Vectors. Graphical Method. Graphical Method. SEEMS SIMPLE? = 30.5 m/s. Graphical Method. Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) S
|
|
|
- Trevor Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vectors Graphical Method General discussion. Vector - A quantity which has magnitude and direction. Velocity, acceleration, Force, E Field, Mag Field, calar - A quantity which has magnitude only. (temp, pressure, time) This chapter: We mainly deal with Displacement D and Velocity = v Discussion is valid for any vector! 2 vectors NOT along the same line: D 1 = 10 km E, D 2 = 5 km N. Resultant =? If D 1 is perpendicular to D 2 D R = 11.2 km Adding vectors in same direction: Graphical Method Vector V is 2.50 cm long, scale is 1 cm = 12.2 m/s, find magnitude. V EEM IMPLE? = 30.5 m/s Graphical Method For 2 vectors NOT along same line, adding is more complicated: Example: D 1 = 10 km East, D 2 = 5 km North. What is the resultant (final) displacement? 2 methods of vector addition: Graphical (2 methods of this also!) Analytical (TRIGONOMETRY) Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) V = V 1 + V 2 1. Draw V 1 & V 2 to scale. 2. Place tail of V 2 at tip of V 1 3. Draw arrow from tail of V 1 to tip of V 2 This arrow is the resultant V (measure length and the angle it makes with the x-axis) 1
2 Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) Graphical Method (Parallelogram) Tip Tail Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) Consider the vectors A and B. Find A + B. A B A B A B C = A + B We can arrange the vectors as we want, as long as we maintain their length and direction!! Graphical Method econd graphical method of adding vectors (parallelogram). V = V 1 + V 2 1. Draw V 1 & V 2 to scale from common origin. 2. Construct parallelogram using V 1 & V 2 as 2 of the 4 sides. Resultant V = diagonal of parallelogram from common origin (measure length and the angle it makes with the x-axis) Graphical Method Adding (3 or more) vectors V = V 1 + V 2 + V 3 Correct Graphical Method Tip To Tail Parallelogram 2
3 Graphically determine the resultant of the following three vector displacements: (1) 34 m, 25º north of east; (2) 48 m, 33º east of north; and (3) 22 m, 56º west of south. The vectors for the problem are drawn approximately to scale. The resultant has a length of 58 m and a direction 48 o north of east. If you actually measured, the actual resultant should be 57.4 m at 47.5 o north of east. 22 ubtraction of Vectors ubtraction of Vectors Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) B Deck of Card Activity 0 degrees from x axis A R = A + B R B A R = A - B A 90 degrees from x axis 180 degrees from x axis R -B 270 degrees from x axis ubtraction of Vectors First, define the negative of a vector: - V vector with the same magnitude (size) as V but with opposite direction. Math: V + (- V) 0 For 2 vectors, A - B A + (-B) 3
4 To do the graphical method we have to measure with ruler and protractor. Takes a lot of time The magnitude (length) of r is found using the Pythagorean theorem: We don t always have an graphic designer on staff to draw our vectors for us. r y o instead we resolve our vectors into its components (x,y) x Decomposition Example V is resolved into components: V x & V y V V x + V y (V x x axis, V y y axis) A coast guard cutter has taken a heading of 30 north of east to find a missing diver. Break up into it s X and Y d = displacement 500 m, 30º N of E Trig Functions to Decompose Vector determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector The direction is given by an angle of IN PROJECTE ALONG ONLY Y CO PROJECTE ALONG ONLY X Vy = sin V Vx = cos * V 47 o below the positive x-axis. 4
5 An airplane is travelling 735 km/hr in a direction 41.5º of north of west (a) Find the components of the velocity vector in the northerly and westerly directions. (b) How far north and how far west has the plane travelled after 3.00 h? x and y components of motion are independent. A man on a train tosses a ball straight up View this from two reference frames: Cart Reference frame on the moving train. Reference frame on the ground. Components are Independent A ball is thrown 23.0 with a velocity of 22.5 m/s. What is its vertical and horizontal velocity components? Conceptual Example 3-6 v 0x = 22.5 m/s cos 23.0 = 20.1 m/s = 22.5 m/s sin 23.0 = 8.79 m/s if v y is 12.4 m/s and v x is 15.4 m/s, find the angle. = 38.8 Demonstration!! Projectile Motion no air resistance a x = 0, v x = constant projectile s weight is only force acting a y = g = 9.8 m/s 2 v y = 0 at max height x, y motions are independent of each other resolve initial velocity into v x, v y and use our basic kinematic equations to solve problem 5
6 Projectile Motion PHYIC: y part of motion: v y = gt, y = (½)g t 2 AME as free fall motion!! An object projected horizontally will reach the ground at the same time as an object dropped vertically from the same point! (x & y motions are independent) DEMO INCE G I ALWAY DOWN, MAKE IT NEGATIVE FOR ALL PROJ MOTION AND POITIVE FOR FREE FALL Vertical: A small cart is rolling at constant velocity on a flat track. It fires a ball straight up into the air as it moves. After it is fired, what happens to the ball? A) it depends on how fast the cart is moving B) it falls behind the cart C) it falls in front of the cart D) it falls right back into the cart Horizontal: Your book says negative, just remember in most cases g will be opposite the initial velocity (so -9.8 m/s) (Except free fall) (no acceleration) E) it remains at rest Pre-Lecture Quiz 03 The same small cart is now rolling down an inclined track and accelerating. It fires a ball straight out of the cannon as it moves. After it is fired, what happens to the ball? A) it depends upon how much the track is tilted B) it falls behind the cart C) it falls in front of the cart D) it falls right back into the cart E) it remains at rest Pre-Lecture Quiz 03 6
7 You drop a package from a plane flying at constant speed in a straight line. Without air resistance, the package will: A) quickly lag behind the plane while falling B) remain vertically under the plane while falling C) move ahead of the plane while falling D) not fall at all How far below an initial straight-line path will a projectile fall in one second? 5 meters. Does your answer depend on the angle of launch or launch speed? No, vertical displacement below any line is ½ gt 2. Pre-Lecture Quiz 03 A rookie soldier in basic training drops his bullet that this same time that another soldiers shoots from his rifle (exactly horizontal) The bullet is dropped at the moment of the shot &no air res.) Which bullet touches the ground first? Galileo's space and time z z' v (x,y,z) (x',y',z') y y' The bullet touch down at the same time. x x' How many dimensions are there? Ball Rolls Across Table & Falls Off In this case I take down as positive since v yo=0 v yo =0 Time is the 4 th dimension, and it is shared by all the others. v y =gt 7
8 Driving off a cliff!! negative y (no acceleration) y is positive upward, y 0 = 0 at top. Also v y0 = 0 How fast must the motorcycle leave the cliff to land at x = 90 m, y = -50 m? v x0 =? A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff that is 40.0 m high. It has a horizontal velocity of 15.0 m/s. We want to find how long it takes the stone to fall to the deck and how far it will travel from the base of the cliff. Plug in the given values: Find x : x = v x t t =2.86 s x = 42.9 m A ball thrown horizontally at 22.2 m/s from the roof of a building lands 36.0 m from the base of the building. How tall is the building? ummary: Ball rolling across the table & falling. Vector velocity v has 2 components: Vector displacement D has 2 components:, The vertical displacement, which is the height of the building, is found by applying. For problems like this if we set y at the top = 0 then gravity is 9/8 m/s2 8
9 How fast does the stone hit in the previous problem? LAUNCHER Which does gravity have a stronger influence on? Does one ball go further than the other? Do both have the same Vo? Do both shots have the same time in air? Are they both free fall motion? Diagram in terms of vectors what is happening? You have a summer job with an insurance company and are helping to investigate a tragic "accident." At the scene, you see a road running straight down a hill. At the bottom of the hill, the road widens into a small, level parking lot overlooking a cliff. The cliff has a vertical drop of 400 m to the horizontal ground below where a car is wrecked 45 m from the base of the cliff. A witness claims that the car was parked on the hill and began coasting down the road, taking about 3 seconds to get down the hill (you calculate the average acceleration of 1.7m/s 2. ) The client insists that the emergency brake was on, as would be required on this hill. As you walk down inspect the wreckage you see the parking brake has been pushed in. Your boss drops a stone from the edge of the cliff and, from the sound of it hitting the ground below, determines that it takes 5.0 seconds to fall to the bottom. Obviously, your boss suspects foul play. Is he right? Does James Want V yo, How much? PLAY JB 5 CLIP HERE Initial velocity is 5.1m/s 9.03s to fall 45.9m from the cliff Projectile Motion 9
10 General Case: Projectile Motion a = g (down always) V yo =V o sin o V xo =V o cos If Bubba is traveling at 33m/s and the ramp is 30 deg will he make a ramp distance of. 2 possible Formulas rsist_safety_mode=1&safe=active 10
11 A ball is given an initial velocity of m/s at an angle of 66.0 to the horizontal. Find how high the. ball will go? v y0 = v 0 sin 0 Find y: v y0 = 20.7 m/s and v y = 0. v y0 = 22.7 m/s (sin 66.0 ) v y0 = 20.7 m/s 2 possible Formulas A confused soldier fires his artillery piece at angle that maximizes Vy. His enemy utilizes an angle of 40 o. If both are in the air for 3 seconds (same height) what was the velocity of the enemy's ball. At Vy Max the Vxo =0, t to the top = 1.5s ince both are in the air for the same amount of time, both have same Vyo y y = 21.9 m 40 You throw a potato at an angle of If it is in the air for 1.55 s, how far did it go? Find the vertical velocity: A naval gun fires a 16 inch projectile. The muzzle velocity (speed of the bullet) is 345 m/s with an angle of What is the range of the shot? Hint since both are at y=o then you don t need the quadratic to solve for time Find the vertical velocity: Find the horizontal velocity: Find the time: Find range: x = m Find the horizontal displacement: t = s The biker has a hang time of 4.5 s. He lands 48 m from the ramp, (assume no ramp height) what was the ramp angle? NEED TO FIND V y0 and V x0 vx 0 = m/s A ball is thrown at some angle. The ball is in the air for 4.50 seconds before it hits. If it travels 45.0 meters before it hits the ground, what was the initial velocity of the ball (magnitude and direction please)? NEED TO FIND t at max height NEED TO FIND Vy t = 2.25 s NEED TO FIND t at max height Vy 0 = m/s = 64 11
12 But what if the height is not the same after landing? A stone is thrown off the top of a building from a height of 45.0 m. The stone has a launch angle of 62.5 and a speed of 31.5 m/s. How long is the stone in flight What is its speed just before it hits the ground? What angle does it hit? Quadratic Equation Vf at bottom from 45 meters A husky kicker wants to provide as much hang time as possible For his coverage team to get down the field. If he kicks the ball with a velocity 40m/s at an angle of 35 degrees above horizontal, how much time does his team have to get down field and pound a cougar? At what distance from kick will we find a pounded cougar returner? Hint since both are at y=o then you don t need the quadratic to solve for time v y0 = v 0 sin v x0 = v 0 cos 35 v y0 = 40 sin 35 v x0 = 40 cos35 v y0 = 22.9 m/s v x0 = 32.7 m/s What is its speed just before it hits the ground? What angle does it hit? Remember that this 2.8 is negative (so will be below horizon) A football leaves a punters foot 1.0 m above the ground at 20.0 m/s. θ 0 = 37º. Find t then x. Vy 0 = 12.0 m/s, θ 0 = 37º FORMULA GIVEN ON AP Quadratic Equation 12
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
1-D and 2-D Motion Test Friday 9/8
 1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
Chapter 3. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS
 AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
Giancoli: PHYSICS. Notes: Ch. 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating
 Giancoli: PHYSICS Name: Notes: Ch. 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating Skim read this chapter and record important concepts that you need to remember here. Guided Notes: Ch. 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics
Giancoli: PHYSICS Name: Notes: Ch. 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating Skim read this chapter and record important concepts that you need to remember here. Guided Notes: Ch. 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998)
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball.
 Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
PHY 1114: Physics I. Quick Question 1. Quick Question 2. Quick Question 3. Quick Question 4. Lecture 5: Motion in 2D
 PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) Justify your answer: Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) 5 10 m/s 3. Show your work: 3 m/s 2
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
3.4 Projectile Motion
 3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Physics 231. Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion. Alex Brown September MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014
 Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider these vectors. What is A-B? a. a c. c b. b d. d 2. Consider
Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider these vectors. What is A-B? a. a c. c b. b d. d 2. Consider
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
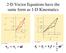 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
physics Chapter 4 Lecture a strategic approach randall d. knight FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS Chapter 4_Lecture1 THIRD EDITION
 Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences
 PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions. Problem Solving
 Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide
 Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide Major Concepts 1 D Motion on the horizontal 1 D motion on the vertical Relationship between velocity and acceleration Difference between constant
Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide Major Concepts 1 D Motion on the horizontal 1 D motion on the vertical Relationship between velocity and acceleration Difference between constant
Chapter 3 2-D Motion
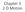 Chapter 3 2-D Motion We will need to use vectors and their properties a lot for this chapter. .. Pythagorean Theorem: Sample problem: First you hike 100 m north. Then hike 50 m west. Finally
Chapter 3 2-D Motion We will need to use vectors and their properties a lot for this chapter. .. Pythagorean Theorem: Sample problem: First you hike 100 m north. Then hike 50 m west. Finally
GALILEAN RELATIVITY. Projectile motion. The Principle of Relativity
 GALILEAN RELATIVITY Projectile motion The Principle of Relativity When we think of the term relativity, the person who comes immediately to mind is of course Einstein. Galileo actually understood what
GALILEAN RELATIVITY Projectile motion The Principle of Relativity When we think of the term relativity, the person who comes immediately to mind is of course Einstein. Galileo actually understood what
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit:
 Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review
 Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration
 Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Physics 201 Homework 1
 Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Vectors and Scalars. Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction.
 Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
b) (6) How far down the road did the car travel during the acceleration?
 General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
Chapter 3 Homework Packet. Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Projectile Motion. v = v 2 + ( v 1 )
 What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
Projectile motion. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/20/14. Identify examples of projectile motion.
 Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
Projectile Launched at an Angle
 Projectile Launched at an Angle by Nada Saab-Ismail, PhD, MAT, MEd, IB nhsaab.weebly.com nhsaab2014@gmail.com P2.2g Apply the independence of the vertical and horizontal initial velocities to solve projectile
Projectile Launched at an Angle by Nada Saab-Ismail, PhD, MAT, MEd, IB nhsaab.weebly.com nhsaab2014@gmail.com P2.2g Apply the independence of the vertical and horizontal initial velocities to solve projectile
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Physics Chapter 3 Notes. Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83)
 Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion
 Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion 2-Dimensional Motion! Definition: motion that occurs with both x and y components.! Example:! Playing pool.! Throwing a ball to another person.! Each dimension of the
Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion 2-Dimensional Motion! Definition: motion that occurs with both x and y components.! Example:! Playing pool.! Throwing a ball to another person.! Each dimension of the
Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet
 Name Pd Date Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet Because perpendicular vectors are independent of each other we can use the kinematic equations to analyze the vertical (y) and horizontal (x) components of
Name Pd Date Two-Dimensional Motion Worksheet Because perpendicular vectors are independent of each other we can use the kinematic equations to analyze the vertical (y) and horizontal (x) components of
Physics 3214 Unit 1 Motion. Vectors and Frames of Reference
 Physics 3214 Unit 1 Motion Vectors and Frames of Reference Review Significant Digits 1D Vector Addition BUT First. Diagnostic QuizTime Rules for Significant DigitsRule #1 All non zero digits are ALWAYS
Physics 3214 Unit 1 Motion Vectors and Frames of Reference Review Significant Digits 1D Vector Addition BUT First. Diagnostic QuizTime Rules for Significant DigitsRule #1 All non zero digits are ALWAYS
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16)
 Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
AP PHYSICS C MECHANICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2018/2019
 AP PHYSICS C MECHANICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2018/2019 This course is equivalent to pre-engineering introductory Physics course for the university students. Comprehension of important physical concepts is
AP PHYSICS C MECHANICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2018/2019 This course is equivalent to pre-engineering introductory Physics course for the university students. Comprehension of important physical concepts is
30º 20º 60º 38º 78º 16º 45º 83º. Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets. 1. DRAW and CALCULATE the X and Y components of the following: A. E. B. F. C. G. D. H.
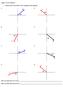 Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets 1. DRAW and CALCULATE the X and Y components of the following: A. E. 10 10 20º 30º B. F. 60º 38º 10 10 C. G. 78º 10 16º 10 D. H. 10 10 83º 45º What s true about all the RED
Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets 1. DRAW and CALCULATE the X and Y components of the following: A. E. 10 10 20º 30º B. F. 60º 38º 10 10 C. G. 78º 10 16º 10 D. H. 10 10 83º 45º What s true about all the RED
Progressive Science Initiative. Click to go to website:
 Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Vocabulary Preview. Oct 21 9:53 AM. Projectile Motion. An object shot through the air is called a projectile.
 Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Break problems down into 1-d components
 Motion in 2-d Up until now, we have only been dealing with motion in one-dimension. However, now we have the tools in place to deal with motion in multiple dimensions. We have seen how vectors can be broken
Motion in 2-d Up until now, we have only been dealing with motion in one-dimension. However, now we have the tools in place to deal with motion in multiple dimensions. We have seen how vectors can be broken
Projectile Motion. v a = -9.8 m/s 2. Good practice problems in book: 3.23, 3.25, 3.27, 3.29, 3.31, 3.33, 3.43, 3.47, 3.51, 3.53, 3.
 v a = -9.8 m/s 2 A projectile is anything experiencing free-fall, particularly in two dimensions. 3.23, 3.25, 3.27, 3.29, 3.31, 3.33, 3.43, 3.47, 3.51, 3.53, 3.55 Projectile Motion Good practice problems
v a = -9.8 m/s 2 A projectile is anything experiencing free-fall, particularly in two dimensions. 3.23, 3.25, 3.27, 3.29, 3.31, 3.33, 3.43, 3.47, 3.51, 3.53, 3.55 Projectile Motion Good practice problems
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment
 Name: Email address (write legibly): AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual
Name: Email address (write legibly): AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet 3 The assignments included here are to be brought to the first day of class to be submitted. They are: Problems from Conceptual
Review Session 1. Page 1
 Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Bell Ringer. x- direction: Ball and car start with same position and velocity, a=0, so always have same position
 Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Full file at
 Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 2-3
 A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
When we throw a ball :
 PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
1. (P2.1A) The picture below shows a ball rolling along a table at 1 second time intervals. What is the object s average velocity after 6 seconds?
 PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
Chapter 3 Kinematics in two and three dimensions. x and y components 1
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in two and three dimensions x and y components 1 Start with 1D Motion 3 independent equations Derive these 2 from the other 3 v = v + at 0 v = 1 avg 2 (v + v) 0 x = x 0 + v 0 t + 1
Chapter 3 Kinematics in two and three dimensions x and y components 1 Start with 1D Motion 3 independent equations Derive these 2 from the other 3 v = v + at 0 v = 1 avg 2 (v + v) 0 x = x 0 + v 0 t + 1
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion?
 Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets. 1. Find the X and Y components of the following: A. 35 m/s at 57 from the x-axis. [X: 19.1 m/s Y: 29.
 Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets 1. Find the X and Y components of the following: A. 35 m/s at 57 from the x-axis. B. 12 m/s at 34 S of W [X: 19.1 m/s Y: 29.4 m/s] C. 8 m/s South [X: -10 m/s Y: -6.7 m/s] D.
Chapter 3 Vectors Worksheets 1. Find the X and Y components of the following: A. 35 m/s at 57 from the x-axis. B. 12 m/s at 34 S of W [X: 19.1 m/s Y: 29.4 m/s] C. 8 m/s South [X: -10 m/s Y: -6.7 m/s] D.
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
Lecture Notes Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration
 Lecture Notes 2.5-2.9 Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The SI unit for acceleration is m/s 2 Acceleration is a vector, and thus has both a magnitude
Lecture Notes 2.5-2.9 Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The SI unit for acceleration is m/s 2 Acceleration is a vector, and thus has both a magnitude
Bill s ball goes up and comes back down to Bill s level. At that point, it is
 ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium
 Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
2. Two Dimensional Kinematics
 . Two Dimensional Kinematics A) Overview We will begin by introducing the concept of vectors that will allow us to generalize what we learned last time in one dimension to two and three dimensions. In
. Two Dimensional Kinematics A) Overview We will begin by introducing the concept of vectors that will allow us to generalize what we learned last time in one dimension to two and three dimensions. In
Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions Section Review 6.1 1. What is the word for the horizontal distance a projectile travels? 2. What does it mean to say a projectile
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions Section Review 6.1 1. What is the word for the horizontal distance a projectile travels? 2. What does it mean to say a projectile
Such a life, with all vision limited to a Point and all motion to a Straight Line, seemed to me inexplicably dreary -Edwin Abbott Abbott (
 AP Physics Motion in 2-D Projectile and Circular Motion Introduction: In previous units, we studied motion along a straight line. Now we broaden our discussion to include motion along a curved path that
AP Physics Motion in 2-D Projectile and Circular Motion Introduction: In previous units, we studied motion along a straight line. Now we broaden our discussion to include motion along a curved path that
Example problem: Free Fall
 Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Lab 5: Projectile Motion
 Concepts to explore Scalars vs. vectors Projectiles Parabolic trajectory As you learned in Lab 4, a quantity that conveys information about magnitude only is called a scalar. However, when a quantity,
Concepts to explore Scalars vs. vectors Projectiles Parabolic trajectory As you learned in Lab 4, a quantity that conveys information about magnitude only is called a scalar. However, when a quantity,
Announcements. Unit 1 homework due tomorrow 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on 3:00P Unit 1. Units 2 & 3 homework sets due 11:59 PM
 Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Exam 2--PHYS 101--F17
 Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review
 AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Kinematics and Dynamics
 AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Lecture III. Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318
 Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318 Lecture III Motion in two dimensions projectile motion The Laws of Motion Forces, Newton s first law Inertia, Newton s second law Newton s third law
Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318 Lecture III Motion in two dimensions projectile motion The Laws of Motion Forces, Newton s first law Inertia, Newton s second law Newton s third law
Chapter 4. Two-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 4. Two-Dimensional Motion 09/1/003 I. Intuitive (Understanding) Review Problems. 1. If a car (object, body, truck) moves with positive velocity and negative acceleration, it means that its a) speed
Chapter 4. Two-Dimensional Motion 09/1/003 I. Intuitive (Understanding) Review Problems. 1. If a car (object, body, truck) moves with positive velocity and negative acceleration, it means that its a) speed
CHAPTER # 2 VECTORS THEORETICAL QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
 CHAPTER # 2 VECTORS THEORETICAL QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS 1. What are vectors and scalar quantities? Give one example of each. (1993, 2012) 2. What are the different methods of adding two vectors? (1988) 3.
CHAPTER # 2 VECTORS THEORETICAL QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS 1. What are vectors and scalar quantities? Give one example of each. (1993, 2012) 2. What are the different methods of adding two vectors? (1988) 3.
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously. This form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion.
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously. This form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion.
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31. Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.
 Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
(a) On the diagram above, draw an arrow showing the direction of velocity of the projectile at point A.
 QUESTION 1 The path of a projectile in a uniform gravitational field is shown in the diagram below. When the projectile reaches its maximum height, at point A, its speed v is 8.0 m s -1. Assume g = 10
QUESTION 1 The path of a projectile in a uniform gravitational field is shown in the diagram below. When the projectile reaches its maximum height, at point A, its speed v is 8.0 m s -1. Assume g = 10
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics. Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014
 Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation
 Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
MOTION IN A PLANE. Chapter Four MCQ I. (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180
 Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Projectile Motion: Vectors
 Projectile Motion: Vectors Ch. 5 in your text book Students will be able to: 1) Add smaller vectors going in the same direction to get one large vector for that direction 2) Draw a resultant vector for
Projectile Motion: Vectors Ch. 5 in your text book Students will be able to: 1) Add smaller vectors going in the same direction to get one large vector for that direction 2) Draw a resultant vector for
Student Content Brief Advanced Level
 Student Content Brief Advanced Level Vectors Background Information Physics and Engineering deal with quantities that have both size and direction. These physical quantities have a special math language
Student Content Brief Advanced Level Vectors Background Information Physics and Engineering deal with quantities that have both size and direction. These physical quantities have a special math language
PROJECTILE Practice Worksheet Ans. Key
 PROJECTILE Practice Worksheet Ans. Key FORMULA BANK Horizontal Motion Formulas: x = vxo t + ½ a t 2 x = ½ (vxo + vxf) t Vertical Motion Formulas: y = yo + vyo t ½ g t 2 y = ½ (vyo + vyf) t Pythagorean
PROJECTILE Practice Worksheet Ans. Key FORMULA BANK Horizontal Motion Formulas: x = vxo t + ½ a t 2 x = ½ (vxo + vxf) t Vertical Motion Formulas: y = yo + vyo t ½ g t 2 y = ½ (vyo + vyf) t Pythagorean
Physic 231 Lecture 5. Main points of today s lecture: Addition i of velocities. Newton s 1 st law: Newton s 2 nd law: F = ma
 Physic 3 Lecture 5 Main points of today s lecture: Addition i of velocities i v = v + vt v is the velocity in the "stationary" frame v is the velocity in the " moving"frame v t is the velocity of the "
Physic 3 Lecture 5 Main points of today s lecture: Addition i of velocities i v = v + vt v is the velocity in the "stationary" frame v is the velocity in the " moving"frame v t is the velocity of the "
Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2
 Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2 PROBLEMS: 1. In an experiment, it is found that the time t required for an object to travel a distance x is given by the equation = where is the acceleration
Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2 PROBLEMS: 1. In an experiment, it is found that the time t required for an object to travel a distance x is given by the equation = where is the acceleration
Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2
 Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2 PROBLEMS: 1. In an experiment, it is found that the time t required for an object to travel a distance x is given by the equation = where is the acceleration
Constants: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s 2 PROBLEMS: 1. In an experiment, it is found that the time t required for an object to travel a distance x is given by the equation = where is the acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Dynamics Notes Name 1 Equations of Motion Vectors and Scalars (Revision of National 5) It is possible to split up quantities in physics into two distinct
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Dynamics Notes Name 1 Equations of Motion Vectors and Scalars (Revision of National 5) It is possible to split up quantities in physics into two distinct
Question 3: Projectiles. Page
 Question 3: Projectiles Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Page Commencement date Questions covered Introduction: breaking velocity
Question 3: Projectiles Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Page Commencement date Questions covered Introduction: breaking velocity
Chapter 2: Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter : Motion in One Dimension Review: velocity can either be constant or changing. What is the mathematical meaning of v avg? The equation of a straight line is y = mx + b. From the definition of average
Chapter : Motion in One Dimension Review: velocity can either be constant or changing. What is the mathematical meaning of v avg? The equation of a straight line is y = mx + b. From the definition of average
1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of
 1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of friction.] A) Its vertical speed remains the same, and its horizontal
1. A baseball player throws a ball horizontally. Which statement best describes the ball's motion after it is thrown? [Neglect the effect of friction.] A) Its vertical speed remains the same, and its horizontal
Projectile Motion I. Projectile motion is an example of. Motion in the x direction is of motion in the y direction
 What is a projectile? Projectile Motion I A projectile is an object upon which the only force acting is gravity. There are a variety of examples of projectiles. An object dropped from rest is a projectile
What is a projectile? Projectile Motion I A projectile is an object upon which the only force acting is gravity. There are a variety of examples of projectiles. An object dropped from rest is a projectile
