RF APERTURE ARCHITECTURES 11 Nov. 08
|
|
|
- Verity Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RF APERTURE ARCHITECTURES 11 Nov. 08 r. Thomas Murphey Space Vehicles irectorate
2 Mitigating Structural eformations Mitigating structural deformations in large apertures: There is always a trade between ACTIVE TECHNOLOGIES (shape correction, metrology and electronic compensation, etc.) and PASSIVE STRUCTURAL TECHNOLOGIES (structural hierarchy, material dimensional stability, deployment) This trade is a specific function of how electromagnetic energy behaves and what about it is being sensed It is not always as simple as keep RMS surface errors less then λ/30 This presentation investigates this relation and derives RF system architecture development recommendations from it
3 Scope eveloped for multi-element RF systems that transmit and receive (phased arrays, phased arrays with reflectors) Radar Imaging, tracking, 3 terrain Communications Applicable to receive only systems as well Many sources of system errors Thermal stability, dynamic stability, electronic stability Under consideration here: Only structural dynamic deformations Only one dimensional apertures Infinite knowledge of structural deformations is assumed when needed Challenges of obtaining this information through metrology or other techniques are not addressed here. 3
4 Phase Measurement Goal is to adjust phase of incoming/ outgoing radiation over entire aperture for coherent beam Assume the sensor (or some element in the optical path) is moving and changing the phase (time delay) of the radiation Assume the motion is sinusoidal (derived from vibrations due to low order structural mode) Consider three levels of phase shift (time delay) adjustment of the sensor to correct for the motions 1) No change ) Adjust time-delay, updated regularly 3) Also adjust rate of change of timedelay (equivalent to frequency shift), updated regularly Can this be translated into structural requirements? Can structural requirements be translated into deployable structure architectures? 4
5 Structural ynamic Excitations Two excitation methods Structure is torqued by CMG or reaction wheel placed at center of aperture Forces from thrusters placed at ends of aperture Moment actuation, force actuation and vibrations all have similar though not identical shapes Bang-bang control scheme employed to slew system 90 degrees Actuators turned on to accelerated aperture, reversed to decelerate it, no coasting period 5
6 Actuation Methods Only Excite a Single Mode Power spectral density plots for post actuation vibrations along aperture length Normalized so that maximum is 1 Mode described in last slide is only mode significantly excited Not the first mode Force actuation spreads energy among modes more significantly, but most is still in one mode 6
7 Estimate Stiffness and eformation Excited structural mode frequency: f λ EI =, λ = πl m Rotational acceleration due to moment and force actuation: α = 3 M α = 3 F 3 ml ml Quasi-static deflection due to constant rotational acceleration: αml Fl 11wl F δ = δ =, w = 3 M F 10 EI 3EI 10EI l Observations: π Equations can be used to determine minimum stiffness for a maximum deformation requirement Force actuation results in 4.7 times less structural deformation eflections decrease with the square of frequency δ M = αλ l f 4 δ F 7 = 1440π αλ l f 4 7
8 eformation Speed and Acceleration Based on the amplitude and frequency of deformations, the maximum speed of the aperture tip is: 11 v = u αλ l M,max 10 3 m EI 7 v = u αλ l F,max 360 And the maximum acceleration of the tip is: a 11 4 = u αλ M,max 10 l a 7 4 = u αλ F,max 360 l 3 m EI 8
9 Three Compensation Strategies 1) No compensation eformations must be less than some fraction of wavelength Stiffness requirement derived from quasi-static deflection δ < coherence requirement EI = u αml δ M ) Adjust time-delay, updated regularly Element must not move more than the allowable coherence error between updates Reduces to a velocity requirement eformation Speed < (coherence requirement)/(update interval) 11 v = u αλ l M,max 10 3 m EI 3) Also adjust rate of change of time-delay (equivalent to frequency EI = u αml δ 7 v = u αλ l F,max 360 shift), updated regularly ifference between true element position and position predicted by constant velocity assumption must be less than coherence requirement t λ 60EI l 5 11αml i EI Δ = u sin M m F 5 3 m EI t λ 180EI l 5 7αml i EI Δ = u sin F m 9
10 3) Time elay and Frequency Compensation t λ 60EI l 5 11αml i EI Δ = u sin M a 11 = u αλ M,max 10 l 40 Δ α = M 4 11 ult λ 4 Error asymptotes to a limit as stiffness decreases m t λ 180EI l 5 7αml i EI Δ = u sin F 11 4 Δ = lim Δ = u αlt λ 7 4 M,max EI 0 M i 40 Δ = lim Δ = u αlt λ F,max EI 0 F i 70 i 1 Δ = at a max max ti i Δ = a 7 = u αλ F,max 360 l Structures with extremely small stiffness perform just as good as a very stiff structures, below a specific rotational acceleration Allows definition of a maximum rotational acceleration, below which any structure will suffice α F = 70 7 Δ ult λ 4 i 4 m 10
11 ISAT GR Innovative Space-based Radar Antenna Technology (ISAT) Program ARPA Funded, AFRL Executed, ended early 007 Program for 300 m deployable radar system with 100:1 compaction ratio Government Reference esign (GR) Used for analytical calculations in this presentation Three longeron tubular truss structure with bending stiffness of EI= N-m and linear mass of kg/m X-band radar panels with a linear mass of 10.0 kg/m were distributed evenly along the length of the truss for a system linear mass of m= kg/m The bus and center of gravity were coincident and located at the mid length of the antenna. While the total antenna length is 300 m, the half length of the system, l=150 m, is used in all equations Bus inertia is neglected because it is much smaller than the antenna inertia (the bus rotational inertia is 0.03% of the antenna) Half system rotational inertia is kg-m Vibration mode excited by a slew has a frequency of Hz (3.63 s period). 1% of critical damping is assumed and implemented as material damping in Abaqus. Slew maneuver: The model was subjected to a 90 deg yaw maneuver actuated with either a 300 N-m (M=150 N-m) moment applied to the system center of gravity or F=1 N tip thrusters for force actuation Both actuation methods result in the same actuation moment, acceleration ( rad/s ) and time to slew (1.45 min) 11
12 Stiffness Results for GR 1
13 Estimate Bending Loads Loads are due to steady-state and vibrations deformations: M = M + u M M = M + u M M ss, M vib, M,, Steady-state deformations are: αm M l x l x ss, M 6 F ss F vib F = ( + )( ) M = x( l + x)( l x) ss, F αm 6 Maximum moment is not always at root: 1 3 x 1 M = αml = = ss, F,max 9 3 l 3 13
14 Estimate Bending Loads Vibration mode shape is: M vib ( cos cosh sin + sinh ) ( ) δei λ φ φ σ φ σ φ x =, φ = λ 1, σ = l λσ cosλ λ σ cosh λ sinλ sinh λ l + + Substitute in deflection and stiffness relations: M M vib, M vib, F ( cos cosh sin + sinh ) + ( + ) ( cos cosh sin + sinh ) + ( + ) λ φ φ σ φ σ φ 11 3 = αml 10 λσ cosλ λ σ coshλ sinλ sinhλ = λ φ φ σ φ σ φ 7 3 αml 360 λσ cosλ λ σ cosh λ sin λ sinh λ With amplification factors of 3 (due to actuator reversal), maximum moments are: 3 x M = αml at = M,max l 3 x M = αml at = F,max l 14
15 Bending Strength M = αml M,max M = αml F,max
16 Truss Structural Performance Bending stiffness and strength per mass requirements drive structural architecture choices Extremely stiff and low mass requirements lead to extreme mechanical complexity to achieve increased hierarchy Relaxed stiffness and mass requirements lead to simpler deployable structures This relationship can be investigated with structural performance metrics Important to consider both strength and stiffness 16
17 Truss Structural Performance Metrics Requirements Bending Strength Bending Stiffness Geometry Indices -Truss architecture -Longeron architecture -Number of longerons Mass Per Length Specific Structural Performance Material Index Two ways to increase structural performance: Materials Hierarchy (geometry) Murphey, Chapter 1: Booms and Trusses in Recent Advances in Gossamer Spacecraft, Ed. Jenkins, AIAA
18 Truss Structural Performance Metrics Metric captures both stiffness and strength requirement 1/5 and powers correctly mass normalize metric Mass does not scale linearly or the same with stiffness and strength Correctly captures constant mass trade between stiffness and strength As truss radius (R) is increased without changing strut cross sections, stiffness increases while strength decreases Murphey, Chapter 1: Booms and Trusses in Recent Advances in Gossamer Spacecraft, Ed. Jenkins, AIAA
19 Steeper slope represents increased performance per mass Increasing Mass Efficiency 19
20 Combined Stiffness and Strength Requirements Requirements plummet below a certain rotational acceleration Above this limit: Limiting total deformations is nearly as good as time delay and frequency compensation Better to forgo active systems for passive structural stability in high dynamic excitation systems Below this limit: Time delay and frequency compensation allow extremely low requirements Time delay compensation has significantly lower requirements than no compensation 0
21 Comparing Architectures TS TS1 SR 3,53 1, Hypothetical Booms ECSMAR FM STT FM ISO FM TT 1
22 evelopment of RF Systems Ideal case is when both time delay and frequency compensation are feasible Stiffness requirement can be greatly reduced Caution: deformations become very large and still impose significant design constraint Update rate must increase to allow more precision operations t i = u α Δ M lλ 4 Some operational modes may require integration times much larger than t i Electronics/processing/software technology development may be required to enable updates during integration period
23 Structural Architectures Assertion: tensioned structures require the same structural stiffness as bending based architectures Tensioned architectures offer fewer benefits when the structural requirements are extreme When structural requirements can be reduced, through time-delay and frequency compensation, tensioned architectures are most advantageous 3
24 Comments on Tensioned Architectures Tension adds stiffness to a structure through two mechanisms Tensioned element axial stiffness (k=ea/l) Approach of tension truss architectures Tension induces transverse stiffness (k=t/l) Approach of blanket solar arrays, tension aligned architectures Bending structures rely purely on material stiffness and stability Extremely different material requirements General tension truss and aligned structures: Material must be stiff, able to support loads for extended periods of time without stress relaxation and able to be packaged and deployed without length changes Aperture shape depends on internal stress distribution. Stress relaxation /dimensional changes alter the stress distribution and antenna shape Flat tension aligned structures Material stiffness and dimensional stability requirements greatly reduced Aperture flatness does not depend material stability, aperture stiffness depends on element tension, not stiffness Large phased array architectures are easier than large shaped apertures Bending structures Material must be stiff, but does not necessarily need to carry constant loads over time (not sensitive to creep) 4
25 Closing Remarks The relationship between antenna deformation compensation methods and structural requirements was investigated Shown that time-delay and frequency compensation, when performed at a sufficiently high rate, can dramatically reduce structural requirements Reduced structural requirements allow new structural architectures Flat tensioned architectures (appropriate for phased arrays) are very promising Most of this material has been submitted for publication in: T. W. Murphey, E. M. Cliff, and S. A. Lane, Matching Space Antenna eformation Electronic Compensation Strategies to Support Structure Architectures, Submitted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems 5
Generation X. Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San. July 27, 2000
 Generation X Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San July 27, 2000 ACS Overview Requirements Assumptions Disturbance Torque Assessment Component and Control Mode Recommendations
Generation X Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San July 27, 2000 ACS Overview Requirements Assumptions Disturbance Torque Assessment Component and Control Mode Recommendations
Communication. Provides the interface between ground and the spacecraft Functions:
 Telecomm Communication Provides the interface between ground and the spacecraft Functions: Lock onto the ground station signal (carrier tracking) Receive uplink and process it (command reception and detection)
Telecomm Communication Provides the interface between ground and the spacecraft Functions: Lock onto the ground station signal (carrier tracking) Receive uplink and process it (command reception and detection)
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space
 Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space Gunnar Tibert KTH Space Center Space Rendezvous, 13 Oct 2016 Large Structures in Space My experience on large space structures: Centrifugally deployed
Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space Gunnar Tibert KTH Space Center Space Rendezvous, 13 Oct 2016 Large Structures in Space My experience on large space structures: Centrifugally deployed
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 The Concept of SPIDER Technology In the past, large inflatable satellites were referred to as gossamer structures. Gossamer literally means tenuous wisps of cobweb blowing in
Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 The Concept of SPIDER Technology In the past, large inflatable satellites were referred to as gossamer structures. Gossamer literally means tenuous wisps of cobweb blowing in
Modeling and Dynamic Analysis of Telescopic Systems of Structural Members with Clearance
 First published in: Modeling and Dynamic Analysis of Telescopic Systems of Structural Members with Clearance P. BARTHELS and J. WAUER Institut für Technische Mechanik, Universität Karlsruhe, D-76128 Karlsruhe,
First published in: Modeling and Dynamic Analysis of Telescopic Systems of Structural Members with Clearance P. BARTHELS and J. WAUER Institut für Technische Mechanik, Universität Karlsruhe, D-76128 Karlsruhe,
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly
 Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
ENAE 483: Principles of Space System Design Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms
 ENAE 483: Principles of Space System Design Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms Team: Vera Klimchenko Kevin Lee Kenneth Murphy Brendan Smyth October 29 th, 2012 Presentation Overview Project Overview Mission
ENAE 483: Principles of Space System Design Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms Team: Vera Klimchenko Kevin Lee Kenneth Murphy Brendan Smyth October 29 th, 2012 Presentation Overview Project Overview Mission
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F
 MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
Advanced Vibrations. Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian
 Advanced Vibrations Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions Relation between Discrete and Distributed
Advanced Vibrations Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions (Lecture 10) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Distributed-Parameter Systems: Exact Solutions Relation between Discrete and Distributed
Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System
 Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System Lulu Liu August, 7 1 Brief Introduction Photometric precision is a major concern in this space mission. A pointing
Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System Lulu Liu August, 7 1 Brief Introduction Photometric precision is a major concern in this space mission. A pointing
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser
 Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Single-track models of an A-double heavy vehicle combination
 Single-track models of an A-double heavy vehicle combination PETER NILSSON KRISTOFFER TAGESSON Department of Applied Mechanics Division of Vehicle Engineering and Autonomous Systems Vehicle Dynamics Group
Single-track models of an A-double heavy vehicle combination PETER NILSSON KRISTOFFER TAGESSON Department of Applied Mechanics Division of Vehicle Engineering and Autonomous Systems Vehicle Dynamics Group
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian
 Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Final Exam Solution Dynamics :45 12:15. Problem 1 Bateau
 Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY
 IAC-02-1.2.06 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY Sherry Draisey President, Good Vibrations Engineering Ltd. Toronto, Canada sherry@gve.on.ca ABSTRACT The International Space
IAC-02-1.2.06 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY Sherry Draisey President, Good Vibrations Engineering Ltd. Toronto, Canada sherry@gve.on.ca ABSTRACT The International Space
Improving Yield for High Pin Count Wafer Probing Applications
 John R. Goulding Martin Elzingre Larry Hendler Technical Marketing Manager 200mm Product Manager Consultant Electroglas, Inc. Electroglas, Inc. Electroglas, Inc. South West Test Workshop June 11-14 th
John R. Goulding Martin Elzingre Larry Hendler Technical Marketing Manager 200mm Product Manager Consultant Electroglas, Inc. Electroglas, Inc. Electroglas, Inc. South West Test Workshop June 11-14 th
Computer Modeling for the Complex Response Analysis of Nonstandard Structural Dynamics Problems
 Computer Modeling for the Complex Response Analysis of Nonstandard Structural Dynamics Problems Abhimanyu Kumar 1 and Atef F. Saleeb 2 Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by UNIVERSITY OF AKRON on 11/06/15.
Computer Modeling for the Complex Response Analysis of Nonstandard Structural Dynamics Problems Abhimanyu Kumar 1 and Atef F. Saleeb 2 Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by UNIVERSITY OF AKRON on 11/06/15.
Modeling of Resonators
 . 23 Modeling of Resonators 23 1 Chapter 23: MODELING OF RESONATORS 23 2 23.1 A GENERIC RESONATOR A second example where simplified discrete modeling has been found valuable is in the assessment of the
. 23 Modeling of Resonators 23 1 Chapter 23: MODELING OF RESONATORS 23 2 23.1 A GENERIC RESONATOR A second example where simplified discrete modeling has been found valuable is in the assessment of the
Benefits of Preview Wind Information for Region 2 Wind Turbine Control
 Benefits of Preview Wind Information for Region 2 Wind Turbine Control Ahmet Arda Ozdemir, Peter Seiler and Gary J Balas Department of Aerospace Engineering & Mechanics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Benefits of Preview Wind Information for Region 2 Wind Turbine Control Ahmet Arda Ozdemir, Peter Seiler and Gary J Balas Department of Aerospace Engineering & Mechanics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect. Synopsis. Introduction
 Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
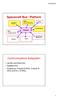 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes. Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005
 Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005 Translation of Title (a.k.a Outline) Tests of the (Weak) Equivalence Principle
Past and Future General Relativity Experiments: Equivalence Principle, Time Delay, and Black Holes Irwin Shapiro 21 October 2005 Translation of Title (a.k.a Outline) Tests of the (Weak) Equivalence Principle
ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam
 ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam Objectives: 1. To find the natural frequencies and mode shapes of a tapered beam using FEA.. To compare the FE solution to analytical solutions of the vibratory
ME 475 Modal Analysis of a Tapered Beam Objectives: 1. To find the natural frequencies and mode shapes of a tapered beam using FEA.. To compare the FE solution to analytical solutions of the vibratory
Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements
 Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force
 Paper Number 66, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force Ahmed M. Reda (1,2), Gareth L. Forbes (2) (1) Atkins, Perth, Australia
Paper Number 66, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force Ahmed M. Reda (1,2), Gareth L. Forbes (2) (1) Atkins, Perth, Australia
Analysis on propulsion shafting coupled torsional-longitudinal vibration under different applied loads
 Analysis on propulsion shafting coupled torsional-longitudinal vibration under different applied loads Qianwen HUANG 1 ; Jia LIU 1 ; Cong ZHANG 1,2 ; inping YAN 1,2 1 Reliability Engineering Institute,
Analysis on propulsion shafting coupled torsional-longitudinal vibration under different applied loads Qianwen HUANG 1 ; Jia LIU 1 ; Cong ZHANG 1,2 ; inping YAN 1,2 1 Reliability Engineering Institute,
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic. FEMAP & NX Nastran
 Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Clustered natural frequencies in multi-span beams with constrained characteristic functions
 Shock and Vibration 18 (2011) 697 707 697 DOI 10.3233/SAV-2010-0592 IOS Press Clustered natural frequencies in multi-span beams with constrained characteristic functions Khodabakhsh Saeedi and Rama B.
Shock and Vibration 18 (2011) 697 707 697 DOI 10.3233/SAV-2010-0592 IOS Press Clustered natural frequencies in multi-span beams with constrained characteristic functions Khodabakhsh Saeedi and Rama B.
Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts
 Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts August 12 th, 2009 U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, D.C. Code 8231-Attitude Control System James Armstrong, Craig Casey, Glenn Creamer,
Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts August 12 th, 2009 U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, D.C. Code 8231-Attitude Control System James Armstrong, Craig Casey, Glenn Creamer,
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS Clemens A.J. Beijers and André de Boer University of Twente P.O. Box 7, 75 AE Enschede, The Netherlands email: c.a.j.beijers@utwente.nl Abstract An important
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS Clemens A.J. Beijers and André de Boer University of Twente P.O. Box 7, 75 AE Enschede, The Netherlands email: c.a.j.beijers@utwente.nl Abstract An important
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011
 EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
IAC-11-C1.5.9 INERTIA-FREE ATTITUDE CONTROL OF SPACECRAFT WITH UNKNOWN TIME-VARYING MASS DISTRIBUTION
 6nd International Astronautical Congress, Cape Town, SA. Copyright by the International Astronautical Federation. All rights reserved IAC--C.5.9 INERTIA-FREE ATTITUDE CONTROL OF SPACECRAFT WITH UNKNOWN
6nd International Astronautical Congress, Cape Town, SA. Copyright by the International Astronautical Federation. All rights reserved IAC--C.5.9 INERTIA-FREE ATTITUDE CONTROL OF SPACECRAFT WITH UNKNOWN
Spacecraft Structures
 Tom Sarafin Instar Engineering and Consulting, Inc. 6901 S. Pierce St., Suite 384, Littleton, CO 80128 303-973-2316 tom.sarafin@instarengineering.com Functions Being Compatible with the Launch Vehicle
Tom Sarafin Instar Engineering and Consulting, Inc. 6901 S. Pierce St., Suite 384, Littleton, CO 80128 303-973-2316 tom.sarafin@instarengineering.com Functions Being Compatible with the Launch Vehicle
Preliminary Design Review: Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms. Michael Cunningham, Shimon Gewirtz, Rajesh Yalamanchili, Thomas Noyes
 Preliminary Design Review: Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms Michael Cunningham, Shimon Gewirtz, Rajesh Yalamanchili, Thomas Noyes Crew Cabin Structure Height of ~3.7m from heat shield to top of the cone
Preliminary Design Review: Loads, Structures, and Mechanisms Michael Cunningham, Shimon Gewirtz, Rajesh Yalamanchili, Thomas Noyes Crew Cabin Structure Height of ~3.7m from heat shield to top of the cone
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT
 APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
Wrinkling Analysis of A Kapton Square Membrane under Tensile Loading
 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Confere 7-10 April 2003, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 2003-1985 Wrinkling Analysis of A Kapton Square Membrane under Tensile Loading Xiaofeng
44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Confere 7-10 April 2003, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 2003-1985 Wrinkling Analysis of A Kapton Square Membrane under Tensile Loading Xiaofeng
EXAMPLE: MODELING THE PT326 PROCESS TRAINER
 CHAPTER 1 By Radu Muresan University of Guelph Page 1 EXAMPLE: MODELING THE PT326 PROCESS TRAINER The PT326 apparatus models common industrial situations in which temperature control is required in the
CHAPTER 1 By Radu Muresan University of Guelph Page 1 EXAMPLE: MODELING THE PT326 PROCESS TRAINER The PT326 apparatus models common industrial situations in which temperature control is required in the
Vibration Suppression Control of a Space Robot with Flexible Appendage based on Simple Dynamic Model*
 213 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) November 3-7, 213 Tokyo, Japan Vibration Suppression Control of a Space Robot with Flexible Appendage based on Simple Dynamic
213 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) November 3-7, 213 Tokyo, Japan Vibration Suppression Control of a Space Robot with Flexible Appendage based on Simple Dynamic
CONTINUUM STRUCTURAL REPRESENTATION OF FLEXURE AND TENSION STIFFENED ONE-DIMENSIONAL SPACECRAFT ARCHITECTURES. Jeffrey James Larsen
 CONTINUUM STRUCTURAL REPRESENTATION OF FLEXURE AND TENSION STIFFENED ONE-DIMENSIONAL SPACECRAFT ARCHITECTURES by Jeffrey James Larsen A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
CONTINUUM STRUCTURAL REPRESENTATION OF FLEXURE AND TENSION STIFFENED ONE-DIMENSIONAL SPACECRAFT ARCHITECTURES by Jeffrey James Larsen A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads
 Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads Mechanical loads can be static or dynamic. Static loads are constant or unchanging, and dynamic loads vary with time. Mechanical loads can also be external or self-contained.
Appendix A Satellite Mechanical Loads Mechanical loads can be static or dynamic. Static loads are constant or unchanging, and dynamic loads vary with time. Mechanical loads can also be external or self-contained.
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever
 Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE
 Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE Dexin Wang and Yuting Rui Research & Vehicle Technology Ford Motor Company ABSTRACT Cyclic stick-slip friction is a well-known
Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE Dexin Wang and Yuting Rui Research & Vehicle Technology Ford Motor Company ABSTRACT Cyclic stick-slip friction is a well-known
Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
e jωt = cos(ωt) + jsin(ωt),
 This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES
 2010/2 PAGES 1 8 RECEIVED 21. 9. 2009 ACCEPTED 20. 1. 2010 Y. KOLEKOVÁ, M. PETRONIJEVIĆ, G. SCHMID SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES ABSTRACT
2010/2 PAGES 1 8 RECEIVED 21. 9. 2009 ACCEPTED 20. 1. 2010 Y. KOLEKOVÁ, M. PETRONIJEVIĆ, G. SCHMID SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES ABSTRACT
VIBRATION SUPPRESSION IN SIMPLE TENSION-ALIGNED STRUCTURES. Tingli Cai
 VIBRATION SUPPRESSION IN SIMPLE TENSION-ALIGNED STRUCTURES By Tingli Cai A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Mechanical Engineering
VIBRATION SUPPRESSION IN SIMPLE TENSION-ALIGNED STRUCTURES By Tingli Cai A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Mechanical Engineering
Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated
 1470 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated Giorgio
1470 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated Giorgio
2 marks Questions and Answers
 1. Define the term strain energy. A: Strain Energy of the elastic body is defined as the internal work done by the external load in deforming or straining the body. 2. Define the terms: Resilience and
1. Define the term strain energy. A: Strain Energy of the elastic body is defined as the internal work done by the external load in deforming or straining the body. 2. Define the terms: Resilience and
Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System
 American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
 Watanabe, N., & Stoten, D. P. (214). Actuator control for a rapid prototyping railway bogie, using a dynamically substructured systems approach. In Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Motion
Watanabe, N., & Stoten, D. P. (214). Actuator control for a rapid prototyping railway bogie, using a dynamically substructured systems approach. In Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Motion
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
Chapter 10: Vibration Isolation of the Source
 Chapter 10: Vibration Isolation of the Source Introduction: High vibration levels can cause machinery failure, as well as objectionable noise levels. A common source of objectionable noise in buildings
Chapter 10: Vibration Isolation of the Source Introduction: High vibration levels can cause machinery failure, as well as objectionable noise levels. A common source of objectionable noise in buildings
Supplement: Statically Indeterminate Frames
 : Statically Indeterminate Frames Approximate Analysis - In this supplement, we consider another approximate method of solving statically indeterminate frames subjected to lateral loads known as the. Like
: Statically Indeterminate Frames Approximate Analysis - In this supplement, we consider another approximate method of solving statically indeterminate frames subjected to lateral loads known as the. Like
Study on Structural Deflection in Attitude Maneuvers of Flexible Satellite Equipped with Fuel-Efficient Input Shaper
 -Science and Engineering-, Vol.4 October 3, 15 Study on Structural Deflection in Attitude Maneuvers of Flexible Satellite Equipped with Fuel-Efficient nput Shaper Setyamartana Parman a,* a) Department
-Science and Engineering-, Vol.4 October 3, 15 Study on Structural Deflection in Attitude Maneuvers of Flexible Satellite Equipped with Fuel-Efficient nput Shaper Setyamartana Parman a,* a) Department
ε t increases from the compressioncontrolled Figure 9.15: Adjusted interaction diagram
 CHAPTER NINE COLUMNS 4 b. The modified axial strength in compression is reduced to account for accidental eccentricity. The magnitude of axial force evaluated in step (a) is multiplied by 0.80 in case
CHAPTER NINE COLUMNS 4 b. The modified axial strength in compression is reduced to account for accidental eccentricity. The magnitude of axial force evaluated in step (a) is multiplied by 0.80 in case
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF ISL S GUIDED SUPERSONIC PROJECTILE. Pierre Wey
 3 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16- APRIL 7 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF ISL S GUIDED SUPERSONIC PROJECTILE Pierre Wey French-German Research Institute of Saint-Louis (ISL) P.O.
3 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16- APRIL 7 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF ISL S GUIDED SUPERSONIC PROJECTILE Pierre Wey French-German Research Institute of Saint-Louis (ISL) P.O.
Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1. Dr./ Ahmed Nagib
 Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1 Dr./ Ahmed Nagib April 30, 2016 Research and Development Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Finite Element Analysis The linear equation of motion
Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1 Dr./ Ahmed Nagib April 30, 2016 Research and Development Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Finite Element Analysis The linear equation of motion
ENG2000 Chapter 7 Beams. ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey Beam: 1
 ENG2000 Chapter 7 Beams ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey Beam: 1 Overview In this chapter, we consider the stresses and moments present in loaded beams shear stress and bending moment diagrams We will also look at
ENG2000 Chapter 7 Beams ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey Beam: 1 Overview In this chapter, we consider the stresses and moments present in loaded beams shear stress and bending moment diagrams We will also look at
Mixed Control Moment Gyro and Momentum Wheel Attitude Control Strategies
 AAS03-558 Mixed Control Moment Gyro and Momentum Wheel Attitude Control Strategies C. Eugene Skelton II and Christopher D. Hall Department of Aerospace & Ocean Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute
AAS03-558 Mixed Control Moment Gyro and Momentum Wheel Attitude Control Strategies C. Eugene Skelton II and Christopher D. Hall Department of Aerospace & Ocean Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute
POWER SYSTEM STABILITY
 LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
Solar Reflector Gravity Tractor for Asteroid Collision Avoidance
 olar eflector Gravity Tractor for steroid Collision voidance r. Jeff Wesley Fisher Fisher I/ strodynamics pecialist Conference & Exhibit Honolulu, HI 0 ugust, 008 4 1 3 I/ strodynamics 008080 GT Created:
olar eflector Gravity Tractor for steroid Collision voidance r. Jeff Wesley Fisher Fisher I/ strodynamics pecialist Conference & Exhibit Honolulu, HI 0 ugust, 008 4 1 3 I/ strodynamics 008080 GT Created:
Structural Scaling Metrics For Tensioned-Blanket Space Systems
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Civil Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 7-12-2014 Structural Scaling Metrics For Tensioned-Blanket Space Systems Jeremy Banik Follow this and additional
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Civil Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 7-12-2014 Structural Scaling Metrics For Tensioned-Blanket Space Systems Jeremy Banik Follow this and additional
Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology. with contributions from the Theia Team
 Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with contributions from the Theia Team P. Douglas Lisman, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory David Spergel,
Team X Study Summary for ASMCS Theia Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with contributions from the Theia Team P. Douglas Lisman, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory David Spergel,
SAMCEF For ROTORS. Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics. This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF A, Page 1
 SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
Analysis and Design of Hybrid AI/Control Systems
 Analysis and Design of Hybrid AI/Control Systems Glen Henshaw, PhD (formerly) Space Systems Laboratory University of Maryland,College Park 13 May 2011 Dynamically Complex Vehicles Increased deployment
Analysis and Design of Hybrid AI/Control Systems Glen Henshaw, PhD (formerly) Space Systems Laboratory University of Maryland,College Park 13 May 2011 Dynamically Complex Vehicles Increased deployment
Free Vibration Analysis of Inflatable Space Structure
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov- Dec. 014), PP 48-53 Free Vibration Analysis of Inflatable Space Structure
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov- Dec. 014), PP 48-53 Free Vibration Analysis of Inflatable Space Structure
Vibration of a Euler Bernoulli uniform beam carrying a rigid body at each end
 Vibration of a Euler Bernoulli uniform beam carrying a rigid body at each end S. Naguleswaran Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand E-Mail: sivapatham.naguleswaran@canterbury.ac.nz
Vibration of a Euler Bernoulli uniform beam carrying a rigid body at each end S. Naguleswaran Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand E-Mail: sivapatham.naguleswaran@canterbury.ac.nz
Design of Sliding Mode Attitude Control for Communication Spacecraft
 Design of Sliding Mode Attitude Control for Communication Spacecraft Erkan Abdulhamitbilal 1 and Elbrous M. Jafarov 1 ISTAVIA Engineering, Istanbul Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering, Istanbul Technical
Design of Sliding Mode Attitude Control for Communication Spacecraft Erkan Abdulhamitbilal 1 and Elbrous M. Jafarov 1 ISTAVIA Engineering, Istanbul Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering, Istanbul Technical
Lecture 19. Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
Final Examination Thursday May Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer
 557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
Parametric Study of Thermal Stability on Continuous Welded Rail
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 4 / December 2010, pp. 126-133 The Korean Society for Railway arametric Study of Thermal Stability on Continuous Welded Rail Dong-Ho Choi* and Ho-Sung Na
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 4 / December 2010, pp. 126-133 The Korean Society for Railway arametric Study of Thermal Stability on Continuous Welded Rail Dong-Ho Choi* and Ho-Sung Na
Mechanical Design in Optical Engineering
 OPTI Buckling Buckling and Stability: As we learned in the previous lectures, structures may fail in a variety of ways, depending on the materials, load and support conditions. We had two primary concerns:
OPTI Buckling Buckling and Stability: As we learned in the previous lectures, structures may fail in a variety of ways, depending on the materials, load and support conditions. We had two primary concerns:
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
Table of Contents. iii
 Table of Contents Foreword..................................................... xv Preface...................................................... xvii Acknowledgements.............................................
Table of Contents Foreword..................................................... xv Preface...................................................... xvii Acknowledgements.............................................
ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS
 IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-14-07-02 ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS Ozan Tekinalp, * Omer Atas INTRODUCTION Utilization of solar sails for the de-orbiting of satellites is
IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-14-07-02 ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS Ozan Tekinalp, * Omer Atas INTRODUCTION Utilization of solar sails for the de-orbiting of satellites is
CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 12 - Structural Dynamics 1/75. To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass
 CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
FORMULA FOR FORCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES USING STATIC FACTORED RESPONSE AS EQUIVALENT DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 FORMULA FOR FORCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES USING STATIC FACTORED RESPONSE AS EQUIVALENT DYNAMIC RESPONSE ABSTRACT By G. C. Ezeokpube, M. Eng. Department of Civil Engineering Anambra State University,
FORMULA FOR FORCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES USING STATIC FACTORED RESPONSE AS EQUIVALENT DYNAMIC RESPONSE ABSTRACT By G. C. Ezeokpube, M. Eng. Department of Civil Engineering Anambra State University,
Launches and On-Orbit Performance
 Launches and On-Orbit Performance An Update on Nanosatellite Missions at the UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Daniel D. Kekez,, Robert E. Zee, Freddy M. Pranajaya Space Flight Laboratory University of Toronto
Launches and On-Orbit Performance An Update on Nanosatellite Missions at the UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Daniel D. Kekez,, Robert E. Zee, Freddy M. Pranajaya Space Flight Laboratory University of Toronto
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Introduction to Structural Member Properties
 Introduction to Structural Member Properties Structural Member Properties Moment of Inertia (I): a mathematical property of a cross-section (measured in inches 4 or in 4 ) that gives important information
Introduction to Structural Member Properties Structural Member Properties Moment of Inertia (I): a mathematical property of a cross-section (measured in inches 4 or in 4 ) that gives important information
Application of singular perturbation theory in modeling and control of flexible robot arm
 Research Article International Journal of Advanced Technology and Engineering Exploration, Vol 3(24) ISSN (Print): 2394-5443 ISSN (Online): 2394-7454 http://dx.doi.org/10.19101/ijatee.2016.324002 Application
Research Article International Journal of Advanced Technology and Engineering Exploration, Vol 3(24) ISSN (Print): 2394-5443 ISSN (Online): 2394-7454 http://dx.doi.org/10.19101/ijatee.2016.324002 Application
Chapter 11. Displacement Method of Analysis Slope Deflection Method
 Chapter 11 Displacement ethod of Analysis Slope Deflection ethod Displacement ethod of Analysis Two main methods of analyzing indeterminate structure Force method The method of consistent deformations
Chapter 11 Displacement ethod of Analysis Slope Deflection ethod Displacement ethod of Analysis Two main methods of analyzing indeterminate structure Force method The method of consistent deformations
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 41514
 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS
 BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS Automotive body structure can be divided into two types: i. Frameworks constructed of beams ii. Panels Classical beam versus typical modern vehicle beam sections Assumptions:
BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS Automotive body structure can be divided into two types: i. Frameworks constructed of beams ii. Panels Classical beam versus typical modern vehicle beam sections Assumptions:
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
Cork Institute of Technology. Summer 2007 Mechanics of Machines (Time: 3 Hours)
 Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
Continuum mechanism: Plates
 Observations of plate tectonics imply that the thin near-surface rocks, that constitute the lithosphere, are rigid, and therefore behave elastically on geological time scales. From the observed bending,
Observations of plate tectonics imply that the thin near-surface rocks, that constitute the lithosphere, are rigid, and therefore behave elastically on geological time scales. From the observed bending,
Determining the Specification of an Aperture Array for Cosmological Surveys
 Determining the Specification of an Aperture Array for Cosmological Surveys P. Alexander University of Cambridge, Department of Physics, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, UK. A. J. aulkner Jodrell Bank
Determining the Specification of an Aperture Array for Cosmological Surveys P. Alexander University of Cambridge, Department of Physics, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, UK. A. J. aulkner Jodrell Bank
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits. G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman
 Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere
 Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere Francoise Delplancke Outline: Basic principle of phase-referencing Atmospheric / astrophysical limitations Phase-referencing requirements: Practical problems: dispersion
Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere Francoise Delplancke Outline: Basic principle of phase-referencing Atmospheric / astrophysical limitations Phase-referencing requirements: Practical problems: dispersion
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
