University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy. PH 105 LeClair Summer Problem Set 3 Solutions
|
|
|
- June Dennis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 105 LeClair Summer 2012 Instructions: Problem Set 3 Solutions 1. Answer all questions below. All questions have equal weight. 2. Show your work for full credit; using the problem template is recommended. 3. All problems are due Friday 1 June 2012 at the start of lecture. 4. You may collaborate, but everyone must turn in their own work. 1. HRW 4.15 A particle leaves the origin with an initial velocity v i = (3.00 î) m/s and a constant acceleration a = ( 1.00 î ĵ) m/s 2. When it reaches its maximum x coordinate, what are its (a) velocity and (b) position vectors? Solution: Given: The initial velocity and acceleration vectors of a particle. Given in vector form, we may write them explicitly in terms of components as well: v i = 3.00 îm/s = v ix î + v iy ĵ (1) = v ix = 3.00 m/s v iy = 0 (2) a = ( 1.00 î ĵ) m/s 2 = a ix î + a iy ĵ (3) = a ix = 1.00 m/s 2 a iy = m/s 2 (4) Find: The maximum x coordinate, and the velocity and position vectors at the corresponding time. Sketch: A sketch may be a bit unnecessary in this case, but here you are: y a y a x a x v Figure 1: A particle at the origin with an initial velocity and acceleration. Relevant equations: Since the acceleration is constant, our usual equations of motion work for the motion along both x and y axes. We know that we have a constant x component of acceleration a x = 1.00 m/s 2, an initial velocity along the x axis of v xi = 3.00 m/s 2, and an initial position of
2 x i =0 since the particle starts at the origin. The velocity and x coordinate are easily found at any time t later: v x (t) = v ix + a x t (5) x(t) = x i + v ix t a xt 2 (6) Since our particle starts out at the origin, x i =0. Similiarly, we can write down the y velocity and position at any later time: v y (t) = v iy + a y t (7) y(t) = y i + v iy t a yt 2 (8) Again, since we start at the origin, y i =0. Now that we have x(t), we can find the time at which it is maximum, t max : by differentiation: dx d 2 x dt = 0 and tmax dt 2 < 0 (9) tmax Next, we need to find the position vector r(t) and velocity vector v(t): r(t) = r i + v i t a t2 = (x i î + y i ĵ) + (v ix î + v iy ĵ)t (a xî + a y ĵ)t 2 (10) v(t) = v i + at = (v ix î + v iy ĵ) + (a x î + a y ĵ)t (11) Again, since the particle starts at the origin, r i = 0; we know all the other quantities already. Finally, we need to evaluate v and r at t max to complete the problem. Symbolic solution: First, we can immediately write down the equation for x(t) and maximize it: x(t) = x i + v ix t a xt 2 dx dt = v ix + a x t max = 0 = t max = v ix tmax d 2 x dt 2 = a x a x (12) The time found this way will correspond to a maximum (rather than a minimum) if the second derivative d 2 x/dt 2 = a x is negative, i.e., so long as the acceleration a x is negative. Since we know
3 a x = 1.00 m/s 2, we have definitely found a maximum. Given the time at which the maximum x coordinate occurs, we can find that x coordinate readily: v(t max ) = v i + at max = v i v ix a x a r(t max ) = r i + v i t max a t2 max = r i v ix v i + v2 ix a x 2a 2 a (13) x Numeric solution: The x components of the velocity and acceleration are a x = 1.00 m/s 2 v x = 3.00 m/s (14) which makes the time for the maximum x coordinate t max = v ix a x = 3.00 s (15) Note also that d 2 x/dt 2 = 1.00, which ensures that we have found a maximum of x(t). At this point, we can just write down the expressions for r(t) and v(t) and plug in the numbers: v(t max ) = v i + a t max = (3.00 m/s î) + ( 1.00 m/s 2 î m/s 2 ĵ ) (3.00 s) = ( 1.5 ĵ) m/s (16) r(t max ) = r i + v i t max a t2 max = 0 + (3.00 m/s î) (3.00 s) + 1 ( 1.00 m/s2 î m/s 2 ĵ ) (3.00 s) 2 2 = (9.00 m î) + ( 4.50 m î 2.25 m ĵ) = (4.5 î 2.25 ĵ) m (17) Double check: We carried the units throughout our calculations, and can be fairly confident that they are correct. We also performed the second derivative test to ensure that we found a maximum in x(t). 2. HRW 4.23 A projectile is fired horizontally from a gun that is 45.0 m above flat ground, emerging from the gun with a speed of 250 m/s. (a) How long does the projectile remain in the air? (b) At what horizontal distance from the firing point does it strike the ground? (c) What is the magnitude of the vertical component of its velocity as it strikes the ground? Solution: Since the particle is launched purely horizontally, there is no initial velocity in the vertical direction. The vertical motion is completely dictated by the gravitational acceleration. For the sake of concreteness, define the +y axis to be up (making gravitational acceleration in the
4 y direction) and the +x axis to be in the direction of the projectile s motion. Let the origin be at the position on the ground directly below he gun (so x=0, y=45.0 m are the launch coordinates). Call the initial height h=45.0 m and the initial velocity v i =250 m/s. Since the vertical motion is independent of the horizontal motion, and completely determined by gravitational acceleration, the projectile will remain in the air exactly as long as it takes the projectile to fall from height h, irrespective of the horizontal launch speed. The equation for y(t) can be written down immediately, and the time at which y = 0 is when the projectile hits the ground. We know the initial height is y i =h and the initial vertical velocity is v iy =0, so: y(t) = y i + v iy t 1 2 gt2 = h 1 2 gt2 = 0 (18) 2h = t hit = 3.03 s (19) g How far does the projectile travel horizontally? We know its horizontal velocity, and we know it has only 3.03 s to travel before it hits the ground. Given x i = 0 and v ix = 250 m/s, and knowing we have no acceleration along the x axis, we can write down the x coordinate as a function of time and then evaluate at the time t hit we just found: x(t) = x i + v ix t a xt 2 = v ix t (20) 2h = x hit = v ix 757 m (21) g Finally, the vertical velocity just before the projectile hits the ground is the same as it would be for any other object dropped from height h. We need only evaluate v y at the time t hit. v y (t) = v iy gt = gt = v y,hit = g (22) 2h g = 2gh 29.7 m/s (23) Negative in this case because the projectile is moving in the y direction. 3. HRW 4.35 A rifle that shoots a bullet at 460 m/s is to be aimed at a target 45.7 m away. If the center of the target is level with the rifle, how high above the target must the rifle barrel be pointed so that the bullet hits dead center? Solution: Given: The magnitude of the initial velocity of a fired bullet v i and its distance from a target d.
5 Find: The height above the target that the shooter must aim y aim. We can easily find this once we know the firing angle θ required for the bullet to hit the target. That is, the angle such that the bullet is at the same height a distance d from where it is fired. Sketch: For convenience, let the origin be at the position the bullet is fired from. Let the +x axis run horizontally, from the bullet to the target, and let the +y axis run vertically. Let time t=0 be the moment the projectile is launched. y x y aim v i O θ d Figure 2: Firing a rifle at a distant target. The bullet s trajectory is (approximately) shown in red. The bullet is fired at an initial velocity v i and angle θ, a distance d from a target. The target is at the same vertical position as the rifle, so we need to find the angle θ and resulting y aim such that the bullet is at y=0 at x=d. Relevant equations: In the x direction, we have constant velocity and no acceleration, with position starting at the origin at t=0: x(t) = v ix t = v i t cos θ (24) In the y direction, we have an initial constant velocity of v iy = v i sin θ and a constant acceleration of a y = g: y(t) = v iy t 1 2 gt2 (25) Solving Eq. 24 for t and substituting into Eq. 25 yields our general projectile equation, giving the path of the projectile y(x) when launched from the origin with initial velocity v i and angle θ above the x axis: y(x) = x tan θ gx 2 2 v i 2 cos 2 θ (26)
6 With our chosen coordinate system and origin, y o = 0. We also need the aiming height above the target in terms of the target distance and firing angle, which we can get from basic trigonometry: tan θ = y aim d (27) Note that one can also use the range equation directly, but this is less instructive. It is fine for you to do this in your own solutions, but keep in mind you will probably not be given these sort of specialized equations on an exam you should know how to derive them. Symbolic solution: We desire the bullet to reach point (d, 0). Substituting these coordinates into Eq. 26, and solving for θ: gx 2 y(x) = x tan θ 2 v i 2 cos 2 θ gd 2 0 = d tan θ 2 v i 2 cos 2 θ gd 2 d tan θ = 2 v i 2 cos 2 θ tan θ cos 2 θ = gd 2 v i 2 sin θ cos θ = 1 sin 2θ = gd 2 2 v i 2 (32) = θ = 1 [ ] gd 2 sin 1 v i 2 (33) (28) (29) (30) (31) Given θ, rearranging Eq. 27 gives us the aiming height: y aim = d tan θ (34) Numeric solution: We are given v i =460 m/s and d=45.7 m: θ = 1 [ ] [( gd 2 sin 1 v i 2 = m/s 2 ) ] (4.57 m) 2 sin 1 (460m/s) (35) Given the angle, we can find the height above the target we need to aim: y aim = d tan θ (45.7 m) tan ( ) sign m = 4.84 cm (36) digits Double check: One check is use the pre-packaged projectile range equation and make sure that
7 we get the same answer. Given θ , we should calculate a range of d. R = v i 2 sin 2θ g = (460 m/s) (sin ) (9.81 m/s 2 ) 45.7 m (37) This is not truly an independent check, since it is derived using the same equations we used above, but it is a nice indication that we haven t gone wrong anywhere. As a more independent estimate, we can first calculate the time it would take the bullet to reach the target in the absence of gravitational acceleration if it were just heading straight toward the target at 460 m/s. This is not so far off the real time, since the firing angle is small anyway: t est = d 0.1 s (38) v i In that time, how far would the bullet fall under the influence of gravity (alone)? y fall 1 2 gt2 est 0.05 m (39) Thus, we estimate that the bullet should fall about 5 cm on its way to the target, meaning we should aim about 5 cm high, in line with what we calculate by more exact means. You can also verify that units come out correctly in Eq. 35 and Eq. 36. The argument of the sin 1 function must be dimensionless, as it is, and y aim should come out in meters, as it does. If you carry the units through the entire calculation, or at least solve the problem symbolically, without numbers until the last step, this sort of check is trivial. 4. A batter hits a baseball coming off of the bat at a 45 angle, making contact a distance 1.22 m above the ground. Over level ground, the batted ball has a range of 107 m. Will the ball clear a 7.32 m tall fence at a distance of 97.5 m? Justify your answer. Hint: use the range equation to get the velocity, then use the trajectory equation to find the path of the ball. Solution: This is problem 4.47 from your textbook. Find: Whether a batted baseball clears a fence, and by what amount it does or does not. Given: The baseball s initial launch height and angle, the range the baseball would have without the fence, the distance to the fence and its height. Sketch: Let the y axis run vertically and the x axis horizontally as shown below. Let the range the baseball would have without the fence be R = 107 m, with the distance to the fence d = 97.5 m
8 and its height h fence = 7.32 m. The baseball is batted at an angle θ = 45 at speed v i a height of h bat =1.22 m above the ground. y h bat x v θ d R h fence Let the origin be at the position the ball leaves the bat. The height of the fence relative to the height of the bat is then δh = h fence h bat What we really need to determine is the ball s y coordinate at x = d. If y > δh, the ball clears the fence. We can use the range the baseball would have without the fence and the launch angle to find the ball s speed, which will allow a complete calculation of the trajectory. Relevant equations: We need only the equations for the range and trajectory of a projectile over level ground: R = v2 i sin 2θ g y(x) = x tan θ gx 2 2v 2 i cos2 θ Symbolic solution: From the range equation above, we can write the velocity in terms of known quantities: v i = Rg sin 2θ The trajectory then becomes y(x) = x tan θ gx2 sin 2θ 2Rg cos 2 θ = x tan θ x2 sin 2θ 2R cos 2 θ The height difference between the ball and the fence is y(d) δh. If it is positive, the ball clears the fence. clearance = y(d) δh = d tan θ d2 sin 2θ 2R cos 2 θ δh = d tan θ d2 sin 2θ 2R cos 2 θ h fence + h bat
9 Numeric solution: Using the numbers given, and noting tan 45 =1, sin 90 =1, and cos 2 45 =1/2 clearance = d d2 R h (97.5 m)2 fence + h bat = 97.5 m 7.32 m m 2.56 m 107 m The ball does clear the fence, by approximately 2.56 m.
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
Random sample problems
 UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 Random sample problems 1. The position of a particle in meters can be described by x = 10t 2.5t 2, where t is in seconds.
UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 Random sample problems 1. The position of a particle in meters can be described by x = 10t 2.5t 2, where t is in seconds.
Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet
 Name Pd Date Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet Because perpendicular vectors are independent of each other we can use the kinematic equations to analyze the vertical (y) and horizontal (x) components of
Name Pd Date Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet Because perpendicular vectors are independent of each other we can use the kinematic equations to analyze the vertical (y) and horizontal (x) components of
Projectile Motion. Chin- Sung Lin STEM GARAGE SCIENCE PHYSICS
 Projectile Motion Chin- Sung Lin Introduction to Projectile Motion q What is Projectile Motion? q Trajectory of a Projectile q Calculation of Projectile Motion Introduction to Projectile Motion q What
Projectile Motion Chin- Sung Lin Introduction to Projectile Motion q What is Projectile Motion? q Trajectory of a Projectile q Calculation of Projectile Motion Introduction to Projectile Motion q What
(483 km) ( 966 km) km. tan km
 Chapter 4 8 Our coordinate system has i pointed east and j pointed north The first displacement is r (483 km)i ˆ AB and the second is r ( 966 km)j ˆ BC (a) The net displacement is r (483 km)i ˆ (966 km)j
Chapter 4 8 Our coordinate system has i pointed east and j pointed north The first displacement is r (483 km)i ˆ AB and the second is r ( 966 km)j ˆ BC (a) The net displacement is r (483 km)i ˆ (966 km)j
Example force problems
 PH 105 / LeClair Fall 2015 Example force problems 1. An advertisement claims that a particular automobile can stop on a dime. What net force would actually be necessary to stop a 850 kg automobile traveling
PH 105 / LeClair Fall 2015 Example force problems 1. An advertisement claims that a particular automobile can stop on a dime. What net force would actually be necessary to stop a 850 kg automobile traveling
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
Chapter 3 2-D Motion
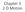 Chapter 3 2-D Motion We will need to use vectors and their properties a lot for this chapter. .. Pythagorean Theorem: Sample problem: First you hike 100 m north. Then hike 50 m west. Finally
Chapter 3 2-D Motion We will need to use vectors and their properties a lot for this chapter. .. Pythagorean Theorem: Sample problem: First you hike 100 m north. Then hike 50 m west. Finally
Chapter 3. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Break problems down into 1-d components
 Motion in 2-d Up until now, we have only been dealing with motion in one-dimension. However, now we have the tools in place to deal with motion in multiple dimensions. We have seen how vectors can be broken
Motion in 2-d Up until now, we have only been dealing with motion in one-dimension. However, now we have the tools in place to deal with motion in multiple dimensions. We have seen how vectors can be broken
Practice Midterm Exam 1. Instructions. You have 60 minutes. No calculators allowed. Show all your work in order to receive full credit.
 MATH202X-F01/UX1 Spring 2015 Practice Midterm Exam 1 Name: Answer Key Instructions You have 60 minutes No calculators allowed Show all your work in order to receive full credit 1 Consider the points P
MATH202X-F01/UX1 Spring 2015 Practice Midterm Exam 1 Name: Answer Key Instructions You have 60 minutes No calculators allowed Show all your work in order to receive full credit 1 Consider the points P
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998)
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Score on each problem:
 95.141 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Section Number Section Instructor Name (last name first) Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided. Show all
95.141 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Section Number Section Instructor Name (last name first) Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided. Show all
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Vectors and Coordinate Systems
 Vectors and Coordinate Systems In Newtonian mechanics, we want to understand how material bodies interact with each other and how this affects their motion through space. In order to be able to make quantitative
Vectors and Coordinate Systems In Newtonian mechanics, we want to understand how material bodies interact with each other and how this affects their motion through space. In order to be able to make quantitative
CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Projectile motion
CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Projectile motion
PH Fall - Section 04 - Version A DRAFT
 1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
Name: Total Points: Physics 201. Midterm 1
 Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
PHYS 111 HOMEWORK #5
 PHYS 111 HOMEWORK #5 Due : 9 Sept. 016 This is a homework set about projectile motion, so we will be using the equations of motion throughout. Therefore, I will collect all those equations here at the
PHYS 111 HOMEWORK #5 Due : 9 Sept. 016 This is a homework set about projectile motion, so we will be using the equations of motion throughout. Therefore, I will collect all those equations here at the
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) Justify your answer: Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) 5 10 m/s 3. Show your work: 3 m/s 2
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
PH Fall - Section 05 - Version C DRAFT
 1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
Physics 8 Friday, October 2, 2015
 Physics 8 Friday, October 2, 2015 Turn in HW4. On Monday, I ll hand out HW5 (due two weeks from today, on Oct. 16). I actually did a careful job writing up the box hanging from spring inside elevator problem
Physics 8 Friday, October 2, 2015 Turn in HW4. On Monday, I ll hand out HW5 (due two weeks from today, on Oct. 16). I actually did a careful job writing up the box hanging from spring inside elevator problem
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
3.4 Projectile Motion
 3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
2. Evaluate C. F d r if F = xyî + (x + y)ĵ and C is the curve y = x 2 from ( 1, 1) to (2, 4).
 Exam 3 Study Guide Math 223 Section 12 Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Gilbert 1. Which of the following vector fields are conservative? If you determine that a vector field is conservative, find a valid potential
Exam 3 Study Guide Math 223 Section 12 Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Gilbert 1. Which of the following vector fields are conservative? If you determine that a vector field is conservative, find a valid potential
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 4. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 35.
 Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
Write these equations in your notes if they re not already there. You will want them for Exam 1 & the Final.
 Tuesday January 24 Assignment 3: Due Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment: 15min before class like every class Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Help Room: Wed. & Thurs. 6-9pm, here
Tuesday January 24 Assignment 3: Due Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment: 15min before class like every class Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Help Room: Wed. & Thurs. 6-9pm, here
Physics 8 Friday, September 29, 2017
 Physics 8 Friday, September 29, 2017 Turn in HW #4 today or Monday. No HW problems next week. Finish reading Ch10 for Monday. The next few chapters (10,11,12) are the most difficult material in the course.
Physics 8 Friday, September 29, 2017 Turn in HW #4 today or Monday. No HW problems next week. Finish reading Ch10 for Monday. The next few chapters (10,11,12) are the most difficult material in the course.
When we throw a ball :
 PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
Physics 111. Lecture 8 (Walker: 4.3-5) 2D Motion Examples. Projectile - General Launch Angle. In general, v 0x = v 0 cos θ and v 0y = v 0 sin θ
 Physics 111 Lecture 8 (Walker: 4.3-5) D Motion Examples February 13, 009 Lecture 8 1/ Projectile - General Launch Angle In general, v 0x = v 0 cos θ and v 0y = v 0 sin θ (This ASSUMES θ is measured CCW
Physics 111 Lecture 8 (Walker: 4.3-5) D Motion Examples February 13, 009 Lecture 8 1/ Projectile - General Launch Angle In general, v 0x = v 0 cos θ and v 0y = v 0 sin θ (This ASSUMES θ is measured CCW
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment
 Name: Email address (write legibly): AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual
Name: Email address (write legibly): AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual
Physics 8 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Physics 8 Friday, October 21, 2011 Bill and Zoey are away next week at Medical Imaging Conference in warm, sunny Valencia, Spain. Simon Hastings (simonhas@sas.upenn.edu) will run the class meetings on
Physics 8 Friday, October 21, 2011 Bill and Zoey are away next week at Medical Imaging Conference in warm, sunny Valencia, Spain. Simon Hastings (simonhas@sas.upenn.edu) will run the class meetings on
Vector Geometry Final Exam Review
 Vector Geometry Final Exam Review Problem 1. Find the center and the radius for the sphere x + 4x 3 + y + z 4y 3 that the center and the radius of a sphere z 7 = 0. Note: Recall x + ax + y + by + z = d
Vector Geometry Final Exam Review Problem 1. Find the center and the radius for the sphere x + 4x 3 + y + z 4y 3 that the center and the radius of a sphere z 7 = 0. Note: Recall x + ax + y + by + z = d
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Lecture4- Projectile Motion Chapter 4
 1 / 32 Lecture4- Projectile Motion Chapter 4 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 28 th, 2018 2 / 32 Objectives Vector
1 / 32 Lecture4- Projectile Motion Chapter 4 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 28 th, 2018 2 / 32 Objectives Vector
Practice Problems for Exam 2 Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
HOMEWORK 3 MA1132: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017
 HOMEWORK MA112: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017 (1) A particle moves along a curve in R with position function given by r(t) = (e t, t 2 + 1, t). Find the velocity v(t), the acceleration a(t), the speed
HOMEWORK MA112: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017 (1) A particle moves along a curve in R with position function given by r(t) = (e t, t 2 + 1, t). Find the velocity v(t), the acceleration a(t), the speed
Projectile Motion. C) 15 m. D) depends on horizontal speed
 Pre-Test - Post-Test 1. A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. One second after it has left your hand its vertical distance bellow the cliff is. A) 5 m. B) 10 m. C) 15 m. D) depends on
Pre-Test - Post-Test 1. A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. One second after it has left your hand its vertical distance bellow the cliff is. A) 5 m. B) 10 m. C) 15 m. D) depends on
Physics 125: Classical Physics A. 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1
 Physics 125: Classical Physics A 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1 Problem 1 The Figure 1 depicts velocity as a function of time for a short run. Find: a) The acceleration at t = 5 seconds. b) The
Physics 125: Classical Physics A 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1 Problem 1 The Figure 1 depicts velocity as a function of time for a short run. Find: a) The acceleration at t = 5 seconds. b) The
(a) Taking the derivative of the position vector with respect to time, we have, in SI units (m/s),
 Chapter 4 Student Solutions Manual. We apply Eq. 4- and Eq. 4-6. (a) Taking the deriatie of the position ector with respect to time, we hae, in SI units (m/s), d ˆ = (i + 4t ˆj + tk) ˆ = 8tˆj + k ˆ. dt
Chapter 4 Student Solutions Manual. We apply Eq. 4- and Eq. 4-6. (a) Taking the deriatie of the position ector with respect to time, we hae, in SI units (m/s), d ˆ = (i + 4t ˆj + tk) ˆ = 8tˆj + k ˆ. dt
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously. This form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion.
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously. This form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion.
3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames
 3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames 3.1 In-class problem A rocket of initial mass m i is fired vertically up from earth and accelerates until its fuel is exhausted. The residual mass
3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames 3.1 In-class problem A rocket of initial mass m i is fired vertically up from earth and accelerates until its fuel is exhausted. The residual mass
Full file at
 Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Physics Final Exam Formulas
 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
Problem Set 1: Solutions 2
 UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 Problems due 15 January 2009. Problem Set 1: Solutions 2 1. A person walks in the following pattern: 3.1 km north,
UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 Problems due 15 January 2009. Problem Set 1: Solutions 2 1. A person walks in the following pattern: 3.1 km north,
AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 1) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 1) Rectilinear Motion
 Rectilinear Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that rectilinear motion means motion in 1D (i.e. along a straight line) Know that a body is a physical object 3 Know that a particle is an idealised body that has
Rectilinear Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that rectilinear motion means motion in 1D (i.e. along a straight line) Know that a body is a physical object 3 Know that a particle is an idealised body that has
Physics 218 Exam I. Fall 2017 (all sections) September 27 th, 2017
 Physics 218 Exam I Fall 2017 (all sections) September 27 th, 2017 Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. Rules of the exam: 1. You
Physics 218 Exam I Fall 2017 (all sections) September 27 th, 2017 Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. Rules of the exam: 1. You
Projectile Motion trajectory Projectile motion
 Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
Physics 231. Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion. Alex Brown September MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Projectile Motion. Objectives. Materials. Introduction
 Projectile Motion Objectives The objectives of this experiment are for you to: 1. Develop confidence in your ability to use the equations of motion to predict the results of an experiment. 2. Gain confidence
Projectile Motion Objectives The objectives of this experiment are for you to: 1. Develop confidence in your ability to use the equations of motion to predict the results of an experiment. 2. Gain confidence
PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I
 PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I Section 584761 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Exam 1 (Chapters 2 6) February 14, 2018 Name: Solutions 1 Instructions: This exam is composed of 10 multiple choice questions and
PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I Section 584761 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Exam 1 (Chapters 2 6) February 14, 2018 Name: Solutions 1 Instructions: This exam is composed of 10 multiple choice questions and
Vectors. Graphical Method. Graphical Method. SEEMS SIMPLE? = 30.5 m/s. Graphical Method. Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) S
 Vectors Graphical Method General discussion. Vector - A quantity which has magnitude and direction. Velocity, acceleration, Force, E Field, Mag Field, calar - A quantity which has magnitude only. (temp,
Vectors Graphical Method General discussion. Vector - A quantity which has magnitude and direction. Velocity, acceleration, Force, E Field, Mag Field, calar - A quantity which has magnitude only. (temp,
Chap. 3: Kinematics (2D) Recap: Kinematics (1D) 1. Vector Kinematics 2. Projectile Motion 3. Uniform Circular Motion 4.
 Chap. 3: Kinematics (2D) Recap: Kinematics (1D) 1. Vector Kinematics 2. Projectile Motion 3. Uniform Circular Motion 4. Relative Velocity 1 Last, This and Next Weeks [Last Week] Chap. 1 and Chap. 2 [This
Chap. 3: Kinematics (2D) Recap: Kinematics (1D) 1. Vector Kinematics 2. Projectile Motion 3. Uniform Circular Motion 4. Relative Velocity 1 Last, This and Next Weeks [Last Week] Chap. 1 and Chap. 2 [This
Lesson 2. Physics 168. Luis Anchordoqui
 Lesson 2 Physics 168 Luis Anchordoqui Deriving Constant-Acceleration Kinematic Equations To obtain an equation for position as a function of time! look at special case of motion with constant velocity!
Lesson 2 Physics 168 Luis Anchordoqui Deriving Constant-Acceleration Kinematic Equations To obtain an equation for position as a function of time! look at special case of motion with constant velocity!
In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion.
 Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
8.01T Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2004
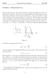 Problem 1. Measurement of g. a) The ball moves in the vertical direction under the influence of the constant force of gravity 1. Hence in our approximation the ball undergoes onedimensional motion with
Problem 1. Measurement of g. a) The ball moves in the vertical direction under the influence of the constant force of gravity 1. Hence in our approximation the ball undergoes onedimensional motion with
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics. Physics 8.01 Fall Problem Set 2: Applications of Newton s Second Law Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall 2012 Problem 1 Problem Set 2: Applications of Newton s Second Law Solutions (a) The static friction force f s can have a magnitude
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall 2012 Problem 1 Problem Set 2: Applications of Newton s Second Law Solutions (a) The static friction force f s can have a magnitude
Motion in Two or Three Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Motion in Two or Three Dimensions PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 3 To use vectors
Chapter 3 Motion in Two or Three Dimensions PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 3 To use vectors
PHY 1114: Physics I. Quick Question 1. Quick Question 2. Quick Question 3. Quick Question 4. Lecture 5: Motion in 2D
 PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics. Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014
 Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
Chap. 3 MATH Annalisa Quaini Office : PGH 662 Lecture : MWF 11AM-12PM Office hours : W 8AM-10AM
 Chap. 3 MATH 1431-18319 Annalisa Quaini quaini@math.uh.edu Office : PGH 662 Lecture : MWF 11AM-12PM Office hours : W 8AM-10AM Daily quiz 6 is due on Friday at 11 AM. Exam 1 is coming - check the scheduler
Chap. 3 MATH 1431-18319 Annalisa Quaini quaini@math.uh.edu Office : PGH 662 Lecture : MWF 11AM-12PM Office hours : W 8AM-10AM Daily quiz 6 is due on Friday at 11 AM. Exam 1 is coming - check the scheduler
Announcements. Unit 1 homework due tomorrow 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on 3:00P Unit 1. Units 2 & 3 homework sets due 11:59 PM
 Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
Clicker Quiz. a) 25.4 b) 37.9 c) 45.0 d) 57.1 e) 65.2
 Clicker Quiz Assume that the rock is launched with an angle of θ = 45. With what angle with respect to the horizontal does the rock strike the ground in front of the castle? v 0 = 14.2 m/s v f = 18.5 m/s
Clicker Quiz Assume that the rock is launched with an angle of θ = 45. With what angle with respect to the horizontal does the rock strike the ground in front of the castle? v 0 = 14.2 m/s v f = 18.5 m/s
The centripetal acceleration for a particle moving in a circle is a c = v 2 /r, where v is its speed and r is its instantaneous radius of rotation.
 skiladæmi 1 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, September 9, 2015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Problem 3.04 The horizontal coordinates of a in a
skiladæmi 1 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, September 9, 2015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Problem 3.04 The horizontal coordinates of a in a
Chapter 4 - Motion in 2D and 3D
 Never confuse motion with action. - Benjamin Franklin David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 211 Position, displacement, velocity and acceleration can be generalized to 3D using vectors. x(t) r(t)
Never confuse motion with action. - Benjamin Franklin David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 211 Position, displacement, velocity and acceleration can be generalized to 3D using vectors. x(t) r(t)
Physics 20 Homework 2 SIMS 2016
 Physics 20 Homework 2 SIMS 2016 Due: Saturday, August 20 th 1. In class, we ignored air resistance in our discussion of projectile motion. Now, let s derive the relevant equation of motion in the case
Physics 20 Homework 2 SIMS 2016 Due: Saturday, August 20 th 1. In class, we ignored air resistance in our discussion of projectile motion. Now, let s derive the relevant equation of motion in the case
Experiment 4: Projectile Motion
 Experiment 4: Projectile Motion EQUIPMENT Figure 4.1: Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) Pasco Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) 2-Meter Stick Meter Stick Ruler Plumb Bob Carbon Paper Target Paper Launch Platform
Experiment 4: Projectile Motion EQUIPMENT Figure 4.1: Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) Pasco Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) 2-Meter Stick Meter Stick Ruler Plumb Bob Carbon Paper Target Paper Launch Platform
Chapter 4 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Vocabulary Preview. Oct 21 9:53 AM. Projectile Motion. An object shot through the air is called a projectile.
 Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only)
 Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
Vectors and Scalars. Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction.
 Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
3.2 Projectile Motion
 Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
b) (6) How far down the road did the car travel during the acceleration?
 General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
Announcement. Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday
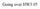 Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
Concept Category 4 (textbook ch. 8) Parametric Equations
 Concept Category 4 (textbook ch. 8) Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations.
Concept Category 4 (textbook ch. 8) Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations.
2D Motion Projectile Motion
 2D Motion Projectile Motion Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 3, 2017 Last time vectors vector operations Warm Up: Quick review of Vector Expressions Let a, b, and c be (non-null) vectors. Let l, m, and
2D Motion Projectile Motion Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 3, 2017 Last time vectors vector operations Warm Up: Quick review of Vector Expressions Let a, b, and c be (non-null) vectors. Let l, m, and
physics Chapter 4 Lecture a strategic approach randall d. knight FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS Chapter 4_Lecture1 THIRD EDITION
 Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Bell Ringer. x- direction: Ball and car start with same position and velocity, a=0, so always have same position
 Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
PHYSICS I. Lecture 1. Charudatt Kadolkar. Jul-Nov IIT Guwahati
 PHYSICS I Lecture 1 Charudatt Kadolkar IIT Guwahati Jul-Nov 2014 Section 1 Introduction to the Course Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics: Kinetic Energy rest mass energy Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics:
PHYSICS I Lecture 1 Charudatt Kadolkar IIT Guwahati Jul-Nov 2014 Section 1 Introduction to the Course Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics: Kinetic Energy rest mass energy Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics:
Ballistic Pendulum. Caution
 Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Demonstrations: 1) Ball falls down and another falls out 2) Parabolic and straight line motion from two different frames. The truck with a dropping
Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Demonstrations: 1) Ball falls down and another falls out 2) Parabolic and straight line motion from two different frames. The truck with a dropping
Chapter 5: Limits and Derivatives
 Chapter 5: Limits and Derivatives Chapter 5 Overview: Introduction to Limits and Derivatives In a later chapter, maximum and minimum points of a curve will be found both by calculator and algebraically.
Chapter 5: Limits and Derivatives Chapter 5 Overview: Introduction to Limits and Derivatives In a later chapter, maximum and minimum points of a curve will be found both by calculator and algebraically.
Ballistic Pendulum. Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION
 Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Linear and Non Linear Motion. Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages
 Linear and Non Linear Motion Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages 73-87 Acceleration Rate of increase of a rate d/t t Increases rate for each increment in time that has passed So there is an
Linear and Non Linear Motion Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages 73-87 Acceleration Rate of increase of a rate d/t t Increases rate for each increment in time that has passed So there is an
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B
 Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
AP Physics B Summer Assignment Packet 3
 AP Physics B Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual Physics Find the Mistake Straightening
AP Physics B Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual Physics Find the Mistake Straightening
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres. Chapter 2 Motion Cengage Learning
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
Feb 6, 2013 PHYSICS I Lecture 5
 95.141 Feb 6, 213 PHYSICS I Lecture 5 Course website: faculty.uml.edu/pchowdhury/95.141/ www.masteringphysics.com Course: UML95141SPRING213 Lecture Capture h"p://echo36.uml.edu/chowdhury213/physics1spring.html
95.141 Feb 6, 213 PHYSICS I Lecture 5 Course website: faculty.uml.edu/pchowdhury/95.141/ www.masteringphysics.com Course: UML95141SPRING213 Lecture Capture h"p://echo36.uml.edu/chowdhury213/physics1spring.html
v v y = v sinθ Component Vectors:
 Component Vectors: Recall that in order to simplify vector calculations we change a complex vector into two simple horizontal (x) and vertical (y) vectors v v y = v sinθ v x = v cosθ 1 Component Vectors:
Component Vectors: Recall that in order to simplify vector calculations we change a complex vector into two simple horizontal (x) and vertical (y) vectors v v y = v sinθ v x = v cosθ 1 Component Vectors:
Physics 201, Lecture 8
 Physics 01, Lecture 8 Today s Topics q Physics 01, Review 1 q Important Notes: v v v v This review is not designed to be complete on its own. It is not meant to replace your own preparation efforts Exercises
Physics 01, Lecture 8 Today s Topics q Physics 01, Review 1 q Important Notes: v v v v This review is not designed to be complete on its own. It is not meant to replace your own preparation efforts Exercises
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Clicker Question 4.3 A mass at rest on a ramp. How does the friction between the mass and the table know how much force will EXACTLY balance the gravity
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Clicker Question 4.3 A mass at rest on a ramp. How does the friction between the mass and the table know how much force will EXACTLY balance the gravity
Vectors. However, cartesian coordinates are really nothing more than a way to pinpoint an object s position in space
 Vectors Definition of Scalars and Vectors - A quantity that requires both magnitude and direction for a complete description is called a vector quantity ex) force, velocity, displacement, position vector,
Vectors Definition of Scalars and Vectors - A quantity that requires both magnitude and direction for a complete description is called a vector quantity ex) force, velocity, displacement, position vector,
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions. Examples: non-linear motion (circles, planetary orbits, etc.) flight of projectiles (shells, golf balls, etc.
 Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
Motion in a 2 and 3 dimensions Ch 4 HRW
 Motion in a and 3 dimensions Ch 4 HRW Motion in a plane D Motion in space 3D Projectile motion Position and Displacement Vectors A position vector r extends from a reference point (usually the origin O)
Motion in a and 3 dimensions Ch 4 HRW Motion in a plane D Motion in space 3D Projectile motion Position and Displacement Vectors A position vector r extends from a reference point (usually the origin O)
Figure 2.1 The Inclined Plane
 PHYS-101 LAB-02 One and Two Dimensional Motion 1. Objectives The objectives of this experiment are: to measure the acceleration due to gravity using one-dimensional motion, i.e. the motion of an object
PHYS-101 LAB-02 One and Two Dimensional Motion 1. Objectives The objectives of this experiment are: to measure the acceleration due to gravity using one-dimensional motion, i.e. the motion of an object
