11.2 Proving Figures are Similar Using Transformations
|
|
|
- Gervase King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
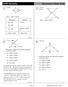
1 Name lass ate 11. Proving igures are Similar Using Transformations ssential Question: How can similarit transformations be used to show two figures are similar? esource ocker plore onfirming Similarit similarit transformation is a transformation in which an image has the same shape as its pre-image. Similarit transformations include reflections, translations, rotations, and dilations. Two plane figures are similar if and onl if one figure can be mapped to the other through one or more similarit transformations. grid shows a map of the cit park. Use tracing paper to confirm that the park elements are similar. Trace patio HG. Turn the paper so that patio HG is mapped onto patio MON. escribe the transformation. What does this confirm about the patios? H -8 - N 0 G 8 O Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan - N M O 0 M - Trace statues and MNO. old the paper so that statue is mapped onto statue MNO. escribe the transformation. What does this confirm about the statues? Module esson
2 escribe the transformation ou can use to map vertices of garden ST to corresponding vertices of garden. What does this confirm about the gardens? S T eflect 1. ook back at all the steps. Were an of the images congruent to the pre-images? If so, what tpes of similarit transformations were performed with these figures? What does this tell ou about the relationship between similar and congruent figures?. If two figures are similar, can ou conclude that corresponding angles are congruent? Wh or wh not? plain 1 etermining If igures are Similar You can represent dilations using the coordinate notation (, ) (k, k), where k is the scale factor and the center of dilation is the origin. If 0 < k < 1, the dilation is a reduction. If k > 1, the dilation is an enlargement. ample 1-0 T Z etermine whether the two figures are similar using similarit transformations. plain. ST and XYZ To X S Y map ST onto XYZ, there must be some factor k that dilates ST. Pre-image Image (0, 1) X (0, 3) S (1, -1) Y (3, -3) T (-1, -1) Z (-3, -3) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Module esson
3 You can see that each coordinate of the pre-image is multiplied b 3 to get the image, so this is a dilation with scale factor 3. Therefore, ST can be mapped onto XYZ b a dilation with center at the origin, which is represented b the coordinate notation (, ) (3, 3). dilation is a similarit transformation, so ST is similar to XYZ. To PQS and WXYZ 10 X(, 9) Y(1, 9) 8 W(, ) Z(1, ) Q(, ) (, ) P(, ) S(, ) map PQS onto WXYZ, there must be some factor k that enlarges PQS. Pre-image P (, ) Image Q (, ) X (, 9) Z (1, ) ind each distance: PQ =, Q =, WX =, and = 7 If kpq = WX, then k =. However. Q = / XY. No value of k can be determined that will map PQS to WXYZ. So, the figures are/are not similar. Your Turn etermine whether the two figures are similar using similarit transformations. plain. 3. MNO and GH 1 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan (, 1) (8, 1) O(1, ) N(, ) G(, ) H(8, ) (1, ) M(, ) Module esson
4 . and MNP. and TUV - 0 M - U 0 T V N P plain inding a Sequence of Similarit Transformations In order for two figures to be similar, there has to be some sequence of similarit transformations that maps one figure to the other. Sometimes there will be a single similarit transformation in the sequence. Sometimes ou must identif more than one transformation to describe a mapping. ample ind a sequence of similarit transformations that maps the first figure to the second figure. Write the coordinate notation for each transformation. to HG - 0 G H Since HG is smaller than, the scale factor k of the dilation must be between 0 and 1. The length of _ is and the length of _ is ; therefore, the scale factor is 1. Write the new coordinates after the dilation: Original oordinates (1, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) oordinates after dilation k = 1 ( 1, 3 ) (, 3 ) (-1, 1) (1, 1) translation right units and down 3 units completes the mapping. oordinates after dilation ( 1_, 3 ) ( _, 3 ) oordinates after translation ( +, - 3) (, 0 ) ( (-1, 1) (1, 1) 9, 0 ) G (1, ) H (3, ) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan The coordinates after translation are the same as the coordinates of GH, so ou can map to HG b the dilation (, ) 1 (, 1 ) followed b a translation (, ) ( +, - 3). Module esson
5 to PQ P Q 8 You can map to PQ with a reflection across the -ais followed b a followed b a counterclockwise rotation about the origin. eflection: (, ) (, -) : (, ) ( ) (, ) ( ) counterclockwise rotation: eflect. Using the figure in ample 3, describe a single dilation that maps to HG. 7. Using the figure in ample 3, describe a different sequence of transformations that will map to PQ. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Your Turn or each pair of similar figures, find a sequence of similarit transformations that maps one figure to the other. Use coordinate notation to describe the transformations. 8. PQS to TUVW -8 - V W U T 0 Q P S 8 Module esson
6 9. to escribe a sequence of similarit transformations that maps MN to VWXYZ. M N W V X Z Y plain 3 Proving ll ircles re Similar You can use the definition of similarit to prove theorems about figures. ircle Similarit Theorem ll circles are similar. ample 3 Prove the ircle Similarit Theorem. Given: ircle with center and radius r. ircle with center and radius s. r s Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Prove: ircle is similar to circle. To prove similarit, ou must show that there is a sequence of similarit transformations that maps circle to circle. Module 11 9 esson
7 Start b transforming circle with a along the vector. s r r ircle ' Through this, the image of point is. et the image of circle be circle ʹ. The center of circle ʹ coincides with point. Transform circle ʹ with the dilation with center of dilation ircle ʹ is made up of all the points at distance from point. and scale factor s_ r. fter the dilation, the image of circle ʹ will consist of all the points at distance from point. These are the same points that form circle. Therefore, the followed b the dilation maps circle to circle. ecause and dilations are, ou can conclude that circle is to circle. eflect 11. an ou show that circle and circle are similar through another sequence of similarit transformations? plain. 1. iscussion Is it possible that circle and circle are congruent? If so, does the proof of the similarit of the circles still work? plain. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan laborate 13. Translations, reflections, and rotations are rigid motions. What unique characteristic keeps dilations from being considered a rigid motion? 1. ssential Question heck-in Two squares in the coordinate plane have horizontal and vertical sides. plain how the are similar using similarit transformations. Module esson
8 valuate: Homework and Practice In ercises 1, determine if the two figures are similar using similarit transformations. plain. 1. GH and Online Homework Hints and Help tra Practice Pre-Image Image - H 0 G -. PQ and STU S - 0 Q T U 3. MN and PQS -8 - Q P 0 M 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan S N Module 11 9 esson
9 . UVW and GHI U W - 0 H G V I or the pair of similar figures in each of ercises 10, find a sequence of similarit transformations that maps one figure to the other. Provide the coordinate notation for each transformation.. Map to PQ.. Map to GH. - 0 Q P H G 7. Map to. 8. Map to MN. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan N M Module 11 9 esson
10 9. Map to M. 10. Map to PQ -8-0 M 8 - Q 0 P omplete the proof. 11. Given: Square with side length. Square GH with side length. H Prove: Square is similar to square GH. G Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Module 11 9 esson
11 1. Given: quilateral with side length j. quilateral PQ with side length p P Prove: is similar to PQ. j p Q 13. Given: with = c, = a, = b c XYZ with YZ =, XY = a, XZ = b a Y Prove: is similar to XYZ. c a c a b X b a Z Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Image redits: ill Hustace/orbis 1. The dimensions of a standard tennis court are 3 feet 78 feet with a net that is 3 feet high in the center. The court is modified for plaers aged 10 and under such that the dimensions are 7 feet 0 feet, and the same net is used. Use similarit to determine if the modified court is similar to the standard court. Module esson
12 1. epresent eal-world Problems scuba flag is used to indicate there is a diver below. In North merica, scuba flags are red with a white stripe from the upper left corner to the lower right corner. ustif the triangles formed on the scuba flag are similar triangles. 1. The most common picture size is inches inches. Other common pictures sizes (in inches) are 7, 8 10, 9 1, 11 1, 1 18, and 1 0. a. re an of these picture sizes similar? plain using similarit transformations. b. What does our conclusion indicate about resizing pictures? 17. Nicole wants to know the height of the snow sculpture but it is too tall to measure. Nicole measured the shadow of the snow sculpture's highest point to be 10 feet long. t the same time of da Nicole's shadow was 0 inches long. If Nicole is feet tall, what is the height of the snow sculpture? 18. Which of the following is a dilation?. (, ) (, 3). (, ) (3, -). (, ) (3, 3). (, ) (, - 3). (, ) ( - 3, - 3) 19. What is not preserved under dilation? Select all that appl.. ngle measure. etweenness. ollinearit. istance. Proportionalit Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Image redits: (t) huck Wagner/Shutterstock; (b) ave eede/esign Pics Inc./lam Module esson
13 H.O.T. ocus on Higher Order Thinking 0. nalze elationships onsider the transformations below. I. Translation II. eflection III. otation IV. ilation a. Which transformations preserve distance? b. Which transformations preserve angle measure? c. Use our knowledge of rigid transformations to compare and contrast congruenc and similarit. ustif easoning or ercises 1 3, use the figure shown. etermine whether the given assumptions are enough to prove that the two triangles are similar. Write the correct correspondence of the vertices. If the two triangles must be similar, describe a sequence of similarit transformations that maps one triangle to the other. If the triangles are not necessaril similar, eplain wh. 1. The lengths X, X, X, and X satisf the equation X X = X X. X. ines and are parallel. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan 3. X is congruent to X. Module esson
14 esson Performance Task nswer the following questions about the dartboard pictured here. 1. re the circles similar? plain, using the concept of a dilation in our eplanation.. You throw a dart and it sticks in a random location on the board. What is the probabilit that it sticks in ircle? ircle? ircle? ircle? plain how ou found our answers. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Module esson
11.2 Proving Figures are Similar Using Transformations
 Name lass ate 11. Poving igues ae Simila Using Tansfomations ssential Question: How can similait tansfomations be used to show two figues ae simila? esouce ocke ploe onfiming Similait similait tansfomation
Name lass ate 11. Poving igues ae Simila Using Tansfomations ssential Question: How can similait tansfomations be used to show two figues ae simila? esouce ocke ploe onfiming Similait similait tansfomation
Evaluate: Homework and Practice
 valuate: Homework and ractice Use the figure for ercises 1 2. Suppose ou use geometr software to construct two chords S and TU that intersect inside a circle at V. Online Homework Hints and Help tra ractice
valuate: Homework and ractice Use the figure for ercises 1 2. Suppose ou use geometr software to construct two chords S and TU that intersect inside a circle at V. Online Homework Hints and Help tra ractice
Cumulative Test 1. Name Date. In Exercises 1 5, use the diagram at the right. Answers
 Name Date umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of ED @##$ and @##$ D. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane D and plane E. 3. re points,, and D collinear? 2.
Name Date umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of ED @##$ and @##$ D. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane D and plane E. 3. re points,, and D collinear? 2.
Cumulative Test 1. Name Date. In Exercises 1 5, use the diagram at the right. Answers
 umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of E @##$ and @##$. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane and plane E. 3. re points,, and collinear? 2. 3. 4. re points
umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of E @##$ and @##$. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane and plane E. 3. re points,, and collinear? 2. 3. 4. re points
15.3 Tangents and Circumscribed Angles
 Name lass ate 15.3 Tangents and ircumscribed ngles Essential uestion: What are the key theorems about tangents to a circle? esource Locker Explore Investigating the Tangent-adius Theorem tangent is a line
Name lass ate 15.3 Tangents and ircumscribed ngles Essential uestion: What are the key theorems about tangents to a circle? esource Locker Explore Investigating the Tangent-adius Theorem tangent is a line
18.3 Special Right Triangles
 Name lass Date 18.3 Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore 1 Investigating an Isosceles Right
Name lass Date 18.3 Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore 1 Investigating an Isosceles Right
12.1 Triangle Proportionality Theorem
 ame lass Date 12.1 Triangle roportionality Theorem ssential Question: When a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, how does it divide those sides? Resource ocker xplore
ame lass Date 12.1 Triangle roportionality Theorem ssential Question: When a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, how does it divide those sides? Resource ocker xplore
7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
14.3 Tangents and Circumscribed Angles
 Name lass Date 14.3 Tangents and ircumscribed ngles Essential uestion: What are the key theorems about tangents to a circle? Explore G.5. Investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships,
Name lass Date 14.3 Tangents and ircumscribed ngles Essential uestion: What are the key theorems about tangents to a circle? Explore G.5. Investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships,
4.1 Circles. Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Circle. Explore
 Name Class Date 4.1 Circles ssential Question: What is the standard form for the equation of a circle, and what does the standard form tell ou about the circle? plore Deriving the Standard-Form quation
Name Class Date 4.1 Circles ssential Question: What is the standard form for the equation of a circle, and what does the standard form tell ou about the circle? plore Deriving the Standard-Form quation
13.3 Special Right Triangles
 Name lass ate. Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore Investigating an Isosceles Right Triangle
Name lass ate. Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore Investigating an Isosceles Right Triangle
Practice For use with pages
 Name ate ON 0. ractice For use with pages 678 686 se ( to draw the described part of the circle.. raw a diameter and label it }.. raw a tangent ra and label it ###$. 3. raw a secant and label it } F. 4.
Name ate ON 0. ractice For use with pages 678 686 se ( to draw the described part of the circle.. raw a diameter and label it }.. raw a tangent ra and label it ###$. 3. raw a secant and label it } F. 4.
15.5 Angle Relationships in Circles
 ame lass ate 15.5 ngle Relationships in ircles ssential uestion: What are the relationships between angles formed by lines that intersect a circle? xplore xploring ngle Measures in ircles The sundial is
ame lass ate 15.5 ngle Relationships in ircles ssential uestion: What are the relationships between angles formed by lines that intersect a circle? xplore xploring ngle Measures in ircles The sundial is
1.2 Perpendicular Lines
 Name lass ate 1.2 erpendicular Lines Essential Question: What are the key ideas about perpendicular bisectors of a segment? 1 Explore onstructing erpendicular isectors and erpendicular Lines You can construct
Name lass ate 1.2 erpendicular Lines Essential Question: What are the key ideas about perpendicular bisectors of a segment? 1 Explore onstructing erpendicular isectors and erpendicular Lines You can construct
8.3 Start Thinking. 8.3 Warm Up. 8.3 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 .3 tart hinking carpentr class is working on a project for the local childcare centers. he students are making wooden trees to go with the centers train sets. he work from a sample that was cut from a
.3 tart hinking carpentr class is working on a project for the local childcare centers. he students are making wooden trees to go with the centers train sets. he work from a sample that was cut from a
Challenge: Skills and Applications For use with pages P( 1, 4) R( 3, 1)
 LESSON 8.4 NME TE hallenge: Skills and pplications For use with pages 480 487 1. Refer to the diagram, where VW YZ. a. Write a similarit statement. b. Write a paragraph proof for our result. V X Y W Z.
LESSON 8.4 NME TE hallenge: Skills and pplications For use with pages 480 487 1. Refer to the diagram, where VW YZ. a. Write a similarit statement. b. Write a paragraph proof for our result. V X Y W Z.
6.3 Interpreting Vertex Form and Standard Form
 Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
7.3 Triangle Inequalities
 Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
KEY EXAMPLE (Lesson 23.1) Find the coordinates of the circumcenter of the triangle. Coordinates: A (-2, -2), B (2, 3), C (2, -2) 2) Midpoint of BC
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan STUDY GUIDE REVIEW Special Segments in Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use special segments in triangles to solve real-world problems? KEY EXMPLE (Lesson
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan STUDY GUIDE REVIEW Special Segments in Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use special segments in triangles to solve real-world problems? KEY EXMPLE (Lesson
) = (0, -2) Midpoint of AC ) = ( 2, MODULE. STUDY GUIDE REVIEW Special Segments in Triangles
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan STUDY GUIDE REVIEW Special Segments in Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use special segments in triangles to solve real-world problems? KEY EXMPLE (Lesson
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan STUDY GUIDE REVIEW Special Segments in Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use special segments in triangles to solve real-world problems? KEY EXMPLE (Lesson
10.2 Graphing Square Root Functions
 Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
Evaluate: Homework and Practice
 valuate: Homework and Practice Identify the chord (s), inscribed angle (s), and central angle (s) in the figure. The center of the circles in xercises 1, 2, and 4 is. Online Homework Hints and Help xtra
valuate: Homework and Practice Identify the chord (s), inscribed angle (s), and central angle (s) in the figure. The center of the circles in xercises 1, 2, and 4 is. Online Homework Hints and Help xtra
NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide and Intervention
 7-1 tudy Guide and Intervention atios and Proportions Write and Use atios ratio is a comparison of two quantities by divisions. The ratio a to b, where b is not zero, can be written as a b or a:b. ample
7-1 tudy Guide and Intervention atios and Proportions Write and Use atios ratio is a comparison of two quantities by divisions. The ratio a to b, where b is not zero, can be written as a b or a:b. ample
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
10.2 Graphing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles
 Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Name Class Date. Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Parabola
 Name Class Date 1. Parabolas Essential Question: How is the distance formula connected with deriving equations for both vertical and horizontal parabolas? Eplore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of
Name Class Date 1. Parabolas Essential Question: How is the distance formula connected with deriving equations for both vertical and horizontal parabolas? Eplore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of
12.1 Triangle Proportionality Theorem
 Name lass Date 12.1 Triangle Proportionality Theorem ssential Question: When a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, how does it divide those sides? Resource Locker xplore
Name lass Date 12.1 Triangle Proportionality Theorem ssential Question: When a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, how does it divide those sides? Resource Locker xplore
Angles and Fractional Parts of a Circle. How can you relate angles and fractional parts of a circle?
 ? Name. Essential Question ngles and Fractional Parts of a ircle How can you relate angles and fractional parts of a circle? Geometry and Measurement.7. MTHEMTIL PROESSES..,..E,..F Investigate Materials
? Name. Essential Question ngles and Fractional Parts of a ircle How can you relate angles and fractional parts of a circle? Geometry and Measurement.7. MTHEMTIL PROESSES..,..E,..F Investigate Materials
Reteaching , or 37.5% 360. Geometric Probability. Name Date Class
 Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
2.4 Investigating Symmetry
 Name Class Date 2.4 Investigating Symmetry Essential Question: How do you determine whether a figure has line symmetry or rotational symmetry? 1 Explore 1 Identifying Line Symmetry A figure has symmetry
Name Class Date 2.4 Investigating Symmetry Essential Question: How do you determine whether a figure has line symmetry or rotational symmetry? 1 Explore 1 Identifying Line Symmetry A figure has symmetry
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided.
 1 st Semester Final xam Review Name: Geometry ate: lock: You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided. Topic #1 (Foundations of Geometry) 1) Multiple hoice:
1 st Semester Final xam Review Name: Geometry ate: lock: You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided. Topic #1 (Foundations of Geometry) 1) Multiple hoice:
Properties of Triangles and Four-Sided Figures Lesson 13.1 Classifying Triangles
 HPT13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
HPT13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 9.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM
 Y VIW I he midterm eam for period is on /, 0:00 to :. he eam will consist of approimatel 0 multiple-choice and open-ended questions. Now is the time to start studing!!! PP eviews all previous assessments.
Y VIW I he midterm eam for period is on /, 0:00 to :. he eam will consist of approimatel 0 multiple-choice and open-ended questions. Now is the time to start studing!!! PP eviews all previous assessments.
13.1 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Given: You try: Given: Prove: ABC ADC. Prove: ABE DCE. 1. Given 1. AB AD BC DC. 2. AC AC 2. Reflexive Prop. of. 3. ABC ADC 3. SSS Post.
 US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
Properties of Triangles and Four-Sided Figures Lesson 13.1 Classifying Triangles
 HPTR13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
HPTR13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
13.2 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
11.1 Double Riemann Sums and Double Integrals over Rectangles
 Chapter 11 Multiple Integrals 11.1 ouble Riemann Sums and ouble Integrals over Rectangles Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated b the following important questions:
Chapter 11 Multiple Integrals 11.1 ouble Riemann Sums and ouble Integrals over Rectangles Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated b the following important questions:
Applications. 12 The Shapes of Algebra. 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates x and y for points on the circle.
 Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
Multiple Choice. 3. The polygons are similar, but not necessarily drawn to scale. Find the values of x and y.
 Accelerated Coordinate Algebra/Analtic Geometr answers the question. Page 1 of 5 Multiple Choice 1. The dashed triangle is an image of the solid triangle. What is the scale factor of the image?. The polgons
Accelerated Coordinate Algebra/Analtic Geometr answers the question. Page 1 of 5 Multiple Choice 1. The dashed triangle is an image of the solid triangle. What is the scale factor of the image?. The polgons
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
Lesson 9.3 Relating Congruent and Similar Figures to Geometric Transformations
 Lesson 9. Relating ongruent and Similar Figures to Geometric Transformations State whether the figure and image are congruent or similar.. Rectangle D is rotated 90 clockwise about verte.. parallelogram
Lesson 9. Relating ongruent and Similar Figures to Geometric Transformations State whether the figure and image are congruent or similar.. Rectangle D is rotated 90 clockwise about verte.. parallelogram
Name Class Date. Understanding How to Graph g(x) = a(x - h ) 2 + k
 Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1
 Ma 2015 page 1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1 In this handout, we will eplore eigenvectors and eigenvalues. We will begin with an eploration, then provide some direct eplanation and worked eamples, and
Ma 2015 page 1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1 In this handout, we will eplore eigenvectors and eigenvalues. We will begin with an eploration, then provide some direct eplanation and worked eamples, and
Unit 2 Review. Determine the scale factor of the dilation below.
 Unit 2 Review 1. oes the graph below represent a dilation? Why or why not? y 10 9 8 7 (0, 7) 6 5 4 3 (0, 3.5) 2 1 (5, 7) (5, 3.5) -10-9 -8-7 -6-5 -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10-1 F -2 (5, 0) -3-4 -5-6
Unit 2 Review 1. oes the graph below represent a dilation? Why or why not? y 10 9 8 7 (0, 7) 6 5 4 3 (0, 3.5) 2 1 (5, 7) (5, 3.5) -10-9 -8-7 -6-5 -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10-1 F -2 (5, 0) -3-4 -5-6
Name Class Date. Inverse of Function. Understanding Inverses of Functions
 Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry software to draw any ABC. a. Bisect B and plot point D at the intersection of the angle bisector and AC.
 .6 Proportionality heorems ssential uestion hat proportionality relationships eist in a triangle intersected by an angle bisector or by a line parallel to one of the sides? iscovering a Proportionality
.6 Proportionality heorems ssential uestion hat proportionality relationships eist in a triangle intersected by an angle bisector or by a line parallel to one of the sides? iscovering a Proportionality
2-6. _ k x and y = _ k. The Graph of. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 2 Lesson 2-6 BIG IDEA The Graph of = _ k and = _ k 2 The graph of the set of points (, ) satisfing = k_, with k constant, is a hperbola with the - and -aes as asmptotes; the graph of the set of
Chapter 2 Lesson 2-6 BIG IDEA The Graph of = _ k and = _ k 2 The graph of the set of points (, ) satisfing = k_, with k constant, is a hperbola with the - and -aes as asmptotes; the graph of the set of
4.2 Parabolas. Explore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. (x - p) 2 + y 2 = (x + p) 2
 COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
UNIT 1: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS. 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1).
 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
Chapter 11 Similarity Problems
 hapter Similarit roblems. ind the ratio of the perimeter of rectangle to the perimeter of rectangle L. L 4. Δ and ΔL are similar. ind the ratio of their corresponding sides. 5 ft ft 9 ft ft 0 m 8 m []
hapter Similarit roblems. ind the ratio of the perimeter of rectangle to the perimeter of rectangle L. L 4. Δ and ΔL are similar. ind the ratio of their corresponding sides. 5 ft ft 9 ft ft 0 m 8 m []
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles
 Name ate lass STION 11 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect ircles ind these vocabulary words in Lesson 11-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary interior of a circle exterior
Name ate lass STION 11 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect ircles ind these vocabulary words in Lesson 11-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary interior of a circle exterior
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3. Topic 1 : Equation of a circle
 Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
); 5 units 5. x = 3 6. r = 5 7. n = 2 8. t =
 . Sample answer: dilation with center at the origin and a scale factor of 1 followed b a translation units right and 1 unit down 5. Sample answer: reflection in the -axis followed b a dilation with center
. Sample answer: dilation with center at the origin and a scale factor of 1 followed b a translation units right and 1 unit down 5. Sample answer: reflection in the -axis followed b a dilation with center
10.3 Start Thinking Warm Up Cumulative Review Warm Up
 10.3 tart hinking etermine if the statement is always true, sometimes true, or never true. plain your reasoning. 1. chord is a diameter. 2. diameter is a chord. 3. chord and a radius have the same measure.
10.3 tart hinking etermine if the statement is always true, sometimes true, or never true. plain your reasoning. 1. chord is a diameter. 2. diameter is a chord. 3. chord and a radius have the same measure.
Review 3. Determine the dimensions, in feet, of his new garden. Show your work. Only an algebraic solution will be accepted.
 Name: Ms. Logan Review Class: Date: 1. David currentl has a square garden. He wants to redesign his garden and make it into a rectangle with a length that is feet shorter than twice its width. He decides
Name: Ms. Logan Review Class: Date: 1. David currentl has a square garden. He wants to redesign his garden and make it into a rectangle with a length that is feet shorter than twice its width. He decides
16.2 Arc Length and Radian Measure
 Name Class Date 16.2 rc Length and Radian Measure Essential Question: How do you find the length of an arc? Explore Deriving the Formula for rc Length n arc is an unbroken part of a circle consisting of
Name Class Date 16.2 rc Length and Radian Measure Essential Question: How do you find the length of an arc? Explore Deriving the Formula for rc Length n arc is an unbroken part of a circle consisting of
Circles in the Coordinate Plane. Find the length of each segment to the nearest tenth y. Distance Formula Square both sides.
 -5 ircles in the oordinate Plane -5. Plan What You ll Learn To write an equation of a circle To find the center and radius of a circle... nd Wh To describe the position and range of three cellular telephone
-5 ircles in the oordinate Plane -5. Plan What You ll Learn To write an equation of a circle To find the center and radius of a circle... nd Wh To describe the position and range of three cellular telephone
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 _ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
_ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
25 true/false Draw reflections, rotations, dilations Symmetry regarding a regular polygon
 Geometry Week 27 ch. 12 review 1. hapter 12 Vocabulary: angle of rotation ais of symmetry center of rotation composition dilation enlargement fied point identity transformation image invariance isometry
Geometry Week 27 ch. 12 review 1. hapter 12 Vocabulary: angle of rotation ais of symmetry center of rotation composition dilation enlargement fied point identity transformation image invariance isometry
For questions 13 16, determine if the described transformation(s) is/are an isometry.
 1. What ter describes a transforation that does not change a figure s size or shape? () siilarit () isoetr () collinearit () setr For questions 4, use the diagra showing parallelogra. H I F 6. regular
1. What ter describes a transforation that does not change a figure s size or shape? () siilarit () isoetr () collinearit () setr For questions 4, use the diagra showing parallelogra. H I F 6. regular
9. AD = 7; By the Parallelogram Opposite Sides Theorem (Thm. 7.3), AD = BC. 10. AE = 7; By the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem (Thm. 7.6), AE = EC.
 3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
Sample Problems For Grade 9 Mathematics. Grade. 1. If x 3
 Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Conic Sections CHAPTER OUTLINE. The Circle Ellipses and Hyperbolas Second-Degree Inequalities and Nonlinear Systems FIGURE 1
 088_0_p676-7 /7/0 :5 PM Page 676 (FPG International / Telegraph Colour Librar) Conic Sections CHAPTER OUTLINE. The Circle. Ellipses and Hperbolas.3 Second-Degree Inequalities and Nonlinear Sstems O ne
088_0_p676-7 /7/0 :5 PM Page 676 (FPG International / Telegraph Colour Librar) Conic Sections CHAPTER OUTLINE. The Circle. Ellipses and Hperbolas.3 Second-Degree Inequalities and Nonlinear Sstems O ne
Using Properties of Segments that Intersect Circles
 ig Idea 1 H UY I I Using roperties of egments that Intersect ircles or Your otebook You learned several relationships between tangents, secants, and chords. ome of these relationships can help you determine
ig Idea 1 H UY I I Using roperties of egments that Intersect ircles or Your otebook You learned several relationships between tangents, secants, and chords. ome of these relationships can help you determine
11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure
 1.2 a.1, a.4, a.5; P..E TEKS Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure Before You used acute angles measured in degrees. Now You will use general angles that ma be measured in radians. Wh? So ou can
1.2 a.1, a.4, a.5; P..E TEKS Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure Before You used acute angles measured in degrees. Now You will use general angles that ma be measured in radians. Wh? So ou can
Final Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice
 Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice Lesson 1-1 1. a. 75; 15 b. 53; 13 c. 19; 19 d. 7; 117 e. (9 ); (1 ). a. ; b..5; 3.5 c. 3; 5 d. 33; 57 e. 5; 5 3. a. 7.5; 17.5 b. 31.5; 1.5 c. 5; 135 d. 59; 11 e. 1.;
Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice Lesson 1-1 1. a. 75; 15 b. 53; 13 c. 19; 19 d. 7; 117 e. (9 ); (1 ). a. ; b..5; 3.5 c. 3; 5 d. 33; 57 e. 5; 5 3. a. 7.5; 17.5 b. 31.5; 1.5 c. 5; 135 d. 59; 11 e. 1.;
You are required to show your work on each problem on this exam. The following rules apply:
 Math 5335 Fall 2017 Eam 2 12/5/18 Time Limit: 80 Minutes Name (Print): KEY This eam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 13 problems heck to see if an pages are missing Enter all requested
Math 5335 Fall 2017 Eam 2 12/5/18 Time Limit: 80 Minutes Name (Print): KEY This eam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 13 problems heck to see if an pages are missing Enter all requested
5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope
 Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
Explore 1 Graphing and Analyzing f(x) = e x. The following table represents the function ƒ (x) = (1 + 1 x) x for several values of x.
 1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
Geometry: A Complete Course
 Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas E. lark Larry E. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module Student Worktext opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas E. lark Larry E. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module Student Worktext opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes.
 Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Lesson 1 Reteach. Example. Exercises. Determine if the two figures are congruent by using transformations.
 Lesson 1 eteach Congruence and Transformations Translation eflection otation length is the same length is the same length is the same orientation is the sarne onentation is different onentation is different
Lesson 1 eteach Congruence and Transformations Translation eflection otation length is the same length is the same length is the same orientation is the sarne onentation is different onentation is different
Sum of Angle Measures in a Triangle 6.8.A. Use a straightedge to draw a large triangle. Label the angles 1, 2, and 3.
 ? LESSON 15.2 ESSENTIL QUESTION Sum of ngle Measures in a Triangle How do you use the sum of angles in a triangle to find an unknown angle measure? Epressions, equations, and relationships 6.8. Etend previous
? LESSON 15.2 ESSENTIL QUESTION Sum of ngle Measures in a Triangle How do you use the sum of angles in a triangle to find an unknown angle measure? Epressions, equations, and relationships 6.8. Etend previous
Number Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometry
 Numer Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometr Now this is m kind of paraola! Chapter Contents :0 The paraola PS, PS, PS Investigation: The graphs of paraolas :0 Paraolas of the form = a + + c PS Fun Spot:
Numer Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometr Now this is m kind of paraola! Chapter Contents :0 The paraola PS, PS, PS Investigation: The graphs of paraolas :0 Paraolas of the form = a + + c PS Fun Spot:
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
The Coordinate Plane. Domain 1 Lesson 10. Getting the Idea
 omain Lesson 0 The oordinate Plane ommon ore Standards:.NS..b,.NS..c Getting the Idea You can use a coordinate plane to locate points. coordinate plane is formed b a horizontal number line, called the
omain Lesson 0 The oordinate Plane ommon ore Standards:.NS..b,.NS..c Getting the Idea You can use a coordinate plane to locate points. coordinate plane is formed b a horizontal number line, called the
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I
 LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
2 Explain 1 Proving the Intersecting Chords Angle Measure Theorem
 xplain 1 Proving the Intersecting hords ngle easure Theorem In the xplore section, you discovered the effects that line segments, such as chords and secants, have on angle measures and their intercepted
xplain 1 Proving the Intersecting hords ngle easure Theorem In the xplore section, you discovered the effects that line segments, such as chords and secants, have on angle measures and their intercepted
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7)
 Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
Chapter 4 Review Formal Geometry Name: Period: Due on the day of your test:
 Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the figure, what is the m 3?. 97 B. 62 97 2 C. 48. 35 35 1 3 2. In the figure, PR SU and QT QU. What
Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the figure, what is the m 3?. 97 B. 62 97 2 C. 48. 35 35 1 3 2. In the figure, PR SU and QT QU. What
Replacement for a Carpenter s Square
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Replacement for a arpenter s Square Inscribed and ircumscribed Triangles and Quadrilaterals Vocabulary nswer each question. 1. How are inscribed polygons and circumscribed
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Replacement for a arpenter s Square Inscribed and ircumscribed Triangles and Quadrilaterals Vocabulary nswer each question. 1. How are inscribed polygons and circumscribed
7.1 Connecting Intercepts and Zeros
 Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
Geometry 1 st Semester review Name
 Geometry 1 st Semester review Name 1. What are the next three numbers in this sequence? 0, 3, 9, 18, For xercises 2 4, refer to the figure to the right. j k 2. Name the point(s) collinear to points H and
Geometry 1 st Semester review Name 1. What are the next three numbers in this sequence? 0, 3, 9, 18, For xercises 2 4, refer to the figure to the right. j k 2. Name the point(s) collinear to points H and
Study Guide and Assessment
 tudy uide and ssessment nderstanding and sing the ocabulary fter completing this chapter, you should be able to define each term, property, or phrase and give an example or two of each. altitude (p. 4)
tudy uide and ssessment nderstanding and sing the ocabulary fter completing this chapter, you should be able to define each term, property, or phrase and give an example or two of each. altitude (p. 4)
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
2.4 Investigating Symmetry
 Locker LESSON 2.4 Investigating Symmetry Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.3.D Identify and distinguish between reflectional and rotational symmetry in a plane figure. Mathematical Processes
Locker LESSON 2.4 Investigating Symmetry Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.3.D Identify and distinguish between reflectional and rotational symmetry in a plane figure. Mathematical Processes
Using Chords. Essential Question What are two ways to determine when a chord is a diameter of a circle?
 10.3 Using hords ssential uestion What are two ways to determine when a chord is a diameter of a circle? rawing iameters OOKI O UU o be proficient in math, you need to look closely to discern a pattern
10.3 Using hords ssential uestion What are two ways to determine when a chord is a diameter of a circle? rawing iameters OOKI O UU o be proficient in math, you need to look closely to discern a pattern
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Final Exam Review Packet
 Student Name # Teacher Class Period MATH 8 FINAL EXAM Review Packet Page 1 of 19 Show all work. 1. The radius of a cylinder is 6 cm. The height is 10 cm. Find the volume of the cylinder. Leave your answer
Student Name # Teacher Class Period MATH 8 FINAL EXAM Review Packet Page 1 of 19 Show all work. 1. The radius of a cylinder is 6 cm. The height is 10 cm. Find the volume of the cylinder. Leave your answer
} = Explain your answer.
 UI RTI Vocabular heck oncept heck kill heck 2. n two of the points; as shown in ample 3 on p. 81, an two points on a line can be use to calculate the slope of the line. RTI ITIO 1. If ~ X, =, an X =, what
UI RTI Vocabular heck oncept heck kill heck 2. n two of the points; as shown in ample 3 on p. 81, an two points on a line can be use to calculate the slope of the line. RTI ITIO 1. If ~ X, =, an X =, what
