Webreview cp physics ch 3 practice test (holt)
|
|
|
- Neil Strickland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Webreview cp physics ch 3 practice test (holt) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Identify the following quantities as scalar or vector: the mass of an object, the number of leaves on a tree, wind velocity. a. vector, scalar, scalar c. scalar, vector, scalar b. scalar, scalar, vector d. vector, scalar, vector 2. Multiplying or dividing vectors by scalars results in a. vectors. b. scalars. c. vectors if multiplied or scalars if divided. d. scalars if multiplied or vectors if divided. 3. A student walks from the door of the house to the end of the driveway and realizes that he missed the bus. The student runs back to the house, traveling three times as fast. Which of the following is the correct expression for the return velocity if the initial velocity is vstudent? a. 3vstudent c. 1 3 v student 1 b. 3 student d. 3vstudent 4. Which of the following is the best coordinate system to analyze a painter climbing a ladder at an angle of 60 to the ground? a. x-axis: horizontal along the ground; y-axis: along the ladder b. x-axis: along the ladder; y-axis: horizontal along the ground c. x-axis: horizontal along the ground; y-axis: up and down d. x-axis: along the ladder; y-axis: up and down 5. Find the resultant of these two vectors: units due east and units 30.0 north of west. a. 300 units, 29.8 north of west c. 546 units, 59.3 north of west b. 581 units, 20.1 north of east d. 248 units, 53.9 north of west 6. Which of the following is the motion of objects moving in two dimensions under the influence of gravity? a. horizontal velocity c. vertical velocity b. directrix d. projectile motion 7. A track star in the long jump goes into the jump at 12 m/s and launches herself at 20.0 above the horizontal. What is the magnitude of her horizontal displacement? (Assume no air resistance and that a y = g = 9.81 m/s 2.) a. 4.6 m c. 13 m b. 9.2 m d. 15 m 1
2 Name: ID: A Short Answer Problem The figure above shows the path of a ball tossed from a building. Air resistance is ignored. 8. In the figure above, what would happen to the width of the ball s path if it were launched with a greater velocity? 9. In the figure above, what would happen to the height of the ball s path if it were launched with a greater velocity? 10. In the figure above, what would happen to the height of the ball s path if it were launched with a lesser velocity? 11. In the figure above, what would happen to the width of the ball s path if it were launched with a lesser velocity? 12. Describe the graph of the horizontal component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. 13. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 14. Briefly explain why the true path of a projectile traveling through Earth s atmosphere is not a parabola. 15. A lightning bug flies at a velocity of 0.25 m/s due east toward another lightning bug seen off in the distance. A light easterly breeze blows on the bug at a velocity of 0.25 m/s. What is the resultant velocity of the lightning bug? 2
3 Name: ID: A 16. A jogger runs 10.0 blocks due east, 5.0 blocks due south, and another 2.0 blocks due east. Assume all blocks are of equal size. Use the graphical method to find the magnitude of the jogger s net displacement. 17. A cave explorer travels 3.0 m eastward, then 2.5 m northward, and finally 15.0 m westward. Use the graphical method to find the magnitude of the net displacement. 18. A quarterback takes the ball from the line of scrimmage and runs backward for m. He then runs sideways, parallel to the line of scrimmage, for 15 m. Next, he throws the ball forward m, perpendicular to the line of scrimmage. The receiver is tackled immediately. How far is the football displaced from its original position? 19. A duck waddles 2.5 m east and 6.0 m north. What are the magnitude and direction of the duck s displacement with respect to its original position? 20. While following directions on a treasure map, a person walks 45.0 m south, then turns and walks 7.50 m east. Which single straight-line displacement could the person have walked to reach the same spot? 21. Vector A is 3.2 m in length and points along the positive y-axis. Vector B is 4.6 m in length and points along a direction 195 counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. What is the magnitude of the resultant when vectors A and B are added? 22. A cow ambles through a break in the barnyard fence and wanders 24 m at 40.0 north of east, and then 13 m east. If the cow s wanderings last 3.0 minutes, what is the cow s average velocity? 23. An hockey puck travels 2.00 m at 10.0 east of south before ricocheting 2.50 m at 75.0 north of east. What is the puck s resultant displacement? 24. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an initial speed of 12 m/s. A stopwatch measures the stone s trajectory time from the top of the cliff to the bottom at 5.60 s. What is the height of the cliff? (Assume no air resistance and that a y = g = 9.81 m/s 2.) 3
4 Webreview cp physics ch 3 practice test (holt) Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. B 2. A 3. D 4. C 5. D 6. D 7. B SHORT ANSWER 8. The width of the ball s path would increase. 9. The height of the ball s path would increase. 10. The height of the ball s path would decrease. 11. The width of the ball s path would decrease. 12. The graph of the horizontal component of the velocity versus time is a straight line parallel to the time axis. 13. The graph of the vertical component of the velocity versus time is a straight line with a negative slope. The slope of the line is 9.81 m/s 2, which is g. 14. With air resistance, a projectile slows down as it collides with air particles. Therefore, the true path of a projectile would not be a parabola. PROBLEM m/s v 1 = 0.25 m/s east v 2 = 0.25 m/s west v R = v 1 v 2 = 0.25 m/s 0.25 m/s = 0.00 m/s blocks Students should use graphical techniques. Their answers can be checked using the techniques presented in Section 2. d = (12.0 blocks) 2 + (5.0 blocks) 2 = 13.0 blocks 1
5 m Students should use graphical techniques. Their answers can be checked using the techniques presented in Section 2. d = (12.0 m) 2 + (2.5 m) 2 = 12.2 m m Δx 1 = m Δy 1 = 15 m Δx 2 = m Δx tot = Δx 1 + Δx 2 = ( m) + ( m) = m Δy tot = Δy 1 = 15 m = (Δx tot ) 2 d = (Δx tot ) 2 = ( m) 2 + ( m) 2 = m m at 67 north of east = 2.5 m east = 6.0 m north Δx = = 2.5 m Δy = = 6.0 m = Δx 2 + Δy 2 d = Δx 2 + Δy 2 = (2.5 m) 2 + (6.0 m) 2 = 6.5 m Ê Δy ˆ Ê θ = tan m ˆ = tan Á Δx Á 2.5 m = 67 d = 6.5 m at 67 north of east 2
6 m at 80.5 south of east = 45.0 m south = 7.50 m east Δx = = 7.50 m Δy = = 45.0 m = Δx 2 + Δy 2 d = Δx 2 + Δy 2 = (7.50 m) 2 + (45.0 m) 2 = 45.6 m Ê Δy ˆ Ê θ = tan m ˆ = tan Á Δx Á 7.50 m = 80.5 d = 45.6 m at 80.5 south of east m = 3.2 m along +y-axis = 4.6 m at 195 counterclockwise from +x-axis = 3.2 m θ 1 = 0.0 = 4.6 m θ 2 = 195 Δx 1 = 0.0 m Δy 1 = 3.2 m Δx 2 = cosθ 2 = (4.6 m)(cos195 ) = 4.4 m Δy 2 = sinθ 2 = (4.6 m)(sin195 ) = 1.2 m Δx tot = Δx 1 + Δx 2 = (0 m) + ( 4.4 m) = 4.4 m Δy tot = Δy 1 + Δy 2 = (3.2 m) + ( 1.2 m) = 2.0 m = (Δx tot ) 2 d = (Δx tot ) 2 = ( 4.4 m) 2 + (2.0 m) 2 = 4.9 m 3
7 m/s, 26 north of east = 24 m θ 1 = 40.0 north of east = 13 m θ 2 = 0 east Δt = (3.0 min)(60 s/min) = 180 s Δx 1 = cosθ 1 = (24 m)(cos 40.0 ) = 18 m Δy 1 = sinθ 1 = (24 m)(sin 40.0 ) = 15 m Δx 2 = 13 m Δy 2 = 0 m Δx tot = Δx 1 + Δx 2 = 18 m + 13 m = 31 m Δy tot = Δy 1 + Δy 2 = 15 m + 0 m = 15 m d = (Δx tot ) 2 = (31 m) 2 + (15 m) 2 = 34 m θ = tan Δy Ê 1 tot 15 m ˆ = tan 1 Δx tot Á 31 m = 26 d = 34 m, 26 north of east v avg = d Δt = 34 m 180 s = 0.19 m/s vavg = 0.19 m/s, 26 north of east 4
8 m at 24 north of east = 2.00 m = 2.50 m θ 1 = 10.0 east of south θ 2 = 75.0 north of east Δx 1 = sinθ 1 = (2.00)(sin10.0 ) = m Δy 1 = cosθ 1 = (2.00 m)(cos10.0 ) = 1.97 m Δx 2 = cosθ 2 = (2.50 m)(cos75.0 ) = m Δy 2 = sinθ 2 = (2.50 m)(sin75.0 ) = 2.41 m Δx tot = Δx 1 + Δx 2 = m m = m Δy tot = Δy 1 + Δy 2 = 1.97 m m = 0.44 m d = (Δx tot ) 2 = (0.994 m) 2 + (0.44 m) 2 = 1.09 m Ê 0.44 m ˆ θ = tan 1 Á m = 24 d = 1.09 m at 24 north of east m v i = 12 m/s at 30.0 above the horizontal Δt = 5.60 s g = 9.81 m/s 2 v i, y = v i sinθ = (12 m/s)(sin30.0 ) = 6.0 m/s Δy = v i, y Δt a y (Δt) 2 = (6.0 m/s)(5.60 s) ( 9.81 m/s 2 )(5.60 s) 2 Δy = 34 m 154 m = 120 m h = 120 m 5
Name: Class: Date: Solution x 1 = units y 1 = 0. x 2 = d 2 cos = = tan 1 y
 Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
The Science of Physics
 Assessment The Science of Physics Chapter Test B MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. A hiker
Assessment The Science of Physics Chapter Test B MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. A hiker
F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example of projectile
Name: Class: Date: ID: A F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example of projectile
Vector Pretest. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Vector Pretest Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A word meaning size often used to describe scalar quantities is: a. magma.
Name: Class: Date: Vector Pretest Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A word meaning size often used to describe scalar quantities is: a. magma.
HOLT PHYSICS Test A Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
 Chapter 3 HOLT PHYSICS Test A Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors MULTIPLE CHOICE On the line at the left of each statement, write the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Chapter 3 HOLT PHYSICS Test A Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors MULTIPLE CHOICE On the line at the left of each statement, write the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
AP MIDTERM SAMPLE. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: B AP MIDTERM SAMPLE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The radius of Earth is 6 370 000 m. Express this measurement
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: B AP MIDTERM SAMPLE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The radius of Earth is 6 370 000 m. Express this measurement
3.2 Projectile Motion
 Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
Progressive Science Initiative. Click to go to website:
 Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Vocabulary Preview. Oct 21 9:53 AM. Projectile Motion. An object shot through the air is called a projectile.
 Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
b) (6) How far down the road did the car travel during the acceleration?
 General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
LAWS OF MOTION. Chapter Five MCQ I
 Chapter Five LAWS OF MOTION MCQ I 5. A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This means that (a) it is at rest. (b) the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform
Chapter Five LAWS OF MOTION MCQ I 5. A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This means that (a) it is at rest. (b) the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform
Full file at
 Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Kinematics and Dynamics
 AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
Review Session 1. Page 1
 Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion?
 Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
1. Less than before. 2. Greater than before. 3. No change. correct
 Version One Homework 3 Schemm 54321 Oct 22, 2004 1 This print-out should have 19 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. The due
Version One Homework 3 Schemm 54321 Oct 22, 2004 1 This print-out should have 19 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. The due
Physics Chapter 3 Notes. Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83)
 Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review
 Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
An object moves back and forth, as shown in the position-time graph. At which points is the velocity positive?
 1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014
 Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball.
 Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
PHYS.1410 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 2016 (version A)
 PHYS.1410 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 016 (version A) Recitation Section Number Name (PRINT) / LAST FIRST Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Fill out the above section of this page and print your last name
PHYS.1410 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 016 (version A) Recitation Section Number Name (PRINT) / LAST FIRST Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Fill out the above section of this page and print your last name
5 Projectile Motion. Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion.
 Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
Physics I Exam 1 Fall 2014 (version A)
 95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Fall 014 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (print) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Fall 014 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (print) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Bell Ringer. x- direction: Ball and car start with same position and velocity, a=0, so always have same position
 Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
1. (P2.1A) The picture below shows a ball rolling along a table at 1 second time intervals. What is the object s average velocity after 6 seconds?
 PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
2-D Kinematics. In general, we have the following 8 equations (4 per dimension): Notes Page 1 of 7
 2-D Kinematics The problem we run into with 1-D kinematics, is that well it s one dimensional. We will now study kinematics in two dimensions. Obviously the real world happens in three dimensions, but
2-D Kinematics The problem we run into with 1-D kinematics, is that well it s one dimensional. We will now study kinematics in two dimensions. Obviously the real world happens in three dimensions, but
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit:
 Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Physics Fall 2014 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. Physics is
Physics Fall 2014 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. Physics is
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
Chapter 3. Vectors. θ that the vector forms with i ˆ is 15. I. Vectors and Scalars
 Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Phys 2425: University Physics I Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 140 c. PHYS 45 d. PHYS 46 Survey Questions no points. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 140 c. PHYS 45 d. PHYS 46 Survey Questions no points. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of
PHY 1114: Physics I. Quick Question 1. Quick Question 2. Quick Question 3. Quick Question 4. Lecture 5: Motion in 2D
 PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B
 Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS. Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3
 INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley
 Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physical quantities can be categorized into one of two types of quantities A scalar is a physical quantity that has magnitude, but no direction A vector is a physical quantity
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physical quantities can be categorized into one of two types of quantities A scalar is a physical quantity that has magnitude, but no direction A vector is a physical quantity
10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0.
![10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. 10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0.](/thumbs/72/66768579.jpg) 10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have V 1 = (V 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. We find the direction from tan θ 1 = V 1y /V
10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have V 1 = (V 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. We find the direction from tan θ 1 = V 1y /V
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Bill s ball goes up and comes back down to Bill s level. At that point, it is
 ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium
 Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems
 Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
A. Basic Concepts and Graphs
 A. Basic Concepts and Graphs A01 [Qual] [Easy] For each of the following, select if it is a vector or a scalar. a) Speed b) Distance traveled c) Velocity d) (Linear) Displacement A02 [Qual] [Easy] Give
A. Basic Concepts and Graphs A01 [Qual] [Easy] For each of the following, select if it is a vector or a scalar. a) Speed b) Distance traveled c) Velocity d) (Linear) Displacement A02 [Qual] [Easy] Give
1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below.
 Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Version PREVIEW Vectors & 2D Chap. 3 sizemore (13756) 1
 Version PREVIEW Vectors & 2D Chap. 3 sizemore (13756) 1 This print-out should have 73 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Rectangular
Version PREVIEW Vectors & 2D Chap. 3 sizemore (13756) 1 This print-out should have 73 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Rectangular
A+B. Scalar quantities are described by magnitude only (examples: distance, speed, temperature, energy, and mass).
 Honors Physics Examination I Review Questions #1-#11 - Vectors & Measurements vector quantity is specified by magnitude and direction (examples: displacement, velocity, acceleration, momentum, and weight).
Honors Physics Examination I Review Questions #1-#11 - Vectors & Measurements vector quantity is specified by magnitude and direction (examples: displacement, velocity, acceleration, momentum, and weight).
In 1-D, all we needed was x. For 2-D motion, we'll need a displacement vector made up of two components: r = r x + r y + r z
 D Kinematics 1. Introduction 1. Vectors. Independence of Motion 3. Independence of Motion 4. x-y motions. Projectile Motion 3. Relative motion Introduction Using + or signs was ok in 1 dimension but is
D Kinematics 1. Introduction 1. Vectors. Independence of Motion 3. Independence of Motion 4. x-y motions. Projectile Motion 3. Relative motion Introduction Using + or signs was ok in 1 dimension but is
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration
 Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions. Examples: non-linear motion (circles, planetary orbits, etc.) flight of projectiles (shells, golf balls, etc.
 Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 018 Time: 90 minutes NAME: Solutions STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 018 Time: 90 minutes NAME: Solutions STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
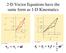 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review
 AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
3 TWO-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS
 Chapter 3 Two-Dimensional Kinematics 95 3 TWO-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Figure 3.1 Everyday motion that we experience is, thankfully, rarely as tortuous as a rollercoaster ride like this the Dragon Khan in
Chapter 3 Two-Dimensional Kinematics 95 3 TWO-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Figure 3.1 Everyday motion that we experience is, thankfully, rarely as tortuous as a rollercoaster ride like this the Dragon Khan in
Exam 2--PHYS 101--F17
 Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
Name: Exam 2--PHYS 0--F7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A ball is thrown in the air at an angle of 30 to the ground, with an initial speed
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16)
 Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style
 Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Chapter 3 Homework Packet. Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Multiple Choice Practice
 Class: Date: Multiple Choice Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An ice skater moving at 10.0 m/s coasts to a halt in 1.0 10 2 m on
Class: Date: Multiple Choice Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An ice skater moving at 10.0 m/s coasts to a halt in 1.0 10 2 m on
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: Section Number:
 Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: Formulae are provided on the last page. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: Formulae are provided on the last page. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences
 PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME:
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
Vectors in Physics. Topics to review:
 Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Midterm Prep. 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?
 Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
Circular motion. Announcements:
 Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2)
 AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
LAHS Physics Semester 1 Final Practice Multiple Choice
 LAHS Physics Semester 1 Final Practice Multiple Choice The following Multiple Choice problems are practice MC for the final. Some or none of these problems may appear on the real exam. Answers are provided
LAHS Physics Semester 1 Final Practice Multiple Choice The following Multiple Choice problems are practice MC for the final. Some or none of these problems may appear on the real exam. Answers are provided
Projectile motion. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/20/14. Identify examples of projectile motion.
 Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
PHYS 211 Exam 1 - Practice Test Solutions
 PHYS Exam - Practice Test Solutions A Although the numbers on the graphs don t exactly fit with wh they should actually be, the ptern or structure of the graph is wh we should be looking. So, based on
PHYS Exam - Practice Test Solutions A Although the numbers on the graphs don t exactly fit with wh they should actually be, the ptern or structure of the graph is wh we should be looking. So, based on
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
Name: Class: Date: Fall 2012 Physics Quiz 4--Introduction to Forces
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Fall 2012 Physics Quiz 4--Introduction to Forces Please do not write on these pages. MC: 1pt each + FR 6pt each = 50 points possible. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Fall 2012 Physics Quiz 4--Introduction to Forces Please do not write on these pages. MC: 1pt each + FR 6pt each = 50 points possible. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects
 v (m/s) a (m/s^2) 1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects So far, we have only looked at objects moving in a horizontal dimension. Today, we ll look at objects moving in the vertical. Then, we ll look at both
v (m/s) a (m/s^2) 1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects So far, we have only looked at objects moving in a horizontal dimension. Today, we ll look at objects moving in the vertical. Then, we ll look at both
STRAIGHT-LINE MOTION UNDER CONSTANT ACCELERATION
 STRAIGHT-LINE MOTION UNDER CONSTANT ACCELERATION Problems involving a body moving in a straight line under constant acceleration have five relevant variables: u = Initial velocity in m/s v = Final velocity
STRAIGHT-LINE MOTION UNDER CONSTANT ACCELERATION Problems involving a body moving in a straight line under constant acceleration have five relevant variables: u = Initial velocity in m/s v = Final velocity
First few slides are additional review problems from Chs. 1 and 2. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 First few slides are additional review problems from Chs. 1 and 2 Average Speed A person travels by car from one city to another with different constant speeds between pairs of cities. She drives for 35
First few slides are additional review problems from Chs. 1 and 2 Average Speed A person travels by car from one city to another with different constant speeds between pairs of cities. She drives for 35
