Lesson 9.3 Relating Congruent and Similar Figures to Geometric Transformations
|
|
|
- Patrick Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 9. Relating ongruent and Similar Figures to Geometric Transformations State whether the figure and image are congruent or similar.. Rectangle D is rotated 90 clockwise about verte.. parallelogram is reflected in the -ais and then reflected in the -ais.. photocopier dilates a picture b a scale factor of.. trapezoid is dilated with center (0, 0) and scale factor.. heagon is rotated 90 counter clockwise about its center (0, 0) and then dilated b a scale factor of. 6. is mapped onto under a transformation. is the image of under another transformation. 0 a) Describe the transformations that map onto and onto. is mapped onto b using a reflection in the line. is mapped onto b using a rotation of about the point (, ). Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 7 hapter 9 Lesson 9.
2 b) If the order of the transformations is reversed, draw and and on the coordinate plane. c) Do the two triangles have the same coordinates? re the congruent? Eplain. Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. Etra Practice ourse 7
3 7. triangle with vertices (, ), (, ) and (6, ) is reflected in the -ais to obtain the image. then is mapped onto shown in the diagram b another transformation a) Draw on the same aes above. b) Describe the transformation that maps onto. c) Describe a single transformation that maps onto. Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 7 hapter 9 Lesson 9.
4 8. triangle PQR with vertices P (, ), Q (, ) and R (, ) is dilated b a scale factor with center P to obtain the image PQR. PQR is then mapped b another transformation onto PQR shown in the diagram. 6 Q Q P P R R a) Draw PQR on the same aes above. b) Describe the transformation that maps PQR on PQR. Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. c) Describe a single transformation that maps PQR onto PQR. Etra Practice ourse 7
5 9. is mapped onto under a transformation. is then mapped onto under another transformation. Describe the sequence of transformations from to. a) 0 Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 76 hapter 9 Lesson 9.
6 b) Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. Etra Practice ourse 77
7 c) Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 78 hapter 9 Lesson 9.
8 0. Quadrilateral D is dilated with center and scale factor.. It is mapped onto PQRS. The length of is feet and the area of D is square feet. 80 D a) Find mqrs. rea = ft 0 ft b) Find the length of PQ. c) Determine the area of PQRS.. The area of a rectangular postcard is 60 square centimeters. dilated cop has an area of 0 square centimeters. what scale factor is the diagonal of the postcard enlarged? Marshall avendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. Etra Practice ourse 79
9 PX X PX 0 P Q Length of PX 0 0 ft Length of the pole P ft In P, 0 8 ft The distance between the walls is 8 feet. In Q, Q ft The length of pole Q is.6 feet. 9. a) st pair: O DO Eplanation: mo mdo (verticall opposite s) mo mdo (alternate s, D) O DO (equiangular) nd pair: OD OEF Eplanation: mod meof (common ) mod moef (corresponding s, D EF) OD OEF (equiangular) rd pair: O FOE Eplanation: mo mfoe (verticall opposite s) mo mfeo (alternate s, EF) O FEO (equiangular) b) OE is not similar to OF. Eplanation: Onl one pair of angles (OE and OF) are equal. The remaining two pairs are not equal. OE is not similar to OF. Lesson 9.. ongruent. ongruent. Similar. ongruent. Similar 6. a) ; 90 clockwise; 0; 0. b) 0 c) No; the coordinates are different because the order of transformations is reversed. Yes; the size and shape of figures remain the same under translations and reflections. 7. a) b) is mapped onto b a rotation of 90 clockwise about origin O. c) reflection about the line will map onto. 8. a) 6 Q Q Q P P P R R R Etra Practice ourse 8
10 b) P Q R is mapped onto P Q R b a reflection about the line =.. c) dilation of scale factor about the point (, ) will map PQR to P Q R. 9. a) is mapped onto b a translation of units to the right and 6 units up. is mapped onto b a rotation of 90 clockwise about the point (0, ). b) is mapped onto b a reflection about the line. is mapped onto b a dilation of scale factor about the point (, ). c) is mapped onto b a rotation of 90 counter clockwise about the point (, 0). is mapped onto b a reflection about the line. 0. D PQRS a) mqrs md 60 md m md (sum of quadrilateral) PQ b). (scale factor) PQ. PQ.. ft rea of PQRS c) (.) rea of D rea of PQRS (.) rea of PQRS (.) 7 ft The area of PQRS is 7 square feet.. Let the scale factor be k. rea of enlargedcop k rea of original postcard 0 k 60 k k The diagonal of the postcard is dilated b a scale factor of. rain@work. Let the height of the big triangle be p. p m p ( m) p m Eq. p n m p (n m) p n m p m + n Eq. Multipl Eq. b : p ( m) 0p 60 m Eq. Multipl Eq. b : p (m n ) 0p m n 8 Eq. Substitute Eq. into Eq. : 60 m m n 8 60 m 60 m n 8 60 m m n m m m n m m n m n m n. XY Z [common angle] YX Z [corr. s] XY and Z are similar. Y Z Z Z XY Z Y XY XW Z [common angle] WX Z [corr. s] XW and Z are similar. W Z Z Z XW Z XW W So, Y XW XY W. Since XW YZ and WZ XY, Y WZ Y YZ YZ W ZW WV So, Y : YZ ZW : W (shown) umulative Practice for hapters 7 to 9. p 6 8 nswers
Chapter 3 Summary 3.1. Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane. Example
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms bases of a trapezoid (.) legs of a trapezoid (.) composite figure (.5).1 Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane The perimeter or area
Chapter Summar Ke Terms bases of a trapezoid (.) legs of a trapezoid (.) composite figure (.5).1 Determining the Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Squares on the Coordinate Plane The perimeter or area
Properties of Triangles and Four-Sided Figures Lesson 13.1 Classifying Triangles
 HPTR13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
HPTR13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
Properties of Triangles and Four-Sided Figures Lesson 13.1 Classifying Triangles
 HPT13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
HPT13 Properties of Triangles and our-sided igures Lesson 13.1 lassifying Triangles 1. lassify the following triangles by sides as a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
Unit 2 Review. Determine the scale factor of the dilation below.
 Unit 2 Review 1. oes the graph below represent a dilation? Why or why not? y 10 9 8 7 (0, 7) 6 5 4 3 (0, 3.5) 2 1 (5, 7) (5, 3.5) -10-9 -8-7 -6-5 -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10-1 F -2 (5, 0) -3-4 -5-6
Unit 2 Review 1. oes the graph below represent a dilation? Why or why not? y 10 9 8 7 (0, 7) 6 5 4 3 (0, 3.5) 2 1 (5, 7) (5, 3.5) -10-9 -8-7 -6-5 -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10-1 F -2 (5, 0) -3-4 -5-6
Exercise. and 13x. We know that, sum of angles of a quadrilateral = x = 360 x = (Common in both triangles) and AC = BD
 9 Exercise 9.1 Question 1. The angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral. Solution Given, the ratio of the angles of quadrilateral are 3 : 5 : 9
9 Exercise 9.1 Question 1. The angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral. Solution Given, the ratio of the angles of quadrilateral are 3 : 5 : 9
Suggested Approach Pythagorean Theorem The Converse of Pythagorean Theorem Applications of Pythagoras Theorem. Notes on Teaching 3
 hapter 10 Pythagorean Theorem Suggested pproach Students can explore Pythagorean Theorem using the GSP activity in lass ctivity 1. There are over 300 proofs of Pythagorean Theorem. Teachers may illustrate
hapter 10 Pythagorean Theorem Suggested pproach Students can explore Pythagorean Theorem using the GSP activity in lass ctivity 1. There are over 300 proofs of Pythagorean Theorem. Teachers may illustrate
3.5. Did you ever think about street names? How does a city or town decide what to. composite figures
 .5 Composite Figures on the Coordinate Plane Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures on the Coordinate Plane LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, ou will: Determine the perimeters and the areas of composite
.5 Composite Figures on the Coordinate Plane Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures on the Coordinate Plane LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, ou will: Determine the perimeters and the areas of composite
Angles. Lesson 12.1 Angles on a Line. Find the unknown marked angles. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. 1. AC is a line. Find the measure of DBE.
 ate: 12 HPTR ngles Lesson 12.1 ngles on a Line ind the unknown marked angles. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. 1. is a line. ind the measure of. 78 47 2009 Marshall avendish International (Singapore)
ate: 12 HPTR ngles Lesson 12.1 ngles on a Line ind the unknown marked angles. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. 1. is a line. ind the measure of. 78 47 2009 Marshall avendish International (Singapore)
Challenge: Skills and Applications For use with pages P( 1, 4) R( 3, 1)
 LESSON 8.4 NME TE hallenge: Skills and pplications For use with pages 480 487 1. Refer to the diagram, where VW YZ. a. Write a similarit statement. b. Write a paragraph proof for our result. V X Y W Z.
LESSON 8.4 NME TE hallenge: Skills and pplications For use with pages 480 487 1. Refer to the diagram, where VW YZ. a. Write a similarit statement. b. Write a paragraph proof for our result. V X Y W Z.
Section 5.1. Perimeter and Area
 Section 5.1 Perimeter and Area Perimeter and Area The perimeter of a closed plane figure is the distance around the figure. The area of a closed plane figure is the number of non-overlapping squares of
Section 5.1 Perimeter and Area Perimeter and Area The perimeter of a closed plane figure is the distance around the figure. The area of a closed plane figure is the number of non-overlapping squares of
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3. Topic 1 : Equation of a circle
 Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Multiple Choice. 3. The polygons are similar, but not necessarily drawn to scale. Find the values of x and y.
 Accelerated Coordinate Algebra/Analtic Geometr answers the question. Page 1 of 5 Multiple Choice 1. The dashed triangle is an image of the solid triangle. What is the scale factor of the image?. The polgons
Accelerated Coordinate Algebra/Analtic Geometr answers the question. Page 1 of 5 Multiple Choice 1. The dashed triangle is an image of the solid triangle. What is the scale factor of the image?. The polgons
Name: Class: Date: c. WZ XY and XW YZ. b. WZ ZY and XW YZ. d. WN NZ and YN NX
 Class: Date: 2nd Semester Exam Review - Geometry CP 1. Complete this statement: A polygon with all sides the same length is said to be. a. regular b. equilateral c. equiangular d. convex 3. Which statement
Class: Date: 2nd Semester Exam Review - Geometry CP 1. Complete this statement: A polygon with all sides the same length is said to be. a. regular b. equilateral c. equiangular d. convex 3. Which statement
1983 FG8.1, 1991 HG9, 1996 HG9
 nswers: (1- HKMO Heat Events) reated by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: 6 February 017 - Individual 1 11 70 6 1160 7 11 8 80 1 10 1 km 6 11-1 Group 6 7 7 6 8 70 10 Individual Events I1 X is a point on
nswers: (1- HKMO Heat Events) reated by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: 6 February 017 - Individual 1 11 70 6 1160 7 11 8 80 1 10 1 km 6 11-1 Group 6 7 7 6 8 70 10 Individual Events I1 X is a point on
9. AD = 7; By the Parallelogram Opposite Sides Theorem (Thm. 7.3), AD = BC. 10. AE = 7; By the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem (Thm. 7.6), AE = EC.
 3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018
 Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018 1. Determine whether 128 feet, 136 feet, and 245 feet can be the lengths of the sides of a triangle. 2. Casey has a 13-inch television and a 52-inch television
Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018 1. Determine whether 128 feet, 136 feet, and 245 feet can be the lengths of the sides of a triangle. 2. Casey has a 13-inch television and a 52-inch television
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Math 200 Spring 2007
 FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
Replacement for a Carpenter s Square
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Replacement for a arpenter s Square Inscribed and ircumscribed Triangles and Quadrilaterals Vocabulary nswer each question. 1. How are inscribed polygons and circumscribed
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Replacement for a arpenter s Square Inscribed and ircumscribed Triangles and Quadrilaterals Vocabulary nswer each question. 1. How are inscribed polygons and circumscribed
Chapter 18 Exercise 18.1
 hapter 18 Eercise 18.1 Q. 1. (i) 180 37 = 143 ( = 143 ) (ii) 180 117 = 63 ( = 63 ) 180 90 = 90 (y = 90 ) (iii) + + 3 + 45 = 180 4.5 = 135 (iv) 180 90 = y 90 = y = 30 45 = y 66 + ( + y) + 47 = 180 + y =
hapter 18 Eercise 18.1 Q. 1. (i) 180 37 = 143 ( = 143 ) (ii) 180 117 = 63 ( = 63 ) 180 90 = 90 (y = 90 ) (iii) + + 3 + 45 = 180 4.5 = 135 (iv) 180 90 = y 90 = y = 30 45 = y 66 + ( + y) + 47 = 180 + y =
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
1 = 1, b d and c d. Chapter 7. Worked-Out Solutions Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 357) Slope of line b:
 hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
Franklin Math Bowl 2007 Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade
 Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade 1. Consecutive integers are integers that increase by one. For eample, 6, 7, and 8 are consecutive integers. If the sum of 9 consecutive integers is 9, what is the
Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade 1. Consecutive integers are integers that increase by one. For eample, 6, 7, and 8 are consecutive integers. If the sum of 9 consecutive integers is 9, what is the
Cumulative Test 1. Name Date. In Exercises 1 5, use the diagram at the right. Answers
 Name Date umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of ED @##$ and @##$ D. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane D and plane E. 3. re points,, and D collinear? 2.
Name Date umulative Test In Eercises 5, use the diagram at the right.. Name the intersection of ED @##$ and @##$ D. E. 2. Name the intersection of plane D and plane E. 3. re points,, and D collinear? 2.
Pre-Algebra Chapter 9 Spatial Thinking
 Pre-Algebra Chapter 9 Spatial Thinking SOME NUMBERED QUESTIONS HAVE BEEN DELETED OR REMOVED. YOU WILL NOT BE USING A CALCULATOR FOR PART I MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS, AND THEREFORE YOU SHOULD NOT USE ONE
Pre-Algebra Chapter 9 Spatial Thinking SOME NUMBERED QUESTIONS HAVE BEEN DELETED OR REMOVED. YOU WILL NOT BE USING A CALCULATOR FOR PART I MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS, AND THEREFORE YOU SHOULD NOT USE ONE
Find the area of the triangle. You try: D C. Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false. Solve for the variables.
 lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide ind the area of the triangle. 9 4 5 D or all right triangles, a + b c where c is the length of the hpotenuse. 5 4 a + b c 9 + b 5 + b 5 b 5 b 44 b 9 he area of a
lameda USD Geometr enchmark Stud Guide ind the area of the triangle. 9 4 5 D or all right triangles, a + b c where c is the length of the hpotenuse. 5 4 a + b c 9 + b 5 + b 5 b 5 b 44 b 9 he area of a
6.2: Isosceles Triangles
 6.2: Isosceles Triangles Dec 5 4:34 PM 1 Define an Isosceles Triangle. A triangle that has (at least) two sides of equal length. Dec 5 4:34 PM 2 Draw an Isosceles Triangle. Label all parts and mark the
6.2: Isosceles Triangles Dec 5 4:34 PM 1 Define an Isosceles Triangle. A triangle that has (at least) two sides of equal length. Dec 5 4:34 PM 2 Draw an Isosceles Triangle. Label all parts and mark the
Applications. 12 The Shapes of Algebra. 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates x and y for points on the circle.
 Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 9.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Meeting Friends The Distance Formula Vocabular Define the term in our own words. 1. Distance Formula Problem Set Archaeologists map the location of
Name: GEOMETRY: EXAM (A) A B C D E F G H D E. 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane?
 GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
GEO REVIEW TEST #1. 1. In which quadrilateral are the diagonals always congruent?
 GEO REVIEW TEST #1 Name: Date: 1. In which quadrilateral are the diagonals always congruent? (1) rectangle (3) rhombus 4. In the accompanying diagram, lines AB and CD intersect at point E. If m AED = (x+10)
GEO REVIEW TEST #1 Name: Date: 1. In which quadrilateral are the diagonals always congruent? (1) rectangle (3) rhombus 4. In the accompanying diagram, lines AB and CD intersect at point E. If m AED = (x+10)
Which statement is true about parallelogram FGHJ and parallelogram F ''G''H''J ''?
 Unit 2 Review 1. Parallelogram FGHJ was translated 3 units down to form parallelogram F 'G'H'J '. Parallelogram F 'G'H'J ' was then rotated 90 counterclockwise about point G' to obtain parallelogram F
Unit 2 Review 1. Parallelogram FGHJ was translated 3 units down to form parallelogram F 'G'H'J '. Parallelogram F 'G'H'J ' was then rotated 90 counterclockwise about point G' to obtain parallelogram F
CONGRUENCE AND SIMILARITY
 CONGRUENCE ND SIMILRITY 1.1CONGRUENT FIGURES The figures that have the same size and the same shape, i.e. one shape fits exactly onto other is called Congruent figures. CONGRUENT TRINGLES: 1. Two triangles
CONGRUENCE ND SIMILRITY 1.1CONGRUENT FIGURES The figures that have the same size and the same shape, i.e. one shape fits exactly onto other is called Congruent figures. CONGRUENT TRINGLES: 1. Two triangles
Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice
 Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice Lesson 1-1 1. a. 75; 15 b. 53; 13 c. 19; 19 d. 7; 117 e. (9 ); (1 ). a. ; b..5; 3.5 c. 3; 5 d. 33; 57 e. 5; 5 3. a. 7.5; 17.5 b. 31.5; 1.5 c. 5; 135 d. 59; 11 e. 1.;
Answers to Course 3 Unit 3 Practice Lesson 1-1 1. a. 75; 15 b. 53; 13 c. 19; 19 d. 7; 117 e. (9 ); (1 ). a. ; b..5; 3.5 c. 3; 5 d. 33; 57 e. 5; 5 3. a. 7.5; 17.5 b. 31.5; 1.5 c. 5; 135 d. 59; 11 e. 1.;
2. A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 5. Diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other and are equal and vice-versa.
 QURILTERLS 1. Sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360. 2. diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 3. In a parallelogram, (i) opposite sides are equal (ii) opposite angles
QURILTERLS 1. Sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360. 2. diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 3. In a parallelogram, (i) opposite sides are equal (ii) opposite angles
Geometric Structures
 Geometric Structures 3 Hour Exams & Final Fall 2003 Exam I Page 1 Exam II Page 6 Exam III Page 10 Final Exam Page 14 Oklahoma State University Terry Williams, Instructor Geometric Structures Exam I Fall
Geometric Structures 3 Hour Exams & Final Fall 2003 Exam I Page 1 Exam II Page 6 Exam III Page 10 Final Exam Page 14 Oklahoma State University Terry Williams, Instructor Geometric Structures Exam I Fall
Lesson 1 Reteach. Example. Exercises. Determine if the two figures are congruent by using transformations.
 Lesson 1 eteach Congruence and Transformations Translation eflection otation length is the same length is the same length is the same orientation is the sarne onentation is different onentation is different
Lesson 1 eteach Congruence and Transformations Translation eflection otation length is the same length is the same length is the same orientation is the sarne onentation is different onentation is different
Name: Date: Period: 1. In the diagram below,. [G.CO.6] 2. The diagram below shows a pair of congruent triangles, with and. [G.CO.
![Name: Date: Period: 1. In the diagram below,. [G.CO.6] 2. The diagram below shows a pair of congruent triangles, with and. [G.CO. Name: Date: Period: 1. In the diagram below,. [G.CO.6] 2. The diagram below shows a pair of congruent triangles, with and. [G.CO.](/thumbs/78/77420594.jpg) Name: Date: Period: Directions: Read each question carefully and choose the best answer for each question. You must show LL of your work to receive credit. 1. In the diagram below,. [G.CO.6] Which statement
Name: Date: Period: Directions: Read each question carefully and choose the best answer for each question. You must show LL of your work to receive credit. 1. In the diagram below,. [G.CO.6] Which statement
Chapter 5 Practice Problem Answers 1.
 hapter 5 Practice Problem nswers 1. raw the Quadrilateral Family Venn iagram with all the associated definitions and properties. aroody Page 1 of 14 Write 5 ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram:
hapter 5 Practice Problem nswers 1. raw the Quadrilateral Family Venn iagram with all the associated definitions and properties. aroody Page 1 of 14 Write 5 ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram:
25 true/false Draw reflections, rotations, dilations Symmetry regarding a regular polygon
 Geometry Week 27 ch. 12 review 1. hapter 12 Vocabulary: angle of rotation ais of symmetry center of rotation composition dilation enlargement fied point identity transformation image invariance isometry
Geometry Week 27 ch. 12 review 1. hapter 12 Vocabulary: angle of rotation ais of symmetry center of rotation composition dilation enlargement fied point identity transformation image invariance isometry
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 5.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Ace Reporter Review of Ratio and Proportion Write a ratio that is equivalent to each ratio. 1. 6 12 2. 7 12 3. 4 4. 14 : 7 1. 3 : 2 6. 1.2 : 7 Solve each proportion.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Ace Reporter Review of Ratio and Proportion Write a ratio that is equivalent to each ratio. 1. 6 12 2. 7 12 3. 4 4. 14 : 7 1. 3 : 2 6. 1.2 : 7 Solve each proportion.
= x. Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit Graphing Quadratic Functions. Math Background
 Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Reteaching , or 37.5% 360. Geometric Probability. Name Date Class
 Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
Name ate lass Reteaching Geometric Probability INV 6 You have calculated probabilities of events that occur when coins are tossed and number cubes are rolled. Now you will learn about geometric probability.
Final Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
Individual Events 1 I2 x 0 I3 a. Group Events. G8 V 1 G9 A 9 G10 a 4 4 B
 Answers: (99-95 HKMO Final Events) Created by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: July 08 I a Individual Events I x 0 I3 a I r 3 I5 a b 3 y 3 b 8 s b c 3 z c t 5 c d w d 0 u d 6 3 6 G6 a 5 G7 a Group Events
Answers: (99-95 HKMO Final Events) Created by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: July 08 I a Individual Events I x 0 I3 a I r 3 I5 a b 3 y 3 b 8 s b c 3 z c t 5 c d w d 0 u d 6 3 6 G6 a 5 G7 a Group Events
9. Yes; translate so that the centers align, and then dilate using the ratio of radii to map one circle to another.
 9. Yes; translate so that the centers align, and then dilate using the ratio of radii to map one circle to another. 10. Keegan dilated using A as the center of dilation instead of the origin. Point A should
9. Yes; translate so that the centers align, and then dilate using the ratio of radii to map one circle to another. 10. Keegan dilated using A as the center of dilation instead of the origin. Point A should
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mathematics SKE, Strand J STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES J4 Matrices Text Contents * * * * Section J4. Matrices: Addition and Subtraction J4.2 Matrices: Multiplication J4.3 Inverse Matrices:
Mathematics SKE, Strand J STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES J4 Matrices Text Contents * * * * Section J4. Matrices: Addition and Subtraction J4.2 Matrices: Multiplication J4.3 Inverse Matrices:
Chapter 6. Worked-Out Solutions. Chapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 299)
 hapter 6 hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 99) 1. Slope perpendicular to y = 1 x 5 is. y = x + b 1 = + b 1 = 9 + b 10 = b n equation of the line is y = x + 10.. Slope perpendicular to y
hapter 6 hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 99) 1. Slope perpendicular to y = 1 x 5 is. y = x + b 1 = + b 1 = 9 + b 10 = b n equation of the line is y = x + 10.. Slope perpendicular to y
Lesson 7.2 Understanding the Distance Formula
 Lesson 7. Understanding the Distance Formula Solve. Show our work. Round our answers to the nearest tenth if necessar.. Points P (, ) and Q (, ) are plotted on a coordinate plane. Find the eact distance
Lesson 7. Understanding the Distance Formula Solve. Show our work. Round our answers to the nearest tenth if necessar.. Points P (, ) and Q (, ) are plotted on a coordinate plane. Find the eact distance
Transforming to a New Level!
 Lesson.1 Assignment Name Date Transforming to a New Level! Using Transformations to Determine Area 1. Franco translates rectangle JKLM so that it has one verte on the origin. The result is rectangle J9K9L9M9.
Lesson.1 Assignment Name Date Transforming to a New Level! Using Transformations to Determine Area 1. Franco translates rectangle JKLM so that it has one verte on the origin. The result is rectangle J9K9L9M9.
Chapter 3 Cumulative Review Answers
 Chapter 3 Cumulative Review Answers 1a. The triangle inequality is violated. 1b. The sum of the angles is not 180º. 1c. Two angles are equal, but the sides opposite those angles are not equal. 1d. The
Chapter 3 Cumulative Review Answers 1a. The triangle inequality is violated. 1b. The sum of the angles is not 180º. 1c. Two angles are equal, but the sides opposite those angles are not equal. 1d. The
Collecting Like Terms
 MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
 The and Its onverse Use the. Use the converse of the. Vocabulary Pythagorean triple Study Tip Look ack To review finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle, see Lesson 1-3. are right triangles used to
The and Its onverse Use the. Use the converse of the. Vocabulary Pythagorean triple Study Tip Look ack To review finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle, see Lesson 1-3. are right triangles used to
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7)
 Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
Int Math 3 Midterm Review Handout (Modules 5-7) 1 Graph f(x) = x and g(x) = 1 x 4. Then describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = x to the graph 2 of g(x) = 1 2 x 4. The transformations are
Similarity of Triangle
 Similarity of Triangle 95 17 Similarity of Triangle 17.1 INTRODUCTION Looking around you will see many objects which are of the same shape but of same or different sizes. For examples, leaves of a tree
Similarity of Triangle 95 17 Similarity of Triangle 17.1 INTRODUCTION Looking around you will see many objects which are of the same shape but of same or different sizes. For examples, leaves of a tree
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2016 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2016 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2016 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
2000 Solutions Euclid Contest
 Canadian Mathematics Competition n activit of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, Universit of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 000 s Euclid Contest (Grade) for The CENTRE for EDUCTION in
Canadian Mathematics Competition n activit of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, Universit of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 000 s Euclid Contest (Grade) for The CENTRE for EDUCTION in
Math 8. Unit 8 Transformations Unit 9 Angles Unit 10 Geometry Unit 11 Scientific Notation. Name Teacher Period
 Math 8 Unit 8 Transformations Unit 9 Angles Unit 10 Geometry Unit 11 Scientific Notation Name Teacher Period 1 Unit 8 Transformations Date Lesson Topic 1 Translations 2 Reflection 3 Reflection 4 Rotations
Math 8 Unit 8 Transformations Unit 9 Angles Unit 10 Geometry Unit 11 Scientific Notation Name Teacher Period 1 Unit 8 Transformations Date Lesson Topic 1 Translations 2 Reflection 3 Reflection 4 Rotations
Theorems on Area. Introduction Axioms of Area. Congruence area axiom. Addition area axiom
 3 Theorems on rea Introduction We know that Geometry originated from the need of measuring land or recasting/refixing its boundaries in the process of distribution of certain land or field among different
3 Theorems on rea Introduction We know that Geometry originated from the need of measuring land or recasting/refixing its boundaries in the process of distribution of certain land or field among different
Lesson 12.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 12.1 Skills Practice Introduction to ircles ircle, Radius, and iameter Vocabulary efine each term in your own words. 1. circle circle is a collection of points on the same plane equidistant from
Lesson 12.1 Skills Practice Introduction to ircles ircle, Radius, and iameter Vocabulary efine each term in your own words. 1. circle circle is a collection of points on the same plane equidistant from
Geometry Cumulative Study Guide Test 8
 Geometry Cumulative Study Guide Test 8 Numeric Response 1. A rectangular plot of land has a length of 3.5 miles and a width of 8.5 miles. What is the area, in square miles, of the plot of land? 2. A circle
Geometry Cumulative Study Guide Test 8 Numeric Response 1. A rectangular plot of land has a length of 3.5 miles and a width of 8.5 miles. What is the area, in square miles, of the plot of land? 2. A circle
For Your Notebook E XAMPLE 1. Factor when b and c are positive KEY CONCEPT. CHECK (x 1 9)(x 1 2) 5 x 2 1 2x 1 9x Factoring x 2 1 bx 1 c
 9.5 Factor x2 1 bx 1 c Before You factored out the greatest common monomial factor. Now You will factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. Why So you can find the dimensions of figures, as in Ex. 61.
9.5 Factor x2 1 bx 1 c Before You factored out the greatest common monomial factor. Now You will factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. Why So you can find the dimensions of figures, as in Ex. 61.
6 th Grade Math Connects
 6 th Grade Math Connects Chapter 1: Multiply and Divide Decimals Multi-Part Lesson 1: Multiply Decimals A: Estimate Products B: Explore Multiply Decimals by Whole Numbers C: Multiply Decimals by Whole
6 th Grade Math Connects Chapter 1: Multiply and Divide Decimals Multi-Part Lesson 1: Multiply Decimals A: Estimate Products B: Explore Multiply Decimals by Whole Numbers C: Multiply Decimals by Whole
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 11.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name ate Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Vocabulary Identify an instance of each term in the diagram. 1. circle X T 2. center of the circle H I
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name ate Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Vocabulary Identify an instance of each term in the diagram. 1. circle X T 2. center of the circle H I
H. Math 2 Benchmark 1 Review
 H. Math 2 enchmark 1 Review Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram C was translated to parallelogram C. 2. Which of the following is a model of a scalene triangle?.. How many units and in which direction were the
H. Math 2 enchmark 1 Review Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram C was translated to parallelogram C. 2. Which of the following is a model of a scalene triangle?.. How many units and in which direction were the
1 st Preparatory. Part (1)
 Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Geometry review two. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Geometr review two Multiple Choice Identif the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a b = 5, then 3a =. 3 2. a. 3b b. 10b c. 5b d. 6b
Name: Class: Date: Geometr review two Multiple Choice Identif the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a b = 5, then 3a =. 3 2. a. 3b b. 10b c. 5b d. 6b
+2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s )
![+2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s ) +2 u, 2s ) [D] ( r+ t + u, 2s )](/thumbs/74/70220114.jpg) 1. Isosceles trapezoid JKLM has legs JK and LM, and base KL. If JK = 3x + 6, KL = 9x 3, and LM = 7x 9. Find the value of x. [A] 15 4 [] 3 4 [] 3 [] 3 4. Which best describes the relationship between the
1. Isosceles trapezoid JKLM has legs JK and LM, and base KL. If JK = 3x + 6, KL = 9x 3, and LM = 7x 9. Find the value of x. [A] 15 4 [] 3 4 [] 3 [] 3 4. Which best describes the relationship between the
Name Class Date. Understanding How to Graph g(x) = a(x - h ) 2 + k
 Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Semester Review
 Class: Date: Semester Review 2017-2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the Area of the Rectangle. a. 20in 2 b. 9in 2 c. 18in 2 d.
Class: Date: Semester Review 2017-2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the Area of the Rectangle. a. 20in 2 b. 9in 2 c. 18in 2 d.
4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes.
 Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments. Geometry. Assessment 2 ASSESSMENT CODE LA08_G_T2_TST_31241
 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments Assessment 2 2008 2009 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments LA08_G_T2_TST_31241 ASSESSMENT ODE 1100209 The test items contained
Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments Assessment 2 2008 2009 Los Angeles Unified School District Periodic Assessments LA08_G_T2_TST_31241 ASSESSMENT ODE 1100209 The test items contained
Honors Geometry Qtr 2 Practice from Chapters 5-8
 Block: Seat: Honors Geometry Qtr 2 Practice from Chapters 5-8 Short Answer 1. Use DEF, where J, K, and L are midpoints of the sides. If DE = 8x + 12 and KL = 10x 9, what is DE? 2. Use DEF, where J, K,
Block: Seat: Honors Geometry Qtr 2 Practice from Chapters 5-8 Short Answer 1. Use DEF, where J, K, and L are midpoints of the sides. If DE = 8x + 12 and KL = 10x 9, what is DE? 2. Use DEF, where J, K,
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
(b) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. [3]
![(b) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. [3] (b) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. [3]](/thumbs/95/126119012.jpg) HORIZON EDUCATION SINGAPORE Additional Mathematics Practice Questions: Coordinate Geometr 1 Set 1 1 In the figure, ABCD is a rhombus with coordinates A(2, 9) and C(8, 1). The diagonals AC and BD cut at
HORIZON EDUCATION SINGAPORE Additional Mathematics Practice Questions: Coordinate Geometr 1 Set 1 1 In the figure, ABCD is a rhombus with coordinates A(2, 9) and C(8, 1). The diagonals AC and BD cut at
4.! ABC ~ DEF,! AC = 6 ft, CB = 3 ft, AB = 7 ft, DF = 9 ft.! What is the measure of EF?
 Name:!!!!!!!!!!!!! Geo(2) GEOMETRY (2) REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM #2 1. If ABC is similar to ADE, then AB AD =? AE. Which replaces the? to make the statement true? A. AC!! B. AE!! C. DE!! D. BC 2. In ABC,
Name:!!!!!!!!!!!!! Geo(2) GEOMETRY (2) REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM #2 1. If ABC is similar to ADE, then AB AD =? AE. Which replaces the? to make the statement true? A. AC!! B. AE!! C. DE!! D. BC 2. In ABC,
123 Holt McDougal Geometry
 44. - 0 - -4 y x heck students estimates; possible answer: pentagon is not equiangular; m = 100 ; m = 113 ; m = 113 ; m = 101 ; m = 113 ; yes, pentagon is not equiangular. 45a. heptagon b. (7 - )180 =
44. - 0 - -4 y x heck students estimates; possible answer: pentagon is not equiangular; m = 100 ; m = 113 ; m = 113 ; m = 101 ; m = 113 ; yes, pentagon is not equiangular. 45a. heptagon b. (7 - )180 =
Questions. Exercise (1)
 Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
The Coordinate Plane. Circles and Polygons on the Coordinate Plane. LESSON 13.1 Skills Practice. Problem Set
 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
Lesson 12-13: Properties of Similarity Transformations
 Lesson 12-13: Properties of Similarity Transformations Learning Target I can define a similarity transformation as the composition of basic rigid motions and dilations. I can define two figures to be similar
Lesson 12-13: Properties of Similarity Transformations Learning Target I can define a similarity transformation as the composition of basic rigid motions and dilations. I can define two figures to be similar
Name Score Period Date. m = 2. Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement.
 Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Given: You try: Given: Prove: ABC ADC. Prove: ABE DCE. 1. Given 1. AB AD BC DC. 2. AC AC 2. Reflexive Prop. of. 3. ABC ADC 3. SSS Post.
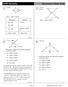 US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018
 Name: Period: The midterm will cover Chapters 1-6. Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018 You WILL NOT receive a formula sheet, but you need to know the following formulas Make sure you memorize
Name: Period: The midterm will cover Chapters 1-6. Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018 You WILL NOT receive a formula sheet, but you need to know the following formulas Make sure you memorize
3 = 1, a c, a d, b c, and b d.
 hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
Block 2 ~ The Pythagorean Theorem Self-Assessment. Progress (shade this in) Name Per. Track your understanding. Lesson #
 Block 2 ~ The Pythagorean Theorem Self-Assessment Track your understanding. Lesson # 2.1 2.2 2.3 2. 2. 2.7 Target I can recognize and find the values of perfect squares. I can estimate the value of square
Block 2 ~ The Pythagorean Theorem Self-Assessment Track your understanding. Lesson # 2.1 2.2 2.3 2. 2. 2.7 Target I can recognize and find the values of perfect squares. I can estimate the value of square
Number Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometry
 Numer Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometr Now this is m kind of paraola! Chapter Contents :0 The paraola PS, PS, PS Investigation: The graphs of paraolas :0 Paraolas of the form = a + + c PS Fun Spot:
Numer Plane Graphs and Coordinate Geometr Now this is m kind of paraola! Chapter Contents :0 The paraola PS, PS, PS Investigation: The graphs of paraolas :0 Paraolas of the form = a + + c PS Fun Spot:
9.2. Length of Line Segments. Lesson Objectives. Find the lengths of line segments on the x-axis and y-axis.
 9.2 Length of Line Segments Lesson Objectives Find lengths of horizontal and vertical line segments on the coordinate plane. Solve real-world problems involving coordinates and a coordinate plane. Learn
9.2 Length of Line Segments Lesson Objectives Find lengths of horizontal and vertical line segments on the coordinate plane. Solve real-world problems involving coordinates and a coordinate plane. Learn
1. How many planes can be drawn through any three noncollinear points? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3. a cm b cm c cm d. 21.
 FALL SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW (Chapters 1-6) CHAPTER 1 1. How many planes can be drawn through any three noncollinear points? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 2. Find the length of PQ. a. 50.9 cm b. 46.3 cm c. 25.7 cm
FALL SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW (Chapters 1-6) CHAPTER 1 1. How many planes can be drawn through any three noncollinear points? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 2. Find the length of PQ. a. 50.9 cm b. 46.3 cm c. 25.7 cm
Answers. Chapter 9 A92. Angles Theorem (Thm. 5.6) then XZY. Base Angles Theorem (Thm. 5.6) 5, 2. then WV WZ;
 9 9. M, 0. M ( 9, 4) 7. If WZ XZ, then ZWX ZXW ; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M 9,. M ( 4, ) 74. If XZ XY, then XZY Y; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M, 4. M ( 9, ) 7. If V WZV, then WV WZ; Converse of
9 9. M, 0. M ( 9, 4) 7. If WZ XZ, then ZWX ZXW ; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M 9,. M ( 4, ) 74. If XZ XY, then XZY Y; Base Angles Theorem (Thm..6). M, 4. M ( 9, ) 7. If V WZV, then WV WZ; Converse of
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition. GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition INSTRUCTIONS GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8 Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition INSTRUCTIONS GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT GRADE 7-8 Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes Mark your
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
 5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Classify each triangle by its angle measures. 1. 2. acute right 3. Simplify 12 4. If a = 6, b = 7, and c = 12, find
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Classify each triangle by its angle measures. 1. 2. acute right 3. Simplify 12 4. If a = 6, b = 7, and c = 12, find
9.3. Practice C For use with pages Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle.
 LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
SEMESTER REVIEW 1: Chapters 1 and 2
 Geometry Fall emester Review (13-14) EEER REVIEW 1: hapters 1 and 2 1. What is Geometry? 2. What are the three undefined terms of geometry? 3. Find the definition of each of the following. a. Postulate
Geometry Fall emester Review (13-14) EEER REVIEW 1: hapters 1 and 2 1. What is Geometry? 2. What are the three undefined terms of geometry? 3. Find the definition of each of the following. a. Postulate
Math 0200 Final Exam Review Questions
 Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
Circles and Arcs. Objectives To find the measures of central angles and arcs To find the circumference and arc length
 10-6 ircles and rcs ommon ore tate tandards G-..1 Know precise definitions of... circle... G-..1 rove that all circles are similar. lso G-..2, G-..5 M 1, M 3, M 4, M 6, M 8 bjectives o find the measures
10-6 ircles and rcs ommon ore tate tandards G-..1 Know precise definitions of... circle... G-..1 rove that all circles are similar. lso G-..2, G-..5 M 1, M 3, M 4, M 6, M 8 bjectives o find the measures
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1
 1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
49. Lesson 1.4 (pp ) RS m ADC 5 m ADB 1 m CDB. 53. a. m DEF 5 m ABC b. m ABG 5 1 } 2. c. m CBG 5 1 } 2. d.
 This section of the book provides step-b-step solutions to eercises with circled eercise numbers. These solutions provide models that can help guide our work with the homework eercises. The separate Selected
This section of the book provides step-b-step solutions to eercises with circled eercise numbers. These solutions provide models that can help guide our work with the homework eercises. The separate Selected
0611ge. Geometry Regents Exam Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below.
 0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
~ 1 ~ Geometry 2 nd Semester Review Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations
 Geometry nd Semester Review 018 Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations. 7. 400 m 1. 7 8. y. 8.9 cm 0 0 9.. 19 6 60 1 11 10. 45 4. 58 5 11. 5. 11 6. 18 1 slide 4.1 meters long
Geometry nd Semester Review 018 Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations. 7. 400 m 1. 7 8. y. 8.9 cm 0 0 9.. 19 6 60 1 11 10. 45 4. 58 5 11. 5. 11 6. 18 1 slide 4.1 meters long
