AN/ARC-34 Made in 1952 by RCA and Magnavox
|
|
|
- Gloria Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /- ade in by and agnavox everse engineered drawings may contain errors. heck my internet site for updates:
2 - ystem wiring + dc volume -0 / control eadset or intercom lamps O G. ush-to talk ransmit igit igit igit igit tone Guard-on ain-on + econd plug on -0 or -0 n k f h j p m s r ike bias emote requency Indicator I- or I Wideband out - / - transceiver + ain G ain G quelched quelched e Z r W X Y d utomatic irection inder - (option) etransfer option W a e k r Y c h n X b f m s Z d j p += ot connected udio signal upply voltage outputs
3 Y-0 olts x x 0 0m m Ω +00 0u k 0 e Z / tone s m r 0 0 guard tone p u odulator 0 0 bias 0 ike 0Ω OO 0 k f h j + k Gain + Oscillators & mechanical ixers rystal eference Guard eceiver 0 Gain k oax ain connector X odule stab d.err 0 side tone elector otor control 0 motor 0 + wr mpl I and udio mplifiers + main guard ux out W Y d quelch mute 0 spare ransmit hassis Wiring --0 kb n ush to talk 0Ω
4 - requency control requency control of the - is done in steps. here is a motor which tunes a voltage controlled oscillator and all and resonant circuits by variable capacitors via a gearbox. econd, the O frequency is locked to a crystal reference, set up using edex stepper motors and a relay, all controlled by the digits on the remote frequency control panel. requency is controlled in digits, in 0. z steps. he crystal reference system has oscillators. he st and nd digit select a harmonic of an. kz crystal oscillator (osc.) he d and th digit control a bank of + + = crystals, for x x = frequencies, using oscillators : osc, osc and osc. he crystals are in ovens. he crystal frequencies are. stepsize / osc. controlled by d digit stepsize /. W. osc. controlled by. X.00 combined d and th digit..000 Y. with 0kz channels has also Xtalls WXY that are 0kz/ higher.0 stepsize /0. osc. controlled by th digit..0. he lowest frequency is + + =.0 at dial xx0.0 he highest frequency is + + =. at dial xx.. kz Osc. rystal eference d digit Osc. st digit x0 x X X nd digit st mixer nd mixer - z O x + x O to receiver. z x transmit d & th digit Osc. th digit Osc. X discr d mixer derr elector he lowest xmit frequency is (.0 + x 0. ) x +. = 00.0 z he highest xmit frequency is (. + x 0. ) x +. =. z he first 0 channels are below the military band of.0. z and result in continuous running of the tuning motor.
5 ixers he first mixer compares the O frequency with the oscillator frequency his gives a first intermediate frequency of.0 -. z. ( first digit=) or when the first digit = he second mixer compares this with the osc. frequency plus. z when the first digit = his gives a second intermediate frequency of. -. z he third mixer compares this with the oscillator frequency his gives a third intermediate frequency of. -. z inally, this signal is compared with the signal from oscillator in a phase detector, resulting in zero z when locked. his is the d err signal. ote derr= 0 occurs also without O signal or large mistuning. herefore, derr= was chosen as the normal value. With kz difference, the output of the phase comparator is a kz sinewave of approx. 0 pp he first (fixed) I in the main receiver is at. z. (.0 for the guard receiver) Guard,- and main I have a common.0 z oscillator to step down to the second I frequency at. z for the main receiver, or.0 z for the guard receiver. he frequency of the O (black), and that of osc. (red) are shown in this plot, with the control panel dial setting on the X-axis. ll values are in z O djustments. he intermediate frequency filters are factory tuned inside a hermetic seal. se of derr he output of the rystal eference ystem, derror, is fed to ) the motor controller (elector), which does the coarse tuning of the master oscillator and all doubler and tripler circuits,. he motor stops when derr = ) and to a reactance tube, which phase-locks the master oscillator to the.
6 uning control ee drawing of the elector ( - / - ) ormally, when tuned, relay is O, (via its holding contact and the positive derr voltage) and the motor does not run. fter a change in selected frequency, derr drops to zero, drops O, and the motor starts running. he variable capacitors are tuned at a speed of z/sec (!) until they are in the right segment, and a negative peak occurs in derr, indicating that the correct frequency was passed. his triggers the thyratrons, and a coil selects low (0.%) reverse gear, so the variable capacitors move backward slowly. he motor itself runs still in forward direction, so the phase detector remains active. he current in the low gear coil sets O, and when the phase lock loop closes, derr becomes positive to compensate for the still slowly moving tuning capacitors. When derr reaches +, turns on and the motor stops. fter 0. sec, drops O, so the thyratrons stop conduction, but remains O to keep the motor off. In this plot, the anode voltage of thyratrons is recorded together with the derr signal. very time the tuning passes the right (0 wide) segment, the anode voltage is +00. ed is the tuned frequency, cycling between 0 and 00 z. he timebase is sec/div. otal tuning takes approx. sec. he phase lock detector is only operative with decreasing frequency, he variable capacitors shafts run at 0 rpm in coarse mode and -0. rpm in fine mode.
7 -/- ube layout --0 kb. odulator - / - estconnector = brown (,, ) 0 00 (,, ) 0 00 (,, ) 0 preamp limiter 0 splitter 0 drivers 00 = QW = 0 rame Y-/- incl dynamotor and main plug ynamotor Y0 input 0 max Output 0 m 0 0 m or at x 0 m or at x 00-0 m. ual I strip - /- estconnector = red dual diode,, 0 0 lang lus subunit with is tubes filament, otherwise identical to Oscillators X- / - estconnector = orange Z0 first osc Z0 mix Z0 mix 0 Z0 discr Z0 mix 0 lus subunits 0 is tubes in this module module - / - ocal osc. train river estconn = yellow estconn = green 0 bal. mixer 0 osc. bal.mixer 0 doubler driver 0 doubler driver 0 osc. pwr dual triode as series stab neon ref and agnavox final ampl - / - estcon = pink estconn=blue ower mpl eceiver 0 pencil 0 pencil 0 mixer 0 tripler first I Guard eceiver - / - estconn = grey mixer 0 first I 0 butler osc. 0 butler osc. 0 elector - / - estconnector = white - ( ) ontrol panel -0 / - o tubes emote indicator I- transistors. odulator. ual I strip Oscillator a ocal osc train b driver + -stab. a final b ain receiver Guard receiver 0 elector otal tubes
8 O -0 (-pin) to I-/ 0 -pin to - z 0 z z 0. z O I or O 0 O ll resistor arrays x 0 Ω I O O 0k log G Ω + G ck X X Wht X X 0 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X 0 z z z 0 0. z G O IIO I /? G ot used ) --G, -poition switch, has sections ontrol head -0/ - (agnavox) 0 nov 0 kb (also -/)?
9 0 delay p ike in 0 Ω + one on 0.u 0 k 0.u 0.u 0 k 0 0 k k k 0k 0 0 k 0.u ? z oscillator k 0 0 n n k n n 0 k k 0k 0k k n 0k k 0k n 0 0.u k 0.u 0p k 0 0 n k 0 0 k 0k k k 0k 0 n +0 0 Gain +00 k imiter 0k level + 00k n n 0k 0. eaters o wideband input not original, but helps to start oscillator icrophone input bandwidth z exagonal testconnector odule connector ain chassis connector estconnector olor = brown not connected ground 0. - / -. odulator - / - /0/0 kb 0u n ike ias
10 rom ain head. z rom Guard head.0 z 0k k k k.0 z.0 z 0p p p k Z0 Z 0.u 0 Z Z0 0 k k k + k ain I. z 0p 0 Guard I z k k 0 0 W ront-end G ain connector contact his module connector contact ex estconnector contacts -- testpoints k estconnector olor = red not connected ground 0 ront-end G 0k 0k 0 X 0.u 0 k k k k k 0.u 0.u +b 0.u +b k k 0.u 0.u 0k 0 0k 0k 0k n 0n 0k 0n 0n 0k 0k 0n 0k 0n 0k p 0k n Y k 0n k - / - k 00k GI 0n 0n 0n k d 0 k k 0p n k squelch k u 0k n n ilaments. I strip - / - /0/0 kb 0k k k u k ute at tuning ide tone +
11 antenna k 0k + O sample derr + x k 0 eactance tube -00 z Oscillator encil tubes 0 k 0 0 stab k k 0 doubler p k. z 0 0 to receiver local oscillator k 0 0 doubler k 0n - z - z - z 0k 0k k 0k k 0n k k 0 idestep oscillator k p. z 0n 0n k Z + x 0 0 k alanced mixer 0- z 0k 0k 0k 0k tripler O signal -z k Z 0 - z - z connector connector 0 k 0k k k to I ampl. 0k gain 0 k 0 0 0k 0 k z steps code k k k 0k x +00 k eversed low gear + 0. uto-reverse at endstops 0 0 k k k k 0 k k 0 0 k. odule --0 kb + stab 0 k 0k k k
12 O sample Ω 0 Ω Ω Ω Ω k 0 heaters + n 0 0 osc. + 0k ovens kz Ω 0 max Ω st mixer 0 0k Z stab. 0 k irst digit Grounded= Open =, +0 stab + Ω + nd mixer d mixer k Z0. z. z Z0 ink to mixer part estpoint connector in on 0 in on 0 ain connector k. z k 0 k 0k. z Z0 elay 0 + raw 0k not used X- / - discriminator 0 0 0n k 0 0 0n 0k 0 0 pp Inhibit during return cycle pp 0 0 st digit + 00k n 0k 0k pp n 00k d error + Ω Ω Ω 0 edex stepper motor 0 Ω econd digit 0 z steps x 0Ω Osc. 0k p k p k hird digit z steps Ω Ω 0 Ω edex stepper motor 0 x 0Ω 0 Osc. 0k p k p k.0000 z Ω Ω ourth digit 0. z steps 0 Ω edex stepper motor 0 0 x 0Ω Osc. 0k p k p k.0 z g osc. osc. osc. osc. h ll relay coils 0Ω j. X- / - rystal eference ystem / /0 kb
13 ntenna + rom transmitte / switch 0 Ω o main receiver p z 0 k 0 0 0p 0 k Z0 0p 0 0p k x =. z 0 z k 0.0 z estconnector olor = gray not connected ground Z0 to I ampl z k 0k k k 0 0 Ω ulova oven 0 utler.o. k k 0 mixer Z0 0 0 k GI - / -. Guard eceiver
14 +00 irst digit ixer odule 0 econd digit 0 0 k k sectors of 0 z each k 0k u n 0 k k 0k odule ariable capacitors shafts 0 uning motor low gearbox k uto reverse at endstops 0 brake - 0 Inhibit during reverse cycle 0 udio mute estconnector olor = white not connected ground + + stab d err -0 0k 0k 0n 0k 0. 0k eaters - / - + On testconnector 0. uning control ( elector ) - / - //0 kb
15 ckt x 0 odulator 0 I & udio 0 Guard 0 ixers mechanical 0 Oscillators +00 bias tone igit + + gain gain sidetone ike Guard squelch main squelch G guard wr_up x Y d X W +00 G main d err igit wr_up guard x elector 0 f h j k igit igit derr + stab. p + audio / Gnd ain plug ohm + (spare) x mute +
16 ulova oven Ω oscillators Ω mixers Ω Ω Ω Ω Ω rystal eference odulator 0. 0m I and udio Ω 0 ulova oven encil tubes encil tubes Guard x encil tubes module. uning control 0. otal filaments. x = W verage ovens. x = W
17 - input current nov 0 Input current from.dc source ilaments. Ovens ( peak ), on average :. Internal fan. ynamotor loss ). ynamotor load x/ x ). /. elays 0. / 0. uning voltage dividers (incl control) 0. otal. /. W / W ( for 0W output ) he tuning motor adds 0. during sec after any frequency change ) ynamotor input current without load. Is about at any input voltage uring run-up the input current is ) ynamotor input current portion due to load, transformed to primary current ynamotor Y0 input 0 max Output 0 m or at x 0 m 0 0 m or at x 00-0 m + =. W + = W output o load dynamotor input current in I in. easured total input current and dynamotor voltages ower supply used: dc with 0 current limit. an disconnected, otherwise complete. - ynamotor run-up with supply in current limit takes seconds. - hen current decreases to. - t 0 sec from turn-on, relay 0 turns on the 00 distribution and the tuning motor. - Input current rises to., with still running tuning motor. and fluctuations up to. due to crystal oven heaters. - With ovens hot, the current decrease to., with every sec a surge when the tuning motor reverses. t lock, the current fluctuates between 0 and. (without fan) upply voltages +0, + and + (stabilized) ll O.
18 - estpoints ach module of the /- has a special -pole test connector to check the + voltages, filament voltage, and oscillator negative grid voltages. hese are measured with the - voltmeter for a quick go/no-go test on each module. he test connectors are color coded. he voltmeter has a -position switch to measure the voltage on a pin of the test connector versus the centre pin of the test connector which is grounded in each module. I measured the following voltages on a healthy set with dc input using a with 0 input impedance. odule odulator modulated 00 x I mplifier rystal eference aster oscillator river ain eceiver ower mp Guard x elector guard x (+0 stab) + Input stab + + (+0 stab) x/ modulated + 0 gear/clutch ee plot + x + x +. + guard + (+0 stab) O- -. osc -0. idestep mixer -. osc butler -.0 osc. -0. doubler -. river -0. mixer -.0 driver he grey positions are not connected in that module. he blue positions shall be checked in ransmit mode ( key down) he guard positions shall be checked with the mode switch on the control panel in the position oth -. osc -0. doubler -0. river -0.0 tripler -. tripler odulator test points and have a series resistor, so measure 0 on a voltmeter with 0 Ω input impedance. elector test point has also series resistor, add 0% when measuring with a x0 probe any test points in the driver or ower mp have series resistor. dd 0%. he readings for the oscillators in the crystal reference module are quite independent of the frequency selected.
19 /- / - adio estset testplug for any connector in - O meter shorted meter shorted -. -, O 0 0 pos, 0 ll 00 ranges k 00k k probe ± 0. pos,, 0 u 00 Ω - 00 ll 0 ranges + 00 Ω k x 0u = 0. - /
The AN/ARC-54. Module Circuit Diagrams
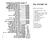 The N/R- Module ircuit iagrams. Tone squelch (selective call). Homing. High requency oscillator HO. Low requency Oscilator LO. Variable I amplifier. R mplifier. Mechanical Tuning Unit. Power mplifier.
The N/R- Module ircuit iagrams. Tone squelch (selective call). Homing. High requency oscillator HO. Low requency Oscilator LO. Variable I amplifier. R mplifier. Mechanical Tuning Unit. Power mplifier.
Racal RA-117 Receiver Section: Notes, Layout, Tube List Page: 1 Dwg. Rev.: 2013 Jan 17
 Notes Early version retains the 0.- setting on RANGE, along with the accompanying L & C, from the RA-. Later version replaces this with the WIDEBAND Ω setting. Early version takes the socket (SK) off SK00
Notes Early version retains the 0.- setting on RANGE, along with the accompanying L & C, from the RA-. Later version replaces this with the WIDEBAND Ω setting. Early version takes the socket (SK) off SK00
HVAC Electrical Wiring Diagrams / Ohm s Law / Sequence of Operation RV
 PLEASE DO NOT BOOKMARK ANY ANYTIMECE WEBPAGES! Our system will remember the last page you viewed when logging out and back in but please DO NOT exit out when taking a test. Your place will NOT be saved.
PLEASE DO NOT BOOKMARK ANY ANYTIMECE WEBPAGES! Our system will remember the last page you viewed when logging out and back in but please DO NOT exit out when taking a test. Your place will NOT be saved.
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I. Objectives
 LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
V7 6AG7 DRIVER DRIVER TUNE ALC RECT VFO TANK V3 12SK7 TONE OSC V10 12SK MHz
 V PA* V SK IF AMP 9 V SNGT MIXER MIXER 0 0 V AG 0 0 PA 0 0 RF TUNE RECT PA* *V AND ARE WITH HEATERS IN SERIES OR WITH HEATERS IN PARALLEL.0-. 0 INRAD XTAL FILTER DIODE BALANCED MODULATOR V SNGT CARRIER
V PA* V SK IF AMP 9 V SNGT MIXER MIXER 0 0 V AG 0 0 PA 0 0 RF TUNE RECT PA* *V AND ARE WITH HEATERS IN SERIES OR WITH HEATERS IN PARALLEL.0-. 0 INRAD XTAL FILTER DIODE BALANCED MODULATOR V SNGT CARRIER
MEP 382: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis
 Faculty of Engineering MEP 38: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis Outline oltage and Current Ohm s Law Kirchoff s laws esistors Series and Parallel oltage Dividers
Faculty of Engineering MEP 38: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis Outline oltage and Current Ohm s Law Kirchoff s laws esistors Series and Parallel oltage Dividers
SC125MS. Data Sheet and Instruction Manual. ! Warning! Salem Controls Inc. Stepper Motor Driver. Last Updated 12/14/2004
 SC125MS Stepper Motor Driver Salem Controls Inc. Last Updated 12/14/2004! Warning! Stepper motors and drivers use high current and voltages capable of causing severe injury. Do not operate this product
SC125MS Stepper Motor Driver Salem Controls Inc. Last Updated 12/14/2004! Warning! Stepper motors and drivers use high current and voltages capable of causing severe injury. Do not operate this product
EXEMPLAR NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 ( ) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 20 C)
 Homework # 4 Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 0 C) Substance Resistivity, Temperature ( m) Coefficient, (C ) - Conductors Silver.59 x 0-0.006 Copper.6 x 0-0.006 Aluminum.65 x 0-0.0049 Tungsten
Homework # 4 Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 0 C) Substance Resistivity, Temperature ( m) Coefficient, (C ) - Conductors Silver.59 x 0-0.006 Copper.6 x 0-0.006 Aluminum.65 x 0-0.0049 Tungsten
MFJ 259/259B Operation & Simplified Calibration
 MFJ 259/259B Operation & Simplified Calibration Bill Leonard N0CU 1 March 2014 What Is An MFJ-259 MFJ lists it as a HF/VHF SWR Analyzer It is essentially a ONE PORT NETWORK ANALYZER Measures the electrical
MFJ 259/259B Operation & Simplified Calibration Bill Leonard N0CU 1 March 2014 What Is An MFJ-259 MFJ lists it as a HF/VHF SWR Analyzer It is essentially a ONE PORT NETWORK ANALYZER Measures the electrical
Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS. Unit 3 Electricity. Question Booklet
 Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS Unit 3 Electricity Question Booklet 1 MONITORING ND MESURING.C. 1. What is the peak voltage of the 230 V mains supply? The frequency of the mains supply is 50 Hz. How many
Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS Unit 3 Electricity Question Booklet 1 MONITORING ND MESURING.C. 1. What is the peak voltage of the 230 V mains supply? The frequency of the mains supply is 50 Hz. How many
Measurement of Electrical Resistance and Ohm s Law
 Measurement of Electrical Resistance and Ohm s Law Objectives In this experiment, measurements of the voltage across a wire coil and the current in the wire coil will be used to accomplish the following
Measurement of Electrical Resistance and Ohm s Law Objectives In this experiment, measurements of the voltage across a wire coil and the current in the wire coil will be used to accomplish the following
11. ELECTRIC CURRENT. Questions and Answers between the forces F e and F c. 3. Write the difference between potential difference and emf. A.
 CLSS-10 1. Explain how electron flow causes electric current with Lorentz-Drude theory of electrons?. Drude and Lorentz, proposed that conductors like metals contain a large number of free electrons while
CLSS-10 1. Explain how electron flow causes electric current with Lorentz-Drude theory of electrons?. Drude and Lorentz, proposed that conductors like metals contain a large number of free electrons while
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Basic operational amplifier circuits. Electronic Systems - C3 13/05/ DDC Storey 1
 Electronic Systems C3 3/05/2009 Politecnico di Torino ICT school Lesson C3 ELECTONIC SYSTEMS C OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES C.3 Op Amp circuits» Application examples» Analysis of amplifier circuits» Single and
Electronic Systems C3 3/05/2009 Politecnico di Torino ICT school Lesson C3 ELECTONIC SYSTEMS C OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES C.3 Op Amp circuits» Application examples» Analysis of amplifier circuits» Single and
Prelim Revision. Questions and Answers. Electricity
 Prelim Revision Questions and Answers Electricity SECTION A Answer questions on the answer sheet 8. Specimen Paper The diagram shows an 8V supply connected to two lamps. The supply has negligible internal
Prelim Revision Questions and Answers Electricity SECTION A Answer questions on the answer sheet 8. Specimen Paper The diagram shows an 8V supply connected to two lamps. The supply has negligible internal
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws
 Universiti Teknologi MR Fakulti Sains Gunaan Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws PHY631: Physical Science ctivity Name: HP: Lab#: Intro Objectives The goal of today s activity is to physically investigate
Universiti Teknologi MR Fakulti Sains Gunaan Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws PHY631: Physical Science ctivity Name: HP: Lab#: Intro Objectives The goal of today s activity is to physically investigate
1 Written and composed by: Prof. Muhammad Ali Malik (M. Phil. Physics), Govt. Degree College, Naushera
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
Potentiometer e.t.c. 1/240 with attach to our switching device 2011
 Potentiometer e.t.c. /20 { = 0. kohm, with centre tap 2 x 0. kohm 2 =.0 kohm, with centre tap 2 x.0 kohm = resistance value linear and part number ^= = 2.0 kohm, with centre tap 2 x 2.0 kohm =.0 kohm,
Potentiometer e.t.c. /20 { = 0. kohm, with centre tap 2 x 0. kohm 2 =.0 kohm, with centre tap 2 x.0 kohm = resistance value linear and part number ^= = 2.0 kohm, with centre tap 2 x 2.0 kohm =.0 kohm,
PRIMARE A32 Power Amplifier Service Manual
 PRIMRE Power mplifier Service Manual . Technical Description.. Error codes.. Bias djustment.. Schematics.. Technical Specifications. onfidential! This document is not allowed to show for third part without
PRIMRE Power mplifier Service Manual . Technical Description.. Error codes.. Bias djustment.. Schematics.. Technical Specifications. onfidential! This document is not allowed to show for third part without
Experiment P43: RC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P43-1 Experiment P43: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 700 P43 P43_RCCI.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P43-1 Experiment P43: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 700 P43 P43_RCCI.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED
AC Circuit. a) Learn the usage of frequently used AC instrument equipment (AC voltmeter, AC ammeter, power meter).
 Experiment 5:Measure the Equivalent arameters in the AC Circuit 1. urpose a) Learn the usage of frequently used AC instrument equipment (AC voltmeter, AC ammeter, power meter). b) Know the basic operational
Experiment 5:Measure the Equivalent arameters in the AC Circuit 1. urpose a) Learn the usage of frequently used AC instrument equipment (AC voltmeter, AC ammeter, power meter). b) Know the basic operational
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 13 May minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 293/02 ELECTRONICS MODULE TEST E1 HIGHER TIER AM WEDNESDAY, 13 May 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 293/02 ELECTRONICS MODULE TEST E1 HIGHER TIER AM WEDNESDAY, 13 May 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction... 7. Electromotive Force... 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel... 4 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules... 6 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements... 8 7.6
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction... 7. Electromotive Force... 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel... 4 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules... 6 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements... 8 7.6
SIMPLE D.C. CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS Background
 SIMPLE D.C. CICUITS AND MEASUEMENTSBackground This unit will discuss simple D.C. (direct current current in only one direction) circuits: The elements in them, the simple arrangements of these elements,
SIMPLE D.C. CICUITS AND MEASUEMENTSBackground This unit will discuss simple D.C. (direct current current in only one direction) circuits: The elements in them, the simple arrangements of these elements,
INSTRUCTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION
 diytube Poseidon Driver for the Dynaco Mark III, IV and DIY INSTRUCTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION Price $0.00 C Star Ground 0VDC J R6 00K 0VDC K R6 K C.uF G KT: blu/wht & grn/wht V AU 6 a a'' R0 6K,
diytube Poseidon Driver for the Dynaco Mark III, IV and DIY INSTRUCTIONS FOR ASSEMBLY AND OPERATION Price $0.00 C Star Ground 0VDC J R6 00K 0VDC K R6 K C.uF G KT: blu/wht & grn/wht V AU 6 a a'' R0 6K,
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA VOLTAGE CONTROLLED MULTIVIBRATOR. Not Recommended for New Designs
 IONUTOR TNI T The 1658 is a voltage controlled multivibrator which provides appropriate level shifting to produce an output compatible with III and 10,000 logic levels. requency control is accomplished
IONUTOR TNI T The 1658 is a voltage controlled multivibrator which provides appropriate level shifting to produce an output compatible with III and 10,000 logic levels. requency control is accomplished
General Description DTS27X X -X X X -X. Lead. 27X coil1. R1 = R2 = 470Ω C1 = C2 = 2.2 μ F The R, C value need to be fine tuned base on coils design.
 Features - On-chip Hall sensor with two different sensitivity and hysteresis settings for - 3.5V to 18V operating voltage - 35mA (avg) output sink current - Built-in protecting diode only for chip reverse
Features - On-chip Hall sensor with two different sensitivity and hysteresis settings for - 3.5V to 18V operating voltage - 35mA (avg) output sink current - Built-in protecting diode only for chip reverse
Lab 5 RC Circuits. What You Need To Know: Physics 212 Lab
 Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
CHV Series Vector Control Inverter Options. Operating Instructions for Tension Control Card
 CHV Series Vector Control Inverter Options Operating Instructions for Control Card 1. Model and Specifications 1.1 Model The model of tension card is CHV00ZL. CHV series inverter can conduct constant
CHV Series Vector Control Inverter Options Operating Instructions for Control Card 1. Model and Specifications 1.1 Model The model of tension card is CHV00ZL. CHV series inverter can conduct constant
04 Matching Networks. Dipl.-Ing. Dr. Michael Gebhart, MSc
 04 Matching Networks 4th unit in course 3, F Basics and omponents ipl.-ing. r. Michael Gebhart, Mc FI Qualification Network, University of pplied ciences, ampus W 013/14, eptember 30 th ontent Introduction:
04 Matching Networks 4th unit in course 3, F Basics and omponents ipl.-ing. r. Michael Gebhart, Mc FI Qualification Network, University of pplied ciences, ampus W 013/14, eptember 30 th ontent Introduction:
National 5 Physics. Electricity and Energy. Notes
 National 5 Physics Electricity and Energy Notes Name. 1 P a g e Key Area Notes, Examples and Questions Page 3 Conservation of energy Page 10 Electrical charge carriers and electric fields and potential
National 5 Physics Electricity and Energy Notes Name. 1 P a g e Key Area Notes, Examples and Questions Page 3 Conservation of energy Page 10 Electrical charge carriers and electric fields and potential
NMR Instrumentation BCMB/CHEM Biomolecular NMR
 NMR Instrumentation BCMB/CHEM 8190 Biomolecular NMR Instrumental Considerations - Block Diagram of an NMR Spectrometer Magnet Sample B 0 Lock Probe Receiver Computer Transmit Superconducting Magnet systems
NMR Instrumentation BCMB/CHEM 8190 Biomolecular NMR Instrumental Considerations - Block Diagram of an NMR Spectrometer Magnet Sample B 0 Lock Probe Receiver Computer Transmit Superconducting Magnet systems
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Resonant Matching Networks
 Chapter 1 Resonant Matching Networks 1.1 Introduction Frequently power from a linear source has to be transferred into a load. If the load impedance may be adjusted, the maximum power theorem states that
Chapter 1 Resonant Matching Networks 1.1 Introduction Frequently power from a linear source has to be transferred into a load. If the load impedance may be adjusted, the maximum power theorem states that
Review of Ohm's Law: The potential drop across a resistor is given by Ohm's Law: V= IR where I is the current and R is the resistance.
 DC Circuits Objectives The objectives of this lab are: 1) to construct an Ohmmeter (a device that measures resistance) using our knowledge of Ohm's Law. 2) to determine an unknown resistance using our
DC Circuits Objectives The objectives of this lab are: 1) to construct an Ohmmeter (a device that measures resistance) using our knowledge of Ohm's Law. 2) to determine an unknown resistance using our
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER]
![NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER] NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER]](/thumbs/86/93982339.jpg) NTIONL QULIFICTIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Physics Electricity Questions and Solutions James Page rthur Baillie [HIGHER] The Scottish Qualifications uthority regularly reviews the arrangements for National
NTIONL QULIFICTIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Physics Electricity Questions and Solutions James Page rthur Baillie [HIGHER] The Scottish Qualifications uthority regularly reviews the arrangements for National
R R V I R. Conventional Current. Ohms Law V = IR
 DC Circuits opics EMF and erminal oltage esistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s ules EMFs in Series and in Parallel Capacitors in Series and in Parallel Ammeters and oltmeters Conventional Current
DC Circuits opics EMF and erminal oltage esistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s ules EMFs in Series and in Parallel Capacitors in Series and in Parallel Ammeters and oltmeters Conventional Current
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
PHYS225 Lecture 9. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 9 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Field Effect Transistors Voltage controlled resistor Various FET circuits Switch Source follower Current source Similar to BJT Draws no input current
PHYS225 Lecture 9 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Field Effect Transistors Voltage controlled resistor Various FET circuits Switch Source follower Current source Similar to BJT Draws no input current
Review. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When more devices are added to a series circuit, the total circuit resistance: a.
Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When more devices are added to a series circuit, the total circuit resistance: a.
Circuit Analysis and Ohm s Law
 Study Unit Circuit Analysis and Ohm s Law By Robert Cecci Circuit analysis is one of the fundamental jobs of an electrician or electronics technician With the knowledge of how voltage, current, and resistance
Study Unit Circuit Analysis and Ohm s Law By Robert Cecci Circuit analysis is one of the fundamental jobs of an electrician or electronics technician With the knowledge of how voltage, current, and resistance
CAUTION. All safety information must be followed as provided in this Technical Sheet and in Service Manual RS
 peed Queen Domestic asher echnical nformation 0 V, 0 Hz Models 70 70 Due to possibility of personal injury or property damage, always contact an authorized technician for servicing or repair of this unit.
peed Queen Domestic asher echnical nformation 0 V, 0 Hz Models 70 70 Due to possibility of personal injury or property damage, always contact an authorized technician for servicing or repair of this unit.
Technical Instructions 5020.B. Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery. Performances. Functions. Movement height 4.40 mm
 Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
PHOTO SCR OPTOCOUPLERS
 PACKAGE SCHEMATIC 6 6 ANODE 6 GATE CATHODE 2 5 ANODE N/C 3 4 CATHODE 6 DESCRIPTION The HC series consists of a gallium-arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled with a light activated silicon
PACKAGE SCHEMATIC 6 6 ANODE 6 GATE CATHODE 2 5 ANODE N/C 3 4 CATHODE 6 DESCRIPTION The HC series consists of a gallium-arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled with a light activated silicon
Singer. Incremental Comfort Systems. K, EK Vintage F. Last Manufactured: Replacement Parts List No Revision C 04/2012
 Replacement Parts List No. 055231000 Revision C 04/2012 Singer Incremental Comfort Systems K, EK 07-15 Vintage F Last Manufactured: 1976 To find your Daikin Applied parts distributor, call 1-800-377-2787
Replacement Parts List No. 055231000 Revision C 04/2012 Singer Incremental Comfort Systems K, EK 07-15 Vintage F Last Manufactured: 1976 To find your Daikin Applied parts distributor, call 1-800-377-2787
Student Name: SE13-17 U1/2
 SE13-17 U1/2 Student Name: Unit 1 Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals Page 1. Student Learning Guide & Record Unit 1 TASK Page TASK TITLE Task 1 7 Energy Task 2 9 Draw a block diagram Task 3 16 Exercise
SE13-17 U1/2 Student Name: Unit 1 Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals Page 1. Student Learning Guide & Record Unit 1 TASK Page TASK TITLE Task 1 7 Energy Task 2 9 Draw a block diagram Task 3 16 Exercise
Symbol Offers Units. R Resistance, ohms. C Capacitance F, Farads. L Inductance H, Henry. E, I Voltage, Current V, Volts, A, Amps. D Signal shaping -
 Electrical Circuits HE 13.11.018 1. Electrical Components hese are tabulated below Component Name Properties esistor Simplest passive element, no dependence on time or frequency Capacitor eactive element,
Electrical Circuits HE 13.11.018 1. Electrical Components hese are tabulated below Component Name Properties esistor Simplest passive element, no dependence on time or frequency Capacitor eactive element,
Physics 142 AC Circuits Page 1. AC Circuits. I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx
 Physics 142 A ircuits Page 1 A ircuits I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx Alternating current: generators and values It is relatively easy to devise a source (a generator
Physics 142 A ircuits Page 1 A ircuits I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx Alternating current: generators and values It is relatively easy to devise a source (a generator
Model 33SZ Basic Unit OPTIONAL FILTER RH COIL CONNECTION PRIMARY/ DEDICATED OUTDOOR AIR MULTI-POINT FLOW SENSOR 5 3/4" (146)
 DESRIPTION: Sensible cooling coil on the induced air inlet handles zone sensible load. Opposite side to controls location. luminum ripple fins (10 PI) and 1/" (13) copper tubes. and of coil connection
DESRIPTION: Sensible cooling coil on the induced air inlet handles zone sensible load. Opposite side to controls location. luminum ripple fins (10 PI) and 1/" (13) copper tubes. and of coil connection
AN6783S. IC for long interval timer. ICs for Timer. Overview. Features. Applications. Block Diagram
 IC for long interval timer Overview The is an IC designed for a long interval timer. It is oscillated by using the external resistor and capacitor, and the oscillation frequency divided by a - stage F.F.
IC for long interval timer Overview The is an IC designed for a long interval timer. It is oscillated by using the external resistor and capacitor, and the oscillation frequency divided by a - stage F.F.
EMC Considerations for DC Power Design
 EMC Considerations for DC Power Design Tzong-Lin Wu, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Power Bus Noise below 5MHz 1 Power Bus Noise below 5MHz (Solution) Add Bulk
EMC Considerations for DC Power Design Tzong-Lin Wu, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Power Bus Noise below 5MHz 1 Power Bus Noise below 5MHz (Solution) Add Bulk
Franck-Hertz Experiment in Neon/Hg
 Franck-Hertz Experiment in Neon/Hg Equipment Franck-Hertz tube (Ne or Hg) & Operating Unit Analog oscilloscope Many Banana cables; 1 BNC cables; 2 BNC-Banana Plug connector Graphing paper Theory This experiment
Franck-Hertz Experiment in Neon/Hg Equipment Franck-Hertz tube (Ne or Hg) & Operating Unit Analog oscilloscope Many Banana cables; 1 BNC cables; 2 BNC-Banana Plug connector Graphing paper Theory This experiment
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #10
 PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #10 Dr. Electric Current and Resistance The Battery Ohm s Law: Resisters Resistivity Electric Power Alternating Current Power Delivered by AC Today s homework is #6, due 10pm,
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #10 Dr. Electric Current and Resistance The Battery Ohm s Law: Resisters Resistivity Electric Power Alternating Current Power Delivered by AC Today s homework is #6, due 10pm,
Ph February, Kirchhoff's Rules Author: John Adams, I. Theory
 Ph 122 23 February, 2006 I. Theory Kirchhoff's Rules Author: John Adams, 1996 quark%/~bland/docs/manuals/ph122/elstat/elstat.doc This experiment seeks to determine if the currents and voltage drops in
Ph 122 23 February, 2006 I. Theory Kirchhoff's Rules Author: John Adams, 1996 quark%/~bland/docs/manuals/ph122/elstat/elstat.doc This experiment seeks to determine if the currents and voltage drops in
EE 560 CHIP INPUT AND OUTPUT (I/0) CIRCUITS. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 CHIP INPUT AND OUTPUT (I/0) CIRCUITS 2 -> ESD PROTECTION CIRCUITS (INPUT PADS) -> ON-CHIP CLOCK GENERATION & DISTRIBUTION -> OUTPUT PADS -> ON-CHIP NOISE DUE TO PARASITIC INDUCTANCE -> SUPER BUFFER
1 EE 560 CHIP INPUT AND OUTPUT (I/0) CIRCUITS 2 -> ESD PROTECTION CIRCUITS (INPUT PADS) -> ON-CHIP CLOCK GENERATION & DISTRIBUTION -> OUTPUT PADS -> ON-CHIP NOISE DUE TO PARASITIC INDUCTANCE -> SUPER BUFFER
Technical Instructions 4210.B. Specification 11 ½''' Dimensions and battery. Performances. Functions. Movement height 4.40 mm
 Specification 11 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
Specification 11 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
SERVOSTAR S- and CD-Series Regeneration Requirements
 www.danaherotion.com SEROSTAR S- and CD-Series Regeneration Requirements One of the key (and often overlooked) considerations for servo system sizing is regeneration requirements. An undersized regeneration
www.danaherotion.com SEROSTAR S- and CD-Series Regeneration Requirements One of the key (and often overlooked) considerations for servo system sizing is regeneration requirements. An undersized regeneration
Trade of Electrician. Power and Energy
 Trade of Electrician Standards Based Apprenticeship Power and Energy Phase 2 Module No. 2.1 Unit No. 2.1.6 COURSE NOTES SOLAS Electrical Course Notes - Unit 2.1.6 Created by Gerry Ryan - Galway TC Revision
Trade of Electrician Standards Based Apprenticeship Power and Energy Phase 2 Module No. 2.1 Unit No. 2.1.6 COURSE NOTES SOLAS Electrical Course Notes - Unit 2.1.6 Created by Gerry Ryan - Galway TC Revision
REVISED HIGHER PHYSICS REVISION BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY
 REVSED HGHER PHYSCS REVSON BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY Kinross High School Monitoring and measuring a.c. Alternating current: Mains supply a.c.; batteries/cells supply d.c. Electrons moving back and forth,
REVSED HGHER PHYSCS REVSON BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY Kinross High School Monitoring and measuring a.c. Alternating current: Mains supply a.c.; batteries/cells supply d.c. Electrons moving back and forth,
SECTION 1 - WHAT IS A BTU METER? BTU's = Flow x ΔT Any ISTEC BTU Meter System consists of the following main components:
 SECTION 1 - WHAT IS A BTU METER? ISTEC BTU Meters measure energy usage by multiplying flow rate and temperature difference. As the water (or other liquid) passes through these lines, the multi-wing turbine
SECTION 1 - WHAT IS A BTU METER? ISTEC BTU Meters measure energy usage by multiplying flow rate and temperature difference. As the water (or other liquid) passes through these lines, the multi-wing turbine
PHYS 1444 Section 002 Lecture #13
 PHYS 1444 Section 002 Lecture #13 Monday, Oct. 16, 2017 Dr. Animesh Chatterjee (disguising as Dr. Yu) Chapter 25 Electric Current Ohm s Law: Resisters, Resistivity Electric Power Alternating Current Microscopic
PHYS 1444 Section 002 Lecture #13 Monday, Oct. 16, 2017 Dr. Animesh Chatterjee (disguising as Dr. Yu) Chapter 25 Electric Current Ohm s Law: Resisters, Resistivity Electric Power Alternating Current Microscopic
NABTEB Past Questions and Answers - Uploaded online
 MAY/JUNE 2008 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 QUESTION 1 1(a) Explain the following terms in relation to atomic structure (i) Proton Neutron (iii) Electron (b) Three cells of emf 1.5 volts
MAY/JUNE 2008 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 QUESTION 1 1(a) Explain the following terms in relation to atomic structure (i) Proton Neutron (iii) Electron (b) Three cells of emf 1.5 volts
NOTE: Opening and Closing Reports must be enabled. See CL 2C Digit Positions 1 and 3 for additional information.
 SYSTM 6 Installation Manual L - 8 & - 68 ommand Location : Installer ombination igit Positions () - (6): Installer ombination ombination must have 6 digits. Valid entries are - 9. ommand Location - 8 and
SYSTM 6 Installation Manual L - 8 & - 68 ommand Location : Installer ombination igit Positions () - (6): Installer ombination ombination must have 6 digits. Valid entries are - 9. ommand Location - 8 and
Lab 5 RC Circuits. What You Need To Know: Physics 212 Lab
 Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
EXPERIMENT 12 OHM S LAW
 EXPERIMENT 12 OHM S LAW INTRODUCTION: We will study electricity as a flow of electric charge, sometimes making analogies to the flow of water through a pipe. In order for electric charge to flow a complete
EXPERIMENT 12 OHM S LAW INTRODUCTION: We will study electricity as a flow of electric charge, sometimes making analogies to the flow of water through a pipe. In order for electric charge to flow a complete
Unit 6 Current Electricity and Circuits
 Unit 6 Current Electricity and Circuits 2 Types of Electricity Electricity that in motion. Electricity that in motion. Occurs whenever an moves through a. 2 Types of Current Electricity Electricity that
Unit 6 Current Electricity and Circuits 2 Types of Electricity Electricity that in motion. Electricity that in motion. Occurs whenever an moves through a. 2 Types of Current Electricity Electricity that
Chapter 2 Circuit Elements
 hapter ircuit Elements hapter ircuit Elements.... Introduction.... ircuit Element onstruction....3 esistor....4 Inductor... 4.5 apacitor... 6.6 Element Basics... 8.6. Element eciprocals... 8.6. eactance...
hapter ircuit Elements hapter ircuit Elements.... Introduction.... ircuit Element onstruction....3 esistor....4 Inductor... 4.5 apacitor... 6.6 Element Basics... 8.6. Element eciprocals... 8.6. eactance...
Accelerated Taylor State Plumes in SSX
 Accelerated Taylor State Plumes in SSX Manjit Kaur Swarthmore College, Swarthmore, PA 19081 J. E. Shrock 18, J. Han 17, D. A. Schaffner & M. R. Brown Research supported by DOE OFES & ARPA-e ALPHA 24 August
Accelerated Taylor State Plumes in SSX Manjit Kaur Swarthmore College, Swarthmore, PA 19081 J. E. Shrock 18, J. Han 17, D. A. Schaffner & M. R. Brown Research supported by DOE OFES & ARPA-e ALPHA 24 August
UNIT G485 Module Capacitors PRACTICE QUESTIONS (4)
 UNIT G485 Module 2 5.2.1 Capacitors PRACTICE QUESTIONS (4) 1 A 2200 µf capacitor is charged to a p.d. of 9.0 V and then discharged through a 100 kω resistor. (a) Calculate : (i) The initial charge stored
UNIT G485 Module 2 5.2.1 Capacitors PRACTICE QUESTIONS (4) 1 A 2200 µf capacitor is charged to a p.d. of 9.0 V and then discharged through a 100 kω resistor. (a) Calculate : (i) The initial charge stored
Incremental Rotary Encoder G58
 Shaft: Type S / L / H Hollow shaft: Type W Mechanical Data Housing diameter: mm Shaft:... 0 mm Hollow shaft:... mm Line counts:... 0.000 signals: S, KI, KS, HTL, TTL, O, Vpp, µapp onnector or output: axial
Shaft: Type S / L / H Hollow shaft: Type W Mechanical Data Housing diameter: mm Shaft:... 0 mm Hollow shaft:... mm Line counts:... 0.000 signals: S, KI, KS, HTL, TTL, O, Vpp, µapp onnector or output: axial
Revision Compare Between. Application
 evision Compare etween Points of Comparison Series Connection Parallel Connection Drawing otal resistance ( ) = + + 3 3 Potential Difference () = + + 3 = = = 3 Electric Current (I) I = I = I = I 3 I =
evision Compare etween Points of Comparison Series Connection Parallel Connection Drawing otal resistance ( ) = + + 3 3 Potential Difference () = + + 3 = = = 3 Electric Current (I) I = I = I = I 3 I =
Technical Description
 Overview It is being digitalized and accelerated with builtin micro processor because of development of computer. It is widely used in industrial NC, ROBOT, servo motors and OA equipment in order to detect
Overview It is being digitalized and accelerated with builtin micro processor because of development of computer. It is widely used in industrial NC, ROBOT, servo motors and OA equipment in order to detect
14 - CURRENT ELECTRICITY Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 14 - CURRENT ELECTRICITY Page 1 1 ) In the circuit, the galvanometer G shows zero deflection. If the batteries A and B have negligible internal resistance, the value of the resistor R will be ( a ) 100
14 - CURRENT ELECTRICITY Page 1 1 ) In the circuit, the galvanometer G shows zero deflection. If the batteries A and B have negligible internal resistance, the value of the resistor R will be ( a ) 100
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150
 PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
DS 200P. Electronic Pressure Switch. Pressure Ports And Process Connections With Flush Welded Stainless Steel Diaphragm
 Pressure Ports And Process Connections With Flush Welded Stainless Steel Diaphragm accuracy according to IEC 600: standard: 0. % FSO option: 0. % FSO Nominal pressure from 0... 00 mbar up to 0... 0 bar
Pressure Ports And Process Connections With Flush Welded Stainless Steel Diaphragm accuracy according to IEC 600: standard: 0. % FSO option: 0. % FSO Nominal pressure from 0... 00 mbar up to 0... 0 bar
Current Balance. Introduction
 Current Balance Objectives a. To find the direction of magnetic field, current and the Lorentz force b. To find the relationship between Lorentz force and current c. To find the relationship between Lorentz
Current Balance Objectives a. To find the direction of magnetic field, current and the Lorentz force b. To find the relationship between Lorentz force and current c. To find the relationship between Lorentz
Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws
 CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 026907363 February 5, 206 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 2 205_206 What is Electrical
CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 026907363 February 5, 206 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 2 205_206 What is Electrical
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
Experiment 4. RC Circuits. Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor.
 Experiment 4 RC Circuits 4.1 Objectives Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. Graphically determine the time constant τ for the decay. 4.2
Experiment 4 RC Circuits 4.1 Objectives Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. Graphically determine the time constant τ for the decay. 4.2
General Instructions :
 Class XII Subject - Physics General Instructions : 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Q. 1 to 5 are Very short Answer type questions (1 Mark each. ) 3. Q. 6 to 12 are short Answer type questions. (2 Marks
Class XII Subject - Physics General Instructions : 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Q. 1 to 5 are Very short Answer type questions (1 Mark each. ) 3. Q. 6 to 12 are short Answer type questions. (2 Marks
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs
 EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL
 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
Fig. 1-1 Current Flow in a Resistive load
 1 Electric Circuits: Current flow in a resistive load flows either from (-) to () which is labeled below as Electron flow or the Conventional flow from () to (-). We will use conventional flow in this
1 Electric Circuits: Current flow in a resistive load flows either from (-) to () which is labeled below as Electron flow or the Conventional flow from () to (-). We will use conventional flow in this
AN019. A Better Approach of Dealing with Ripple Noise of LDO. Introduction. The influence of inductor effect over LDO
 Better pproach of Dealing with ipple Noise of Introduction It has been a trend that cellular phones, audio systems, cordless phones and portable appliances have a requirement for low noise power supplies.
Better pproach of Dealing with ipple Noise of Introduction It has been a trend that cellular phones, audio systems, cordless phones and portable appliances have a requirement for low noise power supplies.
4.2.1 Current, potential difference and resistance
 4.2 Electricity Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter everywhere. Understanding the difference in the microstructure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators makes it possible to design
4.2 Electricity Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter everywhere. Understanding the difference in the microstructure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators makes it possible to design
Panel Mount, Single Phase 120 and 240 Volt Fixed Shaft (click blue text for more details)
 Staco Energy Products Co. has been a leading manufacturer of variable transformers for over 60 years, building standard as well as custom-designed products for industrial, commercial and military applications.
Staco Energy Products Co. has been a leading manufacturer of variable transformers for over 60 years, building standard as well as custom-designed products for industrial, commercial and military applications.
FRENIC-Ace (C2) (Supplement to RS-485 User's Manual)
 (Supplement to RS-485 User's Manual) FRENIC-Ace (C2) This document is a supplement to the RS-485 Communication User s Manual (24A7-E-0082, MEH448), and is comprised of section 5.2 (Data ), to which content
(Supplement to RS-485 User's Manual) FRENIC-Ace (C2) This document is a supplement to the RS-485 Communication User s Manual (24A7-E-0082, MEH448), and is comprised of section 5.2 (Data ), to which content
Experiment 1: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity
 Experiment 1: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity 1. Task: 1. Set up a Sawyer-Tower circuit to measure ferroelectric hysteresis curves. 2. Check the D(E) curves for a capacitor, a resistor and an
Experiment 1: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity 1. Task: 1. Set up a Sawyer-Tower circuit to measure ferroelectric hysteresis curves. 2. Check the D(E) curves for a capacitor, a resistor and an
AC Synchronous Motors
 AC Synchronous Motors A C S Y N C H R O N O U S M O T O R S AC Synchronous Motors Kollmorgen AC synchronous motors are high pole count motors that naturally turn at slower speeds (72 or 60 rpm). at 72
AC Synchronous Motors A C S Y N C H R O N O U S M O T O R S AC Synchronous Motors Kollmorgen AC synchronous motors are high pole count motors that naturally turn at slower speeds (72 or 60 rpm). at 72
ED 701 General Industry Pressure Transmitter
 ED 701 General Industry Pressure Transmitter Standard industrial process connections Complete range of electrical connections 4... 20 ma and Voltage outputs Accuracy: 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.4% FS Quick response
ED 701 General Industry Pressure Transmitter Standard industrial process connections Complete range of electrical connections 4... 20 ma and Voltage outputs Accuracy: 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.4% FS Quick response
Electric Deflection of Electrons
 Electric Deflection of Electrons Objective The purpose of this experiment is to observe that the spacial deflection of an electron in a cathode ray tube is directly proportional to the deflection potential.
Electric Deflection of Electrons Objective The purpose of this experiment is to observe that the spacial deflection of an electron in a cathode ray tube is directly proportional to the deflection potential.
Technical Instructions 4003.B. Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery. Performances. Functions. Movement height 4.40 mm
 Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
Specification 12 ½''' Dimensions and battery ø Total 28.60 mm ø Case fitting 28.00 mm Movement height 4.40 mm Movement rest 0.60 mm Height of stem 1.90 mm Stem: Thread / Distance 0.90 mm / 0.90 mm Battery
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194
 MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
Chapter 7: Stepper Motors. (Revision 6.0, 27/10/2014)
 Chapter 7 Stepper Motors (Revision 6.0, 7/10/014) 1. Stepping Angle Analysis The following analysis derives the formula for the stepping angle of the stepper motor. It has been reproduced and edited from
Chapter 7 Stepper Motors (Revision 6.0, 7/10/014) 1. Stepping Angle Analysis The following analysis derives the formula for the stepping angle of the stepper motor. It has been reproduced and edited from
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
