LEP Results - 1. Pippa Wells CERN
|
|
|
- Tyler Cory Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEP Results - 1 Pippa Wells CERN
2 1: Z Resonance The LEP machine, beam energy, detectors Z lineshape: cross-sections, luminosity Lepton Forward-Backward asymmetry, polarised asymmetries Number o light neutrinos, lepton couplings 2: LEP2 Results WW and ZZ physics at LEP2 b-tagging, electroweak physics with heavy lavours (b and c) Global electroweak its Standard Model Higgs boson - a hint?
3 LEP Time Line 1960 s Glashow-Weinberg-Salam SU(2) U(1) theory o electroweak interactions, prediction o W and Z gauge bosons SU(3) colour QCD theory o strong interactions 1976 CERN study group considers Large Electron-Positron storage ring, s = GeV, L cm 2 s Observation o gluon at PETRA. December: 27 km design approved by CERN council 1983 Chose LEP experiments. W and Z observed at CERN SPS 1989 Scooped! e + e collisions at Z in MARK II at SLC. First collisions in LEP with s M Z 1995 Gradual installation o LEP2 SC RF system starts Energy raised to s = 140 GeV at end o year. Top quark observation at Fermilab conirmed 1996 W pair threshold crossed at LEP Nobel Prize or t Hoot and Veltman or or elucidating the quantum structure o electroweak interactions in physics 2000 Last year o LEP running with s up to 209 GeV.
4 Electron-positron annihilation Cross-section (pb) Z e + e hadrons CESR DORIS PEP PETRA TRISTAN KEKB SLACB LEP I SLC W + W - LEP II Centre-o-mass energy (GeV) γ Z Z/γ LEP collected 4.5 million Z, 12 thousand WW per experiment W e - e + ν e W W W γ Z W W
5 Z resonance lineshape To measure the Z mass, total width and cross-section, partial widths (branching ratios) and couplings: LEP machine gives e + e collisions at a ew energies on and near the Z peak and precise measurement o E beam Detectors ALEPH, DELPHI, L3, OPAL distinguish Z inal states and measure the luminosity rom QED t-channel process e + e e + e (Bhabha scattering) σ( s) = (N observed N background )/ɛl Monte Carlo simulation o the signal eiciency and background. Theoretical prediction o the lineshape Match precision rom 4.5 million Z events per experiment - relative statistical error about Several thousand people involved σ(m Z ) 340 MeV rom UA2+CDF in Hoped to reduce to 10 MeV (limited by beam energy precision) Count the number o generations. 2.5 generations were known in 1989, top quark and ν τ not yet established. Number o light neutrinos limited by big bang nucleosynthesis to < 4. Expected precision o about ±0.2 on the number.
6 Pippa Wells July 2
7 The LEP Collider A good ill lasts around 10 h (LEP1 at Z) or 3 h (LEP2) E (GeV) or L(10 31 cm -2 s -1 ) A day at LEP (example rom 1999) Energy Luminosity Time (hours)
8 Beam energy - resonant depolarisation E beam = e 2π B dl Spin o electrons aligns with vertical B ield due to synchrotron radiation. Slow (hours) build up o transverse polarisation IF beam orbit suiciently smooth. Spins precess in B ield. Number o precessions per turn o LEP: ν s = g e 2 2 e 2πm e B dl = g e 2 2 E beam m e ν s 101.5, 103.5, at s = peak-2, peak, peak+2 Apply oscillating horizontal B ield, ν, at one place. Scan ν. I ν = ν s, polarisation is destroyed. s s Fast sweeping horizontal B ield b x ν scan.474 to to to to to to.477 Polarization (%) Instantaneous precision 100 kev. In 1986 expected limit rom magnetic stability δm Z 10 MeV 22:25 22:30 22:35 22:40 22:45 Daytime
9 Stability? Quadrupole movements... Earth Rotation Axis irst calibrations saw luctuations o order 10 MeV. Earth tides driven by moon and sun. R > 0 ε E R < 0 ε M Moon ecliptic Length o orbit ixed by RF system, but magnets move with ground. Beam no longer goes through centre o quadrupoles. Sensitive to 1mm change in 27 km, typical 10 MeV peak-to-peak. Beam Energy (MeV) Nov. 11th :00 2:00 6:00 10:00 14:00 18:00 22:00 2:00 Daytime Also see ground distortion due to lake level, heavy rain...
10 Stability? Dipole ields : Measured energy at the end o many ills 1995: Measurements o B ield in tunnel dipoles Equivalent Beam Energy (MeV) th August MeV Noisy period Quiet period 16:00 18:00 20:00 22:00 00:00 02:00 04:00 06:00 Daytime Human activity increasing dipole ields during ill: BIAS 5 MeV Long investigation revealed cause - Vagabond electric currents rom nearby trains. Correct earlier years using model o average train behaviour. Final M Z systematic o 1.7 MeV
11 LEP1 data samples Approximate luminosity delivered per year. (Experiments collect 10 15% less) year centre-o-mass total o-peak energies luminosity luminosity [GeV] [pb 1 ] [pb 1 ] , 91.2, , 91.3, In , 6 o-peak points were measured. In 1993 and 1995 only 2 o-peak points were selected, to maximise the statistical precision. The exact values o the energies are chosen to allow resonant depolarisation at the end o each ill.
12 Cut-away view o OPAL Hadron calorimeters and return yoke Electromagnetic calorimeters Muon detectors Jet chamber Vertex chamber Microvertex detector y z θ ϕ x Forward detector Presampler Silicon tungsten luminometer Time o light detector Solenoid and pressure vessel Z chambers Overall size m
13 Hadronic event in ALEPH ALEPH DALI Run=9063 Evt=7848 Made on 9-Sep :43:03 by DREVERMANN with DALI_D1. This example has 3 jets e + e qqg Curved tracks in B ield (ALEPH and DELPHI have superconducting solenoids - B ield about 1.5 T compared to about 0.5 T in OPAL and L3) Many tracks and clusters in calorimeters
14 e + e e + e event in OPAL Run : even t 4093 : 1150 Da t e T ime C t r k (N= 2 Sump= ) Eca l (N= 9 SumE= ) Hca l (N= 0 SumE= 0. 0 ) Ebeam Ev i s Emi s s V t x ( , 0. 08, ) Muon (N= 0 ) Sec V t x (N= 0 ) Fde t (N= 1 SumE= 0. 0 ) Bz= Th r us t = Ap l an= Ob l a t = Sphe r = Y Z X 200. cm GeV Cen t r e o s c r een i s ( , , ) Lepton pair events have low multiplicity Electrons are identiied by a track in the central detector, and a large energy deposit in the electromagnetic calorimeter, E/p = 1.
15 e + e µ + µ event in L3 HCAL BGO Muon Chambers Tracking Muons penetrate the entire detector, and leave little energy in the calorimeters. L3 detector emphasizes lepton and photon id with a precise BGO crystal ECAL, and large muon spectrometer. The tracking volume is relatively small (radius 1m) ALL detectors inside 6m radius solenoid, ield 0.5T.
16 e + e τ + τ event in DELPHI DELPHI Interactive Analysis Beam: 45.6 GeV Proc: 8-Mar-1992 Run: Evt: 581 DAS : 18-Jun :22:19 Scan: 29-Apr-1992 TD TE TS TK TV ST PA Act ( 44) ( 48) ( 0) ( 9) ( 9) ( 0) ( 0) Deact ( 0) ( 4) ( 0) ( 6) ( 5) ( 0) ( 0) Barrel RICH Y Z X Tau lepton decays dominated by 1 and 3 charged tracks, with or without neutrals, missing neutrino(s), back-to-back very narrow jets. DELPHI has extra particle ID detectors, RICH.
17 Event selection A ew very simple cuts can distinguish hadronic, e + e, µ + µ and τ + τ events, and also background rom γγ, cosmic rays... The diicult task is to control systematic errors - how good is Monte Carlo description o data? Example 1: Hadronic event selection rom L e + e hadrons(γ) ( cos θ t 0.74) Events data 1994 e + e hadrons(γ) e + e τ + τ (γ) e + e e + e (γ) e + e µ + µ (γ) N cl
18 Event selection Example 2: Σ p tracks vs ΣE clusters or leptons p total / s µ + µ - τ + τ - OPAL e + e E total / s Representative values (vary rom experiment to experiment) Channel hadron e + e µ + µ τ + τ Eiciency % Background % Syst error %
19 Luminosity Measurement e - e + γ e - e + The t-channel contribution to e + e e + e dominates at small angles. Detectors typically 25 to 60 mrad rom beam. Very clear electron signal in orward detectors (calorimeters). E L /E Beam DELPHI E R /E Beam Accepted cross section at least 2 σ had. 1/θ 3 variation. Experimental diiculty: deine geometric edge o acceptance to give cross-section precision < 0.05%. Common theory error o 0.05% (c 1% in 1989). (BHLUMI program: S. Jadach, B.F.L. Ward et al.)
20 Standard Model relationships Masses o heavy gauge bosons and their couplings to ermions depend on SAME mixing angle cos θ W = M W /M Z SU(2) U(1) coupling constants, g, g, proportional to electric charge e: g = e sin θ W, g = e cos θ W γ Z W ieqγ µ ieγ µ (g v g a γ 5 ) 1 2 sin θ W cos θ W ieγ µ (1 γ 5 ) sin θ W where Q, g a and g v depend on ermion type, with g a = T 3 = ± 1 2 g v = (T 3 2Q sin 2 θ W ) = ± 1 2 (1 4 Q sin2 θ W ) g v /g a gives sin 2 θ W i you know Q.
21 Standard Model relationships Relate e, sin θ W and M W to the best measured parameters: α e2 4π = 1/ (50) G F πα 2M 2 W sin 2 θ W = (1) 10 5 GeV 2 M Z = (21) GeV G F measured rom muon decay; M Z rom LEP. These relations are true at tree level, but to check that they are valid, must take into account radiative corrections, which give sensitivity to virtual heavy particles, and possibly new physics! Aside: Other SM inputs needed are ermion masses, Higgs mass, CKM matrix (quark mass eigenstates are not weak eigenstates), strong coupling constant, α s
22 Radiative corrections Propagator corrections are the same or each ermion type. W H Z/W/γ Z/W/γ Z/W/γ Z/W/γ Z/W/γ Z/W Z/W Z/W QED, QCD and vertex corrections give ermion dependent terms. e - e + γ e - Z e + Electroweak corrections absorbed into eective couplings: Z g V g e V = (1 + ρ)(t 3 2Q sin 2 θ e ) g A g e A = (1 + ρ)t 3 sin 2 θ e = (1 + κ) sin 2 θ W q g q Z t t W b b ρ = 3G FM 2 W 8 2π 2 κ = 3G FM 2 W 8 2π 2 ( M 2 t M 2 W tan 2 θ W [ ln M 2 H ( cot 2 θ W M 2 t M 2 W ]) + MW 2 6 [ ln M H 2 5 ]) + MW 2 6 Extra M 2 t /M 2 W contributions or b quark
23 The value o G F is also modiied: Radiative corrections G F = πα 2M 2 W sin 2 θ W 1 1 r where r = α + r w = α κ + α term incorporates the running o the electromagnetic coupling due to ermion loops in the photon propagator. The diicult part o the calculation is to account or all the hadronic states. Use experimental measurement o e + e hadrons at low s. α(s) = α(0) 1 α α(0) = 1/ (50) ; α(m Z ) = 1/ (46) Quadratic dependence on M t Logarithmic dependence on M H Can it both M t and M H Use programs such as ZFITTER (D Bardin et al.) and TOPAZ0 (G Montagna et al.) or calculations to higher order. Leading order expressions above are or large M H.
24 QED corrections Dominant QED correction rom initial state radiation. Accounted or by radiator unction H. We want σ ew (s) e - e + γ Z σ(s) = 1 dzhqed(z, tot s)σ ew (zs). 4m 2 /s σ had [nb] ALEPH DELPHI L3 OPAL σ 0 20 Γ Z 10 measurements, error bars increased by actor 10 σ rom it QED unolded M Z E cm [GeV]
25 Dierential cross-section Improved Born Approximation or e + e (Ignoring ermion masses, QED/QCD ISR/FSR...) θ e - e + dσ ew d cos θ = πn c 2s 16 χ(s) 2 [ (g 2 Ve + gae)(g 2 V 2 + ga)(1 2 + cos 2 θ) + 8g Ve g Ae g V g A cos θ ] +[γ exchange] + [γz intererence] Where χ(s) = G FM 2 Z 8π 2 s s M 2 Z + isγ Z/M Z χ(s) 2 gives lineshape as a unction o s. Even term in cos θ gives total cross-section σ (g 2 Ve + g 2 Ae)(g 2 V + g 2 A) Odd term in cos θ leads to orward-backward asymmetry: A FB = σ F σ B σ F + σ B where σ F = 1 (dσ/d cos θ)d cos θ. At the Z peak: 0 A 0, FB = 3 4 2g Ve g Ae g 2 Ve + g2 Ae 2g V g A g 2 V + g2 A 3 4 A ea A FB depends on g V /g A, i.e. on sin 2 θ e Cross-section plus A FB allow g V and g A to be derived.
26 Polarised asymmetries Final state ermions in e + e are polarised. Polarisation can be measured or τ lepton inal states at LEP. P τ (σ + σ )/(σ + + σ ) where σ +( ) cross section or producing + (-) helicity τ leptons. Eg. τ πν, momentum o the π depends on the τ helicity Initial state: LEP beams are unpolarised (except or special energy calibration conditions) Stanord Linear Collider - longitudinally polarised electron beam to detector SLD. Electron beam 75% polarised rom e Damping Ring Thermionic Source Polarized e Source Electron Spin Direction Spin Rotation Solenoids (LTR Solenoid) e+ Return Line e+ Damping Ring e+ Source e Spin Vertical Linac Collider Final Arcs Focus IP e Extr. Line Spectrometer e+ Extr. Line Spectrometer Compton Polarimeter Knowing polarisation o inal (τ ) or initial (SLD) state, can construct let-right, let-right-orward-backward... asymmetries, and measure A e or A, eg. A LR (s) = N L N R N L + N R 1 P e, A0 LR A e
27 Cross-section and partial widths Cross-section as a unction o s (rom χ(s) 2 ): Z lineshape sγ 2 Z σ (s) = σ 0 (s M Z ) 2 + s 2 Γ 2 Z /M Z 2 where pole cross-section is σ 0 = 12π M 2 Z Γ ee Γ Γ 2 Z. with Γ /Γ Z = BR(Z ) and partial width is Γ = N c G F M 3 Z 6 2π ( g 2 A + g 2 V) + QED/QCD corrections eg. QCD: Γ q q Γ q q (1 + α s /π + ) Total width o Z Γ Z = Γ had + 3Γ ll + Γ inv = ΣΓ q q + 3Γ ll + N ν Γ νν Comparing total width to partial width gives N ν Cross-sections and widths correlated. Choose to it: M Z, Γ Z, σh 0 Ratios: Re 0 Γ had /Γ ee, Rµ 0 Γ had /Γ µµ, Rτ 0 Γ had /Γ ττ or R 0 l Γ had/γ ll Asymmetries: A 0, e FB, A0, µ FB and A0, τ FB or A0, l FB Extra inormation rom tagging some quark lavours (lecture 2).
28 Cross-sections vs s σ (nb) hadrons ee 1.4 ALEPH σ (nb) µµ ττ s(gev)
29 Lepton orward-backward asymmetries L3 e + e µ + µ (γ) d σ / d cos θ [nb] peak 2 peak peak+2 Forward-backward asymmetry or lepton pairs is straightorward to measure. Charge o lepton rom tracking Asymmetry cos θ varies with centre-o-mass energy. Asymmetry µ + µ - OPAL Ecm
30 Lepton Universality Plot A 0, l FB vs. R0 l = Γ had/γ ll. Contours contain 68% probability. Lepton universality OK. Results agree with SM (arrows) M t = ± 5.1 GeV M H = GeV (low M H preerred) α s (MZ) 2 = ± % CL A 0,l b α l + l e + e µ + µ τ + τ m t m H α s R 0 l=γ had /Γ l Next lecture: interpretation o asymmetries in terms o sin 2 θ lept e
31 LEP combined results Z resonance parameters - recall pre-lep hopes: σ(m Z ) 10 MeV (limited by beam energy precision) Number o generations σ(n ν ) 0.2 Fitted M Z [GeV] ± Γ Z [GeV] ± σ 0 h [nb] ± R 0 l ± A 0, l FB ± Derived Γ inv [MeV] ± 1.5 Γ had [MeV] ± 2.0 Γ ll [MeV] ± N ν ± Summary - Very precise measurements o Z mass, width, cross-sections, partial widths and lepton orward-backward asymmetries. High statistics data samples. Careul control o systematic errors.
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The version of the following full text has not yet been defined or was untraceable and may differ from the publisher's version. For
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The version of the following full text has not yet been defined or was untraceable and may differ from the publisher's version. For
PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS&
 PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS& AT&Z&RESONANCE Z&Lineshape&and&number&of&neutrinos Lecture'2 Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2138214 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/particelle/
PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS& AT&Z&RESONANCE Z&Lineshape&and&number&of&neutrinos Lecture'2 Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2138214 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/particelle/
Measurement of asymmetries. in e e production
 Measurement o asymmetries + + in e e production Daniele Trocino INFN and University o Torino 16th February 009 Particle Physics Ph.D. course (Pro. R. Demina) Outline Introduction quick review o QED/EW
Measurement o asymmetries + + in e e production Daniele Trocino INFN and University o Torino 16th February 009 Particle Physics Ph.D. course (Pro. R. Demina) Outline Introduction quick review o QED/EW
The DELPHI experiment at the LEP accelerator at the CERN laboratory
 The DELPHI experiment at the LEP accelerator at the CERN laboratory Part 1. The LEP accelerator Part 2. The DELPHI experiment Part 3. Particle physics research at LEP The LEP accelerator The study of collisions
The DELPHI experiment at the LEP accelerator at the CERN laboratory Part 1. The LEP accelerator Part 2. The DELPHI experiment Part 3. Particle physics research at LEP The LEP accelerator The study of collisions
The achievements of the CERN proton antiproton collider
 The achievements of the CERN proton antiproton collider Luigi DiLella Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy Motivation of the project The proton antiproton collider UA1 and UA2 detectors Discovery of the
The achievements of the CERN proton antiproton collider Luigi DiLella Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy Motivation of the project The proton antiproton collider UA1 and UA2 detectors Discovery of the
DESY, 12. September Precision Electroweak Measurements. Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen
 DESY, 12. September 2006 Precision Electroweak Measurements Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen Outline 1. Theory of electroweak interaction 2. Precision measurements of electroweak processes 3. Global electroweak
DESY, 12. September 2006 Precision Electroweak Measurements Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen Outline 1. Theory of electroweak interaction 2. Precision measurements of electroweak processes 3. Global electroweak
Number of neutrino families from LEP1 measurements
 1 Number of neutrino families from LEP1 measurements M. Chemarin a a Institut de Physique Nucléaire, IN2P3/CNRS and Université Claude Bernard Lyon, France The number of light neutrino families can be determined
1 Number of neutrino families from LEP1 measurements M. Chemarin a a Institut de Physique Nucléaire, IN2P3/CNRS and Université Claude Bernard Lyon, France The number of light neutrino families can be determined
Discovery of the W and Z 0 Bosons
 Discovery of the W and Z 0 Bosons Status of the Standard Model ~1980 Planning the Search for W ± and Z 0 SppS, UA1 and UA2 The analyses and the observed events First measurements of W ± and Z 0 masses
Discovery of the W and Z 0 Bosons Status of the Standard Model ~1980 Planning the Search for W ± and Z 0 SppS, UA1 and UA2 The analyses and the observed events First measurements of W ± and Z 0 masses
Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP
 Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP Colloquium Frascati,, 8.2.2001 Dieter Schlatter CERN / Geneva 1 Standard Model In 1989 ingredients of Standard Model were known: Matter particles: u,d,s,c,b,t quarks
Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP Colloquium Frascati,, 8.2.2001 Dieter Schlatter CERN / Geneva 1 Standard Model In 1989 ingredients of Standard Model were known: Matter particles: u,d,s,c,b,t quarks
Measurements of the Cross Section for the Process γγ pp at s ee = GeV with the OPAL Detector at LEP
 Measurements of the Cross Section for the Process γγ pp at s ee = 183 189 GeV with the OPAL Detector at LEP Teresa Barillari, MPI Munich Photon 2003, Frascati 10 April 2003 Introduction Kinematics Theory
Measurements of the Cross Section for the Process γγ pp at s ee = 183 189 GeV with the OPAL Detector at LEP Teresa Barillari, MPI Munich Photon 2003, Frascati 10 April 2003 Introduction Kinematics Theory
An Introduction to Modern Particle Physics
 An Introduction to Modern Particle Physics Mark Thomson University of Cambridge Y Z X Science Summer School: 30 th July - 1 st August 2007 1 Course Synopsis Introduction : Particles and Forces - what are
An Introduction to Modern Particle Physics Mark Thomson University of Cambridge Y Z X Science Summer School: 30 th July - 1 st August 2007 1 Course Synopsis Introduction : Particles and Forces - what are
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS
 PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Z Lineshape and number of neutrinos Lecture 2 1 October 212 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 212-213 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Z Lineshape and number of neutrinos Lecture 2 1 October 212 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 212-213 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
Two Photon Physics at a Linear Collider. Richard Nisius, CERN Lund, 13 September 1998
 Two Photon Physics at a Linear Collider Richard Nisius, CERN Lund, 3 September 998 Introduction. The instruments 2. The physics Conclusions VLEPP Photon;photon scattering ( ) ( ) Interaction of two quasi-real
Two Photon Physics at a Linear Collider Richard Nisius, CERN Lund, 3 September 998 Introduction. The instruments 2. The physics Conclusions VLEPP Photon;photon scattering ( ) ( ) Interaction of two quasi-real
Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker
 Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker Significance: Many theories predict that another neutral gauge boson (Z ) may exist. In order to detect this Z, I would use an e + e - linear collider
Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker Significance: Many theories predict that another neutral gauge boson (Z ) may exist. In order to detect this Z, I would use an e + e - linear collider
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 ( )
 Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (9.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 QED Feyman Rules Starting from elm potential exploiting Fermi s gold rule derived QED Feyman
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (9.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 QED Feyman Rules Starting from elm potential exploiting Fermi s gold rule derived QED Feyman
Measurements of the W Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron
 Measurements of the Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron John Ellison University of California, Riverside, USA Selection of and Z events Measurement of the mass Tests of the gauge
Measurements of the Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron John Ellison University of California, Riverside, USA Selection of and Z events Measurement of the mass Tests of the gauge
Hadronic events in e + e -
 Hadronic events in e + e - Hadronic cross-section, asymmetry (Very short on) Accelerators and detectors Events in the continuum; below, above and at the Z Event selection, ISR WW events Selection of heavy-uark
Hadronic events in e + e - Hadronic cross-section, asymmetry (Very short on) Accelerators and detectors Events in the continuum; below, above and at the Z Event selection, ISR WW events Selection of heavy-uark
IX. Electroweak unification
 IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
W + W - The Z pole. e + e hadrons SLC. Cross-section (pb) Centre-of-mass energy (GeV) P529 Spring,
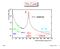 The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
Z boson studies at the ATLAS experiment at CERN. Giacomo Artoni Ph.D Thesis Project June 6, 2011
 Z boson studies at the ATLAS experiment at CERN Giacomo Artoni Ph.D Thesis Project June 6, 2011 Outline Introduction to the LHC and ATLAS ((Very) Brief) Z boson history Measurement of σ Backgrounds Acceptances
Z boson studies at the ATLAS experiment at CERN Giacomo Artoni Ph.D Thesis Project June 6, 2011 Outline Introduction to the LHC and ATLAS ((Very) Brief) Z boson history Measurement of σ Backgrounds Acceptances
Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron
 Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron Adam Lyon / Fermilab for the DØ and CDF collaborations 15 th Topical Conference on Hadron Collider Physics June 2004 Outline Importance Methodology Single Boson Measurements
Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron Adam Lyon / Fermilab for the DØ and CDF collaborations 15 th Topical Conference on Hadron Collider Physics June 2004 Outline Importance Methodology Single Boson Measurements
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS
 PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Asymmetries and Constraints on Standard Model Lecture 4 12 October 2012 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 2012-2013 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Asymmetries and Constraints on Standard Model Lecture 4 12 October 2012 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 2012-2013 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 13 Registration: https://uebungen.physik.uni-heidelberg.de/v/378 Experimental Tests of QED Part 1 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 13 Registration: https://uebungen.physik.uni-heidelberg.de/v/378 Experimental Tests of QED Part 1 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests
The Collider Detector at Fermilab. Amitabh Lath Rutgers University July 25, 2002
 The Collider Detector at Fermilab Amitabh Lath Rutgers University July 25, 2002 What is Fermilab? A user facility with the Tevatron: 4 mile ring with superconducting magnets. Collides protons with antiprotons.
The Collider Detector at Fermilab Amitabh Lath Rutgers University July 25, 2002 What is Fermilab? A user facility with the Tevatron: 4 mile ring with superconducting magnets. Collides protons with antiprotons.
e e Collisions at ELIC
 Physics With Collisions at ELIC Collisions at ELIC E. Chudakov (JLab), June 26, 26 Opportunity to build a collider using the ELIC ring Physics motivation for a high luminosity, polarized collider Discussion
Physics With Collisions at ELIC Collisions at ELIC E. Chudakov (JLab), June 26, 26 Opportunity to build a collider using the ELIC ring Physics motivation for a high luminosity, polarized collider Discussion
The Z lineshape using data from ALEPH
 The Z lineshape using data from ALEPH Standard Model Building blocks of matter Leptons and Quarks Fundamental interactions Coupling between matter ( ν e ) e ν µ µ ( ) ν τ τ ( ) Interaction Carrier ( u
The Z lineshape using data from ALEPH Standard Model Building blocks of matter Leptons and Quarks Fundamental interactions Coupling between matter ( ν e ) e ν µ µ ( ) ν τ τ ( ) Interaction Carrier ( u
7 Physics at Hadron Colliders
 7 Physics at Hadron Colliders The present and future Hadron Colliders - The Tevatron and the LHC Test of the Standard Model at Hadron Colliders Jet, W/Z, Top-quark production Physics of Beauty Quarks (T.
7 Physics at Hadron Colliders The present and future Hadron Colliders - The Tevatron and the LHC Test of the Standard Model at Hadron Colliders Jet, W/Z, Top-quark production Physics of Beauty Quarks (T.
OPEN /12/98
 Precision Electroweak Tests at LEP E. Falk Lund University, Box 118, S-221 00 Lund Sweden Abstract A presentation is given of a selection of the electroweak precision tests that have been carried out at
Precision Electroweak Tests at LEP E. Falk Lund University, Box 118, S-221 00 Lund Sweden Abstract A presentation is given of a selection of the electroweak precision tests that have been carried out at
The W-mass Measurement at CDF
 2010-05 - 10 The W-mass Measurement at CDF Ilija Bizjak, University College London 1/33 Outline 1) Motivation for a W mass measurement Implications for the EW constraints on Higgs mass 2) Measurement of
2010-05 - 10 The W-mass Measurement at CDF Ilija Bizjak, University College London 1/33 Outline 1) Motivation for a W mass measurement Implications for the EW constraints on Higgs mass 2) Measurement of
PoS(EPS-HEP2011)250. Search for Higgs to WW (lνlν, lνqq) with the ATLAS Detector. Jonas Strandberg
 with the ATLAS Detector Royal Institute of Technology, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: jostran@kth.se Higgs boson searches in the H WW ( ) lνlν (l = e, µ) and the H WW ( ) lνqq decay modes, using. fb of
with the ATLAS Detector Royal Institute of Technology, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: jostran@kth.se Higgs boson searches in the H WW ( ) lνlν (l = e, µ) and the H WW ( ) lνqq decay modes, using. fb of
ATLAS-CONF October 15, 2010
 ATLAS-CONF-2010-096 October 15, 2010 Data-driven background estimation for the H τ + τ τ h search at 7 TeV with the ATLAS detector Ian Howley 7 December 2010 1 Motivation One of the primary LHC physics
ATLAS-CONF-2010-096 October 15, 2010 Data-driven background estimation for the H τ + τ τ h search at 7 TeV with the ATLAS detector Ian Howley 7 December 2010 1 Motivation One of the primary LHC physics
Electroweak Theory: The Experimental Evidence and Precision Tests PPP-II Lecture 8 (FS 2012)
 1 Electroweak Theory: The Experimental Evidence and Precision Tests PPP-II Lecture 8 (FS 2012) Michael Dittmar (ETH-Zürich/CMS) 17.4.2012 1950ies From the messy world of hadrons to weak decays and neutrinos.
1 Electroweak Theory: The Experimental Evidence and Precision Tests PPP-II Lecture 8 (FS 2012) Michael Dittmar (ETH-Zürich/CMS) 17.4.2012 1950ies From the messy world of hadrons to weak decays and neutrinos.
Higgs Searches at CMS
 Higgs Searches at CMS Ashok Kumar Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi 110007 Delhi, India 1 Introduction A search for the Higgs boson in the Standard Model (SM) and the Beyond Standard
Higgs Searches at CMS Ashok Kumar Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi 110007 Delhi, India 1 Introduction A search for the Higgs boson in the Standard Model (SM) and the Beyond Standard
A flavour-independent Higgs boson search in e+e- collisions at s up to 209 GeV. 11 th, May, 2009 Kohei Yoshida
 A flavour-independent Higgs boson search in e+e- collisions at s up to 209 GeV 11 th, May, 2009 Kohei Yoshida Introduction Search for the Higgsstrahlung process (e+ e - ZH) ALEPH experiment @ LEP year
A flavour-independent Higgs boson search in e+e- collisions at s up to 209 GeV 11 th, May, 2009 Kohei Yoshida Introduction Search for the Higgsstrahlung process (e+ e - ZH) ALEPH experiment @ LEP year
Physics at Hadron Colliders
 Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
CLEO c. Anders Ryd Cornell University June 7, e e cc D D. D K,D K e
 CLEOc Cornell University June 7, 25 e e cc D D D K,D K e K K e 1 Outline CLEOc experiment and the physics program Some early results D> Absolute hadronic branching fractions Semileptonic decays 2 Testing
CLEOc Cornell University June 7, 25 e e cc D D D K,D K e K K e 1 Outline CLEOc experiment and the physics program Some early results D> Absolute hadronic branching fractions Semileptonic decays 2 Testing
Introduction to the Standard Model. 1. e+e- annihilation and QCD. M. E. Peskin PiTP Summer School July 2005
 Introduction to the Standard Model 1. e+e- annihilation and QCD M. E. Peskin PiTP Summer School July 2005 In these lectures, I will describe the phenomenology of the Standard Model of particle physics.
Introduction to the Standard Model 1. e+e- annihilation and QCD M. E. Peskin PiTP Summer School July 2005 In these lectures, I will describe the phenomenology of the Standard Model of particle physics.
Particle Physics: Problem Sheet 5
 2010 Subatomic: Particle Physics 1 Particle Physics: Problem Sheet 5 Weak, electroweak and LHC Physics 1. Draw a quark level Feynman diagram for the decay K + π + π 0. This is a weak decay. K + has strange
2010 Subatomic: Particle Physics 1 Particle Physics: Problem Sheet 5 Weak, electroweak and LHC Physics 1. Draw a quark level Feynman diagram for the decay K + π + π 0. This is a weak decay. K + has strange
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Results from the Tevatron: Standard Model Measurements and Searches for the Higgs. Ashutosh Kotwal Duke University
 Results from the Tevatron: Standard Model Measurements and Searches for the Higgs Ashutosh Kotwal Duke University SLAC Summer Institute 31 July 2007 Why Build Accelerators? From Atoms to Quarks Scattering
Results from the Tevatron: Standard Model Measurements and Searches for the Higgs Ashutosh Kotwal Duke University SLAC Summer Institute 31 July 2007 Why Build Accelerators? From Atoms to Quarks Scattering
Precise measurements of the W mass at the Tevatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass. Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy Interactions
 Precise measurements of the W mass at the evatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass Rafael Lopes de Sá for the CDF and DØ Collaborations March 11, 212 Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy
Precise measurements of the W mass at the evatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass Rafael Lopes de Sá for the CDF and DØ Collaborations March 11, 212 Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2012
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 W- and Z-Bosons 1 2 Contents Discovery of real W- and Z-bosons Intermezzo: QCD at Hadron Colliders LEP + Detectors W- and Z- Physics at LEP
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 W- and Z-Bosons 1 2 Contents Discovery of real W- and Z-bosons Intermezzo: QCD at Hadron Colliders LEP + Detectors W- and Z- Physics at LEP
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2012
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
ETH Zurich HS Mauro Donegà: Higgs physics meeting name date 1
 Higgs physics - lecture 3 ETH Zurich HS 2015 Mauro Donegà meeting name date 1 Practicalities mauro.donega@cern.ch pasquale.musella@cern.ch Moodle will store slides, exercises, papers and references Detailed
Higgs physics - lecture 3 ETH Zurich HS 2015 Mauro Donegà meeting name date 1 Practicalities mauro.donega@cern.ch pasquale.musella@cern.ch Moodle will store slides, exercises, papers and references Detailed
A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.)
 Physics 557 Lecture 7 A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.) First came the study of the debris from cosmic rays (the God-given particle
Physics 557 Lecture 7 A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.) First came the study of the debris from cosmic rays (the God-given particle
Multi Lepton events at HERA
 St. Petersburg, 25/04/2003 DIS03 Conference Multi Lepton events at HERA Andrea Parenti (on behalf of H and ZEUS Collabs.) Padova University and INFN A.Parenti - Multi Lepton Events at HERA p./?? Outline
St. Petersburg, 25/04/2003 DIS03 Conference Multi Lepton events at HERA Andrea Parenti (on behalf of H and ZEUS Collabs.) Padova University and INFN A.Parenti - Multi Lepton Events at HERA p./?? Outline
More on SM precision measurements. Marina Cobal University of Udine
 More on SM precision measurements Marina Cobal University of Udine Processes described by the SM Charged current processes; @ low energy the theory coincides with Fermi s theory verified in experiments
More on SM precision measurements Marina Cobal University of Udine Processes described by the SM Charged current processes; @ low energy the theory coincides with Fermi s theory verified in experiments
Measurement of the Higgs Couplings by Means of an Exclusive Analysis of its Diphoton decay
 Measurement of the Higgs Couplings by Means of an Exclusive Analysis of its Diphoton decay i.e. what do we know about the Higgs Marco Grassi The Discovery of a New Boson Evidence of a new boson with 5
Measurement of the Higgs Couplings by Means of an Exclusive Analysis of its Diphoton decay i.e. what do we know about the Higgs Marco Grassi The Discovery of a New Boson Evidence of a new boson with 5
Hunting for the Higgs Boson. Ulrich Heintz Brown University
 Hunting for the Higgs Boson Ulrich Heintz Brown University the standard model electromagnetism acts on all charged particles strong force acts on all quarks weak force acts on all particles spin ½ spin
Hunting for the Higgs Boson Ulrich Heintz Brown University the standard model electromagnetism acts on all charged particles strong force acts on all quarks weak force acts on all particles spin ½ spin
Current status and results of the experiments at VEPP-2000
 Current status and results of the experiments at VEPP-2000 Boris Shwartz, BINP, Novosibirsk, Introduction VEPP-2000 status Detectors Preliminary results 17.06.2013 MesonNet meeting, Prague, Czech Republic
Current status and results of the experiments at VEPP-2000 Boris Shwartz, BINP, Novosibirsk, Introduction VEPP-2000 status Detectors Preliminary results 17.06.2013 MesonNet meeting, Prague, Czech Republic
2 ATLAS operations and data taking
 The ATLAS experiment: status report and recent results Ludovico Pontecorvo INFN - Roma and CERN on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration 1 Introduction The ATLAS experiment was designed to explore a broad
The ATLAS experiment: status report and recent results Ludovico Pontecorvo INFN - Roma and CERN on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration 1 Introduction The ATLAS experiment was designed to explore a broad
Introduction to the Standard Model
 Introduction to the Standard Model Bill Murray, RAL, Quarks and leptons Bosons and forces The Higgs March 2002 1 Outline: An introduction to particle physics What is the Higgs Boson? Some unanswered questions
Introduction to the Standard Model Bill Murray, RAL, Quarks and leptons Bosons and forces The Higgs March 2002 1 Outline: An introduction to particle physics What is the Higgs Boson? Some unanswered questions
Observation of a New Particle with a Mass of 125 GeV
 Observation of a New Particle with a Mass of 125 GeV CMS Experiment, CERN 4 July 2012 Summary In a joint seminar today at CERN and the ICHEP 2012 conference[1] in Melbourne, researchers of the Compact
Observation of a New Particle with a Mass of 125 GeV CMS Experiment, CERN 4 July 2012 Summary In a joint seminar today at CERN and the ICHEP 2012 conference[1] in Melbourne, researchers of the Compact
Weak. interactions. V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1
 Weak interactions V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1 The electroweak theory y Gauge invariant theories. y y=x 2 A y =x 2 x y =y x =-x x The equation y=x 2 is symmetric or invariant under the transformation
Weak interactions V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1 The electroweak theory y Gauge invariant theories. y y=x 2 A y =x 2 x y =y x =-x x The equation y=x 2 is symmetric or invariant under the transformation
SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold?
 SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold? Michael Roney University of Victoria 22 March 2011 LNF Outline Very Quick reminder of the EW programme Address
SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold? Michael Roney University of Victoria 22 March 2011 LNF Outline Very Quick reminder of the EW programme Address
Overview. The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions.
 Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1
 Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1 Polarisation at collider machines The HERA storage ring The HERA polarimeters The collider experiments ZEUS and H1 The HERA II upgrade Data
Lepton beam polarisation for the HERA experiments ZEUS and H1 Polarisation at collider machines The HERA storage ring The HERA polarimeters The collider experiments ZEUS and H1 The HERA II upgrade Data
Particle Physics. Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders! Renormalisation in QCD!Asymptotic Freedom and Confinement in QCD! Lepton and Hadron Colliders!R = (e + e!!hadrons)/(e
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders! Renormalisation in QCD!Asymptotic Freedom and Confinement in QCD! Lepton and Hadron Colliders!R = (e + e!!hadrons)/(e
SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM
 SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM USING LEP DATA Elizabeth Locci SPP/DAPNIA Saclay Representing LEP Collaborations 1 Outline LEP performance Theoretical framework Search for neutral Higgs
SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM USING LEP DATA Elizabeth Locci SPP/DAPNIA Saclay Representing LEP Collaborations 1 Outline LEP performance Theoretical framework Search for neutral Higgs
Experimental verification of the Salaam-Weinberg model. Pásztor Attila, Eötvös University Experimental Particle Physics Student Seminar
 Experimental verification of the Salaam-Weinberg model Pásztor Attila, Eötvös University Experimental Particle Physics Student Seminar Contents Theoretical considerations Discovery of W and Z bosons (and
Experimental verification of the Salaam-Weinberg model Pásztor Attila, Eötvös University Experimental Particle Physics Student Seminar Contents Theoretical considerations Discovery of W and Z bosons (and
Results on top physics by CMS
 EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04069 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504069 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Results on top physics by CMS Silvano Tosi 1,2,a, on behalf of the CMS
EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04069 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504069 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Results on top physics by CMS Silvano Tosi 1,2,a, on behalf of the CMS
Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass. Robert Clare UC Riverside
 Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass Robert Clare UC Riverside Robert Clare UC Riverside LoopFest III Apr 1, 2004 2 Outline Electroweak corrections: definitions and strategies Experimental inputs
Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass Robert Clare UC Riverside Robert Clare UC Riverside LoopFest III Apr 1, 2004 2 Outline Electroweak corrections: definitions and strategies Experimental inputs
Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton
 Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton collision: an analysis of the final state containing three leptons with the ATLAS detector Valentina Vecchio,
Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton collision: an analysis of the final state containing three leptons with the ATLAS detector Valentina Vecchio,
From the SM Lagrangian to Phenomenology, including SM Higgs Boson. Fulvio Piccinini
 From the SM Lagrangian to Phenomenology, including SM Higgs Boson Fulvio Piccinini INFN, Sezione di Pavia PhD course 2014, Pavia Bibliography G. Montagna, O. Nicrosini and F. P., arxiv:hep-ph/9802302 LEP
From the SM Lagrangian to Phenomenology, including SM Higgs Boson Fulvio Piccinini INFN, Sezione di Pavia PhD course 2014, Pavia Bibliography G. Montagna, O. Nicrosini and F. P., arxiv:hep-ph/9802302 LEP
The Particle World. This talk: What is our Universe made of? Where does it come from? Why does it behave the way it does?
 The Particle World What is our Universe made of? Where does it come from? Why does it behave the way it does? Particle physics tries to answer these questions. This talk: particles as we understand them
The Particle World What is our Universe made of? Where does it come from? Why does it behave the way it does? Particle physics tries to answer these questions. This talk: particles as we understand them
Nicolas Berger SLAC, Menlo Park, California, U.S.A.
 SLAC-PUB-11414 August 25 Frascati Physics Series Vol. VVVVVV (xxxx), pp. - DAΦNE 24: Physics at meson factories Frascati, June. 7-11, 24 Selected Contribution in Plenary Session INCLUSIVE HADRONIC RESULTS
SLAC-PUB-11414 August 25 Frascati Physics Series Vol. VVVVVV (xxxx), pp. - DAΦNE 24: Physics at meson factories Frascati, June. 7-11, 24 Selected Contribution in Plenary Session INCLUSIVE HADRONIC RESULTS
Linear Collider Beam Instrumentation Overview
 Linear Collider Beam Instrumentation Overview Linear Collider R&D Opportunities Workshop May 31 st, 2002 SLAC Eric Torrence* University of Oregon *with M.Woods and D.Cinabro BI Overview Beam Energy Polarization
Linear Collider Beam Instrumentation Overview Linear Collider R&D Opportunities Workshop May 31 st, 2002 SLAC Eric Torrence* University of Oregon *with M.Woods and D.Cinabro BI Overview Beam Energy Polarization
LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL
 LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL D.G. Charlton School of Physics & Astronomy The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K. ABSTRACT The period 1989-2000 provided a huge yield of precise electroweak
LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL D.G. Charlton School of Physics & Astronomy The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K. ABSTRACT The period 1989-2000 provided a huge yield of precise electroweak
Results on Tau Physics from BaBar
 Results on Tau Physics from BaBar Eric Torrence University of Oregon Search for Lepton Flavor Violation Study of τ 3h 2h + ν τ (5 prong) Tau Lifetime The BaBar Experiment Integrated Luminosity (fb -1 )
Results on Tau Physics from BaBar Eric Torrence University of Oregon Search for Lepton Flavor Violation Study of τ 3h 2h + ν τ (5 prong) Tau Lifetime The BaBar Experiment Integrated Luminosity (fb -1 )
Lecture 11. Weak interactions
 Lecture 11 Weak interactions 1962-66: Formula/on of a Unified Electroweak Theory (Glashow, Salam, Weinberg) 4 intermediate spin 1 interaction carriers ( bosons ): the photon (γ) responsible for all electromagnetic
Lecture 11 Weak interactions 1962-66: Formula/on of a Unified Electroweak Theory (Glashow, Salam, Weinberg) 4 intermediate spin 1 interaction carriers ( bosons ): the photon (γ) responsible for all electromagnetic
Search for a heavy gauge boson W e
 Search for a heavy gauge boson W e Cornell University LEPP Journal Club Seminar April 1, 2011 The LHC Machine 2 The beginning of the LHC era First collisions at 7 TeV confirmed on March 30, 2010 There
Search for a heavy gauge boson W e Cornell University LEPP Journal Club Seminar April 1, 2011 The LHC Machine 2 The beginning of the LHC era First collisions at 7 TeV confirmed on March 30, 2010 There
etectors for High Energy Physics
 3rd WORKSHOP ON PARTICLE PHYSICS NATIONAL CENTRE FOR PHYSICS (QUAID-I-AZAM UNIVERSITY) etectors for High Energy Physics Lecture II General Detector Concepts Gigi Rolandi Cern Geneva - Switzerland http://rolandi.home.cern.ch/rolandi/
3rd WORKSHOP ON PARTICLE PHYSICS NATIONAL CENTRE FOR PHYSICS (QUAID-I-AZAM UNIVERSITY) etectors for High Energy Physics Lecture II General Detector Concepts Gigi Rolandi Cern Geneva - Switzerland http://rolandi.home.cern.ch/rolandi/
Atlas Status and Perspectives
 Atlas Status and Perspectives Bruno Mansoulié (IRFU-Saclay) On behalf of the Topics The hot news: Heavy Ion analysis Data taking in 2010 Luminosity, Data taking & quality, trigger Detector performance
Atlas Status and Perspectives Bruno Mansoulié (IRFU-Saclay) On behalf of the Topics The hot news: Heavy Ion analysis Data taking in 2010 Luminosity, Data taking & quality, trigger Detector performance
14 Top Quark. Completing the Third Generation
 14 Top Quark Completing the Third Generation No one could doubt that there would be a sixth quark, the top or t, but it was equally certain that initially no one knew where it would be found. With the
14 Top Quark Completing the Third Generation No one could doubt that there would be a sixth quark, the top or t, but it was equally certain that initially no one knew where it would be found. With the
From Friday: Neutrino Summary. Three neutrinos in the Standard Model:!e,!µ,!" Only left-handed neutrinos and right-handed antineutrinos are observed.
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
W Physics at LEP. 1. WW cross sections and W branching fractions. Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, Monica Pepe Altarelli
 Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, 998 PROCEEDINGS Physics at LEP INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati and CERN, EP Division E-mail: Monica.Pepe.Altarelli@CERN.CH Abstract: A summary
Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, 998 PROCEEDINGS Physics at LEP INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati and CERN, EP Division E-mail: Monica.Pepe.Altarelli@CERN.CH Abstract: A summary
Top Physics in Hadron Collisions
 Top Physics in Hadron Collisions Dirk Dammann DESY 2010-02-04 1 / 44 Outline 1 2 3 4 2 / 44 Outline Motivation Top Production Top Decay Top Physics 1 Motivation Top Production Top Decay Top Physics 2 3
Top Physics in Hadron Collisions Dirk Dammann DESY 2010-02-04 1 / 44 Outline 1 2 3 4 2 / 44 Outline Motivation Top Production Top Decay Top Physics 1 Motivation Top Production Top Decay Top Physics 2 3
Measurements of e + e hadrons at VEPP-2M
 Measurements of e + e hadrons at VEPP-2M B.Khazin Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics Novosibirsk Centerville, Cape Cod, MA 19-22 June 2006 Cross-section section e + e - hadrons VEPP-2M energy range :
Measurements of e + e hadrons at VEPP-2M B.Khazin Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics Novosibirsk Centerville, Cape Cod, MA 19-22 June 2006 Cross-section section e + e - hadrons VEPP-2M energy range :
Modern Accelerators for High Energy Physics
 Modern Accelerators for High Energy Physics 1. Types of collider beams 2. The Tevatron 3. HERA electron proton collider 4. The physics from colliders 5. Large Hadron Collider 6. Electron Colliders A.V.
Modern Accelerators for High Energy Physics 1. Types of collider beams 2. The Tevatron 3. HERA electron proton collider 4. The physics from colliders 5. Large Hadron Collider 6. Electron Colliders A.V.
Upgrade of ATLAS and CMS for High Luminosity LHC: Detector performance and Physics potential
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 4 C (27) 8 DOI.393/ncc/i27-78-7 Colloquia: IFAE 26 Upgrade of ATLAS and CMS for High Luminosity LHC: Detector performance and Physics potential M. Testa LNF-INFN - Frascati (RM), Italy
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 4 C (27) 8 DOI.393/ncc/i27-78-7 Colloquia: IFAE 26 Upgrade of ATLAS and CMS for High Luminosity LHC: Detector performance and Physics potential M. Testa LNF-INFN - Frascati (RM), Italy
Subatomic Physics: Particle Physics Study Guide
 Subatomic Physics: Particle Physics Study Guide This is a guide of what to revise for the exam. The other material we covered in the course may appear in uestions but it will always be provided if reuired.
Subatomic Physics: Particle Physics Study Guide This is a guide of what to revise for the exam. The other material we covered in the course may appear in uestions but it will always be provided if reuired.
Oliver Stelzer-Chilton University of Oxford High Energy Physics Seminar Michigan State University
 First Run II Measurement of the W Boson Mass by CDF Oliver Stelzer-Chilton University of Oxford High Energy Physics Seminar Michigan State University April 3 rd, 2007 1. Motivation Outline 2. W Production
First Run II Measurement of the W Boson Mass by CDF Oliver Stelzer-Chilton University of Oxford High Energy Physics Seminar Michigan State University April 3 rd, 2007 1. Motivation Outline 2. W Production
Last Friday: pp(bar) Physics Intro, the TeVatron
 Last Friday: pp(bar) Physics Intro, the TeVatron Today: The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) 7 TeV + 7 TeV Protons Protons 10 11 Protons per bunch Bunch Crossings 4x10 7 Hz Proton
Last Friday: pp(bar) Physics Intro, the TeVatron Today: The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) 7 TeV + 7 TeV Protons Protons 10 11 Protons per bunch Bunch Crossings 4x10 7 Hz Proton
Determination of Electroweak Parameters
 Determination of Electroweak Parameters Seminar Particle Physics at the LHC Proceedings R. Gugel Freiburg, 27.05.2014 Contents 1 Motivation 1 2 Template Method 4 3 Mass of the W Boson 5 3.1 Measurement
Determination of Electroweak Parameters Seminar Particle Physics at the LHC Proceedings R. Gugel Freiburg, 27.05.2014 Contents 1 Motivation 1 2 Template Method 4 3 Mass of the W Boson 5 3.1 Measurement
Electroweak Physics. Krishna S. Kumar. University of Massachusetts, Amherst
 Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
Weak. interactions. V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1
 Weak interactions V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1 The electroweak theory y Gauge invariant theories. y y=x 2 A y =x 2 x y =y x =-x x The equation y=x 2 is symmetric or invariant under the transformation
Weak interactions V. Hedberg Weak Interactions 1 The electroweak theory y Gauge invariant theories. y y=x 2 A y =x 2 x y =y x =-x x The equation y=x 2 is symmetric or invariant under the transformation
CMS Higgs Results Adi Bornheim Caltech
 CMS Higgs Results Adi Bornheim Caltech 06.04.2014 1 A brief history of recent times W & Z Boson t-quark H Boson 1964 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 Peter Higgs This talk : Summary of 29 CMS publications and
CMS Higgs Results Adi Bornheim Caltech 06.04.2014 1 A brief history of recent times W & Z Boson t-quark H Boson 1964 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 Peter Higgs This talk : Summary of 29 CMS publications and
Searches for (non-susy) Exotics at HERA
 Searches for (non-susy) Exotics at HERA Linus Lindfeld, University of Zürich UNIVERSITAS TURICENSIS MDCCC III Int. Conference on Supersymmetry and the Unification of Fundamental Interactions Irvine, California,
Searches for (non-susy) Exotics at HERA Linus Lindfeld, University of Zürich UNIVERSITAS TURICENSIS MDCCC III Int. Conference on Supersymmetry and the Unification of Fundamental Interactions Irvine, California,
1. a) What does one mean by running of the strong coupling, and by asymptotic freedom of QCD? (1p)
 FYSH300 Particle physics 2. half-course exam (2. välikoe) 19.12.2012: 4 problems, 4 hours. Return the the question sheet and particle tables together with your answer sheets remember to write down your
FYSH300 Particle physics 2. half-course exam (2. välikoe) 19.12.2012: 4 problems, 4 hours. Return the the question sheet and particle tables together with your answer sheets remember to write down your
e + e - (1) Silicon Vertex Detector
 3.1 GeV (4) Electromagnetic Calorimeter (3) Cerenkov- Detector (2) Drift Chamber (5) 1.5 T Solenoid (6) Instrumented Iron Yoke e + e - (1) Silicon Vertex Detector 9.0 GeV e + e - Colliders as B Factories
3.1 GeV (4) Electromagnetic Calorimeter (3) Cerenkov- Detector (2) Drift Chamber (5) 1.5 T Solenoid (6) Instrumented Iron Yoke e + e - (1) Silicon Vertex Detector 9.0 GeV e + e - Colliders as B Factories
Higgs cross-sections
 Ph.D. Detailed Research Project Search for a Standard Model Higgs boson in the H ZZ ( ) 4l decay channel at the ATLAS Experiment at Cern Ph.D. Candidate: Giacomo Artoni Supervisor: Prof. Carlo Dionisi,
Ph.D. Detailed Research Project Search for a Standard Model Higgs boson in the H ZZ ( ) 4l decay channel at the ATLAS Experiment at Cern Ph.D. Candidate: Giacomo Artoni Supervisor: Prof. Carlo Dionisi,
Richard Hall-Wilton University College London. July 2002
 PPRP, Richard Hall-Wilton University College London July 2002 July 2002, RAL Overview Introduction to HERA and ZEUS Detector Status Central Tracking Detector Microvertex Detector Global Tracking Trigger
PPRP, Richard Hall-Wilton University College London July 2002 July 2002, RAL Overview Introduction to HERA and ZEUS Detector Status Central Tracking Detector Microvertex Detector Global Tracking Trigger
Mojtaba Mohammadi Najafabadi School of Particles and Accelerators, IPM Aban 22- IPM Workshop on Electroweak and Higgs at the LHC
 Electroweak studies for the LHC Mojtaba Mohammadi Najafabadi School of Particles and Accelerators, IPM Aban 22- IPM Workshop on Electroweak and Higgs at the LHC 1 Why accelerator? We live in a cold and
Electroweak studies for the LHC Mojtaba Mohammadi Najafabadi School of Particles and Accelerators, IPM Aban 22- IPM Workshop on Electroweak and Higgs at the LHC 1 Why accelerator? We live in a cold and
Particle Physics Columbia Science Honors Program
 Particle Physics Columbia Science Honors Program Week 10: LHC and Experiments April 8th, 2017 Inês Ochoa, Nevis Labs, Columbia University 1 Course Policies Attendance: Up to four excused absences (two
Particle Physics Columbia Science Honors Program Week 10: LHC and Experiments April 8th, 2017 Inês Ochoa, Nevis Labs, Columbia University 1 Course Policies Attendance: Up to four excused absences (two
Top and Electroweak Physics at. the Tevatron
 Top and Electroweak Physics at 1 the Tevatron Graham W. Wilson University of Kansas for the CDF and DØ Collaborations April APS 2008, St. Louis, MO. April 12 th 2008 Introduction Top Physics Overview Cross-section
Top and Electroweak Physics at 1 the Tevatron Graham W. Wilson University of Kansas for the CDF and DØ Collaborations April APS 2008, St. Louis, MO. April 12 th 2008 Introduction Top Physics Overview Cross-section
Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering. Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors
 1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
Electroweak results. Luca Lista. INFN - Napoli. LHC Physics
 Electroweak results Luca Lista INFN - Napoli EWK processes at LHC p p W and Z production in pp collisions proceeds mainly form the scattering of a valence quark with a sea anti-quark The involved parton
Electroweak results Luca Lista INFN - Napoli EWK processes at LHC p p W and Z production in pp collisions proceeds mainly form the scattering of a valence quark with a sea anti-quark The involved parton
Novel Measurements of Proton Structure at HERA
 Introduction Combined Cross Sections & QCD Fits NC & CC Cross Section Measurements F L Summary Novel Measurements of Proton Structure at HERA Katie Oliver University of Oxford On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS
Introduction Combined Cross Sections & QCD Fits NC & CC Cross Section Measurements F L Summary Novel Measurements of Proton Structure at HERA Katie Oliver University of Oxford On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS
7th International Workshop on Tau Lepton Physics (Tau02), Santa Cruz, CA, September, 2002
 τ physics at LEP Francisco Matorras a a Instituto de Física de Cantabria Santander, Spain This paper gives an overview of some of the more interesting results obtained at LEP in τ physics: precision measurements
τ physics at LEP Francisco Matorras a a Instituto de Física de Cantabria Santander, Spain This paper gives an overview of some of the more interesting results obtained at LEP in τ physics: precision measurements
(a) (b) Fig. 1 - The LEP/LHC tunnel map and (b) the CERN accelerator system.
 Introduction One of the main events in the field of particle physics at the beginning of the next century will be the construction of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). This machine will be installed into
Introduction One of the main events in the field of particle physics at the beginning of the next century will be the construction of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). This machine will be installed into
