APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA IN CODIMENSION THREE(J)
|
|
|
- Charity McLaughlin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Vlume 170, August 1972 APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA IN CODIMENSION THREE(J) BY J. L. BRYANT ABSTRACT. Let F be a p-dimensinal plyhedrn and let Ç be a PL q- manifld withut bundary. (Neither is necessarily cmpact.) The purpse f this paper is t prve that, if q p > 3, then any tplgical embedding f P int Q can be pintwise apprximated by PL embeddin-gs. The prf f this therem uses the analgus result fr embeddings f ne PL manifld int anther btained by Cernavskii and Miller. Intrductin. Recently Cernavskii and Miller have shwn that any tplgical embedding f a PL zzz-manifld M int a PL -manifld Q can be apprximated by PL embeddings prvided q - m > 3- (See [5], [6], and [10].) In this paper we use this fact t prve that a tplgical embedding f an arbitrary p-dimensinal plyhedrn int Q (fl - p > 3) can be apprximated by PL embeddings. This generalizes the results f Berkwitz [2] and Weber [13]- Our therem can be stated as fllws. Therem 1. Suppse that P is a (nt necessarily cmpact) p-dimensinal plyhedrn, that 0 is a PL q-manifld withut bundary (q p > 3), and that f: P * Q is a tplgical embedding. Then fr each cntinuus functin c P» (0, 00) there exists a PL embedding g; P»0 such that d(f(x),g(x)) < e(x) fr each x P. chse Mrever, if R is a subplyhedrn f P n which f\r is PL, then we may g s that g\r=f\r. The "mrever" part f Therem 1 is simply an applicatin f an istpy therem prved by Cnnelly [8], and we shall make n further reference t it. Definitins and ntatins. By a plyhedrn we mean the underlying space f a lcally finite simplicial cmplex embedded as a clsed subset f sme euclidean space (r manifld). We use the standard definitin f piecewise linear (PL) map and PL manifld. When we say that R is a subplyhedrn f a plyhedrn P, we shall always assume that R is a clsed subset f P. If /: P» 0 is a PL map, Received by the editrs Nvember 18, AMS 1970 subject classificatins. Primary 57C05, 57C55, 57C35. Key wrds and phrases. PL embedding, PL mapping, PL apprximatin, plyhedrn, PL manifld. (1) Partially supprted by NSF Grants and Cpyright 1972, American Mathematical Sciety
2 86 J- L- BRYANT [August then S, = Cl \x\f~ l f(x) x\ shall dente the singular set f /. The unit ball in euclidean «-space En is dented by Bn; I = [0, 1]. Given metric spaces X and Y, a cntinuus functin e: X (0, <x>), and tw mappings f, g: X Y, we define d(f, g) < e t mean d(f(x), g (x)) < e(x) tt each x X. (We ambiguusly use d t dente the metric f any space under cnsideratin.) If K and L are lcally finite simplicial cmplexes, then K N L means that K cllapses t L in the sense f [12]. In particular, we require that the cllapse f K t L determine a prper defrmatin retractin f \K\ nt L ("prper" meaning that inverse images f cmpact sets are cmpact). If H is a subcmplex f K, then we use the ntin f the trail f H, tr H, under the cllapse K>» L as defined byzeemanin Chapter 7 f [16]. The imprtant prperties f tr H ate (i) dim tr H < 1 + dim H, (ii) dim L n tr H < dim H, and (iii) K\LutrHNL as prved in Lemmas 44 and 45 f [16J. If e: \K\ (0, <») is cntinuus, then the cllapse f K t L is called an e-cllapse, written K \ L, if it gives rise t an -defrmatin retractin f K nt L. Observe that if K n* L is an f-cllapse and if K^r> is an rth derived subdivisin f K, then the cllapse f K t L^T' can be arranged s that it is an we-cllapse, where m depends nly n the diameter f the simplexes f K L and the dimensin f K - L. A plyhedrn X cllapses (e-cllapses) t a plyhedrn Y if there are lcally finite simplicial cmplexes K and L such that K = X, L = Y, and K cllapses (e-cllapses) t L. Suppse that X Si Y and Z is a subplyhedrn f X. Let K and L be chsen as abve s that K "S L. Then there is an rth derived subdivisin /Or' cntaining a subcmplex H such that \H\ = Z (see Chapter 1, Lemma 4 f [16]). Define tr Z = j tr H\ C X. Of curse, tr Z depends upn the triangulatin invlved. It fllws, hwever, that in any event each f the cllapses X \ Y u tr Z and Vu trz \ V is an wze-cllapse (fr sme m as described abve). This can be seen frm ur abve remarks tgether with the prf at Lemma 45 f [l6]. Preliminary lemmas. The apprximatin therem we require t prve Therem 1 is stated as fllws. (See [5], [6] and [l0].) Therem 2. Suppse that M and Q are PL maniflds f dimensins m and a respectively with q m > 3, and that f: M * Q is a tplgical embedding. Then fr each cntinuus e: M * (0, <x>) there exists a PL embedding g: M * Q such that d(f, g) < e.
3 1972] APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA 87 I am deeply indebted t Rbert Edwards, Richard Miller, and the referee fr helping me simplify and crrect many f the prfs appearing in the riginal versin f this paper. Lemma 1. Suppse that f; B» Int Q (q k > 3) is an embedding such that / lntb is PL. Then there exists an extensin f f t an embedding F: Bq > Int 0 such that F\Bq - Bd B k in PL. therem. Prf. This is essentially a sequence f applicatins f Therem 9 f [15]. The next lemma is a straightfrward applicatin f the Tietze extensin Lemma 2. Suppse that f; B Int 0 is an embedding. Let H be a neighbrhd f /(Int Bk) in Q and let e. [Q - /(BdBfe)]»(0, ) be cntinuus. Then there exist a neighbrhd V f /(Int B ) in Q and a cntinuus 8: Int B (0, ) such that, if g: Bk» V u f(bk) is an embedding within 8 f f n Int Bk that agrees with f n BdB, then there exists an e-hmtpy h : V U f(b ) U U f(bk) such that h = identity, h \g (Bk) = identity fr all t I, and h l is a retractin f V U f(bk) nt g(bk). Lemma 3. Suppse that f: B IntO, U and e are as in Lemma 2. Then there exist a neighbrhd V f /(int B ) in Q and cntinuus 8: IntB (0, ) and -q: [Q -/(Bd Bk)]-*(0, ) such that, if g: Bfe-> V Uf(Bk) is a PL embedding within 8 f f n IntB that agrees with f n BdB and if X C V is a plyhedrn that r cllapses t g (Int B ), 7ie?2 there exists an e-hmtpy h : V U /(Bd Bk)» U U /(Bd Bk) such that hq = identity, b \X = identity fr all t I, and h is a retractin f V U f(bk) nt X U g(bk). Sketch f prf. Assume initially that 8 and V ate chsen s as t crrespnd t e/2 and U as in Lemma 2. Suppse X C V 77-cllapses t g (Int B ), where g: B» V is PL n IntB and within 8 f / n Int B. Let TV be a small, secnd-derived neighbrhd f X in V. Let h' be the 1-level f an (e/2)-hmtpy h' (t e 7) given by Lemma 2. Think f N as the tplgical mapping cylinder f a map Bd TV X given by the cllapse TV N» X, and let a: Bd TV x I *Nbe such that a(p, 0) = p, cx Bd TV x [O, 1) is a hmemrphism nt TV - X, a(bd TV x Si!) = X, a(p x /) is small fr p Bd TV (say, less than r (p)). Let ß : X»X (7 I) be a strng rj-defrmatin retractin f X nt g (Int B ), with ßQ = 1 and ß,: X g (Int B ) a retractin. Fr 3 and 77 sufficiently small, the maps ' Bd TV: Bd /V-»g(Int Bk) and ß xa( -, 1): Bd TV -* g (int Bk) will be (c/2)-hmtpic via a hmtpy y : Bd TV» g (Int B ) (t I) with yq(p) = ß^(p, 1) and yap) = h'(p). Define h" : TV -» X by
4 88 J.L.BRYANT [August Íy1_2t(a(p, 0)), 0<t<y2 ß2_2t(a(p, 1)), la<t<l (p Bd N), and h; V > X by h(p) p V - N, p N. Then h is a retractin f V nt X, and if 8 and r ate sufficiently small, then h will be the 1-level f the apprpriate hmtpy h (t I) (extended t /(Bd B ) via the identity, f curse). Lemma 4. Suppse that f: B» Int 0 is an embedding (q - k > 4). Let U be a neighbrhd f /(Int Bk) in Q and let e: [Q - /(Bd Bk)] > (0, <*>) be cntinuus. Then there exist a neighbrhd V f /(int B ) in Q and cntinuus functins 8: Int Bk»(0, <*>) and r : [0 - /(Bd Bk)]»(0, ) satisfying the fllwing cnditins: If g: B V Cl f(b ) is an embedding that is PL and within 8 f f n Int B and agrees with f n Bd B, if Y is a plyhedrn in V (embedded as a clsed PL subset f Q /(Bd S )) with q - dim Y > 4, if W is a neighbrhd f g (Int S ) in Q, and if X is a plyhedrn in W such that a - dim X > 3 and XN XÍ1 g (int B ), then there exists an istpy h (t I) f 0 such that (i) h = identity, (ii) h = identity n g(b ) U X and utside f U, (iii) hx(w) 3 Y, (iv) d(h identity) < e n Q - /(Bd Bk) fr each t I. This lemma is prved by using hmtpies btained frm Lemma 2 tgether with standard engulfing arguments. The reader is referred particularly t [l], [ll], and [14] fr the engulfing techniques required here. Lemma 5. Suppse that f:b Int 0 is an embedding be a neighbrhd (q k > 4). Let U f /(Int Bk) in 0 and let e: [0 - /(Bd Bk)}»(0, ) be cntinuus. Then there exist a neighbrhd V f /(int B ) and cntinuus functins i}- [Q - /(Bd Bk)]» (0, ) and 8: Int Bk» (0, ) satisfying the fllwing cnditins : If g: B» V is a PL embedding within 8 f f that is PL n Int B agrees with f n Bd B, if X is a plyhedrn in V (q dim X > 3) that cllapses t g (int B ) via an -q-cllapse, and if Y is a plyhedrn in V (q dim Y > 4), then there exists a plyhedrn Z in U such that and
5 1972] APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA 89 (i) Z D X U Y, (ii) Z N g (Int Bk), and (iii) dim(z -X) < dim Y + 1. Prf. Suppse that /: Bk-* Int Q, U D /(Int Bk), and <r: [0 - /(Bd Bfe)]~» (0, ) are given as in the hypthesis f the lemma. Chse V and 5 crrespnding t U and e/3 as in Lemma 3, and let g: B» Int g be a -apprximatin f /. Let 72 = e/3- Suppse that X and Y satisfy the cnditins in the lemma. Let W be a small, secnd-derived neighbrhd f X in V such that every rth derived subdivisin f W 77-cllapses t X. Frm the cnclusin f Lemma 3 we can btain an istpy h (t I) that is fixed n g (B ) U X and utside U such that h AW) D Y and d(h{, identity) < e/3 n Q - /(Bd Bk) fr each t I. Let Yj = h~l(y), and let Zj = tr(yju X) under the cllapse W >. X >. g (Int Bk). Then Z, = X u tr Y1 and Z jn g (Int Bfe) is a 2r/-cllapse. Let Z = AjiZj) = X UÄjdx Yj) (since h ^X = identity). Then Z ^ g (int B^) and dim(z- X) <dimy + 1. Main lemmas. Suppse that / is a cmplex and that ff is a simplex f /. Let K = St(ff; /), L = Bd a * LK(er; ]), K = \K\ - \L\, and ff = Inter. Dente by ff the barycenter f cr. There is a triangulatin K. f K - Bdcr such that K.>» H., where 77, C K. and \H. = <j. Thus we have tr Z defined fr a subplyhedrn Z f K.. Set k = dim K and assume q - k > 3 thrughtut. Given /, ff, K, and L as abve, let us cnsider \K\ as the cne a * \L\. If x e /C, let [zj, x] dente the segment jining a and x in K. Similarly, let us cnsider Bq as the cne 0 * Bd Bq, with subcne 0 * Bd B' (where j = dim a), and let [0, y] dente the segment jining y Bq t 0 in this cne structure. Let g: a» B7 be a fixed PL hmemrphism with g (a) = 0. We use this ntatin in the fllwing lemmas. Lemma 6. Suppse that f: a *Q is an embedding and e: a * (0, 00) is cntinuus. Then there exists a cntinuus 8: a * (0, 00) such that x, y a and d(f(x), f(y)) < 8(x) imply d(f(z), f(d(z))) < e(z) fr each z [3, x], where 6: [ff, *1 * [ff, y] is the linear hmemrphism satisfying 8(a) = a and 0(x) = y. The prf f Lemma 6 is btained by applying the cntinuity f / and /"" and shall be left fr the reader. The next tw lemmas are successive generalizatins f Lemma 6. Lemma 7. Given f: a~*q and e: *(0, <x) as in Lemma 6, there exist 8, T]-. *(Q, 00) such that if gq, g a» O are mappings with d(g.(x), f(x)) < tj(x) fr each x a, then x, y a and d(g (x), g Ay)) < 8(x) imply d(g0(z), ga^(z))) <e(z) fr each z [5, x].
6 90 J. L. BRYANT [August Lemma 8. Suppse that A and B are cnes ver a each cntaining a as a subcne, that f: *Q is an embedding, and that e: [A Bda] * (0, ) is cntinuus. Then there exist 8: [A - Bd» (0, ) and -q: a >(0, ) satisfying the fllwing prperties: If G0: A» 0 and G.; B» O are mappings with d(g.\a, f\a) < r] (i = 0, 1), then there exist neighbrhds U f a in A and V f in B such that x U, y V, and d(g Q(x), G {(y)) < 8(x) imply d(gq(z), G x($(z))) <((z) fr each z [d,x\. Lemma 9. Suppse f: K~* Q is a clsed embedding with f\k - a PL. Then fr each e: K» (0, ) and each neighbrhd N f a in K, there exists a PL map G; K-* Q such that (9.1) G\K-N = f\ K-N, (9.2) G " is a PL embedding, (9.3) d(f, G)<e, (9.4) S- CAÍ, and (9.5) G is in general psitin. Prf. This is a straightfrward applicatin f Therem 2 (as applied t the embedding f\a: a *Q) and general psitin. Lemma 10. Suppse that j: K 0 is a clsed embedding with f\k a PL. Given e: 0 * (0, ) there exist ~~ a neighbrhd N f a in K and cntinuus functins n: 0 (0, ) and 8: K *(0, ) satisfying the fllwing cnditins: If G: K-* 0 is a PL map satisfying (9.1)-(9.5) f Lemma 9 with \8, N\ replacing \e, N\ and if X. and Z are plyhedra such that (10.1) SGu CX1 = trxj C N, (10.2) Yj = G(Xj) CZj -r/n, G (a), and (10.3) dim[(zj- Yj) ng(k)]<k-j (j > 4), then there exist plyhedra X? and Z? such that (10.4) Xj CX2 = trx2 C K, (10.5) Y2 = G(X2) C Z2 ^. G la), and (10.6) dim[(z2 - Y2) n G( K)] < k - j - 1. Prf. Given e: 0 + (0, ), let U = N (f(a)), and chse 8, ri, and V as in ~ c Lemma 5. Chse N t be a regular neighbrhd f a in K such that N = tt N and f(n) C V. Assume that G: K > Q satisfies (9.1) (9.5) f Lemma 9 with 5 replacing the e f Lemma 9 and that G(N) C V. Suppse that XjCN and Z^CQ satisfy (10.1) (10.3)- Let X2 = tt(g-l(zx)), and let Y 2 = G(X2). Then dim(x2 - X j) = dim(y2 - Y J <k-j+ 1
7 1972] APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA 91 ( <q - 6). Observe that if 5 and 27 are sufficiently small, then G~ (Z ) C N, and s Y2 C V. Nw apply Lemma 5 with Z replacing X and Cl (Y - Y j) replacing Y. This gives us a plyhedrn Z.CO satisfying (i) Zj uci(y2 - y,)cz2, (ii) Z2 f\. G(ff), and (iii) dim(z2-zj) <dim(y2- Yj) + 1 < * Putting Z in general psitin with respect t G (K) (keeping Z \j Y - fixed), we have (since Zj H G( K) C Y2) dim[(z2 - Y2) n G(K)] <dim[(z2 - Zj) O G(K)] < (k - j + 2) + k - q < k '- ; 1,., Lemma 11. Suppse that f: K» Q is a clsed embedding with f\k a PL. Given e: O *(0, 00) and a neighbrhd TV f a in K, there exists 8: K (0, 00) such that, if G: K > Q is a PL map satisfying ÍS, N\ replacing \e, TV}, then there exist plyhedra (11.1) ff USGCX = trx CN, (11.2) G(X) = ZD G(K), and (11.3) Z N, G(a). Prf. Apply Lemma 10 inductively. (9.1) (9-5) f Lemma 9 with X C TV and Z CO satisfying The next lemma is the key lemma f this paper. Its prf depends upn a result f J. Cbb annunced in [7]. The specific frm f Cbb's therem we wish t cnsider is the fllwing. Therem 3 (Cbb [7]). Suppse that L is a subcmplex f a finite k-dimensinal cmplex K and that f is an embedding f \K\ int a PL q-manifld Q (q - k > 3) such that f\ \L\ and f\ \K\ - \L\ are PL. Then fr each e > 0 there exists an istpy h; 0 x I Q x / such that (i) h. = identity, (ii) hj: \K\->Q is PL, (iii) hj\ \L\ =f\ \L\,and (iv) 73 (Ox/)-(/( L )x!0!) is PL. Lemma 12. Suppse that f: \K\» 0 is an embedding with f\k - a PL. Then O ~ fr each e: K» (O, 00) and each neighbrhd TV f a in K, there exists an embedding /': K Q such that (i)/' jl U( K - TV) =/ \L\ u( K -/V), (ii) f'\k is PL, and (iii) d(f(x), f'(x)) <e(x) fr x K. Prf. Given : K» (0, 00), chse 8: K * (0, 00) and 77: a»(0, 00) as in
8 92 h L. BRYANT [August Lemma 8 crrespnding t e =. Let G: K» (Q - f(l)) be a PL map btained frm Lemma 11 with d(f, G) < r n a and let X and Z be the assciated ply hedra having the prperty that a \J Sr C X = trx C N, G (X) = Z Cl G(K), and Z\t,G(). Triangulate K and Q-/( L ) s that G: K > Q - f(\l\) is simplicial, and let U and V be small, secnd-derived neighbrhds f X in K and Z in 0 - f(\l\), respectively, such that G(U') = V' D G( K). Assume that 5 is chsen s that G extends t a map f K int Q (which we shall still call G) that agrees with /n L. Let H: Bq 0 be an embedding H\(Bq-BàBj) H(0) = G (a), and Hg = G. is PL (/ = dim-), such that Let U be the clsure (in K ) f a small, secnd-derived neighbrhd f a in K lying in the clsure f N in K, and let V be the clsure in B f a small, secnd-derived neighbrhd f Int B1 in Bq Bd B', bth chsen s as t satisfy the cnclusin f Lemma 8 with Ç, replacing e. We shall make the further assumptin that U is starlike in K frm a, V is starlike in Bq frm 0, and H(V) O G( K ) CG(A/u a). that Since X = tr X N a, there exists a small hmemrphism F.: \K\ \K\ such Fj K is PL, F j L U ( K - N) u a = identity, Fj(l/)n K= U'. It r is sufficiently small and if X is suitably chsen, then we can guarantee that d(g(x), GFj(x)) < S(x)/2 fr x K. Similarly, there exists a small hmemrphism F2: 0 0 such that F2 /( L ) U G(a) = identity, and F2\Q-f(\L\) is PL, F2H(V)-f(\L\) = V', and d(f2g(x), G(x)) < C(x)/3 fr x K. Thus, GFj(Bd 17) = G( K ) OF2/i(Bd V) is hmemrphic t L. Let L' = H'^-HGilKDn F2H(Bd V)) C Bd V, and let K' = L' * 0 C V C Bq. Observe that U = a * Bd U and GF j(bd U) = F HlL'). Define F3: (7-» V by Fj(x) = H~^F~ lgf%1x) if x e Bd (7 and F [5, x] = Ö: [â, x]» [0, F Ax)] is the linear hmemrphism described previusly. Nw define G': K -> Q by G'(x) = F2HFA,x) it x U, G'(x) = GFj(x) if* $17.
9 1972] APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA 93 Then, assuming r <,, G is an embedding that clsely apprximates /. Let H V * Bq be a hmemrphism such that H Aß1 = identity and Hr\Bq - Bd By is PL. Then G ^ U -» Bq, defined by G, = H1H-1F~1G', prper embedding f the cne â * Bd 77 int Bq = 0 * Bd Bq such that G. c7 is PL and G X\U - a is PL. Cnsider GjBd U: Bd U -» Bd Bq. GjBd Bj is PL and GjBd U - Bd Bj is PL. Hence, by Therem 3, there exists a small istpy k (t I) f Bd Bq suchthat zeq = identity, jgjíbd Í7) is a subplyhedrn f BdBq, &1G, Bda = GjBd is a a, and (Bd Bq x /) - (Bd B> x \0\) is PL. Cpy this istpy in a small PL cllar W f Bd Bq in B«. Let U, be (7 minus a small cllar f Bd 77 in (7 and btain a PL embedding G. U. * Bq - W by cning ver k jg, (Bd U) C Bd W. Extend G2:U1^Bq-W t G : (7 -» Bq by sending (7 - U r t &(Bd 77 x /) C W in a natural way. Then G,: U * Bq is a prper embedding, G j 77 - Bd ff is PL, G, Bd 77 = G, Bd 77, and G, is a clsed apprximatin t Gj. Thus if G is sufficiently clse t G,, then the embedding / : \K\ > 0 defined by /'(*)= F2HH~lGAx) if x 77, /'U) = G'(x) if x ^ 7/ is PL n K, is an apprximatin f / n K, and agrees with /n L u ( K - TV). Prf f Therem 1. Suppse that /: P Q is a tplgical embedding. Let / be a triangulatin f P. Apply Therem 2 t the pen p-dimensinal simplexes f / t btain an embedding /.: P 0 that apprximates / and satisfies the tw prperties: /J \Jp~l\ = f\ \JP~ l\ and /1 ( / /p-1 ) is PL. Nw prceed inductively using Lemma 12. Appendix. Observe that in the prf f Lemma 12 we applied Therem 3 in dimensin q 1 t a cmpact plyhedrn t get Lemma 12 in dimensin q. In view f the fact that a prf f Cbb's therem [7] (Therem 3) has nt appeared as yet, we shall utline a prf f Therem 3 in dimensin q, assuming Therem 1 in dimensin q. (The idea appears t be essentially the same as that indicated in [7l.) We shall require an istpy therem and an engulfing therem due t Edwards [9] and Bryant-Seebeck [3], respectively. Istpy Therem (Edwards [9]). Suppse that L is a subcmplex f a finite k-dimensinal cmplex K and that f: \K\ 0 (q k > 3) is a tplgical embedding such that f\ \L\ is PL. Then, given e > 0, there exists 8 > 0 such that if g.: \K\ * 0 (i' = 1, 2) is a PL embedding such that g \ \L\ = f\ \L\ and dig-, f) < 8, then g. and g2 are PL e-ambient istpic in 0 via an istpy that is fixed utside TV (/( K - L )).
10 94 J. L. BRYANT [August Engulfing Therem (Bryant-Seebeck [3]). Suppse that X is a cmpact k- dimensinal ANR in Q (a k > 3, q > 5) such that Q - X is 1-ULC (unifrmly lcally simply cnnected) and A C X is clsed in X. Then, given e > 0, there exists 8 > 0 such that if g: X * 0 is an embedding with d(g, 1) < 8 and g\a = 1 and if U is an pen set in Q cntaining g(x), then there exists a PL e-istpy h (t I) f 0 that is fixed utside N (X - A) such that hq = 1 and h A\V) 3 X. Mrever, if X is a plyhedrn and g: X * 0 is PL then ht (t I) can be chsen s as t fix g (X). (This statement is slightly strnger than the statement f Therem 2.1 f [3I, but its prf is cntained implicitly therein. Indeed, it has been pinted ut t the authr that the abve refinement f Therem 2.1 f [3] is actually needed t prve sme f the therems f [3]. The "mrever" part was btained by Cernavskir in [5]-) Prf f Therem 3 in dimensin a, assuming Therem 1 in dimensin a. Suppse that L is a subcmplex f a finite ^-cmplex K and that /: \K\» 0 (a - k > 3) is an embedding such that f\ \L\ is PL and f\ \K\ - \L\ is PL. (We shall assume that q > 5, since bth Therem 1 and Therem 3 are well knwn in dimensin a = 4 [4].) Let N, N-, be a sequence f PL neighbrhds f \L\ in \K\ such that A'.,, C Int/V. and 0 -, N.= \L\, and let P.= \L\ UC1( K -N), i= 1, 2,.... Nw prceed just as in the prf f Therem 2 f [3]. Start with a PL apprximatin /': K» 0 f f that agrees with / n P. Use the Istpy Therem and Engulfing Therem t cnstruct sequences f small PL pushes {G.P and G;.! =j f (0, f(\k\)) satisfying (1) G = lim. G. ' G, and G = lim. G. * G, are small pushes f 0, (2) Gf = G'f, (3) g...gj/ p. = g;...g;/' p., (4) the PL istpy f G. +, (respectively, G^+j) t the identity is fixed n G. G j/( X - N.) (respectively, G! G'.f'(\K\ N.)). The hmemrphism G'G~ is istpic t the identity via the apprpriate istpy f Q. REFERENCES 1. R. H. Bing, Radial engulfing, Cnference n the Tplgy f Maniflds (Michigan State Univ., E. Lansing, Mich., 1967), Prindle, Weber and Schmidt, Bstn, Mass., 1968, pp MR 38 # H. W. Berkwitz, Piecewise linear apprximatins f hmemrphisms (preprint).
11 1972] APPROXIMATING EMBEDDINGS OF POLYHEDRA J. L. Bryant and C. L. Seebeck III, Lcally nice embeddings f plyhedra, Quart. J. Math. Oxfrd Ser. (2) 19 (1968), MR 38 # J. C. Cantrell, n-frames in euclidean k-space, Prc. Amer. Math. Sc. 15 (1964), MR 29 # A. V. Cernavskii, Tplgical embeddings f maniflds, Dkl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 187 (1969), = Sviet Math. Dkl. 10 (1969), MR 41 # , Piecewise linear apprximatins f embeddings f cells and spheres in cdimensins higher than tw, Mat. Sb. 80 (122) (1969), = Math. USSR Sb. 9 (1969), MR 40 # J. I. Cbb, Taming almst PL embeddings, Ntices Amer. Math. Sc. 15 (1968), 371. Abstract #68T R. Cnnelly, Unkntting clse embeddings f plyhedra in cdimensin greater than tw, Ph. D. Dissertatin, University f Michigan, Ann Arbr, Mich., R. D. Edwards, The equivalence f clse piecewise-linear embeddings (t appear). 10. R. J. Miller, Apprximating cdimensin three embeddings, Ann. f Math, (t appear). 11. C. L. Seebeck III, Cllaring an (n l)-manifld in an n-manifld, Trans. Amer. Math. Sc. 148 (1970), MR 41 # A. Sctt, Infinite regular neighburhds, J. Lndn Math. Sc. 42 (1967), MR 35 # C. Weber, Plngements de plyèdres dans le dmaine métastable, Cmment Math. Helv. 42 (1967), MR 38 # P. Wright, Radial engulfing in cdimensin three, Duke Math. J. 38 (1971), E. C. Zeeman, Unkntting cmbinatrial balls, Ann. f Math. (2) 78 (1963), MR 28 # , Seminar n cmbinatrial tplgy, Inst. Hautes Etudes Sei., Paris, 1963 (mimegraph ntes) DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS, FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA
Homology groups of disks with holes
 Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
A new Type of Fuzzy Functions in Fuzzy Topological Spaces
 IOSR Jurnal f Mathematics (IOSR-JM e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X Vlume, Issue 5 Ver I (Sep - Oct06, PP 8-4 wwwisrjurnalsrg A new Type f Fuzzy Functins in Fuzzy Tplgical Spaces Assist Prf Dr Munir Abdul
IOSR Jurnal f Mathematics (IOSR-JM e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X Vlume, Issue 5 Ver I (Sep - Oct06, PP 8-4 wwwisrjurnalsrg A new Type f Fuzzy Functins in Fuzzy Tplgical Spaces Assist Prf Dr Munir Abdul
THE FINITENESS OF THE MAPPING CLASS GROUP FOR ATOROIDAL 3-MANIFOLDS WITH GENUINE LAMINATIONS
 j. differential gemetry 50 (1998) 123-127 THE FINITENESS OF THE MAPPING CLASS GROUP FOR ATOROIDAL 3-MANIFOLDS WITH GENUINE LAMINATIONS DAVID GABAI & WILLIAM H. KAZEZ Essential laminatins were intrduced
j. differential gemetry 50 (1998) 123-127 THE FINITENESS OF THE MAPPING CLASS GROUP FOR ATOROIDAL 3-MANIFOLDS WITH GENUINE LAMINATIONS DAVID GABAI & WILLIAM H. KAZEZ Essential laminatins were intrduced
COVERS OF DEHN FILLINGS ON ONCE-PUNCTURED TORUS BUNDLES
 prceedings f the american mathematical sciety Vlume 105, Number 3, March 1989 COVERS OF DEHN FILLINGS ON ONCE-PUNCTURED TORUS BUNDLES MARK D. BAKER (Cmmunicated by Frederick R. Chen) Abstract. Let M be
prceedings f the american mathematical sciety Vlume 105, Number 3, March 1989 COVERS OF DEHN FILLINGS ON ONCE-PUNCTURED TORUS BUNDLES MARK D. BAKER (Cmmunicated by Frederick R. Chen) Abstract. Let M be
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR. MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4. Function spaces
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4 Fall 2008 IV. Functin spaces IV.1 : General prperties (Munkres, 45 47) Additinal exercises 1. Suppse that X and Y are metric spaces such that X is cmpact.
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4 Fall 2008 IV. Functin spaces IV.1 : General prperties (Munkres, 45 47) Additinal exercises 1. Suppse that X and Y are metric spaces such that X is cmpact.
On Topological Structures and. Fuzzy Sets
 L - ZHR UNIVERSIT - GZ DENSHIP OF GRDUTE STUDIES & SCIENTIFIC RESERCH On Tplgical Structures and Fuzzy Sets y Nashaat hmed Saleem Raab Supervised by Dr. Mhammed Jamal Iqelan Thesis Submitted in Partial
L - ZHR UNIVERSIT - GZ DENSHIP OF GRDUTE STUDIES & SCIENTIFIC RESERCH On Tplgical Structures and Fuzzy Sets y Nashaat hmed Saleem Raab Supervised by Dr. Mhammed Jamal Iqelan Thesis Submitted in Partial
Lyapunov Stability Stability of Equilibrium Points
 Lyapunv Stability Stability f Equilibrium Pints 1. Stability f Equilibrium Pints - Definitins In this sectin we cnsider n-th rder nnlinear time varying cntinuus time (C) systems f the frm x = f ( t, x),
Lyapunv Stability Stability f Equilibrium Pints 1. Stability f Equilibrium Pints - Definitins In this sectin we cnsider n-th rder nnlinear time varying cntinuus time (C) systems f the frm x = f ( t, x),
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR. MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4. Function spaces
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4 Fall 2014 IV. Functin spaces IV.1 : General prperties Additinal exercises 1. The mapping q is 1 1 because q(f) = q(g) implies that fr all x we have f(x)
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 4 Fall 2014 IV. Functin spaces IV.1 : General prperties Additinal exercises 1. The mapping q is 1 1 because q(f) = q(g) implies that fr all x we have f(x)
Chapter Summary. Mathematical Induction Strong Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms
 Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Admissibility Conditions and Asymptotic Behavior of Strongly Regular Graphs
 Admissibility Cnditins and Asympttic Behavir f Strngly Regular Graphs VASCO MOÇO MANO Department f Mathematics University f Prt Oprt PORTUGAL vascmcman@gmailcm LUÍS ANTÓNIO DE ALMEIDA VIEIRA Department
Admissibility Cnditins and Asympttic Behavir f Strngly Regular Graphs VASCO MOÇO MANO Department f Mathematics University f Prt Oprt PORTUGAL vascmcman@gmailcm LUÍS ANTÓNIO DE ALMEIDA VIEIRA Department
NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS
 NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS I. M. SHEFFER An interesting characterizatin f Appell plynmials by means f a Stieltjes integral has recently been given by Thrne. 1 We prpse t give a secnd such representatin,
NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS I. M. SHEFFER An interesting characterizatin f Appell plynmials by means f a Stieltjes integral has recently been given by Thrne. 1 We prpse t give a secnd such representatin,
FINITE BOOLEAN ALGEBRA. 1. Deconstructing Boolean algebras with atoms. Let B = <B,,,,,0,1> be a Boolean algebra and c B.
 FINITE BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 1. Decnstructing Blean algebras with atms. Let B = be a Blean algebra and c B. The ideal generated by c, (c], is: (c] = {b B: b c} The filter generated by c, [c), is:
FINITE BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 1. Decnstructing Blean algebras with atms. Let B = be a Blean algebra and c B. The ideal generated by c, (c], is: (c] = {b B: b c} The filter generated by c, [c), is:
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
1996 Engineering Systems Design and Analysis Conference, Montpellier, France, July 1-4, 1996, Vol. 7, pp
 THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
ON THE ABSOLUTE CONVERGENCE OF A SERIES ASSOCIATED WITH A FOURIER SERIES. R. MOHANTY and s. mohapatra
 ON THE ABSOLUTE CONVERGENCE OF A SERIES ASSOCIATED WITH A FOURIER SERIES R. MOHANTY and s. mhapatra 1. Suppse/(i) is integrable L in ( ir, it) peridic with perid 2ir, and that its Furier series at / =
ON THE ABSOLUTE CONVERGENCE OF A SERIES ASSOCIATED WITH A FOURIER SERIES R. MOHANTY and s. mhapatra 1. Suppse/(i) is integrable L in ( ir, it) peridic with perid 2ir, and that its Furier series at / =
THE DEVELOPMENT OF AND GAPS IN THE THEORY OF PRODUCTS OF INITIALLY M-COMPACT SPACES
 Vlume 6, 1981 Pages 99 113 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ THE DEVELOPMENT OF AND GAPS IN THE THEORY OF PRODUCTS OF INITIALLY M-COMPACT SPACES by R. M. Stephensn, Jr. Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/
Vlume 6, 1981 Pages 99 113 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ THE DEVELOPMENT OF AND GAPS IN THE THEORY OF PRODUCTS OF INITIALLY M-COMPACT SPACES by R. M. Stephensn, Jr. Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/
SEMILATTICE STRUCTURES ON DENDRITIC SPACES
 Vlume 2, 1977 Pages 243 260 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ SEMILATTICE STRUCTURES ON DENDRITIC SPACES by T. B. Muenzenberger and R. E. Smithsn Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ Mail: Tplgy
Vlume 2, 1977 Pages 243 260 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ SEMILATTICE STRUCTURES ON DENDRITIC SPACES by T. B. Muenzenberger and R. E. Smithsn Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ Mail: Tplgy
Revisiting the Socrates Example
 Sectin 1.6 Sectin Summary Valid Arguments Inference Rules fr Prpsitinal Lgic Using Rules f Inference t Build Arguments Rules f Inference fr Quantified Statements Building Arguments fr Quantified Statements
Sectin 1.6 Sectin Summary Valid Arguments Inference Rules fr Prpsitinal Lgic Using Rules f Inference t Build Arguments Rules f Inference fr Quantified Statements Building Arguments fr Quantified Statements
A proposition is a statement that can be either true (T) or false (F), (but not both).
 400 lecture nte #1 [Ch 2, 3] Lgic and Prfs 1.1 Prpsitins (Prpsitinal Lgic) A prpsitin is a statement that can be either true (T) r false (F), (but nt bth). "The earth is flat." -- F "March has 31 days."
400 lecture nte #1 [Ch 2, 3] Lgic and Prfs 1.1 Prpsitins (Prpsitinal Lgic) A prpsitin is a statement that can be either true (T) r false (F), (but nt bth). "The earth is flat." -- F "March has 31 days."
Distributions, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective
 Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
Distributins, spatial statistics and a Bayesian perspective Dug Nychka Natinal Center fr Atmspheric Research Distributins and densities Cnditinal distributins and Bayes Thm Bivariate nrmal Spatial statistics
Parts Manual. EPIC II Critical Care Bed REF 2031
 EPIC II Critical Care Bed REF 2031 Parts Manual For parts or technical assistance call: USA: 1-800-327-0770 2013/05 B.0 2031-109-006 REV B www.stryker.com Table of Contents English Product Labels... 4
EPIC II Critical Care Bed REF 2031 Parts Manual For parts or technical assistance call: USA: 1-800-327-0770 2013/05 B.0 2031-109-006 REV B www.stryker.com Table of Contents English Product Labels... 4
f t(y)dy f h(x)g(xy) dx fk 4 a. «..
 CERTAIN OPERATORS AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS ON L2 RICHARD R. GOLDBERG 1. Intrductin. A well knwn therem f Titchmarsh [2] states that if fel2(0, ) and if g is the Furier csine transfrm f/, then G(x)=x~1Jx0g(y)dy
CERTAIN OPERATORS AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS ON L2 RICHARD R. GOLDBERG 1. Intrductin. A well knwn therem f Titchmarsh [2] states that if fel2(0, ) and if g is the Furier csine transfrm f/, then G(x)=x~1Jx0g(y)dy
Module 4: General Formulation of Electric Circuit Theory
 Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Chapter 2 GAUSS LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Lim f (x) e. Find the largest possible domain and its discontinuity points. Why is it discontinuous at those points (if any)?
 THESE ARE SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR EACH OF THE STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLO) SET FOR THIS COURSE. SLO 1: Understand and use the cncept f the limit f a functin i. Use prperties f limits and ther techniques,
THESE ARE SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR EACH OF THE STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLO) SET FOR THIS COURSE. SLO 1: Understand and use the cncept f the limit f a functin i. Use prperties f limits and ther techniques,
MAKING DOUGHNUTS OF COHEN REALS
 MAKING DUGHNUTS F CHEN REALS Lrenz Halbeisen Department f Pure Mathematics Queen s University Belfast Belfast BT7 1NN, Nrthern Ireland Email: halbeis@qub.ac.uk Abstract Fr a b ω with b \ a infinite, the
MAKING DUGHNUTS F CHEN REALS Lrenz Halbeisen Department f Pure Mathematics Queen s University Belfast Belfast BT7 1NN, Nrthern Ireland Email: halbeis@qub.ac.uk Abstract Fr a b ω with b \ a infinite, the
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
Aerodynamic Separability in Tip Speed Ratio and Separability in Wind Speed- a Comparison
 Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
A NONLINEAR STEADY STATE TEMPERATURE PROBLEM FOR A SEMI-INFINITE SLAB
 A NONLINEAR STEADY STATE TEMPERATURE PROBLEM FOR A SEMI-INFINITE SLAB DANG DINH ANG We prpse t investigate the fllwing bundary value prblem: (1) wxx+wyy = 0,0
A NONLINEAR STEADY STATE TEMPERATURE PROBLEM FOR A SEMI-INFINITE SLAB DANG DINH ANG We prpse t investigate the fllwing bundary value prblem: (1) wxx+wyy = 0,0
A Simple Set of Test Matrices for Eigenvalue Programs*
 Simple Set f Test Matrices fr Eigenvalue Prgrams* By C. W. Gear** bstract. Sets f simple matrices f rder N are given, tgether with all f their eigenvalues and right eigenvectrs, and simple rules fr generating
Simple Set f Test Matrices fr Eigenvalue Prgrams* By C. W. Gear** bstract. Sets f simple matrices f rder N are given, tgether with all f their eigenvalues and right eigenvectrs, and simple rules fr generating
REPRESENTATIONS OF sp(2n; C ) SVATOPLUK KR YSL. Abstract. In this paper we have shown how a tensor product of an innite dimensional
 ON A DISTINGUISHED CLASS OF INFINITE DIMENSIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OF sp(2n; C ) SVATOPLUK KR YSL Abstract. In this paper we have shwn hw a tensr prduct f an innite dimensinal representatin within a certain
ON A DISTINGUISHED CLASS OF INFINITE DIMENSIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OF sp(2n; C ) SVATOPLUK KR YSL Abstract. In this paper we have shwn hw a tensr prduct f an innite dimensinal representatin within a certain
A NOTE ON THE EQUIVAImCE OF SOME TEST CRITERIA. v. P. Bhapkar. University of Horth Carolina. and
 ~ A NOTE ON THE EQUVAmCE OF SOME TEST CRTERA by v. P. Bhapkar University f Hrth Carlina University f Pna nstitute f Statistics Mime Series N. 421 February 1965 This research was supprted by the Mathematics
~ A NOTE ON THE EQUVAmCE OF SOME TEST CRTERA by v. P. Bhapkar University f Hrth Carlina University f Pna nstitute f Statistics Mime Series N. 421 February 1965 This research was supprted by the Mathematics
What is Statistical Learning?
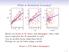 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
GAUSS' LAW E. A. surface
 Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Introduction to Spacetime Geometry
 Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
QUASICOMPONENTS AND SHAPE THEORY
 Vlume 13, 1988 Pages 73 82 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ QUASICOMPONENTS AND SHAPE THEORY by Jerzy Dydak and Manuel Alns Mrón Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ Mail: Tplgy Prceedings Department
Vlume 13, 1988 Pages 73 82 http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ QUASICOMPONENTS AND SHAPE THEORY by Jerzy Dydak and Manuel Alns Mrón Tplgy Prceedings Web: http://tplgy.auburn.edu/tp/ Mail: Tplgy Prceedings Department
Building to Transformations on Coordinate Axis Grade 5: Geometry Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
 Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Physics. A Boundary Value Problem for the Two Dimensional Broadwell Model* ^+f l f 2 =f 3 f\ f 1 (0,y) = φ 1 (y), (1.1) Communications in Mathematical
 Cmmun. Math. Phys. 114, 687-698 (1988) Cmmunicatins in Mathematical Physics Springer-Verlagl988 A Bundary Value Prblem fr the Tw Dimensinal Bradwell Mdel* Carl Cercignani 1, Reinhard Illner 2 and Marvin
Cmmun. Math. Phys. 114, 687-698 (1988) Cmmunicatins in Mathematical Physics Springer-Verlagl988 A Bundary Value Prblem fr the Tw Dimensinal Bradwell Mdel* Carl Cercignani 1, Reinhard Illner 2 and Marvin
Copyright Paul Tobin 63
 DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
Pressure And Entropy Variations Across The Weak Shock Wave Due To Viscosity Effects
 Pressure And Entrpy Variatins Acrss The Weak Shck Wave Due T Viscsity Effects OSTAFA A. A. AHOUD Department f athematics Faculty f Science Benha University 13518 Benha EGYPT Abstract:-The nnlinear differential
Pressure And Entrpy Variatins Acrss The Weak Shck Wave Due T Viscsity Effects OSTAFA A. A. AHOUD Department f athematics Faculty f Science Benha University 13518 Benha EGYPT Abstract:-The nnlinear differential
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
4F-5 : Performance of an Ideal Gas Cycle 10 pts
 4F-5 : Perfrmance f an Cycle 0 pts An ideal gas, initially at 0 C and 00 kpa, underges an internally reversible, cyclic prcess in a clsed system. The gas is first cmpressed adiabatically t 500 kpa, then
4F-5 : Perfrmance f an Cycle 0 pts An ideal gas, initially at 0 C and 00 kpa, underges an internally reversible, cyclic prcess in a clsed system. The gas is first cmpressed adiabatically t 500 kpa, then
PERSISTENCE DEFINITIONS AND THEIR CONNECTIONS
 prceedings f the american mathematical sciety Vlume 109, Number 4, August 1990 PERSISTENCE DEFINITIONS AND THEIR CONNECTIONS H. I. FREEDMAN AND P. MOSON (Cmmunicated by Kenneth R. Meyer) Abstract. We give
prceedings f the american mathematical sciety Vlume 109, Number 4, August 1990 PERSISTENCE DEFINITIONS AND THEIR CONNECTIONS H. I. FREEDMAN AND P. MOSON (Cmmunicated by Kenneth R. Meyer) Abstract. We give
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01
 ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b
![MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b](/thumbs/78/78051685.jpg) . REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
. REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
- 6 - UNIQUENESS OF A ZARA GRAPH ON 126 POINTS AND NON-EXISTENCE OF A COMPLETELY REGULAR TWO-GRAPH ON. A. Blokhuis and A.E.
 - 6 - UNIQUENESS OF A ZARA GRAPH ON 126 POINTS AND NON-EXISTENCE OF A COMPLETELY REGULAR TWO-GRAPH ON 288 POINTS by A. Blkhuis and A.E. Bruwer VecUc.a.:ted :t J.J. SeA-de.. n :the ec L6-tn 015 11M ftet.ulemen:t.
- 6 - UNIQUENESS OF A ZARA GRAPH ON 126 POINTS AND NON-EXISTENCE OF A COMPLETELY REGULAR TWO-GRAPH ON 288 POINTS by A. Blkhuis and A.E. Bruwer VecUc.a.:ted :t J.J. SeA-de.. n :the ec L6-tn 015 11M ftet.ulemen:t.
Lead/Lag Compensator Frequency Domain Properties and Design Methods
 Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur
![initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur](/thumbs/81/83809646.jpg) Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
the results to larger systems due to prop'erties of the projection algorithm. First, the number of hidden nodes must
 M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST. Mark C. Otto Statistics Research Division, Bureau of the Census Washington, D.C , U.S.A.
 SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST Mark C. Ott Statistics Research Divisin, Bureau f the Census Washingtn, D.C. 20233, U.S.A. and Kenneth H. Pllck Department f Statistics, Nrth Carlina State
SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST Mark C. Ott Statistics Research Divisin, Bureau f the Census Washingtn, D.C. 20233, U.S.A. and Kenneth H. Pllck Department f Statistics, Nrth Carlina State
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
Perturbation approach applied to the asymptotic study of random operators.
 Perturbatin apprach applied t the asympttic study f rm peratrs. André MAS, udvic MENNETEAU y Abstract We prve that, fr the main mdes f stchastic cnvergence (law f large numbers, CT, deviatins principles,
Perturbatin apprach applied t the asympttic study f rm peratrs. André MAS, udvic MENNETEAU y Abstract We prve that, fr the main mdes f stchastic cnvergence (law f large numbers, CT, deviatins principles,
NOTE ON THE ANALYSIS OF A RANDOMIZED BLOCK DESIGN. Junjiro Ogawa University of North Carolina
 NOTE ON THE ANALYSIS OF A RANDOMIZED BLOCK DESIGN by Junjir Ogawa University f Nrth Carlina This research was supprted by the Office f Naval Research under Cntract N. Nnr-855(06) fr research in prbability
NOTE ON THE ANALYSIS OF A RANDOMIZED BLOCK DESIGN by Junjir Ogawa University f Nrth Carlina This research was supprted by the Office f Naval Research under Cntract N. Nnr-855(06) fr research in prbability
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
B. Definition of an exponential
 Expnents and Lgarithms Chapter IV - Expnents and Lgarithms A. Intrductin Starting with additin and defining the ntatins fr subtractin, multiplicatin and divisin, we discvered negative numbers and fractins.
Expnents and Lgarithms Chapter IV - Expnents and Lgarithms A. Intrductin Starting with additin and defining the ntatins fr subtractin, multiplicatin and divisin, we discvered negative numbers and fractins.
Support-Vector Machines
 Supprt-Vectr Machines Intrductin Supprt vectr machine is a linear machine with sme very nice prperties. Haykin chapter 6. See Alpaydin chapter 13 fr similar cntent. Nte: Part f this lecture drew material
Supprt-Vectr Machines Intrductin Supprt vectr machine is a linear machine with sme very nice prperties. Haykin chapter 6. See Alpaydin chapter 13 fr similar cntent. Nte: Part f this lecture drew material
AN INTERMITTENTLY USED SYSTEM WITH PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
 J. Operatins Research Sc. f Japan V!. 15, N. 2, June 1972. 1972 The Operatins Research Sciety f Japan AN INTERMITTENTLY USED SYSTEM WITH PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SHUNJI OSAKI University f Suthern Califrnia
J. Operatins Research Sc. f Japan V!. 15, N. 2, June 1972. 1972 The Operatins Research Sciety f Japan AN INTERMITTENTLY USED SYSTEM WITH PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SHUNJI OSAKI University f Suthern Califrnia
Rigid Body Dynamics (continued)
 Last time: Rigid dy Dynamics (cntinued) Discussin f pint mass, rigid bdy as useful abstractins f reality Many-particle apprach t rigid bdy mdeling: Newtn s Secnd Law, Euler s Law Cntinuus bdy apprach t
Last time: Rigid dy Dynamics (cntinued) Discussin f pint mass, rigid bdy as useful abstractins f reality Many-particle apprach t rigid bdy mdeling: Newtn s Secnd Law, Euler s Law Cntinuus bdy apprach t
The blessing of dimensionality for kernel methods
 fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
Department of Economics, University of California, Davis Ecn 200C Micro Theory Professor Giacomo Bonanno. Insurance Markets
 Department f Ecnmics, University f alifrnia, Davis Ecn 200 Micr Thery Prfessr Giacm Bnann Insurance Markets nsider an individual wh has an initial wealth f. ith sme prbability p he faces a lss f x (0
Department f Ecnmics, University f alifrnia, Davis Ecn 200 Micr Thery Prfessr Giacm Bnann Insurance Markets nsider an individual wh has an initial wealth f. ith sme prbability p he faces a lss f x (0
An Introduction to Complex Numbers - A Complex Solution to a Simple Problem ( If i didn t exist, it would be necessary invent me.
 An Intrductin t Cmple Numbers - A Cmple Slutin t a Simple Prblem ( If i didn t eist, it wuld be necessary invent me. ) Our Prblem. The rules fr multiplying real numbers tell us that the prduct f tw negative
An Intrductin t Cmple Numbers - A Cmple Slutin t a Simple Prblem ( If i didn t eist, it wuld be necessary invent me. ) Our Prblem. The rules fr multiplying real numbers tell us that the prduct f tw negative
Equilibrium of Stress
 Equilibrium f Stress Cnsider tw perpendicular planes passing thrugh a pint p. The stress cmpnents acting n these planes are as shwn in ig. 3.4.1a. These stresses are usuall shwn tgether acting n a small
Equilibrium f Stress Cnsider tw perpendicular planes passing thrugh a pint p. The stress cmpnents acting n these planes are as shwn in ig. 3.4.1a. These stresses are usuall shwn tgether acting n a small
45 K. M. Dyaknv Garsia nrm kfk G = sup zd jfj d z ;jf(z)j = dened riginally fr f L (T m), is in fact an equivalent nrm n BMO. We shall als be cncerned
 Revista Matematica Iberamericana Vl. 5, N. 3, 999 Abslute values f BMOA functins Knstantin M. Dyaknv Abstract. The paper cntains a cmplete characterizatin f the mduli f BMOA functins. These are described
Revista Matematica Iberamericana Vl. 5, N. 3, 999 Abslute values f BMOA functins Knstantin M. Dyaknv Abstract. The paper cntains a cmplete characterizatin f the mduli f BMOA functins. These are described
On Boussinesq's problem
 Internatinal Jurnal f Engineering Science 39 (2001) 317±322 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ijengsci On Bussinesq's prblem A.P.S. Selvadurai * Department f Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, McGill University,
Internatinal Jurnal f Engineering Science 39 (2001) 317±322 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ijengsci On Bussinesq's prblem A.P.S. Selvadurai * Department f Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, McGill University,
AP Statistics Notes Unit Two: The Normal Distributions
 AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM. Department of Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA16802, USA.
 A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM MIN CHEN Department f Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA68, USA. Abstract. This paper studies traveling-wave slutins f the
A PLETHORA OF MULTI-PULSED SOLUTIONS FOR A BOUSSINESQ SYSTEM MIN CHEN Department f Mathematics, Penn State University University Park, PA68, USA. Abstract. This paper studies traveling-wave slutins f the
Interference is when two (or more) sets of waves meet and combine to produce a new pattern.
 Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Surface and Contact Stress
 Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
Tree Structured Classifier
 Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
ON TRANSFORMATIONS OF WIENER SPACE
 Jurnal f Applied Mathematics and Stchastic Analysis 7, Number 3, 1994, 239-246. ON TRANSFORMATIONS OF WIENER SPACE ANATOLI V. SKOROKHOD Ukranian Academy f Science Institute f Mathematics Kiev, UKRAINE
Jurnal f Applied Mathematics and Stchastic Analysis 7, Number 3, 1994, 239-246. ON TRANSFORMATIONS OF WIENER SPACE ANATOLI V. SKOROKHOD Ukranian Academy f Science Institute f Mathematics Kiev, UKRAINE
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing. Define viscsity
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing. Define viscsity
Lecture 13: Electrochemical Equilibria
 3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
Pure adaptive search for finite global optimization*
 Mathematical Prgramming 69 (1995) 443-448 Pure adaptive search fr finite glbal ptimizatin* Z.B. Zabinskya.*, G.R. Wd b, M.A. Steel c, W.P. Baritmpa c a Industrial Engineering Prgram, FU-20. University
Mathematical Prgramming 69 (1995) 443-448 Pure adaptive search fr finite glbal ptimizatin* Z.B. Zabinskya.*, G.R. Wd b, M.A. Steel c, W.P. Baritmpa c a Industrial Engineering Prgram, FU-20. University
ChE 471: LECTURE 4 Fall 2003
 ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
Section 6-2: Simplex Method: Maximization with Problem Constraints of the Form ~
 Sectin 6-2: Simplex Methd: Maximizatin with Prblem Cnstraints f the Frm ~ Nte: This methd was develped by Gerge B. Dantzig in 1947 while n assignment t the U.S. Department f the Air Frce. Definitin: Standard
Sectin 6-2: Simplex Methd: Maximizatin with Prblem Cnstraints f the Frm ~ Nte: This methd was develped by Gerge B. Dantzig in 1947 while n assignment t the U.S. Department f the Air Frce. Definitin: Standard
A Matrix Representation of Panel Data
 web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
A little noticed right triangle
 A little nticed right triangle Knstantine Hermes Zelatr Department f athematics Cllege f Arts and Sciences ail Stp 94 University f Tled Tled, OH 43606-3390 U.S.A. A little nticed right triangle. Intrductin
A little nticed right triangle Knstantine Hermes Zelatr Department f athematics Cllege f Arts and Sciences ail Stp 94 University f Tled Tled, OH 43606-3390 U.S.A. A little nticed right triangle. Intrductin
INVARIANTS OF TOPOLOGICAL AND LEGENDRIAN LINKS IN LENS SPACES WITH A UNIVERSALLY TIGHT CONTACT STRUCTURE. Christopher R. Cornwell
 INVARIANTS OF TOPOLOGICAL AND LEGENDRIAN LINKS IN LENS SPACES WITH A UNIVERSALLY TIGHT CONTACT STRUCTURE By Christpher R. Crnwell A DISSERTATION Submitted t Michigan State University in partial fulfillment
INVARIANTS OF TOPOLOGICAL AND LEGENDRIAN LINKS IN LENS SPACES WITH A UNIVERSALLY TIGHT CONTACT STRUCTURE By Christpher R. Crnwell A DISSERTATION Submitted t Michigan State University in partial fulfillment
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Support Vector Machines
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Supprt Vectr Machines Instructr: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/cmp551 Unless therwise nted, all material psted fr this curse
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 11: Supprt Vectr Machines Instructr: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/cmp551 Unless therwise nted, all material psted fr this curse
THE QUADRATIC AND QUARTIC CHARACTER OF CERTAIN QUADRATIC UNITS I PHILIP A. LEONARD AND KENNETH S. WILLIAMS
 PACFC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATCS Vl. 7, N., 977 THE QUADRATC AND QUARTC CHARACTER OF CERTAN QUADRATC UNTS PHLP A. LEONARD AND KENNETH S. WLLAMS Let ε m dente the fundamental unit f the real quadratic field
PACFC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATCS Vl. 7, N., 977 THE QUADRATC AND QUARTC CHARACTER OF CERTAN QUADRATC UNTS PHLP A. LEONARD AND KENNETH S. WLLAMS Let ε m dente the fundamental unit f the real quadratic field
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
E Z, (n l. and, if in addition, for each integer n E Z there is a unique factorization of the form
 Revista Clmbiana de Matematias Vlumen II,1968,pags.6-11 A NOTE ON GENERALIZED MOBIUS f-functions V.S. by ALBIS In [1] the ncept f a cnjugate pair f sets f psi tive integers is int~dued Briefly, if Z dentes
Revista Clmbiana de Matematias Vlumen II,1968,pags.6-11 A NOTE ON GENERALIZED MOBIUS f-functions V.S. by ALBIS In [1] the ncept f a cnjugate pair f sets f psi tive integers is int~dued Briefly, if Z dentes
Chapter 9 Vector Differential Calculus, Grad, Div, Curl
 Chapter 9 Vectr Differential Calculus, Grad, Div, Curl 9.1 Vectrs in 2-Space and 3-Space 9.2 Inner Prduct (Dt Prduct) 9.3 Vectr Prduct (Crss Prduct, Outer Prduct) 9.4 Vectr and Scalar Functins and Fields
Chapter 9 Vectr Differential Calculus, Grad, Div, Curl 9.1 Vectrs in 2-Space and 3-Space 9.2 Inner Prduct (Dt Prduct) 9.3 Vectr Prduct (Crss Prduct, Outer Prduct) 9.4 Vectr and Scalar Functins and Fields
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT
 BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR
 Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Last Updated: Oct 14, 2017
 RSA Last Updated: Oct 14, 2017 Recap Number thery What is a prime number? What is prime factrizatin? What is a GCD? What des relatively prime mean? What des c-prime mean? What des cngruence mean? What
RSA Last Updated: Oct 14, 2017 Recap Number thery What is a prime number? What is prime factrizatin? What is a GCD? What des relatively prime mean? What des c-prime mean? What des cngruence mean? What
DIFFERENTIABILITY OF REAL VALUED FUNCTIONS OF TWO VARIABLES AND EULER S THEOREM. ARUN LEKHA Associate Professor G.C.G., SECTOR-11, CHANDIGARH
 DIFFERENTIABILITY OF REAL VALUED FUNCTIONS OF TWO VARIABLES AND EULER S THEOREM ARUN LEKHA Assciate Pressr G.C.G. SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH FUNCTION OF TWO VARIABLES Deinitin: A variable Z is said t be a unctin
DIFFERENTIABILITY OF REAL VALUED FUNCTIONS OF TWO VARIABLES AND EULER S THEOREM ARUN LEKHA Assciate Pressr G.C.G. SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH FUNCTION OF TWO VARIABLES Deinitin: A variable Z is said t be a unctin
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Multiple Source Multiple. using Network Coding
 Multiple Surce Multiple Destinatin Tplgy Inference using Netwrk Cding Pegah Sattari EECS, UC Irvine Jint wrk with Athina Markpulu, at UCI, Christina Fraguli, at EPFL, Lausanne Outline Netwrk Tmgraphy Gal,
Multiple Surce Multiple Destinatin Tplgy Inference using Netwrk Cding Pegah Sattari EECS, UC Irvine Jint wrk with Athina Markpulu, at UCI, Christina Fraguli, at EPFL, Lausanne Outline Netwrk Tmgraphy Gal,
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Prcessing: Cntinuus and Discrete Fall 2008 Fr infrmatin abut citing these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts Institute
MIT OpenCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Prcessing: Cntinuus and Discrete Fall 2008 Fr infrmatin abut citing these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts Institute
Supplementary Course Notes Adding and Subtracting AC Voltages and Currents
 Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Math 105: Review for Exam I - Solutions
 1. Let f(x) = 3 + x + 5. Math 105: Review fr Exam I - Slutins (a) What is the natural dmain f f? [ 5, ), which means all reals greater than r equal t 5 (b) What is the range f f? [3, ), which means all
1. Let f(x) = 3 + x + 5. Math 105: Review fr Exam I - Slutins (a) What is the natural dmain f f? [ 5, ), which means all reals greater than r equal t 5 (b) What is the range f f? [3, ), which means all
M thematics. National 5 Practice Paper E. Paper 1. Duration 1 hour. Total marks 40
 N5 M thematics Natinal 5 Practice Paper E Paper 1 Duratin 1 hur Ttal marks 40 Yu may NOT use a calculatr Attempt all the questins. Use blue r black ink. Full credit will nly be given t slutins which cntain
N5 M thematics Natinal 5 Practice Paper E Paper 1 Duratin 1 hur Ttal marks 40 Yu may NOT use a calculatr Attempt all the questins. Use blue r black ink. Full credit will nly be given t slutins which cntain
