First Midterm Examination
|
|
|
- Silvester Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 24-25 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins or } 2) The following DFA recognizes the lnguge B over lphet Σ = {, }. Descrie B verlly., q q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 q 6 3) Convert the following NFA to DFA:, q q 2 q 3 ε 4) For the regulr expression [ ( ) ], find n equivlent NFA. 5) Show tht the lnguge A = { 2n n+2 c n 2 n 2} is not regulr.
2 Answers ), 2) Contins t lest two s OR If it strts with zero, chnges symols t lest 3 times, if it strts with, chnges symols t lest 4 times. 3), q q 23
3 4) ε ε 5) Assume A is regulr. Let pumping length e p. Consider s = 2p p+2 c p 2 According to pumping lemm, we cn find x, y, z such tht s = xyz. We lso know tht xy p therefore y consists of s only. Suppose y = k. In this cse xy i z = 2p+ik p+2 c p 2 / A We hve contrdiction, so A is not regulr.
4 24-25 Fll Semester Second Midterm Exmintion ) Find context free grmmr tht recognizes the lnguge over Σ = {, } consisting of strings of odd length where first, middle nd lst symols re the sme. 2) Find PDA tht recognizes the lnguge { n m m > n}. 3) Consider the following lnguges over Σ = {,, c, d}: { n m c m d n } { n n c m d m } { n m c n d m } ) Which one is non-context free? ) Show tht it is not using pumping lemm. 4) Descrie Turing Mchine deciding the lnguge A = { n n2 n }. 5) Wht lnguge does the following Turing mchine recognize? Is it decider? (Input lphet is: Σ = {, }). Sweep from left to right. IF there is ny fter the first, REJECT. 2. Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, cross it. (Replce y ) ELSE, Go to Serch for. IF found, cross it. ELSE, REJECT. 4. Serch for. IF found, cross it. ELSE, REJECT. 5. Go to Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, ACCEPT. ELSE, REJECT.
5 Answers ) S A B A A A A A B B B B B OR S A B A CAC B CBC C 2), ε, ε ε, ε $ ε, ε ε ε, $ ε, ε ε, ε ε 3) ) { n m c n d m } ) Suppose the lnguge is context free. Let p e the pumping length. Choose s s s = n m c n d n where m, n > p. According to pumping lemm, we cn find v, y such tht n m c n d n = uvxyz If v or y contin more thn one type of symol, clerly uv 2 xy 2 z / A ecuse symols re out of order. Therefore v nd y cn consist of single symol only. In this cse, we hve two choices. v must consist of s nd y must consist of c s, or v must consist of s nd y must consist of d s. Both cses violte the rule vxy < p Therefore we cnnot pump this string so the lnguge is not context free.
6 4). Sweep from left to right. IF there is no, or no, or if they re out of order, REJECT. 2. Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, Mrk it. Move right until lnk. Write #. Go to 2. //Write s mny # s s there re s. 3. Serch for #. IF found Mrk it. Unmrk ll mrked s. Shuttle etween s nd s. Mrk one for ech one. IF is not found, Go to 3. IF is not found, REJECT. 4. ELSE (# not found) Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, REJECT. ELSE, ACCEPT. 5) It is decider, it cn not enter ny infinite loops. Its lnguge is: { n m m 2n + }.
7 24-25 Fll Semester Finl Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where w 2 nd the first two nd the lst two digits of w re identicl. For exmple: A, A ut / A, / A 2) Convert the following grmmr into Chomsky norml form: S AA A B B ε B A 3) Let A e the lnguge in {, } mde of strings where the numer of zeros is t lest 3 times the numer of ones. Descrie Turing Mchine recognizing A. 4) You re given set of n distinct positive integers. You wnt to determine if there re two integers p, q in the set such tht p = q 2. Write n lgorithm in pseudo-code for this prolem. Show tht it is in P. 5) Consider the following prolem: Given grph, is there wy to prtition the vertices into 4 susets such tht no two elements in suset re connected? Show tht this prolem is in NP.
8 Answers ) 2) First eliminte B A, then eliminte A ε nd then rek triples to otin: S Y A AY AC A XB Y D XA Y E Y Y B Y X C Y A D BY E AY X Y
9 3). Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, cross it. (Replce y ) ELSE, ACCEPT. 2. Repet 3 times: Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF found, cross it. (Replce y ) ELSE, REJECT. 3. Go to. 4) INPUT Integer A[], A[2],..., A[n] For i = to n For j = to n If A[i] A[i] == A[j] Return TRUE EndIf EndFor EndFor Return FALSE This lgorithm clerly does Θ(n 2 ) opertions, so it is in P. 5) Suppose there re n vertices. Then, there re t most n(n ) 2 = Θ(n 2 ) edges. We cn check given solution y checking ll edges one y one. (We will return FALSE if the two vertices connected y the edge elong to the sme suset) Therefore given solution cn e verified in Θ(n 2 ) opertions. The prolem is in NP.
10 Nme-Surnme:..24 ID Numer: CLASSWORK Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins ut does not contin }.,
11 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK Let: A = {Strings of length t lest 3 whose second nd third items re the sme} over lphet Σ = {, }. Give the stte digrm of the DFA tht recognizes this lnguge.,,,
12 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 2 Find regulr expression equivlent to the lnguge recognized y the following NFA: q q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 ( ) ( )
13 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 2 Find regulr expression equivlent to the lnguge recognized y the following NFA: q q 2 q 3 q 4 [ () ] ( ) ( )
14 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 3 ) Find PDA tht recognizes the lnguge { n 2 n+2 n } ) Find CFG generting the sme lnguge., ε, ε ε, ε $, ε, ε ε, $ ε S S 2 2
15 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 3 ) Find PDA tht recognizes the lnguge { n 2 c 3 d n n } ) Find CFG generting the sme lnguge., ε ε, ε $, ε ε, ε ε c, ε ε ε, $ ε c, ε ε c, ε ε d, ε S Sd 2 c 3
16 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 4 Use the pumping lemm to show tht the following lnguge is not context free: A = { n c 4n n n } Suppose A is context free. Let p e the pumping length. Choose s s s = p c 4p p. According to pumping lemm, we cn findv, y such tht p c 4p p = uvxyz If v or y contin or c, clerly uv 2 xy 2 z / A ecuse it is not in the given formt. Therefore v nd y cn consist of s only. But in this cse, we cn pump t most two of the prts including. The size of the third prt will remin the sme, so pumped string will not e in A. For exmple, v =, y = will result in uv 2 xy 2 z = p+ c 4p+4 p / A Therefore we cnnot pump this string nd A is not context free.
17 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 4 Use the pumping lemm to show tht the following lnguge is not context free: A = { n m c 2n d 2m m, n } Suppose A is context free. Let p e the pumping length. Choose s s s = n m c 2n d 2m nd n, m p. According to pumping lemm, we cn find v, y such tht n m c 2n d 2m = uvxyz If v or y contin more thn one type of symol, clerly uv 2 xy 2 z / A ecuse it is not in the given formt. Therefore v nd y cn consist of single symol only. If v consists of s, then y must consist of (twice s mny) c s. If v consists of s, then y must consist of (twice s mny) d s. In othe cses, vxy > p nd the third condition of pumping lemm is violted. Therefore we cnnot pump this string nd A is not context free.
18 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 5 Descrie Turing Mchine tht gives the output x m, x m,..., x 2, x for the input x, x 2,..., x m, x m.. Move to Strt. Find the first element tht is not crossed. Cll it. Cross it. If not found, Go To Move right until meeting lnk or cross. Move left. Red the element. Cll it. 3. Swp nd if they re different. Cross nd. Go To. 4. Sweep from left to right. Restore ll crossed elements. Return.
19 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 5 Descrie Turing Mchine tht gives the output x, x 2,..., x m, x, x 2,..., x m for the input x, x 2,..., x m.. Move to Strt. Find the first element tht is not crossed. Cross it. If not found, Go To Move right until meeting lnk. 3. Write the element found in. Cross it. Go To. 4. Sweep from left to right. Restore ll crossed elements. Return.
20 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 6 Let A e the lnguge in {, } mde of strings contining n equl numer of s nd s. Descrie Turing Mchine recognizing A. Is it decider?. Move hed to strt. Serch for. 2. IF there s, Cross it. Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF there is, Cross it. Go to. ELSE REJECT. 3. IF there s no, Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF there is, REJECT. ELSE ACCEPT. This mchine stops fter finitely mny steps, ecuse loops re repeted (t most) s mny times s the numer of symols in the input. It is decider.
21 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 6 Let B e the lnguge in {, } mde of strings contining more s thn s. Descrie Turing Mchine recognizing B. Is it decider?. Move hed to strt. Serch for. 2. IF there s, Cross it. Move hed to strt. Serch for. IF there is, Cross it. Go to. ELSE ACCEPT. 3. IF there s no, REJECT. This mchine stops fter finitely mny steps, ecuse loops re repeted (t most) s mny times s the numer of symols in the input. It is decider.
22 Nme-Surnme:.2.24 ID Numer: CLASSWORK 7 Let A e the set of ll 2 2 mtrices with entries from Q. Show tht A is countle. We know tht Q is countle. Suppose list of Q is {q, q 2,...}. We cn count Q Q y mking n infinite tle nd counting digonlly. Suppose we otin list S = {s, s 2,...}. Now mke tle for S S. The list will give elements of A = Q Q Q Q.
23 Nme-Surnme:.2.24 ID Numer: CLASSWORK 7 Let B e the set of ll finite strings sed on the lphet {,,..., 9}. Show tht B is countle. The following gives list of ll finite strings tht cn e written with this lphet: String
24 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 8 STRING MATCHING: You re given string of length n. You re lso given word ( second string) of length k, where k n. You wnt to determine if the word occurs in the string. Show tht the string mtching prolem is in P. INPUT String A[n], Word B[k] For i = to n k + test = TRUE For j = to k If A[i + j ] B[j] test = FALSE Brek EndIf EndFor If test == TRUE Return TRUE EndFor Return FALSE This lgorithm uses nk steps therefore it is Θ(n 2 ). So it is in P.
25 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 8 You re given n distinct positive integers where n 3. You wnt to find the third lrgest integer. Show tht this prolem is in P. INPUT A[n] For i = to 3 mx = A[] For j = 2 to n If A[j] > mx mx = A[j] index = j EndIf EndFor A[index] = EndFor Return mx This lgorithm uses 3n steps therefore it is Θ(n). So it is in P.
26 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 9 The SHORTEST PATH prolem is defined s follows: You re given weighted undirected grph G, nd nodes s nd t in the grph nd numer W. Is there pth from s to t with weight W? Show tht this prolem is in NP. A given solution contins n edges. We cn check ech edge in n steps if ech vertex hs its list of edges. Then we hve to check the sum. Therefore we do (n ) 2 +n opertions, so verifying lgorithm is Θ(n 2 ). This is polynomil, so the prolem is in NP.
27 Nme-Surnme: ID Numer: CLASSWORK 9 The MINIMUM SPANNING TREE prolem is defined s follows: You re given weighted undirected grph G nd numer W. Is there spnning tree with weight W? Show tht this prolem is in NP. A given solution contins Θ(n) edges. We cn check ech edge in Θ(n) steps if ech vertex hs its list of edges. (If we hve n unsorted list of edges, this will require n 2 opertions ut still, it is polynomil) Then we hve to check the sum nd lso we hve to check tht ll vertices re connected. Verifying lgorithm is Θ(n 2 ). This is polynomil, so the prolem is in NP. Prepred y: Dr. Emre Sermutlu (25)
First Midterm Examination
 Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Harvard University Computer Science 121 Midterm October 23, 2012
 Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Assignment 1 Automata, Languages, and Computability. 1 Finite State Automata and Regular Languages
 Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Name Ima Sample ASU ID
 Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
Formal languages, automata, and theory of computation
 Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Revision Sheet. (a) Give a regular expression for each of the following languages:
 Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Homework 4. 0 ε 0. (00) ε 0 ε 0 (00) (11) CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Prof. Marvin Nakayama
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
Worked out examples Finite Automata
 Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Talen en Automaten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, h45 17h30
 Tlen en Automten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, 2015 15h45 17h30 This test consists of four exercises over 5 pges. Explin your pproch, nd write your nswer to ech exercise on seprte pge. You cn score mximum of 100
Tlen en Automten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, 2015 15h45 17h30 This test consists of four exercises over 5 pges. Explin your pproch, nd write your nswer to ech exercise on seprte pge. You cn score mximum of 100
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tle of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lger, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tle of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lger, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Nondeterminism and Nodeterministic Automata
 Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Theory of Computation Regular Languages. (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall / 38
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Homework Solution - Set 5 Due: Friday 10/03/08
 CE 96 Introduction to the Theory of Computtion ll 2008 Homework olution - et 5 Due: ridy 10/0/08 1. Textook, Pge 86, Exercise 1.21. () 1 2 Add new strt stte nd finl stte. Mke originl finl stte non-finl.
CE 96 Introduction to the Theory of Computtion ll 2008 Homework olution - et 5 Due: ridy 10/0/08 1. Textook, Pge 86, Exercise 1.21. () 1 2 Add new strt stte nd finl stte. Mke originl finl stte non-finl.
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
Lecture 08: Feb. 08, 2019
 4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
NFA DFA Example 3 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs (cont.
 NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
Finite Automata-cont d
 Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
5. (±±) Λ = fw j w is string of even lengthg [ 00 = f11,00g 7. (11 [ 00)± Λ = fw j w egins with either 11 or 00g 8. (0 [ ffl)1 Λ = 01 Λ [ 1 Λ 9.
 Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
CS 373, Spring Solutions to Mock midterm 1 (Based on first midterm in CS 273, Fall 2008.)
 CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
Theory of Computation Regular Languages
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CS 301. Lecture 04 Regular Expressions. Stephen Checkoway. January 29, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
Lexical Analysis Finite Automate
 Lexicl Anlysis Finite Automte CMPSC 470 Lecture 04 Topics: Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Nondeterministic Finite Automt (NFA) Regulr Expression NFA DFA A. Finite Automt (FA) FA re grph, like trnsition
Lexicl Anlysis Finite Automte CMPSC 470 Lecture 04 Topics: Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Nondeterministic Finite Automt (NFA) Regulr Expression NFA DFA A. Finite Automt (FA) FA re grph, like trnsition
Scanner. Specifying patterns. Specifying patterns. Operations on languages. A scanner must recognize the units of syntax Some parts are easy:
 Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Regulr lnguges re closed under mny set opertions. Let L 1 nd L 2 e regulr lnguges. (1) L 1 L 2 (the union) is regulr. (2) L 1 L 2 (the conctention) is regulr. (3) L
Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Regulr lnguges re closed under mny set opertions. Let L 1 nd L 2 e regulr lnguges. (1) L 1 L 2 (the union) is regulr. (2) L 1 L 2 (the conctention) is regulr. (3) L
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER LANGUAGES AND COMPUTATION ANSWERS
 The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
1 From NFA to regular expression
 Note 1: How to convert DFA/NFA to regulr expression Version: 1.0 S/EE 374, Fll 2017 Septemer 11, 2017 In this note, we show tht ny DFA cn e converted into regulr expression. Our construction would work
Note 1: How to convert DFA/NFA to regulr expression Version: 1.0 S/EE 374, Fll 2017 Septemer 11, 2017 In this note, we show tht ny DFA cn e converted into regulr expression. Our construction would work
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
CS 311 Homework 3 due 16:30, Thursday, 14 th October 2010
 CS 311 Homework 3 due 16:30, Thursdy, 14 th Octoer 2010 Homework must e sumitted on pper, in clss. Question 1. [15 pts.; 5 pts. ech] Drw stte digrms for NFAs recognizing the following lnguges:. L = {w
CS 311 Homework 3 due 16:30, Thursdy, 14 th Octoer 2010 Homework must e sumitted on pper, in clss. Question 1. [15 pts.; 5 pts. ech] Drw stte digrms for NFAs recognizing the following lnguges:. L = {w
Regular Language. Nonregular Languages The Pumping Lemma. The pumping lemma. Regular Language. The pumping lemma. Infinitely long words 3/17/15
 Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Let's start with an example:
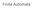 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
12.1 Nondeterminism Nondeterministic Finite Automata. a a b ε. CS125 Lecture 12 Fall 2014
 CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2014 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2014 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
1.4 Nonregular Languages
 74 1.4 Nonregulr Lnguges The number of forml lnguges over ny lphbet (= decision/recognition problems) is uncountble On the other hnd, the number of regulr expressions (= strings) is countble Hence, ll
74 1.4 Nonregulr Lnguges The number of forml lnguges over ny lphbet (= decision/recognition problems) is uncountble On the other hnd, the number of regulr expressions (= strings) is countble Hence, ll
CSC 311 Theory of Computation
 CSC 11 Theory of Computtion Tutoril on DFAs, NFAs, regulr expressions, regulr grmmr, closure of regulr lnguges, context-free grmmrs, non-deterministic push-down utomt, Turing mchines,etc. Tutoril 2 Second
CSC 11 Theory of Computtion Tutoril on DFAs, NFAs, regulr expressions, regulr grmmr, closure of regulr lnguges, context-free grmmrs, non-deterministic push-down utomt, Turing mchines,etc. Tutoril 2 Second
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Kleene s Theorem. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
CSE : Exam 3-ANSWERS, Spring 2011 Time: 50 minutes
 CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents. definitions, examples, designing, regular operations. Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Kleene-*
 Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
I. Theory of Automata II. Theory of Formal Languages III. Theory of Turing Machines
 CI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 16: Non-Context-Free Lnguges Chpter 16: Non-Context-Free Lnguges I. Theory of utomt II. Theory of Forml Lnguges III. Theory of Turing Mchines
CI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 16: Non-Context-Free Lnguges Chpter 16: Non-Context-Free Lnguges I. Theory of utomt II. Theory of Forml Lnguges III. Theory of Turing Mchines
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
For convenience, we rewrite m2 s m2 = m m m ; where m is repeted m times. Since xyz = m m m nd jxyj»m, we hve tht the string y is substring of the fir
 CSCI 2400 Models of Computtion, Section 3 Solutions to Homework 4 Problem 1. ll the solutions below refer to the Pumping Lemm of Theorem 4.8, pge 119. () L = f n b l k : k n + lg Let's ssume for contrdiction
CSCI 2400 Models of Computtion, Section 3 Solutions to Homework 4 Problem 1. ll the solutions below refer to the Pumping Lemm of Theorem 4.8, pge 119. () L = f n b l k : k n + lg Let's ssume for contrdiction
CSC 473 Automata, Grammars & Languages 11/9/10
 CSC 473 utomt, Grmmrs & Lnguges 11/9/10 utomt, Grmmrs nd Lnguges Discourse 06 Decidbility nd Undecidbility Decidble Problems for Regulr Lnguges Theorem 4.1: (embership/cceptnce Prob. for DFs) = {, w is
CSC 473 utomt, Grmmrs & Lnguges 11/9/10 utomt, Grmmrs nd Lnguges Discourse 06 Decidbility nd Undecidbility Decidble Problems for Regulr Lnguges Theorem 4.1: (embership/cceptnce Prob. for DFs) = {, w is
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
12.1 Nondeterminism Nondeterministic Finite Automata. a a b ε. CS125 Lecture 12 Fall 2016
 CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2016 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2016 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
Finite-State Automata: Recap
 Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Exercises Chapter 1. Exercise 1.1. Let Σ be an alphabet. Prove wv = w + v for all strings w and v.
 1 Exercises Chpter 1 Exercise 1.1. Let Σ e n lphet. Prove wv = w + v for ll strings w nd v. Prove # (wv) = # (w)+# (v) for every symol Σ nd every string w,v Σ. Exercise 1.2. Let w 1,w 2,...,w k e k strings,
1 Exercises Chpter 1 Exercise 1.1. Let Σ e n lphet. Prove wv = w + v for ll strings w nd v. Prove # (wv) = # (w)+# (v) for every symol Σ nd every string w,v Σ. Exercise 1.2. Let w 1,w 2,...,w k e k strings,
Coalgebra, Lecture 15: Equations for Deterministic Automata
 Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Formal Languages and Automata
 Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. NFA for (a b)*abb.
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Deterministic Finite Automata
 Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group.
![set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group. set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group.](/thumbs/78/78412113.jpg) Prolem 2.3: Which of the following collections of 2 2 mtrices with rel entries form groups under [ mtrix ] multipliction? i) Those of the form for which c d 2 Answer: The set of such mtrices is not closed
Prolem 2.3: Which of the following collections of 2 2 mtrices with rel entries form groups under [ mtrix ] multipliction? i) Those of the form for which c d 2 Answer: The set of such mtrices is not closed
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. Comparing DFAs and NFAs (cont.) Finite Automata 2
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models Dana Richards, George Mason University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
Table of contents: Lecture N Summary... 3 What does automata mean?... 3 Introduction to languages... 3 Alphabets... 3 Strings...
 Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
Tle of contents: Lecture N0.... 3 ummry... 3 Wht does utomt men?... 3 Introduction to lnguges... 3 Alphets... 3 trings... 3 Defining Lnguges... 4 Lecture N0. 2... 7 ummry... 7 Kleene tr Closure... 7 Recursive
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY. FLAC (15-453) - Spring L. Blum
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY THE PUMPING LEMMA FOR REGULAR LANGUAGES nd REGULAR EXPRESSIONS TUESDAY Jn 21 WHICH OF THESE ARE REGULAR? B = {0 n 1 n n 0} C = { w w hs equl numer of
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY THE PUMPING LEMMA FOR REGULAR LANGUAGES nd REGULAR EXPRESSIONS TUESDAY Jn 21 WHICH OF THESE ARE REGULAR? B = {0 n 1 n n 0} C = { w w hs equl numer of
SWEN 224 Formal Foundations of Programming WITH ANSWERS
 T E W H A R E W Ā N A N G A O T E Ū P O K O O T E I K A A M Ā U I VUW V I C T O R I A UNIVERSITY OF WELLINGTON Time Allowed: 3 Hours EXAMINATIONS 2011 END-OF-YEAR SWEN 224 Forml Foundtions of Progrmming
T E W H A R E W Ā N A N G A O T E Ū P O K O O T E I K A A M Ā U I VUW V I C T O R I A UNIVERSITY OF WELLINGTON Time Allowed: 3 Hours EXAMINATIONS 2011 END-OF-YEAR SWEN 224 Forml Foundtions of Progrmming
Automata and Languages
 Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES. 2.6 Finite State Automata With Output: Transducers
 80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
Thoery of Automata CS402
 Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Thoery of Automt C402 Theory of Automt Tle of contents: Lecture N0. 1... 4 ummry... 4 Wht does utomt men?... 4 Introduction to lnguges... 4 Alphets... 4 trings... 4 Defining Lnguges... 5 Lecture N0. 2...
Midterm 1 Practice. CS 350 Fall 2018 gilray.org/classes/fall2018/cs350/
 Midterm 1 Prctice CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/clsses/fll2018/cs350/ 1 Midterm #1: Thursdy, Septemer 27! Bring less stuff, if possile. Keep ny gs under the tle. You my hve out: pencil, pen, nd/or erser. My
Midterm 1 Prctice CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/clsses/fll2018/cs350/ 1 Midterm #1: Thursdy, Septemer 27! Bring less stuff, if possile. Keep ny gs under the tle. You my hve out: pencil, pen, nd/or erser. My
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata. Fall 2018 Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Compiler Design. Fall Lexical Analysis. Sample Exercises and Solutions. Prof. Pedro C. Diniz
 University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
3 Regular expressions
 3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
Languages & Automata
 Lnguges & Automt Dr. Lim Nughton Lnguges A lnguge is sed on n lphet which is finite set of smols such s {, } or {, } or {,..., z}. If Σ is n lphet, string over Σ is finite sequence of letters from Σ, (strings
Lnguges & Automt Dr. Lim Nughton Lnguges A lnguge is sed on n lphet which is finite set of smols such s {, } or {, } or {,..., z}. If Σ is n lphet, string over Σ is finite sequence of letters from Σ, (strings
FABER Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation
 DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
Converting Regular Expressions to Discrete Finite Automata: A Tutorial
 Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Parse trees, ambiguity, and Chomsky normal form
 Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) Anton Setzer (Bsed on book drft by J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) Anton Setzer (Bsed on book drft by J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CSCI FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 1 CSCI- 2200 FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Spring 2015 My 7, 2015 2 Announcements Homework 9 is due now. Some finl exm review problems will be posted on the web site tody. These re prcqce problems not
1 CSCI- 2200 FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Spring 2015 My 7, 2015 2 Announcements Homework 9 is due now. Some finl exm review problems will be posted on the web site tody. These re prcqce problems not
11.1 Finite Automata. CS125 Lecture 11 Fall Motivation: TMs without a tape: maybe we can at least fully understand such a simple model?
 CS125 Lecture 11 Fll 2016 11.1 Finite Automt Motivtion: TMs without tpe: mybe we cn t lest fully understnd such simple model? Algorithms (e.g. string mtching) Computing with very limited memory Forml verifiction
CS125 Lecture 11 Fll 2016 11.1 Finite Automt Motivtion: TMs without tpe: mybe we cn t lest fully understnd such simple model? Algorithms (e.g. string mtching) Computing with very limited memory Forml verifiction
Solutions Problem Set 2. Problem (a) Let M denote the DFA constructed by swapping the accept and non-accepting state in M.
 Solution Prolem Set 2 Prolem.4 () Let M denote the DFA contructed y wpping the ccept nd non-ccepting tte in M. For ny tring w B, w will e ccepted y M, tht i, fter conuming the tring w, M will e in n ccepting
Solution Prolem Set 2 Prolem.4 () Let M denote the DFA contructed y wpping the ccept nd non-ccepting tte in M. For ny tring w B, w will e ccepted y M, tht i, fter conuming the tring w, M will e in n ccepting
Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
CS415 Compilers. Lexical Analysis and. These slides are based on slides copyrighted by Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Linda Torczon at Rice University
 CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
Linear Inequalities. Work Sheet 1
 Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
1.3 Regular Expressions
 56 1.3 Regulr xpressions These hve n importnt role in describing ptterns in serching for strings in mny pplictions (e.g. wk, grep, Perl,...) All regulr expressions of lphbet re 1.Ønd re regulr expressions,
56 1.3 Regulr xpressions These hve n importnt role in describing ptterns in serching for strings in mny pplictions (e.g. wk, grep, Perl,...) All regulr expressions of lphbet re 1.Ønd re regulr expressions,
Context-Free Grammars and Languages
 Context-Free Grmmrs nd Lnguges (Bsed on Hopcroft, Motwni nd Ullmn (2007) & Cohen (1997)) Introduction Consider n exmple sentence: A smll ct ets the fish English grmmr hs rules for constructing sentences;
Context-Free Grmmrs nd Lnguges (Bsed on Hopcroft, Motwni nd Ullmn (2007) & Cohen (1997)) Introduction Consider n exmple sentence: A smll ct ets the fish English grmmr hs rules for constructing sentences;
Bases for Vector Spaces
 Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
State Minimization for DFAs
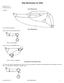 Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Transition Graphs. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Trnsition Grphs Chpter 6 Deprtment of Computer Science Relxing Restrints on Inputs We cn uild n FA tht ccepts only the word! 5 sttes ecuse n FA cn only process one letter t
CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Trnsition Grphs Chpter 6 Deprtment of Computer Science Relxing Restrints on Inputs We cn uild n FA tht ccepts only the word! 5 sttes ecuse n FA cn only process one letter t
Recursively Enumerable and Recursive. Languages
 Recursively Enumerble nd Recursive nguges 1 Recll Definition (clss 19.pdf) Definition 10.4, inz, 6 th, pge 279 et S be set of strings. An enumertion procedure for Turing Mchine tht genertes ll strings
Recursively Enumerble nd Recursive nguges 1 Recll Definition (clss 19.pdf) Definition 10.4, inz, 6 th, pge 279 et S be set of strings. An enumertion procedure for Turing Mchine tht genertes ll strings
Tutorial Automata and formal Languages
 Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
