Discrete scale invariance and Efimov bound states in Weyl systems with coexistence of electron and hole carriers
|
|
|
- MargaretMargaret Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Institute of Advanced Study, Tsinghua, April 19, 017 Discrete scale invariance and Efimov bound states in Weyl systems with coexistence of electron and hole carriers Haiwen Liu ( 刘海文 ) Beijing Normal University 1
2 Collaborators Theorists: X. C. Xie ICQM, Peking University Robert Joynt University of Wisconsin-Madison Z. Q. Wang Boston College Hua Jiang Soochow University Experimentalists: Jian Wang, Huichao Wang ICQM, Peking University Junfeng Wang, Liang Li Wuhan National High Magnetic Field Center Jiaqiang Yan, David Mandrus Oak Ridge National Laboratory References: arxiv: Supported by
3 Outline 1. Experimental results and general background Log-periodic magneto-resistance in ultra-quantum ZrTe5 Brief introduction to discrete scale invariance and Efimov physics. Possible Fermionic Efimov bound states Three-body Schrödinger case with resonant scattering Two-body Weyl Hamiltonian with Coulomb attraction Influence of magnetic field and comparison to experiments 3. Conclusions 3
4 Log-B periodic magneto-resistance oscillation in ZrTe 5 Why? Log-B periodic MR oscillations from 0.T to 55T. 4
5 Discrete Scale Invariance in ZrTe 5 beyond the quantum limit Why? Discrete Scale Invariance in ultra-quantum in ZrTe 5 with coexistence 5 of heavy electron (low mobility) and light hole (high mobility).
6 Discrete scale invariance Fibonacci (Spirals) Fractals Efimov spectrum Mandelbrot set D. Sornette, Physics Reports (1998). E. Braaten, H.-W. Hammer, Physics Reports (006). 6
7 Bosonic Efimov trimers (resonant scattering) Vitaly Efimov When bosons interact with infinite scattering length a, 3 bosons always form a geometric series of bound states. ee ππ ss 0.7 with ss Discrete Scale Invariance 7
8 Resonant scattering (obtained by Feshbach resonance ) 1. Square potential well. Feshbach resonance E. Braaten, H.-W. Hammer, Physics Reports (006). 8
9 9 E. Braaten, H.-W. Hammer, Physics Reports (006). Efimov trimer of identical bosons (near resonance) 1. 1/R^ attraction is a requisite.. Energy spectrum also show Discrete Scale Invariance.
10 Efimov trimer of identical bosons (experimental realization) Rudolf Grimm, Nature 440, 315 (006); PRL 11, (014); Reinhard Dörner, Science 348, 551 (015); Matthias Weidemüller, PRL 11, (014); Cheng Chin, PRL 113, 4040 (014). 10
11 1. Experimental results and general background Log-periodic magneto-resistance in ultra-quantum ZrTe5 Brief introduction to discrete scale invariance and Efimov physics. Possible Fermionic Efimov bound states Three-body Schrödinger case with resonant scattering Two-body Weyl Hamiltonian with Coulomb attraction Influence of magnetic field and comparison to experiments 11
12 Efimov attraction from Born-Oppenheimer approximation Trimer wave-function ψψ TT RR, rr = FF ee RR φφ h rr, RR Schrödinger equation for hole wave-function ħ MM h rr φφ h rr, RR = εε h φφ h rr, RR Hole wave-function: φφ h rr, RR = exp kk h rr RR rr RR + exp kk h rr + RR rr + RR Decay wave-number: kk h = 1 ħ MM hεε h Bethe-Peierls boundary condition: rr rrφφ h rr 0 1 aa kk h RR ee kk hrr = RR aa Energy of hole: kk h RR = ΩΩ Solution of ΩΩ = ee ΩΩ when scattering length aa ± εε h RR ħ ΩΩ MM h RR 1
13 Efimov attraction from Born-Oppenheimer approximation Schrödinger equation for two electrons (center of mass): ħ MM ee RR + εε h RR FF ee RR = EE TT FF ee RR Wave-function for two electrons (center of mass): FF ee RR = RR 1 ff RR YY LLLL θθ Differential equation for radical part: Efimov attraction: VV RR = dd ddrr + VV RR MM eeee TT ħ ff RR = 0 LL LL + 1 RR MM eeωω MM h RR = ss RR Definition: (real ss 0 guarantee a solution) ss 0 = MM ee MM h ΩΩ LL LL Identical fermions: LL = 1 real ss 0 contraint: MM ee MM h > 13.6 This constraint can be matched in solid state systems. 13
14 Efimov Trimers from the Born-Oppenheimer approximation Differential equation for radical part (with real positive ss 0 ): dd ddrr ss RR MM eeee TT ħ ff RR = 0 Definitions and differential equation for auxiliary function: EE TT = ħ kk TT ff RR = RR 1 gg RR RR = kk MM TT RR ee gg RR + 1 RR gg RR ss 0 RR gg RR = 0 [Landau & Lifshitz QM] E=EE TT Solution: ff RR = RR 1 KK iiss0 kk TT RR E 0 Solution: ff RR RR 1 sin ss 0 ln kk TT RR + αα ff 1 RR AARR 1 sin ss 0 lnkk RR + αα Match the wave-function at boundary. Continuous condition of boundary. RR ff RR ff RR at Discrete Scale Invariance kk TT,nn = ee ππ ss 0 nn nn0 ee αα ss 0kk EE BB,nn = ee ππ ss nn nn 0 ħ kk 0 MM ee RR nn kk TT,nn RR nn+1 RR nn = ee ππ ss 0 14
15 Influence of magnetic field on Efimov trimers: small B HH = 1 MM h iii 1 ee cc AA MM ee iii + ee cc AA + 1 MM ee iii 3 + ee cc AA 3 Under small magnetic field, the binding energy of Efimov bound states EE TT is much larger than the Landau level spacing. EE TT,nn = ħ kk TT,nn MM ee ħωω 0 = ħ MM ee ll RR nn = ss 0 kk 1 TT,nn ss 0 ll BB BB Size of Efimov trimers The magnetic field can be treated as perturbation, and the system still possesses approximate hyper-spherical symmetry. In hyper-spherical coordinates: harmonic oscillator potential hyper-spherical operators: rriiii ρρiiii,kk +RR 5 + MM ee ωω BB RR 8ħ rriiii ρρiiii,kk + MM eeωω BB ħ = RR RR RR5 + LL zz iiii,kk LL iiii ħ RR sin + θθ kk 1 RR sin θθ kk MM eeee TT ħ Ψ = 0 LL iiii,kk ħ RR cos θθ kk θθ kk 4 sin θθ kk 15
16 Influence of magnetic field on Efimov trimers: small B The Faddeev decomposition: Ψ = φφ 1 rr 3, ρρ 3,1 + φφ rr 13, ρρ 13, φφ rr 1, ρρ 1,3 The Faddeev equation: Solution ansatz: rr ρρ + MM ee ωω BB RR φφ ii rr, ρρ = φφ 0 8ħ + MM eeωω BB ħ ii (RR,θθ, ρρ) = 1 RR 5/ sin θθ The hyper-angle equation (ll = 1): ll ll+1 θθ + cos θθ Bethe-Peierls boundary condition: 1 zz LL iiii,kk RR 5/ sin θθ nn,ll,mm ff nn,ll ii φφ ii nn,ll θθ; RR = ss ii nn,ll φφ nn,ll rrψ MM eeee TT ħ φφ ii rr, ρρ = 0 ii RR φφ nn,ll θθ; RR rψ rr 0 1 aa θθ; RR YY llll ( ρρ) sin γγ = MM e MM h + MM ee Eigenvalues: 1 ss nn ss nn tan ss nn ππ cos(γγss nn) sin γγ cos(ss nn ππ + sin(γγss nn)/ss nn ) sin ππ γγ cos(ss nn ) = 0 The above secular equation have imaginary solution ss nn = iiss 0 if γγ > 1.199, corresponding to MM 16 ee MM h > 13.6.
17 Influence of magnetic field: approximate discrete scale invariance The hyper-radial equation: ss 0 +1/4 ddrr dd RR + RR 4ll BB ll BB Influence of magnetic field ff nn RR = MM EEEE TT ħ ff nn RR Attractive potential condition: ss 0 + 1/4 RR + RR 4ll BB ll BB < 0 WKB solution of Efimov trimers: RR < RR cc ss 0 ll BB RR nn ss 0 pppppp ħ RR 0 RR 1 RR ss 0 ll BB dddd = ππππħ Approximate discrete scale invariance for RR nn < RR cc : ln RR nn RR nn 1 = ππ ss 0 + RR nn 4ss 0 ll RR nn 1 BBnn 4ss ππ 1, ππ ll BBnn 1 ss 0 ss 0 ss 0 ss 0 ln BB nn+1 BB nn ππ ss 0 1 ss 0, ππ ss ss 0 17
18 Problem, comparison and solution from 3-body to -body 1. How to obtain the resonant scattering condition aa ± with large magnetic field? Not clear. Thus, the prerequisite for Efimov trimers is not met.. In the large magnetic field limit, the system become quasi-1d with cylindrical symmetry. No Efimov trimers in 1D. 3. ZrTe5 is identified as Dirac semimetal by ARPES [Nature Physics 1, 550 (016)], what s the influence of Dirac physics? Efimov equation: dd ddrr ss RR MM eeee TT ħ ff RR = 0 Scale Invariant Dirac equation: mm ħvv FF σσ kk ħvv FF σσ kk mm ΨΨ = EE VV RR ΨΨ Scale invariance is obtained, if mm = 0 and VV RR RR 1. Weyl semimetal with Coulomb attraction. 18
19 Dirac particle with Coulomb attraction Dirac-Kepler problem at large Z, atomic collapse 3D W. Greiner, B. Muller & J. Rafelski, QED of Strong Fields (Springer, 1985). Y. B. Zeldovich and V. S. Popov, Usp. Fiz. Nauk 105, 403 (1971). Subcritical: ZZee 4ππεε 0 ħcc < 1 Ze is central charge. Supercritical: ZZee 4ππεε 0 ħcc > 1 atomic collapse for Z > 137. Atomic collapse in graphene D A. V. Shytov, M. I. Katsnelson, and L. S. Levitov, PRL 99, (007). A. V. Shytov, M. I. Katsnelson, and L. S. Levitov, PRL 99, 4680 (007). V. M. Pereira, J. Nilsson, and A. H. Castro Neto, PRL 99, (007). Quasi-bound states in the supercritical regime of graphene. 19
20 3D Weyl particle + Coulomb attraction + magnetic field 0 ħvv FF σσ kk + ee ħcc σσ AA ħvv FF σσ kk + ee ħcc σσ AA 0 ΨΨ 1 ΨΨ = EE VV(RR) ΨΨ 1 ΨΨ Under small magnetic field, the Coulomb attraction EE TT larger than the Landau level spacing. VV RR nn is much = ZZααħvv FF RR nn EE BB = ħvv FF ll BB RR nn ZZααll BB αα = ee 4ππεε 0 ħvv FF Expanding in spinor spherical harmonic function: Radial equation: dd dddd uu 1 RR uu RR = λλ + RR RR ll BB EE + ZZZZ ħvv FF RR ΨΨ 1 RR ΨΨ RR = YY λλ 1,mm θθ, φφ uu λλ 1 1 RR /RR λλ 1 iiii,mm λλ θθ, φφ uu RR /RR EE + ZZZZ ħvv FF RR λλ RR + RR ll BB uu 1 RR uu RR 0
21 Approximate discrete scale invariance Radial equation (i=1,): dd ddrr uu ii RR = λλ RR + RR ll BB uu ii RR EE ħvv FF + ZZZZ RR uu ii RR Magnetic field B=0: pp RR ħss 0 RR ss 0 (ZZZZ) λλ WKB solution: RR nnpprr ddr = nnnnħ R 0 RR nn /RR nn 1 = ee ππ/ss 0 EE nn = ħvv FFZZZZ RR nn = ħvv FFZZZZ RR 0 ee nnnn/ss 0 With small B: RR < RR cc ss 0 ll BB pp RR ħ RR (ZZZZ) λλ + RR WKB analysis gives the approximate discrete scale invariance: ll BB Bound state dissolves if RR nn > ss 0 ll BB. ln RR nn RR nn 1 ππ ss 0 1 ss 0, ππ ss ss 0 ln BB nn+1 BB nn ππ ss 0 1 ss 0, ππ ss ss 0 1
22 Weyl particle + Coulomb attraction + magnetic field 0 ħvv FF σσ kk + ee ħcc σσ AA ħvv FF σσ kk + ee ħcc σσ AA 0 ΨΨ 1 ΨΨ = EE VV(RR) ΨΨ 1 ΨΨ RR nn ZZααll BB Under very large magnetic field with, we consider the lowest landau level solution in cylindrical symmetry ρρ, zz, φφ. ΨΨ 1 = 0 uu ρρ, zz ee iiiiφφ ΨΨ = 0 vv ρρ, zz ee iiiiφφ uu ρρ, zz = ρρ mm ee ρρ 4ll BBgg zz vv ρρ, zz = iiρρ mm ee ρρ 4ll BBff zz EE VV zz ħvv FF gg zz + dd ff zz = 0 dddd EE VV zz ħvv FF ff zz dd gg zz = 0 dddd VV zz = 0 ZZZZħvv FF zz ρρ mm+1 ee ρρ ll BB 1 mm + 1 ll BB zz ZZZZħvv FF dddd ρρ + zz mm! mm mm+ ll BB Scale Invariant if ll BB zz with 1D Coulomb attraction.
23 Weyl particle + Coulomb attraction + magnetic field ddzz + dd VV zz dddd dd EE VV zz dddd + dd EE VV zz ħvv FF gg zz = 0 dd ddzz 3 4 VV zz EE VV zz VV zz EE VV zz + EE VV zz ħvv FF gg zz EE VV zz = 0 For zz ll BB and EE 0, attractive potential: VV zz = ZZZZħvv FF zz dd ddzz + ZZZZ zz zzgg zz = 0 pp zz ħzzzz zz WKB solution: zz nnppzz ddzz = nnnnħ z 0 zz nn /zz nn 1 = ee ππ/zzzz Discrete scale invariance 3
24 Approximate discrete scale invariance Attractive potential condition: Large magnetic field limit VV zz nn VV zz = ZZZZħvv FF zz 1 ll BB zz = ZZααħvv FF zz nn < EE BB = ħvv FF ll BB ll BB zz nn < 1 ll BB < zz nn ZZZZ WKB solution: zz nnppzz ddz = nnnnħ z 0 Approximate discrete scale invariance: Bound state forms if zz nn > ZZααll BB. pp zz ħzzzz zz 1 ll BB zz ln zz nn = ππ zz nn 1 ZZZZ + ll BB nn zz nn ll BB nn 1 ππ zz nn 1 ZZZZ 4 ZZZZ, ππ ZZZZ + 4 ZZZZ ln BB nn+1 BB nn ππ ZZZZ 8 ZZZZ, ππ ZZZZ + 8 ZZZZ 4
25 Comparison to the experimental results vv FF mm/ss for the Dirac bands in ZrTe 5 [Nature Physics 1, 550 (016)] Approximate discrete scale invariance: ZZZZ 4.87 and ss 0 = ZZZZ Theoretical ratio: Dissolution: Formation: ln BB nn+1 BB nn ππ ss 0 1 ss 0, ππ ss ss 0 BB nn /BB nn+1 (3.03, 4.6) ln BB nn+1 BB nn ππ ZZZZ 8 ZZZZ, ππ ZZZZ + 8 ZZZZ BB nn /BB nn+1 (.59, 5.09) Experimental ratio: BB nn BB nn+1 (.30, 4.00) 5
26 Experimental results in ZrTe 5 1. Clear demonstration of 5 log-b periodic MR oscillations.. The experimental scaling factor BB nn BB nn+1,30,4.00 is comparable to theoretical estimation. 3. The supercritical Coulomb attraction between hole and electron results in two-body Efimov bound states with discrete scale invariance. 4. Under magnetic field, the formation and dissolution of Efimov bound states give rise to log-b periodic MR oscillations beyond the quantum limit. 6
27 Conclusion 1. Coexistence of electron and hole carriers in Weyl system with supercritical Coulomb attraction = twobody Efimov quasi-bound states with discrete scale invariance.. The formation and dissolution of two-body Efimov quasi-bound states under magnetic field give rise to novel log-b periodic oscillations of 3D systems beyond the quantum limit, where the Landau level physics is inapplicable. Thank you! 7
PHL424: Nuclear Shell Model. Indian Institute of Technology Ropar
 PHL424: Nuclear Shell Model Themes and challenges in modern science Complexity out of simplicity Microscopic How the world, with all its apparent complexity and diversity can be constructed out of a few
PHL424: Nuclear Shell Model Themes and challenges in modern science Complexity out of simplicity Microscopic How the world, with all its apparent complexity and diversity can be constructed out of a few
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/11/eaau5096/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Discovery of log-periodic oscillations in ultraquantum topological materials Huichao Wang, Haiwen Liu, Yanan Li, Yongjie
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/11/eaau5096/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Discovery of log-periodic oscillations in ultraquantum topological materials Huichao Wang, Haiwen Liu, Yanan Li, Yongjie
Charge carrier density in metals and semiconductors
 Charge carrier density in metals and semiconductors 1. Introduction The Hall Effect Particles must overlap for the permutation symmetry to be relevant. We saw examples of this in the exchange energy in
Charge carrier density in metals and semiconductors 1. Introduction The Hall Effect Particles must overlap for the permutation symmetry to be relevant. We saw examples of this in the exchange energy in
(1) Introduction: a new basis set
 () Introduction: a new basis set In scattering, we are solving the S eq. for arbitrary VV in integral form We look for solutions to unbound states: certain boundary conditions (EE > 0, plane and spherical
() Introduction: a new basis set In scattering, we are solving the S eq. for arbitrary VV in integral form We look for solutions to unbound states: certain boundary conditions (EE > 0, plane and spherical
Elastic light scattering
 Elastic light scattering 1. Introduction Elastic light scattering in quantum mechanics Elastic scattering is described in quantum mechanics by the Kramers Heisenberg formula for the differential cross
Elastic light scattering 1. Introduction Elastic light scattering in quantum mechanics Elastic scattering is described in quantum mechanics by the Kramers Heisenberg formula for the differential cross
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 1 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Topics 5.7
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 1 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Topics 5.7
PHY103A: Lecture # 4
 Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 4 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 10-Jan-2018 Notes The Solutions to HW # 1 have been
Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 4 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 10-Jan-2018 Notes The Solutions to HW # 1 have been
Dressing up for length gauge: Aspects of a debate in quantum optics
 Dressing up for length gauge: Aspects of a debate in quantum optics Rainer Dick Department of Physics & Engineering Physics University of Saskatchewan rainer.dick@usask.ca 1 Agenda: Attosecond spectroscopy
Dressing up for length gauge: Aspects of a debate in quantum optics Rainer Dick Department of Physics & Engineering Physics University of Saskatchewan rainer.dick@usask.ca 1 Agenda: Attosecond spectroscopy
PHL424: Feynman diagrams
 PHL424: Feynman diagrams In 1940s, R. Feynman developed a diagram technique to describe particle interactions in space-time. Feynman diagram example Richard Feynman time Particles are represented by lines
PHL424: Feynman diagrams In 1940s, R. Feynman developed a diagram technique to describe particle interactions in space-time. Feynman diagram example Richard Feynman time Particles are represented by lines
CHAPTER 4 Structure of the Atom
 CHAPTER 4 Structure of the Atom Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 4.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 4.2 Rutherford Scattering 4.3 The Classic Atomic Model 4.4 The Bohr Model of the
CHAPTER 4 Structure of the Atom Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 4.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 4.2 Rutherford Scattering 4.3 The Classic Atomic Model 4.4 The Bohr Model of the
Lecture 22 Highlights Phys 402
 Lecture 22 Highlights Phys 402 Scattering experiments are one of the most important ways to gain an understanding of the microscopic world that is described by quantum mechanics. The idea is to take a
Lecture 22 Highlights Phys 402 Scattering experiments are one of the most important ways to gain an understanding of the microscopic world that is described by quantum mechanics. The idea is to take a
(2) Orbital angular momentum
 (2) Orbital angular momentum Consider SS = 0 and LL = rr pp, where pp is the canonical momentum Note: SS and LL are generators for different parts of the wave function. Note: from AA BB ii = εε iiiiii
(2) Orbital angular momentum Consider SS = 0 and LL = rr pp, where pp is the canonical momentum Note: SS and LL are generators for different parts of the wave function. Note: from AA BB ii = εε iiiiii
Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality
 Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality Leonid Levitov (MIT) Electron Interactions in Graphene FTPI, University of Minnesota 05/04/2013 Scaling symmetry:
Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality Leonid Levitov (MIT) Electron Interactions in Graphene FTPI, University of Minnesota 05/04/2013 Scaling symmetry:
QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE
 5 CHAPTER QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE 5.1 The Hydrogen Atom 5.2 Shell Model for Many-Electron Atoms 5.3 Aufbau Principle and Electron Configurations 5.4 Shells and the Periodic Table: Photoelectron
5 CHAPTER QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE 5.1 The Hydrogen Atom 5.2 Shell Model for Many-Electron Atoms 5.3 Aufbau Principle and Electron Configurations 5.4 Shells and the Periodic Table: Photoelectron
Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves
 Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves Lecture33: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay As before, we keep in view the four Maxwell s equations for all our discussions.
Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves Lecture33: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay As before, we keep in view the four Maxwell s equations for all our discussions.
Physics 371 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review
 Physics 71 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review Special Relativity Inertial vs. non-inertial reference frames Galilean relativity: Galilean transformation for relative motion along the xx xx direction: xx =
Physics 71 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review Special Relativity Inertial vs. non-inertial reference frames Galilean relativity: Galilean transformation for relative motion along the xx xx direction: xx =
(1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method
 (1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method New method (with the density matrix) Traditional method (from thermal physics courses) ZZ = TTTT ρρ = EE ρρ EE = dddd xx ρρ xx ii FF = UU
(1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method New method (with the density matrix) Traditional method (from thermal physics courses) ZZ = TTTT ρρ = EE ρρ EE = dddd xx ρρ xx ii FF = UU
Quantum Mechanics. An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc.
 Quantum Mechanics An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 3 Experimental Basis of
Quantum Mechanics An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 3 Experimental Basis of
Atomic collapse in graphene
 Atomic collapse in graphene Andrey V. Shytov (BNL) Work done in collaboration with: L.S. Levitov MIT M.I. Katsnelson University of Nijmegen, Netherlands * Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 236801; ibid. 99, 246802
Atomic collapse in graphene Andrey V. Shytov (BNL) Work done in collaboration with: L.S. Levitov MIT M.I. Katsnelson University of Nijmegen, Netherlands * Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 236801; ibid. 99, 246802
The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric. Viorel Laurentiu Cartas
 The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric Viorel Laurentiu Cartas The notion of gravitational force is replaced by the curvature of the spacetime fabric. The mass tells to spacetime how to curve and the
The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric Viorel Laurentiu Cartas The notion of gravitational force is replaced by the curvature of the spacetime fabric. The mass tells to spacetime how to curve and the
Gravitation. Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Gravitation Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 What you are about to learn: Newton's law of universal gravitation About motion in circular and other orbits How to
Gravitation Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 What you are about to learn: Newton's law of universal gravitation About motion in circular and other orbits How to
TECHNICAL NOTE AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF POINT SPRING SUPPORTS BASED ON DEFINED SOIL PROFILES AND COLUMN-FOOTING PROPERTIES
 COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., FEBRUARY 2016 TECHNICAL NOTE AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF POINT SPRING SUPPORTS BASED ON DEFINED SOIL PROFILES AND COLUMN-FOOTING PROPERTIES Introduction This technical note
COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., FEBRUARY 2016 TECHNICAL NOTE AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF POINT SPRING SUPPORTS BASED ON DEFINED SOIL PROFILES AND COLUMN-FOOTING PROPERTIES Introduction This technical note
Gradient expansion formalism for generic spin torques
 Gradient expansion formalism for generic spin torques Atsuo Shitade RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science Atsuo Shitade, arxiv:1708.03424. Outline 1. Spintronics a. Magnetoresistance and spin torques
Gradient expansion formalism for generic spin torques Atsuo Shitade RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science Atsuo Shitade, arxiv:1708.03424. Outline 1. Spintronics a. Magnetoresistance and spin torques
Yang-Hwan Ahn Based on arxiv:
 Yang-Hwan Ahn (CTPU@IBS) Based on arxiv: 1611.08359 1 Introduction Now that the Higgs boson has been discovered at 126 GeV, assuming that it is indeed exactly the one predicted by the SM, there are several
Yang-Hwan Ahn (CTPU@IBS) Based on arxiv: 1611.08359 1 Introduction Now that the Higgs boson has been discovered at 126 GeV, assuming that it is indeed exactly the one predicted by the SM, there are several
Modeling of a non-physical fish barrier
 University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst International Conference on Engineering and Ecohydrology for Fish Passage International Conference on Engineering and Ecohydrology for Fish
University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst International Conference on Engineering and Ecohydrology for Fish Passage International Conference on Engineering and Ecohydrology for Fish
A Posteriori Error Estimates For Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Using Non-polynomial Basis Functions
 Lin Lin A Posteriori DG using Non-Polynomial Basis 1 A Posteriori Error Estimates For Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Using Non-polynomial Basis Functions Lin Lin Department of Mathematics, UC Berkeley;
Lin Lin A Posteriori DG using Non-Polynomial Basis 1 A Posteriori Error Estimates For Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Using Non-polynomial Basis Functions Lin Lin Department of Mathematics, UC Berkeley;
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.016.4 Quantum Hall effect in black phosphorus two-dimensional electron system Likai Li, Fangyuan Yang, Guo Jun Ye, Zuocheng Zhang, Zengwei Zhu, Wen-Kai Lou, Xiaoying Zhou, Liang Li,
DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.016.4 Quantum Hall effect in black phosphorus two-dimensional electron system Likai Li, Fangyuan Yang, Guo Jun Ye, Zuocheng Zhang, Zengwei Zhu, Wen-Kai Lou, Xiaoying Zhou, Liang Li,
PHY103A: Lecture # 9
 Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Cold atoms in optical lattices
 Cold atoms in optical lattices www.lens.unifi.it Tarruel, Nature Esslinger group Optical lattices the big picture We have a textbook model, which is basically exact, describing how a large collection of
Cold atoms in optical lattices www.lens.unifi.it Tarruel, Nature Esslinger group Optical lattices the big picture We have a textbook model, which is basically exact, describing how a large collection of
Radiation. Lecture40: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Radiation Zone Approximation We had seen that the expression for the vector potential for a localized cuent distribution is given by AA (xx, tt) = μμ 4ππ ee iiiiii dd xx eeiiii xx xx xx xx JJ (xx ) In
Radiation Zone Approximation We had seen that the expression for the vector potential for a localized cuent distribution is given by AA (xx, tt) = μμ 4ππ ee iiiiii dd xx eeiiii xx xx xx xx JJ (xx ) In
Module 7 (Lecture 25) RETAINING WALLS
 Module 7 (Lecture 25) RETAINING WALLS Topics Check for Bearing Capacity Failure Example Factor of Safety Against Overturning Factor of Safety Against Sliding Factor of Safety Against Bearing Capacity Failure
Module 7 (Lecture 25) RETAINING WALLS Topics Check for Bearing Capacity Failure Example Factor of Safety Against Overturning Factor of Safety Against Sliding Factor of Safety Against Bearing Capacity Failure
CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity
 CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 Inertial Frames of Reference Conceptual and Experimental
CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 Inertial Frames of Reference Conceptual and Experimental
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS
 4 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS 4.1 Preliminaries: Wave Motion and Light 4.2 Evidence for Energy Quantization in Atoms 4.3 The Bohr Model: Predicting Discrete Energy Levels in Atoms 4.4 Evidence
4 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS 4.1 Preliminaries: Wave Motion and Light 4.2 Evidence for Energy Quantization in Atoms 4.3 The Bohr Model: Predicting Discrete Energy Levels in Atoms 4.4 Evidence
Rotational Motion. Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Rotational Motion Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 We ll look for a way to describe the combined (rotational) motion 2 Angle Measurements θθ ss rr rrrrrrrrrrrrrr
Rotational Motion Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 We ll look for a way to describe the combined (rotational) motion 2 Angle Measurements θθ ss rr rrrrrrrrrrrrrr
Impact of Chamber Pressure on Sputtered Particle Energy
 Wilmert De Bosscher Chief Technology Officer +32 9381 6177 wilmert.debosscher@soleras.com Impact of Chamber Pressure on Sputtered Particle Energy Tampa, October 18 th, 2017 Background Why Sputtering at
Wilmert De Bosscher Chief Technology Officer +32 9381 6177 wilmert.debosscher@soleras.com Impact of Chamber Pressure on Sputtered Particle Energy Tampa, October 18 th, 2017 Background Why Sputtering at
Photons in the universe. Indian Institute of Technology Ropar
 Photons in the universe Photons in the universe Element production on the sun Spectral lines of hydrogen absorption spectrum absorption hydrogen gas Hydrogen emission spectrum Element production on the
Photons in the universe Photons in the universe Element production on the sun Spectral lines of hydrogen absorption spectrum absorption hydrogen gas Hydrogen emission spectrum Element production on the
Photon Interactions in Matter
 Radiation Dosimetry Attix 7 Photon Interactions in Matter Ho Kyung Kim hokyung@pusan.ac.kr Pusan National University References F. H. Attix, Introduction to Radiological Physics and Radiation Dosimetry,
Radiation Dosimetry Attix 7 Photon Interactions in Matter Ho Kyung Kim hokyung@pusan.ac.kr Pusan National University References F. H. Attix, Introduction to Radiological Physics and Radiation Dosimetry,
Problem 4.1 (Verdeyen Problem #8.7) (a) From (7.4.7), simulated emission cross section is defined as following.
 Problem 4.1 (Verdeyen Problem #8.7) (a) From (7.4.7), simulated emission cross section is defined as following. σσ(νν) = AA 21 λλ 2 8ππnn 2 gg(νν) AA 21 = 6 10 6 ssssss 1 From the figure, the emission
Problem 4.1 (Verdeyen Problem #8.7) (a) From (7.4.7), simulated emission cross section is defined as following. σσ(νν) = AA 21 λλ 2 8ππnn 2 gg(νν) AA 21 = 6 10 6 ssssss 1 From the figure, the emission
Wave Motion. Chapter 14 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Wave Motion Chapter 14 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Waves: propagation of energy, not particles 2 Longitudinal Waves: disturbance is along the direction of wave propagation
Wave Motion Chapter 14 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Waves: propagation of energy, not particles 2 Longitudinal Waves: disturbance is along the direction of wave propagation
Variations. ECE 6540, Lecture 02 Multivariate Random Variables & Linear Algebra
 Variations ECE 6540, Lecture 02 Multivariate Random Variables & Linear Algebra Last Time Probability Density Functions Normal Distribution Expectation / Expectation of a function Independence Uncorrelated
Variations ECE 6540, Lecture 02 Multivariate Random Variables & Linear Algebra Last Time Probability Density Functions Normal Distribution Expectation / Expectation of a function Independence Uncorrelated
7.3 The Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel Iterative Methods
 7.3 The Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel Iterative Methods 1 The Jacobi Method Two assumptions made on Jacobi Method: 1.The system given by aa 11 xx 1 + aa 12 xx 2 + aa 1nn xx nn = bb 1 aa 21 xx 1 + aa 22 xx 2
7.3 The Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel Iterative Methods 1 The Jacobi Method Two assumptions made on Jacobi Method: 1.The system given by aa 11 xx 1 + aa 12 xx 2 + aa 1nn xx nn = bb 1 aa 21 xx 1 + aa 22 xx 2
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 8 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 8 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 8 Nov 2017](/thumbs/87/96488236.jpg) Efimov Effect in the Dirac Semi-metals arxiv:1711.03118v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 8 Nov 017 Pengfei Zhang 1 and Hui Zhai 1, 1 Institute for Advanced Study, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China Collaborative
Efimov Effect in the Dirac Semi-metals arxiv:1711.03118v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 8 Nov 017 Pengfei Zhang 1 and Hui Zhai 1, 1 Institute for Advanced Study, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China Collaborative
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS. ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems
 SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa
 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 1 Review for Exam3 12. 11. 2013 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 2 Chapter
57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 1 Review for Exam3 12. 11. 2013 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 2 Chapter
Exam 2 Fall 2015
 1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
Control of Mobile Robots
 Control of Mobile Robots Regulation and trajectory tracking Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Organization and
Control of Mobile Robots Regulation and trajectory tracking Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Organization and
Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam. Problem Worth
 Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Worth 9 6 6 5 9 8 5 8 8 8 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Total 8 5 5 6 6 8 6 6 6 6 6 150 Last Name: First Name: Student ID: Section:
Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Worth 9 6 6 5 9 8 5 8 8 8 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Total 8 5 5 6 6 8 6 6 6 6 6 150 Last Name: First Name: Student ID: Section:
CHEMISTRY Spring, 2018 QUIZ 1 February 16, NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /20
 QUIZ 1 February 16, 018 NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /0 [Numbers without decimal points are to be considered infinitely precise. Show reasonable significant figures and proper units. In particular, use generally
QUIZ 1 February 16, 018 NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /0 [Numbers without decimal points are to be considered infinitely precise. Show reasonable significant figures and proper units. In particular, use generally
Time Domain Analysis of Linear Systems Ch2. University of Central Oklahoma Dr. Mohamed Bingabr
 Time Domain Analysis of Linear Systems Ch2 University of Central Oklahoma Dr. Mohamed Bingabr Outline Zero-input Response Impulse Response h(t) Convolution Zero-State Response System Stability System Response
Time Domain Analysis of Linear Systems Ch2 University of Central Oklahoma Dr. Mohamed Bingabr Outline Zero-input Response Impulse Response h(t) Convolution Zero-State Response System Stability System Response
Grover s algorithm. We want to find aa. Search in an unordered database. QC oracle (as usual) Usual trick
 Grover s algorithm Search in an unordered database Example: phonebook, need to find a person from a phone number Actually, something else, like hard (e.g., NP-complete) problem 0, xx aa Black box ff xx
Grover s algorithm Search in an unordered database Example: phonebook, need to find a person from a phone number Actually, something else, like hard (e.g., NP-complete) problem 0, xx aa Black box ff xx
Interacting atoms and molecules in triangular lattices with varying geometry. Dan Stamper-Kurn, UC Berkeley
 Interacting atoms and molecules in triangular lattices with varying geometry Dan Stamper-Kurn, U erkeley perspective on atoms in optical lattices Gedanken laboratory for study of single-, few- and many-body
Interacting atoms and molecules in triangular lattices with varying geometry Dan Stamper-Kurn, U erkeley perspective on atoms in optical lattices Gedanken laboratory for study of single-, few- and many-body
Haar Basis Wavelets and Morlet Wavelets
 Haar Basis Wavelets and Morlet Wavelets September 9 th, 05 Professor Davi Geiger. The Haar transform, which is one of the earliest transform functions proposed, was proposed in 90 by a Hungarian mathematician
Haar Basis Wavelets and Morlet Wavelets September 9 th, 05 Professor Davi Geiger. The Haar transform, which is one of the earliest transform functions proposed, was proposed in 90 by a Hungarian mathematician
Chemical Engineering 412
 Chemical Engineering 412 Introductory Nuclear Engineering Lecture 12 Radiation/Matter Interactions II 1 Neutron Flux The collisions of neutrons of all energies is given by FF = ΣΣ ii 0 EE φφ EE dddd All
Chemical Engineering 412 Introductory Nuclear Engineering Lecture 12 Radiation/Matter Interactions II 1 Neutron Flux The collisions of neutrons of all energies is given by FF = ΣΣ ii 0 EE φφ EE dddd All
Coulomb s Law and Coulomb s Constant
 Pre-Lab Quiz / PHYS 224 Coulomb s Law and Coulomb s Constant Your Name: Lab Section: 1. What will you investigate in this lab? 2. Consider a capacitor created when two identical conducting plates are placed
Pre-Lab Quiz / PHYS 224 Coulomb s Law and Coulomb s Constant Your Name: Lab Section: 1. What will you investigate in this lab? 2. Consider a capacitor created when two identical conducting plates are placed
Functional RG for few-body physics
 Functional RG for few-body physics Michael C Birse The University of Manchester Review of results from: Schmidt and Moroz, arxiv:0910.4586 Krippa, Walet and Birse, arxiv:0911.4608 Krippa, Walet and Birse,
Functional RG for few-body physics Michael C Birse The University of Manchester Review of results from: Schmidt and Moroz, arxiv:0910.4586 Krippa, Walet and Birse, arxiv:0911.4608 Krippa, Walet and Birse,
SECTION 8: ROOT-LOCUS ANALYSIS. ESE 499 Feedback Control Systems
 SECTION 8: ROOT-LOCUS ANALYSIS ESE 499 Feedback Control Systems 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Consider a general feedback system: Closed-loop transfer function is KKKK ss TT ss = 1 + KKKK ss HH ss GG ss
SECTION 8: ROOT-LOCUS ANALYSIS ESE 499 Feedback Control Systems 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Consider a general feedback system: Closed-loop transfer function is KKKK ss TT ss = 1 + KKKK ss HH ss GG ss
Neutron ββ-decay Angular Correlations
 Neutron ββ-decay Angular Correlations Brad Plaster University of Kentucky Figure Credit: V. Cirigliano, B. Markisch, et al. Figure Credit: https://www.physi.uniheidelberg.de/forschung/anp/perkeo/index.php
Neutron ββ-decay Angular Correlations Brad Plaster University of Kentucky Figure Credit: V. Cirigliano, B. Markisch, et al. Figure Credit: https://www.physi.uniheidelberg.de/forschung/anp/perkeo/index.php
Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries
 Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries Didier Ndengeyintwali Physics Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA (Dated: May 17, 2010) 1. Introduction The Pauli exclusion principle
Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries Didier Ndengeyintwali Physics Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA (Dated: May 17, 2010) 1. Introduction The Pauli exclusion principle
Review of Last Class 1
 Review of Last Class 1 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Bragg formulation Condition of diffraction peak: 2dd sin θθ = nnλλ Review of Last Class 2 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Von Laue formulation
Review of Last Class 1 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Bragg formulation Condition of diffraction peak: 2dd sin θθ = nnλλ Review of Last Class 2 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Von Laue formulation
Module 6 (Lecture 22) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
 Module 6 (Lecture ) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE 1.1 LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE DUE TO SURCHARGE 1. ACTIVE PRESSURE FOR WALL ROTATION ABOUT TOP- BRACED CUT 1.3 ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE FOR TRANSLATION OF RETAINING
Module 6 (Lecture ) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE 1.1 LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE DUE TO SURCHARGE 1. ACTIVE PRESSURE FOR WALL ROTATION ABOUT TOP- BRACED CUT 1.3 ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE FOR TRANSLATION OF RETAINING
A Simple and Usable Wake Vortex Encounter Severity Metric
 A Simple and Usable Wake Vortex Encounter Severity Metric Ivan De Visscher Grégoire Winckelmans WaPT-Wake Prediction Technologies a spin-off company from Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) WakeNet-Europe
A Simple and Usable Wake Vortex Encounter Severity Metric Ivan De Visscher Grégoire Winckelmans WaPT-Wake Prediction Technologies a spin-off company from Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) WakeNet-Europe
CP Properties of Leptons in Mirror Mechanism
 CP Properties of Leptons in Mirror Mechanism Igor T. Dyatlov * Scientific Research Center Kurchatov Institute Petersburg Institute of Nuclear Physics, Gatchina, Russia Formation of quark and lepton mass
CP Properties of Leptons in Mirror Mechanism Igor T. Dyatlov * Scientific Research Center Kurchatov Institute Petersburg Institute of Nuclear Physics, Gatchina, Russia Formation of quark and lepton mass
Last Name _Piatoles_ Given Name Americo ID Number
 Last Name _Piatoles_ Given Name Americo ID Number 20170908 Question n. 1 The "C-V curve" method can be used to test a MEMS in the electromechanical characterization phase. Describe how this procedure is
Last Name _Piatoles_ Given Name Americo ID Number 20170908 Question n. 1 The "C-V curve" method can be used to test a MEMS in the electromechanical characterization phase. Describe how this procedure is
The Bose Einstein quantum statistics
 Page 1 The Bose Einstein quantum statistics 1. Introduction Quantized lattice vibrations Thermal lattice vibrations in a solid are sorted in classical mechanics in normal modes, special oscillation patterns
Page 1 The Bose Einstein quantum statistics 1. Introduction Quantized lattice vibrations Thermal lattice vibrations in a solid are sorted in classical mechanics in normal modes, special oscillation patterns
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa
 Review for Exam3 12. 9. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Review for Exam3 12. 9. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Module 7 (Lecture 27) RETAINING WALLS
 Module 7 (Lecture 27) RETAINING WALLS Topics 1.1 RETAINING WALLS WITH METALLIC STRIP REINFORCEMENT Calculation of Active Horizontal and vertical Pressure Tie Force Factor of Safety Against Tie Failure
Module 7 (Lecture 27) RETAINING WALLS Topics 1.1 RETAINING WALLS WITH METALLIC STRIP REINFORCEMENT Calculation of Active Horizontal and vertical Pressure Tie Force Factor of Safety Against Tie Failure
Classical RSA algorithm
 Classical RSA algorithm We need to discuss some mathematics (number theory) first Modulo-NN arithmetic (modular arithmetic, clock arithmetic) 9 (mod 7) 4 3 5 (mod 7) congruent (I will also use = instead
Classical RSA algorithm We need to discuss some mathematics (number theory) first Modulo-NN arithmetic (modular arithmetic, clock arithmetic) 9 (mod 7) 4 3 5 (mod 7) congruent (I will also use = instead
Mathematics Ext 2. HSC 2014 Solutions. Suite 403, 410 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW 2010 keystoneeducation.com.
 Mathematics Ext HSC 4 Solutions Suite 43, 4 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW info@keystoneeducation.com.au keystoneeducation.com.au Mathematics Extension : HSC 4 Solutions Contents Multiple Choice... 3 Question...
Mathematics Ext HSC 4 Solutions Suite 43, 4 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW info@keystoneeducation.com.au keystoneeducation.com.au Mathematics Extension : HSC 4 Solutions Contents Multiple Choice... 3 Question...
Secondary 3H Unit = 1 = 7. Lesson 3.3 Worksheet. Simplify: Lesson 3.6 Worksheet
 Secondary H Unit Lesson Worksheet Simplify: mm + 2 mm 2 4 mm+6 mm + 2 mm 2 mm 20 mm+4 5 2 9+20 2 0+25 4 +2 2 + 2 8 2 6 5. 2 yy 2 + yy 6. +2 + 5 2 2 2 0 Lesson 6 Worksheet List all asymptotes, holes and
Secondary H Unit Lesson Worksheet Simplify: mm + 2 mm 2 4 mm+6 mm + 2 mm 2 mm 20 mm+4 5 2 9+20 2 0+25 4 +2 2 + 2 8 2 6 5. 2 yy 2 + yy 6. +2 + 5 2 2 2 0 Lesson 6 Worksheet List all asymptotes, holes and
General Strong Polarization
 General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) December 4, 2017 IAS:
General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) December 4, 2017 IAS:
Chapter 5: Spectral Domain From: The Handbook of Spatial Statistics. Dr. Montserrat Fuentes and Dr. Brian Reich Prepared by: Amanda Bell
 Chapter 5: Spectral Domain From: The Handbook of Spatial Statistics Dr. Montserrat Fuentes and Dr. Brian Reich Prepared by: Amanda Bell Background Benefits of Spectral Analysis Type of data Basic Idea
Chapter 5: Spectral Domain From: The Handbook of Spatial Statistics Dr. Montserrat Fuentes and Dr. Brian Reich Prepared by: Amanda Bell Background Benefits of Spectral Analysis Type of data Basic Idea
Lecture 15: Scattering Rutherford scattering Nuclear elastic scattering Nuclear inelastic scattering Quantum description The optical model
 Lecture 15: Scattering Rutherford scattering Nuclear elastic scattering Nuclear inelastic scattering Quantum description The optical model Lecture 15: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu)
Lecture 15: Scattering Rutherford scattering Nuclear elastic scattering Nuclear inelastic scattering Quantum description The optical model Lecture 15: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu)
The Role of Unbound Wavefunctions in Energy Quantization and Quantum Bifurcation
 The Role of Unbound Wavefunctions in Energy Quantization and Quantum Bifurcation Ciann-Dong Yang 1 Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan cdyang@mail.ncku.edu.tw
The Role of Unbound Wavefunctions in Energy Quantization and Quantum Bifurcation Ciann-Dong Yang 1 Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan cdyang@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Quantum state measurement
 Quantum state measurement Introduction The rotation properties of light fields of spin are described by the 3 3 representation of the 0 0 SO(3) group, with the generators JJ ii we found in class, for instance
Quantum state measurement Introduction The rotation properties of light fields of spin are described by the 3 3 representation of the 0 0 SO(3) group, with the generators JJ ii we found in class, for instance
Lecture 13: The Actual Shell Model Recalling schematic SM Single-particle wavefunctions Basis states Truncation Sketch view of a calculation
 Lecture 13: The Actual Shell Model Recalling schematic SM Single-particle wavefunctions Basis states Truncation Sketch view of a calculation Lecture 13: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 2017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu)
Lecture 13: The Actual Shell Model Recalling schematic SM Single-particle wavefunctions Basis states Truncation Sketch view of a calculation Lecture 13: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 2017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu)
Work, Energy, and Power. Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Discovery of the Higgs Boson
 Discovery of the Higgs Boson Seminar: Key Experiments in Particle Physics Martin Vogrin Munich, 22. July 2016 Outline Theoretical part Experiments Results Open problems Motivation The SM is really two
Discovery of the Higgs Boson Seminar: Key Experiments in Particle Physics Martin Vogrin Munich, 22. July 2016 Outline Theoretical part Experiments Results Open problems Motivation The SM is really two
M.5 Modeling the Effect of Functional Responses
 M.5 Modeling the Effect of Functional Responses The functional response is referred to the predation rate as a function of the number of prey per predator. It is recognized that as the number of prey increases,
M.5 Modeling the Effect of Functional Responses The functional response is referred to the predation rate as a function of the number of prey per predator. It is recognized that as the number of prey increases,
Using the Application Builder for Neutron Transport in Discrete Ordinates
 Using the Application Builder for Neutron Transport in Discrete Ordinates C.J. Hurt University of Tennessee Nuclear Engineering Department (This material is based upon work supported under a Department
Using the Application Builder for Neutron Transport in Discrete Ordinates C.J. Hurt University of Tennessee Nuclear Engineering Department (This material is based upon work supported under a Department
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa
 Review for Exam2 11. 13. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Review for Exam2 11. 13. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
PHL424: Nuclear fusion
 PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
PHL424: Nuclear fusion Hot Fusion 5 10 15 5 10 8 projectiles on target compound nuclei 1 atom Hot fusion (1961 1974) successful up to element 106 (Seaborgium) Coulomb barrier V C between projectile and
A Trapped Degenerate Mode Magnetic Acoustic Resonator. Medicine, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK
 A Trapped Degenerate Mode Magnetic Acoustic Resonator Barry J Gallacher *, Jim Burdess *, Zhongxu Hu *, Harriet Grigg *, Carl Dale **, Chen Fu **, Neil Keegan **, John Hedley * and Julia Spoors ** * School
A Trapped Degenerate Mode Magnetic Acoustic Resonator Barry J Gallacher *, Jim Burdess *, Zhongxu Hu *, Harriet Grigg *, Carl Dale **, Chen Fu **, Neil Keegan **, John Hedley * and Julia Spoors ** * School
Continuous Random Variables
 Continuous Random Variables Page Outline Continuous random variables and density Common continuous random variables Moment generating function Seeking a Density Page A continuous random variable has an
Continuous Random Variables Page Outline Continuous random variables and density Common continuous random variables Moment generating function Seeking a Density Page A continuous random variable has an
General Strong Polarization
 General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) May 1, 018 G.Tech:
General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) May 1, 018 G.Tech:
Problem 3.1 (Verdeyen 5.13) First, I calculate the ABCD matrix for beam traveling through the lens and space.
 Problem 3. (Verdeyen 5.3) First, I calculate the ABCD matrix for beam traveling through the lens and space. T = dd 0 0 dd 2 ff 0 = dd 2 dd ff 2 + dd ( dd 2 ff ) dd ff ff Aording to ABCD law, we can have
Problem 3. (Verdeyen 5.3) First, I calculate the ABCD matrix for beam traveling through the lens and space. T = dd 0 0 dd 2 ff 0 = dd 2 dd ff 2 + dd ( dd 2 ff ) dd ff ff Aording to ABCD law, we can have
SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE. ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I
 SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I 2 Fluid Capacitor Fluid Capacitor 3 Consider the following device: Two rigid hemispherical shells Separated by an impermeable elastic
SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I 2 Fluid Capacitor Fluid Capacitor 3 Consider the following device: Two rigid hemispherical shells Separated by an impermeable elastic
Super Efimov effect. Sergej Moroz University of Washington. together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son. Tuesday, April 1, 14
 Super Efimov effect together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son Sergej Moroz University of Washington Few-body problems They are challenging but useful: Newton gravity Quantum atoms Quantum molecules
Super Efimov effect together with Yusuke Nishida and Dam Thanh Son Sergej Moroz University of Washington Few-body problems They are challenging but useful: Newton gravity Quantum atoms Quantum molecules
Interaction with matter
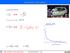 Interaction with matter accelerated motion: ss = bb 2 tt2 tt = 2 ss bb vv = vv 0 bb tt = vv 0 2 ss bb EE = 1 2 mmvv2 dddd dddd = mm vv 0 2 ss bb 1 bb eeeeeeeeeeee llllllll bbbbbbbbbbbbbb dddddddddddddddd
Interaction with matter accelerated motion: ss = bb 2 tt2 tt = 2 ss bb vv = vv 0 bb tt = vv 0 2 ss bb EE = 1 2 mmvv2 dddd dddd = mm vv 0 2 ss bb 1 bb eeeeeeeeeeee llllllll bbbbbbbbbbbbbb dddddddddddddddd
Atomic fluorescence. The intensity of a transition line can be described with a transition probability inversely
 Atomic fluorescence 1. Introduction Transitions in multi-electron atoms Energy levels of the single-electron hydrogen atom are well-described by EE nn = RR nn2, where RR = 13.6 eeee is the Rydberg constant.
Atomic fluorescence 1. Introduction Transitions in multi-electron atoms Energy levels of the single-electron hydrogen atom are well-described by EE nn = RR nn2, where RR = 13.6 eeee is the Rydberg constant.
COMPRESSION FOR QUANTUM POPULATION CODING
 COMPRESSION FOR QUANTUM POPULATION CODING Ge Bai, The University of Hong Kong Collaborative work with: Yuxiang Yang, Giulio Chiribella, Masahito Hayashi INTRODUCTION Population: A group of identical states
COMPRESSION FOR QUANTUM POPULATION CODING Ge Bai, The University of Hong Kong Collaborative work with: Yuxiang Yang, Giulio Chiribella, Masahito Hayashi INTRODUCTION Population: A group of identical states
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics. Algebraic Expressions. Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9. Algebra
 Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Algebraic Expressions Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Algebra Algebraic Expressions Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Algebraic Expressions Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Algebra Algebraic Expressions Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets
" = Y(#,$) % R(r) = 1 4& % " = Y(#,$) % R(r) = Recitation Problems: Week 4. a. 5 B, b. 6. , Ne Mg + 15 P 2+ c. 23 V,
 Recitation Problems: Week 4 1. Which of the following combinations of quantum numbers are allowed for an electron in a one-electron atom: n l m l m s 2 2 1! 3 1 0 -! 5 1 2! 4-1 0! 3 2 1 0 2 0 0 -! 7 2-2!
Recitation Problems: Week 4 1. Which of the following combinations of quantum numbers are allowed for an electron in a one-electron atom: n l m l m s 2 2 1! 3 1 0 -! 5 1 2! 4-1 0! 3 2 1 0 2 0 0 -! 7 2-2!
ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION
 A Study of an N Molecule-Quantized Radiation Field-Hamiltonian BY MICHAEL THOMAS TAVIS DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY, GRADUATE PROGRAM IN PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE, DECEMBER 1968 PROFESSOR FREDERICK
A Study of an N Molecule-Quantized Radiation Field-Hamiltonian BY MICHAEL THOMAS TAVIS DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY, GRADUATE PROGRAM IN PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE, DECEMBER 1968 PROFESSOR FREDERICK
C = V Q. To find the capacitance of two conductors:
 Capacitance Capacitance is a measure of the ability of two conductors to store charge when a given potential difference is established between them. Two conductors, on one of which is charge +Q and on
Capacitance Capacitance is a measure of the ability of two conductors to store charge when a given potential difference is established between them. Two conductors, on one of which is charge +Q and on
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals. Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator
 Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator with boundary conditions S(u) = g(x) on Γ where S is a differential
Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator with boundary conditions S(u) = g(x) on Γ where S is a differential
BB 22 pairs in e+e- Andrzej Kupsc, Uppsala. Time-like elastic (and transition) Form Factors. J/ψ and ψ(2s) decays to B 1 B 2.
 Production of BB 11 BB 22 pairs in e+e- Andrzej Kupsc, Uppsala Time-like elastic (and transition) Form Factors J/ψ and ψ(2s) decays to B 1 B 2 Spin polarization Hyperons from J/ψ and ψ(2s): decay parameters
Production of BB 11 BB 22 pairs in e+e- Andrzej Kupsc, Uppsala Time-like elastic (and transition) Form Factors J/ψ and ψ(2s) decays to B 1 B 2 Spin polarization Hyperons from J/ψ and ψ(2s): decay parameters
Lecture 5: Nuclear Structure 3 Fermi Gas Model Microscopic approach Thermodynamic approach Nuclear level density
 Lecture 5: Nuclear Structure 3 Fermi Gas Model Microscopic approach Thermodynamic approach Nuclear level density Lecture 5: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 2017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu) The nucleus
Lecture 5: Nuclear Structure 3 Fermi Gas Model Microscopic approach Thermodynamic approach Nuclear level density Lecture 5: Ohio University PHYS7501, Fall 2017, Z. Meisel (meisel@ohio.edu) The nucleus
Universal behaviour of four-boson systems from a functional renormalisation group
 Universal behaviour of four-boson systems from a functional renormalisation group Michael C Birse The University of Manchester Results from: Jaramillo Avila and Birse, arxiv:1304.5454 Schmidt and Moroz,
Universal behaviour of four-boson systems from a functional renormalisation group Michael C Birse The University of Manchester Results from: Jaramillo Avila and Birse, arxiv:1304.5454 Schmidt and Moroz,
Lecture 3. STAT161/261 Introduction to Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 2018 Prof. Allie Fletcher
 Lecture 3 STAT161/261 Introduction to Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 2018 Prof. Allie Fletcher Previous lectures What is machine learning? Objectives of machine learning Supervised and
Lecture 3 STAT161/261 Introduction to Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 2018 Prof. Allie Fletcher Previous lectures What is machine learning? Objectives of machine learning Supervised and
