The Electromagnetic Mass of a Charged Particle
|
|
|
- Archibald Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 In mmry f M.I. Kuligina ( ) Th Elctrmagntic Mass f a Chargd Particl V.A. Kuligin, G.A. Kuligina, M.V. Krnva Dpartmnt f Physics, Stat Univrsity Univrsittskaya Sq. 1, Vrnh , Russia A slutin f th f lctrmagntic mass is btaind in th framwrk f Maxwll s quatins. Thr is a mathmatical prf that th lctrmagntic mass psssss th standard prprtis f th inrtial mass. W cnclud that Maxwll s quatins dal with tw kinds f filds. Ths ar lcal filds f chargd particls and th prpagating filds f th lctrmagntic wav. Intrductin Pag 6 APEIRON Vl. 3 Nr. 1 January 1996 Tw aspcts f th lctrmagntic mass (EMM) ar cnsidrd. Th first aspct is th classical prblm f th EMM. Shrtly aftr th discvry f th law f nrgy cnsrvatin by Pynting, it turnd ut that th EMM did nt mt th standard prprtis f an inrtial Mass. Blw w shall cnsidr xampls. Th scnd aspct is th prblm f chargd particl mdls. It is knwn that chargd particl mdls ar nt stabl bcaus f Culmb frcs, which must brak th charg. Th hypthsis was advancd that th inrtial mass f a particl was qual t th sum f th EMM and th nn-lctrmagntic mass (NEM), crating a stabl stat in th particl. Hr a cnstraint was st by th EMM prblm: th bad prprtis f EMM must b balancd by th thr bad prprtis f NEM. Withut a slutin t th prblm f th EMM, th sarch fr a mdl cannt succd (Ivannk 1949; ynman t al. 1964). It smd that a slutin might b prvidd by quantum thry. Hwvr, this did nt ccur. Mrvr, w knw that many difficultis with quantum thry hav classical rts. Th prblm f th EMM is n such prblm. Thus w hav a vicius circl. Is thr a way ut? Epistmlgy rquirs that intrnal cntradictins must nt b allwd in any scintific thry. Thy hav t b rslvd by changing th intrprtatin, transfrmatin f th mdl r mdificatins t th mathmatical frmalism f th thry. Our task is t analy th prblm f th EMM (first aspct). 1. Th Elctrmagntic Mass Prblm W bgin th analysis with xampls whr th prblm can b sn clarly. Th authrs wish t pint ut that th dnsity f nrgy f lctrmagntic wavs is dscribd wll by Pynting s vctr. Hwvr, Pynting s vctr is nt in agrmnt with mchanics. Nwtn s mchanics stats that th cnnctin btwn th mass m and th mmntum P is P=mv In th sam way, th rlatin btwn th dnsity f mass w/c and th dnsity f nrgy flw S is as fllws: S= w v (1.1) Analgusly, w may writ th dnsity f nrgy flw S f th charg. S = wv (1.) whr w = 3 bgradφg th dnsity f lctrmagntic nrgy f a charg. W shall nt cnsidr rlativistic xampls, sinc SRT has pistmlgical rrrs (Kuligin t al. 1989, 1990, 1994). Exampl 1. Lt us assum a charg with unifrm lctrical dnsity. Th charg mvs alng th x-axis with cnstant vlcity v. r cmparisn, w slct tw pints n
2 . W rgard SRT as a qustinabl thry (Kuligin t al. 1989, 1990, 1994). W must thrfr us th mathmatical frmalism f SRT (Lrnt transfrmatin) with xtrm car. igur 1 th surfac f th charg, as shwn in igur 1. With Pynting s vctr w can btain th dnsitis f th lctrmagntic flux at th pint. S =[ E H]= (grad ϕ ) v (pint 1) S =[ E H]=0 (pint ) Th vlcitis and dnsitis f th masss hav qual valus at th tw pints. At pint 1, th flux dnsity S is gratr than xpctd by factr f. At pint, th flux dnsity S is qual t r. What has happnd? If w cnsidr rlativistic vlcitis, thn w hav th prblm f th 4 3 factr, which is discussd in many txtbks (.g. Panfsky and Phillips 196). Exampl. Hr w shall dal with a chargd plan f infinit xtnt. Th plan is plttd in igur If th plan mvs upward with vlcity vycvy << ch, thn th flux dnsity is qual t: S =[ E H]= (grad ϕ ) v (1.3) Hr again w find a vilatin f th classical rul (1.). In any part f th chargd plan, flux dnsity is twic as high as th flux dnsity as in Equatin (1.). W hav th altrnativ rsult if th plan is mvd alng th x-axis: bcaus f th symmtry th magntic fild is absnt. Cnsquntly, th flux dnsity is qual t r. S =[ E H]= (grad ϕ ) v (1.4) Onc again, w find th paradx. In natur, inrtial mass is a scalar quantity. Lgically w must accpt that it has t acquir tnsr prprtis! What prprtis must NEM hav s that th full mass f th particl psssss th standard inrtial prprtis? Mrvr, any EMM f a charg which has th asymmtrical frm (fr xampl llipsidal r tridal frm), must hav tnsr prprtis. Any studnt can chck this. But this is nnsns! It is knwn that th EMM dpnds n intractins (Kuligin t al. 1986). r instanc, if a charg is changd by factr 3 withut any chang in vlum, thn th EMM is changd by a factr 9, nt by a factr 3. rm this pint f viw w shall wrk ut th prblm fr th fr charg, whr thr ar n intractins and th vlcity is cnstant. irst f all, w must ascrtain th cnnctin btwn Nwtn s mchanics and Maxwll s quatins. W writ Maxwll s quatins in Lrnt s gaug and btain th nn-rlativistic quatins, which ar crrct up t scnd rdr f v/c. A =-µ j (.1) φ 1 φ diva + = 0 c whr = + + x y ϕv A = c ρ = (.) (.3) (.4) and j= ρ v (.5) Additinal Equatins (.4) and (.5) ar ncssary fr th analysis. W must shw that Equatins (.1), (.) and (.3) ar cnsistnt with classical mchanics. r this purps, w rplac th vctr ptntial A in Equatin (.1) by th scalar ptntial φ (using Equatins (.4) and (.5)). b A + µ j= 1 rt -gradϕ v c + b-grad ϕg+ vdivb-gradϕg (.6) =0 In th mchanics f cntinuus mdia w hav th prf f th cnditin, whn th vctr a and th intnsity f its fild lins ar cnsrvd (Kchin 1965): a rt[ a v]+ + vdiv a=0 If w rplac th vctr a c by E = gradφ, thn w btain Maxwll s quatin (.1) fr th fr charg. g. Umv s Vctr Nw w shall slv th prblm f EMM in th framwrk f th nn-rlativistic cas nly. Tw cnsidratins lad us t this apprach. 1. Histrically Maxwll s quatins ars du t Culmb s law, Ampr s law and araday s law. W must us xprimntal laws hr. igur APEIRON Vl. 3 Nr. 1 January 1996 Pag 7
3 Similarly, w btain Equatin (.7) frm Equatin (.3). This is th cntinuity quatin f th ptntial in th mchanics f cntinuus mdia. div vϕ + ϕ =0 (.7) In Equatin (.8) th scalar ptntial is gnratd by th surc ρ. ρ φ = (.8) It can radily b sn that quasi-static lctrdynamics and mchanics hav similar quatins. Earlir wrk (Kuligin t al. 1986) dmnstrats this rsult. Nw w bgin th prf f th law f cnsrvatin f nrgy. Prf Lt φ b th ptntial f th surc ρ (Equatin (.8). W writ th intgral I. I = 1 ρ φ 3 d r φ φ d r = 3 (.9) whr d 3 r is a vlum lmnt. With Gauss s frmula w may writ I =- ϕ gradϕ n d σ + grad d 4 b ϕg τ (.10) whr dσ is th surfac lmnt and n is unit surfac nrmal. On th thr hand with Equatin (.6) and Equatin (.7), w may writ Equatin (.9) in th fllwing frm I =- gradϕ v gradϕ n dσ gradϕ dτ 4 Cmparisn f Equatin (.10) with Equatin (.11) yilds Pag 8 APEIRON Vl. 3 Nr. 1 January 1996 (.11) S u n d σ + t w d t =0 (.1) whr S u is th dnsity f lctrmagntic flux r Umv s vctr, R S U V (.13) ϕ Su = - grad ϕ + gradϕ v grad ϕ = vw T W Hr Equatin (.7) was usd; w is th dnsity f lctrmagntic nrgy. (.14) w = gradϕ Equatin (.1) is Umv s law f nrgy cnsrvatin, which was prvd by Umv (1874) fr th mchanics f cntinuus mdia. A scnd prf f Umv s law was givn by us (Kuligin t al. 1986). It is clar that Equatin (.13) and Equatin (.14) crrspnd t th quatins f Nwtn s mchanics (1.1) and (1.). With this rsult, w can calculat th crrct lctrmagntic flux dnsity in xampls discussd prviusly. Nw w calculat th EMM and th mmntum f a charg f arbitrary frm m = w dx dyd ; P S 3. Kintic Enrgy Equilibrium = udx dyd ; P = w v Nw w shall prv anthr imprtant rsult: th kintic nrgy quilibrium quatin. W shall shw that th EMM psssss kintic nrgy. This fact is nt particularity nw. Hwvr, w must hav th full pictur f th phnmnn. irst w cnsidr th physical mdl f th chang f kintic nrgy f th fild. If xtrnal frcs act n th charg, thn th charg is acclratd and its kintic nrgy is changd. Th chang is cnnctd with th currnt dnsity j and th vctr ptntial A. Th acclratd mtin f th charg can b tratd as th jump frm n instantanusly c-mving inrtial fram t th nxt fram. Th instantanusly cmving inrtial fram and th nn-inrtial fram hav qual vlcitis at n instant. Th fild = gradφ is nt tim-dpndnt and th vctr ptntial A is qual t r in th instantanusly c-mving fram. Th acclratd mtin f th charg inducs th additinal lctrical fild E, which is causd by th chang f vctr ptntial A vr tim (s Appndix 1). Th fild E cannt b cnsidrd as a ngligibl quantity. In th instantanusly c-mving fram th fild is qual t A v E =- 1 ϕ =- c (3.1) Th dnsity f th pwr which is gnratd by th charg is qual t pk = ρ = =- µ * v jai Ev 4 K J (3.) Th pwr dnsity ds nt dpnd n th inrtial fram in Nwtn s mchanics. Nw w shall dscrib this mdl mathmatically. T prv th quatin w us Grn s frmula f vctr ptntial E M d τ = dive div M+rtE rtm n dτ whr E and M ar th vctr ptntials f tw arbitrary filds. Lt E = b 1 A t g b th fild which is gnratd by th acclratd charg and M = A µ b th vctr ptntial f th fild dividd by µ. In this cas w btain full kintic nrgy quilibrium quatin, and w can writ th diffrntial frm f this quatin : whr: wk div S k + + pk =0 (3.3) a) pk =- 1 j A =- ja I 4 K J (3.4) is th dnsity f pwr which changs kintic nrgy ; and 1 b) wk = ivba + rt A 4µ (3.5)
4 is th kintic nrgy dnsity. With Equatin (.4) w hav Nwtn s rsult w k * A A I div A + rta v w = c grad = v c = v ϕ µ c) Sk (3.6) i.. th kintic nrgy flux dnsity. W nw illustrat this kintic nrgy quilibrium quatin with a simpl xampl. =- 1 µ 4. Chang f Enrgy f a Currnt Elmnt In quasi-static lctrdynamics th vctr ptntial f a currnt lmnt is qual t : I t dl d A = µ (4.1) 4 π r Substituting Equatin (4.1) int Equatin (3.6) and Equatin (3.8) w hav th fllwing rsults. 1. Th kintic nrgy dnsity is qual t : d µ I( t)dl wk = (4.) 4πr Th distributin f th kintic nrgy dnsity is radially symmtric.. Th kintic nrgy flux dnsity is d Sk = r d wk (4.3) Nw w discuss th pculiar prprtis f th flux dnsity d S k a) Th chang f d ω k is assciatd with d S k. Th flux dnsity d S k dpnds n th chang f squard currnt I in tim. If th currnt incrass, thn th flux dnsity d S k is psitiv and d S k is dirctd tward th radius. This flux incrass th kintic nrgy f th lctrical fild. If th currnt I dcrass, thn th flux cms back tward th currnt withut lss. Th flux tnds t cnsrv th prvius currnt in tim. Th flux dnsity d S k dcrass as 1/ r 3 in spac. b) If th currnt changs, thn th kintic nrgy flux appars simultanusly thrughut spac. c) Cntrary t Umv s vctr, which dals with th transfr f nrgy with vlcity v, th kintic nrgy flux is cnnctd nly with th acclratin f th charg. Th lctrical fild is A E =- 1 W can rgard this as intgral EM (slf-inductin) f a currnt lmnt. This analgy is givn fr illustratin. I Cnclusins 1. W hav invstigatd th prblm f th EMM f a fr charg. Nt that in th prf n hypthss wr usd. Th EMM has Nwtn s mmntum and classical kintic nrgy within th framwrk f Maxwll s quatins.. Th inrtial mass m f th chargd particl is qual t m = m + mn whr: m is th lctrmagntic mass and m n is th nn-lctrmagntic mass. Using th inductin mthd w can prv that th NEM has th standard prprtis f th inrtial mass. Th thsis can b xtndd t th gnral cas. Any inrtial mass must hav standard mchanical prprtis, which d nt dpnd n natur f th mass. This is a vry imprtant rsult. 3. W cnclud that Maxwll s quatins dal with tw kinds f filds : a) th filds f chargs (Culmb s ptntials and Umv s vctrs; th rst EMM f th charg is nt qual t r); b) th filds f th lctrmagntic wavs (rtardd ptntials and Pynting s vctrs; th rst EMM f th lctrmagntic wav is qual t r). If w us nly rtardd ptntials in ur rsarch, thn w cannt giv a full and crrct pictur f natur. It is als pssibl that th quantum prprtis f particls may b xplaind by classical mthds. Th prblm f a classical mdl (r structur) f chargs is nw f prim imprtanc. Acknwldgmnt Th authrs wish t thank Dr. C. Whitny f Tufts Univrsity fr hlpful advic and suggstins in prparing th manuscript. Appndix W writ th intgral variabl f th charg which intract with th ptntial frcs. Th charg dnsity is cnstant and rtatin f th charg is absnt. All pints f th charg mv with th sam vlcity. L * v S= M I O - µ 1- + Λ dτ dtp c (A.1) N * * * * whr: µ = µ + µ n ; µ is th lctrmagntic mass dnsity; µ * n is dnsity f nn-lctrmagntic mass. Th pndrmtiv quatin fllws frm Equatin (A.1). d i d i d i µ * µ * µ * v + v rt v - grad c +grad Λ =0 (A.) a) Supps that xtrnal frcs ar absnt (Λ = 0 ). Th particl is stabl if th fllwing cnditin is mt: grad µ * =gradµ * + grad µ * =0 (A.3) n Q APEIRON Vl. 3 Nr. 1 January 1996 Pag 9
5 b) If xtrnal frcs xist (Λ 0 ), thn w must supps that th structur f th particl is cnsrvd and, hnc, th cnditin (Equatin (A.3)) applis. Nw Equatin (A.) is multiplid by v. With Equatin (A.3) w can writ th prduct. d i d i gradλ 0 (A.4) * * v µ v µ nv + v = Th first trm f Equatin (3.4) is th lctrmagntic pwr f th acclratd charg. I K J (A.5) pk =- v v = 1 j A =- ja µ * 4 Rcall that ρ and φ ar nt tim-dpndnt. Rfrncs ynman, R., Lightn, R.B. and Sands, M., Th inman Lcturs n Physics, vl., Addisn-Wsly. Ivannk, D.D., Sklv, A.A., Klassichskaya Triya Plya Nauka, Mscw,(in Russian). Kchin, N.E., Vctr Calculatins and Elmnts f Tnsr Calculatins, Nauka, Mscw, (in Russian). Kuligin, V.A., Kuligina, G.A. and Krnva, M.V.,1986. Mchanics f quasi-nutral systms f chargs and laws f cnsrvatin f nn-rlativistic lctrdynamics, dpsitd with VINITI, Apr. 9, 1986, # V. 86, Mscw, (in Russian). Kuligin, V.A., Kuligina, G.A. and Krnva, M.V., Lrnt s transfrmatin and pistmlgy, dpsitd with VINITI, Jan. 1, 1989, # V. 89, Mscw, (in Russian). Kuligin, V.A., Kuligina, G.A. and Krnva, M.V., Th paradxs f rlativity mchanics and lctrdynamics, dpsitd with VINITI July 4, 1990, # V. 90. (in Russian). Kuligin, V.A., Kuligina, G.A. and Krnva, M.V., Epistmlgy and spcial rlativity, Apirn 0:1. Panfsky, W. and Phillips, M., 196. Classical Elctricity and Magntism, Addisn-Wsly. Umv (Umff), N.A., Bwg-Glich. d. Enrgi in cntin. Krprn, Zitschriff d. Math. and Phys. V. XIX, Schlmilch. Pag 10 APEIRON Vl. 3 Nr. 1 January 1996
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
A Brief and Elementary Note on Redshift. May 26, 2010.
 A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
N J of oscillators in the three lowest quantum
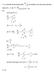 . a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
. a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
MAGNETIC MONOPOLE THEORY
 AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Chapter 33 Gauss s Law
 Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
A Unified Theory of rf Plasma Heating. J.e. Sprott. July 1968
 A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
Cosmological and Intrinsic Redshifts. November 19, 2010.
 Csmlgical and Intrinsic Rdshifts Nvmbr 19, 21. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4625 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract In a rcnt articl, a singl tird light mchanism,
Csmlgical and Intrinsic Rdshifts Nvmbr 19, 21. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4625 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract In a rcnt articl, a singl tird light mchanism,
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Model of the Electron
 Mdl f th Elctrn Ph.M. Kanarv * Th intrprtatin f sm f thrtical fundatins f physics will b changd. Planck s cnstant is knwn t b n f such fundatins, which srvs as a basis f quantum mchanics [1], [3], [6],
Mdl f th Elctrn Ph.M. Kanarv * Th intrprtatin f sm f thrtical fundatins f physics will b changd. Planck s cnstant is knwn t b n f such fundatins, which srvs as a basis f quantum mchanics [1], [3], [6],
Journal of Theoretics
 Jurnal f Thrtics PLANCK S CONSTANT AND THE MODEL OF THE ELECTRON Ph. M. Kanarv Th Kuban Stat Agrarian Univrsity. Dpartmnt f Thrtical Mchanics. Dctr f Txnical Scincs, Prfssr. E-mail: kanphil@mail.kuban.ru
Jurnal f Thrtics PLANCK S CONSTANT AND THE MODEL OF THE ELECTRON Ph. M. Kanarv Th Kuban Stat Agrarian Univrsity. Dpartmnt f Thrtical Mchanics. Dctr f Txnical Scincs, Prfssr. E-mail: kanphil@mail.kuban.ru
FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC B. M. Jovanović, B. Živković
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
MHT-CET 5 (PHYSICS) PHYSICS CENTERS : MUMBAI /DELHI /AKOLA /LUCKNOW / NASHIK /PUNE /NAGPUR / BOKARO / DUBAI # 1
 1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
5 Curl-free fields and electrostatic potential
 5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS
 BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING
 ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
PHYSICS 489/1489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS
 PHYSICS 489/489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS REMINDER Problm st du today 700 in Box F TODAY: W invstigatd th Dirac quation it dscribs a rlativistic spin /2 particl implis th xistnc of antiparticl
PHYSICS 489/489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS REMINDER Problm st du today 700 in Box F TODAY: W invstigatd th Dirac quation it dscribs a rlativistic spin /2 particl implis th xistnc of antiparticl
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER. J. C. Sprott
 SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
120~~60 o D 12~0 1500~30O, 15~30 150~30. ..,u 270,,,, ~"~"-4-~qno 240 2~o 300 v 240 ~70O 300
 1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION
 Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Chapter 2: Examples of Mathematical Models for Chemical Processes
 Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
ELEG 413 Lecture #6. Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Professor The University of Delaware
 LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
6. Negative Feedback in Single- Transistor Circuits
 Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
Introduction to the quantum theory of matter and Schrödinger s equation
 Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
A Redshift Phenomenon in Relativistic Binary System
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
Cosmology. Outline. Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 17 Terry Herter. Redshift (again) The Expanding Universe Applying Hubble s Law
 Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Lecture 2a. Crystal Growth (cont d) ECE723
 Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Chemical Reactions and Equations. Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Kragujevac, Serbia, May 2011
 Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Pair (and Triplet) Production Effect:
 Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Schedule. Time Varying electromagnetic fields (1 Week) 6.1 Overview 6.2 Faraday s law (6.2.1 only) 6.3 Maxwell s equations
 chedule Time Varying electrmagnetic fields (1 Week) 6.1 Overview 6.2 Faraday s law (6.2.1 nly) 6.3 Maxwell s equatins Wave quatin (3 Week) 6.5 Time-Harmnic fields 7.1 Overview 7.2 Plane Waves in Lssless
chedule Time Varying electrmagnetic fields (1 Week) 6.1 Overview 6.2 Faraday s law (6.2.1 nly) 6.3 Maxwell s equatins Wave quatin (3 Week) 6.5 Time-Harmnic fields 7.1 Overview 7.2 Plane Waves in Lssless
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
A Prey-Predator Model with an Alternative Food for the Predator, Harvesting of Both the Species and with A Gestation Period for Interaction
 Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
Chapter 8: Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Derivation of Electron-Electron Interaction Terms in the Multi-Electron Hamiltonian
 Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
:2;$-$(01*%<*=,-./-*=0;"%/;"-*
 !"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
!"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
Chemical Physics II. More Stat. Thermo Kinetics Protein Folding...
 Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES. 1. Statement of results
 BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim and n a positiv intgr, lt ν p (n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and u p (n n/p νp(n th unit part of n. If α
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim and n a positiv intgr, lt ν p (n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and u p (n n/p νp(n th unit part of n. If α
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
(1) Then we could wave our hands over this and it would become:
 MAT* K285 Spring 28 Anthony Bnoit 4/17/28 Wk 12: Laplac Tranform Rading: Kohlr & Johnon, Chaptr 5 to p. 35 HW: 5.1: 3, 7, 1*, 19 5.2: 1, 5*, 13*, 19, 45* 5.3: 1, 11*, 19 * Pla writ-up th problm natly and
MAT* K285 Spring 28 Anthony Bnoit 4/17/28 Wk 12: Laplac Tranform Rading: Kohlr & Johnon, Chaptr 5 to p. 35 HW: 5.1: 3, 7, 1*, 19 5.2: 1, 5*, 13*, 19, 45* 5.3: 1, 11*, 19 * Pla writ-up th problm natly and
Signals and Systems View Point
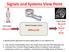 Signals and Sstms Viw Pint Inpt signal Ozt Mdical Imaging Sstm LOzt Otpt signal Izt r Iz r I A signalssstms apprach twards imaging allws s as Enginrs t Gain a bttr ndrstanding f hw th imags frm and what
Signals and Sstms Viw Pint Inpt signal Ozt Mdical Imaging Sstm LOzt Otpt signal Izt r Iz r I A signalssstms apprach twards imaging allws s as Enginrs t Gain a bttr ndrstanding f hw th imags frm and what
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
2. Background Material
 S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
Chapter 2 GAUSS LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
EAcos θ, where θ is the angle between the electric field and
 8.4. Modl: Th lctric flux flows out of a closd surfac around a rgion of spac containing a nt positiv charg and into a closd surfac surrounding a nt ngativ charg. Visualiz: Plas rfr to Figur EX8.4. Lt A
8.4. Modl: Th lctric flux flows out of a closd surfac around a rgion of spac containing a nt positiv charg and into a closd surfac surrounding a nt ngativ charg. Visualiz: Plas rfr to Figur EX8.4. Lt A
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
de/dx Effectively all charged particles except electrons
 de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES
 BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim (implicit in notation and n a positiv intgr, lt ν(n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and U(n n/p ν(n, th unit
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim (implicit in notation and n a positiv intgr, lt ν(n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and U(n n/p ν(n, th unit
10. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Yeu-Sheng Paul Shiue, Ph.D 薛宇盛 Professor and Chair Mechanical Engineering Department Christian Brothers University 650 East Parkway South Memphis, TN
 Yeu-Sheng Paul Shiue, Ph.D 薛宇盛 Prfessr and Chair Mechanical Engineering Department Christian Brthers University 650 East Parkway Suth Memphis, TN 38104 Office: (901) 321-3424 Rm: N-110 Fax : (901) 321-3402
Yeu-Sheng Paul Shiue, Ph.D 薛宇盛 Prfessr and Chair Mechanical Engineering Department Christian Brthers University 650 East Parkway Suth Memphis, TN 38104 Office: (901) 321-3424 Rm: N-110 Fax : (901) 321-3402
Chapter Summary. Mathematical Induction Strong Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms
 Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Self-interaction mass formula that relates all leptons and quarks to the electron
 Slf-intraction mass formula that rlats all lptons and quarks to th lctron GERALD ROSEN (a) Dpartmnt of Physics, Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA 19104, USA PACS. 12.15. Ff Quark and lpton modls spcific thoris
Slf-intraction mass formula that rlats all lptons and quarks to th lctron GERALD ROSEN (a) Dpartmnt of Physics, Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA 19104, USA PACS. 12.15. Ff Quark and lpton modls spcific thoris
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE
 0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
Sundials and Linear Algebra
 Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
ECE602 Exam 1 April 5, You must show ALL of your work for full credit.
 ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
Q1. A string of length L is fixed at both ends. Which one of the following is NOT a possible wavelength for standing waves on this string?
 Term: 111 Thursday, January 05, 2012 Page: 1 Q1. A string f length L is fixed at bth ends. Which ne f the fllwing is NOT a pssible wavelength fr standing waves n this string? Q2. λ n = 2L n = A) 4L B)
Term: 111 Thursday, January 05, 2012 Page: 1 Q1. A string f length L is fixed at bth ends. Which ne f the fllwing is NOT a pssible wavelength fr standing waves n this string? Q2. λ n = 2L n = A) 4L B)
Forces. Quantum ElectroDynamics. α = = We have now:
 W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
u r du = ur+1 r + 1 du = ln u + C u sin u du = cos u + C cos u du = sin u + C sec u tan u du = sec u + C e u du = e u + C
 Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
Module 8 Non equilibrium Thermodynamics
 Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
Schrodinger Equation in 3-d
 Schrodingr Equation in 3-d ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) + + + Vxyz (,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) = Eψ( xyz,, ) m x y z p p p x y + + z m m m + V = E p m + V = E E + k V = E Infinit Wll in 3-d V = x > L, y > L,
Schrodingr Equation in 3-d ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) + + + Vxyz (,, ) ψ( xyz,, ) = Eψ( xyz,, ) m x y z p p p x y + + z m m m + V = E p m + V = E E + k V = E Infinit Wll in 3-d V = x > L, y > L,
The Relativistic Stern-Gerlach Force C. Tschalär 1. Introduction
 Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Approximate Maximum Flow in Undirected Networks by Christiano, Kelner, Madry, Spielmann, Teng (STOC 2011)
 Approximat Maximum Flow in Undirctd Ntworks by Christiano, Klnr, Madry, Spilmann, Tng (STOC 2011) Kurt Mhlhorn Max Planck Institut for Informatics and Saarland Univrsity Sptmbr 28, 2011 Th Rsult High-Lvl
Approximat Maximum Flow in Undirctd Ntworks by Christiano, Klnr, Madry, Spilmann, Tng (STOC 2011) Kurt Mhlhorn Max Planck Institut for Informatics and Saarland Univrsity Sptmbr 28, 2011 Th Rsult High-Lvl
That is, we start with a general matrix: And end with a simpler matrix:
 DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01
 ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Types of Communication
 Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
SECTION where P (cos θ, sin θ) and Q(cos θ, sin θ) are polynomials in cos θ and sin θ, provided Q is never equal to zero.
 SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics Qualifying Examination
 Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
GAUSS' LAW E. A. surface
 Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Gradebook & Midterm & Office Hours
 Your commnts So what do w do whn on of th r's is 0 in th quation GmM(1/r-1/r)? Do w nd to driv all of ths potntial nrgy formulas? I don't undrstand springs This was th first lctur I actually larnd somthing
Your commnts So what do w do whn on of th r's is 0 in th quation GmM(1/r-1/r)? Do w nd to driv all of ths potntial nrgy formulas? I don't undrstand springs This was th first lctur I actually larnd somthing
Introduction to Arithmetic Geometry Fall 2013 Lecture #20 11/14/2013
 18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
Effect of Warm Ionized Plasma Medium on Radiation Properties of Mismatched Microstrip Termination
 J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
