STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
|
|
|
- Dora Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
2 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL Application of statistical techniques to The control of processes Ensure that process meet standards SPC is a process used to monitor standards by taking measurements and corrective action as a product or service is being produced.
3 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL All processes are subject to a certain degree of variability. Types of variability : Natural or common causes Special or assignable causes
4 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL SPC to measure performance of a process A process is said to be operating in statistical control when the only source of variation is common (natural) causes. Provides a statistical signal when assignable causes are present Detect and eliminate assignable causes of variation
5 NATURAL VARIATIONS Also called common causes Affect virtually all production processes Expected amount of variation Output measures follow a probability distribution For any distribution there is a measure of central tendency and dispersion If the distribution of outputs falls within acceptable limits, the process is said to be in control
6 ASSIGNABLE VARIATIONS Also called special causes of variation Generally this is some change in the process Variations that can be traced to a specific reason The objective is to discover when assignable causes are present Eliminate the bad causes Incorporate the good causes
7 Frequency SAMPLES To measure the process, we take samples and analyze the sample statistics following these steps (a) Samples of the product, say five boxes of cereal taken off the filling machine line, vary from each other in weight # # # # # # Each of these represents one sample of five boxes of cereal # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # Weight
8 Frequency SAMPLES To measure the process, we take samples and analyze the sample statistics following these steps (b) After enough samples are taken from a stable process, they form a pattern called a distribution The solid line represents the distribution Figure S6.1 Weight
9 Frequency SAMPLES To measure the process, we take samples and analyze the sample statistics following these steps (c) There are many types of distributions, including the normal (bell-shaped) distribution, but distributions do differ in terms of central tendency (mean), standard deviation or variance, and shape Central tendency Variation Shape Weight Weight Weight
10 Frequency SAMPLES To measure the process, we take samples and analyze the sample statistics following these steps (d) If only natural causes of variation are present, the output of a process forms a distribution that is stable over time and is predictable Weight Prediction Figure S6.1
11 Frequency SAMPLES To measure the process, we take samples and analyze the sample statistics following these steps (e) If assignable causes are present, the process output is not stable over time and is not predicable??????????????????? Prediction Weight Figure S6.1
12 CONTROL CHARTS Constructed from historical data, the purpose of control charts is to help distinguish between natural variations and variations due to assignable causes
13 PROCESS CONTROL Frequency (a) In statistical control and capable of producing within control limits Lower control limit Upper control limit (b) In statistical control but not capable of producing within control limits (c) Out of control Size (weight, length, speed, etc.)
14 CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM Regardless of the distribution of the population, the distribution of sample means drawn from the population will tend to follow a normal curve 1. The mean of the sampling distribution (x ) will be the same as the population mean m x = μ 2. The standard deviation of the sampling distribution (s x ) will equal the population standard deviation (s) divided by the square root of the sample size, n σ x = σ n
15 POPULATION AND SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS Three population distributions Beta Normal Distribution of sample means Mean of sample means = x Standard deviation of the sample means = s x = s n Uniform -3s x -2s x -1s x x +1s x +2s x +3s x 95.45% fall within ± 2s x 99.73% of all x fall within ± 3s x
16 SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION Sampling distribution of means Process distribution of means x = m (mean)
17 TYPES OF DATA Variables Characteristics that can take any real value May be in whole or in fractional numbers Continuous random variables Attributes Defect-related characteristics Classify products as either good or bad or count defects Categorical or discrete random variables
18 CONTROL CHARTS FOR VARIABLES For variables that have continuous dimensions Weight, speed, length, strength, etc. x-charts are to control the central tendency of the process R-charts are to control the dispersion of the process These two charts must be used together
19 SETTING CHART LIMITS For x-charts when we know s Upper Control limit UCL Lower Control limit LCL = x + zσ x = x zσ x where x = mean of the sample means or a target value set for the process z = number of normal standard deviations s x = standard deviation of the sample means = s/ n s = population standard deviation n = sample size
20 EXAMPLE 1 The weights of Oat Flakes within a large production lot are sampled each hour. Managers want to set control limits that include 99.73% of the sample means. Randomly select and weight 9 boxes each hour. Population standard deviation (σ) is known to be 1 ounce. Each of the boxes randomly selected in hours 1 through 12.
21 EXAMPLE 1: SETTING CONTROL LIMITS n = 9 Hour 1 Sample Weight of Number Oat Flakes Mean 16.1 s = 1 Hour Mean Hour Mean For 99.73% control limits, z = 3 UCL = x + zσ x = LCL = x zσ x = = 17 ozs = 15 ozs
22 EXAMPLE 1: SETTING CONTROL LIMITS Control Chart for sample of 9 boxes Out of control Variation due to assignable causes 17 = UCL 16 = Mean Variation due to natural causes 15 = LCL Sample number Out of control Variation due to assignable causes The means of recent sample averages falls outside the UCL and LCL of 17 and 15. The process is NOT in control
23 SETTING CHART LIMITS For R-Charts Upper Control limit UCL R Lower Control limit LCL R = D 4 R = D 3 R where R = average range of the samples D 3 and D 4 = control chart factors from Table
24 CONTROL CHART FACTORS Sample Size Mean Factor Upper Range Lower Range n A 2 D 4 D
25 EXAMPLE 2 The average range of a product at Clinton manufacturing is 5.3 pounds. With a sample size of 5, the owner wants to determine the UCL and LCL. From Table of Control Chart Factor n = 5 D 4 = D 3 = 0
26 EXAMPLE 2 : SETTING CONTROL LIMITS UCL R = D 4 R = (2.115)(5.3) = 11.2 pounds UCL = 11.2 LCL R = D 3 R = (0)(5.3) = 0 pounds Mean = 5.3 LCL = 0
27 MEAN AND RANGE CHARTS (a) These sampling distributions result in the charts below (Sampling mean is shifting upward but range is consistent) x-chart R-chart UCL LCL UCL LCL (x-chart detects shift in central tendency) (R-chart does not detect change in mean)
28 MEAN AND RANGE CHARTS (b) These sampling distributions result in the charts below (Sampling mean is constant but dispersion is increasing) x-chart R-chart UCL LCL UCL LCL (x-chart does not detect the increase in dispersion) (R-chart detects increase in dispersion)
29 CONTROL CHARTS FOR ATTRIBUTES For variables that are categorical Good/bad, yes/no, acceptable/unacceptable Measurement is typically counting defectives Charts may measure Percent defective (p-chart) Number of defects (c-chart)
30 CONTROL LIMITS FOR P-CHARTS Population will be a binomial distribution, but applying the Central Limit Theorem allows us to assume a normal distribution for the sample statistics UCL p = p + zσ p LCL p = p zσ p σ p = p(1 p) n where p = mean fraction defective in the sample z = number of standard deviations ^ s p = standard deviation of the sampling distribution n = sample size
31 EXAMPLE 3 Clerk at IIMS key in thousands of insurance records each day for a variety of client firms. The CEO wants to set control limits to include 99.73% of the random variation in data entry process when it is in control. Sample of work for 20 clerks are gathered. 100 records entered by each clerk are examine and the number of errors are counted. The fraction defective of each sample are computed.
32 EXAMPLE 3 : P-CHART FOR DATA ENTRY Sample Number Fraction Sample Number Fraction Number of Errors Defective Number of Errors Defective Total = 80
33 EXAMPLE 3 : SETTING CONTROL LIMITS p = total number of errors total number of records examined = 80 (100)(20) = 0.04 σ p = (0.04)(1 0.04) 100 = 0.02 UCL p = p + zσ p = = 0.1 LCL p = p zσ p = = 0 We cannot have a negative percent defective
34 Fraction defective EXAMPLE 3 : P-CHART FOR DATA ENTRY Sample number One data-entry clerk (no 17) is out of control. Possible assignable causes present UCL p = 0.10 p = 0.04 LCL p = 0.00 Need to examine that individual s work a bit more closely to see if a serious problem exists.
35 Fraction defective EXAMPLE 3 : P-CHART FOR DATA ENTRY Sample number UCL p = 0.10 p = 0.04 LCL p = 0.00 Two data-entry clerk (no 3 & 19) is reported no errors. Need to examine that individual s work if there are skills or processes that can be applied to other operators..
36 CONTROL LIMITS FOR C-CHARTS Population will be a Poisson distribution, but applying the Central Limit Theorem allows us to assume a normal distribution for the sample statistics UCL c = c + 3 LCL c = c 3 c c where c = mean number defective in the sample
37 EXAMPLE 4 TRC company receives several complaints per day about the behavior of its drivers. Over a 9-day period (days are the units of measure), the owner, received the following numbers of calls from irate passengers: 3, 0, 8, 9, 6, 7, 4, 9, 8 Total complaints = 54 The owner wants to compute 99.73% control limits
38 Number defective EXAMPLE 4: C-CHART c = 54 complaints/9 days = 6 complaints/day UCL c = c + 3 c = = LCL c = c - 3 c = = Day 6 7 UCL c = LCL c = 0 9 c = 6
39 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit Normal behavior. Process is in control.
40 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit One plot out above (or below). Investigate for cause. Process is out of control.
41 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit Trends in either direction, 5 plots. Investigate for cause of progressive change.
42 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit Two plots very near lower (or upper) control. Investigate for cause.
43 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit Run of 5 above (or below) central line. Investigate for cause.
44 PATTERNS IN CONTROL CHARTS Upper control limit Target Lower control limit Erratic behavior. Investigate.
Statistical Process Control
 S6 Statistical Process Control PowerPoint presentation to accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10e Principles of Operations Management, 8e PowerPoint slides by Jeff Heyl S6-1 Statistical
S6 Statistical Process Control PowerPoint presentation to accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10e Principles of Operations Management, 8e PowerPoint slides by Jeff Heyl S6-1 Statistical
Statistical Process Control SCM Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
 S6 Statistical Process Control SCM 352 Outline Statistical Quality Control Common causes vs. assignable causes Different types of data attributes and variables Central limit theorem SPC charts Control
S6 Statistical Process Control SCM 352 Outline Statistical Quality Control Common causes vs. assignable causes Different types of data attributes and variables Central limit theorem SPC charts Control
Statistical Process Control
 Statistical Process Control Outline Statistical Process Control (SPC) Process Capability Acceptance Sampling 2 Learning Objectives When you complete this supplement you should be able to : S6.1 Explain
Statistical Process Control Outline Statistical Process Control (SPC) Process Capability Acceptance Sampling 2 Learning Objectives When you complete this supplement you should be able to : S6.1 Explain
Statistical quality control (SQC)
 Statistical quality control (SQC) The application of statistical techniques to measure and evaluate the quality of a product, service, or process. Two basic categories: I. Statistical process control (SPC):
Statistical quality control (SQC) The application of statistical techniques to measure and evaluate the quality of a product, service, or process. Two basic categories: I. Statistical process control (SPC):
Statistical Process Control
 Statistical Process Control What is a process? Inputs PROCESS Outputs A process can be described as a transformation of set of inputs into desired outputs. Types of Measures Measures where the metric is
Statistical Process Control What is a process? Inputs PROCESS Outputs A process can be described as a transformation of set of inputs into desired outputs. Types of Measures Measures where the metric is
Chapter 12: Inference about One Population
 Chapter 1: Inference about One Population 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we presented the statistical inference methods used when the problem objective is to describe a single population. Sections 1.
Chapter 1: Inference about One Population 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we presented the statistical inference methods used when the problem objective is to describe a single population. Sections 1.
Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD
 Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD Dr. Jitesh J. Thakkar Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Instruction Total No.
Assignment 7 (Solution) Control Charts, Process capability and QFD Dr. Jitesh J. Thakkar Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Instruction Total No.
Normalizing the I Control Chart
 Percent of Count Trade Deficit Normalizing the I Control Chart Dr. Wayne Taylor 80 Chart of Count 30 70 60 50 40 18 30 T E 20 10 0 D A C B E Defect Type Percent within all data. Version: September 30,
Percent of Count Trade Deficit Normalizing the I Control Chart Dr. Wayne Taylor 80 Chart of Count 30 70 60 50 40 18 30 T E 20 10 0 D A C B E Defect Type Percent within all data. Version: September 30,
spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand
 spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand BENEFITS of SPC Monitors and provides feedback for keeping processes in control. Triggers when a problem occurs Differentiates
spc Statistical process control Key Quality characteristic :Forecast Error for demand BENEFITS of SPC Monitors and provides feedback for keeping processes in control. Triggers when a problem occurs Differentiates
Selection of Variable Selecting the right variable for a control chart means understanding the difference between discrete and continuous data.
 Statistical Process Control, or SPC, is a collection of tools that allow a Quality Engineer to ensure that their process is in control, using statistics. Benefit of SPC The primary benefit of a control
Statistical Process Control, or SPC, is a collection of tools that allow a Quality Engineer to ensure that their process is in control, using statistics. Benefit of SPC The primary benefit of a control
Process Performance and Quality
 Chapter 5 Process Performance and Quality Evaluating Process Performance Identify opportunity 1 Define scope 2 Document process 3 Figure 5.1 Implement changes 6 Redesign process 5 Evaluate performance
Chapter 5 Process Performance and Quality Evaluating Process Performance Identify opportunity 1 Define scope 2 Document process 3 Figure 5.1 Implement changes 6 Redesign process 5 Evaluate performance
Statistical Process Control
 Chapter 3 Statistical Process Control 3.1 Introduction Operations managers are responsible for developing and maintaining the production processes that deliver quality products and services. Once the production
Chapter 3 Statistical Process Control 3.1 Introduction Operations managers are responsible for developing and maintaining the production processes that deliver quality products and services. Once the production
Quality. Statistical Process Control: Control Charts Process Capability DEG/FHC 1
 Quality Statistical Process Control: Control Charts Process Capability DEG/FHC 1 SPC Traditional view: Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a statistical method of separating variation resulting from special
Quality Statistical Process Control: Control Charts Process Capability DEG/FHC 1 SPC Traditional view: Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a statistical method of separating variation resulting from special
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER PROBABILITY 7 (The Poisson distribution) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 19.7 PROBABILITY 7 (The Poisson distribution) by A.J.Hobson 19.7.1 The theory 19.7.2 Exercises 19.7.3 Answers to exercises UNIT 19.7 - PROBABILITY 7 THE POISSON DISTRIBUTION
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 19.7 PROBABILITY 7 (The Poisson distribution) by A.J.Hobson 19.7.1 The theory 19.7.2 Exercises 19.7.3 Answers to exercises UNIT 19.7 - PROBABILITY 7 THE POISSON DISTRIBUTION
Statistics Statistical Process Control & Control Charting
 Statistics Statistical Process Control & Control Charting Cayman Systems International 1/22/98 1 Recommended Statistical Course Attendance Basic Business Office, Staff, & Management Advanced Business Selected
Statistics Statistical Process Control & Control Charting Cayman Systems International 1/22/98 1 Recommended Statistical Course Attendance Basic Business Office, Staff, & Management Advanced Business Selected
SMTX1014- PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS UNIT V ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 SMTX1014- PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS UNIT V ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL Introduction and Process Control Control Charts for X and R Control Charts for X and S p Chart np Chart c Chart
SMTX1014- PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS UNIT V ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL Introduction and Process Control Control Charts for X and R Control Charts for X and S p Chart np Chart c Chart
Unit 22: Sampling Distributions
 Unit 22: Sampling Distributions Summary of Video If we know an entire population, then we can compute population parameters such as the population mean or standard deviation. However, we generally don
Unit 22: Sampling Distributions Summary of Video If we know an entire population, then we can compute population parameters such as the population mean or standard deviation. However, we generally don
Chapter 10: Statistical Quality Control
 Chapter 10: Statistical Quality Control 1 Introduction As the marketplace for industrial goods has become more global, manufacturers have realized that quality and reliability of their products must be
Chapter 10: Statistical Quality Control 1 Introduction As the marketplace for industrial goods has become more global, manufacturers have realized that quality and reliability of their products must be
Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control
 Chapter 6 Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control 6.0 Introduction In statistical process control Poisson distribution and binomial distribution play important role. There are situations wherein
Chapter 6 Zero-Inflated Models in Statistical Process Control 6.0 Introduction In statistical process control Poisson distribution and binomial distribution play important role. There are situations wherein
Known probability distributions
 Known probability distributions Engineers frequently wor with data that can be modeled as one of several nown probability distributions. Being able to model the data allows us to: model real systems design
Known probability distributions Engineers frequently wor with data that can be modeled as one of several nown probability distributions. Being able to model the data allows us to: model real systems design
1.0 Continuous Distributions. 5.0 Shapes of Distributions. 6.0 The Normal Curve. 7.0 Discrete Distributions. 8.0 Tolerances. 11.
 Chapter 4 Statistics 45 CHAPTER 4 BASIC QUALITY CONCEPTS 1.0 Continuous Distributions.0 Measures of Central Tendency 3.0 Measures of Spread or Dispersion 4.0 Histograms and Frequency Distributions 5.0
Chapter 4 Statistics 45 CHAPTER 4 BASIC QUALITY CONCEPTS 1.0 Continuous Distributions.0 Measures of Central Tendency 3.0 Measures of Spread or Dispersion 4.0 Histograms and Frequency Distributions 5.0
[ z = 1.48 ; accept H 0 ]
![[ z = 1.48 ; accept H 0 ] [ z = 1.48 ; accept H 0 ]](/thumbs/75/71513647.jpg) CH 13 TESTING OF HYPOTHESIS EXAMPLES Example 13.1 Indicate the type of errors committed in the following cases: (i) H 0 : µ = 500; H 1 : µ 500. H 0 is rejected while H 0 is true (ii) H 0 : µ = 500; H 1
CH 13 TESTING OF HYPOTHESIS EXAMPLES Example 13.1 Indicate the type of errors committed in the following cases: (i) H 0 : µ = 500; H 1 : µ 500. H 0 is rejected while H 0 is true (ii) H 0 : µ = 500; H 1
Techniques for Improving Process and Product Quality in the Wood Products Industry: An Overview of Statistical Process Control
 1 Techniques for Improving Process and Product Quality in the Wood Products Industry: An Overview of Statistical Process Control Scott Leavengood Oregon State University Extension Service The goal: $ 2
1 Techniques for Improving Process and Product Quality in the Wood Products Industry: An Overview of Statistical Process Control Scott Leavengood Oregon State University Extension Service The goal: $ 2
STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL - THE IMPORTANCE OF USING CALIBRATED MEASUREMENT EQUIPMENT. CASE STUDY
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5376 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5376 STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL
Chapter 5. Means and Variances
 1 Chapter 5 Means and Variances Our discussion of probability has taken us from a simple classical view of counting successes relative to total outcomes and has brought us to the idea of a probability
1 Chapter 5 Means and Variances Our discussion of probability has taken us from a simple classical view of counting successes relative to total outcomes and has brought us to the idea of a probability
Sampling (Statistics)
 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 304: Bio-Statistics Random Sampling and Sampling Distributions Dr. Ayman Eldeib Fall 2018 Sampling (Statistics) Sampling is that part of statistical practice
Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 304: Bio-Statistics Random Sampling and Sampling Distributions Dr. Ayman Eldeib Fall 2018 Sampling (Statistics) Sampling is that part of statistical practice
Describing distributions with numbers
 Describing distributions with numbers A large number or numerical methods are available for describing quantitative data sets. Most of these methods measure one of two data characteristics: The central
Describing distributions with numbers A large number or numerical methods are available for describing quantitative data sets. Most of these methods measure one of two data characteristics: The central
OHSU OGI Class ECE-580-DOE :Statistical Process Control and Design of Experiments Steve Brainerd Basic Statistics Sample size?
 ECE-580-DOE :Statistical Process Control and Design of Experiments Steve Basic Statistics Sample size? Sample size determination: text section 2-4-2 Page 41 section 3-7 Page 107 Website::http://www.stat.uiowa.edu/~rlenth/Power/
ECE-580-DOE :Statistical Process Control and Design of Experiments Steve Basic Statistics Sample size? Sample size determination: text section 2-4-2 Page 41 section 3-7 Page 107 Website::http://www.stat.uiowa.edu/~rlenth/Power/
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Discrete Probability Distributions EGR 260 R. Van Til Industrial & Systems Engineering Dept. Copyright 2013. Robert P. Van Til. All rights reserved. 1 What s It All About? The behavior of many random processes
Discrete Probability Distributions EGR 260 R. Van Til Industrial & Systems Engineering Dept. Copyright 2013. Robert P. Van Til. All rights reserved. 1 What s It All About? The behavior of many random processes
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081
 Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
STAT509: Discrete Random Variable
 University of South Carolina September 16, 2014 Motivation So far, we have already known how to calculate probabilities of events. Suppose we toss a fair coin three times, we know that the probability
University of South Carolina September 16, 2014 Motivation So far, we have already known how to calculate probabilities of events. Suppose we toss a fair coin three times, we know that the probability
An-Najah National University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Department. Course : Quantitative Methods (65211)
 An-Najah National University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Department Course : Quantitative Methods (65211) Instructor: Eng. Tamer Haddad 2 nd Semester 2009/2010 Chapter 3 Discrete Random
An-Najah National University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Department Course : Quantitative Methods (65211) Instructor: Eng. Tamer Haddad 2 nd Semester 2009/2010 Chapter 3 Discrete Random
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
 Statistical Process Control (SPC) Can Be Applied To Anything Measured Using Numbers Goal: To Make A Process Behave the Way We Want It to Behave Reality: It s impossible to control a process without tools.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) Can Be Applied To Anything Measured Using Numbers Goal: To Make A Process Behave the Way We Want It to Behave Reality: It s impossible to control a process without tools.
20 Hypothesis Testing, Part I
 20 Hypothesis Testing, Part I Bob has told Alice that the average hourly rate for a lawyer in Virginia is $200 with a standard deviation of $50, but Alice wants to test this claim. If Bob is right, she
20 Hypothesis Testing, Part I Bob has told Alice that the average hourly rate for a lawyer in Virginia is $200 with a standard deviation of $50, but Alice wants to test this claim. If Bob is right, she
CIVL /8904 T R A F F I C F L O W T H E O R Y L E C T U R E - 8
 CIVL - 7904/8904 T R A F F I C F L O W T H E O R Y L E C T U R E - 8 Chi-square Test How to determine the interval from a continuous distribution I = Range 1 + 3.322(logN) I-> Range of the class interval
CIVL - 7904/8904 T R A F F I C F L O W T H E O R Y L E C T U R E - 8 Chi-square Test How to determine the interval from a continuous distribution I = Range 1 + 3.322(logN) I-> Range of the class interval
Quality Control & Statistical Process Control (SPC)
 Quality Control & Statistical Process Control (SPC) DR. RON FRICKER PROFESSOR & HEAD, DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS DATAWORKS CONFERENCE, MARCH 22, 2018 Agenda Some Terminology & Background SPC Methods & Philosophy
Quality Control & Statistical Process Control (SPC) DR. RON FRICKER PROFESSOR & HEAD, DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS DATAWORKS CONFERENCE, MARCH 22, 2018 Agenda Some Terminology & Background SPC Methods & Philosophy
IE 361 Module 24. Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring)
 IE 361 Module 24 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
IE 361 Module 24 Introduction to Shewhart Control Charting Part 1 (Statistical Process Control, or More Helpfully: Statistical Process Monitoring) Reading: Section 3.1 Statistical Methods for Quality Assurance
MAT2377. Ali Karimnezhad. Version December 13, Ali Karimnezhad
 MAT2377 Ali Karimnezhad Version December 13, 2016 Ali Karimnezhad Comments These slides cover material from Chapter 4. In class, I may use a blackboard. I recommend reading these slides before you come
MAT2377 Ali Karimnezhad Version December 13, 2016 Ali Karimnezhad Comments These slides cover material from Chapter 4. In class, I may use a blackboard. I recommend reading these slides before you come
II. The Binomial Distribution
 88 CHAPTER 4 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 進佳數學團隊 Dr. Herbert Lam 林康榮博士 HKDSE Mathematics M1 II. The Binomial Distribution 1. Bernoulli distribution A Bernoulli eperiment results in any one of two possible
88 CHAPTER 4 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 進佳數學團隊 Dr. Herbert Lam 林康榮博士 HKDSE Mathematics M1 II. The Binomial Distribution 1. Bernoulli distribution A Bernoulli eperiment results in any one of two possible
CHAPTER 7. Parameters are numerical descriptive measures for populations.
 CHAPTER 7 Introduction Parameters are numerical descriptive measures for populations. For the normal distribution, the location and shape are described by µ and σ. For a binomial distribution consisting
CHAPTER 7 Introduction Parameters are numerical descriptive measures for populations. For the normal distribution, the location and shape are described by µ and σ. For a binomial distribution consisting
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Sem. 1 Review Ch. 1-3
 AP Stats Sem. 1 Review Ch. 1-3 Name 1. You measure the age, marital status and earned income of an SRS of 1463 women. The number and type of variables you have measured is a. 1463; all quantitative. b.
AP Stats Sem. 1 Review Ch. 1-3 Name 1. You measure the age, marital status and earned income of an SRS of 1463 women. The number and type of variables you have measured is a. 1463; all quantitative. b.
Chi-Squared Tests. Semester 1. Chi-Squared Tests
 Semester 1 Goodness of Fit Up to now, we have tested hypotheses concerning the values of population parameters such as the population mean or proportion. We have not considered testing hypotheses about
Semester 1 Goodness of Fit Up to now, we have tested hypotheses concerning the values of population parameters such as the population mean or proportion. We have not considered testing hypotheses about
Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam
 Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam Instructions: The following sample exam was given several quarters ago in Stat 427. The same topics were covered in the class that year. This sample exam is meant to be
Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam Instructions: The following sample exam was given several quarters ago in Stat 427. The same topics were covered in the class that year. This sample exam is meant to be
Percent
 Data Entry Spreadsheet to Create a C Chart Date Observations Mean UCL +3s LCL -3s +2s -2s +1s -1s CHART --> 01/01/00 2.00 3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00 01/02/00-3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00
Data Entry Spreadsheet to Create a C Chart Date Observations Mean UCL +3s LCL -3s +2s -2s +1s -1s CHART --> 01/01/00 2.00 3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00 01/02/00-3.00 8.20 0.00 6.46 0.00 4.73 0.00
Chapter 8: Regression Models with Qualitative Predictors
 Chapter 8: Regression Models with Qualitative Predictors Some predictors may be binary (e.g., male/female) or otherwise categorical (e.g., small/medium/large). These typically enter the regression model
Chapter 8: Regression Models with Qualitative Predictors Some predictors may be binary (e.g., male/female) or otherwise categorical (e.g., small/medium/large). These typically enter the regression model
STA 584 Supplementary Examples (not to be graded) Fall, 2003
 Page 1 of 8 Central Michigan University Department of Mathematics STA 584 Supplementary Examples (not to be graded) Fall, 003 1. (a) If A and B are independent events, P(A) =.40 and P(B) =.70, find (i)
Page 1 of 8 Central Michigan University Department of Mathematics STA 584 Supplementary Examples (not to be graded) Fall, 003 1. (a) If A and B are independent events, P(A) =.40 and P(B) =.70, find (i)
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. LO5 Describe and compute probabilities for a binomial distribution.
Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. LO5 Describe and compute probabilities for a binomial distribution.
Sample Problems for the Final Exam
 Sample Problems for the Final Exam 1. Hydraulic landing assemblies coming from an aircraft rework facility are each inspected for defects. Historical records indicate that 8% have defects in shafts only,
Sample Problems for the Final Exam 1. Hydraulic landing assemblies coming from an aircraft rework facility are each inspected for defects. Historical records indicate that 8% have defects in shafts only,
Management Programme. MS-08: Quantitative Analysis for Managerial Applications
 MS-08 Management Programme ASSIGNMENT SECOND SEMESTER 2013 MS-08: Quantitative Analysis for Managerial Applications School of Management Studies INDIRA GANDHI NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY MAIDAN GARHI, NEW
MS-08 Management Programme ASSIGNMENT SECOND SEMESTER 2013 MS-08: Quantitative Analysis for Managerial Applications School of Management Studies INDIRA GANDHI NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY MAIDAN GARHI, NEW
4. Probability of an event A for equally likely outcomes:
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions
 Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions 2.11 Definition of random variable 3.1 Definition of a discrete random variable 3.2 Probability distribution of a discrete random
Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions 2.11 Definition of random variable 3.1 Definition of a discrete random variable 3.2 Probability distribution of a discrete random
Using Minitab to construct Attribute charts Control Chart
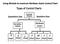 Using Minitab to construct Attribute charts Control Chart Attribute Control Chart Attribute control charts are the charts that plot nonconformities (defects) or nonconforming units (defectives). A nonconformity
Using Minitab to construct Attribute charts Control Chart Attribute Control Chart Attribute control charts are the charts that plot nonconformities (defects) or nonconforming units (defectives). A nonconformity
Test 2 VERSION A STAT 3090 Fall 2017
 Multiple Choice: (Questions 1 20) Answer the following questions on the scantron provided using a #2 pencil. Bubble the response that best answers the question. Each multiple choice correct response is
Multiple Choice: (Questions 1 20) Answer the following questions on the scantron provided using a #2 pencil. Bubble the response that best answers the question. Each multiple choice correct response is
Aflatoxin Analysis: Uncertainty Statistical Process Control Sources of Variability. COMESA Session Five: Technical Courses November 18
 Aflatoxin Analysis: Uncertainty Statistical Process Control Sources of Variability COMESA Session Five: Technical Courses November 18 Uncertainty SOURCES OF VARIABILITY Uncertainty Budget The systematic
Aflatoxin Analysis: Uncertainty Statistical Process Control Sources of Variability COMESA Session Five: Technical Courses November 18 Uncertainty SOURCES OF VARIABILITY Uncertainty Budget The systematic
Glossary. The ISI glossary of statistical terms provides definitions in a number of different languages:
 Glossary The ISI glossary of statistical terms provides definitions in a number of different languages: http://isi.cbs.nl/glossary/index.htm Adjusted r 2 Adjusted R squared measures the proportion of the
Glossary The ISI glossary of statistical terms provides definitions in a number of different languages: http://isi.cbs.nl/glossary/index.htm Adjusted r 2 Adjusted R squared measures the proportion of the
Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions
 Continuous Probability Distributions Learning Objectives 1. Understand the difference between how probabilities are computed for discrete and continuous random variables. 2. Know how to compute probability
Continuous Probability Distributions Learning Objectives 1. Understand the difference between how probabilities are computed for discrete and continuous random variables. 2. Know how to compute probability
AP Final Review II Exploring Data (20% 30%)
 AP Final Review II Exploring Data (20% 30%) Quantitative vs Categorical Variables Quantitative variables are numerical values for which arithmetic operations such as means make sense. It is usually a measure
AP Final Review II Exploring Data (20% 30%) Quantitative vs Categorical Variables Quantitative variables are numerical values for which arithmetic operations such as means make sense. It is usually a measure
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions
 Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions James V. Lambers Department of Mathematics The University of Southern Mississippi James V. Lambers Statistical Data Analysis
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 3: Probability Distributions James V. Lambers Department of Mathematics The University of Southern Mississippi James V. Lambers Statistical Data Analysis
CHAPTER 18 SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION MODELS STAT 203
 1 CHAPTER 18 SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION MODELS STAT 203 Outline 2 Sampling Distribution for Proportions Sample Proportions The mean The standard deviation The Distribution Model Assumptions and Conditions Sampling
1 CHAPTER 18 SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION MODELS STAT 203 Outline 2 Sampling Distribution for Proportions Sample Proportions The mean The standard deviation The Distribution Model Assumptions and Conditions Sampling
3 Continuous Random Variables
 Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
1. Summarize the sample categorical data by creating a frequency table and bar graph. Y Y N Y N N Y Y Y N Y N N N Y Y Y N Y Y
 Lesson 2 1. Summarize the sample categorical data by creating a frequency table and bar graph. Y Y N Y N N Y Y Y N Y N N N Y Y Y N Y Y 2. Explain sample quantitative data summary using CUSS. 3. Sketch
Lesson 2 1. Summarize the sample categorical data by creating a frequency table and bar graph. Y Y N Y N N Y Y Y N Y N N N Y Y Y N Y Y 2. Explain sample quantitative data summary using CUSS. 3. Sketch
Section II: Assessing Chart Performance. (Jim Benneyan)
 Section II: Assessing Chart Performance (Jim Benneyan) 1 Learning Objectives Understand concepts of chart performance Two types of errors o Type 1: Call an in-control process out-of-control o Type 2: Call
Section II: Assessing Chart Performance (Jim Benneyan) 1 Learning Objectives Understand concepts of chart performance Two types of errors o Type 1: Call an in-control process out-of-control o Type 2: Call
Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA. Dec. 6, 2002
 Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA Dec. 6, 2002 Control Chart for Number of Defectives Sometimes, more convenient to make chart by plotting d rather than p. In particular, plotting d appropriate if
Lecture #39 (tape #39) Vishesh Kumar TA Dec. 6, 2002 Control Chart for Number of Defectives Sometimes, more convenient to make chart by plotting d rather than p. In particular, plotting d appropriate if
Our Experience With Westgard Rules
 Our Experience With Westgard Rules Statistical Process Control Wikipedia Is a method of quality control which uses statistical methods. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring
Our Experience With Westgard Rules Statistical Process Control Wikipedia Is a method of quality control which uses statistical methods. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring
A Theoretically Appropriate Poisson Process Monitor
 International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 8, No. 4, July, 2012, pp. 457-461. RAMS Consultants Printed in India A Theoretically Appropriate Poisson Process Monitor RYAN BLACK and JUSTIN
International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 8, No. 4, July, 2012, pp. 457-461. RAMS Consultants Printed in India A Theoretically Appropriate Poisson Process Monitor RYAN BLACK and JUSTIN
AP Statistics Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Test
 Class: Date: AP Statistics Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The central limit theorem refers to which of
Class: Date: AP Statistics Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The central limit theorem refers to which of
SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name
 SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name 1. Mark the following statements True T or False F. (6 points -2 each) T A. A process is out of control if at a particular point in time the reading is more than 3 standard deviations
SMAM 314 Exam 3d Name 1. Mark the following statements True T or False F. (6 points -2 each) T A. A process is out of control if at a particular point in time the reading is more than 3 standard deviations
Rate-Quality Control Method of Identifying Hazardous Road Locations
 44 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1542 Rate-Quality Control Method of Identifying Hazardous Road Locations ROBERT W. STOKES AND MADANIYO I. MUTABAZI A brief historical perspective on the development of
44 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1542 Rate-Quality Control Method of Identifying Hazardous Road Locations ROBERT W. STOKES AND MADANIYO I. MUTABAZI A brief historical perspective on the development of
Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions
 Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions 1 3.4-3 The Binomial random variable The Binomial random variable is related to binomial experiments (Def 3.6) 1. The experiment
Chapter 3. Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions 1 3.4-3 The Binomial random variable The Binomial random variable is related to binomial experiments (Def 3.6) 1. The experiment
Topics for Today. Sampling Distribution. The Central Limit Theorem. Stat203 Page 1 of 28 Fall 2011 Week 5 Lecture 2
 Topics for Today Sampling Distribution The Central Limit Theorem Stat203 Page 1 of 28 Law of Large Numbers Draw at from any population with mean μ. As the number of individuals, the mean,, of the sample
Topics for Today Sampling Distribution The Central Limit Theorem Stat203 Page 1 of 28 Law of Large Numbers Draw at from any population with mean μ. As the number of individuals, the mean,, of the sample
Introduction to Estimation. Martina Litschmannová K210
 Introduction to Estimation Martina Litschmannová martina.litschmannova@vsb.cz K210 Populations vs. Sample A population includes each element from the set of observations that can be made. A sample consists
Introduction to Estimation Martina Litschmannová martina.litschmannova@vsb.cz K210 Populations vs. Sample A population includes each element from the set of observations that can be made. A sample consists
2DI90 Probability & Statistics. 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR
 2DI90 Probability & Statistics 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR Recap - Random Variables ( 2.8 MR)! Example: X is the random variable corresponding to the temperature of the room at time t. x is the measured temperature
2DI90 Probability & Statistics 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR Recap - Random Variables ( 2.8 MR)! Example: X is the random variable corresponding to the temperature of the room at time t. x is the measured temperature
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability
 Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081
 Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
Statistical Quality Control - Stat 3081 Awol S. Department of Statistics College of Computing & Informatics Haramaya University Dire Dawa, Ethiopia March 2015 Introduction Industrial Statistics and Quality
Duration of online examination will be of 1 Hour 20 minutes (80 minutes).
 Program Name: SC Subject: Production and Operations Management Assessment Name: POM - Exam Weightage: 70 Total Marks: 70 Duration: 80 mins Online Examination: Online examination is a Computer based examination.
Program Name: SC Subject: Production and Operations Management Assessment Name: POM - Exam Weightage: 70 Total Marks: 70 Duration: 80 mins Online Examination: Online examination is a Computer based examination.
SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS
 SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS 1. Form the differential equation of the family of curves = + where a and b are parameters. 2. Find the differential equation by eliminating
SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS 1. Form the differential equation of the family of curves = + where a and b are parameters. 2. Find the differential equation by eliminating
A New Demerit Control Chart for Monitoring the Quality of Multivariate Poisson Processes. By Jeh-Nan Pan Chung-I Li Min-Hung Huang
 Athens Journal of Technology and Engineering X Y A New Demerit Control Chart for Monitoring the Quality of Multivariate Poisson Processes By Jeh-Nan Pan Chung-I Li Min-Hung Huang This study aims to develop
Athens Journal of Technology and Engineering X Y A New Demerit Control Chart for Monitoring the Quality of Multivariate Poisson Processes By Jeh-Nan Pan Chung-I Li Min-Hung Huang This study aims to develop
Basic Statistics Made Easy
 Basic Statistics Made Easy Victor R. Prybutok, Ph.D., CQE, CQA, CMQ/OE, PSTAT Regents Professor of Decision Sciences, UNT Dean and Vice Provost, Toulouse Graduate School, UNT 13 October 2017 Agenda Statistics
Basic Statistics Made Easy Victor R. Prybutok, Ph.D., CQE, CQA, CMQ/OE, PSTAT Regents Professor of Decision Sciences, UNT Dean and Vice Provost, Toulouse Graduate School, UNT 13 October 2017 Agenda Statistics
Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions
 Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions Chong Ma Department of Statistics University of South Carolina chongm@email.sc.edu January 18, 2017 Chong Ma (Statistics, USC) STAT 509 Spring
Statistics for Engineers Lecture 2 Discrete Distributions Chong Ma Department of Statistics University of South Carolina chongm@email.sc.edu January 18, 2017 Chong Ma (Statistics, USC) STAT 509 Spring
Mechanical Engineering 101
 Mechanical Engineering 101 University of California, Berkeley Lecture #1 1 Today s lecture Statistical Process Control Process capability Mean shift Control charts eading: pp. 373-383 .Precision 3 Process
Mechanical Engineering 101 University of California, Berkeley Lecture #1 1 Today s lecture Statistical Process Control Process capability Mean shift Control charts eading: pp. 373-383 .Precision 3 Process
Math 2311 Test 1 Review. 1. State whether each situation is categorical or quantitative. If quantitative, state whether it s discrete or continuous.
 Math 2311 Test 1 Review Know all definitions! 1. State whether each situation is categorical or quantitative. If quantitative, state whether it s discrete or continuous. a. The amount a person grew (in
Math 2311 Test 1 Review Know all definitions! 1. State whether each situation is categorical or quantitative. If quantitative, state whether it s discrete or continuous. a. The amount a person grew (in
Chapter. The Normal Probability Distribution 7/24/2011. Section 7.1 Properties of the Normal Distribution
 Chapter The Normal Probability Distribution 3 7 Section 7.1 Properties of the Normal Distribution 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights 2010 reserved Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved 7-2 Illustrating
Chapter The Normal Probability Distribution 3 7 Section 7.1 Properties of the Normal Distribution 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights 2010 reserved Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved 7-2 Illustrating
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Calculator Usage 207 HOW TO USE TI-83, TI-83 PLUS, TI-84 PLUS CALCULATORS FOR STATISTICS CALCULATIONS shows it is an actual calculator key to press 1. Using LISTS to Calculate Mean,
Foundations of Math 11 Calculator Usage 207 HOW TO USE TI-83, TI-83 PLUS, TI-84 PLUS CALCULATORS FOR STATISTICS CALCULATIONS shows it is an actual calculator key to press 1. Using LISTS to Calculate Mean,
PASS Sample Size Software. Poisson Regression
 Chapter 870 Introduction Poisson regression is used when the dependent variable is a count. Following the results of Signorini (99), this procedure calculates power and sample size for testing the hypothesis
Chapter 870 Introduction Poisson regression is used when the dependent variable is a count. Following the results of Signorini (99), this procedure calculates power and sample size for testing the hypothesis
a b *c d Correct Answer Reply: ASQ CQE A-90 Incorrect Answer Reply: = C *(0.40) *(0.60) =
 ConteSolutions 2017 OceanSpray June 7, 2017 Quality Tools Session 1 1-009 Question A process is producing material which is 40 percent defective. Four pieces are selected at random for inspection. What
ConteSolutions 2017 OceanSpray June 7, 2017 Quality Tools Session 1 1-009 Question A process is producing material which is 40 percent defective. Four pieces are selected at random for inspection. What
STATISTICS AND PRINTING: APPLICATIONS OF SPC AND DOE TO THE WEB OFFSET PRINTING INDUSTRY. A Project. Presented. to the Faculty of
 STATISTICS AND PRINTING: APPLICATIONS OF SPC AND DOE TO THE WEB OFFSET PRINTING INDUSTRY A Project Presented to the Faculty of California State University, Dominguez Hills In Partial Fulfillment of the
STATISTICS AND PRINTING: APPLICATIONS OF SPC AND DOE TO THE WEB OFFSET PRINTING INDUSTRY A Project Presented to the Faculty of California State University, Dominguez Hills In Partial Fulfillment of the
2014 SM4 Revision Questions Distributions
 2014 SM4 Revision Questions Distributions Normal Q1. Professor Halen has 184 students in his college mathematics class. The scores on the semester exam are normally distributed with a mean of 72.3 and
2014 SM4 Revision Questions Distributions Normal Q1. Professor Halen has 184 students in his college mathematics class. The scores on the semester exam are normally distributed with a mean of 72.3 and
Design and Optimize Sample Plans at The Dow Chemical Company
 Design and Optimize Sample Plans at The Dow Chemical Company Swee-Teng Chin and Leo Chiang Analytical Technology Center The Dow Chemical Company September 12, 2011 Introduction The Dow Chemical Company
Design and Optimize Sample Plans at The Dow Chemical Company Swee-Teng Chin and Leo Chiang Analytical Technology Center The Dow Chemical Company September 12, 2011 Introduction The Dow Chemical Company
Session XIV. Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart
 Session XIV Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart The P Chart The P Chart is used for data that consist of the proportion of the number of occurrences of an event to the total number of occurrences. It
Session XIV Control Charts For Attributes P-Chart The P Chart The P Chart is used for data that consist of the proportion of the number of occurrences of an event to the total number of occurrences. It
Chapter 3: Discrete Random Variable
 Chapter 3: Discrete Random Variable Shiwen Shen University of South Carolina 2017 Summer 1 / 63 Random Variable Definition: A random variable is a function from a sample space S into the real numbers.
Chapter 3: Discrete Random Variable Shiwen Shen University of South Carolina 2017 Summer 1 / 63 Random Variable Definition: A random variable is a function from a sample space S into the real numbers.
Statistical Quality Control In The Production Of Pepsi Drinks
 Statistical Quality Control In The Production Of Pepsi Drins Lasisi K. E and 2 Abdulazeez K. A Mathematical Sciences, Abubaar Tafawa Balewa University, P.M.B.0248, Bauchi, Nigeria 2 Federal College of
Statistical Quality Control In The Production Of Pepsi Drins Lasisi K. E and 2 Abdulazeez K. A Mathematical Sciences, Abubaar Tafawa Balewa University, P.M.B.0248, Bauchi, Nigeria 2 Federal College of
ISyE 512 Chapter 7. Control Charts for Attributes. Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu. Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison
 ISyE 512 Chapter 7 Control Charts for Attributes Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering
ISyE 512 Chapter 7 Control Charts for Attributes Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering
Know why the real and complex numbers are each a field, and that particular rings are not fields (e.g., integers, polynomial rings, matrix rings)
 COMPETENCY 1.0 ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Know why the real and complex numbers are each a field, and that particular rings are not fields (e.g., integers, polynomial rings, matrix rings)
COMPETENCY 1.0 ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Know why the real and complex numbers are each a field, and that particular rings are not fields (e.g., integers, polynomial rings, matrix rings)
Probability and Statistics for Engineers
 Probability and Statistics for Engineers Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Ruochen Liu Ruochenliu@xidian.edu.cn Institute of Intelligent Information Processing, Xidian University Outline Random variables
Probability and Statistics for Engineers Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Ruochen Liu Ruochenliu@xidian.edu.cn Institute of Intelligent Information Processing, Xidian University Outline Random variables
Performance of X-Bar Chart Associated With Mean Deviation under Three Delta Control Limits and Six Delta Initiatives
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (I) PP 12-16 www.iosrjen.org Performance of X-Bar Chart Associated With Mean Deviation under
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 08, Issue 7 (July. 2018), V (I) PP 12-16 www.iosrjen.org Performance of X-Bar Chart Associated With Mean Deviation under
STATISTICS ( CODE NO. 08 ) PAPER I PART - I
 STATISTICS ( CODE NO. 08 ) PAPER I PART - I 1. Descriptive Statistics Types of data - Concepts of a Statistical population and sample from a population ; qualitative and quantitative data ; nominal and
STATISTICS ( CODE NO. 08 ) PAPER I PART - I 1. Descriptive Statistics Types of data - Concepts of a Statistical population and sample from a population ; qualitative and quantitative data ; nominal and
2. Prove that x must be always lie between the smallest and largest data values.
 Homework 11 12.5 1. A laterally insulated bar of length 10cm and constant cross-sectional area 1cm 2, of density 10.6gm/cm 3, thermal conductivity 1.04cal/(cm sec C), and specific heat 0.056 cal/(gm C)(this
Homework 11 12.5 1. A laterally insulated bar of length 10cm and constant cross-sectional area 1cm 2, of density 10.6gm/cm 3, thermal conductivity 1.04cal/(cm sec C), and specific heat 0.056 cal/(gm C)(this
Plotting data is one method for selecting a probability distribution. The following
 Advanced Analytical Models: Over 800 Models and 300 Applications from the Basel II Accord to Wall Street and Beyond By Johnathan Mun Copyright 008 by Johnathan Mun APPENDIX C Understanding and Choosing
Advanced Analytical Models: Over 800 Models and 300 Applications from the Basel II Accord to Wall Street and Beyond By Johnathan Mun Copyright 008 by Johnathan Mun APPENDIX C Understanding and Choosing
LECTURE 12 CONFIDENCE INTERVAL AND HYPOTHESIS TESTING
 LECTURE 1 CONFIDENCE INTERVAL AND HYPOTHESIS TESTING INTERVAL ESTIMATION Point estimation of : The inference is a guess of a single value as the value of. No accuracy associated with it. Interval estimation
LECTURE 1 CONFIDENCE INTERVAL AND HYPOTHESIS TESTING INTERVAL ESTIMATION Point estimation of : The inference is a guess of a single value as the value of. No accuracy associated with it. Interval estimation
