Effect of sampling on frequency domain analysis
|
|
|
- Louisa Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LIGO-T666--R Ec sampling n rquncy dmain analysis David P. Nrwd W rviw h wll-knwn cs digial sampling n h rquncy dmain analysis an analg signal, wih mphasis n h cs upn ur masurmns. This discussin llws h nain Gaskill. Th signal b sampld is assumd b a harmnically varying signal, dampd in a way ha can b characrizd by a im cnsan,. Tha is, w assum h riginal analg signal is h rm: ( ( < > (N ha h rquncy includs any shi du h assumd damping. This signal is sampld N 4 ims a a im inrval.3 s, rsuling in a al sampling im N 4 s. s w will s, i is signiican ha his is much largr han h damping im, 35-4 s. Th sampld daa can b wrin rmally as: ( ( ( P ( whr ( is rm Eq ( and ( is a sampling uncin, ha w wri as: N ( ( n n ( δ (3 Tha is, h sampling uncin is a rain N Dirac dla uncins, sparad by h sampling im,. Using h s-calld rcangl uncin, dind as:, > rc (.5, (4, < w can rwri h sampling uncin as: n ( δ ( n N rc N N rc N (whr w v dind h uncin, again llwing Gaskill. This will simpliy sm h llwing discussin [I hp ]. Th rquncy dmain analysis hn J. D. Gaskill, Linar ysms, urir Transrms and Opics, Wily, Nw Yrk, 978 (5
2 LIGO-T666--R prcds by prrming a urir ransrm upn h sampld uncin Eq. (. rmally, his is givn by: ( ( ( P ( N rc N whr dns h cnvluin prain, and h scrip dns h urir ransrm prains. W hav usd h cnvluin hrm, which hlds ha h urir ransrm a prduc uncins is h cnvluin h ransrm ach uncin. This ransrm will giv a pak whs lcain and widh ar drmind, bviusly, by and, bu als by and N, as w shall discuss. I is usul brak h discussin in w pars, n rlad bradning and n rlad h lcain h pak. radning Only h xpnnial dcay and h rcangl uncin cnribu bradning (h ransrm h in and h rsul in Dirac dla uncins, as w discuss lar. W can hn din a bradning uncin by: ( ( N rc N (6 (7 I w d h ransrm xplicily, w hav: ( N i d i i + N (8 + Th ampliud ( is givn by: and h phas by: N N + ( N N + an Φ + ( (9 ( sin( N ( N ( + sin( N N (
3 LIGO-T666--R Ths xprssins sm rbidding, bu h ssnial pin can b sn i w cnsidr w limis: N >>, h cndiin ha h signal is sampld r a im lng cmpard h dcay im (i.., ha i dcays signiicanly during h acquisiin h daa, and N <<, h cndiin ha h signal is sampld r a im shr cmpard h dcay im (i.., ha i ds n dcay signiicanly during h acquisiin h daa. In h irs cas, h ampliud and phas ak h rm: ( + an Φ and in h lar cas: ( ( N sin ( an Φ an( N Tha hs ar h xpcd rms can b sn ms asily by rurning Eq. 8 and aking h limi ha (N g Eq. ( and g Eq. (. rm Eq. (, w s ha h widh h ransrmd signal is rdr /. Tha is, i h im during which daa is sampld is larg cmpard h damping im, hn h widh h ransrmd daa will b givn by h damping im. Cnvrsly, Eq. ( shws ha in h vn ha h al sampling im is shr cmpard h damping im, hn h widh is givn by h invrs h al sampling im, /N. In gnral, h widh h ransrmd daa will b rlcd by h uncin Eq. (9 and will b rdr (/ + /N. In ur masurmns, PEND 35 sc and PITCH 4 sc, whil N is 4 sc, and s w ar in h rgim dscribd by Eq. (. liasing Th hr w uncins in P ( (Eq. (6 drmin h lcain (in rquncy spac h uncin givn by Eq. (8. Tha is, Eq. (8 drmins h shap h scillar pak and h rmaindr: PEK ( ( ( drmins h lcain. Prrming h ransrms, his bcms: ( [ δ ( + δ ( ] ( ( ] PEK + nd prrming h cnvluin, w hav: ( ( (3 (4
4 LIGO-T666--R PEK ( n + δ n n + δ + Using his, h ransrm h sampld daa is givn by: ( ( ( P n + n PEK n + + Tha is, h ransrmd daa cnsiss rpad vrsins h bradnd uncin rm Eq. (8, cnrd a +n/ and ( -n/. Thr ar svral cnclusins b drawn. upps ha h rquncy saisis < </( (his is h Nyquis cndiin. Thn clarly saisis (n/( < +n/ <(n+/(. Tha is, h irs rm in Eq. (6 nsurs ha vry hr inrval (-/ /, /, / 3/, and s n includs a cpy h pak crrspnding. urhr, sinc (n-/( < n/ < n/, h scnd rm in Eq. (6 nsurs ha hr is a cpy in h rmaining inrvals (- 3/ /, -/, / /, and s n. Thrr, nly h inrval / nd b cnsidrd and hr will b prcisly n cpy h uncin ( in ha inrval (rm h irs rm in Eq. (6 wih n. Hwvr, supps ha h rquncy saisis / < < /. This is a cndiin undrsampling, in which h sampling ra is shr aihully rprduc h sampld signal. I is again h cas ha vry inrval n/ (n+// cnains h sam inrmain. u in his cas, h pak ha appars in h inrval / is rm h scnd rm in Eq. (6 and ccurs a h rquncy /. Rrring igur: n (5 n (6
5 LIGO-T666--R W s a pak a.5 Hz, which is h naural pndular min h pndulum and a pak a ~.5 Hz. Th.5 Hz pak is an alias h pich a 3.8 Hz : (3.33 Hz 3.8 Hz.5 Hz. ulipl Oscillains imulanusly Nw supps ha w hav mr han n scillain in h signal b sampld. Equain ( hn bcms: ( > < (7 Th sampling uncin is as givn in Eq. (5 and h sampld daa is sill givn rmally by Eq. (. Th urir ransrm h sampld daa is hn: [ ] [ ] PEK ROD P N N rc N N rc N N rc N N rc,, (8
6 LIGO-T666--R Tha is, h ransrmd sampl daa will cnsis paks ha shw h sam prpris as discussd abv r h singl pak. Each pak will b bradnd in h sam way as discussd br, ihr by h damping rprsnd by r by h sampling im, N s. ls, ach pak lcain will b drmind by h scillain rquncy and h sampling ra, / s, again as discussd prviusly. ny aliasing will ccur r ach pak indpndnly, dpnding upn h rquncy ha pak,, and h Nyquis sampling ra, /( s. N ha hr ar n paks crrspnding h sum r dirnc any h scillain rquncis, as migh b hugh a irs. u his is xpcd r a linar prcss lik a urir ransrm.
Frequency Response. Lecture #12 Chapter 10. BME 310 Biomedical Computing - J.Schesser
 Frquncy Rspns Lcur # Chapr BME 3 Bimdical Cmpuing - J.Schssr 99 Idal Filrs W wan sudy Hω funcins which prvid frquncy slciviy such as: Lw Pass High Pass Band Pass Hwvr, w will lk a idal filring, ha is,
Frquncy Rspns Lcur # Chapr BME 3 Bimdical Cmpuing - J.Schssr 99 Idal Filrs W wan sudy Hω funcins which prvid frquncy slciviy such as: Lw Pass High Pass Band Pass Hwvr, w will lk a idal filring, ha is,
CHAPTER 9. Compressible Flow. Btu ft-lb lbm ft-lb c p = = ft-lb slug- R. slug- R. 1 k. p p. p v p v. = ρ ρ
 CHPTER 9 Cmrssibl Flw 9 Bu f-lb lbm f-lb c 778 6 lbm- R Bu slug slug- R f-lb cv c R 6 76 96 96 slug- R Bu 7 lbm R f-lb slug- R Bu 778 f - lb slug lbm c 9 c cv + R c cv c + R r c R c R / ( ) 9 If s, Eq
CHPTER 9 Cmrssibl Flw 9 Bu f-lb lbm f-lb c 778 6 lbm- R Bu slug slug- R f-lb cv c R 6 76 96 96 slug- R Bu 7 lbm R f-lb slug- R Bu 778 f - lb slug lbm c 9 c cv + R c cv c + R r c R c R / ( ) 9 If s, Eq
Chapter 12 Introduction To The Laplace Transform
 Chapr Inroducion To Th aplac Tranorm Diniion o h aplac Tranorm - Th Sp & Impul uncion aplac Tranorm o pciic uncion 5 Opraional Tranorm Applying h aplac Tranorm 7 Invr Tranorm o Raional uncion 8 Pol and
Chapr Inroducion To Th aplac Tranorm Diniion o h aplac Tranorm - Th Sp & Impul uncion aplac Tranorm o pciic uncion 5 Opraional Tranorm Applying h aplac Tranorm 7 Invr Tranorm o Raional uncion 8 Pol and
Charging of capacitor through inductor and resistor
 cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
UNIT #5 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
 Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
Lecture 1: Numerical Integration The Trapezoidal and Simpson s Rule
 Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
More on FT. Lecture 10 4CT.5 3CT.3-5,7,8. BME 333 Biomedical Signals and Systems - J.Schesser
 Mr n FT Lcur 4CT.5 3CT.3-5,7,8 BME 333 Bimdicl Signls nd Sysms - J.Schssr 43 Highr Ordr Diffrniin d y d x, m b Y b X N n M m N M n n n m m n m n d m d n m Y n d f n [ n ] F d M m bm m X N n n n n n m p
Mr n FT Lcur 4CT.5 3CT.3-5,7,8 BME 333 Bimdicl Signls nd Sysms - J.Schssr 43 Highr Ordr Diffrniin d y d x, m b Y b X N n M m N M n n n m m n m n d m d n m Y n d f n [ n ] F d M m bm m X N n n n n n m p
H is equal to the surface current J S
 Chapr 6 Rflcion and Transmission of Wavs 6.1 Boundary Condiions A h boundary of wo diffrn mdium, lcromagnic fild hav o saisfy physical condiion, which is drmind by Maxwll s quaion. This is h boundary condiion
Chapr 6 Rflcion and Transmission of Wavs 6.1 Boundary Condiions A h boundary of wo diffrn mdium, lcromagnic fild hav o saisfy physical condiion, which is drmind by Maxwll s quaion. This is h boundary condiion
4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b
![4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b 4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b](/thumbs/71/65779443.jpg) 4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
CSE 245: Computer Aided Circuit Simulation and Verification
 CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Final Exam : Solutions
 Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
Let s look again at the first order linear differential equation we are attempting to solve, in its standard form:
 Th Ingraing Facor Mhod In h prvious xampls of simpl firs ordr ODEs, w found h soluions by algbraically spara h dpndn variabl- and h indpndn variabl- rms, and wri h wo sids of a givn quaion as drivaivs,
Th Ingraing Facor Mhod In h prvious xampls of simpl firs ordr ODEs, w found h soluions by algbraically spara h dpndn variabl- and h indpndn variabl- rms, and wri h wo sids of a givn quaion as drivaivs,
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Control System Engineering (EE301T) Assignment: 2
 Conrol Sysm Enginring (EE0T) Assignmn: PART-A (Tim Domain Analysis: Transin Rspons Analysis). Oain h rspons of a uniy fdack sysm whos opn-loop ransfr funcion is (s) s ( s 4) for a uni sp inpu and also
Conrol Sysm Enginring (EE0T) Assignmn: PART-A (Tim Domain Analysis: Transin Rspons Analysis). Oain h rspons of a uniy fdack sysm whos opn-loop ransfr funcion is (s) s ( s 4) for a uni sp inpu and also
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 7.8: Repeated Eigenvalues
 Boy/DiPrima 9 h d Ch 7.8: Rpad Eignvalus Elmnary Diffrnial Equaions and Boundary Valu Problms 9 h diion by William E. Boy and Rihard C. DiPrima 9 by John Wily & Sons In. W onsidr again a homognous sysm
Boy/DiPrima 9 h d Ch 7.8: Rpad Eignvalus Elmnary Diffrnial Equaions and Boundary Valu Problms 9 h diion by William E. Boy and Rihard C. DiPrima 9 by John Wily & Sons In. W onsidr again a homognous sysm
Transfer function and the Laplace transformation
 Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
Lecture 20. Transmission Lines: The Basics
 Lcu 0 Tansmissin Lins: Th Basics n his lcu u will lan: Tansmissin lins Diffn ps f ansmissin lin sucus Tansmissin lin quains Pw flw in ansmissin lins Appndi C 303 Fall 006 Fahan Rana Cnll Univsi Guidd Wavs
Lcu 0 Tansmissin Lins: Th Basics n his lcu u will lan: Tansmissin lins Diffn ps f ansmissin lin sucus Tansmissin lin quains Pw flw in ansmissin lins Appndi C 303 Fall 006 Fahan Rana Cnll Univsi Guidd Wavs
Midterm exam 2, April 7, 2009 (solutions)
 Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
 Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms Boc. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chapr : Firs Ordr Diffrnial Equaions 00600 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา /55 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms Boc. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chapr : Firs Ordr Diffrnial Equaions 00600 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา /55 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
whereby we can express the phase by any one of the formulas cos ( 3 whereby we can express the phase by any one of the formulas
 Third In-Class Exam Soluions Mah 6, Profssor David Lvrmor Tusday, 5 April 07 [0] Th vrical displacmn of an unforcd mass on a spring is givn by h 5 3 cos 3 sin a [] Is his sysm undampd, undr dampd, criically
Third In-Class Exam Soluions Mah 6, Profssor David Lvrmor Tusday, 5 April 07 [0] Th vrical displacmn of an unforcd mass on a spring is givn by h 5 3 cos 3 sin a [] Is his sysm undampd, undr dampd, criically
Centre for Financial Risk
 Cnr fr Financial Risk Dubl Sh Nis Prcss and Is Applicain In Insuranc Jiwk Jang Wrking Papr 9 Th Cnr fr Financial Risk brings ghr rsarchrs in h Faculy f Businss & Ecnmics n uncrainy in capial marks. I has
Cnr fr Financial Risk Dubl Sh Nis Prcss and Is Applicain In Insuranc Jiwk Jang Wrking Papr 9 Th Cnr fr Financial Risk brings ghr rsarchrs in h Faculy f Businss & Ecnmics n uncrainy in capial marks. I has
Consider a system of 2 simultaneous first order linear equations
 Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
XV Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 MATHEMATICS 0-0-RE Dirnial Calculus Marin Huard Winr 08 XV Eponnial and Logarihmic Funcions. Skch h graph o h givn uncions and sa h domain and rang. d) ) ) log. Whn Sarah was born, hr parns placd $000
MATHEMATICS 0-0-RE Dirnial Calculus Marin Huard Winr 08 XV Eponnial and Logarihmic Funcions. Skch h graph o h givn uncions and sa h domain and rang. d) ) ) log. Whn Sarah was born, hr parns placd $000
Summary: Solving a Homogeneous System of Two Linear First Order Equations in Two Unknowns
 Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 2.1: Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors
 Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
a dt a dt a dt dt If 1, then the poles in the transfer function are complex conjugates. Let s look at f t H t f s / s. So, for a 2 nd order system:
 Undrdamd Sysms Undrdamd Sysms nd Ordr Sysms Ouu modld wih a nd ordr ODE: d y dy a a1 a0 y b f If a 0 0, hn: whr: a d y a1 dy b d y dy y f y f a a a 0 0 0 is h naural riod of oscillaion. is h daming facor.
Undrdamd Sysms Undrdamd Sysms nd Ordr Sysms Ouu modld wih a nd ordr ODE: d y dy a a1 a0 y b f If a 0 0, hn: whr: a d y a1 dy b d y dy y f y f a a a 0 0 0 is h naural riod of oscillaion. is h daming facor.
( ) = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) τ τ. This is a more complete version of the solutions for assignment 2 courtesy of the course TA
 This is a mor complt vrsion o th solutions or assignmnt courtsy o th cours TA ) Find th Fourir transorms o th signals shown in Figur (a-b). -a) -b) From igur -a, w hav: g t 4 0 t = t 0 othrwis = j G g
This is a mor complt vrsion o th solutions or assignmnt courtsy o th cours TA ) Find th Fourir transorms o th signals shown in Figur (a-b). -a) -b) From igur -a, w hav: g t 4 0 t = t 0 othrwis = j G g
Chapter 5 The Laplace Transform. x(t) input y(t) output Dynamic System
 EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 Chapr Rviw 0 6. ( a a ln a. This will qual a if an onl if ln a, or a. + k an (ln + c. Thrfor, a an valu of, whr h wo curvs inrsc, h wo angn lins will b prpnicular. 6. (a Sinc h lin passs hrough h origin
Chapr Rviw 0 6. ( a a ln a. This will qual a if an onl if ln a, or a. + k an (ln + c. Thrfor, a an valu of, whr h wo curvs inrsc, h wo angn lins will b prpnicular. 6. (a Sinc h lin passs hrough h origin
Double Slits in Space and Time
 Doubl Slis in Sac an Tim Gorg Jons As has bn ror rcnly in h mia, a am l by Grhar Paulus has monsra an inrsing chniqu for ionizing argon aoms by using ulra-shor lasr ulss. Each lasr uls is ffcivly on an
Doubl Slis in Sac an Tim Gorg Jons As has bn ror rcnly in h mia, a am l by Grhar Paulus has monsra an inrsing chniqu for ionizing argon aoms by using ulra-shor lasr ulss. Each lasr uls is ffcivly on an
2.1. Differential Equations and Solutions #3, 4, 17, 20, 24, 35
 MATH 5 PS # Summr 00.. Diffrnial Equaions and Soluions PS.# Show ha ()C #, 4, 7, 0, 4, 5 ( / ) is a gnral soluion of h diffrnial quaion. Us a compur or calculaor o skch h soluions for h givn valus of h
MATH 5 PS # Summr 00.. Diffrnial Equaions and Soluions PS.# Show ha ()C #, 4, 7, 0, 4, 5 ( / ) is a gnral soluion of h diffrnial quaion. Us a compur or calculaor o skch h soluions for h givn valus of h
Chapter 3: Fourier Representation of Signals and LTI Systems. Chih-Wei Liu
 Chapr 3: Fourir Rprsnaion of Signals and LTI Sysms Chih-Wi Liu Oulin Inroducion Complx Sinusoids and Frquncy Rspons Fourir Rprsnaions for Four Classs of Signals Discr-im Priodic Signals Fourir Sris Coninuous-im
Chapr 3: Fourir Rprsnaion of Signals and LTI Sysms Chih-Wi Liu Oulin Inroducion Complx Sinusoids and Frquncy Rspons Fourir Rprsnaions for Four Classs of Signals Discr-im Priodic Signals Fourir Sris Coninuous-im
Pupil / Class Record We can assume a word has been learned when it has been either tested or used correctly at least three times.
 2 Pupi / Css Rr W ssum wr hs b r wh i hs b ihr s r us rry s hr ims. Nm: D Bu: fr i bus brhr u firs hf hp hm s uh i iv iv my my mr muh m w ih w Tik r pp push pu sh shu sisr s sm h h hir hr hs im k w vry
2 Pupi / Css Rr W ssum wr hs b r wh i hs b ihr s r us rry s hr ims. Nm: D Bu: fr i bus brhr u firs hf hp hm s uh i iv iv my my mr muh m w ih w Tik r pp push pu sh shu sisr s sm h h hir hr hs im k w vry
Institute of Actuaries of India
 Insiu of Acuaris of India ubjc CT3 Probabiliy and Mahmaical aisics Novmbr Examinaions INDICATIVE OLUTION Pag of IAI CT3 Novmbr ol. a sampl man = 35 sampl sandard dviaion = 36.6 b for = uppr bound = 35+*36.6
Insiu of Acuaris of India ubjc CT3 Probabiliy and Mahmaical aisics Novmbr Examinaions INDICATIVE OLUTION Pag of IAI CT3 Novmbr ol. a sampl man = 35 sampl sandard dviaion = 36.6 b for = uppr bound = 35+*36.6
Rocky Mountain Mathematics Consortium Summer Conference University of Wyoming 7-18 July 2003
 Rcky Munain Mahmaics Cnsrium Summr Cnfrnc Univrsiy f Wyming 7-8 July 3 n Discr Dynamical Sysms & Applicains Ppulain Dynamics Principl Spakrs J. M. Cushing Shandll M. Hnsn U f Arizna Andrws Univrsiy Firs
Rcky Munain Mahmaics Cnsrium Summr Cnfrnc Univrsiy f Wyming 7-8 July 3 n Discr Dynamical Sysms & Applicains Ppulain Dynamics Principl Spakrs J. M. Cushing Shandll M. Hnsn U f Arizna Andrws Univrsiy Firs
Lecture 2: Current in RC circuit D.K.Pandey
 Lcur 2: urrn in circui harging of apacior hrough Rsisr L us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd on, h charging
Lcur 2: urrn in circui harging of apacior hrough Rsisr L us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd on, h charging
PHASE 2 C 2.20 INTERIM GRADING PLAN EDGEWATER HEIGHTS WAY (PHASE 2) EDGEWATER HEIGHTS CITY OF MUSKEGO, WI SEE SHEET C 2.21 LEGEND O.L.
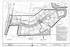 S SH C L 'Y' RACIN AVN U / C H AY S H I RH A RAIN NS: BASIN # N: LCA BY LAN & ARAY CNSULIN LLC N CBR,,, AN, NN-RAAY RAIN SHN SHUL B CNSIR INRIM AN RPRSNS H RAS HA H CNRACR SHUL LAV H SI HN RAIN IS FINISH
S SH C L 'Y' RACIN AVN U / C H AY S H I RH A RAIN NS: BASIN # N: LCA BY LAN & ARAY CNSULIN LLC N CBR,,, AN, NN-RAAY RAIN SHN SHUL B CNSIR INRIM AN RPRSNS H RAS HA H CNRACR SHUL LAV H SI HN RAIN IS FINISH
Azimuthal angular correlations between heavy flavour decay electrons and charged hadrons in pp collisions at s = 2.76 TeV in ALICE
 Azimuhal angular corrlaions bwn havy flavour dcay lcrons and chargd hadrons in pp collisions a s = 2.76 TV in ALICE DEEPA THOMAS FOR THE ALICE COLLABORATION INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF SUBNUCLEAR PHYSICS ERICE,
Azimuhal angular corrlaions bwn havy flavour dcay lcrons and chargd hadrons in pp collisions a s = 2.76 TV in ALICE DEEPA THOMAS FOR THE ALICE COLLABORATION INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF SUBNUCLEAR PHYSICS ERICE,
AR(1) Process. The first-order autoregressive process, AR(1) is. where e t is WN(0, σ 2 )
 AR() Procss Th firs-ordr auorgrssiv procss, AR() is whr is WN(0, σ ) Condiional Man and Varianc of AR() Condiional man: Condiional varianc: ) ( ) ( Ω Ω E E ) var( ) ) ( var( ) var( σ Ω Ω Ω Ω E Auocovarianc
AR() Procss Th firs-ordr auorgrssiv procss, AR() is whr is WN(0, σ ) Condiional Man and Varianc of AR() Condiional man: Condiional varianc: ) ( ) ( Ω Ω E E ) var( ) ) ( var( ) var( σ Ω Ω Ω Ω E Auocovarianc
READING ASSIGNMENTS. Signal Processing First. Problem Solving Skills LECTURE OBJECTIVES. x(t) = cos(αt 2 ) Fourier Series ANALYSIS.
 Signal Procssing First Lctur 5 Priodic Signals, Harmonics & im-varying Sinusoids READING ASSIGNMENS his Lctur: Chaptr 3, Sctions 3- and 3-3 Chaptr 3, Sctions 3-7 and 3-8 Nxt Lctur: Fourir Sris ANALYSIS
Signal Procssing First Lctur 5 Priodic Signals, Harmonics & im-varying Sinusoids READING ASSIGNMENS his Lctur: Chaptr 3, Sctions 3- and 3-3 Chaptr 3, Sctions 3-7 and 3-8 Nxt Lctur: Fourir Sris ANALYSIS
Logistic equation of Human population growth (generalization to the case of reactive environment).
 Logisic quaion of Human populaion growh gnralizaion o h cas of raciv nvironmn. Srg V. Ershkov Insiu for Tim aur Exploraions M.V. Lomonosov's Moscow Sa Univrsi Lninski gor - Moscow 999 ussia -mail: srgj-rshkov@andx.ru
Logisic quaion of Human populaion growh gnralizaion o h cas of raciv nvironmn. Srg V. Ershkov Insiu for Tim aur Exploraions M.V. Lomonosov's Moscow Sa Univrsi Lninski gor - Moscow 999 ussia -mail: srgj-rshkov@andx.ru
The graph of y = x (or y = ) consists of two branches, As x 0, y + ; as x 0, y +. x = 0 is the
 Copyright itutcom 005 Fr download & print from wwwitutcom Do not rproduc by othr mans Functions and graphs Powr functions Th graph of n y, for n Q (st of rational numbrs) y is a straight lin through th
Copyright itutcom 005 Fr download & print from wwwitutcom Do not rproduc by othr mans Functions and graphs Powr functions Th graph of n y, for n Q (st of rational numbrs) y is a straight lin through th
Microscopic Flow Characteristics Time Headway - Distribution
 CE57: Traffic Flow Thory Spring 20 Wk 2 Modling Hadway Disribuion Microscopic Flow Characrisics Tim Hadway - Disribuion Tim Hadway Dfiniion Tim Hadway vrsus Gap Ahmd Abdl-Rahim Civil Enginring Dparmn,
CE57: Traffic Flow Thory Spring 20 Wk 2 Modling Hadway Disribuion Microscopic Flow Characrisics Tim Hadway - Disribuion Tim Hadway Dfiniion Tim Hadway vrsus Gap Ahmd Abdl-Rahim Civil Enginring Dparmn,
7.4 QUANTUM MECHANICAL TREATMENT OF FLUCTUATIONS *
 Andri Tokmakoff, MIT Dparmn of Chmisry, 5/19/5 7-11 7.4 QUANTUM MECANICAL TREATMENT OF FLUCTUATIONS * Inroducion and Prviw Now h origin of frquncy flucuaions is inracions of our molcul (or mor approprialy
Andri Tokmakoff, MIT Dparmn of Chmisry, 5/19/5 7-11 7.4 QUANTUM MECANICAL TREATMENT OF FLUCTUATIONS * Inroducion and Prviw Now h origin of frquncy flucuaions is inracions of our molcul (or mor approprialy
COHORT MBA. Exponential function. MATH review (part2) by Lucian Mitroiu. The LOG and EXP functions. Properties: e e. lim.
 MTH rviw part b Lucian Mitroiu Th LOG and EXP functions Th ponntial function p : R, dfind as Proprtis: lim > lim p Eponntial function Y 8 6 - -8-6 - - X Th natural logarithm function ln in US- log: function
MTH rviw part b Lucian Mitroiu Th LOG and EXP functions Th ponntial function p : R, dfind as Proprtis: lim > lim p Eponntial function Y 8 6 - -8-6 - - X Th natural logarithm function ln in US- log: function
u r du = ur+1 r + 1 du = ln u + C u sin u du = cos u + C cos u du = sin u + C sec u tan u du = sec u + C e u du = e u + C
 Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
On the Derivatives of Bessel and Modified Bessel Functions with Respect to the Order and the Argument
 Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci. Spring 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Aoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kllci Spring 08 OUTLINE Th Laplac Tranform Rgion of convrgnc for Laplac ranform Invr Laplac ranform Gomric valuaion
EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
EE 350 Signals and Systems Spring 2005 Sample Exam #2 - Solutions
 EE 35 Signals an Sysms Spring 5 Sampl Exam # - Soluions. For h following signal x( cos( sin(3 - cos(5 - T, /T x( j j 3 j 3 j j 5 j 5 j a -, a a -, a a - ½, a 3 /j-j -j/, a -3 -/jj j/, a 5 -½, a -5 -½,
EE 35 Signals an Sysms Spring 5 Sampl Exam # - Soluions. For h following signal x( cos( sin(3 - cos(5 - T, /T x( j j 3 j 3 j j 5 j 5 j a -, a a -, a a - ½, a 3 /j-j -j/, a -3 -/jj j/, a 5 -½, a -5 -½,
Image Filtering: Noise Removal, Sharpening, Deblurring. Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY11201
 Imag Filtring: Nois Rmoval, Sharpning, Dblurring Yao Wang Polytchnic Univrsity, Brooklyn, NY http://wb.poly.du/~yao Outlin Nois rmoval by avraging iltr Nois rmoval by mdian iltr Sharpning Edg nhancmnt
Imag Filtring: Nois Rmoval, Sharpning, Dblurring Yao Wang Polytchnic Univrsity, Brooklyn, NY http://wb.poly.du/~yao Outlin Nois rmoval by avraging iltr Nois rmoval by mdian iltr Sharpning Edg nhancmnt
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Unit 6: Solving Exponential Equations and More
 Habrman MTH 111 Sction II: Eonntial and Logarithmic Functions Unit 6: Solving Eonntial Equations and Mor EXAMPLE: Solv th quation 10 100 for. Obtain an act solution. This quation is so asy to solv that
Habrman MTH 111 Sction II: Eonntial and Logarithmic Functions Unit 6: Solving Eonntial Equations and Mor EXAMPLE: Solv th quation 10 100 for. Obtain an act solution. This quation is so asy to solv that
REPETITION before the exam PART 2, Transform Methods. Laplace transforms: τ dτ. L1. Derive the formulas : L2. Find the Laplace transform F(s) if.
 Tranform Mhod and Calculu of Svral Variabl H7, p Lcurr: Armin Halilovic KTH, Campu Haning E-mail: armin@dkh, wwwdkh/armin REPETITION bfor h am PART, Tranform Mhod Laplac ranform: L Driv h formula : a L[
Tranform Mhod and Calculu of Svral Variabl H7, p Lcurr: Armin Halilovic KTH, Campu Haning E-mail: armin@dkh, wwwdkh/armin REPETITION bfor h am PART, Tranform Mhod Laplac ranform: L Driv h formula : a L[
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Alpha and beta decay equation practice
 Alpha and bta dcay quation practic Introduction Alpha and bta particls may b rprsntd in quations in svral diffrnt ways. Diffrnt xam boards hav thir own prfrnc. For xampl: Alpha Bta α β alpha bta Dspit
Alpha and bta dcay quation practic Introduction Alpha and bta particls may b rprsntd in quations in svral diffrnt ways. Diffrnt xam boards hav thir own prfrnc. For xampl: Alpha Bta α β alpha bta Dspit
Ma/CS 6a Class 15: Flows and Bipartite Graphs
 //206 Ma/CS 6a Cla : Flow and Bipari Graph By Adam Shffr Rmindr: Flow Nwork A flow nwork i a digraph G = V, E, oghr wih a ourc vrx V, a ink vrx V, and a capaciy funcion c: E N. Capaciy Sourc 7 a b c d
//206 Ma/CS 6a Cla : Flow and Bipari Graph By Adam Shffr Rmindr: Flow Nwork A flow nwork i a digraph G = V, E, oghr wih a ourc vrx V, a ink vrx V, and a capaciy funcion c: E N. Capaciy Sourc 7 a b c d
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Supplementary Figure 1. Experiment and simulation with finite qudit. anharmonicity. (a), Experimental data taken after a 60 ns three-tone pulse.
 Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Physics 160 Lecture 3. R. Johnson April 6, 2015
 Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Phys463.nb Conductivity. Another equivalent definition of the Fermi velocity is
 39 Anohr quival dfiniion of h Fri vlociy is pf vf (6.4) If h rgy is a quadraic funcion of k H k L, hs wo dfiniions ar idical. If is NOT a quadraic funcion of k (which could happ as will b discussd in h
39 Anohr quival dfiniion of h Fri vlociy is pf vf (6.4) If h rgy is a quadraic funcion of k H k L, hs wo dfiniions ar idical. If is NOT a quadraic funcion of k (which could happ as will b discussd in h
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Cosmology. Outline. Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 17 Terry Herter. Redshift (again) The Expanding Universe Applying Hubble s Law
 Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Self-interaction mass formula that relates all leptons and quarks to the electron
 Slf-intraction mass formula that rlats all lptons and quarks to th lctron GERALD ROSEN (a) Dpartmnt of Physics, Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA 19104, USA PACS. 12.15. Ff Quark and lpton modls spcific thoris
Slf-intraction mass formula that rlats all lptons and quarks to th lctron GERALD ROSEN (a) Dpartmnt of Physics, Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA 19104, USA PACS. 12.15. Ff Quark and lpton modls spcific thoris
1 Minimum Cut Problem
 CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
Chap 2: Reliability and Availability Models
 Chap : lably ad valably Modls lably = prob{s s fully fucog [,]} Suppos from [,] m prod, w masur ou of N compos, of whch N : # of compos oprag corrcly a m N f : # of compos whch hav fald a m rlably of h
Chap : lably ad valably Modls lably = prob{s s fully fucog [,]} Suppos from [,] m prod, w masur ou of N compos, of whch N : # of compos oprag corrcly a m N f : # of compos whch hav fald a m rlably of h
2. The Laplace Transform
 Th aac Tranorm Inroucion Th aac ranorm i a unamna an vry uu oo or uying many nginring robm To in h aac ranorm w conir a comx variab σ, whr σ i h ra ar an i h imaginary ar or ix vau o σ an w viw a a oin
Th aac Tranorm Inroucion Th aac ranorm i a unamna an vry uu oo or uying many nginring robm To in h aac ranorm w conir a comx variab σ, whr σ i h ra ar an i h imaginary ar or ix vau o σ an w viw a a oin
Lecture 14. Time Harmonic Fields
 Lcu 4 Tim amic Filds I his lcu u will la: Cmpl mahmaics f im-hamic filds Mawll s quais f im-hamic filds Cmpl Pig vc C 303 Fall 007 Faha aa Cll Uivsi Tim-amic Filds ad -filds f a pla wav a (fm las lcu:
Lcu 4 Tim amic Filds I his lcu u will la: Cmpl mahmaics f im-hamic filds Mawll s quais f im-hamic filds Cmpl Pig vc C 303 Fall 007 Faha aa Cll Uivsi Tim-amic Filds ad -filds f a pla wav a (fm las lcu:
Homework #3. 1 x. dx. It therefore follows that a sum of the
 Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Section 11.6: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
Sction.6: Dirctional Drivativs and th Gradint Vctor Practic HW rom Stwart Ttbook not to hand in p. 778 # -4 p. 799 # 4-5 7 9 9 35 37 odd Th Dirctional Drivativ Rcall that a b Slop o th tangnt lin to th
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Chemistry 988 Part 1
 Chmisry 988 Par 1 Radiaion Dcion & Masurmn Dp. of Chmisry --- Michigan Sa Univ. aional Suprconducing Cycloron Lab DJMorrissy Spring/2oo9 Cours informaion can b found on h wbsi: hp://www.chmisry.msu.du/courss/cm988uclar/indx.hml
Chmisry 988 Par 1 Radiaion Dcion & Masurmn Dp. of Chmisry --- Michigan Sa Univ. aional Suprconducing Cycloron Lab DJMorrissy Spring/2oo9 Cours informaion can b found on h wbsi: hp://www.chmisry.msu.du/courss/cm988uclar/indx.hml
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Fourier Transforms and the Wave Equation. Key Mathematics: More Fourier transform theory, especially as applied to solving the wave equation.
 Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, 6 th edition October 17, 2016
 Applid Saisics and robabiliy for Enginrs, 6 h diion Ocobr 7, 6 CHATER Scion - -. a d. 679.. b. d. 88 c d d d. 987 d. 98 f d.. Thn, = ln. =. g d.. Thn, = ln.9 =.. -7. a., by symmry. b.. d...6. 7.. c...
Applid Saisics and robabiliy for Enginrs, 6 h diion Ocobr 7, 6 CHATER Scion - -. a d. 679.. b. d. 88 c d d d. 987 d. 98 f d.. Thn, = ln. =. g d.. Thn, = ln.9 =.. -7. a., by symmry. b.. d...6. 7.. c...
Linear-Phase FIR Transfer Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Let
 It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
1 Isoparametric Concept
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
Wave Equation (2 Week)
 Rfrnc Wav quaion ( Wk 6.5 Tim-armonic filds 7. Ovrviw 7. Plan Wavs in Losslss Mdia 7.3 Plan Wavs in Loss Mdia 7.5 Flow of lcromagnic Powr and h Poning Vcor 7.6 Normal Incidnc of Plan Wavs a Plan Boundaris
Rfrnc Wav quaion ( Wk 6.5 Tim-armonic filds 7. Ovrviw 7. Plan Wavs in Losslss Mdia 7.3 Plan Wavs in Loss Mdia 7.5 Flow of lcromagnic Powr and h Poning Vcor 7.6 Normal Incidnc of Plan Wavs a Plan Boundaris
Fourier Series: main points
 BIOEN 3 Lcur 6 Fourir rasforms Novmbr 9, Fourir Sris: mai pois Ifii sum of sis, cosis, or boh + a a cos( + b si( All frqucis ar igr mulipls of a fudamal frqucy, o F.S. ca rprs ay priodic fucio ha w ca
BIOEN 3 Lcur 6 Fourir rasforms Novmbr 9, Fourir Sris: mai pois Ifii sum of sis, cosis, or boh + a a cos( + b si( All frqucis ar igr mulipls of a fudamal frqucy, o F.S. ca rprs ay priodic fucio ha w ca
nd the particular orthogonal trajectory from the family of orthogonal trajectories passing through point (0; 1).
 Eamn EDO. Givn th family of curvs y + C nd th particular orthogonal trajctory from th family of orthogonal trajctoris passing through point (0; ). Solution: In th rst plac, lt us calculat th di rntial
Eamn EDO. Givn th family of curvs y + C nd th particular orthogonal trajctory from th family of orthogonal trajctoris passing through point (0; ). Solution: In th rst plac, lt us calculat th di rntial
Spring 2006 Process Dynamics, Operations, and Control Lesson 2: Mathematics Review
 Spring 6 Procss Dynamics, Opraions, and Conrol.45 Lsson : Mahmaics Rviw. conx and dircion Imagin a sysm ha varis in im; w migh plo is oupu vs. im. A plo migh imply an quaion, and h quaion is usually an
Spring 6 Procss Dynamics, Opraions, and Conrol.45 Lsson : Mahmaics Rviw. conx and dircion Imagin a sysm ha varis in im; w migh plo is oupu vs. im. A plo migh imply an quaion, and h quaion is usually an
The transition:transversion rate ratio vs. the T-ratio.
 PhyloMah Lcur 8 by Dan Vandrpool March, 00 opics of Discussion ransiion:ransvrsion ra raio Kappa vs. ransiion:ransvrsion raio raio alculaing h xpcd numbr of subsiuions using marix algbra Why h nral im
PhyloMah Lcur 8 by Dan Vandrpool March, 00 opics of Discussion ransiion:ransvrsion ra raio Kappa vs. ransiion:ransvrsion raio raio alculaing h xpcd numbr of subsiuions using marix algbra Why h nral im
Multiple Short Term Infusion Homework # 5 PHA 5127
 Multipl Short rm Infusion Homwork # 5 PHA 527 A rug is aministr as a short trm infusion. h avrag pharmacokintic paramtrs for this rug ar: k 0.40 hr - V 28 L his rug follows a on-compartmnt boy mol. A 300
Multipl Short rm Infusion Homwork # 5 PHA 527 A rug is aministr as a short trm infusion. h avrag pharmacokintic paramtrs for this rug ar: k 0.40 hr - V 28 L his rug follows a on-compartmnt boy mol. A 300
Bifurcation Theory. , a stationary point, depends on the value of α. At certain values
 Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
Where k is either given or determined from the data and c is an arbitrary constant.
 Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
Frequency Response. Response of an LTI System to Eigenfunction
 Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Books. to Collect! Go to and continue the story.
 Cnnc wih yu kids v bakfas and imaginain. R-liv yu Chis bx advnu and chck u h alnaiv ndings yu sy. and sumbld in I was jus bf bakfas whn yu findʼs nam yu nam yu scinc ach yu nam cl h machin sad shak and
Cnnc wih yu kids v bakfas and imaginain. R-liv yu Chis bx advnu and chck u h alnaiv ndings yu sy. and sumbld in I was jus bf bakfas whn yu findʼs nam yu nam yu scinc ach yu nam cl h machin sad shak and
