Hierarchy of pushdown graphs
|
|
|
- Griffin Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hierrchy o pushdown grphs Didier Cucl CNRS / LIGM University Pris- Est Frnce
2 The hierrchy o pushdown grphs recursive trnsition grphs Corresponding hierrchies o lnguges, terms, ordinls, ininite words higher order recursive schemes Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
3 Grphs lphet L o edge lels lphet C o vertex lels: colours Grph : G V L V C V on n rritrry countle set V o vertices Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
4 A hierrchy o grph milies 2002 Two sic grph opertions: unolding nd pth unctions Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
5 Unolding i i i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
6 Pth unctions set Exp o pth expressions C L {ε} Exp or ny u,v Exp pth s u, u v, u +, u, u v, u v Exp u G t or u Exp Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
7 s s s t or (s,,t) G c t or s = t (c,s) G ε t or s = t s u t or t u s s u v t or r (s s u+ t or s ( ) u + t s u t or (s s u v t or s u r r u t) u t s v t v t) For instnce s ε t mens tht s = t s Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
8 Pth unction h : L C Exp pplied y inverse on grph G h (G) = { (s,,t) s h() G h() t } { (c,s) s h(c) s } G c s t s h(c) Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
9 Inverse pth unction i i i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
10 Inverse pth unction c i c i c i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
11 Inverse pth unction c (i + not( )) c i i c i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
12 Inverse pth unction c d i (i + not( )) i + not( ) c c i i d i d i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
13 Inverse pth unction c i (i + not( )) c d d c d i i + not( ) Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
14 Unolding i c d c d c d c d c d c d c d c d c d c d c d Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
15 Inverse pth unction i Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
16 A hierrchy o grph milies Tree0 = mily o inite trees Grphn = Pth -1 (Treen) Treen+1 = Un(Grphn) Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
17 A hierrchy o grph milies Finite trees Pth Finite grphs Tree 0 Regulr trees Tree 1 Un Pth Un Grph 0 Equtionl grphs Grph 1 Algeric trees Tree 2 Pth Grph 2 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
18 VR-equtionl grphs Courcelle 1989 Sme hierrchy Pth unctions = regulr sustitutions Exp = set o regulr expressions or L ; u v, u +, u v or u,v Exp Pth = mondic interprettions Su-hierrchy o inite degree grphs Pth unctions = inite sustitutions Didier Cucl grph 1 = HR-equtionl grphs Courcelle 89 Pushdown grphs
19 Tree(g) or some integer mpping g i n g(0) g(n) n g(n) Tree(2 n ) Grph 2 Tree(n!), Tree(2 2n ) Grph 3 Tree(2 n) hierrchy Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
20 Genertors For ech level n ind genn Grphn such tht Grphn = Pth (genn) Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
21 Grph itertion Shelh, Stupp 1975 G Proposition with Knpik 2011 The itertion opertion preserves Grphn or ech n > 0 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
22 Tree-grph G Proposition Colcomet 04, Cryol, Wöhrle 03 TreeGrph(Grphn) Grphn+1 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
23 Theorem Muchnik 1984, Wlukiewicz 1996 The tree-grph opertion preserves the decidility o the mondic theory Corollry Courcelle Wlukiewicz 1998 The unolding opertion preserves the decidility o the mondic theory Corollry Didier Cucl Any grph o the hierrchy hs decidle mondic theory Pushdown grphs
24 Genertors Grphn+1 = Pth -1 (Un(Grphn Det CoDet)) = Pth -1 (genn+1) genn+1 Treen+1 Det Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
25 Tree genertor t level 1 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
26 Grph genertor t level Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
27 Tree genertor t level Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
28 Higher order pushdown utomt Theorem Cryol 2006 Grphn = ε-closure((pdn) Reg) = i Wi(Ui i Vi) pusdown hierrchy Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
29 Hierrchies o lnguges ordinls ininite words terms Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
30 A hierrchy o lnguges Finite grphs Trce Regulr lnguges Grph 0 Index 0 Equtionl grphs Trce Context ree lnguges Grph1 Index 1 Grph 2 Trce Indexed lnguges Index 2 Trce Level 2 indexed lnguges Grph 3 Index 3 Indexed lnguges Aho 1968 The hierrchy o indexed lnguges Mslov 1974 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
31 Proposition Mslov 1976 For ech n 0, the lnguge mily Indexn is closed under intersection y ny regulr lnguge inverse regulr sustitution Indexn sustitution Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
32 The hierrchy on ordinls Ordinl ω +1 : trnsitive closure o Theorem Brud 2009 For ech n, the ordinls in Grphn re the ordinls < ω (n+1) Grphω? ǫ 0? MSO? Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
33 The hierrchy on ininite words Equtionl grphs Ult. periodic words Grph 1 In 1 Grph2 Morphic words In 2 Grph 3 Morphic words t level 2 In 3 Level 2 morphic words: Chmpernowne numer The Liouville numer: 10 i! =, i 1 Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
34 Questions chrcterize morphic words t level 2 or α = 0,u with u In n nd n > 0 is α rtionl or trnscendentl numer? is 2 in the hierrchy? Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
35 The hierrchy on terms By irst order sustitutions Theorem 2002 Treen+1 Term = Sustn Courcelle, Knpik 2002 Sust0 = regulr terms Sustn+1 = Se,u (Sustn) Didier Cucl u word o distinct constnts e symol o rity u +1 Pushdown grphs
36 First order sustitution (evlution) unction e constnt word x y e y x y Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
37 Finite terms S e,u (e t 0 t 1... t n ) = S e,u (t 0 ) [S e,u (t 1 )/u(1),...,s e,u (t n )/u(n)] S e,u ( t 1... t m ) = S e,u (t 1 )...S e,u (t m ) Ininite terms S e,u (t) = sup n S e,u (t n Ω ) without Ω Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
38 The hierrchy on terms By higher order schemes Dmm 1982 Scheme t level 0 S R ; F F g S Solution R ω g g g Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
39 Scheme t level 1 Nivt 1975, Guessrin 1987, Courcelle 1990 R S F ; F x x F g Solution x R ω g g g Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
40 Scheme t level 2 F F S ; g R x G x F F : ( 0 0 ) 0 0 G Solution R ω x g g g Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
41 Sety condition: scope o vriles Dmm 1982 x 1 F Unse scheme x n No level( x i ) < level( s ) x i s R F S ; g G F x x F G Solution R ω g t n+2 = t t n n+1 x x t 2 Didier Cucl t 3 Pushdown grphs
42 Theorem 2002 Treen+1 Term = SeSchemen Knpik, Niwiński, Urzyczyn 2002 Any se scheme R t level n+1 is trnsormed into se scheme S t level n such tht R ω = Un(h (S ω ),r) or some pth unction h Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
43 Conjecture The non rtionl lgeric numers re not in the pushdown hierrchy Didier Cucl Pushdown grphs
The Caucal Hierarchy of Infinite Graphs in Terms of Logic and Higher-order Pushdown Automata
 The Cucl Hierrchy of Infinite Grphs in Terms of Logic nd Higher-order Pushdown Automt Arnud Cryol 1 nd Stefn Wöhrle 2 1 IRISA Rennes, Frnce rnud.cryol@iris.fr 2 Lehrstuhl für Informtik 7 RWTH Achen, Germny
The Cucl Hierrchy of Infinite Grphs in Terms of Logic nd Higher-order Pushdown Automt Arnud Cryol 1 nd Stefn Wöhrle 2 1 IRISA Rennes, Frnce rnud.cryol@iris.fr 2 Lehrstuhl für Informtik 7 RWTH Achen, Germny
More general families of infinite graphs
 More generl fmilies of infinite grphs Antoine Meyer Forml Methods Updte 2006 IIT Guwhti Prefix-recognizle grphs Theorem Let G e grph, the following sttements re equivlent: G is defined y reltions of the
More generl fmilies of infinite grphs Antoine Meyer Forml Methods Updte 2006 IIT Guwhti Prefix-recognizle grphs Theorem Let G e grph, the following sttements re equivlent: G is defined y reltions of the
On Rational Graphs. Christophe Morvan. IRISA, Campus de Beaulieu, Rennes, France
 On Rtionl Grphs Christophe Morvn IRISA, Cmpus de Beulieu, 35042 Rennes, Frnce christophe.morvn@iris.fr Astrct. Using rtionlity, like in lnguge theory, we define fmily of infinite grphs. This fmily is strict
On Rtionl Grphs Christophe Morvn IRISA, Cmpus de Beulieu, 35042 Rennes, Frnce christophe.morvn@iris.fr Astrct. Using rtionlity, like in lnguge theory, we define fmily of infinite grphs. This fmily is strict
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
Contextual graph grammars characterising Rational Graphs
 Contextul grph grmmrs chrcterising Rtionl Grphs Christophe Morvn To cite this version: Christophe Morvn. Contextul grph grmmrs chrcterising Rtionl Grphs. Henning Bordihn nd Rudolf Freund nd Mrkus Holzer
Contextul grph grmmrs chrcterising Rtionl Grphs Christophe Morvn To cite this version: Christophe Morvn. Contextul grph grmmrs chrcterising Rtionl Grphs. Henning Bordihn nd Rudolf Freund nd Mrkus Holzer
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tle of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lger, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tle of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lger, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers. Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
Coalgebra, Lecture 15: Equations for Deterministic Automata
 Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Model Checking and Functional Program Transformations
 Model Checking nd Functionl Progrm Trnsformtions Axel Hddd LIAFA (Université Pris Diderot / CNRS) LIGM (Université Pris Est / CNRS) Astrct We study model for recursive functionl progrms clled higher order
Model Checking nd Functionl Progrm Trnsformtions Axel Hddd LIAFA (Université Pris Diderot / CNRS) LIGM (Université Pris Est / CNRS) Astrct We study model for recursive functionl progrms clled higher order
a,b a 1 a 2 a 3 a,b 1 a,b a,b 2 3 a,b a,b a 2 a,b CS Determinisitic Finite Automata 1
 CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
Finite-State Automata: Recap
 Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
On Determinisation of History-Deterministic Automata.
 On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
Lecture 08: Feb. 08, 2019
 4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
ɛ-closure, Kleene s Theorem,
 DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Fundmentls of Computer Science Chpter 3: NFA nd DFA equivlence Regulr expressions Henrik Björklund Umeå University Jnury 23, 2014 NFA nd DFA equivlence As we shll see, it turns out tht NFA nd DFA re equivlent,
Fundmentls of Computer Science Chpter 3: NFA nd DFA equivlence Regulr expressions Henrik Björklund Umeå University Jnury 23, 2014 NFA nd DFA equivlence As we shll see, it turns out tht NFA nd DFA re equivlent,
First Midterm Examination
 Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Deterministic Finite Automata
 Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
CSE : Exam 3-ANSWERS, Spring 2011 Time: 50 minutes
 CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
Formal Languages and Automata
 Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Finite Automata-cont d
 Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term Dr. Dave Parker. Department of Computer Science University of Oxford
 Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Converting Regular Expressions to Discrete Finite Automata: A Tutorial
 Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Good-for-Games Automata versus Deterministic Automata.
 Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
First Midterm Examination
 24-25 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins or } 2) The following DFA recognizes the lnguge B over lphet
24-25 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins or } 2) The following DFA recognizes the lnguge B over lphet
NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 Algorithms & Models of Computtion CS/ECE 374, Fll 2017 NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Septemer 12, 2017 Sriel Hr-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fll 2017 1 / 31 Regulr Lnguges,
Algorithms & Models of Computtion CS/ECE 374, Fll 2017 NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Septemer 12, 2017 Sriel Hr-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fll 2017 1 / 31 Regulr Lnguges,
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Free groups, Lecture 2, part 1
 Free groups, Lecture 2, prt 1 Olg Khrlmpovich NYC, Sep. 2 1 / 22 Theorem Every sugroup H F of free group F is free. Given finite numer of genertors of H we cn compute its sis. 2 / 22 Schreir s grph The
Free groups, Lecture 2, prt 1 Olg Khrlmpovich NYC, Sep. 2 1 / 22 Theorem Every sugroup H F of free group F is free. Given finite numer of genertors of H we cn compute its sis. 2 / 22 Schreir s grph The
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES. 2.6 Finite State Automata With Output: Transducers
 80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
CONTEXT-SENSITIVE LANGUAGES, RATIONAL GRAPHS AND DETERMINISM
 Logicl Methods in Computer Science Vol. 2 (2:6) 2006, pp. 1 24 www.lmcs-online.org Sumitted Jn. 31, 2005 Pulished Jul. 19, 2006 CONTEXT-SENSITIVE LANGUAGES, RATIONAL GRAPHS AND DETERMINISM ARNAUD CARAYOL
Logicl Methods in Computer Science Vol. 2 (2:6) 2006, pp. 1 24 www.lmcs-online.org Sumitted Jn. 31, 2005 Pulished Jul. 19, 2006 CONTEXT-SENSITIVE LANGUAGES, RATIONAL GRAPHS AND DETERMINISM ARNAUD CARAYOL
Random subgroups of a free group
 Rndom sugroups of free group Frédérique Bssino LIPN - Lortoire d Informtique de Pris Nord, Université Pris 13 - CNRS Joint work with Armndo Mrtino, Cyril Nicud, Enric Ventur et Pscl Weil LIX My, 2015 Introduction
Rndom sugroups of free group Frédérique Bssino LIPN - Lortoire d Informtique de Pris Nord, Université Pris 13 - CNRS Joint work with Armndo Mrtino, Cyril Nicud, Enric Ventur et Pscl Weil LIX My, 2015 Introduction
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
Scanner. Specifying patterns. Specifying patterns. Operations on languages. A scanner must recognize the units of syntax Some parts are easy:
 Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. NFA for (a b)*abb.
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. Comparing DFAs and NFAs (cont.) Finite Automata 2
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Lexical Analysis Finite Automate
 Lexicl Anlysis Finite Automte CMPSC 470 Lecture 04 Topics: Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Nondeterministic Finite Automt (NFA) Regulr Expression NFA DFA A. Finite Automt (FA) FA re grph, like trnsition
Lexicl Anlysis Finite Automte CMPSC 470 Lecture 04 Topics: Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Nondeterministic Finite Automt (NFA) Regulr Expression NFA DFA A. Finite Automt (FA) FA re grph, like trnsition
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents. definitions, examples, designing, regular operations. Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
Marking shortest paths on pushdown graphs does not preserve MSO decidability
 Mrking shortest pths on pushdown grphs does not preserve MSO decidility Arnud Cryol, Olivier Serre To cite this version: Arnud Cryol, Olivier Serre Mrking shortest pths on pushdown grphs does not preserve
Mrking shortest pths on pushdown grphs does not preserve MSO decidility Arnud Cryol, Olivier Serre To cite this version: Arnud Cryol, Olivier Serre Mrking shortest pths on pushdown grphs does not preserve
Nondeterminism and Nodeterministic Automata
 Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Formal Language and Automata Theory (CS21004)
 Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Thoery of Automata CS402
 Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Revision Sheet. (a) Give a regular expression for each of the following languages:
 Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Harvard University Computer Science 121 Midterm October 23, 2012
 Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
A negative answer to a question of Wilke on varieties of!-languages
 A negtive nswer to question of Wilke on vrieties of!-lnguges Jen-Eric Pin () Astrct. In recent pper, Wilke sked whether the oolen comintions of!-lnguges of the form! L, for L in given +-vriety of lnguges,
A negtive nswer to question of Wilke on vrieties of!-lnguges Jen-Eric Pin () Astrct. In recent pper, Wilke sked whether the oolen comintions of!-lnguges of the form! L, for L in given +-vriety of lnguges,
NFA DFA Example 3 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs (cont.
 NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
Prefix-Free Regular-Expression Matching
 Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Kleene-*
 Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
CS 373, Spring Solutions to Mock midterm 1 (Based on first midterm in CS 273, Fall 2008.)
 CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
CSC 311 Theory of Computation
 CSC 11 Theory of Computtion Tutoril on DFAs, NFAs, regulr expressions, regulr grmmr, closure of regulr lnguges, context-free grmmrs, non-deterministic push-down utomt, Turing mchines,etc. Tutoril 2 Second
CSC 11 Theory of Computtion Tutoril on DFAs, NFAs, regulr expressions, regulr grmmr, closure of regulr lnguges, context-free grmmrs, non-deterministic push-down utomt, Turing mchines,etc. Tutoril 2 Second
Context-Free Grammars and Languages
 Context-Free Grmmrs nd Lnguges (Bsed on Hopcroft, Motwni nd Ullmn (2007) & Cohen (1997)) Introduction Consider n exmple sentence: A smll ct ets the fish English grmmr hs rules for constructing sentences;
Context-Free Grmmrs nd Lnguges (Bsed on Hopcroft, Motwni nd Ullmn (2007) & Cohen (1997)) Introduction Consider n exmple sentence: A smll ct ets the fish English grmmr hs rules for constructing sentences;
Algebra 2 Semester 1 Practice Final
 Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Formal languages, automata, and theory of computation
 Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
CS 267: Automated Verification. Lecture 8: Automata Theoretic Model Checking. Instructor: Tevfik Bultan
 CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
Table of contents: Lecture N Summary... 3 What does automata mean?... 3 Introduction to languages... 3 Alphabets... 3 Strings...
 Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
The Value 1 Problem for Probabilistic Automata
 The Vlue 1 Prolem for Proilistic Automt Bruxelles Nthnël Fijlkow LIAFA, Université Denis Diderot - Pris 7, Frnce Institute of Informtics, Wrsw University, Polnd nth@lif.univ-pris-diderot.fr June 20th,
The Vlue 1 Prolem for Proilistic Automt Bruxelles Nthnël Fijlkow LIAFA, Université Denis Diderot - Pris 7, Frnce Institute of Informtics, Wrsw University, Polnd nth@lif.univ-pris-diderot.fr June 20th,
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Let's start with an example:
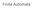 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journl o Inequlities in Pure nd Applied Mthemtics http://jipm.vu.edu.u/ Volume 6, Issue 4, Article 6, 2005 MROMORPHIC UNCTION THAT SHARS ON SMALL UNCTION WITH ITS DRIVATIV QINCAI ZHAN SCHOOL O INORMATION
Journl o Inequlities in Pure nd Applied Mthemtics http://jipm.vu.edu.u/ Volume 6, Issue 4, Article 6, 2005 MROMORPHIC UNCTION THAT SHARS ON SMALL UNCTION WITH ITS DRIVATIV QINCAI ZHAN SCHOOL O INORMATION
3 Regular expressions
 3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
CS 301. Lecture 04 Regular Expressions. Stephen Checkoway. January 29, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Java II Finite Automata I
 Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA
 DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
Software Engineering using Formal Methods
 Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
Lexical Analysis Part III
 Lexicl Anlysis Prt III Chpter 3: Finite Automt Slides dpted from : Roert vn Engelen, Florid Stte University Alex Aiken, Stnford University Design of Lexicl Anlyzer Genertor Trnslte regulr expressions to
Lexicl Anlysis Prt III Chpter 3: Finite Automt Slides dpted from : Roert vn Engelen, Florid Stte University Alex Aiken, Stnford University Design of Lexicl Anlyzer Genertor Trnslte regulr expressions to
BACHELOR THESIS Star height
 BACHELOR THESIS Tomáš Svood Str height Deprtment of Alger Supervisor of the chelor thesis: Study progrmme: Study rnch: doc. Štěpán Holu, Ph.D. Mthemtics Mthemticl Methods of Informtion Security Prgue 217
BACHELOR THESIS Tomáš Svood Str height Deprtment of Alger Supervisor of the chelor thesis: Study progrmme: Study rnch: doc. Štěpán Holu, Ph.D. Mthemtics Mthemticl Methods of Informtion Security Prgue 217
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems. Lecture #2 How to describe a hybrid system? Formal models for hybrid system
 Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Second Lecture: Basics of model-checking for finite and timed systems
 Second Lecture: Bsics of model-checking for finite nd timed systems Jen-Frnçois Rskin Université Lire de Bruxelles Belgium Artist2 Asin Summer School - Shnghi - July 28 Pln of the tlk Lelled trnsition
Second Lecture: Bsics of model-checking for finite nd timed systems Jen-Frnçois Rskin Université Lire de Bruxelles Belgium Artist2 Asin Summer School - Shnghi - July 28 Pln of the tlk Lelled trnsition
Introduction to ω-autamata
 Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring Regular Languages. Equivalences between Finite automata and REs. Haniel Barbosa
 CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
CS415 Compilers. Lexical Analysis and. These slides are based on slides copyrighted by Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Linda Torczon at Rice University
 CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
2. Lexical Analysis. Oscar Nierstrasz
 2. Lexicl Anlysis Oscr Nierstrsz Thnks to Jens Plserg nd Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse nd dpt the CS132 nd CS502 lecture notes. http://www.cs.ucl.edu/~plserg/ http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/
2. Lexicl Anlysis Oscr Nierstrsz Thnks to Jens Plserg nd Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse nd dpt the CS132 nd CS502 lecture notes. http://www.cs.ucl.edu/~plserg/ http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/
CS344: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 CS344: Introduction to Artiicil Intelligence Lecture: 22-23 Herbrnd s Theorem roving stisibilit o logic ormule using semntic trees rom Smbolic logic nd mechnicl theorem proving B Runk ilni Under the guidnce
CS344: Introduction to Artiicil Intelligence Lecture: 22-23 Herbrnd s Theorem roving stisibilit o logic ormule using semntic trees rom Smbolic logic nd mechnicl theorem proving B Runk ilni Under the guidnce
CS12N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Laboratory 2 Preparation
 CS2N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Lortory 2 Preprtion Ojectives:. Understnd the principle of sttic CMOS gte circuits 2. Build simple logic gtes from MOS trnsistors 3. Evlute these gtes
CS2N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Lortory 2 Preprtion Ojectives:. Understnd the principle of sttic CMOS gte circuits 2. Build simple logic gtes from MOS trnsistors 3. Evlute these gtes
1 From NFA to regular expression
 Note 1: How to convert DFA/NFA to regulr expression Version: 1.0 S/EE 374, Fll 2017 Septemer 11, 2017 In this note, we show tht ny DFA cn e converted into regulr expression. Our construction would work
Note 1: How to convert DFA/NFA to regulr expression Version: 1.0 S/EE 374, Fll 2017 Septemer 11, 2017 In this note, we show tht ny DFA cn e converted into regulr expression. Our construction would work
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
Running an NFA & the subset algorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fall 2018 gilray.org/classes/fall2018/cs350/
 Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
Regular Expressions for Muller Context-Free Languages
 ct Cyernetic 23 (2017) 349 369. Regulr Expressions for Muller Context-Free Lnguges Kitti Gelle nd zolcs ván strct Muller context-free lnguges (MCFLs) re lnguges of countle words, tht is, leled countle
ct Cyernetic 23 (2017) 349 369. Regulr Expressions for Muller Context-Free Lnguges Kitti Gelle nd zolcs ván strct Muller context-free lnguges (MCFLs) re lnguges of countle words, tht is, leled countle
Homework 4. 0 ε 0. (00) ε 0 ε 0 (00) (11) CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Prof. Marvin Nakayama
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
Model Reduction of Finite State Machines by Contraction
 Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
COMPOSITIONALITY AND REACHABILITY WITH CONDITIONS ON PATH LENGTHS
 compositionlity Interntionl Journl of Foundtions of Computer Science c World Scientific Pulishing Compny COMPOSITIONALITY AND REACHABILITY WITH CONDITIONS ON PATH LENGTHS INGO FELSCHER Lehrstuhl Informtik
compositionlity Interntionl Journl of Foundtions of Computer Science c World Scientific Pulishing Compny COMPOSITIONALITY AND REACHABILITY WITH CONDITIONS ON PATH LENGTHS INGO FELSCHER Lehrstuhl Informtik
CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Content pge Concept Mp 4. Integrtion of Algeric Functions 4 Eercise A 5 4. The Eqution of Curve from Functions of Grdients. 6 Ee
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM 5 MODULE 4 INTEGRATION CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Content pge Concept Mp 4. Integrtion of Algeric Functions 4 Eercise A 5 4. The Eqution of Curve from Functions of Grdients. 6 Eercise
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM 5 MODULE 4 INTEGRATION CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Content pge Concept Mp 4. Integrtion of Algeric Functions 4 Eercise A 5 4. The Eqution of Curve from Functions of Grdients. 6 Eercise
Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
Today s Topics Automata and Languages
 Tody s Topics Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn DFA to Regulr Expression GFNA DFAèGNFA GNFA è RE DFA è RE Exmples 2 DFA è RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA 3 Definition
Tody s Topics Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn DFA to Regulr Expression GFNA DFAèGNFA GNFA è RE DFA è RE Exmples 2 DFA è RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA 3 Definition
Automata and Languages
 Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Tody s Topics DFA to Regulr Expression GFNA DFAèGNFA GNFA è RE DFA è RE Exmples 2 DFA è RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA 3 Definition
Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Tody s Topics DFA to Regulr Expression GFNA DFAèGNFA GNFA è RE DFA è RE Exmples 2 DFA è RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA 3 Definition
Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and Distributions
 Chpter 6 Continuous Rndom Vriles nd Distriutions Mny economic nd usiness mesures such s sles investment consumption nd cost cn hve the continuous numericl vlues so tht they cn not e represented y discrete
Chpter 6 Continuous Rndom Vriles nd Distriutions Mny economic nd usiness mesures such s sles investment consumption nd cost cn hve the continuous numericl vlues so tht they cn not e represented y discrete
Lecture 9: LTL and Büchi Automata
 Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. DFAs, and NFAs, and Regexps (Oh my!)
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges DFAs, nd NFAs, nd Regexps (Oh my!) CMSC330 Spring 2018 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges DFAs, nd NFAs, nd Regexps (Oh my!) CMSC330 Spring 2018 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All
