The Phase Field Method
|
|
|
- Theodore Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Phase Field Method To simulate microstructural evolutions in materials Nele Moelans Group meeting 8 June 2004
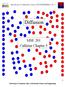
2 Outline Introduction Phase Field equations Phase Field simulations Grain growth Diffusion couples Conclusions
3 Introduction Phase Field Methode Phase Field variables Composition: c, x Structure: φ, η Continuous variation in time and space => no boundary conditions at moving interfaces => diffuse interfaces
4 Thermodynamics for phase equilibria T,p,c constant CALPHAD-method Thermodynamic function : Gm( T, p, xk) Minimization of G m at T,p thermodynamic equilibrium G m -expressions according to thermodynamic models Optimization of parameters using experimental data G G 0 x B 1 α β 0 x B 1 G( x, x, T) = x G + x G + RT( x ln( x ) + x ln( x )) + x x L( x, x, T) A B A A B B A A B B A B A B
5 Thermodynamics of heterogeneous systems Homogeneous versus heterogeneous systems:
6 Gibbs energy for heterogeneous systems Cahn-Hilliard (1958) Several contributions to Gibbs energy g (, c η) = g (, c η) + g (, c η) + g (, c η) +... hom chem elast mag Interface energy flat surface + ( ) 2 σ = g() c + κ dc/ dx dx = + 2 G () ( ) V ghom c κ c dv 2 2 G = g (, ) ( ) ( ) V hom c η + κ c + α η dv
7 Equilibrium for heterogeneous systems Conserved variables: Non-conserved variables: G g = hom = φ φ 2 2α φ 0 G = cte c G fhom 2 2 = 2κ c= µ hom 2κ c= cte c c G = 0 φ
8 Linear kinetic theory c,x conserved Mass balance: Onsager: η, φ not conserved c t J = M µ k η G = L t η = J k jk j j k
9 Phase Field equations Cahn-Hilliard c g M hom = i κ c + r t t c Time dependent Ginzburg-Landau η g L hom = α η + ζ t η Cahn-Allen φ g hom 2 = L 2α φ t φ ( ζ ) 2 2 (, ) ( r t ) 2 2 (, )
10 Phase Field simulations Phase field equations c g hom 2 = M 2κ c t c η g hom 2 = L 2α η t η Determination of parameters Numerical solution of partial differential equations
11 Phase Field simulations for real materials A lot of phenomenological parameters Phase equilibria Influence of inhomogenieties Kinetic properties c ghom(, c η) 2 = M(, c η) 2κ( c, η) c t c η g 2 (, ) hom (, c η) = L c η 2 α( c, η) η t η
12 Numerical solution Discretisation in time and space Algebraic set of (nonlinear) equations For each phase field variable: Nx*Ny unknowns Discretisation techniques finite differences finite elements spectral methods
13 Grain Growth Model of D. Fan Phase field variables: η i g hom Gibbs energy 4 2 ηi ηi = ( ) + 2* 4 2 Minima p p p i= 1 i= 1 j= 1 j i η η 2 2 i j (η 1,η 2,,η p )=(1,0,0,,0),(0,1,0,,0),,(0,0,,1),(-1,0,,0),
14 Grain Growth Influence second phase particles Variable: φ Particle: φ=1 Outside particle: φ=1 Minima Gibbs energy (φ, η 1,η 2,,η p )=(1, 0,0, 0), (0, 1,0,,0),(0, 0,1,,0),
15 Grain Growth Evolution second phase particles Composition variable: c Particle: c=c particle Outside particle: c=c matrix Minima free energy (c, η 1,η 2,,η p )=(c particle, 0,0, 0), (c matrix, 1,0,,0),(c matrix, 0,1,,0), Precipitation, coarsening, dissolution of particles Solute drag
16 Grain Growth simulation
17 Diffusion couples Adjustable complexity Coupling with CALPHAD and DICTRA strategy to determine parameters Technically relevant Theoretical insights
18 Phase equilibria: coupling with CALPHAD CALPHAD G gc (,0, T) = G gc (,1, T) = Phase field g(, c φ, T) α m β m (, c T) V m (, c T) V m
19 Coupling with CALPHAD G Phenomenological phase field variables α β, φ) = ( 1 p( φ) ) G ( c ) + p( φ) G ( c ) + g( φ) W ( c ) m( ck m k m k k p φ φ φ 2 ( ) = (3 2 ) g 2 2 ( φ) = φ (1 φ) Physical order parameters Landau expansion polynomial gc (, η ) = gc (,0) + Bc () η + C() cηη + D () cηηη k i i ij i j ijk i j k i ij ijk + Eijkl( c) ηηη i j kηl +... ijkl
20 DICTRA Kinetics: coupling with DICTRA Diffusion in lattice reference frame: Atomic mobilities: M = x Ω k Va kva J = x x k k Va ΩkVa µ k V x m Arrhenius expression for temperature dependence: 1 0 Mk = Mk exp( Qk / RT) RT 0 RT ln( RTM ) = RT ln( M ) Q =Φ+Θ k k k Redlich-Kister expansion for composition dependence: Φ = xφ + xx Φ k i 0 ki, i j kij, i i j> i
21 Kinetics: coupling with DICTRA Phase field Onsagers law: J k = L ki µ x het i Laboratory reference frame Diffusion experiments Fick s law c Jk = Dk x Interdiffusion, tracer, intrinsic
22 Conclusions Consistent and powerful theory Main problems Large amount of parameters to determine Computer resources Further work More efficient implementation Coupling between Phase Field Method and other thermodynamic modeling techniques Case studies
Phase Field Method. From fundamental theories to a phenomenological simulation method. Nele Moelans 24 June 2003
 Phase Field Method From fundamental theories to a phenomenologial simulation method Nele Moelans 4 June 003 Outline Introdution Important onepts: Diffuse interphase-phase field variables Thermodynamis
Phase Field Method From fundamental theories to a phenomenologial simulation method Nele Moelans 4 June 003 Outline Introdution Important onepts: Diffuse interphase-phase field variables Thermodynamis
Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials. Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC
 Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC What do we need to account for? Multi-phase states: thermodynamic systems
Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC What do we need to account for? Multi-phase states: thermodynamic systems
VIII. Phase Transformations. Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition
 VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
Modeling IMC growth in leadfree solder joints using the phase-field method coupled with the COST-531 thermodynamic database
 Modeling IMC growth in leadfree solder joints using the phase-field method coupled with the COST-531 thermodynamic database Nele Moelans, A. Durga, Yuanyuan Guan Bo Sundman, Alan Dinsdale, Suzana Fries
Modeling IMC growth in leadfree solder joints using the phase-field method coupled with the COST-531 thermodynamic database Nele Moelans, A. Durga, Yuanyuan Guan Bo Sundman, Alan Dinsdale, Suzana Fries
Computing the effective diffusivity using a spectral method
 Materials Science and Engineering A311 (2001) 135 141 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea Computing the effective diffusivity using a spectral method Jingzhi Zhu a, *, Long-Qing Chen a, Jie Shen b, Veena Tikare
Materials Science and Engineering A311 (2001) 135 141 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea Computing the effective diffusivity using a spectral method Jingzhi Zhu a, *, Long-Qing Chen a, Jie Shen b, Veena Tikare
Diffuse Interface Field Approach (DIFA) to Modeling and Simulation of Particle-based Materials Processes
 Diffuse Interface Field Approach (DIFA) to Modeling and Simulation of Particle-based Materials Processes Yu U. Wang Department Michigan Technological University Motivation Extend phase field method to
Diffuse Interface Field Approach (DIFA) to Modeling and Simulation of Particle-based Materials Processes Yu U. Wang Department Michigan Technological University Motivation Extend phase field method to
Spinodal decomposition
 Part V. Solid-solid transformations II Module 1 : Spinodal decomposition Part V. Solid-solid transformations II In this part, we discuss two transformations namely spinodal decomposition and ordering.
Part V. Solid-solid transformations II Module 1 : Spinodal decomposition Part V. Solid-solid transformations II In this part, we discuss two transformations namely spinodal decomposition and ordering.
Major Concepts Lecture #11 Rigoberto Hernandez. TST & Transport 1
 Major Concepts Onsager s Regression Hypothesis Relaxation of a perturbation Regression of fluctuations Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem Proof of FDT & relation to Onsager s Regression Hypothesis Response
Major Concepts Onsager s Regression Hypothesis Relaxation of a perturbation Regression of fluctuations Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem Proof of FDT & relation to Onsager s Regression Hypothesis Response
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany
 Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 18 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 18 Nov 2016 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 18 Nov 2016](/thumbs/92/109062392.jpg) arxiv:169.74v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 18 Nov 216 A comparison of Redlich-Kister polynomial and cubic spline representations of the chemical potential in phase field computations Gregory H. Teichert a, N.
arxiv:169.74v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 18 Nov 216 A comparison of Redlich-Kister polynomial and cubic spline representations of the chemical potential in phase field computations Gregory H. Teichert a, N.
Finite Difference Solution of the Heat Equation
 Finite Difference Solution of the Heat Equation Adam Powell 22.091 March 13 15, 2002 In example 4.3 (p. 10) of his lecture notes for March 11, Rodolfo Rosales gives the constant-density heat equation as:
Finite Difference Solution of the Heat Equation Adam Powell 22.091 March 13 15, 2002 In example 4.3 (p. 10) of his lecture notes for March 11, Rodolfo Rosales gives the constant-density heat equation as:
Phase-Field Simulation of the Effect of Elastic Inhomogeneity on Microstructure Evolution in Ni-Based Superalloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 4 (2009) pp. 744 to 748 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Phase-Field Simulation of the Effect of Elastic Inhomogeneity on Microstructure Evolution in Ni-Based Superalloys
Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 4 (2009) pp. 744 to 748 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Phase-Field Simulation of the Effect of Elastic Inhomogeneity on Microstructure Evolution in Ni-Based Superalloys
PHASE-FIELD MODELS FOR MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION
 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2002. 32:113 40 doi: 10.1146/annurev.matsci.32.112001.132041 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PHASE-FIELD MODELS FOR MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION Long-Qing Chen
Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2002. 32:113 40 doi: 10.1146/annurev.matsci.32.112001.132041 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PHASE-FIELD MODELS FOR MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION Long-Qing Chen
Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-2
 Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-2 PD Dr. Nikolay Zotov zotov@imw.uni-stuttgart.de Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Part III Lectures Solid State Reactions Short Description
Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-2 PD Dr. Nikolay Zotov zotov@imw.uni-stuttgart.de Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Part III Lectures Solid State Reactions Short Description
Chemical reactors. H has thermal contribution, pressure contribution (often negligible) and reaction contribution ( source - like)
 Chemical reactors - chemical transformation of reactants into products Classification: a) according to the type of equipment o batch stirred tanks small-scale production, mostly liquids o continuous stirred
Chemical reactors - chemical transformation of reactants into products Classification: a) according to the type of equipment o batch stirred tanks small-scale production, mostly liquids o continuous stirred
Thermodynamic description and growth kinetics of stoichiometric precipitates in the phase-field approach
 Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry 31 (2007) 303 312 www.elsevier.com/locate/calphad Thermodynamic description and growth kinetics of stoichiometric precipitates in the phase-field
Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry 31 (2007) 303 312 www.elsevier.com/locate/calphad Thermodynamic description and growth kinetics of stoichiometric precipitates in the phase-field
Interface Profiles in Field Theory
 Florian König Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Münster January 10, 2011 / Forschungsseminar Quantenfeldtheorie Outline φ 4 -Theory in Statistical Physics Critical Phenomena and Order Parameter
Florian König Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Münster January 10, 2011 / Forschungsseminar Quantenfeldtheorie Outline φ 4 -Theory in Statistical Physics Critical Phenomena and Order Parameter
INFLUENCE OF AN APPLIED STRAIN FIELD ON MICROSTRUCTURAL EVOLUTION DURING THE α 2 O- PHASE TRANSFORMATION IN Ti Al Nb SYSTEM
 Acta mater. 49 (2001) 13 20 www.elsevier.com/locate/actamat INFLUENCE OF AN APPLIED STRAIN FIELD ON MICROSTRUCTURAL EVOLUTION DURING THE α 2 O- PHASE TRANSFORMATION IN Ti Al Nb SYSTEM Y. H. WEN 1, 2 *,
Acta mater. 49 (2001) 13 20 www.elsevier.com/locate/actamat INFLUENCE OF AN APPLIED STRAIN FIELD ON MICROSTRUCTURAL EVOLUTION DURING THE α 2 O- PHASE TRANSFORMATION IN Ti Al Nb SYSTEM Y. H. WEN 1, 2 *,
Similarities and differences:
 How does the system reach equilibrium? I./9 Chemical equilibrium I./ Equilibrium electrochemistry III./ Molecules in motion physical processes, non-reactive systems III./5-7 Reaction rate, mechanism, molecular
How does the system reach equilibrium? I./9 Chemical equilibrium I./ Equilibrium electrochemistry III./ Molecules in motion physical processes, non-reactive systems III./5-7 Reaction rate, mechanism, molecular
Effect of Elastic Anisotropy and Inhomogeneity on Coring Structure Evolution in Pu-Ga Alloys Phase-field modeling
 J Computer-Aided Mater Des (2007) 14:389 402 DOI 10.1007/s10820-007-9050-4 Effect of Elastic Anisotropy and Inhomogeneity on Coring Structure Evolution in Pu-Ga Alloys Phase-field modeling S. Y. Hu M.
J Computer-Aided Mater Des (2007) 14:389 402 DOI 10.1007/s10820-007-9050-4 Effect of Elastic Anisotropy and Inhomogeneity on Coring Structure Evolution in Pu-Ga Alloys Phase-field modeling S. Y. Hu M.
Multi Physics/Scale Modeling/Simulation of Nanomaterials
 Multi Physics/Scale Modeling/Simulation of Nanomaterials Kasra Momeni AEGSO Summer 2013 Outline Introduction Materials Modeling Multiphysics Multiscale Modeling Lab instructions 2 Introduction Conceptual
Multi Physics/Scale Modeling/Simulation of Nanomaterials Kasra Momeni AEGSO Summer 2013 Outline Introduction Materials Modeling Multiphysics Multiscale Modeling Lab instructions 2 Introduction Conceptual
Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at
 Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Diffusion in multicomponent solids. Anton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
MESOSCALE TRANSPORT AND RHEOLOGY
 MESOSCALE TRANSPORT AND RHEOLOGY Jorge Viñals School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota MESOSCALE THEMES 1 Nonequilibrium evolution Slow ( hydrodynamic ) but unstable motion of collective
MESOSCALE TRANSPORT AND RHEOLOGY Jorge Viñals School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota MESOSCALE THEMES 1 Nonequilibrium evolution Slow ( hydrodynamic ) but unstable motion of collective
Sub -T g Relaxation in Thin Glass
 Sub -T g Relaxation in Thin Glass Prabhat Gupta The Ohio State University ( Go Bucks! ) Kyoto (January 7, 2008) 2008/01/07 PK Gupta(Kyoto) 1 Outline 1. Phenomenology (Review). A. Liquid to Glass Transition
Sub -T g Relaxation in Thin Glass Prabhat Gupta The Ohio State University ( Go Bucks! ) Kyoto (January 7, 2008) 2008/01/07 PK Gupta(Kyoto) 1 Outline 1. Phenomenology (Review). A. Liquid to Glass Transition
2D Spinodal Decomposition in Forced Turbulence: Structure Formation in a Challenging Analogue of 2D MHD Turbulence
 2D Spinodal Decomposition in Forced Turbulence: Structure Formation in a Challenging Analogue of 2D MHD Turbulence 1 Xiang Fan 1, P H Diamond 1, Luis Chacon 2, Hui Li 2 1 University of California,San Diego
2D Spinodal Decomposition in Forced Turbulence: Structure Formation in a Challenging Analogue of 2D MHD Turbulence 1 Xiang Fan 1, P H Diamond 1, Luis Chacon 2, Hui Li 2 1 University of California,San Diego
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05)
 3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
A sharp diffuse interface tracking method for approximating evolving interfaces
 A sharp diffuse interface tracking method for approximating evolving interfaces Vanessa Styles and Charlie Elliott University of Sussex Overview Introduction Phase field models Double well and double obstacle
A sharp diffuse interface tracking method for approximating evolving interfaces Vanessa Styles and Charlie Elliott University of Sussex Overview Introduction Phase field models Double well and double obstacle
Phase Field Formulation for Microstructure Evolution in Oxide Ceramics
 Phase Field Formulation for Microstructure Evolution in Oxide Ceramics Corning Problem Presenter: Leslie Button (Corning) Problem Participants: Daniel Anderson 1, Chris Breward 2, Yanping Chen 3, Brendan
Phase Field Formulation for Microstructure Evolution in Oxide Ceramics Corning Problem Presenter: Leslie Button (Corning) Problem Participants: Daniel Anderson 1, Chris Breward 2, Yanping Chen 3, Brendan
Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale. Miguel Rubi
 Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale Miguel Rubi References S.R. de Groot and P. Mazur, Non equilibrium Thermodynamics, Dover, New York, 1984 J.M. Vilar and
Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale Miguel Rubi References S.R. de Groot and P. Mazur, Non equilibrium Thermodynamics, Dover, New York, 1984 J.M. Vilar and
Lecture 2. Chemical Kinetics. Chemical Kinetics 6/26/11. One (elementary) step reaction
 Lecture Chemical Kinetics 1 One (elementary) step reaction im i i M i is the number of species i, i are the stoichiometric coefficients i i Chemical Kinetics =0ifi is not a reactant =0ifi is not a product
Lecture Chemical Kinetics 1 One (elementary) step reaction im i i M i is the number of species i, i are the stoichiometric coefficients i i Chemical Kinetics =0ifi is not a reactant =0ifi is not a product
Module 16. Diffusion in solids II. Lecture 16. Diffusion in solids II
 Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Hamed Babaei a, Valery I. Levitas b. Abstract
 Phase-field approach for stress- and temperature-induced phase transformations that satisfies lattice instability conditions. Part 2. Simulations of phase transformations Si I Si II Hamed Babaei a, Valery
Phase-field approach for stress- and temperature-induced phase transformations that satisfies lattice instability conditions. Part 2. Simulations of phase transformations Si I Si II Hamed Babaei a, Valery
Modelling of interfaces and free boundaries
 University of Regensburg Regensburg, March 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Obstacle problems 3 Stefan problem 4 Shape optimization Introduction What is a free boundary problem? Solve a partial differential
University of Regensburg Regensburg, March 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Obstacle problems 3 Stefan problem 4 Shape optimization Introduction What is a free boundary problem? Solve a partial differential
The Weierstrass Theory For Elliptic Functions. The Burn 2007
 The Weierstrass Theory For Elliptic Functions Including The Generalisation To Higher Genus Department of Mathematics, MACS Heriot Watt University Edinburgh The Burn 2007 Outline Elliptic Function Theory
The Weierstrass Theory For Elliptic Functions Including The Generalisation To Higher Genus Department of Mathematics, MACS Heriot Watt University Edinburgh The Burn 2007 Outline Elliptic Function Theory
Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-1
 Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-1 PD Dr. Nikolay Zotov zotov@imw.uni-stuttgart.de Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Part III Lectures Solid State Reactions Short Description
Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Lecture III-1 PD Dr. Nikolay Zotov zotov@imw.uni-stuttgart.de Atomic Transport & Phase Transformations Part III Lectures Solid State Reactions Short Description
Statistical Mechanics
 Statistical Mechanics Newton's laws in principle tell us how anything works But in a system with many particles, the actual computations can become complicated. We will therefore be happy to get some 'average'
Statistical Mechanics Newton's laws in principle tell us how anything works But in a system with many particles, the actual computations can become complicated. We will therefore be happy to get some 'average'
Appendix 4. Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases
 Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Mathematical Modeling All Solid State Batteries
 Katharina Becker-Steinberger, Stefan Funken, Manuel Landsdorfer, Karsten Urban Institute of Numerical Mathematics Konstanz, 04.03.2010 Mathematical Modeling All Solid State Batteries Page 1/31 Mathematical
Katharina Becker-Steinberger, Stefan Funken, Manuel Landsdorfer, Karsten Urban Institute of Numerical Mathematics Konstanz, 04.03.2010 Mathematical Modeling All Solid State Batteries Page 1/31 Mathematical
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School PHASE FIELD MODEL FOR THE NUCLEATION IN SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS: THEORIES,
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School PHASE FIELD MODEL FOR THE NUCLEATION IN SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS: THEORIES, ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS A Dissertation in Mathematics by Lei
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School PHASE FIELD MODEL FOR THE NUCLEATION IN SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS: THEORIES, ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS A Dissertation in Mathematics by Lei
Kirkwood-Buff Integrals for Aqueous Urea Solutions Based upon the Quantum Chemical Electrostatic Potential and Interaction Energies
 Supporting Information for Kirkwood-Buff Integrals for Aqueous Urea Solutions Based upon the Quantum Chemical Electrostatic Potential and Interaction Energies Shuntaro Chiba, 1* Tadaomi Furuta, 2 and Seishi
Supporting Information for Kirkwood-Buff Integrals for Aqueous Urea Solutions Based upon the Quantum Chemical Electrostatic Potential and Interaction Energies Shuntaro Chiba, 1* Tadaomi Furuta, 2 and Seishi
macroscopic view (phenomenological) microscopic view (atomistic) computing reaction rate rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics
 Rate Theory (overview) macroscopic view (phenomenological) rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics Van t Hoff & Arrhenius equation microscopic view (atomistic) statistical mechanics transition state
Rate Theory (overview) macroscopic view (phenomenological) rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics Van t Hoff & Arrhenius equation microscopic view (atomistic) statistical mechanics transition state
Role of thermodynamics in modeling the behavior of complex solids
 IWNET Summer School 2015 Role of thermodynamics in modeling the behavior of complex solids Bob Svendsen Material Mechanics RWTH Aachen University Microstructure Physics and Alloy Design Max-Planck-Institut
IWNET Summer School 2015 Role of thermodynamics in modeling the behavior of complex solids Bob Svendsen Material Mechanics RWTH Aachen University Microstructure Physics and Alloy Design Max-Planck-Institut
macroscopic view (phenomenological) microscopic view (atomistic) computing reaction rate rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics
 Rate heory (overview) macroscopic view (phenomenological) rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics Van t Hoff & Arrhenius equation microscopic view (atomistic) statistical mechanics transition state
Rate heory (overview) macroscopic view (phenomenological) rate of reactions experiments thermodynamics Van t Hoff & Arrhenius equation microscopic view (atomistic) statistical mechanics transition state
Theory of Nonequilibrium Superconductivity *
 Theory of Nonequilibrium Superconductivity * NIKOLAI B.KOPNIN Low Temperature Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Finland and L.D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Moscow, Russia CLARENDON
Theory of Nonequilibrium Superconductivity * NIKOLAI B.KOPNIN Low Temperature Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Finland and L.D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Moscow, Russia CLARENDON
Dispersion relations, stability and linearization
 Dispersion relations, stability and linearization 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient partial differential
Dispersion relations, stability and linearization 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient partial differential
with deterministic and noise terms for a general non-homogeneous Cahn-Hilliard equation Modeling and Asymptotics
 12-3-2009 Modeling and Asymptotics for a general non-homogeneous Cahn-Hilliard equation with deterministic and noise terms D.C. Antonopoulou (Joint with G. Karali and G. Kossioris) Department of Applied
12-3-2009 Modeling and Asymptotics for a general non-homogeneous Cahn-Hilliard equation with deterministic and noise terms D.C. Antonopoulou (Joint with G. Karali and G. Kossioris) Department of Applied
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR CONSERVED PHASE FIELD MODELS: SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS MOHSEN ASLE ZAEEM
 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR CONSERVED PHASE FIELD MODELS: SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS By MOHSEN ASLE ZAEEM A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR CONSERVED PHASE FIELD MODELS: SOLID STATE PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS By MOHSEN ASLE ZAEEM A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR
The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or. smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is
 1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State
 Chapter 2 Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 1 October 2012 2.1 Introduction The simple theory of nucleation that we introduced in
Chapter 2 Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 1 October 2012 2.1 Introduction The simple theory of nucleation that we introduced in
Surface stress-induced self-assembly
 Surface stress-induced self-assembly Zhigang Suo Work with Wei Lu Solid surface Liquid surface Stretched solid surface Energy per surface atom depends on stretch Stretched liquid surface Energy per surface
Surface stress-induced self-assembly Zhigang Suo Work with Wei Lu Solid surface Liquid surface Stretched solid surface Energy per surface atom depends on stretch Stretched liquid surface Energy per surface
Modelling the phase and crystallisation behaviour of fat mixtures
 Modelling the phase and crystallisation behaviour of fat mixtures Jan Los & Elias Vlieg IMM Solid State Chemistry, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Introduction Equilibrium Kinetics The full
Modelling the phase and crystallisation behaviour of fat mixtures Jan Los & Elias Vlieg IMM Solid State Chemistry, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Introduction Equilibrium Kinetics The full
Thermodynamics of diffusion (extracurricular material - not tested)
 Thermodynamics of diffusion (etracurricular material - not tested) riving force for diffusion iffusion in ideal and real solutions Thermodynamic factor iffusion against the concentration gradient Spinodal
Thermodynamics of diffusion (etracurricular material - not tested) riving force for diffusion iffusion in ideal and real solutions Thermodynamic factor iffusion against the concentration gradient Spinodal
Electrochemical Cell - Basics
 Electrochemical Cell - Basics The electrochemical cell e - (a) Load (b) Load e - M + M + Negative electrode Positive electrode Negative electrode Positive electrode Cathode Anode Anode Cathode Anode Anode
Electrochemical Cell - Basics The electrochemical cell e - (a) Load (b) Load e - M + M + Negative electrode Positive electrode Negative electrode Positive electrode Cathode Anode Anode Cathode Anode Anode
Recitation: 12 12/04/03
 Recitation: 12 12/4/3 Regular Solution Solution: In an ideal solution, the only contribution to the Gibbs free energy of ing is the configurational entropy due to a random ture: ΔG id G id = x + x µ µ
Recitation: 12 12/4/3 Regular Solution Solution: In an ideal solution, the only contribution to the Gibbs free energy of ing is the configurational entropy due to a random ture: ΔG id G id = x + x µ µ
Adsorption Equilibria. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Equilibria Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Adsorption isotherm models Langmuir isotherm Volmer isotherm Fowler-Guggenheim isotherm Hill-deBoer
Adsorption Equilibria Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Adsorption isotherm models Langmuir isotherm Volmer isotherm Fowler-Guggenheim isotherm Hill-deBoer
Precipitation. Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration!
 Precipitation Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration! Precipitation Four major questions: 1. Why do molecules/ions precipitate? 2. What determines the size? 3. What determines the size distribution?
Precipitation Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration! Precipitation Four major questions: 1. Why do molecules/ions precipitate? 2. What determines the size? 3. What determines the size distribution?
A Differential Variational Inequality Approach for the Simulation of Heterogeneous Materials
 A Differential Variational Inequality Approach for the Simulation of Heterogeneous Materials Lei Wang 1, Jungho Lee 1, Mihai Anitescu 1, Anter El Azab 2, Lois Curfman McInnes 1, Todd Munson 1, Barry Smith
A Differential Variational Inequality Approach for the Simulation of Heterogeneous Materials Lei Wang 1, Jungho Lee 1, Mihai Anitescu 1, Anter El Azab 2, Lois Curfman McInnes 1, Todd Munson 1, Barry Smith
Foundations of Chemical Kinetics. Lecture 12: Transition-state theory: The thermodynamic formalism
 Foundations of Chemical Kinetics Lecture 12: Transition-state theory: The thermodynamic formalism Marc R. Roussel Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Breaking it down We can break down an elementary
Foundations of Chemical Kinetics Lecture 12: Transition-state theory: The thermodynamic formalism Marc R. Roussel Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Breaking it down We can break down an elementary
3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions Issued: Fall 2003 Graded problems due:
 3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions 3.012 Issued: 11.17.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 11.26.03 Graded problems: 1. Analysis of equilibrium phases with a binary phase diagram. Shown below is the phase diagram
3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions 3.012 Issued: 11.17.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 11.26.03 Graded problems: 1. Analysis of equilibrium phases with a binary phase diagram. Shown below is the phase diagram
Coarsening Dynamics for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation. Jaudat Rashed
 Coarsening Dynamics for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation Jaudat Rashed Coarsening Dynamics for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation Research Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
Coarsening Dynamics for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation Jaudat Rashed Coarsening Dynamics for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation Research Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
Project Mentor(s): Dr. Evelyn Sander and Dr. Thomas Wanner
 STABILITY OF EQUILIBRIA IN ONE DIMENSION FOR DIBLOCK COPOLYMER EQUATION Olga Stulov Department of Mathematics, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York at New Paltz
STABILITY OF EQUILIBRIA IN ONE DIMENSION FOR DIBLOCK COPOLYMER EQUATION Olga Stulov Department of Mathematics, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York at New Paltz
Supporting information for: A multi-fluid model for microstructure. formation in polymer membranes
 Electronic Supplementary Material ESI for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for: A multi-fluid model for microstructure formation in polymer membranes
Electronic Supplementary Material ESI for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for: A multi-fluid model for microstructure formation in polymer membranes
The Chemical Potential
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
EMA4303/5305 Electrochemical Engineering Lecture 03 Electrochemical Kinetics
 EMA4303/5305 Electrochemical Engineering Lecture 03 Electrochemical Kinetics Dr. Junheng Xing, Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University 2 Electrochemical Kinetics
EMA4303/5305 Electrochemical Engineering Lecture 03 Electrochemical Kinetics Dr. Junheng Xing, Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University 2 Electrochemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics. What Influences Kinetics?
 Chemical Kinetics Predictions of likelihood for a reaction to occur have been based on difference in energy between products and reactants: Thermodynamics only compares reactants to products, says nothing
Chemical Kinetics Predictions of likelihood for a reaction to occur have been based on difference in energy between products and reactants: Thermodynamics only compares reactants to products, says nothing
A PRACTICALLY UNCONDITIONALLY GRADIENT STABLE SCHEME FOR THE N-COMPONENT CAHN HILLIARD SYSTEM
 A PRACTICALLY UNCONDITIONALLY GRADIENT STABLE SCHEME FOR THE N-COMPONENT CAHN HILLIARD SYSTEM Hyun Geun LEE 1, Jeong-Whan CHOI 1 and Junseok KIM 1 1) Department of Mathematics, Korea University, Seoul
A PRACTICALLY UNCONDITIONALLY GRADIENT STABLE SCHEME FOR THE N-COMPONENT CAHN HILLIARD SYSTEM Hyun Geun LEE 1, Jeong-Whan CHOI 1 and Junseok KIM 1 1) Department of Mathematics, Korea University, Seoul
Wang-Landau Monte Carlo simulation. Aleš Vítek IT4I, VP3
 Wang-Landau Monte Carlo simulation Aleš Vítek IT4I, VP3 PART 1 Classical Monte Carlo Methods Outline 1. Statistical thermodynamics, ensembles 2. Numerical evaluation of integrals, crude Monte Carlo (MC)
Wang-Landau Monte Carlo simulation Aleš Vítek IT4I, VP3 PART 1 Classical Monte Carlo Methods Outline 1. Statistical thermodynamics, ensembles 2. Numerical evaluation of integrals, crude Monte Carlo (MC)
Review: control, feedback, etc. Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization
 Plan of the Lecture Review: control, feedback, etc Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization Goal: a general framework that encompasses all examples of interest Once we have mastered
Plan of the Lecture Review: control, feedback, etc Today s topic: state-space models of systems; linearization Goal: a general framework that encompasses all examples of interest Once we have mastered
Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices
 Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices Anupam Kundu Abhishek Chaudhuri Dibyendu Roy Abhishek Dhar Joel Lebowitz Herbert Spohn Raman Research Institute NUS, Singapore February
Heat conduction and phonon localization in disordered harmonic lattices Anupam Kundu Abhishek Chaudhuri Dibyendu Roy Abhishek Dhar Joel Lebowitz Herbert Spohn Raman Research Institute NUS, Singapore February
Dispersion relations, linearization and linearized dynamics in PDE models
 Dispersion relations, linearization and linearized dynamics in PDE models 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient
Dispersion relations, linearization and linearized dynamics in PDE models 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient
Non-equilibrium mixtures of gases: modeling and computation
 Non-equilibrium mixtures of gases: modeling and computation Lecture 1: and kinetic theory of gases Srboljub Simić University of Novi Sad, Serbia Aim and outline of the course Aim of the course To present
Non-equilibrium mixtures of gases: modeling and computation Lecture 1: and kinetic theory of gases Srboljub Simić University of Novi Sad, Serbia Aim and outline of the course Aim of the course To present
Computer Simulation of Interdiffusion Microstructures in Multi-Component and Multiphase Systems
 Computer Simulation of Interdiffusion Microstructures in Multi-Component and Multiphase Systems DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in
Computer Simulation of Interdiffusion Microstructures in Multi-Component and Multiphase Systems DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in
Step Bunching in Epitaxial Growth with Elasticity Effects
 Step Bunching in Epitaxial Growth with Elasticity Effects Tao Luo Department of Mathematics The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology joint work with Yang Xiang, Aaron Yip 05 Jan 2017 Tao Luo
Step Bunching in Epitaxial Growth with Elasticity Effects Tao Luo Department of Mathematics The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology joint work with Yang Xiang, Aaron Yip 05 Jan 2017 Tao Luo
COARSE-GRAINING AND THERMODYNAMICS IN FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEMS
 Vol. 44 (2013) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 5 COARSE-GRAINING AND THERMODYNAMICS IN FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEMS J. Miguel Rubí, A. Pérez-Madrid Departament de Física Fonamental, Facultat de Física, Universitat
Vol. 44 (2013) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 5 COARSE-GRAINING AND THERMODYNAMICS IN FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEMS J. Miguel Rubí, A. Pérez-Madrid Departament de Física Fonamental, Facultat de Física, Universitat
Attenuation and dispersion
 Attenuation and dispersion! Mechanisms: Absorption (inelastic); Scattering (elastic).! Mathematical descriptions! Measurement! Frequency dependence! Dispersion, its relation to attenuation Reading: Sheriff
Attenuation and dispersion! Mechanisms: Absorption (inelastic); Scattering (elastic).! Mathematical descriptions! Measurement! Frequency dependence! Dispersion, its relation to attenuation Reading: Sheriff
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models
 Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3
 The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
Constraints on Fluid Dynamics From Equilibrium Partition Func
 Constraints on Fluid Dynamics From Equilibrium Partition Function Nabamita Banerjee Nikhef, Amsterdam LPTENS, Paris 1203.3544, 1206.6499 J. Bhattacharya, S. Jain, S. Bhattacharyya, S. Minwalla, T. Sharma,
Constraints on Fluid Dynamics From Equilibrium Partition Function Nabamita Banerjee Nikhef, Amsterdam LPTENS, Paris 1203.3544, 1206.6499 J. Bhattacharya, S. Jain, S. Bhattacharyya, S. Minwalla, T. Sharma,
Chapter 15. Landau-Ginzburg theory The Landau model
 Chapter 15 Landau-Ginzburg theory We have seen in Chap. 6.1 that Phase transitions are caused most of the time by the interaction between particles, with an expectation being the Bose-Einstein condensation
Chapter 15 Landau-Ginzburg theory We have seen in Chap. 6.1 that Phase transitions are caused most of the time by the interaction between particles, with an expectation being the Bose-Einstein condensation
Phase-Field Modeling of Technical Alloy Systems Problems and Solutions
 Thermo-Calc User Meeting, Sept 8-9 2011, Aachen Phase-Field Modeling of Technical Alloy Systems Problems and Solutions B. Böttger ACCESS e.v., RWTH Aachen University, Germany Outline 1. Introduction 2.
Thermo-Calc User Meeting, Sept 8-9 2011, Aachen Phase-Field Modeling of Technical Alloy Systems Problems and Solutions B. Böttger ACCESS e.v., RWTH Aachen University, Germany Outline 1. Introduction 2.
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
Stability Analysis of Stationary Solutions for the Cahn Hilliard Equation
 Stability Analysis of Stationary Solutions for the Cahn Hilliard Equation Peter Howard, Texas A&M University University of Louisville, Oct. 19, 2007 References d = 1: Commun. Math. Phys. 269 (2007) 765
Stability Analysis of Stationary Solutions for the Cahn Hilliard Equation Peter Howard, Texas A&M University University of Louisville, Oct. 19, 2007 References d = 1: Commun. Math. Phys. 269 (2007) 765
Complex Fluids. University of California - Santa Barbara, CA April 26, Abstract
 Gravitational Effects on Structure Development in Quenched Complex Fluids V. E. Badalassi, a H. D. Ceniceros b and S. Banerjee c a,c Department of Chemical Engineering, b Department of Mathematics University
Gravitational Effects on Structure Development in Quenched Complex Fluids V. E. Badalassi, a H. D. Ceniceros b and S. Banerjee c a,c Department of Chemical Engineering, b Department of Mathematics University
Numerical Studies on Phase Field Diffusion and Flow Solvers
 Numerical Studies on Phase Field Diffusion and Flow Solvers Author: E. Man Supervisors: Prof.dr.ir. C.R. Kleijn, M.Sc. H.G. Pimpalgaonkar May 7, 2014 Delft University of Technology Facaulty of Applied
Numerical Studies on Phase Field Diffusion and Flow Solvers Author: E. Man Supervisors: Prof.dr.ir. C.R. Kleijn, M.Sc. H.G. Pimpalgaonkar May 7, 2014 Delft University of Technology Facaulty of Applied
Higher dimensional Kerr-Schild spacetimes 1
 Higher dimensional Kerr-Schild spacetimes 1 Marcello Ortaggio Institute of Mathematics Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Bremen August 2008 1 Joint work with V. Pravda and A. Pravdová, arxiv:0808.2165
Higher dimensional Kerr-Schild spacetimes 1 Marcello Ortaggio Institute of Mathematics Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Bremen August 2008 1 Joint work with V. Pravda and A. Pravdová, arxiv:0808.2165
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces
 Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Calculus of Variations Summer Term 2015
 Calculus of Variations Summer Term 2015 Lecture 12 Universität des Saarlandes 17. Juni 2015 c Daria Apushkinskaya (UdS) Calculus of variations lecture 12 17. Juni 2015 1 / 31 Purpose of Lesson Purpose
Calculus of Variations Summer Term 2015 Lecture 12 Universität des Saarlandes 17. Juni 2015 c Daria Apushkinskaya (UdS) Calculus of variations lecture 12 17. Juni 2015 1 / 31 Purpose of Lesson Purpose
Basic Concepts of Electrochemistry
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
A model of alignment interaction for oriented particles with phase transition
 A model of alignment interaction for oriented particles with phase transition Amic Frouvelle ACMAC Joint work with Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University, USA) and Pierre Degond (Institut de Mathématiques de Toulouse,
A model of alignment interaction for oriented particles with phase transition Amic Frouvelle ACMAC Joint work with Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University, USA) and Pierre Degond (Institut de Mathématiques de Toulouse,
CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering
 CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering Dr. Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore 54590 mrusman.icet@pu.edu.pk 1 Advanced Chemical
CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering Dr. Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore 54590 mrusman.icet@pu.edu.pk 1 Advanced Chemical
Equilibria in Materials
 009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
Coarsening kinetics from a variable-mobility Cahn-Hilliard equation: Application of a semi-implicit Fourier spectral method
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 1999 Coarsening kinetics from a variable-mobility Cahn-Hilliard equation: Application of a semi-implicit Fourier spectral method Jingzhi Zhu and Long-Qing
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 1999 Coarsening kinetics from a variable-mobility Cahn-Hilliard equation: Application of a semi-implicit Fourier spectral method Jingzhi Zhu and Long-Qing
Understanding the enhancement effect of high-temperature steam on the carbonation reaction of CaO with CO 2
 5th IEAGHG Network Meeting and Technical Workshop n High Temperature Solid Looping Cycles Cambridge University 2th-3th of September, 2013 Understanding the enhancement effect of high-temperature steam
5th IEAGHG Network Meeting and Technical Workshop n High Temperature Solid Looping Cycles Cambridge University 2th-3th of September, 2013 Understanding the enhancement effect of high-temperature steam
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling
 Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Weak solutions for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility
 Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Shibin Dai Qiang Du Weak solutions for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility Abstract In this paper,
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Shibin Dai Qiang Du Weak solutions for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility Abstract In this paper,
June 21, Peking University. Dual Connections. Zhengchao Wan. Overview. Duality of connections. Divergence: general contrast functions
 Dual Peking University June 21, 2016 Divergences: Riemannian connection Let M be a manifold on which there is given a Riemannian metric g =,. A connection satisfying Z X, Y = Z X, Y + X, Z Y (1) for all
Dual Peking University June 21, 2016 Divergences: Riemannian connection Let M be a manifold on which there is given a Riemannian metric g =,. A connection satisfying Z X, Y = Z X, Y + X, Z Y (1) for all
