10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
|
|
|
- Ira Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource Locker Eplore Finding the Inverse of a Man-to-One Function The function ƒ () is defined b the following ordered pairs: (-, ), (-1, ), (0, 0), (1, ), and (, ). A Find the inverse function of ƒ (), ƒ -1 (), b reversing the coordinates in the ordered pairs. B Is the inverse also a function? Eplain. C If necessar, restrict the domain of ƒ () such that the inverse, ƒ -1 (), is a function. To restrict the domain of ƒ () so that its inverse is a function, ou can restrict it to D With the restricted domain of ƒ (), what ordered pairs define the inverse function ƒ -1 ()? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Reflect 1. Discussion Look again at the ordered pairs that define ƒ (). Without reversing the order of the coordinates, how could ou have known that the inverse of ƒ () would not be a function?. How will restricting the domain of ƒ () affect the range of its inverse? Module Lesson 1
2 Eplain 1 Finding and Graphing the Inverse of a Simple Quadratic Function The function ƒ () = is a man-to-one function, so its domain must be restricted in order to find its inverse function. If the domain is restricted to 0, then the inverse function is ƒ -1 () = _ ; if the domain is restricted to 0, then the inverse function is ƒ -1 () = - _. The inverse of a quadratic function is a square root function, which is a function whose rule involves _. The parent square root function is g () = _. A square root function is defined onl for values of that make the epression under the radical sign nonnegative. Eample 1 Restrict the domain of each quadratic function and find its inverse. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. Graph the function and its inverse. A ƒ () = 0.5 Restrict the domain. 0 Find the inverse. Replace ƒ () with. = 0.5 Multipl both sides b. = Use the definition of positive square root. Switch and to write the inverse. Replace with ƒ -1 (). _ = _ = ƒ -1 () = _ Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. ƒ -1 (ƒ()) = ƒ -1 (0.5 ) ƒ ( ƒ -1 ()) = 0.5 ( _ ) = (0.5 ) = 0.5 () = _ = for 0 = for Since ƒ (ƒ()) = for 0 and ƒ (ƒ () ) = for 0, it has been confirmed that ƒ -1 () = _ for 0 is the inverse function of ƒ () = 0.5 for 0. Graph ƒ -1 () b graphing ƒ () over the restricted domain and reflecting the graph over the line =. 3 1 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module Lesson 1
3 B ƒ () = - 7 Find the inverse. Restrict the domain. Replace ƒ () with. = - 7 Add 7 to both sides. Use the definition of positive square root. = = Switch and to write the inverse. Replace with ƒ -1 (). Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. ƒ -1 (ƒ () ) = ƒ -1 ( ) ƒ ( ƒ -1 () ) = f ( ) = ( ) - 7 = = - 7 = = Since ƒ -1 (ƒ () ) = for and ƒ ( ) = for, it has been confirmed that ƒ -1 () = for is the inverse function of ƒ () = - 7 for. Graph ƒ -1 () b graphing ƒ () over the restricted domain and reflecting the graph over the line =. 8 6 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module Lesson 1
4 Your Turn Restrict the domain of each quadratic function and find its inverse. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. Graph the function and its inverse. 3. ƒ () = Eplain Finding the Inverse of a Quadratic Model In man instances, quadratic functions are used to model real-world applications. It is often useful to find and interpret the inverse of a quadratic model. Note that when working with real-world applications, it is more useful to use the notation () for the inverse of () instead of the notation -1 (). Eample Find the inverse of each of the quadratic functions. Use the inverse to solve the application. A The function d (t) = 16 t gives the distance d in feet that a dropped object falls in t seconds. Write the inverse function t (d) to find the time t in seconds it takes for an object to fall a distance of d feet. Then estimate how long it will take a penn dropped into a well to fall 8 feet. The original function d (t) = 16 t is a quadratic function with a domain restricted to t 0. Find the inverse function. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credit: CreativeNature.nl/Shutterstock Write d (t) as d. d = 16 t Divide both sides b 16. Use the definition of positive square root. d_ 16 = t d_ 16 = t Module 10 8 Lesson 1
5 Write t as t (d). d_ 16 = t (d) The inverse function is t (d) = d_ for d Use the inverse function to estimate how long it will take a penn dropped into a well to fall 8 feet. Substitute d = 8 into the inverse function. Write the function. t (d) = d_ 16 Substitute 8 for d. t (8) = _ 8 16 Simplif. t (8) = _ 3 Use a calculator to estimate. t (8) 1.7 So, it will take about 1.7 seconds for a penn to fall 8 feet into the well. B The function E (v) = v gives the kinetic energ E in Joules of an 8-kg object that is traveling at a velocit of v meters per second. Write and graph the inverse function v (E) to find the velocit v in meters per second required for an 8-kg object to have a kinetic energ of E Joules. Then estimate the velocit required for an 8-kg object to have a kinetic energ of 60 Joules. The original function E (v) = v is a function with a domain restricted to v. Find the inverse function. Write E (v) as E. Divide both sides b. Use the definition of positive square root. = v = v = v Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: CreativeNature.nl/Shutterstock Write v as v (E). The inverse function is v (E) = for E. Use the inverse function to estimate the velocit required for an 8-kg object to have a kinetic energ of 60 Joules. Substitute E = 60 into the inverse function. Write the function. v (E) = Substitute 60 for E. Simplif. Use a calculator to estimate. v = So, an 8-kg object with kinetic energ of 60 Joules is traveling at a velocit of per second. meters Module Lesson 1
6 Your Turn Find the inverse of the quadratic function. Use the inverse to solve the application.. The function A (r) = π r gives the area of a circular object with respect to its radius r. Write the inverse function r (A) to find the radius r required for area of A. Then estimate the radius of a circular object that has an area of 0 c m. Eplain 3 Finding and Graphing the Inverse of a Simple Cubic Function Note that the function ƒ () = 3 is a one-to-one function, so its domain does not need to be restricted in order to find its inverse function. The inverse of ƒ () = 3 is ƒ -1 () = 3. The inverse of a cubic function is a cube root function, which is a function whose rule involves 3. The parent cube root function is g () = 3. Eample 3 Find the inverse of each cubic function. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. Graph the function and its inverse. A ƒ () = Find each inverse. Graph the function and its inverse. Replace ƒ () with. = Multipl both sides b. = 3 Use the definition of cube root. Switch and to write the inverse. Replace with ƒ -1 (). Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. ƒ -1 (ƒ()) = ƒ -1 ( ) ƒ (ƒ ()) = ƒ ( ) = 3 (0.5 3 ) = 0.5 ( 3 3 ) = 3 3 = = = 0.5 () 3 = 3 = 3 = ƒ -1 () Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module 10 8 Lesson 1
7 Since ƒ -1 (ƒ () ) = and ƒ (ƒ -1 () ) =, it has been confirmed that ƒ -1 3 () = is the inverse function of ƒ () = Graph ƒ -1 () b graphing ƒ () and reflecting ƒ () over the line = B ƒ () = 3-9 Find the inverse. Replace ƒ () with. = 3-9 Add 9 to both sides. = 3 Use the definition of cube root. = Switch and to write the inverse. Replace with ƒ -1 (). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. ƒ -1 (ƒ () ) = ƒ -1 ( ) ƒ (ƒ -1 () ) = ƒ ( ) = = = = = = Since ƒ -1 (ƒ () ) = and ƒ (ƒ -1 () ) =, it has been confirmed that ƒ -1 () = is the inverse function of ƒ () = 3-9. Module Lesson 1
8 Graph ƒ -1 () b graphing ƒ () and reflecting ƒ () over the line = Your Turn Find each inverse. Graph the function and its inverse. 5. ƒ () = Eplain Finding the Inverse of a Cubic Model Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan In man instances, cubic functions are used to model real-world applications. It is often useful to find and interpret the inverse of cubic models. As with quadratic real-world applications, it is more useful to use the notation () for the inverse of () instead of the notation -1 (). Module Lesson 1
9 Eample Find the inverse of each of the following cubic functions. A The function m (L) = L 3 gives the mass m in kilograms of a red snapper of length L centimeters. Find the inverse function L (m) to find the length L in centimeters of a red snapper that has a mass of m kilograms. The original function m (L) = L 3 is a cubic function. Find the inverse function. Write m (L) as m. m = L 3 Multipl both sides b 100, ,000m = L 3 Use the definition of cube root. Write L as L (m). The inverse function is L(m) = 3 100,000m = L 3 100,000m = L (m) 3 100, 000m. B The function A (r) = _ 3 π r 3 gives the surface area A of a sphere with radius r. Find the inverse function r (A) to find the radius r of a sphere with surface area A. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: Vladimir Melnik/Shutterstock The original function A (r) = Find the inverse function. Write A (r) as A. _ 3 π r 3 is a function. = _ 3 π r 3 Divide both sides b _ 3 π. = r 3 Use the definition of cube root. Write r as r (A). The inverse function is r(a) =. Your Turn 6. The function m (r) = _ 3 π r 3 gives the mass in grams of a spherical lead ball with a radius of r centimeters. Find the inverse function r (m) to find the radius r of a lead sphere with mass m. = r Module Lesson 1
10 Elaborate 7. What is the general form of the inverse function for the function ƒ () = a? State an restrictions on the domains. 8. What is the general form of the inverse function for the function ƒ () = a 3? State an restrictions on the domains. 9. Essential Question Check-In Wh must the domain be restricted when finding the inverse of a quadratic function, but not when finding the inverse of a cubic function? Evaluate: Homework and Practice Restrict the domain of the quadratic function and find its inverse. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. Graph the function and its inverse. Online Homework Hints and Help Etra Practice 1. ƒ () = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module Lesson 1
11 . ƒ () = ƒ () = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Restrict the domain of the quadratic function and find its inverse. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition.. ƒ () = 15 Module Lesson 1
12 5. ƒ () = - 3_ 6. ƒ () = The function d (s) = s models the average depth d in feet of the water over which a tsunami travels, where s is the speed in miles per hour. Write the inverse function s (d) to find the speed required for a depth of d feet. Then estimate the speed of a tsunami over water with an average depth of 1500 feet. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: Nejron Photo/Shutterstock Module Lesson 1
13 T 8. The function (T) = 9.8 ( π ) gives the length in meters for a pendulum to swing for a period of T seconds. Write the inverse function to find the period of a pendulum in seconds. The period of a pendulum is the time it takes the pendulum to complete one back-and-forth swing. Find the period of a pendulum with length of 5 meters. Find the inverse of each cubic function. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. Graph the function and its inverse. 9. ƒ () = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: James Stevenson/Science Photo Librar 10. ƒ () = Module Lesson 1
14 Find the inverse of the cubic function. Confirm the inverse relationship using composition. 11. ƒ () = 3-5_ 6 1. ƒ () = The function m (r) = 31 r 3 models the mass in grams of a spherical zinc ball as a function of the ball s radius in centimeters. Write the inverse model to represent the radius r in cm of a spherical zinc ball as a function of the ball s mass m in g. 1. The function m (r) = 1 r 3 models the mass in grams of a spherical titanium ball as a function of the ball s radius in centimeters. Write the inverse model to represent the radius r in centimeters of a spherical titanium ball as a function of the ball s mass m in grams. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: oorka/ Shutterstock Module 10 9 Lesson 1
15 15. The weight w in pounds that a shelf can support can be modeled b w (d) = 8.9 d 3 where d is the distance, in inches, between the supports for the shelf. Write the inverse model to represent the distance d in inches between the supports of a shelf as a function of the weight w in pounds that the shelf can support. H.O.T. Focus on Higher Order Thinking 16. Eplain the Error A student was asked to find the inverse of the function ƒ () = ( ) What did the student do wrong? Find the correct inverse. ƒ () = ( _ ) = ( _ ) = ( _ ) 3-18 = = = ƒ -1 () = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan c Multi-Step A framing store uses the function ( 0.5 ) = a to determine the total area of a piece of glass with respect to the cost before installation of the glass. Write the inverse function for the cost c in dollars of glass for a picture with an area of a in square centimeters. Then write a new function to represent the total cost C the store charges if it costs $6.00 for installation. Use the total cost function to estimate the cost if the area of the glass is 19 cm². Module Lesson 1
16 18. Make a Conjecture The function ƒ () = must have its domain restricted to have its inverse be a function. The function ƒ () = 3 does not need to have its domain restricted to have its inverse be a function. Make a conjecture about which power functions need to have their domains restricted to have their inverses be functions and which do not. Lesson Performance Task One method used to irrigate crops is the center-pivot irrigation sstem. In this method, sprinklers rotate in a circle to water crops. The challenge for the farmer is to determine where to place the pivot in order to water the desired number of acres. The farmer knows the area but needs to find the radius of the circle necessar to define that area. How can the farmer determine this from the formula for the area of a circle A = π r? Find the formula the farmer could use to determine the radius necessar to irrigate a given number of acres, A. (Hint: One acre is 3,560 square feet.) What would be the radius necessar for the sprinklers to irrigate an area of 133 acres? Area = πr r Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module 10 9 Lesson 1
11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
10.2 Graphing Square Root Functions
 Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
10.2 Graphing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
6.3 Interpreting Vertex Form and Standard Form
 Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
9.5 Solving Nonlinear Systems
 Name Class Date 9.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? Eplore Determining the Possible Number of
Name Class Date 9.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? Eplore Determining the Possible Number of
20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date. Inverse of Function. Understanding Inverses of Functions
 Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope
 Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
13.2 Exponential Decay Functions
 Name Class Date 13. Eponential Deca Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b h + k where < b < 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f () = ( 1 and f ()
Name Class Date 13. Eponential Deca Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b h + k where < b < 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f () = ( 1 and f ()
Name Class Date. Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Parabola
 Name Class Date 1. Parabolas Essential Question: How is the distance formula connected with deriving equations for both vertical and horizontal parabolas? Eplore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of
Name Class Date 1. Parabolas Essential Question: How is the distance formula connected with deriving equations for both vertical and horizontal parabolas? Eplore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
13.1 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
6.5 Comparing Properties of Linear Functions
 Name Class Date 6.5 Comparing Properties of Linear Functions Essential Question: How can ou compare linear functions that are represented in different was? Resource Locker Eplore Comparing Properties of
Name Class Date 6.5 Comparing Properties of Linear Functions Essential Question: How can ou compare linear functions that are represented in different was? Resource Locker Eplore Comparing Properties of
13.2 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
5.1 Understanding Linear Functions
 Name Class Date 5.1 Understanding Linear Functions Essential Question: What is a linear function? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Recognizing Linear Functions A race car can travel up to 210 mph. If the car could
Name Class Date 5.1 Understanding Linear Functions Essential Question: What is a linear function? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Recognizing Linear Functions A race car can travel up to 210 mph. If the car could
14.3 Constructing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 1.3 Constructing Eponential Functions Essential Question: What are discrete eponential functions and how do ou represent them? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Discrete Eponential Functions
Name Class Date 1.3 Constructing Eponential Functions Essential Question: What are discrete eponential functions and how do ou represent them? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Discrete Eponential Functions
5.2 Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Domain, Range, and End Behavior
 Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 _ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
_ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
7.1 Connecting Intercepts and Zeros
 Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions
 TEKS 6.5 2A.4.B, 2A.9.A, 2A.9.B, 2A.9.F Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph square root and cube root functions. Wh? So ou can graph the
TEKS 6.5 2A.4.B, 2A.9.A, 2A.9.B, 2A.9.F Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph square root and cube root functions. Wh? So ou can graph the
13.3 Exponential Decay Functions
 6 6 - - Locker LESSON. Eponential Deca Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.B Formulate eponential and logarithmic equations that model real-world situations, including eponential
6 6 - - Locker LESSON. Eponential Deca Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.B Formulate eponential and logarithmic equations that model real-world situations, including eponential
2.3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities
 Name Class Date.3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Essential Question: What are two was to solve an absolute value inequalit? Resource Locker Eplore Visualizing the Solution Set of an Absolute Value
Name Class Date.3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Essential Question: What are two was to solve an absolute value inequalit? Resource Locker Eplore Visualizing the Solution Set of an Absolute Value
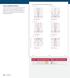
D: all real; R: y g (x) = 3 _ 2 x 2 5. g (x) = 5 x g (x) = - 4 x 2 7. g (x) = -4 x 2. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
 AVOID COMMON ERRORS Watch for students who do not graph points on both sides of the verte of the parabola. Remind these students that a parabola is U-shaped and smmetric, and the can use that smmetr to
AVOID COMMON ERRORS Watch for students who do not graph points on both sides of the verte of the parabola. Remind these students that a parabola is U-shaped and smmetric, and the can use that smmetr to
Quadratic Function. Parabola. Parent quadratic function. Vertex. Axis of Symmetry
 Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions
 Name Class Date 13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions Essential Question: How are piecewise-defined functions different from other functions? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Piecewise-Defined
Name Class Date 13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions Essential Question: How are piecewise-defined functions different from other functions? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Piecewise-Defined
Essential Question: How can you compare linear functions that are represented in different ways? Explore Comparing Properties of Linear Functions
 Locker LESSON 6.5 Comparing Properties of Linear Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.9 Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different wa (algebraicall,
Locker LESSON 6.5 Comparing Properties of Linear Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.9 Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different wa (algebraicall,
9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Name Class Date 9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? Resource Locker Eplore Identifying Ecluded Values Given a rational epression,
Name Class Date 9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? Resource Locker Eplore Identifying Ecluded Values Given a rational epression,
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Exponents. p Evaluate nth roots and study rational exponents. VOCABULARY. Index of a radical
 . Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA2a, MMA2b, MMAd Your Notes Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Eponents Goal VOCABULARY nth root of a p Evaluate nth roots and stud rational eponents. Inde of a radical
. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA2a, MMA2b, MMAd Your Notes Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Eponents Goal VOCABULARY nth root of a p Evaluate nth roots and stud rational eponents. Inde of a radical
4.2 Parabolas. Explore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. (x - p) 2 + y 2 = (x + p) 2
 COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
9-3 Linear Functions Going Deeper
 Name Class Date 9-3 Linear Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou graph a linear function? 1 CC.8.EE.5 EXPLORE Investigating Change video tutor The U.S. Department of Agriculture defines
Name Class Date 9-3 Linear Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou graph a linear function? 1 CC.8.EE.5 EXPLORE Investigating Change video tutor The U.S. Department of Agriculture defines
4.1 Circles. Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Circle. Explore
 Name Class Date 4.1 Circles ssential Question: What is the standard form for the equation of a circle, and what does the standard form tell ou about the circle? plore Deriving the Standard-Form quation
Name Class Date 4.1 Circles ssential Question: What is the standard form for the equation of a circle, and what does the standard form tell ou about the circle? plore Deriving the Standard-Form quation
11.3 Solving Radical Equations
 Name Class Date 11.3 Solving Radical Equations Essential Question: How can you solve equations involving square roots and cube roots? Explore Investigating Solutions of Square Root Equations Resource Locker
Name Class Date 11.3 Solving Radical Equations Essential Question: How can you solve equations involving square roots and cube roots? Explore Investigating Solutions of Square Root Equations Resource Locker
2.3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities
 .3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Essential Question: What are two was to solve an absolute value inequalit? Resource Locker Eplore Visualizing the Solution Set of an Absolute Value Inequalit You
.3 Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Essential Question: What are two was to solve an absolute value inequalit? Resource Locker Eplore Visualizing the Solution Set of an Absolute Value Inequalit You
14.2 Choosing Among Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models
 Name Class Date 14.2 Choosing Among Linear, Quadratic, and Eponential Models Essential Question: How do ou choose among, linear, quadratic, and eponential models for a given set of data? Resource Locker
Name Class Date 14.2 Choosing Among Linear, Quadratic, and Eponential Models Essential Question: How do ou choose among, linear, quadratic, and eponential models for a given set of data? Resource Locker
Name Class Date. Finding Real Roots of Polynomial Equations Extension: Graphing Factorable Polynomial Functions
 Name Class Date -1 Finding Real Roots of Polnomial Equations Etension: Graphing Factorable Polnomial Functions Essential question: How do ou use zeros to graph polnomial functions? Video Tutor prep for
Name Class Date -1 Finding Real Roots of Polnomial Equations Etension: Graphing Factorable Polnomial Functions Essential question: How do ou use zeros to graph polnomial functions? Video Tutor prep for
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
6.2 Multiplying Polynomials
 Locker LESSON 6. Multiplying Polynomials PAGE 7 BEGINS HERE Name Class Date 6. Multiplying Polynomials Essential Question: How do you multiply polynomials, and what type of epression is the result? Common
Locker LESSON 6. Multiplying Polynomials PAGE 7 BEGINS HERE Name Class Date 6. Multiplying Polynomials Essential Question: How do you multiply polynomials, and what type of epression is the result? Common
10.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Name Class Date 10.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? A2.7.F Determine the sum, difference of rational epressions with integral
Name Class Date 10.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? A2.7.F Determine the sum, difference of rational epressions with integral
Name Class Date. Understanding How to Graph g(x) = a(x - h ) 2 + k
 Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
8.2 Graphing More Complicated Rational Functions
 1 Locker LESSON 8. Graphing More Complicated Rational Functions PAGE 33 Name Class Date 8. Graphing More Complicated Rational Functions Essential Question: What features of the graph of a rational function
1 Locker LESSON 8. Graphing More Complicated Rational Functions PAGE 33 Name Class Date 8. Graphing More Complicated Rational Functions Essential Question: What features of the graph of a rational function
11.4 Solving Linear Systems by Multiplying First
 Name Class Date 11. Solving Linear Systems by Multiplying First Essential Question: How can you solve a system of linear equations by using multiplication and elimination? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Understanding
Name Class Date 11. Solving Linear Systems by Multiplying First Essential Question: How can you solve a system of linear equations by using multiplication and elimination? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Understanding
22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots
 Name Class Date 22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: How can you solve quadratic equations using square roots? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Square Roots Recall that the
Name Class Date 22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: How can you solve quadratic equations using square roots? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Square Roots Recall that the
Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations
 COMMON CORE y - 0 y - - 0 - Locker LESSON 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Name Class Date 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the
COMMON CORE y - 0 y - - 0 - Locker LESSON 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Name Class Date 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the
Explore 1 Graphing and Analyzing f(x) = e x. The following table represents the function ƒ (x) = (1 + 1 x) x for several values of x.
 1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
7.2 Multiplying Polynomials
 Locker LESSON 7. Multiplying Polynomials Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.7.B Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Mathematical Processes A.1.E Create and use representations to organize,
Locker LESSON 7. Multiplying Polynomials Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.7.B Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Mathematical Processes A.1.E Create and use representations to organize,
Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers. (3 + 4x) (2 x) = 6 + ( 3x) + +
 Name Class Date 11.2 Complex Numbers Essential Question: What is a complex number, and how can you add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers? Explore Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers In
Name Class Date 11.2 Complex Numbers Essential Question: What is a complex number, and how can you add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers? Explore Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers In
7.3 Triangle Inequalities
 Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions
 TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
14.2 Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents and Radicals
 Name Class Date 14. Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents and Radicals Essential Question: How can you write a radical expression as an expression with a rational exponent? Resource Locker Explore
Name Class Date 14. Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents and Radicals Essential Question: How can you write a radical expression as an expression with a rational exponent? Resource Locker Explore
4.1 Identifying and Graphing Sequences
 Name Class Date 4.1 Identifing and Graphing Sequences Essential Question: What is a sequence and how are sequences and functions related? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Sequences A go-kart racing
Name Class Date 4.1 Identifing and Graphing Sequences Essential Question: What is a sequence and how are sequences and functions related? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Sequences A go-kart racing
Inverse of a Function
 . Inverse o a Function Essential Question How can ou sketch the graph o the inverse o a unction? Graphing Functions and Their Inverses CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proicient in math, ou need to
. Inverse o a Function Essential Question How can ou sketch the graph o the inverse o a unction? Graphing Functions and Their Inverses CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proicient in math, ou need to
13.2 Exponential Decay Functions
 6 6 - - Locker LESSON. Eponential Deca Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.BF. Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() + k, kf(), f(k), and f( + k) for specific
6 6 - - Locker LESSON. Eponential Deca Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.BF. Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() + k, kf(), f(k), and f( + k) for specific
20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations
 20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore Understanding
20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore Understanding
18.3 Special Right Triangles
 Name lass Date 18.3 Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore 1 Investigating an Isosceles Right
Name lass Date 18.3 Special Right Triangles Essential Question: What do you know about the side lengths and the trigonometric ratios in special right triangles? Eplore 1 Investigating an Isosceles Right
10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles
 Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Name Class Date. Solving by Graphing and Algebraically
 Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
10.3 Solving Nonlinear Systems of Equations
 60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
Use Properties of Exponents
 4. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMAa Your Notes Use Properties of Eponents Goal p Simplif epressions involving powers. VOCABULARY Scientific notation PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS Let a and b be real numbers
4. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMAa Your Notes Use Properties of Eponents Goal p Simplif epressions involving powers. VOCABULARY Scientific notation PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS Let a and b be real numbers
Properties of Rational Exponents PROPERTIES OF RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICALS. =, a 0 25 º1/ =, b /3 2. b m
 Page of 8. Properties of Rational Eponents What ou should learn GOAL Use properties of rational eponents to evaluate and simplif epressions. GOAL Use properties of rational eponents to solve real-life
Page of 8. Properties of Rational Eponents What ou should learn GOAL Use properties of rational eponents to evaluate and simplif epressions. GOAL Use properties of rational eponents to solve real-life
MA 15800, Summer 2016 Lesson 25 Notes Solving a System of Equations by substitution (or elimination) Matrices. 2 A System of Equations
 MA 800, Summer 06 Lesson Notes Solving a Sstem of Equations b substitution (or elimination) Matrices Consider the graphs of the two equations below. A Sstem of Equations From our mathematics eperience,
MA 800, Summer 06 Lesson Notes Solving a Sstem of Equations b substitution (or elimination) Matrices Consider the graphs of the two equations below. A Sstem of Equations From our mathematics eperience,
(2) Find the domain of f (x) = 2x3 5 x 2 + x 6
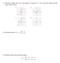 CHAPTER FUNCTIONS AND MODELS () Determine whether the curve is the graph of a function of. If it is state the domain and the range of the function. 5 8 Determine whether the curve is the graph of a function
CHAPTER FUNCTIONS AND MODELS () Determine whether the curve is the graph of a function of. If it is state the domain and the range of the function. 5 8 Determine whether the curve is the graph of a function
2.4 Library of Functions; Piecewise-defined Functions. 1 Graph the Functions Listed in the Library of Functions
 80 CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Problems 8 88 require the following discussion of a secant line. The slope of the secant line containing the two points, f and + h, f + h on the graph of a function
80 CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Problems 8 88 require the following discussion of a secant line. The slope of the secant line containing the two points, f and + h, f + h on the graph of a function
3.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots
 COMMON CORE -8-16 1 1 10 8 6 0 y Locker LESSON.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Name Class Date.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: What is an imaginary
COMMON CORE -8-16 1 1 10 8 6 0 y Locker LESSON.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Name Class Date.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: What is an imaginary
16.2 Arc Length and Radian Measure
 Name Class Date 16.2 rc Length and Radian Measure Essential Question: How do you find the length of an arc? Explore Deriving the Formula for rc Length n arc is an unbroken part of a circle consisting of
Name Class Date 16.2 rc Length and Radian Measure Essential Question: How do you find the length of an arc? Explore Deriving the Formula for rc Length n arc is an unbroken part of a circle consisting of
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
11.3 Solving Radical Equations
 Locker LESSON 11. Solving Radical Equations Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: A-REI. Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable, and give examples showing how extraneous
Locker LESSON 11. Solving Radical Equations Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: A-REI. Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable, and give examples showing how extraneous
4.1 Circles. Explore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation
 COMMON CORE r Locker LESSON Circles.1 Name Class Date.1 Circles Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A.3 Represent constraints b equations or inequalities,... and interpret
COMMON CORE r Locker LESSON Circles.1 Name Class Date.1 Circles Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A.3 Represent constraints b equations or inequalities,... and interpret
Fair Game Review. Chapter 9. Find the square root(s) ± Find the side length of the square. 7. Simplify Simplify 63.
 Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Appendix D: Variation
 A96 Appendi D Variation Appendi D: Variation Direct Variation There are two basic types of linear models. The more general model has a y-intercept that is nonzero. y m b, b 0 The simpler model y k has
A96 Appendi D Variation Appendi D: Variation Direct Variation There are two basic types of linear models. The more general model has a y-intercept that is nonzero. y m b, b 0 The simpler model y k has
12.2 Simplifying Radical Expressions
 Name Class Date 1. Simplifying Radical Expressions Essential Question: How can you simplify expressions containing rational exponents or radicals involving nth roots? Explore A.7.G Rewrite radical expressions
Name Class Date 1. Simplifying Radical Expressions Essential Question: How can you simplify expressions containing rational exponents or radicals involving nth roots? Explore A.7.G Rewrite radical expressions
1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior
 Name Class Date 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Essential Question: How can ou determine the domain, range, and end behavior of a function? Resource Locker Eplore Representing an Interval on a Number
Name Class Date 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Essential Question: How can ou determine the domain, range, and end behavior of a function? Resource Locker Eplore Representing an Interval on a Number
Factoring Polynomials
 5. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS 2A.7.D 2A.7.E Factoring Polnomials Essential Question How can ou factor a polnomial? Factoring Polnomials Work with a partner. Match each polnomial equation with
5. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS 2A.7.D 2A.7.E Factoring Polnomials Essential Question How can ou factor a polnomial? Factoring Polnomials Work with a partner. Match each polnomial equation with
Practice A ( 1, 3 ( 0, 1. Match the function with its graph. 3 x. Explain how the graph of g can be obtained from the graph of f. 5 x.
 8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
6 p p } 5. x 26 x 5 x 3 5 x Product of powers property x4 y x 3 y 2 6
 Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
11.3 Solving Linear Systems by Adding or Subtracting
 Name Class Date 11.3 Solving Linear Systems by Adding or Subtracting Essential Question: How can you solve a system of linear equations by adding and subtracting? Resource Locker Explore Exploring the
Name Class Date 11.3 Solving Linear Systems by Adding or Subtracting Essential Question: How can you solve a system of linear equations by adding and subtracting? Resource Locker Explore Exploring the
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations
 Name Class Date 2. Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore
Name Class Date 2. Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore
Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. Equation 1 Equation 2. Check (2, 1) in Equation 1 and Equation 2: 2x y 5?
 3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
11.3 Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations
 Name Class Date 11.3 Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the complex solutions of any quadratic equation? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Real Solutions
Name Class Date 11.3 Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the complex solutions of any quadratic equation? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Real Solutions
Fair Game Review. Chapter 8. Graph the linear equation. Big Ideas Math Algebra Record and Practice Journal
 Name Date Chapter Graph the linear equation. Fair Game Review. =. = +. =. =. = +. = + Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Algebra Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued) Evaluate the
Name Date Chapter Graph the linear equation. Fair Game Review. =. = +. =. =. = +. = + Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Algebra Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued) Evaluate the
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY REVIEW EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES
 Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? Resource Locker Eplore Identifying Ecluded Values Given a rational epression, identify
9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational epressions? Resource Locker Eplore Identifying Ecluded Values Given a rational epression, identify
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 5.4
 Overview of Section 5. Introduction In this chapter, students have worked with nth roots, writing them in radical form and with rational exponents. The learned that the properties of exponents can be applied
Overview of Section 5. Introduction In this chapter, students have worked with nth roots, writing them in radical form and with rational exponents. The learned that the properties of exponents can be applied
2.3 Solving for a Variable
 Name Class Date 2.3 Solving for a Variable Essential Question: How do you rewrite formulas and literal equations? Explore Rearranging Mathematical Formulas Resource Locker Literal Equations are equations
Name Class Date 2.3 Solving for a Variable Essential Question: How do you rewrite formulas and literal equations? Explore Rearranging Mathematical Formulas Resource Locker Literal Equations are equations
Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
 .1..... Rational Eponents and Radical Functions nth Roots and Rational Eponents Properties of Rational Eponents and Radicals Graphing Radical Functions Solving Radical Equations and Inequalities Performing
.1..... Rational Eponents and Radical Functions nth Roots and Rational Eponents Properties of Rational Eponents and Radicals Graphing Radical Functions Solving Radical Equations and Inequalities Performing
In the same way that you used proportional reasoning to find the length of an arc, you can use proportional reasoning to find the area of a sector.
 Name Class Date 16.3 Sector rea Essential Question: How do you find the area of a sector of a circle? Explore Derive the Formula for the rea of a Sector sector of a circle is a region bounded by two radii
Name Class Date 16.3 Sector rea Essential Question: How do you find the area of a sector of a circle? Explore Derive the Formula for the rea of a Sector sector of a circle is a region bounded by two radii
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Find the -intercept of the graph of the linear equation. 1. = + 3. = 3 + 5 3. = 10 75. = ( 9) 5. 7( 10) = +. 5 + 15 = 0 Find the distance between the two points.
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Find the -intercept of the graph of the linear equation. 1. = + 3. = 3 + 5 3. = 10 75. = ( 9) 5. 7( 10) = +. 5 + 15 = 0 Find the distance between the two points.
Keira Godwin. Time Allotment: 13 days. Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to:
 Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Review of Exponent Rules
 Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
10.7. Interpret the Discriminant. For Your Notebook. x5 2b 6 Ï} b 2 2 4ac E XAMPLE 1. Use the discriminant KEY CONCEPT
 10.7 Interpret the Discriminant Before You used the quadratic formula. Now You will use the value of the discriminant. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about gmnastics, as in E. 49. Ke Vocabular discriminant
10.7 Interpret the Discriminant Before You used the quadratic formula. Now You will use the value of the discriminant. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about gmnastics, as in E. 49. Ke Vocabular discriminant
