Supersonic plasma jet interaction with gases and plasmas
|
|
|
- Marsha Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICPP 2008 FUKUOKA september 11, 2008 Supersonic plasma jet interaction with gases and plasmas Ph. Nicolaï 3.5 ns 8.5 ns 13.5 ns He 15 bars 2 mm CELIA, Université Bordeaux 1 - CNRS - CEA, Talence, France
2 Co-authors C. Stenz, X. Ribeyre, V. Tikhonchuk CELIA, Université Bordeaux 1 - CNRS - CEA, Talence, France A. Kasperczuk and T. Pisarczyk Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion, Warsaw, Poland L. Juha, E. Krousky, K. Masek, M. Pfeifer, K. Rohlena, J. Skala Institute of Physics AS CR, Prague, Czech Republic J. Ullschmied Institute of Plasma Physics, Prague, Czech Republic D. Klir, J. Kravarik, P. Kubes, M. Kalal Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic
3 Motivations Issues relevant to astrophysical objets Collimation and propagation of jets over long distance Interaction of these jets with suroudding media X-ray emission of these jets Issues relevant to the inertial fusion joints surface bumps fill tubes, ) Test for large multi D radiation hydrodynamic codes Clumpy HH jet Hartigan 2006
4 Convergent plasma flows produce jets (radiative collapse) Multi-beams X-rays Z-pinch B laser laser X Jet laser laser X Jet Jet X conical target holhraum wire array laser laser Jet These jets can be scaled to astrophysical conditions D. Farley et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1982 (1999) J Foster et al,phys. Plasma 9, 2251 (2002) S. Lebedev et al, Astrophys. J 564, 113 (2002) D. Ryutov et al, Astron. Astrophys. 518, 821 (1999) Foam-filled cone target B. Loupias et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. (2007)
5 Jet formation using a single laser beam The experiment was carried out at the PALS iodine laser facility: low energy, simple and reproducible conditions target jet 600 µm Laser E 100 J t 300 ps Experimental electron density distribution Mach number : M = Length : L = 3-4 mm Velocity : U = 500 km/s duration τ 10 ns The jet is produced due to the radiative cooling of plasma Competition between expansion time and radiation cooling time Confirmed by 2D radiation magneto hydrodynamic code This jet can also be scaled to astrophysical parameters Ph. Nicolaï et al, Phys. Plasmas 13, (2006), T. Pisarczyk et al, ibid, (2006)
6 Experimental setup The experiment was carried out at the PALS iodine laser facility The laser beam: E ~ 100, λ = μm, t = 300 ps, R = 300 μm L L L L The gas puff : Argon or helium gas. Presssure ~2-40 bars The plasma density profiles were obtained by means of a 3-frame interferometric system (3ω) The plasma X-ray emission were obtained by means of a 4-frame X-ray pinhole camera (.01-1kev)
7 Structure and evolution of the working surface Shadowgraphic and interferometric images 0.5 argon (10b) t = 4ns bow shock t = 7ns Cu copper jet laser marks t =10ns density accumulation narrow tip nozzle other shot reverse shock copper jet t = 7ns laser marks Detailed structure with three sequential snapshots Very good reproducibility shot after shot
8 Structure and evolution of the working surface X-ray images [10 ev 1 kev] 2 mm bow shock (a) Cu jet noze 0 ns 5 ns 10 ns 30 tilt density accumulation (b) 2 mm 0 ns 5 ns 10 ns Good correspondence between X-ray images and interferograms bow shock, Cu jet, narrow tip and density accumulation
9 Effect of Ar gaz pressure on the working surface shadowgraphic images copper jet bow shock 0 bar 2 bars 5 bars reverse shock bow shock reverse shock 15 bars laser marks Gas pressure strongly modifies the working surface shape from an arrow form to a more spherical shape The decrease of the WS thickness linked to radiation losses
10 Effect of Ar gaz pressure on the working surface 2 mm (a) 8 ns 2 bars 2 mm 13 ns (b) 9 ns 10 bars 14 ns X-ray images confirm the change of the WS shape For 10 bars Ar, hydrodynamic instabilities appear in the WS
11 Bow shock position and density ratio For each pressure, several shots have been done improving confidence mean value (mm) Bow shock position 10 ns 7 ns 4 ns gas pressure (bar) By balancing the momentum fluxes at the jet head and at bow shock ρ (v v ) ρ v 2 2 jet jet bs gas bs one can estimate the bow shock velocity v v 1+ bs jet η ( 1/2 ) 1 with η = ρ ρ jet gas A pressure increase induces a shorter propagartion length The relative velocities between 4ns and 10 ns, corresponding to the density plateau, equal 140 km/s (15 bars), 185 km/s (10 bars), 210 km/s (5 bars) Given the jet velocity ~ 400 km/s, the density ratio, η, varies between 0.3 (15 bars) and 1.2 (5 bars) The Working Surface thickness decreases as gas pressure increases, from 0.85 mm to 0.5 mm for 7 ns. After 10 ns, the W.S. becomes thinner.
12 Effect of He gas pressure on the working surface Cu 10 bars 15 bars WS He 20 bars reverse shock bow shock 30 bars 0.1 nozzle copper jet Contrary to Ar plasma, He gas pressure variation does not induce significant change in the WS shape: the radiation losses are small The WS thickness slightly decreases as the gas pressure increases and the distance of the Cu jet propagation through gas decreases
13 X-ray images for various HELIUM gaz pressures 9.5 ns 10.5 ns 2 mm 10 bars 20 bars 9.5 ns 2 mm 8.5 ns 30 bars 40 bars One does not have the agreement of the X-ray images with previous shadowgrams Emission just arises from copper material - bow shock in He gas is not visible The shape remains the same similitude with the low Ar gas pressure
14 Bow shock position and W.S. thickness (mm) ns 7 ns * * * * * * * * * bow shock Mach disk working surface thickness gas pressure (bar) A pressure increase induces a shorter propagation length, 20 The relative velocities varies between 270 km/s (15 bars) and 195 km/s (40 bars) which involve a density ratio between 4 (15 bars) and 1 (40 bars) The working surface thickness exceeds 1 mm for all pressures indicates more adiabatic conditions in the interaction zone
15 Estimate of Radiation losses For a plane slab of thickness d, the cooling time writes : Energy density * d ρ d C T Z+1 v -3 1 τ c = = = f ( τ) T κ m radiation flux 2FR A where f (τ) is a function of the optical depth τ = dρκ m κ m = mean Planck opacity 15 = 4 π 0 κ 3 u ν u e du hν with u = T cm 2 /g κ argon ν helium ρ = 4 10 / g cc T = 100 ev ν (ev) 2 Ar : κm = 79cm / g τc 2ns 2 He : κm =.089cm / g τc 2 µ s from bremsstrahlung emission Ar : τ c He : τ 450 ns 3 s c µ to be compared with the jet propagation time ~ 5 ns Drake, High-Energy-Density Physics, Springer, 2006 Tsakiris JQSRT Vol. 38, No 5, pp. 353 (1987)
16 0. 4 ns bow shock interface 7 ns 10 ns copper Structure and evolution of the working surface Simulation* correctly reproduces interaction zone laser marks Helium gas, pressure ~ 10 bars interface copper helium interface bow shock 0. - bow shock reverse shock reverse shock reverse shock Simulation allows to identify physical processes : bow shock in gas, reverse shock in copper jet, laser absorption, The gas behind the bow shock remains warm implicating a large W.S. Helium gas induces an adiabatic evolution of the w.s. *PH Maire et al, SIAM JSC 29, 1781 (2007), J. Breil et al, J. Comp. Phys. 224, 785 (2007)
17 Effect of gaz pressure on Working Surface Helium gas [7 ns] 7 b bow shock 15 b bow shock 30 b bow shock 0. - interface copper helium reverse shock interface helium reverse shock copper interface laser marks reverse shock The working surface shape remains the same As Cu jet propagation through gas decreases as gas pressure increases (lateral and longitudinal expansions are reduced) Simulation images agree with experiment
18 Structure and evolution of the working surface X-ray images [10 ev 1 kev] 7 bars 15 bars 30 bars tilt ns 2 mm 10.5 ns 20 bars 30 bars Only copper plasma emits X-rays The bow shock propagation through helium gas does not appear The copper jet form remains (more or less) identical
19 Structure and evolution of the working surface 0. - copper argon 10ns tip reverse non adiabatic case : argon gas argon copper 10ns tip reverse laser marks 3 bars shock 6 bars shock w.s. 12 bars tip argon 0. As the pressure increases as the w.s. form changes a narrow tip appears for high pressure The interaction zone structure strongly differs from the helium case. Formation of a dense/thin shell due to radiative cooling which reduces temperature behind the «bow» shock The argon gas accumulation in shell may lead to hydrodynamic instabilities Blondin et al, Astrophys. J, 360, 370 (1990)
20 Structure and evolution of the working surface X-ray images [10 ev 1 kev] 3 bars 6 bars 2 mm ns Conformity between previous density distributions and X-ray images Shape change Density accumulation and nose cone also observed in X-ray image
21 Similarity conditions Can the experiment be scaled to an astrophysical jet?
22 Conclusion Supersonic jet study using a 100J single laser beam facility Adiabatic or cooling jet structures observed by changing gas composition These structures are correctly simulated by our 2D radiation hydrocode These jets verify the similarity criteria and apply to astroϕ conditions More details in ref; Ph. Nicolaï et al, Phys. Plasmas 15, (2008)
23 The numerical tool We use the 2 D radiative magneto-hydrodynamic code, CHIC* second order cell centered Lagrangian scheme ALE scheme unstructured meshes classical or nonlocal thermal conduction nine points scheme thermal coupling detailled radiation transport LTE or NLTE opacities real Equation of State (QEOS and Sesame) 3D ray tracing for laser propagation self-generated magnetic fields thermonuclear burn *PH Maire et al, SIAM JSC 29, 1781 (2007), *J. Breil et al, J. Comp. Phys. 224, 785 (2007)
24 The use Conditions of hydrocode One has to verify that the mean free paths are shorter than the dimensions of structures observed in experiment Fast copper ions are slowed down in collisions with the ions and e- of ambiant gas By using the NRL plasma formulary!, the collision frequencies read υ = 9.10 nzz Λ ( A + A ) A ε s 8 a /2 3/2 1 Cu a i a Cu Cu a Cu a Cu Cu υ nz Λ A T s /2 1 Cu e e Cu Cu e Cu e For our parameters; kinetic energy of Cu ion ε 50 kev, T~100 ev, ρ~10-4 g/cc 9 1 υ υ 4.10 Cu a Cu e s Given the jet velocity v Cu = 400 km/s, the m.f.p; λ = v /( υ + υ ) 50μ Cu Cu Cu a Cu e m The gas is not motionless (bow shock), and the relative velocity should be smaller. As! J. Huba, NRL, Washington DC, (2007) 4 λcu v if v v/2 λcu λcu /16
25 Energie balance : Helium gas case (15 bars) (J) Copper w/o gas kinetic energy thermal energy X-ray losses (ns) E las. = 100J (J) Without gas X-ray Copper with He gas kinetic Cu He thermal After 9 ns, 20% of the energy lost through X-ray emission, 66% transformed in kinetic energy and 11% in thermal energy. At the laser pulse end, thermal energy reaches 52% With helium gas After 9 ns, radiated energy (21%) and copper thermal energy (11%) remain the same. Only the copper kinetic energy is reduced (40%) and decreases with time. Energy lost by copper is transformed into kinetic (10%) and thermal (15%) energies of He gas (ns)
26 Energie balance : argon gas case (6 bars) (J) Copper w/o gas kinetic energy thermal energy X-ray losses (ns) E las. = 100J (J) Without gas thermal Copper with Ar gas kinetic Cu Ar X-ray (ns) After 9 ns, 20% of the energy lost through X-ray emission, 66% transformed in kinetic energy and 11% in thermal energy. With argon gas After 9 ns, radiated energy (30%) and copper thermal energy (15%) increase. The copper kinetic energy only represents 29%. Fast increase of argon energies for first ns then decrease due to X-ray losses Losses are greater than energy gain from copper material
27 Density maps obtained from interferograms unfolded with Abel inversion Helium gas pressure = 10 bars a b 3D view (10 ns) t = 10 ns c end of the density plateau d One accesses to the density range and a more detailed information
28 Bow shock position and W.S. thickness For each pressure, several shots have been done improving confidence mean value (mm) Bow shock position * * * * 10 ns 4 ns * * * * * on axis off axis (mm) * * 10 ns * * 7 ns bow shock mach disk * * * working surface thickness gas pressure (bar) gas pressure (bar) «Off axis» and «on axis» positions converge to the same value as the P increases the bow shock shape becomes spherical The triangular shape elongates with time at low pressure The Working Surface thickness decreases as gas pressure increases, from 0.85 mm to 0.5 mm for 7 ns. After 10 ns, the W.S. becomes thinner. P. Hartigan, Astrophys. J. 339, 987 (1989)
29 Experiment Effect of the target atomic number Experimental electron density distribution E = 100 J λ= μm R = 300 μm 400 ps pulse aluminium copper silver The jet is produced due to the radiative cooling of plasma
INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY Division of Physical and Chemical Sciences Physics Section
 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY Division of Physical and Chemical Sciences Physics Section Second Research Co-ordination Meeting Co-ordinated of the ordinated Research Project on Elements of Power Plant
INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY Division of Physical and Chemical Sciences Physics Section Second Research Co-ordination Meeting Co-ordinated of the ordinated Research Project on Elements of Power Plant
Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions
 Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Formation of Episodic Magnetically Driven Radiatively Cooled Plasma Jets in the Laboratory
 Formation of Episodic Magnetically Driven Radiatively Cooled Plasma Jets in the Laboratory F. Suzuki-Vidal 1, S. V. Lebedev 1, A. Ciardi 2, S. N. Bland 1, J. P. Chittenden 1, G. N. Hall 1, A. Harvey- Thompson
Formation of Episodic Magnetically Driven Radiatively Cooled Plasma Jets in the Laboratory F. Suzuki-Vidal 1, S. V. Lebedev 1, A. Ciardi 2, S. N. Bland 1, J. P. Chittenden 1, G. N. Hall 1, A. Harvey- Thompson
Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities
 Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities S.V. Lebedev, F. Suzuki-Vidal, S.N. Bland, A. Harvey-Thompson, G. Hall, A. Marocchino, J.P. Chittenden Imperial College
Laboratory Astrophysics: magnetically driven plasma jets on pulsed power facilities S.V. Lebedev, F. Suzuki-Vidal, S.N. Bland, A. Harvey-Thompson, G. Hall, A. Marocchino, J.P. Chittenden Imperial College
Laser ion acceleration with low density targets: a new path towards high intensity, high energy ion beams
 Laser ion acceleration with low density targets: a new path towards high intensity, high energy ion beams P. Antici 1,2,3, J.Boeker 4, F. Cardelli 1,S. Chen 2,J.L. Feugeas 5, F. Filippi 1, M. Glesser 2,3,
Laser ion acceleration with low density targets: a new path towards high intensity, high energy ion beams P. Antici 1,2,3, J.Boeker 4, F. Cardelli 1,S. Chen 2,J.L. Feugeas 5, F. Filippi 1, M. Glesser 2,3,
Experimental and theoretical investigations of crater formation in an aluminium target in a PALS experiment
 NUKLEONIKA 2004;49(1):7 14 ORIGINAL PAPER Experimental and theoretical investigations of crater formation in an aluminium target in a PALS experiment Stefan Borodziuk, Igor Ya. Doskach, Sergei Gus kov,
NUKLEONIKA 2004;49(1):7 14 ORIGINAL PAPER Experimental and theoretical investigations of crater formation in an aluminium target in a PALS experiment Stefan Borodziuk, Igor Ya. Doskach, Sergei Gus kov,
PIC simulations of laser interactions with solid targets
 PIC simulations of laser interactions with solid targets J. Limpouch, O. Klimo Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Břehová 7, Praha 1, Czech Republic
PIC simulations of laser interactions with solid targets J. Limpouch, O. Klimo Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Břehová 7, Praha 1, Czech Republic
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities
 Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma
 LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
Influence of gas conditions on electron temperature inside a pinch column of plasma-focus discharge
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of gas conditions on electron temperature inside a pinch column of plasma-focus discharge To cite this article: D R Zaloga et al 218 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of gas conditions on electron temperature inside a pinch column of plasma-focus discharge To cite this article: D R Zaloga et al 218 J.
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics
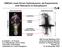 OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
A Detailed Postprocess Analysis of an Argon Gas Puff Z-pinch Plasma Using SPEC2D
 A Detailed Postprocess Analysis of an Argon Gas Puff Z-pinch Plasma Using SPEC2D Y. K. Chong, T. Kammash and J. Davis* Dept. of Nuclear Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 *Radiation
A Detailed Postprocess Analysis of an Argon Gas Puff Z-pinch Plasma Using SPEC2D Y. K. Chong, T. Kammash and J. Davis* Dept. of Nuclear Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 *Radiation
Energy Transformations in Z-Pinches
 Energy Transformations in Z-Pinches P. Kubeš, J. Kravárik Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic M. Scholz, M. Paduch, K. Tomaszewski, L. Rić Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion,
Energy Transformations in Z-Pinches P. Kubeš, J. Kravárik Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic M. Scholz, M. Paduch, K. Tomaszewski, L. Rić Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion,
Molecular Pillars in the Sky and in the Lab
 Molecular Pillars in the Sky and in the Lab 30 Years of Photodissociation Regions Asilomar, CA June 29, 2015 Jave Kane LLNL-PRES-673855 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
Molecular Pillars in the Sky and in the Lab 30 Years of Photodissociation Regions Asilomar, CA June 29, 2015 Jave Kane LLNL-PRES-673855 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
Plasma Jets Production at Laser-Burnt-Through Foils and their Interaction with Secondary Targets
 Plasma Jets Production at Laser-Burnt-Through Foils and their Interaction with Secondary Targets O. Renner, J. Cihelka, L. Juha, J. Krása, E. Krouský, J. Nejdl, J. Skála, A. Velyhan, T. Pisarczyk 2, T.
Plasma Jets Production at Laser-Burnt-Through Foils and their Interaction with Secondary Targets O. Renner, J. Cihelka, L. Juha, J. Krása, E. Krouský, J. Nejdl, J. Skála, A. Velyhan, T. Pisarczyk 2, T.
Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses
 Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses Sargis Ter-Avetisyan ELI - Extreme Light Infrastructure Science and Technology with
Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses Sargis Ter-Avetisyan ELI - Extreme Light Infrastructure Science and Technology with
GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS
 GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS by C.A. BACK, P. AUDBERT, S.D. BATON, S.BASTIANI-CECCOTTI, P. GUILLOU, L. LECHERBOURG, B. BARBREL, E. GAUCI,
GA A25842 STUDY OF NON-LTE SPECTRA DEPENDENCE ON TARGET MASS IN SHORT PULSE LASER EXPERIMENTS by C.A. BACK, P. AUDBERT, S.D. BATON, S.BASTIANI-CECCOTTI, P. GUILLOU, L. LECHERBOURG, B. BARBREL, E. GAUCI,
Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources
 Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources M. M. Basko, V. G. Novikov, A. S. Grushin Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, Moscow, Russia RnD-ISAN, Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources M. M. Basko, V. G. Novikov, A. S. Grushin Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, Moscow, Russia RnD-ISAN, Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
plasma optics Amplification of light pulses: non-ionised media
 Amplification of light pulses: non-ionised media since invention of laser: constant push towards increasing focused intensity of the light pulses Chirped pulse amplification D. Strickland, G. Mourou, Optics
Amplification of light pulses: non-ionised media since invention of laser: constant push towards increasing focused intensity of the light pulses Chirped pulse amplification D. Strickland, G. Mourou, Optics
Modeling of laser-induced damage in KDP crystals
 Modeling of laser-induced damage in KDP crystals Guillaume Duchateau and Ludovic Hallo CEA, Centre d Etudes du Ripault, BP6, 76 Monts CELIA, 5 Cours de la Libération, 45 Talence KDP crystals frequency
Modeling of laser-induced damage in KDP crystals Guillaume Duchateau and Ludovic Hallo CEA, Centre d Etudes du Ripault, BP6, 76 Monts CELIA, 5 Cours de la Libération, 45 Talence KDP crystals frequency
Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility
 Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility B = 1 mm n e [1 18 cm -3 ] 1 Mario Manuel Magnetic Meeting University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics April 23
Magnetic Disruption of Inertially Collimated Flows on the Titan Laser Facility B = 1 mm n e [1 18 cm -3 ] 1 Mario Manuel Magnetic Meeting University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics April 23
Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets
 1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
Thermal Smoothing of Laser Imprint in Double-Pulse Plasma
 Thermal Smoothing of Laser Imprint in Double-Pulse Plasma M. KÁLAL and J. LIMPOUCH Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, % HKRYi 19, Praha 1, Czech
Thermal Smoothing of Laser Imprint in Double-Pulse Plasma M. KÁLAL and J. LIMPOUCH Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, % HKRYi 19, Praha 1, Czech
Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens
 Plasma Interface Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens Extraction Lens (-2000 volts) ION OPTICS Tip of the sampler cone is positioned to be in the region of maximum ionization Ions no longer under control
Plasma Interface Interface (backside) & Extraction Lens Extraction Lens (-2000 volts) ION OPTICS Tip of the sampler cone is positioned to be in the region of maximum ionization Ions no longer under control
Laser Plasma Monochromatic Soft X-ray Source Using Nitrogen Gas Puff Target
 Laser Plasma Monochromatic Soft X-ray Source Using Nitrogen Gas Puff Target M. Vrbova 1, P. Vrba 2, S.V. Zakharov 3, V.S. Zakharov 4, M. Müller 5, D. Pánek 1, T. Parkman 1, P.Brůža 1 1 Czech Technical
Laser Plasma Monochromatic Soft X-ray Source Using Nitrogen Gas Puff Target M. Vrbova 1, P. Vrba 2, S.V. Zakharov 3, V.S. Zakharov 4, M. Müller 5, D. Pánek 1, T. Parkman 1, P.Brůža 1 1 Czech Technical
Review of recent experiments carried out on the 1MJ Plasma-Focus PF-1000U device.
 Review of recent experiments carried out on the 1MJ Plasma-Focus PF-1000U device. Ryszard Miklaszewski, Marian Paduch, Andrzej Kasperczuk Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion, Warsaw, Poland
Review of recent experiments carried out on the 1MJ Plasma-Focus PF-1000U device. Ryszard Miklaszewski, Marian Paduch, Andrzej Kasperczuk Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion, Warsaw, Poland
Politecnico di Torino. Porto Institutional Repository
 Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] An Investigation of the Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets in Astrophysical Conditions Original Citation: M. Belan; S. Massaglia; M. Mirzaei;
Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] An Investigation of the Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets in Astrophysical Conditions Original Citation: M. Belan; S. Massaglia; M. Mirzaei;
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Sep 2015](/thumbs/92/110459609.jpg) New opacity measurement principle for LMJ-PETAL laser facility M. Le Pennec a, X. Ribeyre b, J.-E. Ducret a,b, S. Turck-Chièze a arxiv:1509.03563v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Sep 2015 a Service d Astrophysique,
New opacity measurement principle for LMJ-PETAL laser facility M. Le Pennec a, X. Ribeyre b, J.-E. Ducret a,b, S. Turck-Chièze a arxiv:1509.03563v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Sep 2015 a Service d Astrophysique,
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability
 Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions
 Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL
 PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
PETAL+ plasma diagnostics The PETAL+ project X-ray and particle diagnostics for plasma experiments at LMJ - PETAL Jean-Éric Ducret CEA-Saclay/IRFU/Service d Astrophysique & CELIA UMR5107, U. Bordeaux CEA
Optimization of laser-produced plasma light sources for EUV lithography
 page 1 of 17 Optimization of laser-produced plasma light sources for EUV lithography M. S. Tillack and Y. Tao 1 University of California, San Diego Center for Energy Research 1 Currently at Cymer Inc.
page 1 of 17 Optimization of laser-produced plasma light sources for EUV lithography M. S. Tillack and Y. Tao 1 University of California, San Diego Center for Energy Research 1 Currently at Cymer Inc.
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cluster fusion in a high magnetic field
 Santa Fe July 28, 2009 Cluster fusion in a high magnetic field Roger Bengtson, Boris Breizman Institute for Fusion Studies, Fusion Research Center The University of Texas at Austin In collaboration with:
Santa Fe July 28, 2009 Cluster fusion in a high magnetic field Roger Bengtson, Boris Breizman Institute for Fusion Studies, Fusion Research Center The University of Texas at Austin In collaboration with:
Laser-plasma interactions
 Chapter 2 Laser-plasma interactions This chapter reviews a variety of processes which may take place during the interaction of a laser pulse with a plasma. The discussion focuses on the features that are
Chapter 2 Laser-plasma interactions This chapter reviews a variety of processes which may take place during the interaction of a laser pulse with a plasma. The discussion focuses on the features that are
Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX)
 1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
Monochromatic 8.05-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets
 Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction
 -1 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction Peter Bodenheimer University of California Santa Cruz, USA Gregory P. Laughlin University of California Santa Cruz,
-1 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction Peter Bodenheimer University of California Santa Cruz, USA Gregory P. Laughlin University of California Santa Cruz,
Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil
 Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil A.V. Brantov 1, V. Yu. Bychenkov 1, D. V. Romanov 2, A. Maksimchuk 3 1 P. N. Lebedev Physics Institute RAS, Moscow 119991, Russia 2 All-Russia Research
Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil A.V. Brantov 1, V. Yu. Bychenkov 1, D. V. Romanov 2, A. Maksimchuk 3 1 P. N. Lebedev Physics Institute RAS, Moscow 119991, Russia 2 All-Russia Research
FIG. 1. "Flower-like" configuration of filaments used for modelling. Magnetic field values for this configuration can be described analytically. Induc
 Ion Motion Modelling within Dynamic Filamentary PF-Pinch Column A. Gaψlkowski 1), A. Pasternak 2), M. Sadowski 2) 1) Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion, Warsaw, Poland 2) The Andrzej Soltan
Ion Motion Modelling within Dynamic Filamentary PF-Pinch Column A. Gaψlkowski 1), A. Pasternak 2), M. Sadowski 2) 1) Institute of Plasma Physics and Laser Microfusion, Warsaw, Poland 2) The Andrzej Soltan
ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants
 Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants I. E. Golovkin 1, J. J. MacFarlane 1, P. Woodruff 1, J. E. Bailey 2, G. Rochau 2, K. Peterson 2, T.
Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants I. E. Golovkin 1, J. J. MacFarlane 1, P. Woodruff 1, J. E. Bailey 2, G. Rochau 2, K. Peterson 2, T.
Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy
 Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy Tara Desai 1 *, J.T. Mendonca 2, Dimitri Batani 1 and Andrea Bernardinello 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Ò G.Occhialini Ó and INFM, Universitˆ
Cluster Induced Ignition - A New Approach to Inertial Fusion Energy Tara Desai 1 *, J.T. Mendonca 2, Dimitri Batani 1 and Andrea Bernardinello 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Ò G.Occhialini Ó and INFM, Universitˆ
EUV lithography and Source Technology
 EUV lithography and Source Technology History and Present Akira Endo Hilase Project 22. September 2017 EXTATIC, Prague Optical wavelength and EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) VIS 13.5nm 92eV Characteristics of
EUV lithography and Source Technology History and Present Akira Endo Hilase Project 22. September 2017 EXTATIC, Prague Optical wavelength and EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) VIS 13.5nm 92eV Characteristics of
Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering
 Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering March 11, 2015 LLNL-PRES-XXXXXX This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344.
Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering March 11, 2015 LLNL-PRES-XXXXXX This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344.
Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition. H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University
 Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition and Related Laser Plasma Physics H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University Y. Sentoku University of Nevada
Multi-Scale Simulations for Fast Ignition and Related Laser Plasma Physics H. Nagatomo, T. Johzaki, A. Sunahara, and K. Mima Institute of Laser Engineering g Osaka University Y. Sentoku University of Nevada
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma
 Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility
 2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
Los Alamos National Laboratory Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 1 LA-UR
 Rayleigh-Taylor instability is generated when a heavy fluid sits above a lighter fluid in a gravitational field. The flow behavior is described in terms of bubbles of light fluid rising into the heavier
Rayleigh-Taylor instability is generated when a heavy fluid sits above a lighter fluid in a gravitational field. The flow behavior is described in terms of bubbles of light fluid rising into the heavier
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
ION ACCELERATION ENHANCEMENT IN LASER-GENERATED PLASMAS BY METALLIC DOPED HYDROGENATED POLYMERS
 DOI: 10.1478/C1A0901003 Atti della Accademia Peloritana dei Pericolanti Classe di Scienze Fisiche, Matematiche e Naturali ISSN 1825-1242 Vol. LXXXVII, C1A0901003 (2009) ION ACCELERATION ENHANCEMENT IN
DOI: 10.1478/C1A0901003 Atti della Accademia Peloritana dei Pericolanti Classe di Scienze Fisiche, Matematiche e Naturali ISSN 1825-1242 Vol. LXXXVII, C1A0901003 (2009) ION ACCELERATION ENHANCEMENT IN
188 L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski temperature. Some examples of the registered X-ray images are shown in Fig.1. Figure 1. X-ray pinhole images from
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA
 Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil.
 Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2018](/thumbs/85/91885877.jpg) Article submitted to: High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018 April 10, 2018 Laboratory radiative accretion shocks on GEKKO XII laser facility for POLAR project arxiv:1804.02714v1 [astro-ph.he]
Article submitted to: High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018 April 10, 2018 Laboratory radiative accretion shocks on GEKKO XII laser facility for POLAR project arxiv:1804.02714v1 [astro-ph.he]
Shock formation in supersonic cluster jets and its effect on axially modulated laser-produced plasma waveguides
 Shock formation in supersonic cluster jets and its effect on axially modulated laser-produced plasma waveguides S. J. Yoon, A. J. Goers, G. A. Hine, J. D. Magill, J. A. Elle, Y.-H. Chen, and H. M. Milchberg
Shock formation in supersonic cluster jets and its effect on axially modulated laser-produced plasma waveguides S. J. Yoon, A. J. Goers, G. A. Hine, J. D. Magill, J. A. Elle, Y.-H. Chen, and H. M. Milchberg
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008
 Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations
 Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
International Symposium on Plasma Focus in series SPFE 2013
 International Symposium on Plasma Focus in series SPFE 2013 Scaling Trends for Deuteron Beam Properties at Plasma Focus Pinch Exit S H Saw 1,2 and S Lee 1,2,3 1 INTI International University, 71800 Nilai,
International Symposium on Plasma Focus in series SPFE 2013 Scaling Trends for Deuteron Beam Properties at Plasma Focus Pinch Exit S H Saw 1,2 and S Lee 1,2,3 1 INTI International University, 71800 Nilai,
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma
 Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry
 High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I
 1 IF/P7-18 Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I H. Nagatomo 1), T. Johzaki 1), H. Sakagami 2) Y. Sentoku 3), A. Sunahara 4), T. Taguchi 5), Y. Nakao 6), H. Shiraga 1), H. Azechi 1), K.
1 IF/P7-18 Numerical Study of Advanced Target Design for FIREX-I H. Nagatomo 1), T. Johzaki 1), H. Sakagami 2) Y. Sentoku 3), A. Sunahara 4), T. Taguchi 5), Y. Nakao 6), H. Shiraga 1), H. Azechi 1), K.
Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1
 J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
arxiv: v2 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Sep 2012
![arxiv: v2 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Sep 2012 arxiv: v2 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Sep 2012](/thumbs/94/118994467.jpg) Short Intense Laser Pulse Collapse in Near-Critical Plasma F. Sylla, A. Flacco, S. Kahaly, M. Veltcheva, A. Lifschitz, and V. Malka Laboratoire d Optique Appliquée, ENSTA, CNRS, Ecole Polytechnique, UMR
Short Intense Laser Pulse Collapse in Near-Critical Plasma F. Sylla, A. Flacco, S. Kahaly, M. Veltcheva, A. Lifschitz, and V. Malka Laboratoire d Optique Appliquée, ENSTA, CNRS, Ecole Polytechnique, UMR
Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR
 Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR J. J. MacFarlane, P. Wang, I. E. Golovkin, P. R. Woodruff Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. Madison, WI (USA) http://www.prism-cs.com
Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR J. J. MacFarlane, P. Wang, I. E. Golovkin, P. R. Woodruff Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. Madison, WI (USA) http://www.prism-cs.com
Laboratory Astrophysics Experiments with Magnetically Driven Plasma Jets
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Laboratory Astrophysics Experiments with Magnetically Driven Plasma Jets To cite this article: F Suzuki-Vidal et al 214 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 511 125 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Laboratory Astrophysics Experiments with Magnetically Driven Plasma Jets To cite this article: F Suzuki-Vidal et al 214 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 511 125 View
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 7 Jul 1999
 Gamma-ray Burst Energetics Pawan Kumar Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, NJ 08540 Abstract arxiv:astro-ph/9907096v1 7 Jul 1999 We estimate the fraction of the total energy in a Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB)
Gamma-ray Burst Energetics Pawan Kumar Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, NJ 08540 Abstract arxiv:astro-ph/9907096v1 7 Jul 1999 We estimate the fraction of the total energy in a Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB)
FUSION WITH Z-PINCHES. Don Cook. Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185
 FUSION WITH Z-PINCHES Don Cook Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185 RECEIVED JUN 1 5 1998 Sandia is a multiprogmm laboratory operated by Sandia C o r p w I t 1oli, h Lockheed Martin
FUSION WITH Z-PINCHES Don Cook Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185 RECEIVED JUN 1 5 1998 Sandia is a multiprogmm laboratory operated by Sandia C o r p w I t 1oli, h Lockheed Martin
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
THE SLOW FOCUS MODE IN PLASMA FOCUS FOR FAST PLASMA STREAM NANO-MATERIALS FABRICATION: SELECTION OF ENERGY OF BOMBARDING PARTICLES BY PRESSURE CONTROL
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS THE SLOW FOCUS MODE IN PLASMA FOCUS FOR FAST PLASMA STREAM NANO-MATERIALS FABRICATION: SELECTION OF ENERGY OF BOMBARDING PARTICLES BY PRESSURE CONTROL 1,2,3 S. Lee*,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS THE SLOW FOCUS MODE IN PLASMA FOCUS FOR FAST PLASMA STREAM NANO-MATERIALS FABRICATION: SELECTION OF ENERGY OF BOMBARDING PARTICLES BY PRESSURE CONTROL 1,2,3 S. Lee*,
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information 3 Supplementary Figures 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Absorbing material placed between two dielectric media The incident electromagnetic wave propagates in stratified
1 Supplementary Information 3 Supplementary Figures 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Absorbing material placed between two dielectric media The incident electromagnetic wave propagates in stratified
Large Plasma Device (LAPD)
 Large Plasma Device (LAPD) Over 450 Access ports Computer Controlled Data Acquisition Microwave Interferometers Laser Induced Fluorescence DC Magnetic Field: 0.05-4 kg, variable on axis Highly Ionized
Large Plasma Device (LAPD) Over 450 Access ports Computer Controlled Data Acquisition Microwave Interferometers Laser Induced Fluorescence DC Magnetic Field: 0.05-4 kg, variable on axis Highly Ionized
Opacity and Optical Depth
 Opacity and Optical Depth Absorption dominated intensity change can be written as di λ = κ λ ρ I λ ds with κ λ the absorption coefficient, or opacity The initial intensity I λ 0 of a light beam will be
Opacity and Optical Depth Absorption dominated intensity change can be written as di λ = κ λ ρ I λ ds with κ λ the absorption coefficient, or opacity The initial intensity I λ 0 of a light beam will be
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015](/thumbs/82/85900018.jpg) Creation of Magnetized Jet Using a Ring of Laser Beams arxiv:1409.4273v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 Wen Fu a, Edison P. Liang a, Petros Tzeferacos b, Donald Q. Lamb b a Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Creation of Magnetized Jet Using a Ring of Laser Beams arxiv:1409.4273v2 [astro-ph.he] 11 Dec 2015 Wen Fu a, Edison P. Liang a, Petros Tzeferacos b, Donald Q. Lamb b a Department of Physics and Astronomy,
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission
 Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission Ø From line λ, can determine element, ionization state, and energy levels involved Ø From line shape, can determine bulk and thermal velocity and often
Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission Ø From line λ, can determine element, ionization state, and energy levels involved Ø From line shape, can determine bulk and thermal velocity and often
Construction and Physics of the Dense Plasma Focus device
 2370-3 School and Training Course on Dense Magnetized Plasma as a Source of Ionizing Radiations, their Diagnostics and Applications 8-12 October 2012 Construction and Physics of the Dense Plasma Focus
2370-3 School and Training Course on Dense Magnetized Plasma as a Source of Ionizing Radiations, their Diagnostics and Applications 8-12 October 2012 Construction and Physics of the Dense Plasma Focus
1D study of radiation-dominated implosion of a cylindrical tungsten plasma column
 1D study of radiation-dominated implosion of a cylindrical tungsten plasma column M M Basko 1,2, P V Sasorov 1, M Murakami 2, V G Novikov 3 and A S Grushin 3 1 Alikhanov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental
1D study of radiation-dominated implosion of a cylindrical tungsten plasma column M M Basko 1,2, P V Sasorov 1, M Murakami 2, V G Novikov 3 and A S Grushin 3 1 Alikhanov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental
RELATIVISTIC EFFECTS IN ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE HEATING AND CURRENT DRIVE
 RELATIVISTIC EFFECTS IN ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE HEATING AND CURRENT DRIVE Abhay K. Ram Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139. U.S.A. Joan Decker
RELATIVISTIC EFFECTS IN ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE HEATING AND CURRENT DRIVE Abhay K. Ram Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139. U.S.A. Joan Decker
Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas
 2014 US-Japan JIFT Workshop on Progress in kinetic plasma simulations Oct.31-Nov.1, 2014, Salon F, New Orleans Marriott, New Orleans, LA, U.S.A Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas T. Johzaki
2014 US-Japan JIFT Workshop on Progress in kinetic plasma simulations Oct.31-Nov.1, 2014, Salon F, New Orleans Marriott, New Orleans, LA, U.S.A Numerical Modeling of Radiative Kinetic Plasmas T. Johzaki
Laser matter interaction
 Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Plasma EUV source has been studied to achieve 180W of power at λ=13.5nm, which is required for the next generation microlithography
 Acknowledgement K. Nishihara, H. Nishimura, S. Fujioka Institute for Laser Engineering, Osaka University A. Sunahara, H. Furukawa Institute for Laser Technology T. Nishikawa, Okayama University F. Koike,
Acknowledgement K. Nishihara, H. Nishimura, S. Fujioka Institute for Laser Engineering, Osaka University A. Sunahara, H. Furukawa Institute for Laser Technology T. Nishikawa, Okayama University F. Koike,
Two-dimensional model of thermal smoothing of laser imprint in a double-pulse plasma
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2000 Two-dimensional model of thermal smoothing of laser imprint in a double-pulse plasma A. B. Iskakov and V. F. Tishkin Institute of Mathematical Modeling,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2000 Two-dimensional model of thermal smoothing of laser imprint in a double-pulse plasma A. B. Iskakov and V. F. Tishkin Institute of Mathematical Modeling,
Status and Prospect of Laser Fusion Research at ILE Osaka University
 Fusion Power Associates 39th Annual Meeting and Symposium Fusion Energy: Strategies and Expectations through the 2020s Status and Prospect of Laser Fusion Research at ILE Osaka University Introduction
Fusion Power Associates 39th Annual Meeting and Symposium Fusion Energy: Strategies and Expectations through the 2020s Status and Prospect of Laser Fusion Research at ILE Osaka University Introduction
Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations
 1 Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations Yu.A.Mikhailov, L.A.Nikitina, G.V.Sklizkov, A.N.Starodub, M.A.Zhurovich P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute,
1 Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations Yu.A.Mikhailov, L.A.Nikitina, G.V.Sklizkov, A.N.Starodub, M.A.Zhurovich P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute,
FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016
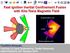 B-generation coil Cone Dense plasma core FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016 1 Summary Fast ignition with external B-field A critical problem
B-generation coil Cone Dense plasma core FUJIOKA Shinsuke Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University IAEA-FEC2016, 20 th October 2016 1 Summary Fast ignition with external B-field A critical problem
Preparation of the concerned sectors for educational and R&D activities related to the Hungarian ELI project
 Preparation of the concerned sectors for educational and R&D activities related to the Hungarian ELI project Ion acceleration in plasmas Lecture 10. Collisionless shock wave acceleration in plasmas pas
Preparation of the concerned sectors for educational and R&D activities related to the Hungarian ELI project Ion acceleration in plasmas Lecture 10. Collisionless shock wave acceleration in plasmas pas
PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS
 Chapter 6 PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS 10 26 10 24 Solar Center Electron density (e/cm 3 ) 10 22 10 20 10 18 10 16 10 14 10 12 High pressure arcs Chromosphere Discharge plasmas Solar interior Nd (nω) laserproduced
Chapter 6 PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS 10 26 10 24 Solar Center Electron density (e/cm 3 ) 10 22 10 20 10 18 10 16 10 14 10 12 High pressure arcs Chromosphere Discharge plasmas Solar interior Nd (nω) laserproduced
Laser-produced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source plasma for the next generation lithography application
 Laser-produced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source plasma for the next generation lithography application EUV light source plasma Tin icrodroplet Main pulse (CO2 laser pulse) Pre-pulse (Nd:YAG laser
Laser-produced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source plasma for the next generation lithography application EUV light source plasma Tin icrodroplet Main pulse (CO2 laser pulse) Pre-pulse (Nd:YAG laser
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets
 Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
Integrated simulations of fast ignition of inertial fusion targets Javier Honrubia School of Aerospace Engineering Technical University of Madrid, Spain 11 th RES Users Meeting, Santiago de Compostela,
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
IEPC M. Bodendorfer 1, K. Altwegg 2 and P. Wurz 3 University of Bern, 3012 Bern, Switzerland. and
 Future thruster application: combination of numerical simulation of ECR zone and plasma X-ray Bremsstrahlung measurement of the SWISSCASE ECR ion source IEPC-2009-234 Presented at the 31st International
Future thruster application: combination of numerical simulation of ECR zone and plasma X-ray Bremsstrahlung measurement of the SWISSCASE ECR ion source IEPC-2009-234 Presented at the 31st International
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2009](/thumbs/77/76266620.jpg) Laboratory Experiments, Numerical Simulations, and Astronomical Observations of Deflected Supersonic Jets: Application to HH 110 arxiv:0910.0318v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2009 P. Hartigan 1, J. M. Foster 2
Laboratory Experiments, Numerical Simulations, and Astronomical Observations of Deflected Supersonic Jets: Application to HH 110 arxiv:0910.0318v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2009 P. Hartigan 1, J. M. Foster 2
Analyses on the Ionization Instability of Non-Equilibrium Seeded Plasma in an MHD Generator
 Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.18, No.6, Jun. 2016 Analyses on the Ionization Instability of Non-Equilibrium Seeded Plasma in an MHD Generator Le Chi KIEN Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology
Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.18, No.6, Jun. 2016 Analyses on the Ionization Instability of Non-Equilibrium Seeded Plasma in an MHD Generator Le Chi KIEN Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology
Progress in MJ plasma focus research at IPPLM
 NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(2):183 188 ORIGINAL PAPER Progress in MJ plasma focus research at IPPLM Marek Scholz, Lesław Karpinski, Viacheslav I. Krauz, Pavel Kubeš, Marian Paduch, Marek J. Sadowski Abstract. The
NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(2):183 188 ORIGINAL PAPER Progress in MJ plasma focus research at IPPLM Marek Scholz, Lesław Karpinski, Viacheslav I. Krauz, Pavel Kubeš, Marian Paduch, Marek J. Sadowski Abstract. The
Attosecond-correlated dynamics of two electrons in argon
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 1 journal of January 2014 physics pp. 79 85 Attosecond-correlated dynamics of two electrons in argon V SHARMA 1,,NCAMUS 2, B FISCHER 2, M KREMER 2, A RUDENKO
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 1 journal of January 2014 physics pp. 79 85 Attosecond-correlated dynamics of two electrons in argon V SHARMA 1,,NCAMUS 2, B FISCHER 2, M KREMER 2, A RUDENKO
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016 12 High Harmonic Generation 12.1 Atomic units 12.2 The three step model 12.2.1 Ionization 12.2.2 Propagation 12.2.3 Recombination 12.3 Attosecond
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 12: January 15, 2016 12 High Harmonic Generation 12.1 Atomic units 12.2 The three step model 12.2.1 Ionization 12.2.2 Propagation 12.2.3 Recombination 12.3 Attosecond
M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e
 USj-WS on HIF & HEDP at Utsunomiya 29 Sep,. 2005 M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e Kazuyoshi KOYAMA, Takayuki WATANABE
USj-WS on HIF & HEDP at Utsunomiya 29 Sep,. 2005 M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e Kazuyoshi KOYAMA, Takayuki WATANABE
Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser pulse irradiation
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
Disk modelling by global radiation-mhd simulations
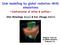 Disk modelling by global radiation-mhd simulations ~Confrontation of inflow & outflow~ Shin Mineshige (Kyoto) & Ken Ohsuga (NAOJ) Magnetic tower jet by RMHD simulation (Takeuchi+11) Outline Introduction
Disk modelling by global radiation-mhd simulations ~Confrontation of inflow & outflow~ Shin Mineshige (Kyoto) & Ken Ohsuga (NAOJ) Magnetic tower jet by RMHD simulation (Takeuchi+11) Outline Introduction
