Chapter 2: Examples of Mathematical Models for Chemical Processes
|
|
|
- Adelia Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius chaptr t guid th radr thrugh varius xampls. Th gal is t giv th radr a mthdlgy t tackl mr cmplicatd prcsss that ar nt cvrd in this chaptr and that can b und in bks listd in th rrnc. Th rganizatin this chaptr includs xampls systms that can b dscribd by rdinary dirntial quatins (ODE), i.. lumpd paramtr systms llwd by xampls distributd paramtrs systms, i.. ths dscribd by partial dirntial quatins (PDE). Th xampls cvr bth hmgnus and htrgnus systms. Ordinary dirntial quatins (ODE) ar asir t slv and ar rducd t simpl algbraic quatins at stady stat. Th slutin partial dirntial quatins (PDE) n th thr hand is a mr diicult task. But w will b intrstd in th cass wr PDE's ar rducd t ODE's. This is naturally th cas whr undr apprpriat assumptins, th PDE's is a n-dimnsinal quatin at stady stat cnditins. It is wrth t rcall, as ntd in th prvius chaptrs, that th distinctin btwn lumpd and distributd paramtr mdls dpnds smtims n th assumptins put rward by th mdlr. Systms that ar nrmally distributd paramtr can b mdld undr apprpriat assumptins as lumpd paramtr systms. This chaptr includs sm xampls this situatin. 28
2 2.1 Exampls Lumpd Paramtr Systms Liquid Strag Tank Cnsidr th prctly mixd strag tank shwn in igur 2.1. Liquid stram with vlumtric rat F (m 3 /s) and dnsity ρ lw int th tank. Th utlt stram has vlumtric rat F and dnsity ρ ο. Our bjctiv is t dvlp a mdl r th variatins th tank hldup, i.. vlum th tank. Th systm is thrr th liquid in th tank. W will assum that it is prctly mixd and that th dnsity th lunt is th sam as that tank cntnt. W will als assum that th tank is isthrmal, i.. n variatins in th tmpratur. T mdl th tank w nd nly t writ a mass balanc quatin. ρ F ρ F Figur 2-1 Liquid Strag Tank Sinc th systm is prctly mixd, th systm prprtis d nt vary with psitin insid th tank. Th nly variatins ar with tim. Th mass balanc quatin can b writtn thn n th whl systm and nt nly n a dirntial lmnt it. This lads t thrr t a macrscpic mdl. W apply th gnral balanc quatin (Eq. 1.2), t th ttal mass m = ρv. This yilds: Mass lw in: ρ F (2.1) 29
3 Mass lw ut: ρ F (2.2) Accumulatin: dm d(ρv = ) (2.3) Th gnratin trm is zr sinc th mass is cnsrvd. Th balanc quatin yilds: ρ F = ρ F d(ρv ) + (2.4) Fr cnsistncy w can chck that all th trms in th quatin hav th SI unit kg/s. Th rsulting mdl (Eq. 2.4) is an rdinary dirntial quatin (ODE) irst rdr whr tim (t) is th nly indpndnt variabl. This is thrr a lumpd paramtr mdl. T slv it w nd n initial cnditin that givs th valu th vlum at initial tim t i, i.. V(t i ) = V i (2.5) Undr isthrmal cnditins w can urthr assum that th dnsity th liquid is cnstant i.. ρ = ρ =ρ. In this cas Eq. 2.4 is rducd t: dv = F F (2.6) Th vlum V is rlatd t th hight th tank L and t th crss sctinal ara A by: V = AL (2.7) 30
4 Sinc (A) is cnstant thn w btain th quatin in trms th stat variabl L: dl A = F F (2.8) with initial cnditin: L(t i ) = L i (2.9) Dgr rdm analysis Fr th systm dscribd by Eq. 2.8 w hav th llwing inrmatin: Paramtr cnstant valus: A Variabls which valus can b xtrnally ixd (Frcd variabl): F Rmaining variabls: L and F Numbr quatins: 1 (Eq. 2.8) Thrr th dgr rdm is: Numbr rmaining variabls Numbr quatins = 2 1 = 1 Fr th systm t b xactly spciid w nd thrr n mr quatins. This xtra rlatin is btaind rm practical nginring cnsidratins. I th systm is pratd withut cntrl (at pn lp) thn th utlt lw rat F is a unctin th liquid lvl L. Gnrally a rlatin th rm: F = α L (2.10) culd b usd, whr α is th discharg cicint. I n th thr hand th liquid lvl is undr cntrl, thn its valu is kpt cnstant at crtain dsird valu L s. I F is usd t cntrl th hight thn a cntrl law rlats F t L and L s : 31
5 F = F (L,L s ) (2.11) Fr instant, i a prprtinal cntrllr K c is usd thn th cntrl law is givn by: F = K c (L L s ) + F b (2.12) Whr F b th bias, i.. th cnstant valu F whn th lvl is at th dsird valu i.., L = L s. Nt that at stady stat, th accumulatin trm is zr (hight ds nt chang with tim), i.., dl/ = 0. Th mdl th tank is rducd t th simpl algbraic quatin: F 0 = F (2.13) Stirrd Tank Hatr W cnsidr th liquid tank th last xampl but at nn-isthrmal cnditins. Th liquid ntrs th tank with a lw rat F (m 3 /s), dnsity ρ (kg/m 3 ) and tmpratur T (K). It is hatd with an xtrnal hat supply tmpratur T st (K), assumd cnstant. Th lunt stram is lw rat F (m 3 /s), dnsity ρ (kg/m 3 ) and tmpratur T(K) (Fig. 2.2). Our bjctiv is t mdl bth th variatin liquid lvl and its tmpratur. As in th prvius xampl w carry ut a macrscpic mdl vr th whl systm. Assuming that th variatins tmpratur ar nt as larg as t act th dnsity thn th mass balanc Eq. 2.8 rmains valid. T dscrib th variatins th tmpratur w nd t writ an nrgy balanc quatin. In th llwing w dvlp th nrgy balanc r any macrscpic systm (Fig. 2.3) and thn w apply it t ur xampl stirrd tank hatr. Th nrgy E(J) any systm (Fig. 2.3) is th sum its intrnal U(J), kintic K(J) and ptntial nrgy φ(j): E = U + K + φ (2.14) Cnsquntly, th lw nrgy int th systm is: 32
6 ρ F ( U + K + φ ) (2.15) whr th ( ) dnts th spciic nrgy (J/kg). F,T, ρ L Q T st Hat Supply Figur 2-2 Stirrd Tank Hatr Inlts F 2 F 1 Q Systm F 1 utlts F 2 F n Ws Figur 2-3 Gnral Macrscpic Systm F 3 Th lw nrgy ut th systm is: ρ F ( U + K + φ ) (2.16) Th rat accumulatin nrgy is: 33
7 ( V ( U + K + φ ) d ρ ) (2.17) As r th rat gnratin nrgy, it was mntind in Sctin 1.8.4, that th nrgy xchangd btwn th systm and th surrundings may includ hat ractin Q r (J/s), hat xchangd with surrundings Q (J/s) and th rat wrk dn against prssur rcs (lw wrk) W pv (J/s), in additin t any thr wrk W. Th lw wrk W pv dn by th systm is givn by: W pv = F P F P (2.18) whr P and P ar th inlt and utlt prssur, rspctivly. In this cas, th rat nrgy gnratin is: Q + Q W + F P F P ) (2.19) r ( Substituting all ths trms in th gnral balanc quatin (Eq. 1.7) yilds: d ( ρv ( U + K + φ ) = ρ F ( U + K + φ ) ρ F ( ) U + K + φ ) + Q + Q r ( W + F P F P ) (2.20) W can chck that all trms this quatin hav th SI unit (J/s). Equatin (2.20) can b als writtn as: d ( ρ V ( U + K + φ) ) = ρ F ( U + K + φ ) ρ F ( U + K + φ ) + Q + Q r W F ρ P ρ + F ρ P ρ (2.21) 34
8 Th trm V = 1/ ρ is th spciic vlum (m 3 /kg). Thus Eq can b writtn as: ( V ( U + K + φ )) = ρ F ( U + P V + K + φ ) ρ F ( d ρ U + PV + K + φ ) (2.22) + Q + Q W r Th trm U + PV that appars in th quatin is th spciic nthalpy h. Thrr, th gnral nrgy balanc quatin r a macrscpic systm can b writtn as: d ( ρ V U + K + φ) ) = ρ F ( h + K + φ ) ρf ( h + K + φ ) + Q + Qr W ( (2.23) W rturn nw t th liquid stirrd tank hatr. A numbr simpliying assumptins can b intrducd: W can nglct kintic nrgy unlss th lw vlcitis ar high. W can nglct th ptntial nrgy unlss th lw dirnc btwn th inlt and utlt lvatin is larg. All th wrk thr than lw wrk is nglctd, i.. W = 0. Thr is n ractin invlvd, i.. Q r = 0. Th nrgy balanc (Eq. 2.23) is rducd t: ( VU ) d ρ = ρ F h ρf h + Q (2.24) Hr Q is th hat (J/s) supplid by th xtrnal surc. Furthrmr, as mntind in Sctin 1.12, th intrnal nrgy U r liquids can b apprximatd by nthalpy, h. Th nthalpy is gnrally a unctin tmpratur, prssur and cmpsitin. Hwvr, it can b saly stimatd rm hat capacity rlatins as llws: 35
9 h = Cp( T ) (2.25) T r whr C p is th avrag hat capacity. Furthrmr sinc th tank is wll mixd th lunt tmpratur T is qual t prcss tmpratur T. Th nrgy balanc quatin can b writtn, assuming cnstant dnsity ρ = ρ = ρ, as llws: ( V ( T T )) d r (2.26) ρ C p = ρf C p( T Tr ) ρfc p( T Tr ) + Q Taking T r = 0 r simplicity and sinc V = AL rsult in: ( LT ) d (2.27) ρc p A = ρf C pt ρfc pt + Q r quivalntly: ( LT ) d Q A = F T FT + ρc p (2.28) Sinc ( LT ) d( L) d( T ) d A = AT + AL (2.29) and using th mass balanc (Eq. 2.8) w gt: dt AL + T ( F F ) = F T FT + ρc p Q (2.30) r quivalntly: 36
10 dt Q AL = F ( T T ) + ρc p (2.31) Th stirrd tank hatr is mdld, thn by th llwing cupld ODE's: dl A = F F (2.32) dt Q AL = F ( T T ) + ρc p (2.33) This systm ODE's can b slvd i it is xactly spciid and i cnditins at initial tim ar knwn, L(t i ) = L i and T(t i ) = T i (2.34) Dgr rdms analysis Fr this systm w can mak th llwing simpl analysis: Paramtr cnstant valus: A, ρ and C p (Frcd variabl): F and T Rmaining variabls: L, F, T, Q Numbr quatins: 2 (Eq and Eq. 2.33) Th dgr rdm is thrr, 4 2 = 2. W still nd tw rlatins r ur prblm t b xactly spciid. Similarly t th prvius xampl, i th systm is pratd withut cntrl thn F is rlatd t L thrugh (Eq. 2.10). On additinal rlatin is btaind rm th hat transr rlatin that spciis th amunt hat supplid: Q = UA H (T st T ) (2.35) 37
11 U and A H ar hat transr cicint and hat transr ara. Th surc tmpratur T st was assumd t b knwn. I n th thr hand bth th hight and tmpratur ar undr cntrl, i.. kpt cnstant at dsird valus L s and T s thn thr ar tw cntrl laws that rlat rspctivly F t L and L s and Q t T and T s : F = F (L, L s ), and Q = Q (T, T s ) (2.36) Isthrmal CSTR W rvisit th prctly mixd tank th irst xampl but whr a liquid phas chmical ractins taking plac: A k B (2.37) Th ractin is assumd t b irrvrsibl and irst rdr. As shwn in igur 2.4, th d ntrs th ractr with vlumtric rat F (m 3 /s), dnsity ρ (kg/m 3 ) and cncntratin C A (ml/m 3 ). Th utput cms ut th ractr at vlumtric rat F, dnsity ρ 0 and cncntratin C A (ml/m 3 ) and C B (ml/m 3 ). W assum isthrmal cnditins. Our bjctiv is t dvlp a mdl r th variatin th vlum th ractr and th cncntratin spcis A and B. Th assumptins xampl still hld and th ttal mass balanc quatin (Eq. 2.6) is thrr unchangd F ρ ο C A V F ρ C A C B A k B Figur 2.4 Isthrmal CSTR 38
12 Th cmpnnt balanc n spcis A is btaind by th applicatin (Eq. 1.3) t th numbr mls (n A = C A V ). Sinc th systm is wll mixd th lunt cncntratin C A and C B ar qual t th prcss cncntratin C A and C B. Flw mls A in: F C A (2.38) Flw mls A ut: F C A (2.39) Rat accumulatin: dn d( VC = A) (2.40) Rat gnratin: -rv whr r (mls/m 3 s) is th rat ractin. Substituting ths trms in th gnral quatin (Eq. 1.3) yilds: d( VCA) (2.41) = F CA F CA rv W can chck that all trms in th quatin hav th unit (ml/s). W culd writ a similar cmpnnt balanc n spcis B but it is nt ndd sinc it will nt rprsnt an indpndnt quatin. In act, as a gnral rul, a systm n spcis is xactly spciid by n indpndnt quatins. W can writ ithr th ttal mass balanc alng with (n 1) cmpnnt balanc quatins, r w can writ n cmpnnt balanc quatins. 39
13 Using th dirntial principls, quatin (2.41) can b writtn as llws: d( VCA) d( C d V V A) ( ) (2.42) = + CA = F CA F CA rv Substituting Equatin (2.6) int (2.42) and with sm algbraic manipulatins w btain: V d( CA) (2.43) = F ( C A C A) rv In rdr t ully din th mdl, w nd t din th ractin rat which is r a irst-rdr irrvrsibl ractin: r = k C A (2.44) Equatins 2.6 and 2.43 din th dynamic bhavir th ractr. Thy can b slvd i th systm is xactly spciid and i th initial cnditins ar givn: V(t i ) = V i and C A (t i ) = C Ai (2.45) Dgrs rdm analysis Paramtr cnstant valus: A (Frcd variabl): F and C A Rmaining variabls: V, F, and C A Numbr quatins: 2 (Eq. 2.6 and Eq. 2.43) Th dgr rdm is thrr 3 2 =1. Th xtra rlatin is btaind by th rlatin btwn th lunt lw F and th lvl in pn lp pratin (Eq. 2.10) r in clsd lp pratin (Eq. 2.11). Th stady stat bhavir can b simply btaind by stting th accumulatin trms t zr. Equatin 2.6 and 2.43 bcm: 40
14 F 0 = F (2.46) F ( C C ) rv (2.47) A A = Mr cmplx situatins can als b mdld in th sam ashin. catalytic hydrgnatin thyln: Cnsidr th A + B P (2.48) whr A rprsnts hydrgn, B rprsnts thyln and P is th prduct (than). Th ractin taks plac in th CSTR shwn in igur 2.5. Tw strams ar ding th ractr. On cncntratd d with lw rat F 1 (m 3 /s) and cncntratin C B1 (ml/m 3 ) and anthr dilut stram with lw rat F 2 (m 3 /s) and cncntratin C B2 (ml/m 3 ). Th lunt has lw rat F (m 3 /s) and cncntratin C B (ml/m 3 ). Th ractant A is assumd t b in xcss. F 1 C B1 F 2 C B2 V F C B Figur 2-5 Ractin in a CSTR Th ractin rat is assumd t b: k1c B 3 r = ( ml / m. s) 2 (1 + k C ) 2 B (2.49) 41
15 whr k 1 is th ractin rat cnstant and k 2 is th adsrptin quilibrium cnstant. Assuming th pratin t b isthrmal and th dnsity is cnstant, and llwing th sam prcdur th prvius xampl w gt th llwing mdl: Ttal mass balanc: dl A F + F = 1 2 F (2.50) Cmpnnt B balanc: V d( C A ) = F ( C C ) + F ( C C ) rv 1 B1 B 2 B2 B (2.51) Dgrs rdm analysis Paramtr cnstant valus: A, k 1 and k 1 (Frcd variabl): F 1 F 2 C B1 and C B2 Rmaining variabls: V, F, and C B Numbr quatins: 2 (Eq and Eq. 2.51) Th dgr rdm is thrr 3 2 =1. Th xtra rlatin is btwn th lunt lw F and th lvl L as in th prvius xampl Gas-Phas Prssurizd CSTR S ar w hav cnsidrd nly liquid-phas ractin whr dnsity can b takn cnstant. T illustrat th ct gas-phas chmical ractin n mass balanc quatin, w cnsidr th llwing lmntary rvrsibl ractin: A 2B (2.52) taking plac in prctly mixd vssl sktchd in igur 2.6. Th inlunt t th vssl has vlumtric rat F (m 3 /s), dnsity ρ (kg/m 3 ), and ml ractin y. Prduct cms ut th ractr with vlumtric rat F, dnsity ρ, and ml ractin y. Th tmpratur 42
16 and vlum insid th vssl ar cnstant. Th ractr lunt passs thrugh cntrl valv which rgulat th gas prssur at cnstant prssur P g. P, T, V, y F, ρ, y F, ρ, y Figur 2-6 Gas Prssurizd Ractr Writing th macrscpic ttal mass balanc arund th vssl givs: d( ρv ) = ρ F ρ F (2.53) Sinc V is cnstant w hav: V dρ = ρ F ρ F (2.54) Writing th cmpnnt balanc, r ixd V, rsults in: V dc A = F C A F C rv + rv 0 A 1 2 (2.55) Th ractin rats r th rvrsibl ractin ar assumd t b: r 1 = k 1 C A (2.56) 2 2 k2cb r = (2.57) Equatins (2.54) and (2.55) din th variatins dnsity and mlar cncntratin. On can als rwrit th quatin t din th bhavir th prssur (P) and ml 43
17 ractin (y). Th cncntratin can b xprssd in trm th dnsity thrugh idal gas law: C A = yp/rt (2.58) C B = (1 y)p/rt (2.59) Similarly, th dnsity can b rlatd t th prssur using idal gas law: ρ = MP/RT = [M A y + M B (1 y)]p/rt (2.60) Whr M A and M B ar th mlcular wight A and B rspctivly. Thrr n can substitut quatins (2.58) t (2.60) int quatins (2.54 & 2.55) in rdr t xplicitly writ th lattr tw quatins in trms y and P. Or, altrnativly, n can slv all quatins simultanusly. Dgrs rdm analysis: Paramtrs: V, k 1, k 2, R, T, M A and M B Frcing unctin: F, C A, y Variabls: C A, C B, y, P, ρ, F Numbr quatins: 5 (Eqs. 2.54, 2.55, 2.58, 2.59, 2.60) Th dgr rdm is thrr 6 5 =1. Th xtra rlatin rlats th utlt lw t th prssur as llws: F = C v P P ρ g (2.61) whr C v is th valv-sizing cicint. Rcall als that P g is assumd t b cnstant Nn-Isthrmal CSTR W rcnsidr th prvius CSTR xampl (Sc 2.1.3), but r nn-isthrmal cnditins. Th ractin A B is xthrmic and th hat gnratd in th ractr is 44
18 rmvd via a cling systm as shwn in igur 2.7. Th lunt tmpratur is dirnt rm th inlt tmpratur du t hat gnratin by th xthrmic ractin. F, C A, T Q V F 0, C A, T Figur 2-7 Nn-isthrmal CSTR Assuming cnstant dnsity, th macrscpic ttal mass balanc (Eq. 2.6) and mass cmpnnt balanc (Eq. 2.43) rmain th sam as br. Hwvr, n mr ODE will b prducd rm th applying th cnsrvatin law (quatin 2.23) r ttal nrgy balanc. Th dpndnc th rat cnstant n th tmpratur: k = k -E/RT (2.62) shuld b mphasizd. Th gnral nrgy balanc (Eq. 2.23) r macrscpic systms applid t th CSTR yilds, assuming cnstant dnsity and avrag hat capacity: ( V ( T T )) d r ρ Cp = ρf Cp( T Tr ) ρfc p( T Tr ) + Q r Q (2.63) whr Q r (J/s) is th hat gnratd by th ractin, and Q (J/s) th rat hat rmvd by th cling systm. Assuming T r = 0 r simplicity and using th dirntiatin principls, quatin 2.63 can b writtn as llws: dt dv (2.64) ρc pv + ρc pt = ρf C pt ρfc pt + Qr Q 45
19 Substituting Equatin 2.6 int th last quatin and rarranging yilds: dt (2.65) ρ CpV = ρf C p( T T ) + Qr Q Th rat hat xchangd Q r du t ractin is givn by: Q r = ( H r )Vr (2.66) whr H r (J/ml) is th hat ractin (has ngativ valu r xthrmic ractin and psitiv valu r nhrmic ractin). Th nn-isthrmal CSTR is thrr mdld by thr ODE's: dv = F F (2.67) V d( CA) (2.68) = F ( C A C A) rv dt ρ CpV = ρf C p( T T ) + ( Hr ) Vr Q (2.69) whr th rat (r) is givn by: r = k -E/RT C A (2.70) Th systm can b slvd i th systm is xactly spciid and i th initial cnditins ar givn: V(t i ) = V i T(t i ) = T i and C A (t i ) = C Ai (2.71) Dgrs rdm analysis Paramtr cnstant valus: ρ, E, R, C p, H r and k (Frcd variabl): F, C A and T 46
20 Rmaining variabls: V, F, T, C A and Q Numbr quatins: 3 (Eq and 2.69) Th dgr rdm is 5 3 = 2. Fllwing th analysis xampl 2.1.3, th tw xtra rlatins ar btwn th lunt stram (F ) and th vlum (V) n n hand and btwn th rat hat xchangd (Q ) and tmpratur (T) n th thr hand, in ithr pn lp r clsd lp pratins. A mr labrat mdl th CSTR wuld includ th dynamic th cling jackt (Fig. 2.8). Assuming th jackt t b prctly mixd with cnstant vlum V j, dnsity ρ j and cnstant avrag thrmal capacity Cp j, th dynamic th cling jackt tmpratur can b mdld by simply applying th macrscpic nrgy balanc n th whl jackt: dtj (2.72) ρ jcp V j = ρ jfjcp ( Tj Tj ) + Q j j Sinc V j, ρ j, Cp j and T j ar cnstant r knwn, th additin this quatin intrducs nly n variabl (T j ). Th systm is still xactly spciid. V j ρ j C pj T j Figur 2-8 Jacktd Nn-isthrmal CSTR Mixing Prcss Cnsidr th tank igur 2.9 whr tw slutins 1 and 2 cntaining matrials A and B ar bing mixd. Stram 1 has lw rat F 1 (m 3 /s), dnsity ρ 1 (kg/m 3 ), T 1 (K), 47
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
Lecture 2a. Crystal Growth (cont d) ECE723
 Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
N J of oscillators in the three lowest quantum
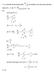 . a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
. a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
ADSORPTION BASIC NOTION
 bruary 8, 005 ChE 505 CHPTER DSORPTION BSIC NOTION dsrptin is a prcss by which a chmical cmpnnt (spcis) frm a fluid phas (gas r liquid) is rmvd by attachmnt t a slid phas. Th spcis bing adsrbd is ftn calld
bruary 8, 005 ChE 505 CHPTER DSORPTION BSIC NOTION dsrptin is a prcss by which a chmical cmpnnt (spcis) frm a fluid phas (gas r liquid) is rmvd by attachmnt t a slid phas. Th spcis bing adsrbd is ftn calld
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
Operating parameters for representative BWR and PWR designs are given below. For the PWR hot channel and the BWR average channel compute and plot:
 Opratin paramtrs r rprsntativ BWR an PWR sins ar ivn blw. Fr t PWR t cannl an t BWR avra cannl cmput an plt: 1) t vi an quality istributins ) Dtrmin t iniviual cmpnnts an t ttal prssur rp Cmpar t rsults
Opratin paramtrs r rprsntativ BWR an PWR sins ar ivn blw. Fr t PWR t cannl an t BWR avra cannl cmput an plt: 1) t vi an quality istributins ) Dtrmin t iniviual cmpnnts an t ttal prssur rp Cmpar t rsults
A Unified Theory of rf Plasma Heating. J.e. Sprott. July 1968
 A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
Chapter 33 Gauss s Law
 Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Chemical Physics II. More Stat. Thermo Kinetics Protein Folding...
 Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
A Brief and Elementary Note on Redshift. May 26, 2010.
 A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
Performance of Microstrip Directional Coupler Using Synthesis Technique
 ISSN: 78 8875 Vl., Issu, March 0 Prrmanc Micrstrip Dirctinal uplr Using Synthsis Tchniqu Vijayan T Asst. Prssr, Dpt E&I, Bharath Univrsity, hnnai-60007, India ABSTRAT: Th intrducd dsign mthd rquirs nly
ISSN: 78 8875 Vl., Issu, March 0 Prrmanc Micrstrip Dirctinal uplr Using Synthsis Tchniqu Vijayan T Asst. Prssr, Dpt E&I, Bharath Univrsity, hnnai-60007, India ABSTRAT: Th intrducd dsign mthd rquirs nly
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING
 Intrnatinal Jurnal n Architctural Scinc, Vlum 6, Numbr 1, p.1-6, 005 EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING Guiyin Fang*, Lin Xing*, Fan Yang* and Hui Li #
Intrnatinal Jurnal n Architctural Scinc, Vlum 6, Numbr 1, p.1-6, 005 EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING Guiyin Fang*, Lin Xing*, Fan Yang* and Hui Li #
Section 11.6: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
:2;$-$(01*%<*=,-./-*=0;"%/;"-*
 !"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
!"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Kragujevac, Serbia, May 2011
 Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Cosmology. Outline. Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 17 Terry Herter. Redshift (again) The Expanding Universe Applying Hubble s Law
 Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
6. Negative Feedback in Single- Transistor Circuits
 Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
FEM FOR HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEMS دانشگاه صنعتي اصفهان- دانشكده مكانيك
 FEM FOR HE RNSFER PROBLEMS 1 Fild problms Gnral orm o systm quations o D linar stady stat ild problms: For 1D problms: D D g Q y y (Hlmholtz quation) d D g Q d Fild problms Hat transr in D in h h ( D D
FEM FOR HE RNSFER PROBLEMS 1 Fild problms Gnral orm o systm quations o D linar stady stat ild problms: For 1D problms: D D g Q y y (Hlmholtz quation) d D g Q d Fild problms Hat transr in D in h h ( D D
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics Qualifying Examination
 Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Need to understand interaction of macroscopic measures
 CE 322 Transportation Enginring Dr. Ahmd Abdl-Rahim, h. D.,.E. Nd to undrstand intraction o macroscopic masurs Spd vs Dnsity Flow vs Dnsity Spd vs Flow Equation 5.14 hlps gnraliz Thr ar svral dirnt orms
CE 322 Transportation Enginring Dr. Ahmd Abdl-Rahim, h. D.,.E. Nd to undrstand intraction o macroscopic masurs Spd vs Dnsity Flow vs Dnsity Spd vs Flow Equation 5.14 hlps gnraliz Thr ar svral dirnt orms
Where k is either given or determined from the data and c is an arbitrary constant.
 Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC B. M. Jovanović, B. Živković
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
Principles of Humidity Dalton s law
 Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
MHT-CET 5 (PHYSICS) PHYSICS CENTERS : MUMBAI /DELHI /AKOLA /LUCKNOW / NASHIK /PUNE /NAGPUR / BOKARO / DUBAI # 1
 1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Math 34A. Final Review
 Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Chemical Reactions and Equations. Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
EE 119 Homework 6 Solution
 EE 9 Hmwrk 6 Slutin Prr: J Bkr TA: Xi Lu Slutin: (a) Th angular magniicatin a tlcp i m / th cal lngth th bjctiv ln i m 4 45 80cm (b) Th clar aprtur th xit pupil i 35 mm Th ditanc btwn th bjctiv ln and
EE 9 Hmwrk 6 Slutin Prr: J Bkr TA: Xi Lu Slutin: (a) Th angular magniicatin a tlcp i m / th cal lngth th bjctiv ln i m 4 45 80cm (b) Th clar aprtur th xit pupil i 35 mm Th ditanc btwn th bjctiv ln and
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
A Prey-Predator Model with an Alternative Food for the Predator, Harvesting of Both the Species and with A Gestation Period for Interaction
 Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
ChE 471: LECTURE 4 Fall 2003
 ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
MODEL-INVERSE BASED REPETITIVE CONTROL
 MODEL-INVERSE BASED REPETITIVE CONTROL T. Hart*, J. Hätönn*, D.H. Owns* Dparmnt f Autmatic Cntrl and Systms Enginring Th Univrsity f Shffild Mappin Strt S1 3JD Shffild Unitd Kingdm Tl: +44(01114 550 Fax:
MODEL-INVERSE BASED REPETITIVE CONTROL T. Hart*, J. Hätönn*, D.H. Owns* Dparmnt f Autmatic Cntrl and Systms Enginring Th Univrsity f Shffild Mappin Strt S1 3JD Shffild Unitd Kingdm Tl: +44(01114 550 Fax:
Introduction to Arithmetic Geometry Fall 2013 Lecture #20 11/14/2013
 18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
Contemporary, atomic, nuclear, and particle physics
 Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
Outline. Heat Exchangers. Heat Exchangers. Compact Heat Exchangers. Compact Heat Exchangers II. Heat Exchangers April 18, ME 375 Heat Transfer 1
 Hat Exangr April 8, 007 Hat Exangr Larry artt Manial Engrg 375 Hat ranfr April 8, 007 Outl Bai ida f at xangr Ovrall at tranfr ffiint Lg-man tmpratur diffrn mtd Efftivn NU mtd ratial nidratin Hat Exangr
Hat Exangr April 8, 007 Hat Exangr Larry artt Manial Engrg 375 Hat ranfr April 8, 007 Outl Bai ida f at xangr Ovrall at tranfr ffiint Lg-man tmpratur diffrn mtd Efftivn NU mtd ratial nidratin Hat Exangr
PHYSICS 489/1489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS
 PHYSICS 489/489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS REMINDER Problm st du today 700 in Box F TODAY: W invstigatd th Dirac quation it dscribs a rlativistic spin /2 particl implis th xistnc of antiparticl
PHYSICS 489/489 LECTURE 7: QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS REMINDER Problm st du today 700 in Box F TODAY: W invstigatd th Dirac quation it dscribs a rlativistic spin /2 particl implis th xistnc of antiparticl
Differential Equations
 UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
Answer Homework 5 PHA5127 Fall 1999 Jeff Stark
 Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
P3-4 (a) Note: This problem can have many solutions as data fitting can be done in many ways. Using Arrhenius Equation For Fire flies: T(in K)
 # Hnc "r k " K ( $ is th rquird rat law. P- Solution is in th dcoding algorithm availabl sparatly from th author. P-4 (a Not: This problm can hav many solutions as data fitting can b don in many ways.
# Hnc "r k " K ( $ is th rquird rat law. P- Solution is in th dcoding algorithm availabl sparatly from th author. P-4 (a Not: This problm can hav many solutions as data fitting can b don in many ways.
Note If the candidate believes that e x = 0 solves to x = 0 or gives an extra solution of x = 0, then withhold the final accuracy mark.
 . (a) Eithr y = or ( 0, ) (b) Whn =, y = ( 0 + ) = 0 = 0 ( + ) = 0 ( )( ) = 0 Eithr = (for possibly abov) or = A 3. Not If th candidat blivs that = 0 solvs to = 0 or givs an tra solution of = 0, thn withhold
. (a) Eithr y = or ( 0, ) (b) Whn =, y = ( 0 + ) = 0 = 0 ( + ) = 0 ( )( ) = 0 Eithr = (for possibly abov) or = A 3. Not If th candidat blivs that = 0 solvs to = 0 or givs an tra solution of = 0, thn withhold
Module 8 Non equilibrium Thermodynamics
 Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Sec 2.3 Modeling with First Order Equations
 Sc.3 Modling with First Ordr Equations Mathmatical modls charactriz physical systms, oftn using diffrntial quations. Modl Construction: Translating physical situation into mathmatical trms. Clarly stat
Sc.3 Modling with First Ordr Equations Mathmatical modls charactriz physical systms, oftn using diffrntial quations. Modl Construction: Translating physical situation into mathmatical trms. Clarly stat
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
are given in the table below. t (hours)
 CALCULUS WORKSHEET ON INTEGRATION WITH DATA Work th following on notbook papr. Giv dcimal answrs corrct to thr dcimal placs.. A tank contains gallons of oil at tim t = hours. Oil is bing pumpd into th
CALCULUS WORKSHEET ON INTEGRATION WITH DATA Work th following on notbook papr. Giv dcimal answrs corrct to thr dcimal placs.. A tank contains gallons of oil at tim t = hours. Oil is bing pumpd into th
Effect of sampling on frequency domain analysis
 LIGO-T666--R Ec sampling n rquncy dmain analysis David P. Nrwd W rviw h wll-knwn cs digial sampling n h rquncy dmain analysis an analg signal, wih mphasis n h cs upn ur masurmns. This discussin llws h
LIGO-T666--R Ec sampling n rquncy dmain analysis David P. Nrwd W rviw h wll-knwn cs digial sampling n h rquncy dmain analysis an analg signal, wih mphasis n h cs upn ur masurmns. This discussin llws h
The Electromagnetic Mass of a Charged Particle
 In mmry f M.I. Kuligina (1914 1994) Th Elctrmagntic Mass f a Chargd Particl V.A. Kuligin, G.A. Kuligina, M.V. Krnva Dpartmnt f Physics, Stat Univrsity Univrsittskaya Sq. 1, Vrnh 394693, Russia A slutin
In mmry f M.I. Kuligina (1914 1994) Th Elctrmagntic Mass f a Chargd Particl V.A. Kuligin, G.A. Kuligina, M.V. Krnva Dpartmnt f Physics, Stat Univrsity Univrsittskaya Sq. 1, Vrnh 394693, Russia A slutin
VSMN30 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA
 VSMN3 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA 1-11-6 kl. 8.-1. Maximum points: 4, Rquird points to pass: Assistanc: CALFEM manual and calculator Problm 1 ( 8p ) 8 7 6 5 y 4 1. m x 1 3 1. m Th isotropic two-dimnsional
VSMN3 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA 1-11-6 kl. 8.-1. Maximum points: 4, Rquird points to pass: Assistanc: CALFEM manual and calculator Problm 1 ( 8p ) 8 7 6 5 y 4 1. m x 1 3 1. m Th isotropic two-dimnsional
Text: WMM, Chapter 5. Sections , ,
 Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
First derivative analysis
 Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Byeong-Joo Lee
 OSECH - MSE calphad@postch.ac.kr Equipartition horm h avrag nrgy o a particl pr indpndnt componnt o motion is ε ε ' ε '' ε ''' U ln Z Z ε < ε > U ln Z β ( ε ' ε '' ε ''' / Z' Z translational kintic nrgy
OSECH - MSE calphad@postch.ac.kr Equipartition horm h avrag nrgy o a particl pr indpndnt componnt o motion is ε ε ' ε '' ε ''' U ln Z Z ε < ε > U ln Z β ( ε ' ε '' ε ''' / Z' Z translational kintic nrgy
5 Curl-free fields and electrostatic potential
 5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
Revision: August 21, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Fourier Transforms and the Wave Equation. Key Mathematics: More Fourier transform theory, especially as applied to solving the wave equation.
 Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING
 ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
MATHEMATICS FOR MANAGEMENT BBMP1103
 Objctivs: TOPIC : EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHM FUNCTIONS. Idntif pnntils nd lgrithmic functins. Idntif th grph f n pnntil nd lgrithmic functins. Clcult qutins using prprtis f pnntils. Clcult qutins using
Objctivs: TOPIC : EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHM FUNCTIONS. Idntif pnntils nd lgrithmic functins. Idntif th grph f n pnntil nd lgrithmic functins. Clcult qutins using prprtis f pnntils. Clcult qutins using
Prod.C [A] t. rate = = =
![Prod.C [A] t. rate = = = Prod.C [A] t. rate = = =](/thumbs/93/114514838.jpg) Concntration Concntration Practic Problms: Kintics KEY CHEM 1B 1. Basd on th data and graph blow: Ract. A Prod. B Prod.C..25.. 5..149.11.5 1..16.144.72 15..83.167.84 2..68.182.91 25..57.193.96 3..5.2.1
Concntration Concntration Practic Problms: Kintics KEY CHEM 1B 1. Basd on th data and graph blow: Ract. A Prod. B Prod.C..25.. 5..149.11.5 1..16.144.72 15..83.167.84 2..68.182.91 25..57.193.96 3..5.2.1
The Frequency Response of a Quarter-Wave Matching Network
 4/1/29 Th Frquncy Rsons o a Quartr 1/9 Th Frquncy Rsons o a Quartr-Wav Matchg Ntwork Q: You hav onc aga rovidd us with conusg and rhas uslss ormation. Th quartr-wav matchg ntwork has an xact SFG o: a Τ
4/1/29 Th Frquncy Rsons o a Quartr 1/9 Th Frquncy Rsons o a Quartr-Wav Matchg Ntwork Q: You hav onc aga rovidd us with conusg and rhas uslss ormation. Th quartr-wav matchg ntwork has an xact SFG o: a Τ
Engineering Differential Equations Practice Final Exam Solutions Fall 2011
 9.6 Enginring Diffrntial Equation Practic Final Exam Solution Fall 0 Problm. (0 pt.) Solv th following initial valu problm: x y = xy, y() = 4. Thi i a linar d.. bcau y and y appar only to th firt powr.
9.6 Enginring Diffrntial Equation Practic Final Exam Solution Fall 0 Problm. (0 pt.) Solv th following initial valu problm: x y = xy, y() = 4. Thi i a linar d.. bcau y and y appar only to th firt powr.
Multiple Short Term Infusion Homework # 5 PHA 5127
 Multipl Short rm Infusion Homwork # 5 PHA 527 A rug is aministr as a short trm infusion. h avrag pharmacokintic paramtrs for this rug ar: k 0.40 hr - V 28 L his rug follows a on-compartmnt boy mol. A 300
Multipl Short rm Infusion Homwork # 5 PHA 527 A rug is aministr as a short trm infusion. h avrag pharmacokintic paramtrs for this rug ar: k 0.40 hr - V 28 L his rug follows a on-compartmnt boy mol. A 300
Electrochemistry L E O
 Rmmbr from CHM151 A rdox raction in on in which lctrons ar transfrrd lctrochmistry L O Rduction os lctrons xidation G R ain lctrons duction W can dtrmin which lmnt is oxidizd or rducd by assigning oxidation
Rmmbr from CHM151 A rdox raction in on in which lctrons ar transfrrd lctrochmistry L O Rduction os lctrons xidation G R ain lctrons duction W can dtrmin which lmnt is oxidizd or rducd by assigning oxidation
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Direct Approach for Discrete Systems One-Dimensional Elements
 CONTINUUM & FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms On-Dimnsional Elmnts Pro. Song Jin Par Mchanical Enginring, POSTECH Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms Dirct approach has th ollowing aturs:
CONTINUUM & FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms On-Dimnsional Elmnts Pro. Song Jin Par Mchanical Enginring, POSTECH Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms Dirct approach has th ollowing aturs:
Electrochemical Energy Systems Spring 2014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant. Midterm Exam
 10.66 Elctrochmical Enrgy Systms Spring 014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant Midtrm Exam Instructions. This is a tak-hom, opn-book xam du in Lctur. Lat xams will not b accptd. You may consult any books, handouts, or
10.66 Elctrochmical Enrgy Systms Spring 014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant Midtrm Exam Instructions. This is a tak-hom, opn-book xam du in Lctur. Lat xams will not b accptd. You may consult any books, handouts, or
section 1 Influencing Change Toolkit How to: Influence People
 Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finit Elmnt Analysis for Mchanical and Arospac Dsign Cornll Univrsity, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Matrials Procss Dsign and Control Laboratory Sibly School of Mchanical and Arospac Enginring
MAE4700/5700 Finit Elmnt Analysis for Mchanical and Arospac Dsign Cornll Univrsity, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Matrials Procss Dsign and Control Laboratory Sibly School of Mchanical and Arospac Enginring
Random Process Part 1
 Random Procss Part A random procss t (, ζ is a signal or wavform in tim. t : tim ζ : outcom in th sampl spac Each tim w rapat th xprimnt, a nw wavform is gnratd. ( W will adopt t for short. Tim sampls
Random Procss Part A random procss t (, ζ is a signal or wavform in tim. t : tim ζ : outcom in th sampl spac Each tim w rapat th xprimnt, a nw wavform is gnratd. ( W will adopt t for short. Tim sampls
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
Continuous probability distributions
 Continuous probability distributions Many continuous probability distributions, including: Uniform Normal Gamma Eponntial Chi-Squard Lognormal Wibull EGR 5 Ch. 6 Uniform distribution Simplst charactrizd
Continuous probability distributions Many continuous probability distributions, including: Uniform Normal Gamma Eponntial Chi-Squard Lognormal Wibull EGR 5 Ch. 6 Uniform distribution Simplst charactrizd
Partial Derivatives: Suppose that z = f(x, y) is a function of two variables.
 Chaptr Functions o Two Variabls Applid Calculus 61 Sction : Calculus o Functions o Two Variabls Now that ou hav som amiliarit with unctions o two variabls it s tim to start appling calculus to hlp us solv
Chaptr Functions o Two Variabls Applid Calculus 61 Sction : Calculus o Functions o Two Variabls Now that ou hav som amiliarit with unctions o two variabls it s tim to start appling calculus to hlp us solv
4 x 4, and. where x is Town Square
 Accumulation and Population Dnsity E. A city locatd along a straight highway has a population whos dnsity can b approimatd by th function p 5 4 th distanc from th town squar, masurd in mils, whr 4 4, and
Accumulation and Population Dnsity E. A city locatd along a straight highway has a population whos dnsity can b approimatd by th function p 5 4 th distanc from th town squar, masurd in mils, whr 4 4, and
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
120~~60 o D 12~0 1500~30O, 15~30 150~30. ..,u 270,,,, ~"~"-4-~qno 240 2~o 300 v 240 ~70O 300
 1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
ELEG 413 Lecture #6. Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Professor The University of Delaware
 LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
Lesson 8 Case Studies
 0.43 Lssn 8 Cas Studis Yu Will Larn Instrumntatin fr:. Lasr phtchmistry and phtlctrchmistry B. Scanning Prb Micrscpy C. PI cntrl in chmical nginring s wll as data tratmnt and prsntatin 1. Lasr phtchmistry
0.43 Lssn 8 Cas Studis Yu Will Larn Instrumntatin fr:. Lasr phtchmistry and phtlctrchmistry B. Scanning Prb Micrscpy C. PI cntrl in chmical nginring s wll as data tratmnt and prsntatin 1. Lasr phtchmistry
Higher order derivatives
 Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
MAGNETIC MONOPOLE THEORY
 AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
Pair (and Triplet) Production Effect:
 Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
Pair (and riplt Production Effct: In both Pair and riplt production, a positron (anti-lctron and an lctron (or ngatron ar producd spontanously as a photon intracts with a strong lctric fild from ithr a
In this lecture... Subsonic and supersonic nozzles Working of these nozzles Performance parameters for nozzles
 Lct-30 Lct-30 In this lctur... Subsonic and suprsonic nozzls Working of ths nozzls rformanc paramtrs for nozzls rof. Bhaskar Roy, rof. A M radp, Dpartmnt of Arospac, II Bombay Lct-30 Variation of fluid
Lct-30 Lct-30 In this lctur... Subsonic and suprsonic nozzls Working of ths nozzls rformanc paramtrs for nozzls rof. Bhaskar Roy, rof. A M radp, Dpartmnt of Arospac, II Bombay Lct-30 Variation of fluid
Lecture Outline. Skin Depth Power Flow 8/7/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics. Topic 3e
 8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
