MOLECULAR LIGHT SCATTERING AND OPTICAL ACTIVITY
|
|
|
- Chrystal Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MOLECULAR LIGHT SCATTERING AND OPTICAL ACTIVITY Second edition, revised and enlarged LAURENCE D. BARRON, F.R.S.E. Gardiner Professor of Chemistry, University of Glasgow 122. CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
2 Contents Preface to the first edition page xi Preface to the second edition xv List of symbols xviii 1 A historical review of optical activity phenomena Introduction Natural optical rotation and circular dichroism Magnetic optical rotation and circular dichroism Light scattering from optically active molecules Vibrational optical activity X-ray optical activity Magnetochiral phenomena The Ken and Cotton Mouton effects Symmetry and optical activity 24 Spatial symmetry and optical activity Inversion symmetry and physical laws Inversion symmetry and optical rotation Inversion symmetry and optical activity in light scattering Motion-dependent enantiomorphism: true and false chirality Symmetry violation: the fall of parity and time reversal invariance Chirality and relativity Chirality in two dimensions 2 Molecules in electric and magnetic fields Introduction Electromagnetic waves 54 Maxwell's equations Plane monochromatic waves Force and energy The scalar and vector potentials 2.3 Polarized light 61 Pure polarization Partial polarization 2.4 Electric and magnetic multipole moments 67 vii
3 viii Contents Electric multipole moments Magnetic multipole moments Static electric multipole fields Static magnetic multipole fields Dynamic electromagnetic multipole fields 2.5 The energy of charges and currents in electric and magnetic fields 78 Electric and magnetic multipole moments in static fields Electric and magnetic multipole moments in dynamic fields 2.6 Molecules in electric and magnetic fields 85 A molecule in static fields A molecule in a radiation field A molecule in a radiation field at absorbing frequencies Kramers Kronig relations The dynamic molecular property tensors in a static approximation 2.7 A molecule in a radiation field in the presence of other perturbations Molecular transition tensors 107 The Raman transition polarizability The adiabatic approximation The vibrational Raman transition tensors in Placzek's approximation Vibronic interactions: the Herzberg Teller approximation 3 Molecular scattering of polarized light Introduction Molecular scattering of light Radiation by induced oscillating molecular multipole moments Polarization phenomena in transmitted light 127 Refraction as a consequence of light scattering Refringent scattering of polarized light Simple absorption Linear dichroism and birefringence (the Kerr effect) Electric field gradient-induced birefringence: measurement of molecular electric quadrupole moments and the problem of origin invariante Natural optical rotation and circular dichroism Magnetic optical rotation and circular dichroism Magnetochiral birefringence and dichroism Nonreciprocal (gyrotropic) birefringence The Jones birefringence Electric optical rotation (electrogyration) and circular dichroism 3.5 Polarization phenomena in Rayleigh and Raman scattered light 151 Nonrefringent scattering of polarized light Symmetrie scattering Antisymmetric scattering Natural Rayleigh and Raman optical activity Magnetic Rayleigh and Raman optical activity Electric Rayleigh and Raman optical activity 4 Symmetry and optical activity Introduction Cartesian tensors 170
4 Contents ix Scalars, vectors and tensors Rotation of axes Polar and axial tensors Some algebra of unit tensors Isotropic averages of tensor components Principal axes 4.3 Inversion symmetry in quantum mechanics 187 Space inversion Time reversal The parity and reversality classification of optical activity observables Optical enantiomers, two-state systems and parity violation Symmetry breaking and symmetry violation CP violation and molecular physics 4.4 The symmetry classification of molecular property tensors 217 Polar and axial, time-even and time-odd tensors Neumann's principle Time reversal and the permutation symmetry of molecular property and transition tensors The spatial symmetry of molecular property tensors Irreducible cartesian tensors Matrix elements of irreducible spherical tensor operators 4.5 Permutation symmetry and chirality 242 Chirality functions Permutations and the symmetric group Chirality functions: qualitative completeness Chirality functions: explicit forms Active and inactive ligand partitions: chirality numbers Homochirality Chirality functions: concluding remarks 5 Natural electronic optical activity Introduction General aspects of natural optical rotation and circular dichroism 264 The basic equations Optical rotation and circular dichroism through circular differential refraction Experimental quantities Sum rules 5.3 The generation of natural optical activity within molecules 272 The static coupling model The dynamic coupling model Exciton coupling (the degenerate coupled oscillator model) 5.4 Illustrative examples 291 The carbonyl chromophore and the octant rule The Co3+ chromophore: visible, near ultraviolet and X-ray circular dichroism Finite helices: hexahelicene 5.5 Vibrational structure in circular dichroism spectra 304 Introduction The vibronically perturbed rotational strength The carbonyl chromophore 6 Magnetic electronic optical activity Introduction General aspects of magnetic optical rotation and circular dichroism 312 The basic equations Interpretation of the Faraday A-, B- and C-terms
5 x Contents 6.3 Illustrative examples 317 Porphyrins Charge transfer transitions in Fe(CN) 36- The influence of intramolecular perturbations an magnetic optical activity: the carbonyl chromophore 6.4 Magnetochiral birefringence and dichroism Natural vibrational optical activity Introduction Natural vibrational optical rotation and circular dichroism 332 The basic equations The fixed partial charge model The bond dipole mode! A perturbation theory of vibrational circular dichroism 7.3 Natural vibrational Raman optical activity 342 The basic equations Experimental quantities Optical activity in transmitted and scattered light The two-group mode! of Rayleigh optical activity The bond polarizability mode! of Raman optical activity The bond polarizability model in forward, backward and 90 scattering 7.4 The bond dipole and bond polarizability models applied to simple chiral structures 362 A simple two-group structure Methyl torsions in a hindered single-bladed propellor Intrinsic group optical activity tensors 7.5 Coupling models Raman optical activity of biomolecules Antisymmetric scattering and magnetic Raman optical activity Introduction Symmetry considerations A vibronic development of the vibrational Raman transition tensors Antisymmetric scattering 393 The antisymmetric transition tensors in the zeroth-order Herzberg-Teller approximation Resonance Rayleigh scattering in atomic sodium Resonance Raman scattering in totally Symmetrie vibrations of iridium (IV) hexahalides Antisymmetric transition tensors generated through vibronic coupling Resonance Raman scattering in porphyrins 8.5 Magnetic Rayleigh and Raman optical activity 407 The basic equations Resonance Rayleigh scattering in atomic sodium Vibrational resonance Raman scattering in IrCe and Spin-flip transitions and Raman electron paramagnetic resonance Electronic resonance Raman scattering in uranocene Resonance Raman scattering in porphyrins References 423 Index 436
The Raman Effect. A Unified Treatment of the Theory of Raman Scattering by Molecules. DerekA. Long
 The Raman Effect A Unified Treatment of the Theory of Raman Scattering by Molecules DerekA. Long Emeritus Professor ofstructural Chemistry University of Bradford Bradford, UK JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Vll
The Raman Effect A Unified Treatment of the Theory of Raman Scattering by Molecules DerekA. Long Emeritus Professor ofstructural Chemistry University of Bradford Bradford, UK JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Vll
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY
 MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman. Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION
 P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles
 Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles Vladimir G. Baryshevsky Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Belarusian State University 1> World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI
Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles Vladimir G. Baryshevsky Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Belarusian State University 1> World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI
Raman Optical Activity Comes of Age
 Raman Optical Activity Comes of Age Laurence D. Barron Department of Chemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ, UK E-mail: laurence.barron@glasgow.ac.uk Raman optical activity (ROA) provides vibrational
Raman Optical Activity Comes of Age Laurence D. Barron Department of Chemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ, UK E-mail: laurence.barron@glasgow.ac.uk Raman optical activity (ROA) provides vibrational
PAPER No. : 8 (PHYSICAL SPECTROSCOPY) MODULE No. : 5 (TRANSITION PROBABILITIES AND TRANSITION DIPOLE MOMENT. OVERVIEW OF SELECTION RULES)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8 and Physical Spectroscopy 5 and Transition probabilities and transition dipole moment, Overview of selection rules CHE_P8_M5 TABLE
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8 and Physical Spectroscopy 5 and Transition probabilities and transition dipole moment, Overview of selection rules CHE_P8_M5 TABLE
Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion. Proteins (KCsa) Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA CHEM 305. Many biomolecules are α-helical!
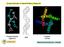 Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA Proteins (KCsa) Many biomolecules are α-helical! How can we measure the amount and changes in amount of helical structure
Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA Proteins (KCsa) Many biomolecules are α-helical! How can we measure the amount and changes in amount of helical structure
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 3: (Crash course in) Theory of optical activity Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 3: (Crash course in) Theory of optical activity Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45
LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS
 LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS GORDON BAYM Unitsersity of Illinois A II I' Advanced Bock Progrant A Member of the Perseus Books Group CONTENTS Preface v Chapter 1 Photon Polarization 1 Transformation of
LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS GORDON BAYM Unitsersity of Illinois A II I' Advanced Bock Progrant A Member of the Perseus Books Group CONTENTS Preface v Chapter 1 Photon Polarization 1 Transformation of
Wolfgang Demtroder. Molecular Physics. Theoretical Principles and Experimental Methods WILEY- VCH. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.
 Wolfgang Demtroder Molecular Physics Theoretical Principles and Experimental Methods WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA v Preface xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Short Historical Overview 2 1.2 Molecular
Wolfgang Demtroder Molecular Physics Theoretical Principles and Experimental Methods WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA v Preface xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Short Historical Overview 2 1.2 Molecular
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy
 4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
Quantum Mechanics: Foundations and Applications
 Arno Böhm Quantum Mechanics: Foundations and Applications Third Edition, Revised and Enlarged Prepared with Mark Loewe With 96 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
Arno Böhm Quantum Mechanics: Foundations and Applications Third Edition, Revised and Enlarged Prepared with Mark Loewe With 96 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
QUANTUM MECHANICS. Franz Schwabl. Translated by Ronald Kates. ff Springer
 Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Liquid Crystals IAM-CHOON 1(1100 .,4 WILEY 2007 WILEY-INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION. 'i; Second Edition. n z
 Liquid Crystals Second Edition IAM-CHOON 1(1100.,4 z 'i; BICENTCNNIAL 1 8 0 7 WILEY 2007 DICENTENNIAL n z z r WILEY-INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii Chapter 1.
Liquid Crystals Second Edition IAM-CHOON 1(1100.,4 z 'i; BICENTCNNIAL 1 8 0 7 WILEY 2007 DICENTENNIAL n z z r WILEY-INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii Chapter 1.
Polarized Light. Second Edition, Revised and Expanded. Dennis Goldstein Air Force Research Laboratory Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, U.S.A.
 Polarized Light Second Edition, Revised and Expanded Dennis Goldstein Air Force Research Laboratory Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, U.S.A. ш DEK KER MARCEL DEKKER, INC. NEW YORK BASEL Contents Preface to
Polarized Light Second Edition, Revised and Expanded Dennis Goldstein Air Force Research Laboratory Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, U.S.A. ш DEK KER MARCEL DEKKER, INC. NEW YORK BASEL Contents Preface to
ELECTRODYNAMICS OF CONTINUOUS MEDIA
 ELECTRODYNAMICS OF CONTINUOUS MEDIA by L. D. LANDAU and E. M. LIFSHITZ Institute of Physical Problems, USSR Academy of Sciences Volume 8 of Course of Theoretical Physics Translated from the Russian by
ELECTRODYNAMICS OF CONTINUOUS MEDIA by L. D. LANDAU and E. M. LIFSHITZ Institute of Physical Problems, USSR Academy of Sciences Volume 8 of Course of Theoretical Physics Translated from the Russian by
Chem 442 Review of Spectroscopy
 Chem 44 Review of Spectroscopy General spectroscopy Wavelength (nm), frequency (s -1 ), wavenumber (cm -1 ) Frequency (s -1 ): n= c l Wavenumbers (cm -1 ): n =1 l Chart of photon energies and spectroscopies
Chem 44 Review of Spectroscopy General spectroscopy Wavelength (nm), frequency (s -1 ), wavenumber (cm -1 ) Frequency (s -1 ): n= c l Wavenumbers (cm -1 ): n =1 l Chart of photon energies and spectroscopies
INTRODUCTION TO MODERN VIBRATIONAL SPECTROSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION TO MODERN VIBRATIONAL SPECTROSCOPY MAX DIEM Department of Chemistry City University of New York Hunter College A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
INTRODUCTION TO MODERN VIBRATIONAL SPECTROSCOPY MAX DIEM Department of Chemistry City University of New York Hunter College A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
Molecular Symmetry. Symmetry is relevant to: spectroscopy, chirality, polarity, Group Theory, Molecular Orbitals
 Molecular Symmetry Symmetry is relevant to: spectroscopy, chirality, polarity, Group Theory, Molecular Orbitals - A molecule has a symmetry element if it is unchanged by a particular symmetry operation
Molecular Symmetry Symmetry is relevant to: spectroscopy, chirality, polarity, Group Theory, Molecular Orbitals - A molecule has a symmetry element if it is unchanged by a particular symmetry operation
OPTI 501, Electromagnetic Waves (3)
 OPTI 501, Electromagnetic Waves (3) Vector fields, Maxwell s equations, electromagnetic field energy, wave equations, free-space solutions, box modes, Fresnel equations, scalar and vector potentials, gauge
OPTI 501, Electromagnetic Waves (3) Vector fields, Maxwell s equations, electromagnetic field energy, wave equations, free-space solutions, box modes, Fresnel equations, scalar and vector potentials, gauge
Quantum. Mechanics. Y y. A Modern Development. 2nd Edition. Leslie E Ballentine. World Scientific. Simon Fraser University, Canada TAIPEI BEIJING
 BEIJING TAIPEI Quantum Mechanics A Modern Development 2nd Edition Leslie E Ballentine Simon Fraser University, Canada Y y NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE World Scientific SHANGHAI HONG KONG CHENNAI Contents
BEIJING TAIPEI Quantum Mechanics A Modern Development 2nd Edition Leslie E Ballentine Simon Fraser University, Canada Y y NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE World Scientific SHANGHAI HONG KONG CHENNAI Contents
Contents. xiii. Preface v
 Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
Contents Preface Chapter 1 Biological Macromolecules 1.1 General PrincipIes 1.1.1 Macrornolecules 1.2 1.1.2 Configuration and Conformation Molecular lnteractions in Macromolecular Structures 1.2.1 Weak
Rotational Raman Spectroscopy
 Rotational Raman Spectroscopy If EM radiation falls upon an atom or molecule, it may be absorbed if the energy of the radiation corresponds to the separation of two energy levels of the atoms or molecules.
Rotational Raman Spectroscopy If EM radiation falls upon an atom or molecule, it may be absorbed if the energy of the radiation corresponds to the separation of two energy levels of the atoms or molecules.
M.S. Dresselhaus G. Dresselhaus A. Jorio. Group Theory. Application to the Physics of Condensed Matter. With 131 Figures and 219 Tables.
 M.S. Dresselhaus G. Dresselhaus A. Jorio Group Theory Application to the Physics of Condensed Matter With 131 Figures and 219 Tables 4) Springer Contents Part I Basic Mathematics 1 Basic Mathematical Background:
M.S. Dresselhaus G. Dresselhaus A. Jorio Group Theory Application to the Physics of Condensed Matter With 131 Figures and 219 Tables 4) Springer Contents Part I Basic Mathematics 1 Basic Mathematical Background:
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY
 CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
Specialized Raman Techniques. Strictly speaking the radiation-induced dipole moment should be expressed as
 Nonlinear effects Specialized Raman Techniques Strictly speaking the radiation-induced dipole moment should be expressed as M = E + ½E 2 + (1/6)E 3 +... Where and are the first and second hyperpolarizabilities.
Nonlinear effects Specialized Raman Techniques Strictly speaking the radiation-induced dipole moment should be expressed as M = E + ½E 2 + (1/6)E 3 +... Where and are the first and second hyperpolarizabilities.
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
3.4 Elliptical Parameters of the Polarization Ellipse References
 Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition A Historical Note Edward Collett iii v xiii PART 1: THE CLASSICAL OPTICAL FIELD Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Introduction
Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition A Historical Note Edward Collett iii v xiii PART 1: THE CLASSICAL OPTICAL FIELD Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Introduction
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE - 411007 SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course Each Student will be required to do 3 courses, out of which two are common courses. The third course syllabus
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE - 411007 SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course Each Student will be required to do 3 courses, out of which two are common courses. The third course syllabus
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
 An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
CONTENTS. vii. CHAPTER 2 Operators 15
 CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
Classical Electrodynamics
 Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Principles of Physical Biochemistry
 Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Modern Optical Spectroscopy
 Modern Optical Spectroscopy With Exercises and Examples from Biophysics and Biochemistry von William W Parson 1. Auflage Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2006 Verlag C.H. Beck im Internet: www.beck.de
Modern Optical Spectroscopy With Exercises and Examples from Biophysics and Biochemistry von William W Parson 1. Auflage Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2006 Verlag C.H. Beck im Internet: www.beck.de
24/ Rayleigh and Raman scattering. Stokes and anti-stokes lines. Rotational Raman spectroscopy. Polarizability ellipsoid. Selection rules.
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8/ Physical Spectroscopy 24/ Rayleigh and Raman scattering. Stokes and anti-stokes lines. Rotational Raman spectroscopy. Polarizability
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 8/ Physical Spectroscopy 24/ Rayleigh and Raman scattering. Stokes and anti-stokes lines. Rotational Raman spectroscopy. Polarizability
Ψ t = ih Ψ t t. Time Dependent Wave Equation Quantum Mechanical Description. Hamiltonian Static/Time-dependent. Time-dependent Energy operator
 Time Dependent Wave Equation Quantum Mechanical Description Hamiltonian Static/Time-dependent Time-dependent Energy operator H 0 + H t Ψ t = ih Ψ t t The Hamiltonian and wavefunction are time-dependent
Time Dependent Wave Equation Quantum Mechanical Description Hamiltonian Static/Time-dependent Time-dependent Energy operator H 0 + H t Ψ t = ih Ψ t t The Hamiltonian and wavefunction are time-dependent
Spectra of Atoms and Molecules. Peter F. Bernath
 Spectra of Atoms and Molecules Peter F. Bernath New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1 Introduction 3 Waves, Particles, and Units 3 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 6 Interaction of Radiation
Spectra of Atoms and Molecules Peter F. Bernath New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1 Introduction 3 Waves, Particles, and Units 3 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 6 Interaction of Radiation
Lecture 6: Physical Methods II. UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy
 Lecture 6: Physical Methods II UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy Physical Methods used in bioinorganic chemistry X ray crystallography X ray absorption (XAS)
Lecture 6: Physical Methods II UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy Physical Methods used in bioinorganic chemistry X ray crystallography X ray absorption (XAS)
Chap. 4. Electromagnetic Propagation in Anisotropic Media
 Chap. 4. Electromagnetic Propagation in Anisotropic Media - Optical properties depend on the direction of propagation and the polarization of the light. - Crystals such as calcite, quartz, KDP, and liquid
Chap. 4. Electromagnetic Propagation in Anisotropic Media - Optical properties depend on the direction of propagation and the polarization of the light. - Crystals such as calcite, quartz, KDP, and liquid
Contents. Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition
 Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Notes xiii xv xvii 1 Basic Concepts 1 1.1 History 1 1.1.1 The Origins of Nuclear Physics 1 1.1.2 The Emergence of Particle Physics: the
Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition Notes xiii xv xvii 1 Basic Concepts 1 1.1 History 1 1.1.1 The Origins of Nuclear Physics 1 1.1.2 The Emergence of Particle Physics: the
GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS
 GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS Wu-Ki Tung World Scientific Philadelphia Singapore CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 4 PREFACE INTRODUCTION 1.1 Particle on a One-Dimensional Lattice 1.2 Representations
GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS Wu-Ki Tung World Scientific Philadelphia Singapore CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 4 PREFACE INTRODUCTION 1.1 Particle on a One-Dimensional Lattice 1.2 Representations
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
List of Comprehensive Exams Topics
 List of Comprehensive Exams Topics Mechanics 1. Basic Mechanics Newton s laws and conservation laws, the virial theorem 2. The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism The Lagrange formalism and the principle
List of Comprehensive Exams Topics Mechanics 1. Basic Mechanics Newton s laws and conservation laws, the virial theorem 2. The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism The Lagrange formalism and the principle
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5, pm SES
 Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chemistry 416 Spectroscopy Winter Semester 1996 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 416 Spectroscopy Winter Semester 1996 Dr. Rainer Glaser First 1-our Examination UV/Vis Spectroscopy Friday, February 9, 1996, 8:40-9:30 Name: Max Yours Question 1 10 Question 2 10 Question 3
Chemistry 416 Spectroscopy Winter Semester 1996 Dr. Rainer Glaser First 1-our Examination UV/Vis Spectroscopy Friday, February 9, 1996, 8:40-9:30 Name: Max Yours Question 1 10 Question 2 10 Question 3
Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition iii v 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Relevance for Climate and Weather........... 1 1.1.1 Solar Radiation.................. 2 1.1.2 Thermal Infrared
Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition iii v 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Relevance for Climate and Weather........... 1 1.1.1 Solar Radiation.................. 2 1.1.2 Thermal Infrared
PMARIZED LI6HT FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS EBWABD COLLETT. Measurement Concepts, Inc. Colts Neck, New Jersey
 PMARIZED LI6HT FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS EBWABD COLLETT Measurement Concepts, Inc. Colts Neck, New Jersey Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York Basel Hong Kong About the Series Preface A Historical Note iii
PMARIZED LI6HT FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS EBWABD COLLETT Measurement Concepts, Inc. Colts Neck, New Jersey Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York Basel Hong Kong About the Series Preface A Historical Note iii
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods
 Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
What happens when light falls on a material? Transmission Reflection Absorption Luminescence. Elastic Scattering Inelastic Scattering
 Raman Spectroscopy What happens when light falls on a material? Transmission Reflection Absorption Luminescence Elastic Scattering Inelastic Scattering Raman, Fluorescence and IR Scattering Absorption
Raman Spectroscopy What happens when light falls on a material? Transmission Reflection Absorption Luminescence Elastic Scattering Inelastic Scattering Raman, Fluorescence and IR Scattering Absorption
The vibrational spectroscopy of polymers
 D. I. BOWER Reader in Polymer Spectroscopy Interdisciplinary Research Centre in Polymer Science & Technology Department of Physics, University of Leeds W.F. MADDAMS Senior Visiting Fellow Department of
D. I. BOWER Reader in Polymer Spectroscopy Interdisciplinary Research Centre in Polymer Science & Technology Department of Physics, University of Leeds W.F. MADDAMS Senior Visiting Fellow Department of
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS
 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS Second Edition DAVID J. GRIFFITHS Department of Physics Reed College PRENTICE HALL, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS Preface xi Advertisement 1 1 Vector Analysis
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRODYNAMICS Second Edition DAVID J. GRIFFITHS Department of Physics Reed College PRENTICE HALL, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS Preface xi Advertisement 1 1 Vector Analysis
Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals
 Kurt Gottfried Tung-Mow Yan Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals Second Edition With 75 Figures Springer Preface vii Fundamental Concepts 1 1.1 Complementarity and Uncertainty 1 (a) Complementarity 2 (b) The
Kurt Gottfried Tung-Mow Yan Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals Second Edition With 75 Figures Springer Preface vii Fundamental Concepts 1 1.1 Complementarity and Uncertainty 1 (a) Complementarity 2 (b) The
Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis)
 Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis) 2 2. Circular dichroism (optical activity) CD / ORD 3 3. Fluorescence spectroscopy and energy transfer Electromagnetic Spectrum Electronic Molecular
Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis) 2 2. Circular dichroism (optical activity) CD / ORD 3 3. Fluorescence spectroscopy and energy transfer Electromagnetic Spectrum Electronic Molecular
Contents. 1 Basic Equations 1. Acknowledgment. 1.1 The Maxwell Equations Constitutive Relations 11
 Preface Foreword Acknowledgment xvi xviii xix 1 Basic Equations 1 1.1 The Maxwell Equations 1 1.1.1 Boundary Conditions at Interfaces 4 1.1.2 Energy Conservation and Poynting s Theorem 9 1.2 Constitutive
Preface Foreword Acknowledgment xvi xviii xix 1 Basic Equations 1 1.1 The Maxwell Equations 1 1.1.1 Boundary Conditions at Interfaces 4 1.1.2 Energy Conservation and Poynting s Theorem 9 1.2 Constitutive
PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY
 PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Shaul Mukamel University of Rochester Rochester, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1. Introduction 3 Linear versus Nonlinear Spectroscopy
PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Shaul Mukamel University of Rochester Rochester, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1. Introduction 3 Linear versus Nonlinear Spectroscopy
B7 Symmetry : Questions
 B7 Symmetry 009-10: Questions 1. Using the definition of a group, prove the Rearrangement Theorem, that the set of h products RS obtained for a fixed element S, when R ranges over the h elements of the
B7 Symmetry 009-10: Questions 1. Using the definition of a group, prove the Rearrangement Theorem, that the set of h products RS obtained for a fixed element S, when R ranges over the h elements of the
Practical Quantum Mechanics
 Siegfried Flügge Practical Quantum Mechanics With 78 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Volume I I. General Concepts 1. Law of probability
Siegfried Flügge Practical Quantum Mechanics With 78 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Volume I I. General Concepts 1. Law of probability
Shigeji Fujita and Salvador V Godoy. Mathematical Physics WILEY- VCH. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
 Shigeji Fujita and Salvador V Godoy Mathematical Physics WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XIII Table of Contents and Categories XV Constants, Signs, Symbols, and General Remarks
Shigeji Fujita and Salvador V Godoy Mathematical Physics WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XIII Table of Contents and Categories XV Constants, Signs, Symbols, and General Remarks
Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons
 Department of Chemistry Physical Chemistry Göteborg University KEN140 Spektroskopi Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons WARNING! The laser gives a pulsed very energetic and
Department of Chemistry Physical Chemistry Göteborg University KEN140 Spektroskopi Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons WARNING! The laser gives a pulsed very energetic and
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes. Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes. Objectives
 Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Light scattering- elastic and inelastic-processes,
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Light scattering- elastic and inelastic-processes,
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 INTRODUCTION TO Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy ESR, NMR, NQR D. N. SATHYANARAYANA Formerly, Chairman Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore % I.K. International
INTRODUCTION TO Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy ESR, NMR, NQR D. N. SATHYANARAYANA Formerly, Chairman Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore % I.K. International
PHYSICS. Course Syllabus. Section 1: Mathematical Physics. Subject Code: PH. Course Structure. Electromagnetic Theory
 PHYSICS Subject Code: PH Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Mathematical Physics Classical Mechanics Electromagnetic
PHYSICS Subject Code: PH Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Mathematical Physics Classical Mechanics Electromagnetic
Nonlinear Optics. Second Editio n. Robert W. Boyd
 Nonlinear Optics Second Editio n Robert W. Boyd Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xv 1. The Nonlinear Optical Susceptibility 1 1.1. Introduction to Nonlinear Optics 1 1.2.
Nonlinear Optics Second Editio n Robert W. Boyd Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xv 1. The Nonlinear Optical Susceptibility 1 1.1. Introduction to Nonlinear Optics 1 1.2.
A very brief history of the study of light
 1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
16.1 Molecular Vibrations
 16.1 Molecular Vibrations molecular degrees of freedom are used to predict the number of vibrational modes vibrations occur as coordinated movement among many nuclei the harmonic oscillator approximation
16.1 Molecular Vibrations molecular degrees of freedom are used to predict the number of vibrational modes vibrations occur as coordinated movement among many nuclei the harmonic oscillator approximation
Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Scattering Introduction - Consider a localized object that contains charges
Lecture 8 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Scattering Introduction - Consider a localized object that contains charges
ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY
 ALAN CORNEY ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1977 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Planck's radiation law. 1 1.2. The photoelectric effect 4 1.3. Early atomic spectroscopy 5 1.4. The postulates
ALAN CORNEY ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1977 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Planck's radiation law. 1 1.2. The photoelectric effect 4 1.3. Early atomic spectroscopy 5 1.4. The postulates
COX & GIULI'S PRINCIPLES OF STELLAR STRUCTURE
 COX & GIULI'S PRINCIPLES OF STELLAR STRUCTURE Extended Second Edition A. Weiss, W. Hillebrandt, H.-C. Thomas and H. Ritter Max-Planck-lnstitut fur Astrophysik, Garching, Germany C S P CONTENTS PREFACE
COX & GIULI'S PRINCIPLES OF STELLAR STRUCTURE Extended Second Edition A. Weiss, W. Hillebrandt, H.-C. Thomas and H. Ritter Max-Planck-lnstitut fur Astrophysik, Garching, Germany C S P CONTENTS PREFACE
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS. \Hp. Ni Jun TSINGHUA. Physics. From Quantum Field Theory. to Classical Mechanics. World Scientific. Vol.2. Report and Review in
 LONDON BEIJING HONG TSINGHUA Report and Review in Physics Vol2 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS From Quantum Field Theory to Classical Mechanics Ni Jun Tsinghua University, China NEW JERSEY \Hp SINGAPORE World Scientific
LONDON BEIJING HONG TSINGHUA Report and Review in Physics Vol2 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS From Quantum Field Theory to Classical Mechanics Ni Jun Tsinghua University, China NEW JERSEY \Hp SINGAPORE World Scientific
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing. Course Outline 2009
 Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Group Theory and Its Applications in Physics
 T. Inui Y Tanabe Y. Onodera Group Theory and Its Applications in Physics With 72 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Contents Sections marked with
T. Inui Y Tanabe Y. Onodera Group Theory and Its Applications in Physics With 72 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Contents Sections marked with
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 THIRD EDITION ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM EDWARD M. PURCELL DAVID J. MORIN Harvard University, Massachusetts Щ CAMBRIDGE Ell UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the third edition of Volume 2 XIII CONTENTS Preface
THIRD EDITION ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM EDWARD M. PURCELL DAVID J. MORIN Harvard University, Massachusetts Щ CAMBRIDGE Ell UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the third edition of Volume 2 XIII CONTENTS Preface
Classical Field Theory
 April 13, 2010 Field Theory : Introduction A classical field theory is a physical theory that describes the study of how one or more physical fields interact with matter. The word classical is used in
April 13, 2010 Field Theory : Introduction A classical field theory is a physical theory that describes the study of how one or more physical fields interact with matter. The word classical is used in
Types of Molecular Vibrations
 Important concepts in IR spectroscopy Vibrations that result in change of dipole moment give rise to IR absorptions. The oscillating electric field of the radiation couples with the molecular vibration
Important concepts in IR spectroscopy Vibrations that result in change of dipole moment give rise to IR absorptions. The oscillating electric field of the radiation couples with the molecular vibration
Symmetry. Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane Office: CTH 311 Phone Office Hours:
 Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane e-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: CT 311 Phone 257-4941 Office ours: M,W 8:00-9:00 & 11:00-12:00 am; Tu,Th, F 9:30-11:30 a.m. April 4, 2017:
Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane e-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: CT 311 Phone 257-4941 Office ours: M,W 8:00-9:00 & 11:00-12:00 am; Tu,Th, F 9:30-11:30 a.m. April 4, 2017:
CHAPTER 9 FUNDAMENTAL OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 CHAPTER 9 FUNDAMENTAL OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Alan Miller Department of Physics and Astronomy Uni ersity of St. Andrews St. Andrews, Scotland and Center for Research and Education in Optics and Lasers
CHAPTER 9 FUNDAMENTAL OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Alan Miller Department of Physics and Astronomy Uni ersity of St. Andrews St. Andrews, Scotland and Center for Research and Education in Optics and Lasers
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions
 Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions Richard R. Ernst, Geoffrey Bodenhausen, and Alexander Wokaun Laboratorium für Physikalische Chemie Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions Richard R. Ernst, Geoffrey Bodenhausen, and Alexander Wokaun Laboratorium für Physikalische Chemie Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule
Vibrational states of molecules. Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules
 Vibrational states of molecules Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules Diatomic molecules V v 1 v 0 Re Q Birge-Sponer plot The solution of the Schrödinger equation can be solved analytically for the
Vibrational states of molecules Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules Diatomic molecules V v 1 v 0 Re Q Birge-Sponer plot The solution of the Schrödinger equation can be solved analytically for the
CHM Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material. 1. Einstein A and B coefficients
 CHM 3411 - Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material 1. Einstein A and B coefficients Consider two singly degenerate states in an atom, molecule, or ion, with wavefunctions 1 (for the lower
CHM 3411 - Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material 1. Einstein A and B coefficients Consider two singly degenerate states in an atom, molecule, or ion, with wavefunctions 1 (for the lower
NPTEL/IITM. Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2. Prof.K. Mangala Sunder Page 1 of 15. Topics. Part I : Introductory concepts Topics
 Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF THE RAMAN EFFECT
 INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF THE RAMAN EFFECT INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF THE RAMAN EFFECT by J. A. KONINGSTEIN Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada D. REIDEL PUBLISHING COMPANY DORDRECHT-HOLLAND Library
INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF THE RAMAN EFFECT INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF THE RAMAN EFFECT by J. A. KONINGSTEIN Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada D. REIDEL PUBLISHING COMPANY DORDRECHT-HOLLAND Library
THE VIBRATIONAL SPECTRA OF A POLYATOMIC MOLECULE (Revised 3/27/2006)
 THE VIBRATIONAL SPECTRA OF A POLYATOMIC MOLECULE (Revised 3/27/2006) 1) INTRODUCTION The vibrational motion of a molecule is quantized and the resulting energy level spacings give rise to transitions in
THE VIBRATIONAL SPECTRA OF A POLYATOMIC MOLECULE (Revised 3/27/2006) 1) INTRODUCTION The vibrational motion of a molecule is quantized and the resulting energy level spacings give rise to transitions in
Topics for the Qualifying Examination
 Topics for the Qualifying Examination Quantum Mechanics I and II 1. Quantum kinematics and dynamics 1.1 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics. 1.2 Configuration space vs. Hilbert space, wave function vs. state
Topics for the Qualifying Examination Quantum Mechanics I and II 1. Quantum kinematics and dynamics 1.1 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics. 1.2 Configuration space vs. Hilbert space, wave function vs. state
LECTURE 3 DIRECT PRODUCTS AND SPECTROSCOPIC SELECTION RULES
 SYMMETRY II. J. M. GOICOECHEA. LECTURE 3 1 LECTURE 3 DIRECT PRODUCTS AND SPECTROSCOPIC SELECTION RULES 3.1 Direct products and many electron states Consider the problem of deciding upon the symmetry of
SYMMETRY II. J. M. GOICOECHEA. LECTURE 3 1 LECTURE 3 DIRECT PRODUCTS AND SPECTROSCOPIC SELECTION RULES 3.1 Direct products and many electron states Consider the problem of deciding upon the symmetry of
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
( ) x10 8 m. The energy in a mole of 400 nm photons is calculated by: ' & sec( ) ( & % ) 6.022x10 23 photons' E = h! = hc & 6.
 Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopic techniques are widely used to detect molecules, to measure the concentration of a species in solution, and to determine molecular structure. For proteins, most
Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopic techniques are widely used to detect molecules, to measure the concentration of a species in solution, and to determine molecular structure. For proteins, most
Chemistry 5325/5326. Angelo R. Rossi Department of Chemistry The University of Connecticut. January 17-24, 2012
 Symmetry and Group Theory for Computational Chemistry Applications Chemistry 5325/5326 Angelo R. Rossi Department of Chemistry The University of Connecticut angelo.rossi@uconn.edu January 17-24, 2012 Infrared
Symmetry and Group Theory for Computational Chemistry Applications Chemistry 5325/5326 Angelo R. Rossi Department of Chemistry The University of Connecticut angelo.rossi@uconn.edu January 17-24, 2012 Infrared
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 347 Index a AC fields 81 119 electric 81, 109 116 laser 81, 136 magnetic 112 microwave 107 109 AC field traps see Traps AC Stark effect 82, 84, 90, 96, 97 101, 104 109 Adiabatic approximation 3, 10, 32
347 Index a AC fields 81 119 electric 81, 109 116 laser 81, 136 magnetic 112 microwave 107 109 AC field traps see Traps AC Stark effect 82, 84, 90, 96, 97 101, 104 109 Adiabatic approximation 3, 10, 32
An Introduction to Polymer Physics
 An Introduction to Polymer Physics David I. Bower Formerly at the University of Leeds (CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xii xv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Polymers and the scope of the book
An Introduction to Polymer Physics David I. Bower Formerly at the University of Leeds (CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xii xv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Polymers and the scope of the book
Lecture Notes. Quantum Theory. Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer. Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology. covering the contents of
 Lecture Notes Quantum Theory by Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology covering the contents of 136.019 Quantentheorie I and 136.027 Quantentheorie II
Lecture Notes Quantum Theory by Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology covering the contents of 136.019 Quantentheorie I and 136.027 Quantentheorie II
QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS
 QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS Formerly, Professor and Head of Physics and Dean, Faculty of Science University of Kerala New Delhi-110001 2009 QUANTUM MECHANICS, 2nd Ed. G. Aruldhas 2009
QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS Formerly, Professor and Head of Physics and Dean, Faculty of Science University of Kerala New Delhi-110001 2009 QUANTUM MECHANICS, 2nd Ed. G. Aruldhas 2009
The Physics of Semiconductors
 The Physics of Semiconductors with applications to optoelectronic devices KEVIN F. BRENNAN CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xi Chapter1 Basic Concepts in Quantum Mechanics 1.1 Introduction
The Physics of Semiconductors with applications to optoelectronic devices KEVIN F. BRENNAN CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xi Chapter1 Basic Concepts in Quantum Mechanics 1.1 Introduction
Electronic Spectra of Complexes
 Electronic Spectra of Complexes Interpret electronic spectra of coordination compounds Correlate with bonding Orbital filling and electronic transitions Electron-electron repulsion Application of MO theory
Electronic Spectra of Complexes Interpret electronic spectra of coordination compounds Correlate with bonding Orbital filling and electronic transitions Electron-electron repulsion Application of MO theory
Lecture 11: Polarized Light. Fundamentals of Polarized Light. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Scattering Polarization. Zeeman Effect.
 Lecture 11: Polarized Light Outline 1 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect 5 Hanle Effect Fundamentals of Polarized Light Electromagnetic
Lecture 11: Polarized Light Outline 1 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect 5 Hanle Effect Fundamentals of Polarized Light Electromagnetic
Quote from Eugene Paul Wigner
 Quote from Eugene Paul Wigner See also: Current Science, vol. 69, no. 4, 25 August 1995, p. 375 From the preface to his book on group theory: Wigner relates a conversation with von Laue on the use of group
Quote from Eugene Paul Wigner See also: Current Science, vol. 69, no. 4, 25 August 1995, p. 375 From the preface to his book on group theory: Wigner relates a conversation with von Laue on the use of group
13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Chemistry 13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory 27, Group theory and vibrational spectroscopy: Part-IV(Selection rules for IR
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Chemistry 13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory 27, Group theory and vibrational spectroscopy: Part-IV(Selection rules for IR
Spectroscopic Selection Rules
 E 0 v = 0 v = 1 v = 2 v = 4 v = 3 For a vibrational fundamental (Δv = ±1), the transition will have nonzero intensity in either the infrared or Raman spectrum if the appropriate transition moment is nonzero.
E 0 v = 0 v = 1 v = 2 v = 4 v = 3 For a vibrational fundamental (Δv = ±1), the transition will have nonzero intensity in either the infrared or Raman spectrum if the appropriate transition moment is nonzero.
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS. An Introduction to Theory and Experiment
 Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Handbook of Radiation and Scattering of Waves:
 Handbook of Radiation and Scattering of Waves: Acoustic Waves in Fluids Elastic Waves in Solids Electromagnetic Waves Adrianus T. de Hoop Professor of Electromagnetic Theory and Applied Mathematics Delft
Handbook of Radiation and Scattering of Waves: Acoustic Waves in Fluids Elastic Waves in Solids Electromagnetic Waves Adrianus T. de Hoop Professor of Electromagnetic Theory and Applied Mathematics Delft
