Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors
|
|
|
- Nicholas Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors
2 Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction are all that is needed. You do need to be careful about the signs, as the figure indicates. The resultant vector is the vector sum of the two vectors being added
3 If the motion is in two dimensions, the situation is somewhat more complicated. Here, the actual travel paths are at right angles to one another; we can find the displacement by using the Pythagorean Theorem. The angle can be found by using trig. D tanθ = 2 D 1
4 Adding the vectors in the opposite order gives the same result:
5 The relationship on the previous slide (see below), is generally called a vector equation or relationship. The vectors D D R = D 1 + D 1 and D 2 were added using the tip to tail or 2 head to tail method to form a D R vector diagram (on left). The D 2 resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the D 1 head of the final vector. In the previous example, to find the magnitude of the vector, the Pythagorean theorem could be used because the vector diagram is a right angled triangle. What happens if the two vectors being added are not at right angles?
6 If two vectors being added are not at right angles it takes the Cosine and Sine laws to solve for resultant vector. For example, in the situation below. The lengths of the triangle are related to the magnitude of the vectors, and the angles can give direction. The relationship d 3 = d 1 + d 2, has a θ corresponding vector diagram. Cosine and Sine Laws: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2abcosC A c B b a C sin A a = sin B b d 1 = sinc c d 3 d 2
7 Here is another example of vectors being added graphically by using the tail-to-tip or Head to tail method. In this case we are adding 3 vectors rather than the usual two. The vector relationship is: V R = V 1 + V 2 + V 3
8 Other points about vectors The direction of a 2-d vector is usually given by an angle relative to the x or y axis Another way to indicate direction is by using bearings format. One uses N,S,E, and W, and indicated by making reference to these directions. A 2-D vector is generally represented by a positive magnitude (no such thing as a negative magnitude for vectors) and a direction. W N S y E x
9 Example 1: Solution: 5 km, 37 0 N of E.
10 Example 2: A hiker walked 9.00 km 30 0 W of N at 3.00 km/h, then walked 16.0 km 20 0 N of W at 2.00 km/h. a) What was his final position (displacement)? b) What was the duration of the trip? c) Calculate his average speed and average velocity over the entire trip.
11 a) First define your position vectors and state a vector relationship: Solution: d = 9.00 km W of N = km d2 N of W d 3 =? d 3 = d 1 + d 2 Now draw the vector diagram: d 2 Using cosine law: d 32 = (9)(16)cos(140 0 ) = d 3 = 23.6 km d 3 And using sine law: sinθ 16 = sin(140) θ = Finally, d 3 = 23.6 km W of N 20 0 d ϴ
12 b) t= 9/3 + 16/2 = 2 + 8= 11 h c) Average speed = (total distance travelled)/ time = 25 km/ 11 h= 2.27 km/h Average velocity = (change in displacement)/ time υ = 2.15 km/h W of N = 23.6 km/ 11 h= 2.15 km/h Notes: The average velocity is a vector, so it has a direction. It shares the same direction as the net change in position (displacement) vector. When adding vectors head to tail it is useful to draw the dotted axis lines (see dotted blue lines on previous slide). This helps to determine the angles in the vector diagram. Normally you should give the final direction of a vector relative to the x or y axis.
13 Adding Vectors by Components Any vector can be expressed as the sum of two other vectors, which are called its components. Usually the other vectors are chosen so that they are perpendicular to each other (x and y component vectors).
14 If the components are perpendicular, they can be found using trigonometric functions.
15 The components are effectively one-dimensional, so they can be added arithmetically:
16 In summary, if the the vector relationship were: V = V 1 + V 2 Then, V x = V 1x + V 2 x and V y = V 1y + V 2 y The x component of vector is equal to sum of the x components of the other two vectors. A similar statement could be made about the y components. V
17 Adding Vectors by Components Adding vectors: 1. Draw a diagram; add the vectors graphically. 2. Choose x and y axes. 3. Resolve each vector into x and y components. 4. Calculate each component using sines and cosines. 5. Add the components in each direction. 6. To find the length and direction of the vector, use:
18 Example 3: In this example we will use the same vectors added in example 1 (slide 10) but add using components. d = 9.00 km W of N, = 16.0 km d2 N of W. Find d3 where: d 3 = d 1 + d 2 Solution: 1) First find the components of both vectors d 2 d 1x 30 0 d 1y d 2y x d 2x d 1 d 1x = -(9)(sin30)= -4.5 d 1y = (9)(cos30)=7.794 d 2x = -(16)(cos20)= d 2y = (16)(sin20)= d 3x =d 1x +d 2x = km d 3y =d 1y +d 2y = km 3) Add the x and y components of d 3 (head to tail) to find its magnitude and direction: d 3 = ( ) 2 + (13.267) 2 = 23.6 km d y +x tan -1 (13.267/ ) = ) Find the components of d 3
19 Subtraction of Vectors, and Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar In order to subtract vectors, we define the negative of a vector, which has the same magnitude but points in the opposite direction. Then we add (Tail to Tip method) the negative vector:
20 Subtraction of Vectors, and Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar A vector V can be multiplied by a scalar c; the result is a vector cv that has the same direction but a magnitude cv. If c is negative, the resultant vector points in the opposite direction.
21 A vector subtraction can be written as an addition. For instance perhaps one is interested in finding, where: d 3 d 3 = d 2 d 1 One could rewrite the vector relationship as: d 3 = d 2 + ( d 1 ) Realizing that d 1 is in the opposite direction to. One can just add d 2 and d 1 head to tail to find d3. d1 Yet another option is to add d 1 to both sides of the original vector relationship which gives: d1 + d 3 = d 2 I have done a fully worked example on a vector subtraction looking at the above options and by using components to do the subtraction. Please see Vector Subtraction example.. in the notes section. If you use any of these techniques please follow the method I have demonstrated. A common time to perform a vector subtraction could be in the following: relative velocities, change in velocity, and change in momentum.
22 Projectile Motion(2-D) A projectile is an object moving in two dimensions under the influence of Earth's gravity; its path is a parabola.
23 It can be understood by analyzing the horizontal and vertical motions separately.
24 The speed in the x-direction is constant; in the y- direction the object moves with constant acceleration g. This photograph shows two balls that start to fall at the same time. The one on the right has an initial speed in the x-direction. It can be seen that vertical positions of the two balls are identical at identical times, while the horizontal position of the yellow ball increases linearly.
25 If an object is launched at an initial angle of θ 0 with the horizontal, the analysis is similar except that the initial velocity has a vertical component.
26 Solving Problems Involving Projectile Motion Projectile motion is motion with constant acceleration in two dimensions, where the acceleration is g and is down.
27 1. Read the problem carefully, and choose the object(s) you are going to analyze. 2. Draw a diagram. 3. Choose an origin and a coordinate system. 4. Decide on the time interval; this is the same in both directions, and includes only the time the object is moving with constant acceleration g. 5. Examine the x and y motions separately.
28 6. List known and unknown quantities. Remember that v x never changes, and that v y = 0 at the highest point. 7. Plan how you will proceed. Use the appropriate equations; you may have to combine some of them.
29 Projectile Motion Is Parabolic In order to demonstrate that projectile motion is parabolic, we need to write y as a function of x. When we do, we find that it has the form: This is indeed the equation for a parabola.
30 Relative Velocities Velocities like anything else are measured relative to the observer. The motion of an object will (could) have a different velocity relative to an observer in different reference frame. To state a velocity there is a certain useful notation where the object and frame are indicated. A common reference frame is the ground frame (g). This is the reference frame where one is stationary relative to earth when making an observation. For example if one said the velocity of object A was 10.0 m/s north one could write: υ A/g = 10 m/s North The observer (in the ground frame) observed the velocity to be 10 m/s north.
31 1-D Relative Velocities One can gain an understanding of the mathematical process of determining relative velocities by examining the 1- d case. Example: a) Object A is travelling to the right at 2.00 m/s and object B is travelling to the left at 3.00 m/s. What is object A s velocity relative to object B ( V A/B )? Or in other words if you were an observer on object B, what velocity would you measure object A s to be? Let the positive x direction be to the right. +x Answer: One can see intuitively it would be 5.00 m/s in the positive x direction Answer: On can see it would be m/s A v A/g = 2.00 m/s v B/g = 3.00 m/s b) What is object B s velocity relative to object A ( V B/A )? B
32 In the previous example what vector operation was applied? One can see that there was a vector subtraction. In part a) one was trying find the object A s velocity relative to object B. One in effect wishes to put object B at rest (subtract B s velocity). The vector operation for a) is: VA/B = V A/g V B/g = 3-(-2) = 5 m/s In part b) one is trying to find object B s velocity relative A. Therefore, V B/A = V B/g V A/g = -3-2 = -5 m/s Example: Object A was travelling left at 7.00 m/s and object B was also travelling left at 3.00 m/s. What is the velocity of object B relative to A? Solution: V B/A = V B/g V A/g = -3-(-7) = 4 m/s +x The same mathematical rules apply to relative velocities in two dimensions.
33 A cool problem which is much more easily answered using relative velocities. Two trains (initially 40 km apart) approach each other on a collision course. One train is travels east at 20 km/h while the other travels west at 45 km/h. Meanwhile a fly left the front of one train and travels back and forth from the fronts of both trains until the the trains collide. If the fly travels with an average speed of 50 km/h, what total distance would the fly travel? Solution: Use relative velocities to determine the elapsed time till the trains collide. t= distance/velocity = 40 km/ 65 km/h = h The distance the fly travelled: vt= (50 km/h)( h) = 31 Km
34 2-D Relative Velocities Example: A Boeing 747 has a velocity of 650 km/h north, while a Cessna 172 has a velocity of 250 km/h east. What is the velocity of the Boeing relative to the Cessna? 1) Define your vectors and state a vector relationship first 2) Construct a vector diagram 3) Solve triangle for desired vector. Solution V A/g = 650 km/h N V B/g = 250 km/h E V B/g = 250 km/h W V A/B =? Construct the vector diagram: v B/g = 250 Km/h V A/B = V A/g V B/g V A/B = [ ] 0.5 or = 696 km/h V A/B = V A/g + ( V B/g ) v A/B v A/g = 650 km/h Θ= tan -1 [250/650]= One could have use vector components to complete the vector subtraction and find the same result.
35 In the previous example the original vector relationship could be restated as follows V A/B = V A/g V B/g VB/g + V A/B = V Adding V B/g to both A/g sides gives: Vector relationship A Vector relationship B The vector diagram based on this vector relationship (B) is give by: v A/B Solving this vector triangle will give the same result as on the previous slide. v A/g = 650 km/h The subscript notation that has been introduced can be used to verify the vector relationship: v = 250 Km/h B/g Examining the subscripts of relationship A (subtraction means divide subscripts): A B = A g B g Examining the subscripts of relationship B (addition means B A = A g B g multiply subscripts): One can see that the left hand side equals the right hand side in each case, verifying our relationships are set up correctly according to our definitions of relative velocities.
36 Example: A boat travels at m/s in still water. It aims directly across a river (800 m wide). There is a river current of 7.50 m/s to the left. The river will inevitably carry the boat downstream. a) State the vector relationship relating the vectors: the boat s velocity relative to the water v b/w, the water s velocity relative to ground v w/g, and the boat s velocity relative to the shore (ground) v b/g 800 m b) Sketch the vector diagram relating the three vectors. c) Determine the boats velocity relative to the shore. v b/g d) How long does it take the boat to reach the other side of the river? e) At what angle should the boat aim upstream in order to move straight across the river (relative to shore)? What is the velocity of the boat relative to the shore in this case? Redraw the vector diagram. f) How long will the boat take to cross the river in this latter case?
37 Solution: v b/w a) v w/g v =? b/g 1 st List what you know about the vectors = m/s straight across = 7.50 m/s left v b/w + v w/g = b/g 2 nd State the vector relationship: v 800 m v w/g v b/g b) v b/w c) v b/g = (7.50) 2 + (11.11) 2 = 13.4 m/s θ = tan = d) t= (800 m)/( m/s) = 72.0 s 3 rd Sketch the vector diagram according to the relationship. e) v w/g v b/w = m/s?(direction unknown) v w/g = 7.50 m/s left v b/g =? (direction straight across) f) t= (800 m/ m/s) = 97.6 s v b/g v b/w v b/g = (11.11) 2 (7.50) 2 = 8.20 m/s θ = sin =
38 Some additional points: An object s water speed or air (wind) speed, is by definition, the magnitude of the velocity of the object relative to the water or the air. In the previous example the vector diagrams were convenient right angled triangles. This is a special case. Often one would have to solve using cosine and sine laws, or use components to find the vector in question.
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Units of Chapter 3 Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Subtraction of Vectors, and Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Adding Vectors
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Units of Chapter 3 Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Subtraction of Vectors, and Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Adding Vectors
9/29/2014. Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors. 3-1 Vectors and Scalars. Contents of Chapter Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed
 Chapter 6 - Vectors Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed Vector Quantities - express magnitude and direction. ie. velocity 80 km/h, 58 displacement 10 km (E) acceleration
Chapter 6 - Vectors Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed Vector Quantities - express magnitude and direction. ie. velocity 80 km/h, 58 displacement 10 km (E) acceleration
Chapter 3. Vectors. θ that the vector forms with i ˆ is 15. I. Vectors and Scalars
 Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Objectives and Essential Questions
 VECTORS Objectives and Essential Questions Objectives Distinguish between basic trigonometric functions (SOH CAH TOA) Distinguish between vector and scalar quantities Add vectors using graphical and analytical
VECTORS Objectives and Essential Questions Objectives Distinguish between basic trigonometric functions (SOH CAH TOA) Distinguish between vector and scalar quantities Add vectors using graphical and analytical
Physics Chapter 3 Notes. Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83)
 Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Physics Chapter 3 Notes Section 3-1: Introduction to Vectors (pages 80-83) We can use vectors to indicate both the magnitude of a quantity, and the direction. Vectors are often used in 2- dimensional problems.
Vector components and motion
 Vector components and motion Objectives Distinguish between vectors and scalars and give examples of each. Use vector diagrams to interpret the relationships among vector quantities such as force and acceleration.
Vector components and motion Objectives Distinguish between vectors and scalars and give examples of each. Use vector diagrams to interpret the relationships among vector quantities such as force and acceleration.
Name: Class: Date: Solution x 1 = units y 1 = 0. x 2 = d 2 cos = = tan 1 y
 Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Student Exploration: Vectors
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
Vectors and 2D Kinematics. AIT AP Physics C
 Vectors and 2D Kinematics Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels
Vectors and 2D Kinematics Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product. reading assignment read chap 3
 New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
Chapter 3. Vectors and. Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review
 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size) and
Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size) and
Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration
 Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Vectors. Chapter 3. Arithmetic. Resultant. Drawing Vectors. Sometimes objects have two velocities! Sometimes direction matters!
 Vectors Chapter 3 Vector and Vector Addition Sometimes direction matters! (vector) Force Velocity Momentum Sometimes it doesn t! (scalar) Mass Speed Time Arithmetic Arithmetic works for scalars. 2 apples
Vectors Chapter 3 Vector and Vector Addition Sometimes direction matters! (vector) Force Velocity Momentum Sometimes it doesn t! (scalar) Mass Speed Time Arithmetic Arithmetic works for scalars. 2 apples
A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units.
 Vectors and Scalars A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units. Scalar Example Speed Distance Age Heat Number
Vectors and Scalars A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units. Scalar Example Speed Distance Age Heat Number
Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review
 Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
What is Relative Motion
 RELATIVE MOTION What is Relative Motion Strictly speaking all motion is relative to something. Usually that something is a reference point that is assumed to be at rest (i.e. the earth). Motion can be
RELATIVE MOTION What is Relative Motion Strictly speaking all motion is relative to something. Usually that something is a reference point that is assumed to be at rest (i.e. the earth). Motion can be
4/13/2015. I. Vectors and Scalars. II. Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods. a. Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods
 I. Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocity, force, momentum A scalar has only a magnitude. Some scalar quantities: mass, time, temperature
I. Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocity, force, momentum A scalar has only a magnitude. Some scalar quantities: mass, time, temperature
Unit 1: Math Toolbox Math Review Guiding Light #1
 Unit 1: Math Toolbox Math Review Guiding Light #1 Academic Physics Unit 1: Math Toolbox Math Review Guiding Light #1 Table of Contents Topic Slides Algebra Review 2 8 Trigonometry Review 9 16 Scalar &
Unit 1: Math Toolbox Math Review Guiding Light #1 Academic Physics Unit 1: Math Toolbox Math Review Guiding Light #1 Table of Contents Topic Slides Algebra Review 2 8 Trigonometry Review 9 16 Scalar &
UNIT V: Multi-Dimensional Kinematics and Dynamics Page 1
 UNIT V: Multi-Dimensional Kinematics and Dynamics Page 1 UNIT V: Multi-Dimensional Kinematics and Dynamics As we have already discussed, the study of the rules of nature (a.k.a. Physics) involves both
UNIT V: Multi-Dimensional Kinematics and Dynamics Page 1 UNIT V: Multi-Dimensional Kinematics and Dynamics As we have already discussed, the study of the rules of nature (a.k.a. Physics) involves both
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
Chapter 3: Vectors and Projectile Motion Vectors and Scalars You might remember from math class the term vector. We define a vector as something with both magnitude and direction. For example, 15 meters/second
3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion
 May 25, 1998 3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion Kinematics of a Particle Moving in a Plane Motion in two dimensions is easily comprehended if one thinks of the motion as being made up of two independent
May 25, 1998 3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion Kinematics of a Particle Moving in a Plane Motion in two dimensions is easily comprehended if one thinks of the motion as being made up of two independent
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31. Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.
 Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods
 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Displacement can be determined graphically using a scale map, such as this one of the Hawaiian Islands. A journey from Hawai i to
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Displacement can be determined graphically using a scale map, such as this one of the Hawaiian Islands. A journey from Hawai i to
Chapter 2 A Mathematical Toolbox
 Chapter 2 Mathematical Toolbox Vectors and Scalars 1) Scalars have only a magnitude (numerical value) Denoted by a symbol, a 2) Vectors have a magnitude and direction Denoted by a bold symbol (), or symbol
Chapter 2 Mathematical Toolbox Vectors and Scalars 1) Scalars have only a magnitude (numerical value) Denoted by a symbol, a 2) Vectors have a magnitude and direction Denoted by a bold symbol (), or symbol
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium
 Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Vectors in Physics. Topics to review:
 Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball.
 Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley
 Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physical quantities can be categorized into one of two types of quantities A scalar is a physical quantity that has magnitude, but no direction A vector is a physical quantity
Physics 1-2 Mr. Chumbley Physical quantities can be categorized into one of two types of quantities A scalar is a physical quantity that has magnitude, but no direction A vector is a physical quantity
CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPONENTS DESCRIBE MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS
 CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPOETS DESCRIBE MOTIO I TWO DIMESIOS 2.1 Vector Methods in One Dimension Vectors may be pictured with sketches in which arrows represent quantities such as displacement, force and velocity.
CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPOETS DESCRIBE MOTIO I TWO DIMESIOS 2.1 Vector Methods in One Dimension Vectors may be pictured with sketches in which arrows represent quantities such as displacement, force and velocity.
Kinematics in Two-Dimensions
 Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 Kinematics in Two-Dimensions www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 92 How to Use this File Each topic is composed of brief direct instruction There are formative assessment questions after
Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 Kinematics in Two-Dimensions www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 92 How to Use this File Each topic is composed of brief direct instruction There are formative assessment questions after
Newton 3 & Vectors. Action/Reaction. You Can OnlyTouch as Hard as You Are Touched 9/7/2009
 Newton 3 & Vectors Action/Reaction When you lean against a wall, you exert a force on the wall. The wall simultaneously exerts an equal and opposite force on you. You Can OnlyTouch as Hard as You Are Touched
Newton 3 & Vectors Action/Reaction When you lean against a wall, you exert a force on the wall. The wall simultaneously exerts an equal and opposite force on you. You Can OnlyTouch as Hard as You Are Touched
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics
 Review: Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Description of motion in one dimension Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Review: Motion with Constant Acceleration Free fall: constant acceleration g =
Review: Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Description of motion in one dimension Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Review: Motion with Constant Acceleration Free fall: constant acceleration g =
Introduction to vectors
 Lecture 4 Introduction to vectors Course website: http://facult.uml.edu/andri_danlov/teaching/phsicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danlov2013/phsics1fall.html 95.141, Fall 2013, Lecture 3 Outline
Lecture 4 Introduction to vectors Course website: http://facult.uml.edu/andri_danlov/teaching/phsicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danlov2013/phsics1fall.html 95.141, Fall 2013, Lecture 3 Outline
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit:
 Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS
 AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes
 Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
b) (6) How far down the road did the car travel during the acceleration?
 General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
General Physics I Quiz 2 - Ch. 2-1D Kinematics June 17, 2009 Name: For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, all the essential steps, and results with correct units
Unit IV: Introduction to Vector Analysis
 Unit IV: Introduction to Vector nalysis s you learned in the last unit, there is a difference between speed and velocity. Speed is an example of a scalar: a quantity that has only magnitude. Velocity is
Unit IV: Introduction to Vector nalysis s you learned in the last unit, there is a difference between speed and velocity. Speed is an example of a scalar: a quantity that has only magnitude. Velocity is
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension
 Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
Kinematics. Vector solutions. Vectors
 Kinematics Study of motion Accelerated vs unaccelerated motion Translational vs Rotational motion Vector solutions required for problems of 2- directional motion Vector solutions Possible solution sets
Kinematics Study of motion Accelerated vs unaccelerated motion Translational vs Rotational motion Vector solutions required for problems of 2- directional motion Vector solutions Possible solution sets
Graphical Vector Addition
 Vectors Chapter 4 Vectors and Scalars Measured quantities can be of two types Scalar quantities: only require magnitude (and proper unit) for description. Examples: distance, speed, mass, temperature,
Vectors Chapter 4 Vectors and Scalars Measured quantities can be of two types Scalar quantities: only require magnitude (and proper unit) for description. Examples: distance, speed, mass, temperature,
Describing motion: Kinematics in two dimension
 Describing motion: Kinematics in two dimension Scientist Galileo Galilei Issac Newton Vocabulary Vector scalars Resultant Displacement Components Resolving vectors Unit vector into its components Average
Describing motion: Kinematics in two dimension Scientist Galileo Galilei Issac Newton Vocabulary Vector scalars Resultant Displacement Components Resolving vectors Unit vector into its components Average
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Notes: Vectors and Scalars
 A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
Chapter 3 Homework Packet. Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE
 (Section 6.3: Vectors in the Plane) 6.18 SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE Assume a, b, c, and d are real numbers. PART A: INTRO A scalar has magnitude but not direction. We think of real numbers as scalars,
(Section 6.3: Vectors in the Plane) 6.18 SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE Assume a, b, c, and d are real numbers. PART A: INTRO A scalar has magnitude but not direction. We think of real numbers as scalars,
ISSUED BY K V - DOWNLOADED FROM KINEMATICS
 KINEMATICS *rest and Motion are relative terms, nobody can exist in a state of absolute rest or of absolute motion. *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion
KINEMATICS *rest and Motion are relative terms, nobody can exist in a state of absolute rest or of absolute motion. *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion
Vectors and Scalars. Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction.
 Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
Vectors and Scalars Scalar: A quantity specified by its magnitude only Vector: A quantity specified both by its magnitude and direction. To distinguish a vector from a scalar quantity, it is usually written
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998)
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Vectors A Guideline For Motion
 AP Physics-1 Vectors A Guideline For Motion Introduction: You deal with scalar quantities in many aspects of your everyday activities. For example, you know that 2 liters plus 2 liters is 4 liters. The
AP Physics-1 Vectors A Guideline For Motion Introduction: You deal with scalar quantities in many aspects of your everyday activities. For example, you know that 2 liters plus 2 liters is 4 liters. The
Significant Figures & Vectors
 You have to complete this reading Booklet before you attempt the Substantive Assignment. Significant Figures Significant Figures & Vectors There are two kinds of numbers in the world Exact: o Example:
You have to complete this reading Booklet before you attempt the Substantive Assignment. Significant Figures Significant Figures & Vectors There are two kinds of numbers in the world Exact: o Example:
Need to have some new mathematical techniques to do this: however you may need to revise your basic trigonometry. Basic Trigonometry
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions Kinematics in 2-dimensions. By the end of this you will 1. Remember your Trigonometry 2. Know how to handle vectors 3. be able to handle problems in 2-dimensions 4. understand
Kinematics in Two Dimensions Kinematics in 2-dimensions. By the end of this you will 1. Remember your Trigonometry 2. Know how to handle vectors 3. be able to handle problems in 2-dimensions 4. understand
Math Review -- Conceptual Solutions
 Math Review Math Review -- Conceptual Solutions 1.) Is three plus four always equal to seven? Explain. Solution: If the numbers are scalars written in base 10, the answer is yes (if the numbers are in
Math Review Math Review -- Conceptual Solutions 1.) Is three plus four always equal to seven? Explain. Solution: If the numbers are scalars written in base 10, the answer is yes (if the numbers are in
Physics 1A. Lecture 3B. "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook
 Physics 1A Lecture 3B "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook Trajectories Since there is no horizontal acceleration (a x = 0) the horizontal position,
Physics 1A Lecture 3B "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook Trajectories Since there is no horizontal acceleration (a x = 0) the horizontal position,
Chapter 3 Vectors Prof. Raymond Lee, revised
 Chapter 3 Vectors Prof. Raymond Lee, revised 9-2-2010 1 Coordinate systems Used to describe a point s position in space Coordinate system consists of fixed reference point called origin specific axes with
Chapter 3 Vectors Prof. Raymond Lee, revised 9-2-2010 1 Coordinate systems Used to describe a point s position in space Coordinate system consists of fixed reference point called origin specific axes with
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
Vectors. Vector Practice Problems: Odd-numbered problems from
 Vectors Vector Practice Problems: Odd-numbered problems from 3.1-3.21 After today, you should be able to: Understand vector notation Use basic trigonometry in order to find the x and y components of a
Vectors Vector Practice Problems: Odd-numbered problems from 3.1-3.21 After today, you should be able to: Understand vector notation Use basic trigonometry in order to find the x and y components of a
RELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS (Section 12.10)
 RELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS (Section 1.10) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand translating frames of reference. b) Use translating frames of reference to analyze relative motion. APPLICATIONS
RELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS (Section 1.10) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand translating frames of reference. b) Use translating frames of reference to analyze relative motion. APPLICATIONS
Vectors. AP/Honors Physics Mr. Velazquez
 Vectors AP/Honors Physics Mr. Velazquez The Basics Any quantity that refers to a magnitude and a direction is known as a vector quantity. Velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, displacement Other quantities
Vectors AP/Honors Physics Mr. Velazquez The Basics Any quantity that refers to a magnitude and a direction is known as a vector quantity. Velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, displacement Other quantities
STEP Support Programme. Mechanics STEP Questions
 STEP Support Programme Mechanics STEP Questions This is a selection of mainly STEP I questions with a couple of STEP II questions at the end. STEP I and STEP II papers follow the same specification, the
STEP Support Programme Mechanics STEP Questions This is a selection of mainly STEP I questions with a couple of STEP II questions at the end. STEP I and STEP II papers follow the same specification, the
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
VECTORS. 3-1 What is Physics? 3-2 Vectors and Scalars CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 VECTORS 3-1 What is Physics? Physics deals with a great many quantities that have both size and direction, and it needs a special mathematical language the language of vectors to describe those
CHAPTER 3 VECTORS 3-1 What is Physics? Physics deals with a great many quantities that have both size and direction, and it needs a special mathematical language the language of vectors to describe those
Chapter 5: Forces in Two Dimensions. Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue.
 Chapter 5: Forces in Two Dimensions Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions In this chapter you will: Represent vector quantities both graphically and algebraically.
Chapter 5: Forces in Two Dimensions Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions In this chapter you will: Represent vector quantities both graphically and algebraically.
Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions
 Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 17, 2017 Last time vectors and trig Overview wrap up vectors introduction to motion in 2 dimensions constant velocity in
Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 17, 2017 Last time vectors and trig Overview wrap up vectors introduction to motion in 2 dimensions constant velocity in
Lesson 7. Chapter 3: Two-Dimensional Kinematics COLLEGE PHYSICS VECTORS. Video Narrated by Jason Harlow, Physics Department, University of Toronto
 COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 3: Two-Dimensional Kinematics Lesson 7 Video Narrated by Jason Harlow, Physics Department, University of Toronto VECTORS A quantity having both a magnitude and a direction is called
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 3: Two-Dimensional Kinematics Lesson 7 Video Narrated by Jason Harlow, Physics Department, University of Toronto VECTORS A quantity having both a magnitude and a direction is called
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
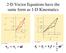 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
Graphical Analysis; and Vectors
 Graphical Analysis; and Vectors Graphs Drawing good pictures can be the secret to solving physics problems. It's amazing how much information you can get from a diagram. We also usually need equations
Graphical Analysis; and Vectors Graphs Drawing good pictures can be the secret to solving physics problems. It's amazing how much information you can get from a diagram. We also usually need equations
Welcome back to Physics 215
 Welcome back to Physics 215 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 2-2.1: An object moves with constant acceleration, starting from
Welcome back to Physics 215 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 2-2.1: An object moves with constant acceleration, starting from
2- Scalars and Vectors
 2- Scalars and Vectors Scalars : have magnitude only : Length, time, mass, speed and volume is example of scalar. v Vectors : have magnitude and direction. v The magnitude of is written v v Position, displacement,
2- Scalars and Vectors Scalars : have magnitude only : Length, time, mass, speed and volume is example of scalar. v Vectors : have magnitude and direction. v The magnitude of is written v v Position, displacement,
Relative Motion. David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006
 Relative Motion David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006 What is Relative Motion? First of all the physics concept involved is KINEMATICS (the study of motion of objects - the relation among displacement, velocity,
Relative Motion David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006 What is Relative Motion? First of all the physics concept involved is KINEMATICS (the study of motion of objects - the relation among displacement, velocity,
Chapter 3. Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion 1 Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size)
Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion 1 Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size)
Projectile Motion and 2-D Dynamics
 Projectile Motion and 2-D Dynamics Vector Notation Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics 11, you learned the difference between vectors and scalars. A vector is a quantity that includes both direction and magnitude
Projectile Motion and 2-D Dynamics Vector Notation Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics 11, you learned the difference between vectors and scalars. A vector is a quantity that includes both direction and magnitude
Progressive Science Initiative. Click to go to website:
 Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Vectors. An Introduction
 Vectors An Introduction There are two kinds of quantities Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only, such as position speed time mass Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction,
Vectors An Introduction There are two kinds of quantities Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only, such as position speed time mass Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction,
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION
 FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
Coordinate Systems. Chapter 3. Cartesian Coordinate System. Polar Coordinate System
 Chapter 3 Vectors Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels instructions
Chapter 3 Vectors Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels instructions
adjacent hypotenuse opposite adjacent Thursday January 25 opposite hypotenuse This lecture: 2-dimensional motion Vectors Components
 Thursday January 25 Assignments 1&2 Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment 15min before class like every class Bring your lab print-out to lab Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Or by
Thursday January 25 Assignments 1&2 Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment 15min before class like every class Bring your lab print-out to lab Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Or by
Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions)
 Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions) You are the navigator of a TWA flight scheduled to fly from New Orleans due north to St. Louis, a distance of 673 miles. Your instruments tell you
Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions) You are the navigator of a TWA flight scheduled to fly from New Orleans due north to St. Louis, a distance of 673 miles. Your instruments tell you
Chapter 5. Forces in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions In this chapter you will: Represent vector quantities both graphically and algebraically. Use Newton s laws to analyze motion when
Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions In this chapter you will: Represent vector quantities both graphically and algebraically. Use Newton s laws to analyze motion when
In 1-D, all we needed was x. For 2-D motion, we'll need a displacement vector made up of two components: r = r x + r y + r z
 D Kinematics 1. Introduction 1. Vectors. Independence of Motion 3. Independence of Motion 4. x-y motions. Projectile Motion 3. Relative motion Introduction Using + or signs was ok in 1 dimension but is
D Kinematics 1. Introduction 1. Vectors. Independence of Motion 3. Independence of Motion 4. x-y motions. Projectile Motion 3. Relative motion Introduction Using + or signs was ok in 1 dimension but is
Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions
 Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions Lana heridan De Anza College Jan 31, 2018 Last time vectors and trig Overview introduction to motion in 2 dimensions constant velocity in 2 dimensions relative
Introduction to Mechanics Motion in 2 Dimensions Lana heridan De Anza College Jan 31, 2018 Last time vectors and trig Overview introduction to motion in 2 dimensions constant velocity in 2 dimensions relative
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors
 Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
5 Projectile Motion. Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion.
 Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics
 Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Is 1+1 always =2? Not true for vectors. Direction matters. Vectors in opposite directions can partially cancel. Position vectors, displacement, velocity, momentum, and forces
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Is 1+1 always =2? Not true for vectors. Direction matters. Vectors in opposite directions can partially cancel. Position vectors, displacement, velocity, momentum, and forces
Physics 2A Chapter 1 - Vectors Fall 2017
 These notes are eight pages. That includes some diagrams, but I realize reading them could get a bit tedious. So here is a quick summary: A vector quantity is one for which direction is relevant, like
These notes are eight pages. That includes some diagrams, but I realize reading them could get a bit tedious. So here is a quick summary: A vector quantity is one for which direction is relevant, like
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS. Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3
 INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
UNIT-05 VECTORS. 3. Utilize the characteristics of two or more vectors that are concurrent, or collinear, or coplanar.
 UNIT-05 VECTORS Introduction: physical quantity that can be specified by just a number the magnitude is known as a scalar. In everyday life you deal mostly with scalars such as time, temperature, length
UNIT-05 VECTORS Introduction: physical quantity that can be specified by just a number the magnitude is known as a scalar. In everyday life you deal mostly with scalars such as time, temperature, length
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Units of Chapter 3 Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Units of Chapter 3 Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Vectors, Parametrics, Polars, & Complex Numbers. A: Initial Point (start); B: Terminal Point (end) : ( ) ( )
 Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
