Chapter VIII: Statistical Process Control - Exercises
|
|
|
- Morgan Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter VIII: Statistical Process Control - Exercises Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING
2 Exercise An industrial process produces a speed sensor for an ABS electronic control. The sensor specifications require that the variable X = impedance is 30 kohms ±10 kohms. To perform the statistical control of this process 6 sample sensors are collected every half hour. With the collected data, a total of 30 samples, the following information were obtained: x = and ŝ x = a) Construct control charts to monitor that the population mean and variance remain constant. b) When there is a change in the mean of +3 kohms, what is the probability of detecting it in the next sample after the mismatch? Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
3 SOLUTION: a) The control chart for the mean is UCL = µ + 3 σ n CL = µ LCL = µ 3 σ n UCL = x + 3 ŝ x 2.00 c 4 n = = CL = x = LCL = x + 3 ŝ x 2.00 c 4 n = = where µ has been estimated by the total sample mean x = x = and σ has been estimated by the mean of the sample standard deviationsŝ x as ˆσ = ŝ x/c 4 where for n = 6 we have that c 4 = The control chart for the standard deviations is UCL = B 4ŝ x = = 3.94 CL = ŝ x = 2.00 LCL = B 3ŝ x = = 0.06 where we used the fact that, when n = 6, B 3 = and B 4 = Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
4 SOLUTION: b) The data suggest that the sample means are Normal distributed with the following parameters ( ( ) ) x N 30.11, 6 If we have a change in the mean of +3 kohms than the new sample means ( ȳ ) will have (estimated) distribution ( ȳ N 33.11, ). However the control limits do not change and stay UCL = and LCL = We will detect the change in the sample mean if its graph will move out of the limit region, i.e. Pr (alarm) = 1 Pr (27.54 ȳ 32.69) ( ) = 1 Pr z = 1 Pr ( 6.50 z 0.49) = = 68.8% Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
5 Exercise In a foundry a statistical process control takes place by measuring the hardness (X) of ingots. It is assumed that X is normally distributed with mean µ and standard deviation σ, both known. If samples of size n are taken. a) Establish the limits and the centerline of the control chart for average hardness. b) Calculate how many ingots ( n ) we must use if we want to detect changes in the average hardness of magnitude +2σ, with probability 0.8, assuming constant the variance. Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
6 SOLUTION: a) Since x N(µ, σ/ n) the control limits are µ ± 3σ/ n and the center line is the mean µ b) If the mean has changed by an amount +2σ the sample means ( ȳ ) will be distributed as ȳ N(µ + 2σ, σ/ n) and so we will get an alarm if its graph will go out of the controlled region µ ± 3σ/ n taht stays unchanged. So we can compute the alarm probability as Pr (alarm) = 1 Pr ( µ 3σ/ n ȳ µ + 3σ/ n ) ( µ 3σ/ n (µ + 2σ) = 1 Pr σ/ z µ + 3σ/ ) n (µ + 2σ) n σ/ n = 1 Pr ( 3 2 n z n ) Since we want Pr (alarm) = 80% we get that Pr ( 3 2 n z n ) Pr ( z n ) = 20% and hence n = z 0.2 = 0.84 that gives ( ) n > = 3.60 n = 4 2 Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
7 Exercise The following graph shows the time series of the magnitudes of the last 75 earthquakes detected in the peninsula, measured by the Richter scale. We work in logarithms to provide a variable more similar to normal than the one obtained by looking directly at the values in the original scale. It has been thought to make a control chart in this series X = log(magnitude) to detect if at any time seismic conditions are going through some period away from stationarity, and to help predict increases in seismic activity. It has been thought to make a graph of averages with subgroups of size n = 3 of the variable X = log(magnitude). The sample mean is x = and the sample standard deviation is ŝ x = Compute the control limits of mean graph would be obtained with the values provided in the preceding paragraph. Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
8 Exercise The following graph shows the time series of the magnitudes of the last 75 earthquakes detected in the peninsula, measured by the Richter scale. We work in logarithms to provide a variable more similar to normal than the one obtained by looking directly at the values in the original scale. It has been thought to make a control chart in this series X = log(magnitude) to detect if at any time seismic conditions are going through some period away from stationarity, and to help predict increases in seismic activity. It has been thought to make a graph of averages with subgroups of size n = 3 of the variable X = log(magnitude). The sample mean is x = and the sample standard deviation is ŝ x = Compute the control limits of mean graph would be obtained with the values provided in the preceding paragraph. SOLUTION: The control chart for the mean is: UCL = ; CenterLine = 0.587; LCL = Bernardo D Auria (UC3M - Computer Engineering) / 7
Chapter IV: Random Variables - Exercises
 Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING 2010-2011 The time to repair a machine expressed in hour is a random variable with distribution function
Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING 2010-2011 The time to repair a machine expressed in hour is a random variable with distribution function
A. Evaluate log Evaluate Logarithms
 A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
Chapter IX: Regression - Exercises
 Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING December 14 th, 2010 The file FrenosITV.sf3 has some properties of a sample of vehicles. We want
Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING December 14 th, 2010 The file FrenosITV.sf3 has some properties of a sample of vehicles. We want
Control of Manufacturing Processes
 Control of Manufacturing Processes Subject 2.830 Spring 2004 Lecture #8 Hypothesis Testing and Shewhart Charts March 2, 2004 3/2/04 Lecture 8 D.E. Hardt, all rights reserved 1 Applying Statistics to Manufacturing:
Control of Manufacturing Processes Subject 2.830 Spring 2004 Lecture #8 Hypothesis Testing and Shewhart Charts March 2, 2004 3/2/04 Lecture 8 D.E. Hardt, all rights reserved 1 Applying Statistics to Manufacturing:
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Multivariate T-Squared Control Chart
 Multivariate T-Squared Control Chart Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Summary... 4 Analysis Options... 5 T-Squared Chart... 6 Multivariate Control Chart Report... 7 Generalized Variance Chart... 8
Multivariate T-Squared Control Chart Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Summary... 4 Analysis Options... 5 T-Squared Chart... 6 Multivariate Control Chart Report... 7 Generalized Variance Chart... 8
MA30118: MANAGEMENT STATISTICS Assessed Coursework: Quality Control. x ji and r j = max(x ji ) min(x ji ).
 1. (a) For each j, Hence, MA0118: MANAGEMENT STATISTICS Assessed Coursework: Quality Control x j = 1 i=1 x ji and r j = max(x ji ) min(x ji ). i i x 21 = 170.9744 = 4.19488, r 21 = 4.2240 4.1760 = 0.0480,
1. (a) For each j, Hence, MA0118: MANAGEMENT STATISTICS Assessed Coursework: Quality Control x j = 1 i=1 x ji and r j = max(x ji ) min(x ji ). i i x 21 = 170.9744 = 4.19488, r 21 = 4.2240 4.1760 = 0.0480,
IE 361 Module 25. Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 2 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring)
 IE 361 Module 25 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 2 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
IE 361 Module 25 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 2 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
STAT 111 Recitation 7
 STAT 111 Recitation 7 Xin Lu Tan xtan@wharton.upenn.edu October 25, 2013 1 / 13 Miscellaneous Please turn in homework 6. Please pick up homework 7 and the graded homework 5. Please check your grade and
STAT 111 Recitation 7 Xin Lu Tan xtan@wharton.upenn.edu October 25, 2013 1 / 13 Miscellaneous Please turn in homework 6. Please pick up homework 7 and the graded homework 5. Please check your grade and
Practice Test - Chapter 3
 Sketch and analyze the graph of each function. Describe its domain, range, intercepts, asymptotes, end behavior, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = e x + 7 Evaluate the function
Sketch and analyze the graph of each function. Describe its domain, range, intercepts, asymptotes, end behavior, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = e x + 7 Evaluate the function
Session XIV. Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart
 Session XIV Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart The P Chart The P Chart is used for data that consist of the proportion of the number of occurrences of an event to the total number of occurrences. It
Session XIV Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart The P Chart The P Chart is used for data that consist of the proportion of the number of occurrences of an event to the total number of occurrences. It
Selection of Variable Selecting the right variable for a control chart means understanding the difference between discrete and continuous data.
 Statistical Process Control, or SPC, is a collection of tools that allow a Quality Engineer to ensure that their process is in control, using statistics. Benefit of SPC The primary benefit of a control
Statistical Process Control, or SPC, is a collection of tools that allow a Quality Engineer to ensure that their process is in control, using statistics. Benefit of SPC The primary benefit of a control
Power Functions for. Process Behavior Charts
 Power Functions for Process Behavior Charts Donald J. Wheeler and Rip Stauffer Every data set contains noise (random, meaningless variation). Some data sets contain signals (nonrandom, meaningful variation).
Power Functions for Process Behavior Charts Donald J. Wheeler and Rip Stauffer Every data set contains noise (random, meaningless variation). Some data sets contain signals (nonrandom, meaningful variation).
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/term
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/term
Sample Control Chart Calculations. Here is a worked example of the x and R control chart calculations.
 Sample Control Chart Calculations Here is a worked example of the x and R control chart calculations. Step 1: The appropriate characteristic to measure was defined and the measurement methodology determined.
Sample Control Chart Calculations Here is a worked example of the x and R control chart calculations. Step 1: The appropriate characteristic to measure was defined and the measurement methodology determined.
Paired comparisons. We assume that
 To compare to methods, A and B, one can collect a sample of n pairs of observations. Pair i provides two measurements, Y Ai and Y Bi, one for each method: If we want to compare a reaction of patients to
To compare to methods, A and B, one can collect a sample of n pairs of observations. Pair i provides two measurements, Y Ai and Y Bi, one for each method: If we want to compare a reaction of patients to
Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA. Dec. 6, 2002
 Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA Dec. 6, 2002 Control Chart for Number of Defectives Sometimes, more convenient to make chart by plotting d rather than p. In particular, plotting d appropriate if
Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA Dec. 6, 2002 Control Chart for Number of Defectives Sometimes, more convenient to make chart by plotting d rather than p. In particular, plotting d appropriate if
Statistical Process Control
 Statistical Process Control What is a process? Inputs PROCESS Outputs A process can be described as a transformation of set of inputs into desired outputs. Types of Measures Measures where the metric is
Statistical Process Control What is a process? Inputs PROCESS Outputs A process can be described as a transformation of set of inputs into desired outputs. Types of Measures Measures where the metric is
Statistical Process Control SCM Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
 S6 Statistical Process Control SCM 352 Outline Statistical Quality Control Common causes vs. assignable causes Different types of data attributes and variables Central limit theorem SPC charts Control
S6 Statistical Process Control SCM 352 Outline Statistical Quality Control Common causes vs. assignable causes Different types of data attributes and variables Central limit theorem SPC charts Control
Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release.
 Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release. Epicentre: the point on the ground surface immediately above the focus (closest point on the surface to the focus). Types of
Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release. Epicentre: the point on the ground surface immediately above the focus (closest point on the surface to the focus). Types of
A first look at the performances of a Bayesian chart to monitor. the ratio of two Weibull percentiles
 A first loo at the performances of a Bayesian chart to monitor the ratio of two Weibull percentiles Pasquale Erto University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy e-mail: ertopa@unina.it Abstract. The aim
A first loo at the performances of a Bayesian chart to monitor the ratio of two Weibull percentiles Pasquale Erto University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy e-mail: ertopa@unina.it Abstract. The aim
Scenario 5: Internet Usage Solution. θ j
 Scenario : Internet Usage Solution Some more information would be interesting about the study in order to know if we can generalize possible findings. For example: Does each data point consist of the total
Scenario : Internet Usage Solution Some more information would be interesting about the study in order to know if we can generalize possible findings. For example: Does each data point consist of the total
ISyE 512 Chapter 7. Control Charts for Attributes. Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu. Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison
 ISyE 512 Chapter 7 Control Charts for Attributes Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering
ISyE 512 Chapter 7 Control Charts for Attributes Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering
EVALUATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS ON A MEDIUM RISE BUILDING
 7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 8-11, 214. La Cité, Nantes, France More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17121 EVALUATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS ON A MEDIUM
7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 8-11, 214. La Cité, Nantes, France More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17121 EVALUATION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS ON A MEDIUM
Earthquake Model Investigations
 Earthquake Model Investigations Name Part 1 Pre Lab Worksheet Watch as your teacher demonstrates how the Earthquake model works. In this pre lab, you will predict what you think will be the relationship
Earthquake Model Investigations Name Part 1 Pre Lab Worksheet Watch as your teacher demonstrates how the Earthquake model works. In this pre lab, you will predict what you think will be the relationship
Formulas and Tables. for Elementary Statistics, Tenth Edition, by Mario F. Triola Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. ˆp E p ˆp E Proportion
 Formulas and Tables for Elementary Statistics, Tenth Edition, by Mario F. Triola Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Ch. 3: Descriptive Statistics x Sf. x x Sf Mean S(x 2 x) 2 s Å n 2 1 n(sx 2 ) 2 (Sx)
Formulas and Tables for Elementary Statistics, Tenth Edition, by Mario F. Triola Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Ch. 3: Descriptive Statistics x Sf. x x Sf Mean S(x 2 x) 2 s Å n 2 1 n(sx 2 ) 2 (Sx)
Formulas and Tables for Elementary Statistics, Eighth Edition, by Mario F. Triola 2001 by Addison Wesley Longman Publishing Company, Inc.
 Formulas and Tables for Elementary Statistics, Eighth Edition, by Mario F. Triola 2001 by Addison Wesley Longman Publishing Company, Inc. Ch. 2: Descriptive Statistics x Sf. x x Sf Mean S(x 2 x) 2 s 2
Formulas and Tables for Elementary Statistics, Eighth Edition, by Mario F. Triola 2001 by Addison Wesley Longman Publishing Company, Inc. Ch. 2: Descriptive Statistics x Sf. x x Sf Mean S(x 2 x) 2 s 2
Formulas and Tables by Mario F. Triola
 Copyright 010 Pearson Education, Inc. Ch. 3: Descriptive Statistics x f # x x f Mean 1x - x s - 1 n 1 x - 1 x s 1n - 1 s B variance s Ch. 4: Probability Mean (frequency table) Standard deviation P1A or
Copyright 010 Pearson Education, Inc. Ch. 3: Descriptive Statistics x f # x x f Mean 1x - x s - 1 n 1 x - 1 x s 1n - 1 s B variance s Ch. 4: Probability Mean (frequency table) Standard deviation P1A or
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7
 Choose a word or term from the list above that best completes each statement or phrase. 1. A function of the form f (x) = b x where b > 1 is a(n) function. exponential growth 2. In x = b y, the variable
Choose a word or term from the list above that best completes each statement or phrase. 1. A function of the form f (x) = b x where b > 1 is a(n) function. exponential growth 2. In x = b y, the variable
Solutions to Problems 1,2 and 7 followed by 3,4,5,6 and 8.
 DSES-423 Quality Control Spring 22 Solution to Homework Assignment #2 Solutions to Problems 1,2 and 7 followed by 3,4,,6 and 8. 1. The cause-and-effect diagram below was created by a department of the
DSES-423 Quality Control Spring 22 Solution to Homework Assignment #2 Solutions to Problems 1,2 and 7 followed by 3,4,,6 and 8. 1. The cause-and-effect diagram below was created by a department of the
Mechanical Engineering 101
 Mechanical Engineering 101 University of California, Berkeley Lecture #1 1 Today s lecture Statistical Process Control Process capability Mean shift Control charts eading: pp. 373-383 .Precision 3 Process
Mechanical Engineering 101 University of California, Berkeley Lecture #1 1 Today s lecture Statistical Process Control Process capability Mean shift Control charts eading: pp. 373-383 .Precision 3 Process
Geostatistics for Seismic Data Integration in Earth Models
 2003 Distinguished Instructor Short Course Distinguished Instructor Series, No. 6 sponsored by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers SUB Gottingen 7
2003 Distinguished Instructor Short Course Distinguished Instructor Series, No. 6 sponsored by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers SUB Gottingen 7
log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =
![log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) = log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =](/thumbs/92/109466632.jpg) Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Chapter 7: SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS & POINT ESTIMATION OF PARAMETERS. Part 2: Differences in sample means
 Chapter 7: SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS & POINT ESTIMATION OF PARAMETERS Part 2: Differences in sample means What if we re interested in estimating the difference in means between two populations? Value of interest:
Chapter 7: SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS & POINT ESTIMATION OF PARAMETERS Part 2: Differences in sample means What if we re interested in estimating the difference in means between two populations? Value of interest:
THE DETECTION OF SHIFTS IN AUTOCORRELATED PROCESSES WITH MR AND EWMA CHARTS
 THE DETECTION OF SHIFTS IN AUTOCORRELATED PROCESSES WITH MR AND EWMA CHARTS Karin Kandananond, kandananond@hotmail.com Faculty of Industrial Technology, Rajabhat University Valaya-Alongkorn, Prathumthani,
THE DETECTION OF SHIFTS IN AUTOCORRELATED PROCESSES WITH MR AND EWMA CHARTS Karin Kandananond, kandananond@hotmail.com Faculty of Industrial Technology, Rajabhat University Valaya-Alongkorn, Prathumthani,
3.5. Equation Solving and Modeling. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 3.5 Equation Solving and Modeling Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Solving Exponential Equations Solving Logarithmic Equations Orders of Magnitude and Logarithmic Models Newton s Law
3.5 Equation Solving and Modeling Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Solving Exponential Equations Solving Logarithmic Equations Orders of Magnitude and Logarithmic Models Newton s Law
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name
 SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name 1. Mark the following statements True T or False F. (6 points -2 each) T A. A process is out of control if at a particular point in time the reading is more than 3 standard deviations
SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name 1. Mark the following statements True T or False F. (6 points -2 each) T A. A process is out of control if at a particular point in time the reading is more than 3 standard deviations
Math 1311 Check courseware for all due dates. Section 4.5: Logarithmic Functions
 Math 1311 Check courseware for all due dates Section 4.5: Logarithmic Functions In the last couple of sections, we looked at exponential functions. With an exponential function like NN(tt) = 2 tt, a small
Math 1311 Check courseware for all due dates Section 4.5: Logarithmic Functions In the last couple of sections, we looked at exponential functions. With an exponential function like NN(tt) = 2 tt, a small
Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control
 Chapter 6 Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control 6.0 Introduction In statistical process control Poisson distribution and binomial distribution play important role. There are situations wherein
Chapter 6 Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control 6.0 Introduction In statistical process control Poisson distribution and binomial distribution play important role. There are situations wherein
9.7 Common Logarithms, Natural Logarithms, and Change of Base
 580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
Logarithmic Scales 1
 Logarithmic Scales 1 Instruction Richter Scale Definition: The Richter scale, which measures the magnitude of earthquakes, was developed in 1935 by Charles F. Richter at the California Institute of Technology.
Logarithmic Scales 1 Instruction Richter Scale Definition: The Richter scale, which measures the magnitude of earthquakes, was developed in 1935 by Charles F. Richter at the California Institute of Technology.
Name Date Per. Ms. Williams/Mrs. Hertel
 Name Date Per. Ms. Williams/Mrs. Hertel Day 7: Solving Exponential Word Problems involving Logarithms Warm Up Exponential growth occurs when a quantity increases by the same rate r in each period t. When
Name Date Per. Ms. Williams/Mrs. Hertel Day 7: Solving Exponential Word Problems involving Logarithms Warm Up Exponential growth occurs when a quantity increases by the same rate r in each period t. When
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303)
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Monitoring Expense Report Errors: Control Charts Under Independence and Dependence. Darren Williams. (Under the direction of Dr.
 Monitoring Expense Report Errors: Control Charts Under Independence and Dependence by Darren Williams (Under the direction of Dr. Lynne Seymour) Abstract Control charts were devised to evaluate offices
Monitoring Expense Report Errors: Control Charts Under Independence and Dependence by Darren Williams (Under the direction of Dr. Lynne Seymour) Abstract Control charts were devised to evaluate offices
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Section II: Assessing Chart Performance. (Jim Benneyan)
 Section II: Assessing Chart Performance (Jim Benneyan) 1 Learning Objectives Understand concepts of chart performance Two types of errors o Type 1: Call an in-control process out-of-control o Type 2: Call
Section II: Assessing Chart Performance (Jim Benneyan) 1 Learning Objectives Understand concepts of chart performance Two types of errors o Type 1: Call an in-control process out-of-control o Type 2: Call
Multivariate Control and Model-Based SPC
 Multivariate Control and Model-Based SPC T 2, evolutionary operation, regression chart. 1 Multivariate Control Often, many variables must be controlled at the same time. Controlling p independent parameters
Multivariate Control and Model-Based SPC T 2, evolutionary operation, regression chart. 1 Multivariate Control Often, many variables must be controlled at the same time. Controlling p independent parameters
Published: 26 April 2016
 Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA, Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal. http://siba-ese.unisalento.it/index.php/ejasa/index e-issn: 2070-5948 DOI: 10.1285/i20705948v9n1p111 A robust dispersion
Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA, Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal. http://siba-ese.unisalento.it/index.php/ejasa/index e-issn: 2070-5948 DOI: 10.1285/i20705948v9n1p111 A robust dispersion
Evaluation of X and S charts when Standards Vary Randomly *Aamir Saghir Department of Statistics, UAJK Muzaffrabad, Pakistan.
 Evaluation of and charts when tandards Vary Randomly *Aamir aghir Department of tatistics, UAJK Muzaffrabad, Pakistan. E-mail: aamirstat@yahoo.com. Abstract The study proposes control limits for and charts
Evaluation of and charts when tandards Vary Randomly *Aamir aghir Department of tatistics, UAJK Muzaffrabad, Pakistan. E-mail: aamirstat@yahoo.com. Abstract The study proposes control limits for and charts
Statistical Process Control
 Chapter 3 Statistical Process Control 3.1 Introduction Operations managers are responsible for developing and maintaining the production processes that deliver quality products and services. Once the production
Chapter 3 Statistical Process Control 3.1 Introduction Operations managers are responsible for developing and maintaining the production processes that deliver quality products and services. Once the production
RESEARCH PAPERS FACULTY OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN TRNAVA SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY IN BRATISLAVA
 RESEARCH PAPERS FACULTY OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN TRNAVA SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY IN BRATISLAVA 20 Number 30 THE PROCESS CAPABILITY STUDY OF PRESSING PROCESS FOR FORCE CLOSED Katarína
RESEARCH PAPERS FACULTY OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN TRNAVA SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY IN BRATISLAVA 20 Number 30 THE PROCESS CAPABILITY STUDY OF PRESSING PROCESS FOR FORCE CLOSED Katarína
Department of Industrial Engineering Statistical Quality Control presented by Dr. Eng. Abed Schokry
 Department of Indstrial Engineering Statistical Qality Control presented by Dr. Eng. Abed Schokry Department of Indstrial Engineering Statistical Qality Control C and U Chart presented by Dr. Eng. Abed
Department of Indstrial Engineering Statistical Qality Control presented by Dr. Eng. Abed Schokry Department of Indstrial Engineering Statistical Qality Control C and U Chart presented by Dr. Eng. Abed
i=1 X i/n i=1 (X i X) 2 /(n 1). Find the constant c so that the statistic c(x X n+1 )/S has a t-distribution. If n = 8, determine k such that
 Math 47 Homework Assignment 4 Problem 411 Let X 1, X,, X n, X n+1 be a random sample of size n + 1, n > 1, from a distribution that is N(µ, σ ) Let X = n i=1 X i/n and S = n i=1 (X i X) /(n 1) Find the
Math 47 Homework Assignment 4 Problem 411 Let X 1, X,, X n, X n+1 be a random sample of size n + 1, n > 1, from a distribution that is N(µ, σ ) Let X = n i=1 X i/n and S = n i=1 (X i X) /(n 1) Find the
First Semester Dr. Abed Schokry SQC Chapter 9: Cumulative Sum and Exponential Weighted Moving Average Control Charts
 Department of Industrial Engineering First Semester 2014-2015 Dr. Abed Schokry SQC Chapter 9: Cumulative Sum and Exponential Weighted Moving Average Control Charts Learning Outcomes After completing this
Department of Industrial Engineering First Semester 2014-2015 Dr. Abed Schokry SQC Chapter 9: Cumulative Sum and Exponential Weighted Moving Average Control Charts Learning Outcomes After completing this
Correction factors for Shewhart and control charts to achieve desired unconditional ARL
 International Journal of Production Research ISSN: 0020-7543 (Print) 1366-588X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tprs20 Correction factors for Shewhart and control charts to achieve
International Journal of Production Research ISSN: 0020-7543 (Print) 1366-588X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tprs20 Correction factors for Shewhart and control charts to achieve
TEXTY PRO KURS LJA2 kombinovaného magisterského studia. PhDr. Marcela Borecká
 TEXTY PRO KURS LJA2 kombinovaného magisterského studia PhDr. Marcela Borecká Earthquake detector 1) A seismograph is an instrument that locates the origin and force of earthquakes. Although there are many
TEXTY PRO KURS LJA2 kombinovaného magisterského studia PhDr. Marcela Borecká Earthquake detector 1) A seismograph is an instrument that locates the origin and force of earthquakes. Although there are many
A COMPARISON OF PHASE I CONTROL CHARTS. University of Pretoria, South Africa 1 4
 A COMPARISON OF PHASE I CONTROL CHARTS M.L.I Coelho 1, S. Chakraborti 2,3 & M.A. Graham 4 1,2,4 Department of Statistics University of Pretoria, South Africa 1 margicoelho@gmail.com, 4 marien.graham@up.ac.za
A COMPARISON OF PHASE I CONTROL CHARTS M.L.I Coelho 1, S. Chakraborti 2,3 & M.A. Graham 4 1,2,4 Department of Statistics University of Pretoria, South Africa 1 margicoelho@gmail.com, 4 marien.graham@up.ac.za
Percent
 Data Entry Spreadsheet to Create a C Chart Date Observations Mean UCL +3s LCL -3s +2s -2s +1s -1s CHART --> 01/01/00 2.00 3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00 01/02/00-3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00
Data Entry Spreadsheet to Create a C Chart Date Observations Mean UCL +3s LCL -3s +2s -2s +1s -1s CHART --> 01/01/00 2.00 3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00 01/02/00-3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00
Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD
 Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD Dr. Jitesh J. Thakkar Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Instruction Total No.
Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD Dr. Jitesh J. Thakkar Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Instruction Total No.
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081
 Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter
 Bulletin No. 100 Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter How to determine the range of acceptable results for your calorimeter. Standard methods specify parameters by which calorimetry results
Bulletin No. 100 Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter How to determine the range of acceptable results for your calorimeter. Standard methods specify parameters by which calorimetry results
IE 361 Module 24. Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring)
 IE 361 Module 24 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
IE 361 Module 24 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d
 The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d 3150/4150 Lecture 4 Ragnar Nymoen 27 January 2012 The model with transformed variables Regression with transformed variables I References HGL Ch 2.8
The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d 3150/4150 Lecture 4 Ragnar Nymoen 27 January 2012 The model with transformed variables Regression with transformed variables I References HGL Ch 2.8
Total Quality Management (TQM)
 Total Quality Management (TQM) Use of statistical techniques for controlling and improving quality and their integration in the management system Statistical Process Control (SPC) Univariate and multivariate
Total Quality Management (TQM) Use of statistical techniques for controlling and improving quality and their integration in the management system Statistical Process Control (SPC) Univariate and multivariate
Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter
 Bulletin No. 100 Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter How to determine the range of acceptable results for your calorimeter. Standard methods specify parameters by which calorimetry results
Bulletin No. 100 Precision and Accuracy Assessing your Calorimeter How to determine the range of acceptable results for your calorimeter. Standard methods specify parameters by which calorimetry results
434 CHAP. 8 NUMERICAL OPTIMIZATION. Powell's Method. Powell s Method
 434 CHAP. 8 NUMERICAL OPTIMIZATION Powell's Method Powell s Method Let X be an initial guess at the location of the minimum of the function z = f (x, x 2,...,x N ). Assume that the partial derivatives
434 CHAP. 8 NUMERICAL OPTIMIZATION Powell's Method Powell s Method Let X be an initial guess at the location of the minimum of the function z = f (x, x 2,...,x N ). Assume that the partial derivatives
Homework sheet 4: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS. DIAGONALIZATION (with solutions) Year ? Why or why not? 6 9
 Bachelor in Statistics and Business Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Mathematical Methods II María Barbero Liñán Homework sheet 4: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS DIAGONALIZATION (with solutions) Year - Is
Bachelor in Statistics and Business Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Mathematical Methods II María Barbero Liñán Homework sheet 4: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS DIAGONALIZATION (with solutions) Year - Is
Max. Likelihood Estimation. Outline. Econometrics II. Ricardo Mora. Notes. Notes
 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Econometrics II Department of Economics Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Máster Universitario en Desarrollo y Crecimiento Económico Outline 1 3 4 General Approaches to Parameter
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Econometrics II Department of Economics Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Máster Universitario en Desarrollo y Crecimiento Económico Outline 1 3 4 General Approaches to Parameter
Directed Reading. Section: How and Where Earthquakes Happen WHY EARTHQUAKES HAPPEN. Skills Worksheet. 1. Define earthquake.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How and Where Earthquakes Happen 1. Define earthquake. 2. When do earthquakes usually occur? 3. What is a fault? WHY EARTHQUAKES HAPPEN 4. Rocks along both sides
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How and Where Earthquakes Happen 1. Define earthquake. 2. When do earthquakes usually occur? 3. What is a fault? WHY EARTHQUAKES HAPPEN 4. Rocks along both sides
EARTH STRUCTURE & DYNAMICS EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY PRACTICALS. G.R. Foulger
 1 EARTH STRUCTURE & DYNAMICS EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY PRACTICALS G.R. Foulger 1. A large earthquake is recorded well at a three-component seismic station in Hawaii (coordinates 205 E, 20 N). The epicentral
1 EARTH STRUCTURE & DYNAMICS EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY PRACTICALS G.R. Foulger 1. A large earthquake is recorded well at a three-component seismic station in Hawaii (coordinates 205 E, 20 N). The epicentral
spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand
 spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand BENEFITS of SPC Monitors and provides feedback for keeping processes in control. Triggers when a problem occurs Differentiates
spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand BENEFITS of SPC Monitors and provides feedback for keeping processes in control. Triggers when a problem occurs Differentiates
Control Charts for Zero-Inflated Poisson Models
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 56, 2791-2803 Control Charts for Zero-Inflated Poisson Models Narunchara Katemee Department of Applied Statistics, Faculty of Applied Science King Mongkut
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 56, 2791-2803 Control Charts for Zero-Inflated Poisson Models Narunchara Katemee Department of Applied Statistics, Faculty of Applied Science King Mongkut
21.1 Traditional Monitoring Techniques Extensions of Statistical Process Control Multivariate Statistical Techniques
 1 Process Monitoring 21.1 Traditional Monitoring Techniques 21.2 Quality Control Charts 21.3 Extensions of Statistical Process Control 21.4 Multivariate Statistical Techniques 21.5 Control Performance
1 Process Monitoring 21.1 Traditional Monitoring Techniques 21.2 Quality Control Charts 21.3 Extensions of Statistical Process Control 21.4 Multivariate Statistical Techniques 21.5 Control Performance
Robust control charts for time series data
 Robust control charts for time series data Christophe Croux K.U. Leuven & Tilburg University Sarah Gelper Erasmus University Rotterdam Koen Mahieu K.U. Leuven Abstract This article presents a control chart
Robust control charts for time series data Christophe Croux K.U. Leuven & Tilburg University Sarah Gelper Erasmus University Rotterdam Koen Mahieu K.U. Leuven Abstract This article presents a control chart
A Multivariate Process Variability Monitoring Based on Individual Observations
 www.ccsenet.org/mas Modern Applied Science Vol. 4, No. 10; October 010 A Multivariate Process Variability Monitoring Based on Individual Observations Maman A. Djauhari (Corresponding author) Department
www.ccsenet.org/mas Modern Applied Science Vol. 4, No. 10; October 010 A Multivariate Process Variability Monitoring Based on Individual Observations Maman A. Djauhari (Corresponding author) Department
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Sampling Distributions
 Sampling Distributions Prof. Jacob M. Montgomery Quantitative Political Methodology (L32 363) September 14, 2016 Lecture 5 (QPM 2016) Sampling Distributions September 14, 2016 1 / 6 Sampling Distributions
Sampling Distributions Prof. Jacob M. Montgomery Quantitative Political Methodology (L32 363) September 14, 2016 Lecture 5 (QPM 2016) Sampling Distributions September 14, 2016 1 / 6 Sampling Distributions
F3: Classical normal linear rgression model distribution, interval estimation and hypothesis testing
 F3: Classical normal linear rgression model distribution, interval estimation and hypothesis testing Feng Li Department of Statistics, Stockholm University What we have learned last time... 1 Estimating
F3: Classical normal linear rgression model distribution, interval estimation and hypothesis testing Feng Li Department of Statistics, Stockholm University What we have learned last time... 1 Estimating
CS 195-5: Machine Learning Problem Set 1
 CS 95-5: Machine Learning Problem Set Douglas Lanman dlanman@brown.edu 7 September Regression Problem Show that the prediction errors y f(x; ŵ) are necessarily uncorrelated with any linear function of
CS 95-5: Machine Learning Problem Set Douglas Lanman dlanman@brown.edu 7 September Regression Problem Show that the prediction errors y f(x; ŵ) are necessarily uncorrelated with any linear function of
FREQUENCY RESPONSE ANALYSIS Closed Loop Frequency Response
 Closed Loop Frequency Response The Bode plot is generally constructed for an open loop transfer function of a system. In order to draw the Bode plot for a closed loop system, the transfer function has
Closed Loop Frequency Response The Bode plot is generally constructed for an open loop transfer function of a system. In order to draw the Bode plot for a closed loop system, the transfer function has
Reactant A (g) Reactant B (ml) Product (ml)
 Pre-Test Key Name: Chemical Reactions Date: 1. The chart below shows the amount of gas that is produced when two reactants (a solid and a liquid) are combined. However, one of the boxes is missing information.
Pre-Test Key Name: Chemical Reactions Date: 1. The chart below shows the amount of gas that is produced when two reactants (a solid and a liquid) are combined. However, one of the boxes is missing information.
F-tests and Nested Models
 F-tests and Nested Models Nested Models: A core concept in statistics is comparing nested s. Consider the Y = β 0 + β 1 x 1 + β 2 x 2 + ǫ. (1) The following reduced s are special cases (nested within)
F-tests and Nested Models Nested Models: A core concept in statistics is comparing nested s. Consider the Y = β 0 + β 1 x 1 + β 2 x 2 + ǫ. (1) The following reduced s are special cases (nested within)
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS Study program/ Specialization: Spring semester, 20... Open / Restricted access Writer: Faculty supervisor: (Writer s signature) External supervisor(s):
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS Study program/ Specialization: Spring semester, 20... Open / Restricted access Writer: Faculty supervisor: (Writer s signature) External supervisor(s):
Confirmation Sample Control Charts
 Confirmation Sample Control Charts Stefan H. Steiner Dept. of Statistics and Actuarial Sciences University of Waterloo Waterloo, NL 3G1 Canada Control charts such as X and R charts are widely used in industry
Confirmation Sample Control Charts Stefan H. Steiner Dept. of Statistics and Actuarial Sciences University of Waterloo Waterloo, NL 3G1 Canada Control charts such as X and R charts are widely used in industry
ECE 510 Lecture 7 Goodness of Fit, Maximum Likelihood. Scott Johnson Glenn Shirley
 ECE 510 Lecture 7 Goodness of Fit, Maximum Likelihood Scott Johnson Glenn Shirley Confidence Limits 30 Jan 2013 ECE 510 S.C.Johnson, C.G.Shirley 2 Binomial Confidence Limits (Solution 6.2) UCL: Prob of
ECE 510 Lecture 7 Goodness of Fit, Maximum Likelihood Scott Johnson Glenn Shirley Confidence Limits 30 Jan 2013 ECE 510 S.C.Johnson, C.G.Shirley 2 Binomial Confidence Limits (Solution 6.2) UCL: Prob of
STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL - THE IMPORTANCE OF USING CALIBRATED MEASUREMENT EQUIPMENT. CASE STUDY
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5376 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5376 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
Statistical Process Control
 Statistical Process Control Outline Statistical Process Control (SPC) Process Capability Acceptance Sampling 2 Learning Objectives When you complete this supplement you should be able to : S6.1 Explain
Statistical Process Control Outline Statistical Process Control (SPC) Process Capability Acceptance Sampling 2 Learning Objectives When you complete this supplement you should be able to : S6.1 Explain
Logarithmic Functions
 Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
CHAPTER 21: TIME SERIES ECONOMETRICS: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS
 CHAPTER 21: TIME SERIES ECONOMETRICS: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS 21.1 A stochastic process is said to be weakly stationary if its mean and variance are constant over time and if the value of the covariance between
CHAPTER 21: TIME SERIES ECONOMETRICS: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS 21.1 A stochastic process is said to be weakly stationary if its mean and variance are constant over time and if the value of the covariance between
: œ Ö: =? À =ß> real numbers. œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example,! is translated to :)
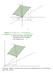 â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
STAT 3022 Spring 2007
 Simple Linear Regression Example These commands reproduce what we did in class. You should enter these in R and see what they do. Start by typing > set.seed(42) to reset the random number generator so
Simple Linear Regression Example These commands reproduce what we did in class. You should enter these in R and see what they do. Start by typing > set.seed(42) to reset the random number generator so
NEGATIVE z Scores. TABLE A-2 Standard Normal (z) Distribution: Cumulative Area from the LEFT. (continued)
 NEGATIVE z Score z 0 TALE A- Standard Normal (z) Ditribution: Cumulative Area from the LEFT z.00.01.0.03.04.05.06.07.08.09-3.50 and lower.0001-3.4.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.000-3.3.0005.0005.0005.0004.0004.0004.0004.0004.0004.0003-3..0007.0007.0006.0006.0006.0006.0006.0005.0005.0005-3.1.0010.0009.0009.0009.0008.0008.0008.0008.0007.0007-3.0.0013.0013.0013.001.001.0011.0011.0011.0010.0010
NEGATIVE z Score z 0 TALE A- Standard Normal (z) Ditribution: Cumulative Area from the LEFT z.00.01.0.03.04.05.06.07.08.09-3.50 and lower.0001-3.4.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.0003.000-3.3.0005.0005.0005.0004.0004.0004.0004.0004.0004.0003-3..0007.0007.0006.0006.0006.0006.0006.0005.0005.0005-3.1.0010.0009.0009.0009.0008.0008.0008.0008.0007.0007-3.0.0013.0013.0013.001.001.0011.0011.0011.0010.0010
Plate Tectonics and Earth s Structure
 Plate Tectonics and Earth s Structure Chapter Eight: Plate Tectonics Chapter Nine: Earthquakes Chapter Ten: Volcanoes Chapter Nine: Earthquakes 9.1 What is an Earthquake? 9.2 Seismic Waves 9.3 Measuring
Plate Tectonics and Earth s Structure Chapter Eight: Plate Tectonics Chapter Nine: Earthquakes Chapter Ten: Volcanoes Chapter Nine: Earthquakes 9.1 What is an Earthquake? 9.2 Seismic Waves 9.3 Measuring
Moment Generating Functions
 MATH 382 Moment Generating Functions Dr. Neal, WKU Definition. Let X be a random variable. The moment generating function (mgf) of X is the function M X : R R given by M X (t ) = E[e X t ], defined for
MATH 382 Moment Generating Functions Dr. Neal, WKU Definition. Let X be a random variable. The moment generating function (mgf) of X is the function M X : R R given by M X (t ) = E[e X t ], defined for
The WhatPower Function à An Introduction to Logarithms
 Classwork Work with your partner or group to solve each of the following equations for x. a. 2 # = 2 % b. 2 # = 2 c. 2 # = 6 d. 2 # 64 = 0 e. 2 # = 0 f. 2 %# = 64 Exploring the WhatPower Function with
Classwork Work with your partner or group to solve each of the following equations for x. a. 2 # = 2 % b. 2 # = 2 c. 2 # = 6 d. 2 # 64 = 0 e. 2 # = 0 f. 2 %# = 64 Exploring the WhatPower Function with
STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL Application of statistical techniques to The control of processes Ensure that process meet standards SPC is a process used to monitor standards by
STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL Application of statistical techniques to The control of processes Ensure that process meet standards SPC is a process used to monitor standards by
Richter Scale and Logarithms
 activity 7.1 Richter Scale and Logarithms In this activity, you will investigate earthquake data and explore the Richter scale as a measure of the intensity of an earthquake. You will consider how numbers
activity 7.1 Richter Scale and Logarithms In this activity, you will investigate earthquake data and explore the Richter scale as a measure of the intensity of an earthquake. You will consider how numbers
STAT Regression Methods
 STAT 501 - Regression Methods Unit 9 Examples Example 1: Quake Data Let y t = the annual number of worldwide earthquakes with magnitude greater than 7 on the Richter scale for n = 99 years. Figure 1 gives
STAT 501 - Regression Methods Unit 9 Examples Example 1: Quake Data Let y t = the annual number of worldwide earthquakes with magnitude greater than 7 on the Richter scale for n = 99 years. Figure 1 gives
A Study on the Power Functions of the Shewhart X Chart via Monte Carlo Simulation
 A Study on the Power Functions of the Shewhart X Chart via Monte Carlo Simulation M.B.C. Khoo Abstract The Shewhart X control chart is used to monitor shifts in the process mean. However, it is less sensitive
A Study on the Power Functions of the Shewhart X Chart via Monte Carlo Simulation M.B.C. Khoo Abstract The Shewhart X control chart is used to monitor shifts in the process mean. However, it is less sensitive
