Structural Design for Vibration Reduction in Brushless DC Stator
|
|
|
- Dorthy Bradford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Eletr Eng Tehnol.017; 1(5): ISSN(Print) ISSN(Online) Strutural Design for Vibration Redution in Brushless DC Stator Mehrdad Jafarboland and Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi* Abstrat Reduing the noise and vibration of the BLDC otors is very essential for soe speial appliations. In this paper, a new strutural design is introdued to inrease the natural frequenies of the stator in BLDC otors as inreasing the natural frequenies an redue the severe effets of the strutural resonanes, inluding high levels of noise and vibration. The design is based on plaing a single hole on definite regions at the stator ross setional area (eah region ontains one tooth and its upper parts in the stator yoke) in an optiu way by whih the natural frequenies at different odes are shifted to the higher values. The optiu diaeter and loations for the holes are extrated by the Response Surfae Methodology (RSM) and the odal analyses in the iterative proess are done by Finite Eleent Method (FEM). Moreover, the otor perforane by the optiu stator struture is analyzed by FEM and opared with the prototype otor. Preventing the stator agneti saturation and the otor ogging torque enhaneent are the two onstraints of the optiization proble. The optial strutural design ethod is applied experientally and the validity of the design ethod is onfired by the siulated and experiental results. Keywords: BLDC stator, Hole plaeent, Modal analysis, Natural frequenies, Strutural design 1. Introdution Brushless DC (BLDC) otors are aong the ost appliable otors in various industries. They are used in any appliations nowadays. Cal and quiet operation of the BLDC otors is generally needed in various appliations, but in soe espeial ases, it is essential. Therefore, various studies have been done in this field and different ways of reduing the noise and vibration have been introdued. Nevertheless, applying different ways of reduing the noise and vibration in the otor design and onstrution proess without paying attention to reduing or eliinating the effets of strutural resonanes is not reasonable. This is due to the severe effets of the resonane ourrene. Strutural resonane auses high levels of noise and vibration that overoes the redutions ahieved by applying different ethods of reduing the noise and vibration. Soe researhers have worked on the entioned issue and their works have been done for different kinds of otors suh as peranent agnet (PM) ones. A ethod to derease the agnetially indued vibrations of a PM otor is introdued in [1] whih is developed by perforing agneti and strutural finite eleent (FE) analyses and optiization. The otor vibrations aused by the agneti fores were extrated by the ode superposition ethod. The results were experientally validated. The stator natural frequenies were opared with the Corresponding Author: Malek-Ashtar University of Tehnology, Iran. (j_ehrdad405@hotail.o) * Malek-Ashtar University of Tehnology, Iran. (hbaqerian@gail.o) Reeived: Noveber 15, 016; Aepted: May 16, 017 radial fores ating on the stator in []. An experiental investigation about the effets of the strutural dynai harateristis, like the ode shapes and natural frequenies and the eletroagneti exitation fores, on a PM otor vibrations and noise is reported in the study. In [3] a new design (inluding eletroagnetis and strutural parts) is developed in order to derease the noise in a prototype PM otor. In the eletroagneti design part, the haroni aplitude of agneti fores influenes the teeth and the torque ripple are dereased by an optial ethod. In the strutural part of the design, the natural frequenies were shifted to higher values to inrease the stiffness of the stator struture. Soe of the natural frequenies of a prototype stator struture are derived by siulation and experiental test in [4]. The harateristis of the tangential and radial agneti fores applied on the stator teeth in a PM otor and the agnetially indued vibrations are investigated in the study under flux weakening ontrol. The stator vibration aused by the radial fores is studied in [5] and an iproved stator odel is introdued. The vibration of the prototype and iproved odels were evaluated by both FEM and experiental tests. In [6] a strutural FE odel of a PM otor is introdued whih inludes stiffness of ball bearings and verified by oparing the natural frequenies derived by siulations and experiental tests. The agneti fores are extrated and then transfored into the nodal fores and the vibrations of the prototype interior PM otor are investigated. The natural frequenies of the systes an be odified by hanging soe objets that have definite effets on the size, inertia or fores of the systes. The iruferential 184 Copyright The Korean Institute of Eletrial Engineers This is an Open-Aess artile distributed under the ters of the Creative Coons Attribution Non-Coerial Liense ( lienses/by-n/3.0/) whih perits unrestrited non-oerial use, distribution, and reprodution in any ediu, provided the original work is properly ited.
2 Mehrdad Jafarboland and Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi vibration odes an have different values for 0 to. The lower ode nubers are ore iportant than the higher ones as the natural frequenies at higher ode nubers ight be out of the onerned range [7]. In this paper, a new strutural design is presented in order to shift the natural frequenies of a prototype stator of a BLDC otor to higher values and inrease the stator s stiffness. When one of the frequeny oponents of an exitation fore oinides with one of the natural frequenies of the BLDC otor with odified stator struture and the strutural resonane ours, the produed noise and vibration have lower intensities as the fore oponent agnitude has lower value at higher frequenies. The stator struture odifiation an also oit the resonane ourrene in soe ases. The odal analysis in this study is done by the Solidworks software whih is based on the Finite Eleent Analysis (FEA). In this software, an Eigen value approah is used to deterine the natural vibration odes for different geoetries. The proposed strutural design an be applied in the design stage of the stator for all types of eletri otors suh as BLDC ones. The new strutural design is based on plaing a single hole, with definite diaeter and loation, on definite regions at the stator ross setional area. Eah region ontains a tooth and its upper part at the stator yoke. The diaeter and loations of the holes are alulated by RSM in a ylindrial oordinates and the odal analyses in the iterative proess are done by FEM. Preventing the stator struture agneti saturation and the otor ogging torque enhaneent are the optiization proble onstraints whih are evaluated by the otor perforane derived by FEM. The design ethod validity is tested and onfired experientally..1 Exitation fores. Theory The noise and vibration produed during the otor operation is aused by the exitation fores [8] and these fores have different origins. The frequeny oponents of eletroagneti exitation fores in the BLDC otors are given here. The Frequenies of the radial agneti fore oponents an be alulated by: fr = n P X (1) Where n is an integer (representing the haroni nuber), P and X are the otor pole nubers and its rotating frequeny, respetively. The frequenies of the tangential agneti fore oponents are: ft = n G X () where G is the least oon ultiplier of the otor s poles and slots nubers. The frequenies of the exitation fore oponents generated by the swithing proess are: f = n 3P X (3) s The leading haroni order of the vibration obtained by the superiposition of eah exitation haroni order an be expressed as: f = n LCM ( f, f, f ) (4) ex r t s In Eq. (4), LCM stands for least oon ultiplier. Eq. (4) expresses an essential haroni oponent of the vibration generation as shown in the next Eq. (9). th G = LCM ( f, f, f ) / P (5) r t s. Natural frequenies of the stator ore In this setion, the odal vibration behavior of the stator struture is disussed analytially. An analytial approah for alulating the stator ore s natural frequenies are investigated and its auray is disussed. The natural frequeny of the th iruferential vibrational ode of the stator struture an be alulated by [8]: ( ) f ( ) K = 1 p M (6) K (N/) and (kg) in Eq. (6) are the luped stiffness and the luped ass of the stator struture respetively. If the stator struture is onsidered as a ylindrial shell with infinite length, the natural frequeny of the syste for the th iruferential ode an be alulated by [10]: f Ω E = p D r (1 n ) - Where E is the elastiity odulus, r is the ass density, D is the stator ean diaeter, n is the Poisson ratio for the stator ore and W is the roots of the harateristi equation of otion. Aording to the Donnel- Mushtari theory [8], W is 1 for the iruferential ode =0 ( W = 0 ) and for the iruferential odes ³ 1 is: Ω = ((1 + + k ) ± (1 + + k ) - 4 k ) (8) Where the paraeter k is (7) h 3D in whih h is the
3 Strutural Design for Vibration Redution in Brushless DC Stator stator yoke thikness. The luped stiffness and ass an be expressed in the fors of the Eqs. (9) and (10) if we want to show Eq. (7) in the for of Eq. (6): K ( ) 4Ω p Li h E = D 1-n M i (9) = pr D L h (10) L i in the Eqs. (9) and (10) is the effetive length of the stator ore [8]. In the stator ore, the windings are loated in slots whih are separated by the steel teeth. The tooth-slot zone with the windings an be onsidered as an additional ring internal to the stator ore (yoke). The natural frequeny of the stator syste with the windings an be alulated by: ( ) f ( ) ( w) + K 1 K = (11) p M + M Where K (N/) and (kg) are defined like Eq. (6), ( w) K is the luped stiffness of tooth-slot zone inluding the windings and M w is the ass of the teeth, windings, and insulation. In order to extrat the equations for the natural frequenies of stator struture, the analytial equations should be written for a ylindrial shell, but beause of the shell s urvature, a oupling exists aong the vibrations in the radial, axial and tangential diretions. Therefore, the exitations in one diretion ause vibrations in the three entioned diretions and this is ore doinant at lower frequenies. Thus, any siplifiations and approxiations are needed in the analytial solution proess and solving the vibration equations diretly is so hard [11] and hene the auray of the analytial solution is low. Consequently, in this study, to onsider the effets of the strutural odifiations in the stator, the low auray of the analytial solutions akes the insuffiient to be used and the nuerial approahes should be applied. Therefore, the finite eleent ethod is used for the analyses of this study. The rotor natural frequenies an also be derived independently. The natural frequenies of a syste an be alulated by the ode superposition ethod [8]..3 Aplitude of vibration displaeents The aplitude of vibration displaeents of the th vibrational ode an be alulated by: A = F M - r + r ( w w ) 4z w w w (1) In Eq. (1), M is the ass (kg) of the shell with ylindrial shape (by whih the stator is odeled), w and wr are the angular natural frequeny of the th ode and the angular frequeny of the fore oponent with order r respetively, and z is the odal daping ratio. F is the aplitude of fore whih an be alulated by: F = p D L P (13) 1in i r Where D1in and L i are the stator ore s inner diaeter and its effetive length, respetively, and P r is the agneti pressure agnitude with order r [8]. Deterining the odal daping ratio z by analytial ethods is not straightforward and generally its deterination is done by the experiental ethods [8]. An equation derived fro the experiental ethods, whih is for eletri ahines with sall and ediu sizes, is expressed as [1]: 1 ( f 0.06) z = + (14) p Where f is natural frequeny of ode. Considering Eq. (1), it an be laied that when the frequeny of the exitation fore oponent is lose to one of the natural frequenies of the stator struture, axiu vibration and noise an be produed. Therefore, in the stator vibration analysis, onsidering the eletroagneti fore oponents whih their frequenies are lose to the natural frequenies of the stator struture ay be enough [8]. 3. Strutural Design In this setion, an optiized strutural design approah is introdued to ove the strutural resonanes of the stator struture to higher frequenies in order to enhane the stiffness. As entioned before, the approah ontains holes plaeent on definite regions of the stator ross setional area in an optiu way by using response surfae ethodology (RSM) and heking the perforanes of the prototype and optial otors by FEM. 3.1 Modeling of the stator The prototype otor whih is odeled for this study is a 4000 rp BLDC otor with 10 poles and 1 slots. The speifiations of the odeled stator are shown in Table 1. The steel type is ASTM-A677 whih is the produt of the Table 1. The odeled stator speifiations Outer Diaeter 5.4 Inner Diaeter 5.7 Length 4.5 Nuber of Slots 1 Steel Type ASTM-A677-64F00 Produt of Cogent Co J Eletr Eng Tehnol.017; 1(5):
4 Mehrdad Jafarboland and Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi Table. The properties of the stator aterial Property (unit) Value Young odulus (psi) Rolling diretion.68e10 Transverse diretion.97e10 Poisson s ratio 0.9 Shear odulus (psi) Mass density (Kg/ ) 7600 Tensile strength (psi) Yield strength (psi) Table 3. The natural frequenies of the prototype stator Mode nuber Natural frequeny Mode nuber Natural frequeny Table 4. The frequeny values for the oponents of the eletroagneti fores in the BLDC otor. No. Frequeny Frequeny Type No. Type r *,t **,s *** r, s 1333 r r r, s r r r, t, s r r r, t, s r r r, s r * radial, ** tangential, *** swithing Fig.. The stator ross setional area regions in the strutural design Fig. 1. The prototype stator struture Cogent Copany (64F00). The steel thikness is inh. The aterial properties of the steel are presented in Table (extrated fro the produt s brohure). The stator struture with its entioned detailed speifiations and aterial properties has been odeled in the Solidworks software environent. One of the unique features of this study is the aurate odeling of the lainated stator struture in the software. In [6] the lainated struture of the otor is odeled by using an orthotropi aterial, but in this study the lainations are diretly applied in the odal analysis. The odeled struture is shown in Fig. 1. Note that the lainations in the odel are bonded to eah other. Considering the poles and slots nubers and the rated speed, the upper bound frequeny in the odal analysis is seleted near 10 KHz beause the frequeny oponents of the exitation fores in the otor do not have onsiderable values in the ranges above 10 KHz. The upper bound frequeny for the study is obtained aording to the results presented in [13]. The natural frequenies of the prototype stator struture are presented in Table 3 (only the elasti odes are presented). Considering Eqs. (1) to (3), we have P=10, S=1 and X=66.67 Hz. The frequeny oponents of the different types of fores produed in the prototype BLDC otor have overlaps at soe frequenies. The frequenies of the different fore oponents up to 10 KHz (the seleted upper bound frequeny) are presented in Table 4. The exitation fore types (radial, tangential and swithing) are defined for eah frequeny oponent. As entioned before, onsidering the eletroagneti fore oponents whih their frequenies are lose to the natural frequenies of the stator struture ay be enough in the stator vibration analysis. 3. Strutural design approah In this part, for the stator whih is odeled in the software, the new strutural design has been applied by whih the natural frequenies at different ode shapes are shifted to higher values, and the stator stiffness is inreased. As entioned before, the design is based on plaing a hole with definite diaeter and loation on speifi regions at the stator ross setional area. Eah region ontains one stator tooth with its upper parts in the stator yoke. The regions for the prototype stator are shown in Fig.. Preventing the stator struture with holes fro agneti saturation is onsidered as a onstraint for the proble. The other onstraint is preventing the otor ogging torque inreent as plaing the holes auses soe hanges in the relutane of the passes whih the agneti flux follows. The entioned onstraints have been applied by heking the otor perforane by FEM. The loations and diaeters of the holes are defined by the RSM, and the odal analyses in the iterative proess of the optiization algorith are done by FEM. In RSM, the
5 Strutural Design for Vibration Redution in Brushless DC Stator Table 5. The optiu values of the paraeters. Paraeter Value D 1 R 3.6 A 60 Table 6. The natural frequenies of the optiu stator Fig. 3. The optiization paraeters used for RSM hole s optiu loation is extrated by defining different loations of the hole in a ylindrial oordinate syste with the stator enter as the origin. The paraeters whih are used for RSM are shown in Fig. 3. In Fig. 3, D is the diaeter of the hole, R is the distane between the enter of the hole and the oordinate syste origin and A is the angle whih is defined in the ylindrial oordinate syste. The iniu and axiu diaeters of the holes are set at 0.5 and 1.5 for the algorith, respetively. For the prototype stator struture, plaing holes with diaeters saller than 0.5 does not have any onsiderable effets on the natural frequenies. Also, plaing holes with diaeters larger than 1.5 ight ause agneti saturation of the stator. The diaeters of the holes are odified by 0.1 steps during the iterative proess in the optiization algorith. The odifiation steps for the paraeters R and A are 0. and 1 degree, respetively. The onstraints for paraeters D, R and A are given in Eqs. (15) to (17). Note that the optiu values whih are derived for the paraeters in region 1 (onsidering Figs. and 3) are used to derive the hole diaeter and loation at the other regions ( D and R are the sae at different regions and A is subtrated by 30 degrees for region ; added by 30 degrees for region 1, 60 degrees for region 11, et.). 0.5 D 1.5 (15) 13 R 6 (16) 45 A 75 (17) It should be noted that in the response surfae design proess for the prototype stator, the iniu and axiu values for A depend on the value of R. For exaple, when R is lower than 4, the peritted range for the hanges of A dereases in oparison with Eq. (17). For region 1 the optiu values of the paraeters are presented in Table 5 and for the other regions, the paraeters an be derived using the values in this table. The results show that the optiu hole loations are where the holes enters are loated on the stator s radii going through the stator teeth tip enters (for all of the regions). Mode nuber Natural frequeny Mode nuber Natural frequeny Fig. 4. The optiu stator odel with holes The optiu odel in the software environent is shown in Fig. 4. The natural frequenies of the optiu stator struture are presented in Table 6 (only the elasti odes are presented). As entioned before, the upper bound frequeny is near 10 KHz. The natural frequenies of the prototype and the optiu stator strutures an be alulated theoretially by Eqs. (6) to (10). Considering the paraeters in the equations, it an be seen that the alulated natural frequenies will be the sae for the both stators despite their strutural differenes aused by plaing the holes. This shows the insuffiient auray of the theoretial equations for this study and therefore only the nuerial ethods like FEM an be used for the ase. The results in Tables 3 and 6 show that the natural frequenies at all ode shapes inrease by plaing the holes with optiu diaeter and loations. Considering Tables 3 and 6, the frequeny oponents whih are lose to the natural frequenies of the prototype and optiu stator strutures are extrated fro Table 4. Then by using Eqs. (1) to (14), the aount of vibration displaeents aplitude redution ahieved by plaing the holes with the optiu diaeters and loations on the stator regions is alulated. Considering the redution at different ode shapes, the aplitude of the vibration displaeents dereases about the total average of 56% in the optiu stator struture opared to the prototype one. In order to progress the proble onstraints, the otor with the optiu stator struture derived by RSM and the odal analysis is analyzed by FEM to evaluate its perforane in oparison with the prototype otor. The results show that plaing the holes does not ause the stator 1846 J Eletr Eng Tehnol.017; 1(5):
6 Mehrdad Jafarboland and Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi Table 7. FEA results for the prototype and optiu otors Paraeter Prototype Motor Optiu Motor Output speed (rp) Output torque (N.) Torque ripple (%) Effiieny (perent) Fig. 5. The agneti flux densities in the otors Fig. 6. The ogging torque profile versus tie in the otors with the prototype and optiu stators Fig. 7. The agneti flux lines in the otors agneti saturation (the stator axiu agneti flux density is about 1.5 Tesla). The agneti flux densities on the two otor ross setional areas are shown in Fig. 5. Considering Fig. 5, it an be seen that the expeted partial agneti saturation around the hole is negligible. The results of the analysis also show that plaing the holes with optiu diaeters and loations does not inrease the otor ogging torque. The ogging torque profiles and their peak to peak values (about 0.48 N.) are the sae for the two otors aording to the FEM results. The ogging torque profile versus tie in the otors with the prototype and optiu stators are shown in Fig. 6. Coparing the perforanes of the prototype and the optiu otors also shows that plaing the optial holes does not ause any iportant hanges in the otor perforane and no penalties exist for the proposed strutural design. The agneti flux lines on the two otors ross setional area are shown in Fig. 7. The flux lines harateristis in Fig. 7 shows that plaing Fig. 8. Bak EMF wavefors for one phase: (a) prototype otor, (b) optiu otor the optiu holes does not ause iportant disturbanes in the flux ontinuity. The bak EMF wavefors of the two otors, for one phase, are shown in Fig. 8. As an be seen in Fig. 8, the bak EMF wavefors for the two otors in the sae phase are exatly siilar. The effiieny, output torque, speed and other harateristis of the prototype and optiu otors are the sae aording to the FEA results. Soe of the analysis results are presented in Table 7. Coparing the results in Table 7 shows that the optiization proess does not have any negative influenes on the otor perforane. 4. Experiental Verifiations In order to validate the proposed strutural design experientally, two BLDC otors were designed and onstruted. The oponents and strutures of the two otors were the sae exept for the stator strutures. The studied prototype stator struture and the optiu stator struture with holes were used in the two otors. The otors with their stator strutures are shown in Fig. 9. Soe of the holes on the optial otor s stator are shown in Fig. 9(b). The other holes on the optiu stator ross setional area have been overed during the otor winding proess. One of the ore lainates of the two stators are shown in Fig. 9(). The vibration spetru of the two onstruted otors have been easured and reorded in the frequeny range 0-16 KHz. The upper bound frequeny in the easureent has been seleted ore than the axiu interested
7 Strutural Design for Vibration Redution in Brushless DC Stator Fig. 11. The vibration spetru of the prototype and the optiu otors at 4000 rp Fig. 9. (a) The prototype and optiu onstruted otors; (b) The prototype and optiu stator strutures used in the otors; () One of the ore lainates of the two stators. Fig. 10. The otors vibration spetru easureent setup frequeny to onfir that no iportant oponent reains in the frequenies greater than 10 KHz. The two otors vibration spetru has been easured at the otor rated speed 4000 rp and their vibration spetru easureent setup is shown in Fig. 10. The vibration spetru of the prototype and the optial otor at the rated speed are shown in Fig. 11. The vibration spetru over the 5000 Hz had negligible aplitude and has not been shown in the figure. As an be seen in Fig. 11, the vibration oponents aplitude in the optial otor has dereased at ost of the frequenies. Also, it an be seen that a resonane ours at 1333 Hz in the prototype otor whih is due the interferene between the radial agneti fore oponent and the natural frequeny of the otor. Considering the figure, it an be seen that as the natural frequeny at the first elasti ode has been shifted to an upper value at Fig. 1. The vibration spetru of the prototype and the optiu otors at different speeds, a)1000 rp, b) 000 rp, )3000 rp the optiu otor, the resonane ourrene has been disappeared in this otor (the otor aelerations is about 4 ties saller for the optiu otor). Siilar onditions exist at the frequeny 4667 Hz in the prototype otor and a resonane with lower severity ours (as the exitation fore oponents have lower agnitudes at higher frequenies). This resonane ourrene also disappeared in the optiu otor as the natural frequeny at the third elasti ode has been shifted to a higher frequeny. The otor aeleration values at soe other exitation fores frequenies also have been shown and it an be seen that the otor vibration has dereased at these frequenies. The applied strutural design aused the natural frequenies of the whole otor to inrease (by inreasing the stator s natural frequenies), so the optiu otor vibration levels, aused by the fores at different frequenies have been dereased (the otor stiffness is inreased) as an be seen 1848 J Eletr Eng Tehnol.017; 1(5):
8 Mehrdad Jafarboland and Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi Fig. 13. The urrent wavefors of the two otor in Fig. 11. The types of the exitation fore oponents shown in Fig. 11 an be derived fro Table 4. Sine the otor vibration harateristis are varied by soe of the otor operational onditions like its speed and swithing frequeny, the vibration spetru of the prototype and optiu otors have been easured and reorded at soe other rotor speeds. The two otors vibration spetrus at the rotor speeds 1000, 000 and 3000 rp are presented in Fig. 1. As an be seen in Fig. 1, the vibration spetru aplitudes in the optiu otor have dereased at ost of the frequeny oponents for all of the rotor speeds. It shows that the proposed ethod an be effetive at different rotor speeds besides the rated one. To give soe exaples showing the influenes of applying the optiu holes on reduing or oitting the resonane effets, soe points with their exitation fore types, frequeny and aeleration values are indiated in Fig. 1 (points 1 to 4). Moreover, the experiental test results show that the two otors perforanes (e.g. effiieny, output torque, speed, urrents, et.) are the sae. For exaple, the urrent wavefors of the otors under a definite load are alost the sae. The urrent wavefors are shown in Fig Conlusion An optial strutural design was introdued in this paper in order to inrease the stator stiffness of a BLDC otor and to redue its vibration by shifting the natural frequenies of the stator to higher values. Inreasing the natural frequenies of the stator struture dereases the severe effets of the strutural resonanes, inluding high levels of noise and vibration, as the frequeny oponents of the exitation fores in BLDC otors have lower agnitudes at higher frequenies. The proposed design ethod was based on plaing a single hole on definite regions at the stator ross setional area in suh a way that no agneti saturations and otor ogging torque enhaneent our. The optiu diaeter and loations of the holes were extrated by RSM and the odal analyses in the iterative proess were done by FEM. The optiu stator struture, with definite diaeter and loations of the holes, was introdued. The natural frequenies of the optiu struture at different ode nubers inreased about 190 to 50 Hz and its vibration displaeents aplitude was 56% lower than the prototype stator struture. The perforanes of the prototype and the optiu otors were analyzed by FEM and the results showed that no agneti saturation and ogging torque inreent our due to plaing the optiu holes at the regions. The validity of the optial design was tested and verified experientally. The experiental results showed that the resonane ourrene in the prototype otor was disappeared in the optiu one by shifting the natural frequenies of the stator struture to higher values. Also, the otor vibration levels at different frequeny oponents were dereased in the optiu otor. The FEM analysis and experiental test results also showed that plaing the holes does not ause any negative effets on the otor perforane. Referenes [1] D. Y. Ki, J. K. Na and G. H. Jang, Redution of Magnetially Indued Vibration of a Spoke-Type IPM Motor using Magnetoehanial Coupled Analysis and Optiization, IEEE Trans. Magnetis, vol. 49, no. 9, pp , Sep. 01. [] Hong-Seok Ko and Kwang-Joon Ki, Charaterization of Noise and Vibration Soures in Interior Peranent-Magnet Brushless DC Motors, IEEE Trans. Magnetis, vol. 40, no. 6, pp , Nov [3] Sang-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo Hong, Sang-Moon Hwang, Woo-Taik Lee, Ji-Young and Youbg-Kyoun Ki, Optial Design for Noise Redution in Interior Peranent-Magnet Motor, IEEE Trans. Industry Appliations, vol. 45, no. 6, pp , Nov./De [4] D. Y. Ki, G. H. Jang and J. K. Na, Magnetially Indued Vibrations in an IPM Motor due to Distorted Magneti Fores Arising fro Flux Weakening Control, IEEE Trans. Magnetis, vol. 49, no. 7, pp , Nov [5] Ji-Min Ki, Tao Sun, Sang-Ho Lee, Do-Jin Ki, Jung-Pyo Hong, Evaluation and Iproved Design about Aousti Noise and Vibration in IPMSM, in Proeeding of IEEE Eletrial Mahines and Systes Conferene, Inheon, South Korea, Ot [6] K. H. Yi, J. W. Jang, G. H. Jang, M. G. Ki, K. N. Ki, Fored Vibration Analysis of an IPM Motor for Eletrial Vehiles due to Magneti Fore, IEEE Trans. Magnetis, vol. 48, no. 11, pp , Nov. 01. [7] P. Vijayraghavan and R. Krishnan, Noise in Eletri Mahines: a Review, IEEE Trans. Industry Appliations, vol. 35, no. 5, pp , Apr [8] Jaek F. Gieras, Chong Wang and Joseph Cho Lai, Noise of Polyphase Eletri Motors. Boa Raton, FL:
9 Strutural Design for Vibration Redution in Brushless DC Stator CRC Press, 006. [9] Jin Hur, Jin-Wook Reu, Byeong-Woo Ki and Gyu-Hong Kang, Vibration Redution of IPM- Type BLDC Motor Using Negative Third Haroni Eliination Method of Air-Gap Flux Density, IEEE Trans. Industry Appliations, vol. 47, no. 3, pp , May/June 011. [10] Arthur W. Leissa, Vibration of Shells. New York, NY, USA: Aousti Soiety of Aeria, Aerian Institute of Physis, [11] Werner Soedel, Vibrations of Shells and Plates. NY: Marel Dekker, [1] S. J. Yang, Low-Noise Eletrial Motors. Oxford, United Kingdo: Clarendon Press, [13] Tao Sun, Ji-Min Ki, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo Hong and Myung-Ryul Choi, Effet of Pole and Slot Cobination on Noise and Vibration in Peranent Magnet Synhronous Motor, IEEE Trans. Magnetis, vol. 47, no. 5, pp , May 011. Mehrdad Jafaboland He reeived the B.S. and M.S. degrees in eletrial engineering fro Siene and Industrial University in 1979 and Tarbiat Modares University in 198, respetively. He reeived the PH.D. Degree in eletrial engineering fro Siene and Researh unit of Tehran University. After graduating, he beae an assoiate professor in the eletrial engineering Departent of Malek-ashtar University of Tehnology. Hossein Bagherian Farahabadi He reeived the B. S. and M. S. degrees in eletrial engineering fro Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, Iran, in 010 and 01, respetively. He is urrently working toward the Ph.D. degree in eletrial engineering at Malek Ashtar University of Tehnology, Isfahan, Iran. His researh interests inlude PM otors, power eletronis and drives J Eletr Eng Tehnol.017; 1(5):
Uniaxial Concrete Material Behavior
 COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., JULY 215 TECHNICAL NOTE MODIFIED DARWIN-PECKNOLD 2-D REINFORCED CONCRETE MATERIAL MODEL Overview This tehnial note desribes the Modified Darwin-Peknold reinfored onrete
COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., JULY 215 TECHNICAL NOTE MODIFIED DARWIN-PECKNOLD 2-D REINFORCED CONCRETE MATERIAL MODEL Overview This tehnial note desribes the Modified Darwin-Peknold reinfored onrete
[2006] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Youguang Guo1, Jianguo Zhu, Jiaxin Chen1 and Jianxun Jin, Performance Analysis of a PM Claw Pole SMC
![[2006] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Youguang Guo1, Jianguo Zhu, Jiaxin Chen1 and Jianxun Jin, Performance Analysis of a PM Claw Pole SMC [2006] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Youguang Guo1, Jianguo Zhu, Jiaxin Chen1 and Jianxun Jin, Performance Analysis of a PM Claw Pole SMC](/thumbs/95/125571658.jpg) [26] IEEE. Reprinted, with perission, fro [Youguang Guo1, Jianguo Zhu, Jiaxin Chen1 and Jianxun Jin, Perforane Analysis of a P Claw Pole SC otor with Brushless DC Control Shee, Power Eletronis and otion
[26] IEEE. Reprinted, with perission, fro [Youguang Guo1, Jianguo Zhu, Jiaxin Chen1 and Jianxun Jin, Perforane Analysis of a P Claw Pole SC otor with Brushless DC Control Shee, Power Eletronis and otion
Physics (Theory) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. 1 to 8 are very short answer type questions and carry one mark each.
 Physis (Theory) Tie allowed: 3 hours] [Maxiu arks:7 General Instrutions: (i) ll uestions are opulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 3 uestions in total. Question Nos. to 8 are very short answer
Physis (Theory) Tie allowed: 3 hours] [Maxiu arks:7 General Instrutions: (i) ll uestions are opulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 3 uestions in total. Question Nos. to 8 are very short answer
Fractional Order Controller for PMSM Speed Servo System Based on Bode s Ideal Transfer Function
 Sensors & Transduers, Vol. 73, Issue 6, June 24, pp. -7 Sensors & Transduers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.o Frational Order Controller for PMSM Speed Servo Syste Based on Bode
Sensors & Transduers, Vol. 73, Issue 6, June 24, pp. -7 Sensors & Transduers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.o Frational Order Controller for PMSM Speed Servo Syste Based on Bode
MOMENT CONTROL OF THE SOUND RADIATED FROM AN AXIALLY EXCITED CYLINDRICAL SHELL. James A. Forrest
 ICSV4 Cairns Australia 9- July, 007 MOMENT CONTROL O THE SOUND RADIATED ROM AN AXIALLY EXCITED CYLINDRICAL SHELL Jaes A. orrest Maritie Platfors Division, Defene Siene & Tehnology Organisation, PO Box
ICSV4 Cairns Australia 9- July, 007 MOMENT CONTROL O THE SOUND RADIATED ROM AN AXIALLY EXCITED CYLINDRICAL SHELL Jaes A. orrest Maritie Platfors Division, Defene Siene & Tehnology Organisation, PO Box
General Closed-form Analytical Expressions of Air-gap Inductances for Surfacemounted Permanent Magnet and Induction Machines
 General Closed-form Analytial Expressions of Air-gap Indutanes for Surfaemounted Permanent Magnet and Indution Mahines Ronghai Qu, Member, IEEE Eletroni & Photoni Systems Tehnologies General Eletri Company
General Closed-form Analytial Expressions of Air-gap Indutanes for Surfaemounted Permanent Magnet and Indution Mahines Ronghai Qu, Member, IEEE Eletroni & Photoni Systems Tehnologies General Eletri Company
Derivation of Non-Einsteinian Relativistic Equations from Momentum Conservation Law
 Asian Journal of Applied Siene and Engineering, Volue, No 1/13 ISSN 35-915X(p); 37-9584(e) Derivation of Non-Einsteinian Relativisti Equations fro Moentu Conservation Law M.O.G. Talukder Varendra University,
Asian Journal of Applied Siene and Engineering, Volue, No 1/13 ISSN 35-915X(p); 37-9584(e) Derivation of Non-Einsteinian Relativisti Equations fro Moentu Conservation Law M.O.G. Talukder Varendra University,
x(t) y(t) c c F(t) F(t) EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Homework 6: Forced Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018
 EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoewor 6: Fored Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. The vibration isolation syste shown in the figure has =20g, = 19.8 N / = 1.259 Ns
EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoewor 6: Fored Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. The vibration isolation syste shown in the figure has =20g, = 19.8 N / = 1.259 Ns
Modeling the modulated acoustic radiation force distribution in a viscoelastic medium driven by a spherically focused ultrasound transducer
 Modeling the odulated aousti radiation fore distribution in a visoelasti ediu driven by a spherially foused ultrasound transduer F.C. Meral a, T. J Royston b and R. L Magin a a University of Illinois,
Modeling the odulated aousti radiation fore distribution in a visoelasti ediu driven by a spherially foused ultrasound transduer F.C. Meral a, T. J Royston b and R. L Magin a a University of Illinois,
Lecture 17. Phys. 207: Waves and Light Physics Department Yarmouk University Irbid Jordan
 Leture 17 Phys. 7: Waves and Light Physis Departent Yarouk University 1163 Irbid Jordan Dr. Nidal Ershaidat http://taps.yu.edu.jo/physis/courses/phys7/le5-1 Maxwell s Equations In 187, Jaes Clerk Maxwell's
Leture 17 Phys. 7: Waves and Light Physis Departent Yarouk University 1163 Irbid Jordan Dr. Nidal Ershaidat http://taps.yu.edu.jo/physis/courses/phys7/le5-1 Maxwell s Equations In 187, Jaes Clerk Maxwell's
Kinematics of Elastic Neutron Scattering
 .05 Reator Physis - Part Fourteen Kineatis of Elasti Neutron Sattering. Multi-Group Theory: The next ethod that we will study for reator analysis and design is ulti-group theory. This approah entails dividing
.05 Reator Physis - Part Fourteen Kineatis of Elasti Neutron Sattering. Multi-Group Theory: The next ethod that we will study for reator analysis and design is ulti-group theory. This approah entails dividing
International Journal of Thermodynamics, Vol. 18, No. 1, P (2015). Sergey G.
 International Journal of Therodynais Vol. 8 No. P. 3-4 (5). http://dx.doi.org/.554/ijot.5343 Four-diensional equation of otion for visous opressible and harged fluid with regard to the aeleration field
International Journal of Therodynais Vol. 8 No. P. 3-4 (5). http://dx.doi.org/.554/ijot.5343 Four-diensional equation of otion for visous opressible and harged fluid with regard to the aeleration field
Speed Regulation of a Small BLDC Motor using Genetic-Based Proportional Control
 World Aademy of Siene, Engineering and Tehnology 47 8 Speed Regulation of a Small BLDC Motor using Geneti-Based Proportional Control S. Poonsawat, and T. Kulworawanihpong Abstrat This paper presents the
World Aademy of Siene, Engineering and Tehnology 47 8 Speed Regulation of a Small BLDC Motor using Geneti-Based Proportional Control S. Poonsawat, and T. Kulworawanihpong Abstrat This paper presents the
CHAPTER 3 PROBLEMS. δ = where A is the cross-sectional area, and E is the modulus of elasticity.
 CHPTER 3 PROLEMS d SPRING-MSS-DMPER PPLICTIONS Proble 3.1 The buoy shown in figure P3.1 has a irular ross-setion with diaeter d and has length L. Most of the weight of the buoy, w, is onentrated in the
CHPTER 3 PROLEMS d SPRING-MSS-DMPER PPLICTIONS Proble 3.1 The buoy shown in figure P3.1 has a irular ross-setion with diaeter d and has length L. Most of the weight of the buoy, w, is onentrated in the
Electromagnetic Waves
 Eletroagneti Waves Physis 6C Eletroagneti (EM) waves an be produed by atoi transitions (ore on this later), or by an alternating urrent in a wire. As the harges in the wire osillate bak and forth, the
Eletroagneti Waves Physis 6C Eletroagneti (EM) waves an be produed by atoi transitions (ore on this later), or by an alternating urrent in a wire. As the harges in the wire osillate bak and forth, the
Determining the optimum length of a bridge opening with a specified reliability level of water runoff
 MATE Web o onerenes 7, 0004 (07) DOI: 0.05/ ateon/0770004 XXVI R-S-P Seinar 07, Theoretial Foundation o ivil Engineering Deterining the optiu length o a bridge opening with a speiied reliability level
MATE Web o onerenes 7, 0004 (07) DOI: 0.05/ ateon/0770004 XXVI R-S-P Seinar 07, Theoretial Foundation o ivil Engineering Deterining the optiu length o a bridge opening with a speiied reliability level
and ζ in 1.1)? 1.2 What is the value of the magnification factor M for system A, (with force frequency ω = ωn
 EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoework 6: Fored Vibrations, Rigid Body Kineatis Due Friday April 7, 017 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. Syste A in the figure is ritially daped. The aplitude of the
EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoework 6: Fored Vibrations, Rigid Body Kineatis Due Friday April 7, 017 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. Syste A in the figure is ritially daped. The aplitude of the
MAIN TOPICS iensional i l Analysis Bukingha Pi Theore eterination of Pi Ters Coents about iensional Analysis Coon iensionless Groups in Fluid Mehanis
 FUNAMENTALS OF FLUI MECHANICS Chapter 7 iensional Analysis Modeling, and Siilitude MAIN TOPICS iensional i l Analysis Bukingha Pi Theore eterination of Pi Ters Coents about iensional Analysis Coon iensionless
FUNAMENTALS OF FLUI MECHANICS Chapter 7 iensional Analysis Modeling, and Siilitude MAIN TOPICS iensional i l Analysis Bukingha Pi Theore eterination of Pi Ters Coents about iensional Analysis Coon iensionless
Numerical Studies of Counterflow Turbulence
 Nonae anusript No. will be inserted by the editor Nuerial Studies of Counterflow Turbulene Veloity Distribution of Vorties Hiroyuki Adahi Makoto Tsubota Reeived: date Aepted: date Abstrat We perfored the
Nonae anusript No. will be inserted by the editor Nuerial Studies of Counterflow Turbulene Veloity Distribution of Vorties Hiroyuki Adahi Makoto Tsubota Reeived: date Aepted: date Abstrat We perfored the
Millennium Relativity Acceleration Composition. The Relativistic Relationship between Acceleration and Uniform Motion
 Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
Design of Output Feedback Compensator
 Design of Output Feedbak Copensator Vanita Jain, B.K.Lande Professor, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College of Engineering, Pashi Vihar, New Delhi-0063 Prinipal, Shah and Anhor Kuthhi Engineering College, Chebur,
Design of Output Feedbak Copensator Vanita Jain, B.K.Lande Professor, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College of Engineering, Pashi Vihar, New Delhi-0063 Prinipal, Shah and Anhor Kuthhi Engineering College, Chebur,
1. Which two values of temperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when measured on the Kelvin and on the
 . Whih two values of teperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when easured on the Kelvin and on the Celsius sales of teperature? Kelvin sale Celsius sale A. 40 33 B. 273 00 C. 33 40 D. 373 0 2.
. Whih two values of teperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when easured on the Kelvin and on the Celsius sales of teperature? Kelvin sale Celsius sale A. 40 33 B. 273 00 C. 33 40 D. 373 0 2.
IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CURVED BEAMS WITH VARIABLE CROSS-SECTIONS CARRYING ADDITIONAL MASS
 11 th International Conferene on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-1 September 013 IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CURVED BEAMS WITH VARIABLE CROSS-SECTIONS CARRYING ADDITIONAL
11 th International Conferene on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-1 September 013 IN-PLANE VIBRATIONS OF CURVED BEAMS WITH VARIABLE CROSS-SECTIONS CARRYING ADDITIONAL
Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and volume numbers)
 A omparison between ylindrial and ross-shaped magneti vibration isolators : ideal and pratial van Casteren, D.T.E.H.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E. Published in: Arhives of Eletrial Engineering DOI: 10.1515/aee-2015-0044
A omparison between ylindrial and ross-shaped magneti vibration isolators : ideal and pratial van Casteren, D.T.E.H.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E. Published in: Arhives of Eletrial Engineering DOI: 10.1515/aee-2015-0044
Strength of Materials
 Strength of Materials Session Pure Bending 04 Leture note : Praudianto, M.Eng. g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà Pure Bending: Prisati
Strength of Materials Session Pure Bending 04 Leture note : Praudianto, M.Eng. g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà Pure Bending: Prisati
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
Energy Dissipation in Spacecraft Structures Incorporating Bolted Joints with Viscoelastic Layers
 Energy Dissipation in Spaeraft Strutures Inorporating Bolted Joints with Visoelasti Layers R. Wang and A. D. Croobe University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey, GU 7XH, UK G. Rihardson Surrey Spae Tehnology
Energy Dissipation in Spaeraft Strutures Inorporating Bolted Joints with Visoelasti Layers R. Wang and A. D. Croobe University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey, GU 7XH, UK G. Rihardson Surrey Spae Tehnology
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
DETERMINATION OF TWO LAYER EARTH STRUCTURE PARAMETERS
 DETERMINATION OF TWO LAYER EARTH STRUCTURE PARAMETERS Ioannis F. GONOS, Vassiliki T. KONTARGYRI, Ioannis A. STATHOPULOS, National Tehnial University of Athens, Shool of Eletrial and Coputer Engineering,
DETERMINATION OF TWO LAYER EARTH STRUCTURE PARAMETERS Ioannis F. GONOS, Vassiliki T. KONTARGYRI, Ioannis A. STATHOPULOS, National Tehnial University of Athens, Shool of Eletrial and Coputer Engineering,
Combined Tilt and Thickness Measurements on Nematic Liquid Crystal Samples
 This artile was downloaded by: [Mihigan State University] On: 10 February 2015, At: 11:16 Publisher: Taylor & Franis Infora Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Nuber: 1072954 Registered offie:
This artile was downloaded by: [Mihigan State University] On: 10 February 2015, At: 11:16 Publisher: Taylor & Franis Infora Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Nuber: 1072954 Registered offie:
Stabilization of the Precision Positioning Stage Working in the Vacuum Environment by Using the Disturbance Observer
 Proeedings of the 4th IIAE International Conferene on Industrial Appliation Engineering 216 Stabilization of the Preision Positioning Stage Working in the Vauum Environment by Using the Disturbane Observer
Proeedings of the 4th IIAE International Conferene on Industrial Appliation Engineering 216 Stabilization of the Preision Positioning Stage Working in the Vauum Environment by Using the Disturbane Observer
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) Design
 Peranent Magnet Synhronou Motor (PMSM) Deign Part 1 General Conideration Peranent Magnet (PM) Motor Charaterized by peranent agnet on rotor Known for it ipliity and low aintenane No opper lo on rotor High
Peranent Magnet Synhronou Motor (PMSM) Deign Part 1 General Conideration Peranent Magnet (PM) Motor Charaterized by peranent agnet on rotor Known for it ipliity and low aintenane No opper lo on rotor High
Speed-feedback Direct-drive Control of a Low-speed Transverse Flux-type Motor with Large Number of Poles for Ship Propulsion
 Speed-feedbak Diret-drive Control of a Low-speed Transverse Flux-type Motor with Large Number of Poles for Ship Propulsion Y. Yamamoto, T. Nakamura 2, Y. Takada, T. Koseki, Y. Aoyama 3, and Y. Iwaji 3
Speed-feedbak Diret-drive Control of a Low-speed Transverse Flux-type Motor with Large Number of Poles for Ship Propulsion Y. Yamamoto, T. Nakamura 2, Y. Takada, T. Koseki, Y. Aoyama 3, and Y. Iwaji 3
DIGITAL DISTANCE RELAYING SCHEME FOR PARALLEL TRANSMISSION LINES DURING INTER-CIRCUIT FAULTS
 CHAPTER 4 DIGITAL DISTANCE RELAYING SCHEME FOR PARALLEL TRANSMISSION LINES DURING INTER-CIRCUIT FAULTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Around the world, environmental and ost onsiousness are foring utilities to install
CHAPTER 4 DIGITAL DISTANCE RELAYING SCHEME FOR PARALLEL TRANSMISSION LINES DURING INTER-CIRCUIT FAULTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Around the world, environmental and ost onsiousness are foring utilities to install
Effect of magnetization process on levitation force between a superconducting. disk and a permanent magnet
 Effet of magnetization proess on levitation fore between a superonduting disk and a permanent magnet L. Liu, Y. Hou, C.Y. He, Z.X. Gao Department of Physis, State Key Laboratory for Artifiial Mirostruture
Effet of magnetization proess on levitation fore between a superonduting disk and a permanent magnet L. Liu, Y. Hou, C.Y. He, Z.X. Gao Department of Physis, State Key Laboratory for Artifiial Mirostruture
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 4 Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 4 Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 3 Failure Theories and Concrete Plasticity
 .54/.54 Mehanis and Design of Conrete trutures pring 4 Prof. Oral Buyukozturk Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Outline.54/.54 Mehanis and Design of Conrete trutures (--9) Outline Failure Theories and
.54/.54 Mehanis and Design of Conrete trutures pring 4 Prof. Oral Buyukozturk Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Outline.54/.54 Mehanis and Design of Conrete trutures (--9) Outline Failure Theories and
Dynamics of Structures. Giacomo Boffi. Definitions. Dynamics of Structures. Giacomo Boffi. Introduction. Characteristics of a Dynamical Problem
 An to Dipartiento di Ingegneria Civile e Abientale, Politenio di Milano Part I Marh 1, 014 Definitions Definitions Let s start with soe definitions Dynais the branh of ehanis onerned with the effets of
An to Dipartiento di Ingegneria Civile e Abientale, Politenio di Milano Part I Marh 1, 014 Definitions Definitions Let s start with soe definitions Dynais the branh of ehanis onerned with the effets of
Optimizing Single Sweep Range and Doppler Processing for FMCW Radar using Inverse Filtering
 Optiizing Single Sweep and Doppler Proessing for FMCW Radar using Inverse Filtering AJ de Jong and Ph van Dorp Oude Waalsdorperweg 63 2597 AK, Den Haag The Netherlands ajdejong@feltnonl ABSTRACT We disuss
Optiizing Single Sweep and Doppler Proessing for FMCW Radar using Inverse Filtering AJ de Jong and Ph van Dorp Oude Waalsdorperweg 63 2597 AK, Den Haag The Netherlands ajdejong@feltnonl ABSTRACT We disuss
The Gravitation As An Electric Effect
 The Gravitation As An Eletri Effet Hans-Jörg Hoheker Donaustr 30519 Hannover e-ail: johoer@yahoode Web-Site: http://wwwhohekereu Abstrat: The eletri fores are iensely great in oparison with the gravitational
The Gravitation As An Eletri Effet Hans-Jörg Hoheker Donaustr 30519 Hannover e-ail: johoer@yahoode Web-Site: http://wwwhohekereu Abstrat: The eletri fores are iensely great in oparison with the gravitational
Analytical Analysis and Numerical Prediction of Seven DOF Human Vibratory Model for the Various Cars Driving Posture Swami Mahesh, Kosbe Pradnya
 ISSN: - ISO 9:8 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Tehnology (IJEIT) Volue, Issue, May Analytial Analysis and Nuerial Predition of Seven DOF Huan Vibratory Model for the Various
ISSN: - ISO 9:8 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Tehnology (IJEIT) Volue, Issue, May Analytial Analysis and Nuerial Predition of Seven DOF Huan Vibratory Model for the Various
Evaluation of a Dual-Load Nondestructive Testing System To Better Discriminate Near-Surface Layer Moduli
 52 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1355 Evaluation of a Dual-Load Nondestrutive Testing System To Better Disriminate Near-Surfae Layer Moduli REYNALDO ROQUE, PEDRO ROMERO, AND BYRON E. RUTH Theoretial analyses
52 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1355 Evaluation of a Dual-Load Nondestrutive Testing System To Better Disriminate Near-Surfae Layer Moduli REYNALDO ROQUE, PEDRO ROMERO, AND BYRON E. RUTH Theoretial analyses
Optimal sliding mode control of the pendubot
 International Researh Journal of Coputer Siene and Inforation Systes (IRJCSIS Vol. ( pp. 45-5, April, Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjcsis Copyright International Researh Journals Full
International Researh Journal of Coputer Siene and Inforation Systes (IRJCSIS Vol. ( pp. 45-5, April, Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjcsis Copyright International Researh Journals Full
Part G-4: Sample Exams
 Part G-4: Sample Exams 1 Cairo University M.S.: Eletronis Cooling Faulty of Engineering Final Exam (Sample 1) Mehanial Power Engineering Dept. Time allowed 2 Hours Solve as muh as you an. 1. A heat sink
Part G-4: Sample Exams 1 Cairo University M.S.: Eletronis Cooling Faulty of Engineering Final Exam (Sample 1) Mehanial Power Engineering Dept. Time allowed 2 Hours Solve as muh as you an. 1. A heat sink
Balancing of a Variable Speed Rotary Compressor: Experimental and Numerical Investigations
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Copressor ngineering Conferene Shool of Mehanial ngineering 2 Balaning of a Variable Speed Rotary Copressor: xperiental and Nuerial Investigations F. Seve
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Copressor ngineering Conferene Shool of Mehanial ngineering 2 Balaning of a Variable Speed Rotary Copressor: xperiental and Nuerial Investigations F. Seve
Designing a Permanent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Element Method.
 Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Chapter 3. Problem Solutions
 Capter. Proble Solutions. A poton and a partile ave te sae wavelengt. Can anyting be said about ow teir linear oenta opare? About ow te poton's energy opares wit te partile's total energy? About ow te
Capter. Proble Solutions. A poton and a partile ave te sae wavelengt. Can anyting be said about ow teir linear oenta opare? About ow te poton's energy opares wit te partile's total energy? About ow te
Journal of Theoretics Vol.4-4
 Journal of Theoretis ol.4-4 Cherenko s Partiles as Magnetons Dipl. Ing. Andrija Radoić Nike Strugara 3a, 3 Beograd, Yugoslaia Eail: andrijar@eunet.yu Abstrat: The artile will show that the forula for Cherenko
Journal of Theoretis ol.4-4 Cherenko s Partiles as Magnetons Dipl. Ing. Andrija Radoić Nike Strugara 3a, 3 Beograd, Yugoslaia Eail: andrijar@eunet.yu Abstrat: The artile will show that the forula for Cherenko
"Research Note" ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF A FISSION CHAMBER DETECTOR USING MCNP4C AND SRIM MONTE CARLO CODES *
 Iranian Journal of Siene & Tehnology, Transation A, Vol. 33, o. A3 Printed in the Islami Republi of Iran, 9 Shiraz University "Researh ote" AALYSIS AD OPTIMIZATIO OF A FISSIO CHAMBER DETECTOR USIG MCP4C
Iranian Journal of Siene & Tehnology, Transation A, Vol. 33, o. A3 Printed in the Islami Republi of Iran, 9 Shiraz University "Researh ote" AALYSIS AD OPTIMIZATIO OF A FISSIO CHAMBER DETECTOR USIG MCP4C
Green s Function for Potential Field Extrapolation
 Green s Funtion for Potential Field Extrapolation. Soe Preliinaries on the Potential Magneti Field By definition, a potential agneti field is one for whih the eletri urrent density vanishes. That is, J
Green s Funtion for Potential Field Extrapolation. Soe Preliinaries on the Potential Magneti Field By definition, a potential agneti field is one for whih the eletri urrent density vanishes. That is, J
PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR PAP261 Introduction to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin)
 SPMS Physis Club PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR 009-0 PAP6 Introdution to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin) Question (a) - Three basi eleents required: avity, gain, and pup.
SPMS Physis Club PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR 009-0 PAP6 Introdution to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin) Question (a) - Three basi eleents required: avity, gain, and pup.
Advances in Radio Science
 Advanes in adio Siene 2003) 1: 99 104 Copernius GmbH 2003 Advanes in adio Siene A hybrid method ombining the FDTD and a time domain boundary-integral equation marhing-on-in-time algorithm A Beker and V
Advanes in adio Siene 2003) 1: 99 104 Copernius GmbH 2003 Advanes in adio Siene A hybrid method ombining the FDTD and a time domain boundary-integral equation marhing-on-in-time algorithm A Beker and V
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 006 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. ll rights reserved. Fourth E CHTER ure ECHNCS OF TERLS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit ECHNCS
006 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. ll rights reserved. Fourth E CHTER ure ECHNCS OF TERLS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit ECHNCS
Modeling of vibration systems
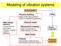 Modeling of vibration systes Atual syste Mae design deision Choose physial paraeters, hange or augent syste if neessary Physial odeling Mae siple approiations based on engineering judgeent Physial odel
Modeling of vibration systes Atual syste Mae design deision Choose physial paraeters, hange or augent syste if neessary Physial odeling Mae siple approiations based on engineering judgeent Physial odel
Evaluation of effect of blade internal modes on sensitivity of Advanced LIGO
 Evaluation of effet of blade internal modes on sensitivity of Advaned LIGO T0074-00-R Norna A Robertson 5 th Otober 00. Introdution The urrent model used to estimate the isolation ahieved by the quadruple
Evaluation of effet of blade internal modes on sensitivity of Advaned LIGO T0074-00-R Norna A Robertson 5 th Otober 00. Introdution The urrent model used to estimate the isolation ahieved by the quadruple
ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC STUDY OF LATERAL IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF PRESSURIZED PIPELINES AND INFLUENCE OF INTERNAL PRESSURE
 DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
Chapter 28 Special Relativity
 Galilean Relatiity Chapter 8 Speial Relatiity A passenger in an airplane throws a ball straight up. It appears to oe in a ertial path. The law of graity and equations of otion under unifor aeleration are
Galilean Relatiity Chapter 8 Speial Relatiity A passenger in an airplane throws a ball straight up. It appears to oe in a ertial path. The law of graity and equations of otion under unifor aeleration are
Developing Excel Macros for Solving Heat Diffusion Problems
 Session 50 Developing Exel Maros for Solving Heat Diffusion Problems N. N. Sarker and M. A. Ketkar Department of Engineering Tehnology Prairie View A&M University Prairie View, TX 77446 Abstrat This paper
Session 50 Developing Exel Maros for Solving Heat Diffusion Problems N. N. Sarker and M. A. Ketkar Department of Engineering Tehnology Prairie View A&M University Prairie View, TX 77446 Abstrat This paper
Active Magnetic Bearings for Frictionless Rotating Machineries
 Ative Magneti Bearings for Fritionless Rotating Mahineries Joga Dharma Setiawan Abstrat Ative magneti bearing (AMB systems an support a rotor without physial ontat and enable users to preisely ontrol rotor
Ative Magneti Bearings for Fritionless Rotating Mahineries Joga Dharma Setiawan Abstrat Ative magneti bearing (AMB systems an support a rotor without physial ontat and enable users to preisely ontrol rotor
Singular Event Detection
 Singular Event Detetion Rafael S. Garía Eletrial Engineering University of Puerto Rio at Mayagüez Rafael.Garia@ee.uprm.edu Faulty Mentor: S. Shankar Sastry Researh Supervisor: Jonathan Sprinkle Graduate
Singular Event Detetion Rafael S. Garía Eletrial Engineering University of Puerto Rio at Mayagüez Rafael.Garia@ee.uprm.edu Faulty Mentor: S. Shankar Sastry Researh Supervisor: Jonathan Sprinkle Graduate
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor
 1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
Chameleon mechanism. Lecture 2
 Chaeleon ehanis Leture Cosi aeleration Many independent data sets indiate that the expansion of the Universe is aelerating Siilar to preise tests of GR? Dark energy v Dark gravity Standard odel based on
Chaeleon ehanis Leture Cosi aeleration Many independent data sets indiate that the expansion of the Universe is aelerating Siilar to preise tests of GR? Dark energy v Dark gravity Standard odel based on
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 4, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume, No 4, 01 Copyright 010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing servies Researh artile ISSN 0976 4399 Strutural Modelling of Stability
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume, No 4, 01 Copyright 010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing servies Researh artile ISSN 0976 4399 Strutural Modelling of Stability
Method of removing Fe particulate matters from subway environments
 International Journal of Environmental onitoring and Analysis 5; 3(): -6 Published online Deember 3, 4 (http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ijema) doi:.648/j.ijema.53. ISSN: 38-7659 (Print); ISSN: 38-7667
International Journal of Environmental onitoring and Analysis 5; 3(): -6 Published online Deember 3, 4 (http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ijema) doi:.648/j.ijema.53. ISSN: 38-7659 (Print); ISSN: 38-7667
A NONLILEAR CONTROLLER FOR SHIP AUTOPILOTS
 Vietnam Journal of Mehanis, VAST, Vol. 4, No. (), pp. A NONLILEAR CONTROLLER FOR SHIP AUTOPILOTS Le Thanh Tung Hanoi University of Siene and Tehnology, Vietnam Abstrat. Conventional ship autopilots are
Vietnam Journal of Mehanis, VAST, Vol. 4, No. (), pp. A NONLILEAR CONTROLLER FOR SHIP AUTOPILOTS Le Thanh Tung Hanoi University of Siene and Tehnology, Vietnam Abstrat. Conventional ship autopilots are
Analysis of Leakage Paths Induced by Longitudinal Differential Settlement of the Shield-driven Tunneling
 2016 rd International Conferene on Engineering Tehnology and Appliation (ICETA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-8-0 Analysis of Leakage Paths Indued by Longitudinal Differential Settlement of the Shield-driven
2016 rd International Conferene on Engineering Tehnology and Appliation (ICETA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-8-0 Analysis of Leakage Paths Indued by Longitudinal Differential Settlement of the Shield-driven
ME357 Problem Set The wheel is a thin homogeneous disk that rolls without slip. sin. The wall moves with a specified motion x t. sin..
 ME357 Proble Set 3 Derive the equation(s) of otion for the systes shown using Newton s Method. For ultiple degree of freedo systes put you answer in atri for. Unless otherwise speified the degrees of freedo
ME357 Proble Set 3 Derive the equation(s) of otion for the systes shown using Newton s Method. For ultiple degree of freedo systes put you answer in atri for. Unless otherwise speified the degrees of freedo
(Newton s 2 nd Law for linear motion)
 PHYSICS 3 Final Exaination ( Deeber Tie liit 3 hours Answer all 6 questions You and an assistant are holding the (opposite ends of a long plank when oops! the butterfingered assistant drops his end If
PHYSICS 3 Final Exaination ( Deeber Tie liit 3 hours Answer all 6 questions You and an assistant are holding the (opposite ends of a long plank when oops! the butterfingered assistant drops his end If
Comparison of Deadtime Correction Factors for Passive Neutron Multiplicity Counting of Correlated and Non-Correlated Neutron Sources
 Coparison of Deadtie Corretion Fators for Passive Neutron Multipliity Counting of Correlated and Non-Correlated Neutron oures - 9298 L.G. Evans 1,. Croft 2, N. Menaa 2, P.I. Noran 1 1. hool of Physis and
Coparison of Deadtie Corretion Fators for Passive Neutron Multipliity Counting of Correlated and Non-Correlated Neutron oures - 9298 L.G. Evans 1,. Croft 2, N. Menaa 2, P.I. Noran 1 1. hool of Physis and
A Spatiotemporal Approach to Passive Sound Source Localization
 A Spatiotemporal Approah Passive Sound Soure Loalization Pasi Pertilä, Mikko Parviainen, Teemu Korhonen and Ari Visa Institute of Signal Proessing Tampere University of Tehnology, P.O.Box 553, FIN-330,
A Spatiotemporal Approah Passive Sound Soure Loalization Pasi Pertilä, Mikko Parviainen, Teemu Korhonen and Ari Visa Institute of Signal Proessing Tampere University of Tehnology, P.O.Box 553, FIN-330,
TAP 702-6: Binary stars
 TAP 702-6: Binary stars Orbiting binary stars: A type of ariable star. This type of ariable star onsists of two stars orbiting around eah other. When the dier star is in front of the brighter one, the
TAP 702-6: Binary stars Orbiting binary stars: A type of ariable star. This type of ariable star onsists of two stars orbiting around eah other. When the dier star is in front of the brighter one, the
Fiber Optic Cable Transmission Losses with Perturbation Effects
 Fiber Opti Cable Transmission Losses with Perturbation Effets Kampanat Namngam 1*, Preeha Yupapin 2 and Pakkinee Chitsakul 1 1 Department of Mathematis and Computer Siene, Faulty of Siene, King Mongkut
Fiber Opti Cable Transmission Losses with Perturbation Effets Kampanat Namngam 1*, Preeha Yupapin 2 and Pakkinee Chitsakul 1 1 Department of Mathematis and Computer Siene, Faulty of Siene, King Mongkut
Practical Convergence-Divergence Checks for Stresses from FEA
 Pratial Convergene-Divergene Cheks for Stresses fro FEA G.B. Sinlair Departent of Mehanial Engineering, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803 J.R. Beishei Developent Departent, ANSYS In., Canonsburg,
Pratial Convergene-Divergene Cheks for Stresses fro FEA G.B. Sinlair Departent of Mehanial Engineering, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803 J.R. Beishei Developent Departent, ANSYS In., Canonsburg,
Application of the Dyson-type boson mapping for low-lying electron excited states in molecules
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 05, 063I0 ( pages DOI: 0.093/ptep/ptv068 Appliation of the Dyson-type boson mapping for low-lying eletron exited states in moleules adao Ohkido, and Makoto Takahashi Teaher-training
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 05, 063I0 ( pages DOI: 0.093/ptep/ptv068 Appliation of the Dyson-type boson mapping for low-lying eletron exited states in moleules adao Ohkido, and Makoto Takahashi Teaher-training
Theoretical and Experimental Research on the Yoke of the Axial Piston Pumps
 Theoretial and Experimental Researh on the Yoke of the Axial Piston Pumps Vasiliu Niolae, P.E., Ph.D., Professor University "Politehnia" of Buharest, Fluid Power Department Rosu Cristian Adrian, M.E.,
Theoretial and Experimental Researh on the Yoke of the Axial Piston Pumps Vasiliu Niolae, P.E., Ph.D., Professor University "Politehnia" of Buharest, Fluid Power Department Rosu Cristian Adrian, M.E.,
Design of 25 KA Current Injection Transformer Core with Finite Element Method
 1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
Determination of Neutron Beam Diameter in 3 rd Horizontal Channel of Dalat Nuclear Reactor Nguyen AS 1*, Dang L 1 and Ho HT 2 1
 Deterination of Neutron Bea Diaeter in 3 rd Horizontal Channel of Dalat Nulear Reator Nguyen S 1*, Dang L 1 and Ho HT 1 Dalat University, 01 Phu Dong Thien Vuong, Dalat, Vietna Nulear Researh Institute,
Deterination of Neutron Bea Diaeter in 3 rd Horizontal Channel of Dalat Nulear Reator Nguyen S 1*, Dang L 1 and Ho HT 1 Dalat University, 01 Phu Dong Thien Vuong, Dalat, Vietna Nulear Researh Institute,
' ' , and z ' components ( u u u'
 Mesosale Meteorology: Gravity Waves 3 April 07 Introdution Here, we priarily onsider internal gravity waves, or waves that propagate in a density-stratified fluid (noinally, a stably-stratified fluid,
Mesosale Meteorology: Gravity Waves 3 April 07 Introdution Here, we priarily onsider internal gravity waves, or waves that propagate in a density-stratified fluid (noinally, a stably-stratified fluid,
FEATURE SELECTION BASED ON SURVIVAL CAUCHY-SCHWARTZ MUTUAL INFORMATION
 04 IEEE International Conferene on Aousti, peeh and ignal Proessing (ICAP FEATURE ELECTIO BAED O URVIVAL CAUCHY-CHWARTZ MUTUAL IFORMATIO Badong Chen, iaohan Yang, Hua Qu, Jihong Zhao, anning Zheng, Jose
04 IEEE International Conferene on Aousti, peeh and ignal Proessing (ICAP FEATURE ELECTIO BAED O URVIVAL CAUCHY-CHWARTZ MUTUAL IFORMATIO Badong Chen, iaohan Yang, Hua Qu, Jihong Zhao, anning Zheng, Jose
22.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 2004) Chapter 6 (2/24/04) Energy Transfer Kernel F(E E')
 22.54 Neutron Interations and Appliations (Spring 2004) Chapter 6 (2/24/04) Energy Transfer Kernel F(E E') Referenes -- J. R. Lamarsh, Introdution to Nulear Reator Theory (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1966),
22.54 Neutron Interations and Appliations (Spring 2004) Chapter 6 (2/24/04) Energy Transfer Kernel F(E E') Referenes -- J. R. Lamarsh, Introdution to Nulear Reator Theory (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1966),
Estimating Mutual Information Using Gaussian Mixture Model for Feature Ranking and Selection
 Estiating utual Inforation Using Gaussian ixture odel for Feature Ranking and Seletion Tian Lan, Deniz Erdogus, Uut Ozerte, Yonghong Huang Abstrat Feature seletion is a ritial step for pattern reognition
Estiating utual Inforation Using Gaussian ixture odel for Feature Ranking and Seletion Tian Lan, Deniz Erdogus, Uut Ozerte, Yonghong Huang Abstrat Feature seletion is a ritial step for pattern reognition
The Seesaw Mechanism
 The Seesaw ehanis By obert. Klauber www.quantufieldtheory.info 1 Bakground It ay see unusual to have suh low values for asses of neutrinos, when all other partiles like eletrons, quarks, et are uh heavier,
The Seesaw ehanis By obert. Klauber www.quantufieldtheory.info 1 Bakground It ay see unusual to have suh low values for asses of neutrinos, when all other partiles like eletrons, quarks, et are uh heavier,
Simplified Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Permanent Magnet Brushless Direct Current Motors for Sensorless Operation
 Amerian Journal of Applied Sienes 9 (7): 1046-1054, 2012 ISSN 1546-9239 2012 Siene Publiations Simplified Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Permanent Magnet Brushless Diret Current Motors for Sensorless
Amerian Journal of Applied Sienes 9 (7): 1046-1054, 2012 ISSN 1546-9239 2012 Siene Publiations Simplified Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Permanent Magnet Brushless Diret Current Motors for Sensorless
Intro Wb3303 Kineto-statics and Dynamics
 Wb333 Kineto-statis and Dynais 8 ineto-statis and Dynais...8. 8. Introdution...8. 8. Virtual wor and equilibriu equations (statis)...8.3 8.. General priniple...8.3 8.. Driving fores...8.5 8..3 Support
Wb333 Kineto-statis and Dynais 8 ineto-statis and Dynais...8. 8. Introdution...8. 8. Virtual wor and equilibriu equations (statis)...8.3 8.. General priniple...8.3 8.. Driving fores...8.5 8..3 Support
WRAP-AROUND GUSSET PLATES
 WRAP-AROUND GUSSET PLATES Where a horizontal brae is loated at a beam-to-olumn intersetion, the gusset plate must be ut out around the olumn as shown in Figure. These are alled wrap-around gusset plates.
WRAP-AROUND GUSSET PLATES Where a horizontal brae is loated at a beam-to-olumn intersetion, the gusset plate must be ut out around the olumn as shown in Figure. These are alled wrap-around gusset plates.
Crack Detection of Pipe Using Static Deflection Measurement Method
 International Journal of Engineering Researh & Tehnology (IJERT) ISSN: 78-08 Vol. 3 Issue, January - 04 Crak Detetion of Pipe Using Stati Defletion easurement ethod Jatin. Patel #, Prof. itesh J. ungla
International Journal of Engineering Researh & Tehnology (IJERT) ISSN: 78-08 Vol. 3 Issue, January - 04 Crak Detetion of Pipe Using Stati Defletion easurement ethod Jatin. Patel #, Prof. itesh J. ungla
THREE-DIMENSIONAL NON-LINEAR EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES
 HREE-DIMESIOAL O-LIEAR EARHQUAKE RESPOSE AALYSIS OF REIFORCED COCREE SRUCURES K. ishiura 1), K. akiguhi 2), and H. H. guen 3) 1) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Arhiteture and Building Engineering, oko Institute
HREE-DIMESIOAL O-LIEAR EARHQUAKE RESPOSE AALYSIS OF REIFORCED COCREE SRUCURES K. ishiura 1), K. akiguhi 2), and H. H. guen 3) 1) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Arhiteture and Building Engineering, oko Institute
Slenderness Effects for Concrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnification Method
 Slenderness Effets for Conrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnifiation Method Slender Conrete Column Design in Sway Frame Buildings Evaluate slenderness effet for olumns in a sway frame multistory
Slenderness Effets for Conrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnifiation Method Slender Conrete Column Design in Sway Frame Buildings Evaluate slenderness effet for olumns in a sway frame multistory
Failure Assessment Diagram Analysis of Creep Crack Initiation in 316H Stainless Steel
 Failure Assessment Diagram Analysis of Creep Crak Initiation in 316H Stainless Steel C. M. Davies *, N. P. O Dowd, D. W. Dean, K. M. Nikbin, R. A. Ainsworth Department of Mehanial Engineering, Imperial
Failure Assessment Diagram Analysis of Creep Crak Initiation in 316H Stainless Steel C. M. Davies *, N. P. O Dowd, D. W. Dean, K. M. Nikbin, R. A. Ainsworth Department of Mehanial Engineering, Imperial
Theory. Coupled Rooms
 Theory of Coupled Rooms For: nternal only Report No.: R/50/TCR Prepared by:. N. taey B.., MO Otober 00 .00 Objet.. The objet of this doument is present the theory alulations to estimate the reverberant
Theory of Coupled Rooms For: nternal only Report No.: R/50/TCR Prepared by:. N. taey B.., MO Otober 00 .00 Objet.. The objet of this doument is present the theory alulations to estimate the reverberant
Relationship between the number of labeled samples and classification accuracy based on sparse representation
 Relationship between the nuber of labeled saples and lassifiation auray based on sparse representation 1 Shool of Coputer Siene and Engineering, Beifang University for Nationalities,Yinhuan, 75001,China
Relationship between the nuber of labeled saples and lassifiation auray based on sparse representation 1 Shool of Coputer Siene and Engineering, Beifang University for Nationalities,Yinhuan, 75001,China
Simplified Buckling Analysis of Skeletal Structures
 Simplified Bukling Analysis of Skeletal Strutures B.A. Izzuddin 1 ABSRAC A simplified approah is proposed for bukling analysis of skeletal strutures, whih employs a rotational spring analogy for the formulation
Simplified Bukling Analysis of Skeletal Strutures B.A. Izzuddin 1 ABSRAC A simplified approah is proposed for bukling analysis of skeletal strutures, whih employs a rotational spring analogy for the formulation
An Adaptive Optimization Approach to Active Cancellation of Repeated Transient Vibration Disturbances
 An aptive Optimization Approah to Ative Canellation of Repeated Transient Vibration Disturbanes David L. Bowen RH Lyon Corp / Aenteh, 33 Moulton St., Cambridge, MA 138, U.S.A., owen@lyonorp.om J. Gregory
An aptive Optimization Approah to Ative Canellation of Repeated Transient Vibration Disturbanes David L. Bowen RH Lyon Corp / Aenteh, 33 Moulton St., Cambridge, MA 138, U.S.A., owen@lyonorp.om J. Gregory
Reference. R. K. Herz,
 Identifiation of CVD kinetis by the ethod of Koiyaa, et al. Coparison to 1D odel (2012) filenae: CVD_Koiyaa_1D_odel Koiyaa, et al. (1999) disussed ethods to identify the iportant steps in a CVD reation
Identifiation of CVD kinetis by the ethod of Koiyaa, et al. Coparison to 1D odel (2012) filenae: CVD_Koiyaa_1D_odel Koiyaa, et al. (1999) disussed ethods to identify the iportant steps in a CVD reation
Hankel Optimal Model Order Reduction 1
 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene 6.245: MULTIVARIABLE CONTROL SYSTEMS by A. Megretski Hankel Optimal Model Order Redution 1 This leture overs both
Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene 6.245: MULTIVARIABLE CONTROL SYSTEMS by A. Megretski Hankel Optimal Model Order Redution 1 This leture overs both
Four-dimensional equation of motion for viscous compressible substance with regard to the acceleration field, pressure field and dissipation field
 Four-dimensional equation of motion for visous ompressible substane with regard to the aeleration field, pressure field and dissipation field Sergey G. Fedosin PO box 6488, Sviazeva str. -79, Perm, Russia
Four-dimensional equation of motion for visous ompressible substane with regard to the aeleration field, pressure field and dissipation field Sergey G. Fedosin PO box 6488, Sviazeva str. -79, Perm, Russia
Stress triaxiality to evaluate the effective distance in the volumetric approach in fracture mechanics
 IOSR Journal of ehanial and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. IV (Nov- De. 014), PP 1-6 Stress triaxiality to evaluate the effetive distane in the volumetri
IOSR Journal of ehanial and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. IV (Nov- De. 014), PP 1-6 Stress triaxiality to evaluate the effetive distane in the volumetri
Measuring & Inducing Neural Activity Using Extracellular Fields I: Inverse systems approach
 Measuring & Induing Neural Ativity Using Extraellular Fields I: Inverse systems approah Keith Dillon Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr. La
Measuring & Induing Neural Ativity Using Extraellular Fields I: Inverse systems approah Keith Dillon Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr. La
FW Phys 130 G:\130 lecture\130 tests\formulas final03.docx page 1 of 7
 FW Phys 13 G:\13 leture\13 tests\forulas final3.dox page 1 of 7 dr dr r x y z ur ru (1.1) dt dt All onseratie fores derie fro a potential funtion U(x,y,z) (1.) U U U F gradu U,, x y z 1 MG 1 dr MG E K
FW Phys 13 G:\13 leture\13 tests\forulas final3.dox page 1 of 7 dr dr r x y z ur ru (1.1) dt dt All onseratie fores derie fro a potential funtion U(x,y,z) (1.) U U U F gradu U,, x y z 1 MG 1 dr MG E K
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction From The Faraday Acyclic Generator
 Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
