Advanced Algebra 2A course parallels each other in content and time. The Advanced Algebra
Subject Area Mathematics Senior High Course Name Advanced Algebra 2A (Prentice Hall Mathematics) Date April 2010 The Advanced Algebra 2A course parallels each other in content and time. The Advanced Algebra
Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data. Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data 1 / 27
 Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data 1 / 27 Categorical Data Four ways to display categorical data: 1 Frequency and Relative Frequency Table 2 Bar graph (Pareto chart)
Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data Chapter 7: Statistics Describing Data 1 / 27 Categorical Data Four ways to display categorical data: 1 Frequency and Relative Frequency Table 2 Bar graph (Pareto chart)
Administrivia. Blobs and Graphs. Assignment 2. Prof. Noah Snavely CS1114. First part due tomorrow by 5pm Second part due next Friday by 5pm
 Blobs and Graphs Prof. Noah Snavely CS1114 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1114 Administrivia Assignment 2 First part due tomorrow by 5pm Second part due next Friday by 5pm 2 Prelims Prelim 1: March
Blobs and Graphs Prof. Noah Snavely CS1114 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1114 Administrivia Assignment 2 First part due tomorrow by 5pm Second part due next Friday by 5pm 2 Prelims Prelim 1: March
v t 2 2t 8. Fig. 7 (i) Write down the velocity of the insect when t 0. (ii) Show that the insect is instantaneously at rest when t 2and when t 4.
 1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
A Modified Method Using the Bethe Hessian Matrix to Estimate the Number of Communities
 Journal of Advanced Statistics, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2018 https://dx.doi.org/10.22606/jas.2018.32001 15 A Modified Method Using the Bethe Hessian Matrix to Estimate the Number of Communities Laala Zeyneb
Journal of Advanced Statistics, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2018 https://dx.doi.org/10.22606/jas.2018.32001 15 A Modified Method Using the Bethe Hessian Matrix to Estimate the Number of Communities Laala Zeyneb
y z ). Write all solutions using only positive
 1. a) Graph the equation x y =. b) What is the x-intercept? What is the y-intercept? d) What is the slope of this line?. a) Find the slope of the line joining the points and ( b) Find the equation of this
1. a) Graph the equation x y =. b) What is the x-intercept? What is the y-intercept? d) What is the slope of this line?. a) Find the slope of the line joining the points and ( b) Find the equation of this
Long Term Evolution of Networks CS224W Final Report
 Long Term Evolution of Networks CS224W Final Report Jave Kane (SUNET ID javekane), Conrad Roche (SUNET ID conradr) Nov. 13, 2014 Introduction and Motivation Many studies in social networking and computer
Long Term Evolution of Networks CS224W Final Report Jave Kane (SUNET ID javekane), Conrad Roche (SUNET ID conradr) Nov. 13, 2014 Introduction and Motivation Many studies in social networking and computer
Infinite Limits of Other Random Graphs
 Infinite Limits of Other Random Graphs Richard Elwes, University of Leeds 29 July 2016 Erdős - Rényi Graphs Definition (Erdős & Rényi, 1960) Fix p (0, 1) and n N {ω}. Form a random graph G n (p) with n
Infinite Limits of Other Random Graphs Richard Elwes, University of Leeds 29 July 2016 Erdős - Rényi Graphs Definition (Erdős & Rényi, 1960) Fix p (0, 1) and n N {ω}. Form a random graph G n (p) with n
Chapter 2 Fitness-Based Generative Models for Power-Law Networks
 Chapter 2 Fitness-Based Generative Models for Power-Law Networks Khanh Nguyen and Duc A. Tran Abstract Many real-world complex networks exhibit a power-law degree distribution. A dominant concept traditionally
Chapter 2 Fitness-Based Generative Models for Power-Law Networks Khanh Nguyen and Duc A. Tran Abstract Many real-world complex networks exhibit a power-law degree distribution. A dominant concept traditionally
arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.dl] 22 Sep 2006
![arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.dl] 22 Sep 2006 arxiv:cs/ v1 [cs.dl] 22 Sep 2006](/thumbs/74/69871643.jpg) Submitted to: Learned Publishing E-prints and Journal Articles in Astronomy: a Productive Co-existence arxiv:cs/0609126v1 [cs.dl] 22 Sep 2006 Edwin A. Henneken 1, Michael J. Kurtz 1, Simeon Warner 2, Paul
Submitted to: Learned Publishing E-prints and Journal Articles in Astronomy: a Productive Co-existence arxiv:cs/0609126v1 [cs.dl] 22 Sep 2006 Edwin A. Henneken 1, Michael J. Kurtz 1, Simeon Warner 2, Paul
Commonly observed in nature and in the social sciences are
 Nonuniversal power law scaling in the probability distribution of scientific citations George J. Peterson a, Steve Pressé b, and Ken A. Dill b,1 a Biophysics Graduate Group, and b Department of Pharmaceutical
Nonuniversal power law scaling in the probability distribution of scientific citations George J. Peterson a, Steve Pressé b, and Ken A. Dill b,1 a Biophysics Graduate Group, and b Department of Pharmaceutical
Linear graph theory. Basic definitions of linear graphs
 Linear graph theory Linear graph theory, a branch of combinatorial mathematics has proved to be a useful tool for the study of large or complex systems. Leonhard Euler wrote perhaps the first paper on
Linear graph theory Linear graph theory, a branch of combinatorial mathematics has proved to be a useful tool for the study of large or complex systems. Leonhard Euler wrote perhaps the first paper on
Efficient Network Structures with Separable Heterogeneous Connection Costs
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Efficient Network Structures with Separable Heterogeneous Connection Costs Babak Heydari and Mohsen Mosleh and Kia Dalili School of Systems and Enterprises, Stevens Institute
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Efficient Network Structures with Separable Heterogeneous Connection Costs Babak Heydari and Mohsen Mosleh and Kia Dalili School of Systems and Enterprises, Stevens Institute
Link Prediction. Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan
 Link Prediction Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan 11-06-2013 Link Prediction Which pair of nodes should be connected? Applications Facebook friend suggestion Recommendation systems Monitoring and controlling
Link Prediction Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan 11-06-2013 Link Prediction Which pair of nodes should be connected? Applications Facebook friend suggestion Recommendation systems Monitoring and controlling
Equivalent Formulations of the Bunk Bed Conjecture
 North Carolina Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 2, Pages 23 28 (Accepted May 27, 2016, published May 31, 2016) ISSN 2380-7539 Equivalent Formulations of the Bunk Bed Conjecture James Rudzinski
North Carolina Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 2, Pages 23 28 (Accepted May 27, 2016, published May 31, 2016) ISSN 2380-7539 Equivalent Formulations of the Bunk Bed Conjecture James Rudzinski
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Daniel Inequalities Inequalities on number lines 1 Grade 4 Objective: Represent the solution of a linear inequality on a number line. Question 1 Draw diagrams to represent these
PLC Papers Created For: Daniel Inequalities Inequalities on number lines 1 Grade 4 Objective: Represent the solution of a linear inequality on a number line. Question 1 Draw diagrams to represent these
Recent BaBar results on CP Violation in B decays
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Recent BaBar results on CP Violation in B decays To cite this article: Arantza Oyanguren 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 447 012029 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Recent BaBar results on CP Violation in B decays To cite this article: Arantza Oyanguren 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 447 012029 View the article online for
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 4.1: Writing Equations to Describe Patterns
 Master 4.20 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 4.1: Writing Equations to Describe Patterns 1. In each equation, determine the value of A when n is 3. a) A = 2n + 1 b) A = 3n 2 c) A = 4n + 3 d) A = 30 2n 2. The pattern
Master 4.20 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 4.1: Writing Equations to Describe Patterns 1. In each equation, determine the value of A when n is 3. a) A = 2n + 1 b) A = 3n 2 c) A = 4n + 3 d) A = 30 2n 2. The pattern
Self Similar (Scale Free, Power Law) Networks (I)
 Self Similar (Scale Free, Power Law) Networks (I) E6083: lecture 4 Prof. Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA {predrag}@ee.columbia.edu February 7, 2007
Self Similar (Scale Free, Power Law) Networks (I) E6083: lecture 4 Prof. Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA {predrag}@ee.columbia.edu February 7, 2007
Test Your Strength AB Calculus: Section A 35 questions No calculator allowed. A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. nonexistent. . Which of the following
 Test Your Strength AB Calculus: Section A 35 questions No calculator allowed Directions: Use the answer sheet to input your answers. Caps or lower case are OK. If you need to guess, put an X in the guess
Test Your Strength AB Calculus: Section A 35 questions No calculator allowed Directions: Use the answer sheet to input your answers. Caps or lower case are OK. If you need to guess, put an X in the guess
Discovering molecular pathways from protein interaction and ge
 Discovering molecular pathways from protein interaction and gene expression data 9-4-2008 Aim To have a mechanism for inferring pathways from gene expression and protein interaction data. Motivation Why
Discovering molecular pathways from protein interaction and gene expression data 9-4-2008 Aim To have a mechanism for inferring pathways from gene expression and protein interaction data. Motivation Why
MATH-AII Boulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MTH-II oulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:G9SY6 1 If f (x ) = x 3 + x - 8, what is f (-8)? -568 456-456 568 Which of the following functions does NOT have a range
MTH-II oulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:G9SY6 1 If f (x ) = x 3 + x - 8, what is f (-8)? -568 456-456 568 Which of the following functions does NOT have a range
ECS 253 / MAE 253 April 26, Intro to Biological Networks, Motifs, and Model selection/validation
 ECS 253 / MAE 253 April 26, 2016 Intro to Biological Networks, Motifs, and Model selection/validation Announcement HW2, due May 3 (one week) HW2b, due May 5 HW2a, due May 5. Will be posted on Smartsite.
ECS 253 / MAE 253 April 26, 2016 Intro to Biological Networks, Motifs, and Model selection/validation Announcement HW2, due May 3 (one week) HW2b, due May 5 HW2a, due May 5. Will be posted on Smartsite.
Additional Test Scores. Test Scores Cross Test Scores Subscores Now let's look at what to do next: Areas of Strength
 SAT Practice Test D This test scanned: September 22, 2016 Verbal 770 Your Progress 1600 100 Math 660 Total* 130 / 1600 130 1200 1000 910 990 1060 800 600 00 Test A 8//2016 Test B 8/13/2016 Test C 8/27/2016
SAT Practice Test D This test scanned: September 22, 2016 Verbal 770 Your Progress 1600 100 Math 660 Total* 130 / 1600 130 1200 1000 910 990 1060 800 600 00 Test A 8//2016 Test B 8/13/2016 Test C 8/27/2016
Heavy Tails: The Origins and Implications for Large Scale Biological & Information Systems
 Heavy Tails: The Origins and Implications for Large Scale Biological & Information Systems Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA {predrag}@ee.columbia.edu
Heavy Tails: The Origins and Implications for Large Scale Biological & Information Systems Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA {predrag}@ee.columbia.edu
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Generalizing Convolutional Neural Networks to Graphstructured. Ben Walker Department of Mathematics, UNC-Chapel Hill 5/4/2018
 Generalizing Convolutional Neural Networks to Graphstructured Data Ben Walker Department of Mathematics, UNC-Chapel Hill 5/4/2018 Overview Relational structure in data and how to approach it Defferrard,
Generalizing Convolutional Neural Networks to Graphstructured Data Ben Walker Department of Mathematics, UNC-Chapel Hill 5/4/2018 Overview Relational structure in data and how to approach it Defferrard,
Indiana Academic Super Bowl. Math Round Coaches Practice. A Program of the Indiana Association of School Principals
 Indiana Academic Super Bowl Math Round 2017 Coaches Practice A Program of the Indiana Association of School Principals Students: Throughout this round we will be pronouncing mathematic symbols and concepts
Indiana Academic Super Bowl Math Round 2017 Coaches Practice A Program of the Indiana Association of School Principals Students: Throughout this round we will be pronouncing mathematic symbols and concepts
WORLD AREA FORECAST SYSTEM OPERATIONS GROUP (WAFSOPSG) PROGRESS REPORT OF WAFSOPSG/5-WP/15
 WORLD AREA FORECAST SYSTEM OPERATIONS GROUP (WAFSOPSG) FIFTH MEETING Paris, France, 16 to 18 September 2009 PROGRESS REPORT OF WAFSOPSG/5-WP/15 VISUALISATION OF WAFS FORECASTS: WEB-BASED DISTRIBUTION (Prepared
WORLD AREA FORECAST SYSTEM OPERATIONS GROUP (WAFSOPSG) FIFTH MEETING Paris, France, 16 to 18 September 2009 PROGRESS REPORT OF WAFSOPSG/5-WP/15 VISUALISATION OF WAFS FORECASTS: WEB-BASED DISTRIBUTION (Prepared
Reachability of recurrent positions in the chip-firing game
 Egerváry Research Group on Combinatorial Optimization Technical reports TR-2015-10. Published by the Egerváry Research Group, Pázmány P. sétány 1/C, H 1117, Budapest, Hungary. Web site: www.cs.elte.hu/egres.
Egerváry Research Group on Combinatorial Optimization Technical reports TR-2015-10. Published by the Egerváry Research Group, Pázmány P. sétány 1/C, H 1117, Budapest, Hungary. Web site: www.cs.elte.hu/egres.
Protein Complex Identification by Supervised Graph Clustering
 Protein Complex Identification by Supervised Graph Clustering Yanjun Qi 1, Fernanda Balem 2, Christos Faloutsos 1, Judith Klein- Seetharaman 1,2, Ziv Bar-Joseph 1 1 School of Computer Science, Carnegie
Protein Complex Identification by Supervised Graph Clustering Yanjun Qi 1, Fernanda Balem 2, Christos Faloutsos 1, Judith Klein- Seetharaman 1,2, Ziv Bar-Joseph 1 1 School of Computer Science, Carnegie
Network Science & Telecommunications
 Network Science & Telecommunications Piet Van Mieghem 1 ITC30 Networking Science Vision Day 5 September 2018, Vienna Outline Networks Birth of Network Science Function and graph Outlook 1 Network: service(s)
Network Science & Telecommunications Piet Van Mieghem 1 ITC30 Networking Science Vision Day 5 September 2018, Vienna Outline Networks Birth of Network Science Function and graph Outlook 1 Network: service(s)
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
arxiv: v1 [math.st] 1 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.st] 1 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.st] 1 Nov 2017](/thumbs/94/119463642.jpg) ASSESSING THE RELIABILITY POLYNOMIAL BASED ON PERCOLATION THEORY arxiv:1711.00303v1 [math.st] 1 Nov 2017 SAJADI, FARKHONDEH A. Department of Statistics, University of Isfahan, Isfahan 81744,Iran; f.sajadi@sci.ui.ac.ir
ASSESSING THE RELIABILITY POLYNOMIAL BASED ON PERCOLATION THEORY arxiv:1711.00303v1 [math.st] 1 Nov 2017 SAJADI, FARKHONDEH A. Department of Statistics, University of Isfahan, Isfahan 81744,Iran; f.sajadi@sci.ui.ac.ir
Chapter 9: Relations Relations
 Chapter 9: Relations 9.1 - Relations Definition 1 (Relation). Let A and B be sets. A binary relation from A to B is a subset R A B, i.e., R is a set of ordered pairs where the first element from each pair
Chapter 9: Relations 9.1 - Relations Definition 1 (Relation). Let A and B be sets. A binary relation from A to B is a subset R A B, i.e., R is a set of ordered pairs where the first element from each pair
Strongly 2-connected orientations of graphs
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 04, 2018 Strongly 2-connected orientations of graphs Thomassen, Carsten Published in: Journal of Combinatorial Theory. Series B Link to article, DOI: 10.1016/j.jctb.2014.07.004
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 04, 2018 Strongly 2-connected orientations of graphs Thomassen, Carsten Published in: Journal of Combinatorial Theory. Series B Link to article, DOI: 10.1016/j.jctb.2014.07.004
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
RTM: Laws and a Recursive Generator for Weighted Time-Evolving Graphs
 RTM: Laws and a Recursive Generator for Weighted Time-Evolving Graphs Leman Akoglu Mary McGlohon Christos Faloutsos Carnegie Mellon University, School of Computer Science {lakoglu, mmcgloho, christos}@cs.cmu.edu
RTM: Laws and a Recursive Generator for Weighted Time-Evolving Graphs Leman Akoglu Mary McGlohon Christos Faloutsos Carnegie Mellon University, School of Computer Science {lakoglu, mmcgloho, christos}@cs.cmu.edu
AP CALCULUS - BC BC LECTURE NOTES MS. RUSSELL Section Number: Topics: Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids
 AP CALCULUS - BC BC LECTURE NOTES MS. RUSSELL Section Number: Topics: Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids Part: 1 of 2 Mass 7.6 Center of Mass in a One-Dimensional System Center of Mass in a Two-Dimensional
AP CALCULUS - BC BC LECTURE NOTES MS. RUSSELL Section Number: Topics: Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids Part: 1 of 2 Mass 7.6 Center of Mass in a One-Dimensional System Center of Mass in a Two-Dimensional
Dynamics of Real-world Networks
 Dynamics of Real-world Networks Thesis proposal Jurij Leskovec Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University May 2, 2007 Thesis committee: Christos Faloutsos, CMU Avrim Blum, CMU John Lafferty,
Dynamics of Real-world Networks Thesis proposal Jurij Leskovec Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University May 2, 2007 Thesis committee: Christos Faloutsos, CMU Avrim Blum, CMU John Lafferty,
Groups of vertices and Core-periphery structure. By: Ralucca Gera, Applied math department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA, USA
 Groups of vertices and Core-periphery structure By: Ralucca Gera, Applied math department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA, USA Mostly observed real networks have: Why? Heavy tail (powerlaw most
Groups of vertices and Core-periphery structure By: Ralucca Gera, Applied math department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA, USA Mostly observed real networks have: Why? Heavy tail (powerlaw most
Relation between Graphs
 Max Planck Intitute for Math. in the Sciences, Leipzig, Germany Joint work with Jan Hubička, Jürgen Jost, Peter F. Stadler and Ling Yang SCAC2012, SJTU, Shanghai Outline Motivation and Background 1 Motivation
Max Planck Intitute for Math. in the Sciences, Leipzig, Germany Joint work with Jan Hubička, Jürgen Jost, Peter F. Stadler and Ling Yang SCAC2012, SJTU, Shanghai Outline Motivation and Background 1 Motivation
Climate Data for Non-experts: Standards-based Interoperability
 Climate Data for Non-experts: Standards-based Interoperability Ben Domenico Unidata Program Center University Corporation for Atmospheric Research April 2010 Working Together on A Mosaic for Atmospheric
Climate Data for Non-experts: Standards-based Interoperability Ben Domenico Unidata Program Center University Corporation for Atmospheric Research April 2010 Working Together on A Mosaic for Atmospheric
Communities Via Laplacian Matrices. Degree, Adjacency, and Laplacian Matrices Eigenvectors of Laplacian Matrices
 Communities Via Laplacian Matrices Degree, Adjacency, and Laplacian Matrices Eigenvectors of Laplacian Matrices The Laplacian Approach As with betweenness approach, we want to divide a social graph into
Communities Via Laplacian Matrices Degree, Adjacency, and Laplacian Matrices Eigenvectors of Laplacian Matrices The Laplacian Approach As with betweenness approach, we want to divide a social graph into
Móstoles, Spain. Keywords: complex networks, dual graph, line graph, line digraph.
 Int. J. Complex Systems in Science vol. 1(2) (2011), pp. 100 106 Line graphs for directed and undirected networks: An structural and analytical comparison Regino Criado 1, Julio Flores 1, Alejandro García
Int. J. Complex Systems in Science vol. 1(2) (2011), pp. 100 106 Line graphs for directed and undirected networks: An structural and analytical comparison Regino Criado 1, Julio Flores 1, Alejandro García
