PRECISION MEASUREMENTS
|
|
|
- Felicia Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Asymmetries and Constraints on Standard Model Lecture 4 12 October 2012 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico
2 ASYMMETRIES Lineshape measurements allowed the determination of total Z width partial Z width in hadrons and leptons Z mass total of 6 parameters Several observable asymmetries sensitive to fundamental parameters of Standard Model angular distribution to spin 1 of Z boson different couplings for left and right handed fermions possibly use polarization of initial state electrons 33
3 FORWARD- BACKWARD ASYMMETRY Terms proportional to cos θw provide test of parity violation 2s π 1 N f c dσ ew dcos θ (e+ e ff) = α(s)q f 2 (1 + cos 2 θ) }{{} σ γ 8R { α (s)q f χ(s) [ G Ve G Vf (1 + cos 2 θ)+2g Ae G Af cos θ ]} }{{} γ Z interference +16 χ(s) 2 [( G Ve 2 + G Ae 2 )( G Vf 2 + G Af 2 )(1 + cos 2 θ) } +8R {G Ve G Ae } R {G Vf G Af } cos θ] {{ } σ Z Electron direction assumed as positive hemisphere Asymmetry has dependency on s Contribute only to asymmetry: canceled if integrated over solid angle Contribute only to total cross section and Z width Discrimination of fermions and anti-fermions charge for leptons A FB = N F N B, for quarks look at all info: tagging with leptons N F + N B and displaced vertices for b and c quarks (flavor tagging) e -, f + f, e + 34
4 CROSS SECTION DEPENDENCY ON POLARIZATION gl gr gl tree = ρ 0 (T3 f Q f sin 2 θw tree ) gr tree = ρ 0 Q f sin 2 θw tree, dσ Ll dcosθ dσ Rr dcosθ dσ Lr dcosθ dσ Rl dcosθ gle 2 g2 Lf (1 + cos θ)2 gre 2 g2 Rf (1 + cos θ)2 gle 2 g2 Rf (1 cos θ)2 g 2 Re g2 Lf (1 cos θ)2. L, R: polarization of initial state electron typically sum over possible polarizations At SLC polarized electron beam l, r: polarization of final state fermion Since coupling constants are different --> very different cross sections to measure 35
5 DIFFERENTIAL CROSS SECTION AND POLARIZATION [ dσ ff dcosθ = 3 [ 8 σtot ff (1 Pe A e )(1 + cos 2 θ)+2(a e P e )A f cos θ ] P e = N el! N er N el + N er P e = 0 at LEP cos θ terms vanish if integrated measure differential cross section in bins of cos θ integrate only in forward or backward hemisphere (σf and σb) 65 SLC with polarized electron beam allows measurement of each terms separately P A f = g2 Lf g 2 Rf g 2 Lf + g2 Rf Even for unpolarized beams (LEP) since Z coupling is different for L and R, there are observable LR, FB asymmetries in the final state A = 2g Vfg Af g 2 Vf + g2 Af g Vf /g Af =2 1+(g Vf /g Af ) 2 sensimve to different V and A coupling for each fermion 36
6 MIXING ANGLE FROM ASYMMETRY MEASUREMENT A f = g2 Lf g 2 Rf g 2 Lf + g2 Rf A = 2g Vfg Af g 2 Vf + g2 Af g Vf /g Af =2 1+(g Vf /g Af ) 2 g Vf g Af = 1 2Q f T f 3 sin 2 θ f eff = 1 4 Q f sin 2 θ f eff asymmetry very sensitive to mixing angle fermion charge plays important role in terms of power of measurement leptons: Q 2 = 1 up quarks: Q 2 = (2/3) 2 = 0.44 down quarks: Q 2 = (1/3) 2 = 0.11 A f ν e e L Al Family T T 3 Q ν µ µ Ac L ν τ τ L Ab 1/2 +1/2 1/2 0 1 ν er ν µr ν τr e R µ R τ R u c t +1/2 +2/3 1/2 d s b 1/2 1/3 L L u R c R t R /3 d R s R b R 0 0 1/3 L Less sensitive when smaller factor in front of sin θ sin 2 θ f eff 37
7 Utilize lifetime of decay products: larger for b and c quarks data MC uds MC udsc MC all In addition can use mass of final 10-2 state to separate b and c quarks V No. of Hemispheres uds c LIFETIME TAGGING DELPHI b s Data MC rate rate OPAL data Monte 2000 Carlo b Monte Carlo c Monte Carlo uds uds decay length 4 significance 5 L/$ 6 L V Table 5.2: b-tagging 10-6 performance of the different experiments at the cut where the R b a are performed. The lifetime tagging is combined with other information (see text). The tag is an OR-8of a secondary -6-4 vertex and -2 a lepton 0 tag tagging variable B Mass (GeV/c 2 ) No. of Hemispheres c b Data MC Mass (GeV/c 2 ) Figure 5.4: Reconstructed vertex mass from SLD for data and simulation. ALEPH DELPHI L3 OPAL SLD bpurity[%] befficiency [%]
8 LEPTON FLAVOR Γ 3 TAGGING Exploit semi-leptonic b and c decays Distinctive spectrum for leptons in final states depending on flavor of original fermion Charge of leptons correlated with parent fermion Higher momentum for leptons from b quark because of higher mass Γ 1 B + ( 40.1 ± 1.3 ) % Γ 2 B 0 ( 40.1 ± 1.3 ) % B 0 s ( 11.3 ± 1.3 ) % Γ 4 b -baryon ( 8.5 ± 2.2 ) % Γ 5 B c DECAY MODES Semileptonic and leptonic modes Γ 6 ν anything ( 23.1 ± 1.5 ) % Γ 7 l + ν l anything [a] ( 10.69± 0.22) % Γ 8 e + ν e anything ( 10.86± 0.35) % Γ 9 µ + ν µ anything ( )% Γ 10 D l + ν l anything [a] ( 2.2 ± 0.4 ) % S=1.8 Γ 11 D π + l + ν l anything ( 4.9 ± 1.9 ) 10 3 Γ 12 D π l + ν l anything ( 2.6 ± 1.6 ) 10 3 Γ 13 D 0 l + ν l anything [a] ( 6.84± 0.35) % Γ 14 D 0 π l + ν l anything ( 1.07± 0.27) % Γ 15 D 0 π + l + ν l anything ( 2.3 ± 1.6 ) 10 3 Γ 16 D l + ν l anything [a] ( 2.75± 0.19) % Γ 17 D π l + ν l anything ( 6 ± 7 ) 10 4 Γ 18 D π + l + ν l anything ( 4.8 ± 1.0 ) 10 3 Γ 19 D 0 j l+ ν l anything [a,b] ( 2.6 ± 0.9 ) 10 3 B(D 0 j D + π ) B mesons L L3 Page 4 Created: 7/30/ :47 Number of muons Data uds c fake l b#l b#c#l Number of muons Data uds c fake l b#l b#c#l Muon momentum (GeV/c) Muon transverse momentum (GeV/c) 39
9 LEFT- RIGHT ASYMMETRIES dσ ff dcosθ = 3 [ 8 σtot ff (1 Pe A e )(1 + cos 2 θ)+2(a e P e )A f cos θ ] Additional asymmetries sensitive to Af and Ae measurement P A FB = σ F σ B σ F + σ B A LR = σ L σ R 1 σ L + σ R P e F = B = Z 1 0 Z 0 A LRFB = (σ F σ B ) L (σ F σ B ) R (σ F + σ B ) L +(σ F + σ B ) R 1 P e 1 d cos d d cos d cos d d cos d(σ r σ l ) dcosθ d(σ r + σ l ) dcosθ / P f = d(σ r σ l ) dcosθ = 3 8 σtot ff = 3 8 σtot ff / d(σr + σ l ) dcosθ [ [ Af (1 + cos 2 θ)+2a e cos θ ] [ (1 + cos 2 θ)+2a e A f cos θ ] Polarization can be determined from L and R cross sections P f (cos θ) = A f(1 + cos 2 θ)+2a e cos θ (1 + cos 2 θ)+2a f A e cos θ P f = σ r σ l σ r + σ l A pol FB = (σ r σ l ) F (σ r σ l ) B (σ r + σ l ) F +(σ r + σ l ) B Measurement of polarization possible in the tau tau channel (tesina) 40
10 POLARIZED ELECTRON SLC Polarization of Electron Beam (%) Source Laser Wavelenght Optimized # # Beam Polarization SLD Data Strained Lattice Cathode for 1994 SLD Run # # Strained Lattice Cathode for 1993 SLD Run 1996 Run Strained Lattice Cathode for 1997 SLD Run # x 10 2 Z Count 60% of data in last 2 years of operation Figure 1.5: The amount of longitudinal electron polarisation as a function of the number of recorded Z decays at SLD. 41
11 b- TAGGING AT SLD Displaced secondary vertex clear signature of b decays 42
12 EXPERIMENTAL ASYMMETRIES A FB = σ F σ B σ F + σ B A LR = σ L σ R 1 σ L + σ R P e A LRFB = (σ F σ B ) L (σ F σ B ) R (σ F + σ B ) L +(σ F + σ B ) R 1 P e pol = 0 at LEP Measurement at Z pole after corrections A 0, f 3 FB = 4 A ea f A 0 LR = A e A 0 LRFB = 3 4 A f For electron final state Both asymmetries sensitive to mixing angle but ALR has larger sensitivity sin θ = 0.23 sin 2 θ = sin 4 θ = much harder to measure experimentally! 43
13 A LR ASYMMETRY AT SLD P e A LR A 0 LR sin 2 θ lept eff ±0.006 ±0.044 ± ±0.044 ± ± ± ±0.011 ± ± ± ± ± ± / ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± / ± ± ± ± ± ± ± All combined ± ± ± ± Table 3.3: Summary of the SLD A LR measurements for all runs. Listed are the luminosityweighted mean electron polarisation ( P e ), the measured A LR,itsvaluecorrectedtotheZ-pole (A 0 LR )andsin2 θ lept eff. For P e the total error shown is dominantly systematic. For the other quantities, the errors are the statistical and systematic components respectively. The final combined result accounts for correlated uncertainties. 44
14 ion 1.5. The energy dependence of the muon and tau crosse to the hadronic A one. FB ASYMMETRY In e + e final states IN ee however, AND diagrams μμ t-channel and their interference with the s-channel diagrams ntributions are shown as a function of centre-of-mass energy L3 e + e! # e + e! (") 4. d $ / d cos + [nb] + peak!2 peak 1 peak+2 the Lepton Forward-Backward Asymmetries ry, A FB,isdefinedbythenumbersofevents,N F and N B,in forward (cos θ l > 0) or backward (cos θ l < 0) with respect 0.5 electron, A FB =(N F N B )/(N F + N B ). This definition of cceptance cuts applied on the production polar angle, cos θ, ts of A FB (l + l )requirethedeterminationofcosθ and the ptons based on their electric charges, which are determined 0 in the magnetic -1 fields of the 0.5 central 1 detectors. For µ + µ and cos + y determined from un-binned maximum-likelihood fits to the ions of the form dσ/dcos θ 1+cos 2 θ +8/3 A FB cos θ. This he available information and hence leads to slightly smaller s way the A FB measurements are insensitive to any distortions Figure 2.5: Distribution of the production polar angle, cos θ, fore + e and µ + µ events at the three principal energies during the years , measured in the L3 (left) and DELPHI (right) detectors, respectively. The curves show the SM prediction from ALIBABA [52] for e + e 45
15 INTEREFERENCE OF t- CHANNEL IN ee 1 $ [nb] L3 e + e! # e + e! (") 44 o < + < 136 o s-channel A fb 0.5 L3 e + e! # e + e! (") 44 o < + < 136 o t-channel 0 t-channel interference 0 s-channel interference ratio *s difference *s no peaking structure in cross section due to t-channel 46
16 RESULTS OF PRECISION MEASUREMENTS
17 FIT RESULTS Parameter Average Correlations [MeV] Γ ff Without Lepton Universality Γ had Γ ee Γ µµ Γ ττ Γ bb Γ cc Γ inv Γ had ± Γ ee ± Γ µµ ± Γ ττ ± Γ bb ± Γ cc ± Γ inv ± Without lepton universality Correlations χ 2 /dof = 32.6/27 m Z Γ Z σhad 0 Re 0 Rµ 0 Rτ 0 A 0, e FB A 0,µ FB m Z ± Γ Z ± σhad 0 [nb] ± Re ± Rµ ± Rτ ± A 0, e FB ± A 0,µ FB ± A 0, τ FB ± A 0, τ FB 48
18 Z BRANCHING FRACTIONS Parameter Average Correlations B(Z ff) [%] Without Lepton Universality qq e + e µ + µ τ + τ bb cc inv qq ± e + e ± µ + µ ± τ + τ ± bb ± cc ± inv ±
19 RESULTS ASSUMING LEPTON UNIVERSALITY Without lepton universality Correlations χ 2 /dof = 32.6/27 m Z Γ Z σhad 0 Re 0 Rµ 0 Rτ 0 A 0, e FB A 0,µ FB m Z ± Γ Z ± σhad 0 [nb] ± Re ± Rµ ± Rτ ± A 0, e FB ± A 0,µ FB ± A 0, τ FB ± With lepton universality Correlations χ 2 /dof = 36.5/31 m Z Γ Z σhad 0 Rl 0 A 0, l FB m Z ± Γ Z ± σhad 0 [nb] ± Rl ± A 0, l FB ± A 0, τ FB 50
20 LEPTON UNIVERSALITY % CL Standard Model Prediction A 0,l fb l + l! e + e! µ + µ! ' + '! () m t m H ) s R 0 l=% had /% ll m t =178.0 ± 4.3 GeV,m H = GeV, and α S (m 2 Z)=0.118 ± 0.003, he arrow showing the small dependence on the hadronic vacuum polarisation Z 51
21 COUPLING CONSTANTS BEFORE LEP g Vl 2002 m t m H νµ e () l + l! e + e! µ + µ! ' + '! 68% CL g Al g V 0.0 e + e - µ + µ ν e - e ν µ e - ν e - e ν e- e g A 52
22 COUPLING CONSTANTS FOR LEPTONS m t = ± 4.3 GeV m H = GeV m H g Vl l + l! e + e! µ + µ! ' + '! m t () 68% CL g Al m t =178.0 ± 4.3 GeVandm H = GeV; ± 53
23 CONSTRAINTS ON TOP LEP 200 M t Tevatron SM constraint 68% CL 50 Direct search lower limit (95% CL) Year 54
24 SM INPUT TO Z- POLE MEASUREMENTS Precision measurements at LEP rely on parameters not known a-priori coupling constants for weak, electromagnetic, and strong interaction fermion masses vector boson masses Correlation between photon, W and Z mass Higgs mass Some parameters are well known, others can be constrained from precision measurements Light fermion masses well known. Small and well calculated corrections at Z pole Photon mass fixed to be zero from QED Z mass: can be measured precisely at Z pole W mass: correlated to Z mass and Fermi Constant GF GF known with very high precision far beyond reach for mw measurements Assume GF to be fixed and treat mw as function of mz to be constrained with data m 2 W = m2 Z 2 πα GF m 2 Z 1 1 r G F ~c = 2 8 From measurement of muon lifetime Calculation at 2-loop level g 2 m 2 W Running of α = (1) 10 5 GeV 2 55
25 W AND Z MASS MEASUREMENT W J = 1 AREVIEWGOESHERE CheckourWWWListofReviews W MASS The W -mass listed here corresponds to the mass parameter in a Breit- Wigner distribution with mass-dependent width. To obtain the world average, common systematic uncertainties between experiments are properly taken into account. The LEP-2 average W mass based on published results is ± GeV [CERN-PH-EP/ ]. The combined Tevatron data yields an average W mass of ± GeV [FERMILAB-TM E]. OUR FIT uses these average LEP and Tevatron mass values and combines them assuming no correlations. VALUE (GeV) EVTS DOCUMENT ID TECN COMMENT ± OUR FIT ± k 1 pp ABAZOV 09AB D0 E cm =1.96TeV ± 0.055± k 2 ABDALLAH 08A DLPH E ee cm = GeV ± 0.034± k 3 pp AALTONEN 07F CDF E cm =1.96TeV ± 0.042± ABBIENDI 06 OPAL E ee cm = GeV ± 0.046± ACHARD 06 L3 E ee cm = GeV ± 0.043± SCHAEL 06 ALEP E ee cm = GeV ± pp ABAZOV 02D D0 E cm =1.8 TeV We use the following data for averages but not for fits ± pp AFFOLDER 01E CDF E cm =1.8TeV We do not use the following data for averages, fits, limits, etc ± AKTAS 06 H1 e ± p νe (ν e )X, s 300 GeV 80.3 ± 2.1 ± 1.2 ± CHEKANOV 02C ZEUS e p νe X, s= ± GeV BREITWEG 00D ZEUS e + p νe X, s 300 GeV ± 0.22 ± ALITTI 92B UA2 See W /Z ratio below ± 0.31 ± ALITTI 90B UA2 pp E cm =546,630GeV 80.0 ± 3.3 ± pp ABE 89I CDF E cm =1.8 TeV 82.7 ± 1.0 ± pp ALBAJAR 89 UA1 E cm =546,630GeV ± ALBAJAR 89 UA1 pp E cm =546,630GeV 89 ± 3 ± ALBAJAR 89 UA1 pp E cm =546,630GeV 81. ± 5. 6 ARNISON 83 UA1 E ee cm =546GeV BANNER 83B UA2 Repl. by ALITTI 90B Z J = 1 AREVIEWGOESHERE CheckourWWWListofReviews Z MASS OUR FIT is obtained using the fit procedure and correlations as determined by the LEP Electroweak Working Group (see the note The Z boson and ref. LEP-SLC 06). The fit is performed using the Z mass and width, the Z hadronic pole cross section, the ratios of hadronic to leptonic partial widths, and the Z pole forward-backward lepton asymmetries. This set is believed to be most free of correlations. The Z-boson mass listed here corresponds to the mass parameter in a Breit-Wigner distribution with mass dependent width. The value is 34 MeV greater than the real part of the position of the pole (in the energysquared plane) in the Z-boson propagator. Also the LEP experiments have generally assumed a fixed value of the γ Z interferences term based on the standard model. Keeping this term as free parameter leads to a somewhat larger error on the fitted Z mass. See ACCIARRI 00Q and ABBIENDI 04G for a detailed investigation of both these issues. VALUE (GeV) EVTS DOCUMENT ID TECN COMMENT ± OUR FIT ± M 1 ABBIENDI 01A OPAL E ee cm =88 94GeV ± M 2 ABREU 00F DLPH E ee cm =88 94GeV ± M 3 ACCIARRI 00C L3 E ee cm =88 94GeV ± M 4 BARATE 00C ALEP E ee cm =88 94GeV We do not use the following data for averages, fits, limits, etc ± ABBIENDI 04G OPAL E ee cm =LEP GeV ±0.032 ± ACHARD 04C L3 E ee cm = GeV ± M 7 ACCIARRI 00Q L3 E ee cm =LEP GeV ± MIYABAYASHI 95 TOPZ E ee cm =57.8 GeV ±0.28 ± pp ALITTI 92B UA2 E cm =630GeV 90.9 ±0.3 ± pp ABE 89C CDF E cm =1.8 TeV ± ABRAMS 89B MRK2 E ee cm =89 93GeV 93.1 ±1.0 ± pp ALBAJAR 89 UA1 E cm =546,630GeV 1 ABBIENDI 01A error includes approximately 2.3 MeVduetostatisticsand1.8 MeVdue to LEP energy uncertainty. 2 The error includes 1.6 MeVduetoLEPenergyuncertainty. 3 The error includes 1.8 MeVduetoLEPenergyuncertainty. 4 BARATE 00C error includes approximately 2.4 MeVduetostatistics,0.2MeV due to experimental systematics, and 1.7MeV due to LEP energy uncertainty. 5 ABBIENDI 04G obtain this result using the S matrix formalism for a combined fit to their cross section and asymmetry data at the Z peak and their data at GeV. The authors have corrected the measurement for the 34 MeV shift with respect to the Breit Wigner fits. 56
26 SM PARAMETERS TO BE EXTRACTED FROM MEASUREMENTS (m 2 Z) QED coupling constant more precisely the hadronic corrections to it (m 2 Z)! had (m 2 Z) QCD coupling constant S (m 2 Z) most precise measurement if EW sector well understood Z mass m Z And more importantly two parameters not directly accessible at LEP Higgs mass m H Top mass m t Source δ Γ Z σhad 0 Rl 0 Rb 0 ρ l sin 2 θ lept eff m W [MeV] [nb] [MeV] α (5) had (m2 Z) α S (m 2 Z ) m Z 2.1 MeV m t 4.3 GeV log 10 (m H /GeV) Theory Experiment
27 RUNNING OF α QED QED coupling constant must be determined at mz scale running due to fermion loops ",Z/W α(s) = α eµτ (s)+ α top (s)+ α (5) had (s). Lepton correction calculated with negligible uncertainty Top correction rather small and computed Light quark corrections difficult to compute perturbative QCD not feasible because of low mass measured from hadronic cross sections at low energy ee collisions Rather than α(s) determine Δαhad(s) from fit to data f ",Z/W! f /f α(s) = α(0) 1 α(s) α(0) = 1/ / [84]. The c α eµτ (m 2 Z )= uncertainty [201]. Since h α top (m 2 Z )= ( α (5) had (m2 Z) = ±
28 PSEUDO- OBSERVABLES Measurements at the Z pole both at LEP and SLC Low Q 2 νn measurements constraints on couplings Direct measurement of W mass and width from Tevatron and LEP χ 2 /dof = 32.6/27 m Z ± Γ Z ± σhad 0 [nb] ± Re ± Rµ ± Rτ ± A 0, e FB ± A 0,µ FB ± A 0, τ FB ± Direct measurement of top at Tevatron once became available 59
29 CHOOSING BEST PSEUDO- OBSERVABLES Each experimental measurement has different sensitivity to SM parameters we want to constrain. Choose those with highest sensitivity to mt and mh (through radiative corrections) small dependency on QCD corrections Parameters most sensitive to radiative corrections will be most powerful ρ 0 = m 2 W. m 2 Z cos 2 θw tree ( ) ρ f R(R f ) = 1+ ρ se + ρ f flavor κ f R(K f ) = 1+ κ se + κ f specific sin 2 θ f eff κ f sin 2 θ W g Vf ρ f (T f 3 2Q f sin 2 θ f eff ) g Af ρ f T f 3, self-energy ρ se = 3G Fm 2 W 8 2π 2 κ se = 3G Fm 2 W 8 2π 2 [ m 2 t m 2 W [ m 2 t m 2 W ( sin2 θ W cos 2 θ W cos 2 θ W sin 2 10 θ W 9 ln m2 H ( m 2 W 5 6 ) ln m2 H m 2 W ) ] + ] 60
30 SENSITIVITY TO M t AND M H () (5) had () (5) had M Z M Z % Z $ 0 had R 0 l A 0,l fb A l (P ' ) R 0 b R 0 c A 0,b fb A 0,c fb e + e! "/Z! t t W b! b e + e! "/Z W W t b! b % Z $ 0 had R 0 l A 0,l fb A l (P ' ) R 0 b R 0 c A 0,b fb A 0,c fb A b A b A c A l (SLD) sin 2 + lept eff (Q fb ) m W * % W * A c A l (SLD) sin 2 + lept eff (Q fb ) m W * % W * M t Q W (Cs) sin 2 +!!(e! e! MS ) sin 2 + W (&N) g 2 L (&N) g 2 R (&N) 1O theo /1M t &(M t )/$ meas *preliminary M t Q W (Cs) sin 2 +!!(e! e! MS ) sin 2 + W (&N) g 2 L (&N) g 2 R (&N) *preliminary O theo /1logM H &(logm H )/$ meas 61
31 Γ INV DEPENDENCY ON M t AND M H 250 Measurement m t 175 () (5) had = ± ) s = ± m H = GeV % inv Measurement m H () (5) had = ± ) s = ± m t = ± 4.3 GeV % inv 62
32 EFFECTIVE MIXING ANGLE A 0,l fb ± A l (P ' ) ± A l (SLD) ± A 0,b fb ± A 0,c fb ± Q had fb ± Average ± , 2 /d.o.f.: 11.8 / 5 m H 10 2 () had = ± () (5) m t = ± 4.3 GeV sin 2 + lept eff 63
33 mh very sensitive to red value sin 2 θ lept eff only parameter sensitive to Source of sensitivity of Higgs mass to eff α (5) had (m2 Z ) eff α (5) had (m2 Z ) Z- POLE RESULTS red value sin 2 θ lept eff m t % CL % ll m W prel. sin 2 + lept eff () R b 130 Parameter Value Correlations α (5) had (m2 Z ) α S(m 2 Z ) m Z m t log 10 (m H /GeV) α (5) had (m2 Z) ± α S (m 2 Z ) ± m Z ± m t 173± log 10 (m H /GeV) 2.05± m H 111± m H 64
34 IMPLICATION OF PRECISION MEASUREMENTS ρ f R(R f ) = 1+ ρ se + ρ f flavor κ f R(K f ) = 1+ κ se + κ f specific self-energy sin 2 θ f eff κ f sin 2 θ W g Vf ρ f (T f 3 2Q f sin 2 θ f eff ) g Af ρ f T f 3, sin 2 θ W = ± sin 2 θ lept eff = ± κ l = ± sin 2 θ b eff = ± κ b = ± ρ l = ± r w = ± ρ b = ± r = ±
35 CONSTRAINTS ON TOP AND W MASS Top-Quark Mass W-Boson Mass CDF ± 6.6 D ± 5.1 Average ± m t, 2 /DoF: 2.6 / 4 LEP1/SLD ! 10.2 LEP1/SLD/m W /% W ! 9.5 TEVATRON ± LEP ± Average ± m W, 2 /DoF: 0.3 / 1 NuTeV ± LEP1/SLD ± LEP1/SLD/m t ±
36 CONSTRAINTS ON HIGGS MASS 80.5 LEP1, SLD data LEP2 (prel.), pp! data 68% CL m W 80.4 () 80.3 m H m t 67
37 INCLUSION OF LHC m W March 2012 LHC excluded LEP2 and Tevatron LEP1 and SLD 68% CL 80.3 m H m t 68
38 IMPORTANCE OF DIRECT W AND TOP MEASUREMENTS 80.5 High Q 2 except m W /% W 68% CL 200 High Q 2 except m t 68% CL m W 80.4 m W (LEP2 prel., pp! ) m t 180 m t (Tevatron) 80.3 Excluded m H 160 Excluded m H Parameter Value Correlations α (5) had (m2 Z ) α S(m 2 Z ) m Z m t log 10 (m H /GeV) α (5) had (m2 Z) ± α S (m 2 Z ) ± m Z ± m t 178.5± log 10 (m H /GeV) 2.11± m H 129±
39 LIMIT ON HIGGS MASS Theory uncertainty () had = () (5) ± ± incl. low Q 2 data (, Excluded m H 70
40 UPDATED LIMIT ON HIGGS m h = GeV [m h < 160 GeV one-sided 95% CL] χ March 2008 Theory uncertainty α (5) α had = ± ± incl. low Q 2 data m Limit = 160 GeV probability per GeV % 5% Excluded Preliminary m H M H Including the direct LEP search data yields m h < 190 GeV at 95% CL. 71
PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS&
 PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS& AT&Z&RESONANCE Z&Lineshape&and&number&of&neutrinos Lecture'2 Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2138214 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/particelle/
PRECISION&MEASUREMENTS& AT&Z&RESONANCE Z&Lineshape&and&number&of&neutrinos Lecture'2 Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2138214 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/particelle/
Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass. Robert Clare UC Riverside
 Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass Robert Clare UC Riverside Robert Clare UC Riverside LoopFest III Apr 1, 2004 2 Outline Electroweak corrections: definitions and strategies Experimental inputs
Electroweak Data Fits & the Higgs Boson Mass Robert Clare UC Riverside Robert Clare UC Riverside LoopFest III Apr 1, 2004 2 Outline Electroweak corrections: definitions and strategies Experimental inputs
IX. Electroweak unification
 IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS
 PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Z Lineshape and number of neutrinos Lecture 2 1 October 212 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 212-213 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
PRECISION MEASUREMENTS AT Z RESONANCE Z Lineshape and number of neutrinos Lecture 2 1 October 212 Shahram Rahatlou Fisica Nucleare e Subnucleare III, Anno Accademico 212-213 http://www.roma1.infn.it/people/rahatlou/fns3/
Measurement of asymmetries. in e e production
 Measurement o asymmetries + + in e e production Daniele Trocino INFN and University o Torino 16th February 009 Particle Physics Ph.D. course (Pro. R. Demina) Outline Introduction quick review o QED/EW
Measurement o asymmetries + + in e e production Daniele Trocino INFN and University o Torino 16th February 009 Particle Physics Ph.D. course (Pro. R. Demina) Outline Introduction quick review o QED/EW
DESY, 12. September Precision Electroweak Measurements. Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen
 DESY, 12. September 2006 Precision Electroweak Measurements Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen Outline 1. Theory of electroweak interaction 2. Precision measurements of electroweak processes 3. Global electroweak
DESY, 12. September 2006 Precision Electroweak Measurements Stefan Roth RWTH Aachen Outline 1. Theory of electroweak interaction 2. Precision measurements of electroweak processes 3. Global electroweak
Electroweak Physics. Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective. LEP/SLC Physics. Probing the Standard Model. Beyond the Standard Model
 Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
W + W - The Z pole. e + e hadrons SLC. Cross-section (pb) Centre-of-mass energy (GeV) P529 Spring,
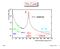 The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
Top, electroweak and recent results from CDF and combinations from the Tevatron
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 181 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i20177181-7 Colloquia: LaThuile 2017 Top, electroweak and recent results from CDF and combinations from the Tevatron D. Lucchesi( 1 )( 2 ) on behalf of
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 181 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i20177181-7 Colloquia: LaThuile 2017 Top, electroweak and recent results from CDF and combinations from the Tevatron D. Lucchesi( 1 )( 2 ) on behalf of
Measurements of the W Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron
 Measurements of the Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron John Ellison University of California, Riverside, USA Selection of and Z events Measurement of the mass Tests of the gauge
Measurements of the Boson Mass and Trilinear Gauge Boson Couplings at the Tevatron John Ellison University of California, Riverside, USA Selection of and Z events Measurement of the mass Tests of the gauge
The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II
 The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II Radiative corrections, renormalization, and physical observables Laura Reina Maria Laach School, Bautzen, September 2011 Outline of Lectures II Radiative
The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II Radiative corrections, renormalization, and physical observables Laura Reina Maria Laach School, Bautzen, September 2011 Outline of Lectures II Radiative
Results on top physics by CMS
 EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04069 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504069 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Results on top physics by CMS Silvano Tosi 1,2,a, on behalf of the CMS
EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04069 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504069 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Results on top physics by CMS Silvano Tosi 1,2,a, on behalf of the CMS
SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold?
 SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold? Michael Roney University of Victoria 22 March 2011 LNF Outline Very Quick reminder of the EW programme Address
SuperB EW Physics Update: Is there a strong EW case for polarisaton at the charm threshold? Michael Roney University of Victoria 22 March 2011 LNF Outline Very Quick reminder of the EW programme Address
LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL
 LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL D.G. Charlton School of Physics & Astronomy The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K. ABSTRACT The period 1989-2000 provided a huge yield of precise electroweak
LEP, SLC AND THE STANDARD MODEL D.G. Charlton School of Physics & Astronomy The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K. ABSTRACT The period 1989-2000 provided a huge yield of precise electroweak
La ricerca dell Higgs Standard Model a CDF
 La ricerca dell Higgs Standard Model a CDF Melisa Rossi INFN-TS Giornata di seminari INFN Trieste - 7 Luglio 2009 FNAL: Fermi National Accelerator Lab Tevatron currently provides the highest energy proton-antiproton
La ricerca dell Higgs Standard Model a CDF Melisa Rossi INFN-TS Giornata di seminari INFN Trieste - 7 Luglio 2009 FNAL: Fermi National Accelerator Lab Tevatron currently provides the highest energy proton-antiproton
Physics at Hadron Colliders
 Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP
 Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP Colloquium Frascati,, 8.2.2001 Dieter Schlatter CERN / Geneva 1 Standard Model In 1989 ingredients of Standard Model were known: Matter particles: u,d,s,c,b,t quarks
Physics Highlights from 12 Years at LEP Colloquium Frascati,, 8.2.2001 Dieter Schlatter CERN / Geneva 1 Standard Model In 1989 ingredients of Standard Model were known: Matter particles: u,d,s,c,b,t quarks
More on SM precision measurements. Marina Cobal University of Udine
 More on SM precision measurements Marina Cobal University of Udine Processes described by the SM Charged current processes; @ low energy the theory coincides with Fermi s theory verified in experiments
More on SM precision measurements Marina Cobal University of Udine Processes described by the SM Charged current processes; @ low energy the theory coincides with Fermi s theory verified in experiments
The electroweak fit at NNLO and prospects for LHC and ILC. Klaus Mönig
 The electroweak fit at NNLO and prospects for LHC and ILC Klaus Mönig The idea of electroweak fits Electroweak interactions are the puzzling part of the Standard Model: parity (and CP) violation non-trivial
The electroweak fit at NNLO and prospects for LHC and ILC Klaus Mönig The idea of electroweak fits Electroweak interactions are the puzzling part of the Standard Model: parity (and CP) violation non-trivial
Precise measurements of the W mass at the Tevatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass. Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy Interactions
 Precise measurements of the W mass at the evatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass Rafael Lopes de Sá for the CDF and DØ Collaborations March 11, 212 Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy
Precise measurements of the W mass at the evatron and indirect constraints on the Higgs mass Rafael Lopes de Sá for the CDF and DØ Collaborations March 11, 212 Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High Energy
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The version of the following full text has not yet been defined or was untraceable and may differ from the publisher's version. For
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The version of the following full text has not yet been defined or was untraceable and may differ from the publisher's version. For
The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment. Conference Report. Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2013/016 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 18 January 2013 (v2, 21 January 2013)
Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2013/016 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 18 January 2013 (v2, 21 January 2013)
W Physics at LEP. 1. WW cross sections and W branching fractions. Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, Monica Pepe Altarelli
 Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, 998 PROCEEDINGS Physics at LEP INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati and CERN, EP Division E-mail: Monica.Pepe.Altarelli@CERN.CH Abstract: A summary
Corfu Summer Institute on Elementary Particle Physics, 998 PROCEEDINGS Physics at LEP INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati and CERN, EP Division E-mail: Monica.Pepe.Altarelli@CERN.CH Abstract: A summary
Measurement of Properties of Electroweak Bosons with the DØ Detector
 Measurement of Properties of Electroweak Bosons with the DØ Detector Laboratoire de Physique Subatomique et de Cosmologie, 53, rue des Martyrs, 38026, Grenoble Cedex, France. E-mail: Hengne.Li@in2p3.fr
Measurement of Properties of Electroweak Bosons with the DØ Detector Laboratoire de Physique Subatomique et de Cosmologie, 53, rue des Martyrs, 38026, Grenoble Cedex, France. E-mail: Hengne.Li@in2p3.fr
Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA May 16, 2002
 NEW RESULTS ON MIXING FROM LEP STEPHEN ARMSTRONG European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) EP Division Geneva, Switzerland Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
NEW RESULTS ON MIXING FROM LEP STEPHEN ARMSTRONG European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) EP Division Geneva, Switzerland Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Precision Electroweak Measurements at the Tevatron
 Precision Electroweak Measurements at the Tevatron The W mass @ Tevatron Effec9ve weak mixing angle The Top Mass @ Tevatron Iain Bertram, Lancaster University for the D0 Collabora9on DIS 2017-6 April 2017
Precision Electroweak Measurements at the Tevatron The W mass @ Tevatron Effec9ve weak mixing angle The Top Mass @ Tevatron Iain Bertram, Lancaster University for the D0 Collabora9on DIS 2017-6 April 2017
Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker
 Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker Significance: Many theories predict that another neutral gauge boson (Z ) may exist. In order to detect this Z, I would use an e + e - linear collider
Search for a Z at an e + e - Collider Thomas Walker Significance: Many theories predict that another neutral gauge boson (Z ) may exist. In order to detect this Z, I would use an e + e - linear collider
The search for the (SM) Higgs Boson
 Tevatron and LHC WS16/17 TUM S.Bethke, F. Simon V9: Search for the Higgs Boson (1) 1 Lecture 9: The search for the (SM) Higgs Boson theoretical basics Higgs production and decay Higgs search in e + e annihilation
Tevatron and LHC WS16/17 TUM S.Bethke, F. Simon V9: Search for the Higgs Boson (1) 1 Lecture 9: The search for the (SM) Higgs Boson theoretical basics Higgs production and decay Higgs search in e + e annihilation
Tests of the Electroweak Theory
 Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
LEP Polarization Team. Geneve TGV. Zimeysa. Meyrin RAIL. LEP beam pipe LEP NMR
 RECENT RESULTS FROM LEP AT THE Z ON ELECTROWEAK AND HEAVY FLAVOR PHYSICS Klaus Monig CERN/PPE 1211 Geneve 23 Switzerland ABSTRACT The four LEP experiments ALEPH, DELPHI, L3, and OPAL have collected about
RECENT RESULTS FROM LEP AT THE Z ON ELECTROWEAK AND HEAVY FLAVOR PHYSICS Klaus Monig CERN/PPE 1211 Geneve 23 Switzerland ABSTRACT The four LEP experiments ALEPH, DELPHI, L3, and OPAL have collected about
Non-Standard Higgs Decays
 Non-Standard Higgs Decays David Kaplan Johns Hopkins University in collaboration with M McEvoy, K Rehermann, and M Schwartz Standard Higgs Decays Standard Higgs Decays 1 _ bb 140 GeV WW BR for SM Higgs
Non-Standard Higgs Decays David Kaplan Johns Hopkins University in collaboration with M McEvoy, K Rehermann, and M Schwartz Standard Higgs Decays Standard Higgs Decays 1 _ bb 140 GeV WW BR for SM Higgs
Search for Higgs Bosons at LEP. Haijun Yang University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
 Search for Higgs Bosons at LEP Haijun Yang University of Michigan, Ann Arbor L3 On behalf of the L3 Collaboration American Physical Society Meeting(APS03), Philadelphia April 5-8, 2003 OUTLINE Introduction
Search for Higgs Bosons at LEP Haijun Yang University of Michigan, Ann Arbor L3 On behalf of the L3 Collaboration American Physical Society Meeting(APS03), Philadelphia April 5-8, 2003 OUTLINE Introduction
Measurements of the Vector boson production with the ATLAS Detector
 Measurements of the Vector boson production with the ATLAS Detector Pavel Staroba for ATLAS Collaboration 1 W/Z measurements at ATLAS More than 50 publications in total. Wide range of topics is covered.
Measurements of the Vector boson production with the ATLAS Detector Pavel Staroba for ATLAS Collaboration 1 W/Z measurements at ATLAS More than 50 publications in total. Wide range of topics is covered.
Physics at Tevatron. Koji Sato KEK Theory Meeting 2005 Particle Physics Phenomenology March 3, Contents
 Physics at Tevatron Contents Koji Sato KEK Theory Meeting 5 Particle Physics Phenomenology March 3, 5 mass measurement Top physics cross section Top mass measurement SM Higgs search Tevatron Run II Started
Physics at Tevatron Contents Koji Sato KEK Theory Meeting 5 Particle Physics Phenomenology March 3, 5 mass measurement Top physics cross section Top mass measurement SM Higgs search Tevatron Run II Started
WZ di-boson production at CMS
 WZ di-boson production at CMS 1 Outline Physics motivations Existing results (Tevatron s = 1.96TeV) Existing prospects for CMS at s = 14TeV Preliminary prospects for CMS at s = 7TeV 2 WZ Physics motivation
WZ di-boson production at CMS 1 Outline Physics motivations Existing results (Tevatron s = 1.96TeV) Existing prospects for CMS at s = 14TeV Preliminary prospects for CMS at s = 7TeV 2 WZ Physics motivation
Invited Contribution to XXXVII th Recontres de Moriond Electroweak Conference. March 2002, Les Arcs 1800, France.
 15th May, 22 Measurement of the W Mass at LEP2 C.J. Parkes a On behalf of the Lep Collaborations Department of Physics and Astronomy, Kelvin Building, University Avenue, Glasgow G12 8QQ, Scotland, U.K.
15th May, 22 Measurement of the W Mass at LEP2 C.J. Parkes a On behalf of the Lep Collaborations Department of Physics and Astronomy, Kelvin Building, University Avenue, Glasgow G12 8QQ, Scotland, U.K.
Weak Decays, CKM, Anders Ryd Cornell University
 Weak Decays, CKM, CP Violation Anders Ryd Cornell University Presented at the International Conference on Weak Interactions and Neutrinos Delphi, Greece, June 6-11, 2005 Page: 1 Flavor Physics The study
Weak Decays, CKM, CP Violation Anders Ryd Cornell University Presented at the International Conference on Weak Interactions and Neutrinos Delphi, Greece, June 6-11, 2005 Page: 1 Flavor Physics The study
e e Collisions at ELIC
 Physics With Collisions at ELIC Collisions at ELIC E. Chudakov (JLab), June 26, 26 Opportunity to build a collider using the ELIC ring Physics motivation for a high luminosity, polarized collider Discussion
Physics With Collisions at ELIC Collisions at ELIC E. Chudakov (JLab), June 26, 26 Opportunity to build a collider using the ELIC ring Physics motivation for a high luminosity, polarized collider Discussion
Higgs Searches and Properties Measurement with ATLAS. Haijun Yang (on behalf of the ATLAS) Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 Higgs Searches and Properties Measurement with ATLAS Haijun Yang (on behalf of the ATLAS) Shanghai Jiao Tong University LHEP, Hainan, China, January 11-14, 2013 Outline Introduction of SM Higgs Searches
Higgs Searches and Properties Measurement with ATLAS Haijun Yang (on behalf of the ATLAS) Shanghai Jiao Tong University LHEP, Hainan, China, January 11-14, 2013 Outline Introduction of SM Higgs Searches
R b,r c Measurements at SLD and LEP-I 1
 SLAC-PUB-8668 December/2000 R b,r c Measurements at SLD and LEP-I 1 D. Su Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, P.O.Box 4349, Stanford, CA 93409, USA E-mail: sudong@slac.stanford.edu Abstract This report
SLAC-PUB-8668 December/2000 R b,r c Measurements at SLD and LEP-I 1 D. Su Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, P.O.Box 4349, Stanford, CA 93409, USA E-mail: sudong@slac.stanford.edu Abstract This report
From Friday: Neutrino Summary. Three neutrinos in the Standard Model:!e,!µ,!" Only left-handed neutrinos and right-handed antineutrinos are observed.
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
Basics of Higgs Physics
 Basics of iggs Physics Sven einemeyer, IFCA (Santander) Karlsruhe, 07/2007 1. The iggs Boson in the SM 2. The iggs Boson in the MSSM Sven einemeyer Basics of iggs Physics presusy07 (Karlsruhe) 23.07.2007
Basics of iggs Physics Sven einemeyer, IFCA (Santander) Karlsruhe, 07/2007 1. The iggs Boson in the SM 2. The iggs Boson in the MSSM Sven einemeyer Basics of iggs Physics presusy07 (Karlsruhe) 23.07.2007
Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron
 Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron Adam Lyon / Fermilab for the DØ and CDF collaborations 15 th Topical Conference on Hadron Collider Physics June 2004 Outline Importance Methodology Single Boson Measurements
Electroweak Physics at the Tevatron Adam Lyon / Fermilab for the DØ and CDF collaborations 15 th Topical Conference on Hadron Collider Physics June 2004 Outline Importance Methodology Single Boson Measurements
Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton
 Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton collision: an analysis of the final state containing three leptons with the ATLAS detector Valentina Vecchio,
Identification of the Higgs boson produced in association with top quark pairs in proton-proton collision: an analysis of the final state containing three leptons with the ATLAS detector Valentina Vecchio,
Electroweak measurements at HERA
 Electroweak measurements at HERA Alex Tapper DESY forum 1 th & 13 th September 006 Precision electroweak measurements: What can HERA contribute? Outline Introduction High Q physics at HERA Review of recent
Electroweak measurements at HERA Alex Tapper DESY forum 1 th & 13 th September 006 Precision electroweak measurements: What can HERA contribute? Outline Introduction High Q physics at HERA Review of recent
Higgs Searches at CMS
 Higgs Searches at CMS Ashok Kumar Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi 110007 Delhi, India 1 Introduction A search for the Higgs boson in the Standard Model (SM) and the Beyond Standard
Higgs Searches at CMS Ashok Kumar Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi 110007 Delhi, India 1 Introduction A search for the Higgs boson in the Standard Model (SM) and the Beyond Standard
Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F2 c c and F2 b b at HERA
 Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F c c and F b b at HERA Vladimir Chekelian MPI for Physics, Germany E-mail: shekeln@mail.desy.de Inclusive charm and beauty production is studied
Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F c c and F b b at HERA Vladimir Chekelian MPI for Physics, Germany E-mail: shekeln@mail.desy.de Inclusive charm and beauty production is studied
Searches for exotica at LHCb
 Searches for exotica at LHCb Lorenzo Sestini Università di Padova e INFN LHCb Implications Workshop, Geneve-Cern, 3-11-2015 Searches for exotics LHCb can be complementary to ATLAS and CMS in the search
Searches for exotica at LHCb Lorenzo Sestini Università di Padova e INFN LHCb Implications Workshop, Geneve-Cern, 3-11-2015 Searches for exotics LHCb can be complementary to ATLAS and CMS in the search
Determination of Electroweak Parameters
 Determination of Electroweak Parameters Seminar Particle Physics at the LHC Proceedings R. Gugel Freiburg, 27.05.2014 Contents 1 Motivation 1 2 Template Method 4 3 Mass of the W Boson 5 3.1 Measurement
Determination of Electroweak Parameters Seminar Particle Physics at the LHC Proceedings R. Gugel Freiburg, 27.05.2014 Contents 1 Motivation 1 2 Template Method 4 3 Mass of the W Boson 5 3.1 Measurement
14 Top Quark. Completing the Third Generation
 14 Top Quark Completing the Third Generation No one could doubt that there would be a sixth quark, the top or t, but it was equally certain that initially no one knew where it would be found. With the
14 Top Quark Completing the Third Generation No one could doubt that there would be a sixth quark, the top or t, but it was equally certain that initially no one knew where it would be found. With the
Top production at the Tevatron
 Top production at the Tevatron Bob Hirosky University of Virginia for the CDF and D0 Collaborations Moriond Moriond QCD 2017 1 Top production at the Tevatron Top mass from differential cross section Polarization
Top production at the Tevatron Bob Hirosky University of Virginia for the CDF and D0 Collaborations Moriond Moriond QCD 2017 1 Top production at the Tevatron Top mass from differential cross section Polarization
Why Higgs Boson Searches?
 Why Higgs Boson Searches? Not just a search for a new particle... The missing piece in a spectacularly successful theory construct: the Standard Model of the fundamental interactions A massive experimental
Why Higgs Boson Searches? Not just a search for a new particle... The missing piece in a spectacularly successful theory construct: the Standard Model of the fundamental interactions A massive experimental
La Fisica dei Sapori Pesanti
 La Fisica dei Sapori Pesanti Lina Barbaro Galtieri Simposio in onore di Romano Bizzarri Roma, La Sapienza, 10 Febbraio 2004 Lina Galtieri Simposio in onore di Romano Bizzarri, Roma 10 Febbraio 2004 1 Heavy
La Fisica dei Sapori Pesanti Lina Barbaro Galtieri Simposio in onore di Romano Bizzarri Roma, La Sapienza, 10 Febbraio 2004 Lina Galtieri Simposio in onore di Romano Bizzarri, Roma 10 Febbraio 2004 1 Heavy
Results on Tau Physics from BaBar
 Results on Tau Physics from BaBar Eric Torrence University of Oregon Search for Lepton Flavor Violation Study of τ 3h 2h + ν τ (5 prong) Tau Lifetime The BaBar Experiment Integrated Luminosity (fb -1 )
Results on Tau Physics from BaBar Eric Torrence University of Oregon Search for Lepton Flavor Violation Study of τ 3h 2h + ν τ (5 prong) Tau Lifetime The BaBar Experiment Integrated Luminosity (fb -1 )
FERMI NATIONAL ACCELERATOR LABORATORY
 FERMI NATIONAL ACCELERATOR LABORATORY arxiv:0908.1374v1 [hep-ex] 10 Aug 2009 TEVEWWG/WZ 2009/01 FERMILAB-TM-2439-E CDF Note 9859 D0 Note 5965 10 th August 2009 Updated Combination of CDF and D0 Results
FERMI NATIONAL ACCELERATOR LABORATORY arxiv:0908.1374v1 [hep-ex] 10 Aug 2009 TEVEWWG/WZ 2009/01 FERMILAB-TM-2439-E CDF Note 9859 D0 Note 5965 10 th August 2009 Updated Combination of CDF and D0 Results
µ = (15.4 ± 0.2) 10 10
 L µ L a Exp µ [1 1 ] a µ = a Exp µ a SM µ [1 1 ] 26.1 ± 8. (3.3 ) 31.6 ± 7.9 (4. ) 1165928.9 ± 6.3 33.5 ± 8.2 (4.1 ) 28.3 ± 8.7 (3.3 ) 29. ± 9. (3.2 ) 28.7 ± 8. (3.6 ) a EW µ = (15.4 ±.2) 1 1 µ µ L µ L
L µ L a Exp µ [1 1 ] a µ = a Exp µ a SM µ [1 1 ] 26.1 ± 8. (3.3 ) 31.6 ± 7.9 (4. ) 1165928.9 ± 6.3 33.5 ± 8.2 (4.1 ) 28.3 ± 8.7 (3.3 ) 29. ± 9. (3.2 ) 28.7 ± 8. (3.6 ) a EW µ = (15.4 ±.2) 1 1 µ µ L µ L
Physics at the LHC: from Standard Model to new discoveries
 Physics at the LHC: from Standard Model to new discoveries Kirill Melnikov University of Hawaii May 2006 Sendai, June 2006 Physics at the LHC: from Standard Model to new discoveries p. 1/22 Outline Standard
Physics at the LHC: from Standard Model to new discoveries Kirill Melnikov University of Hawaii May 2006 Sendai, June 2006 Physics at the LHC: from Standard Model to new discoveries p. 1/22 Outline Standard
Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA
 Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA Uwe Schneekloth DESY On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS Collaborations 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics 5.08.009 Outline Introduction
Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA Uwe Schneekloth DESY On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS Collaborations 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics 5.08.009 Outline Introduction
Particle Physics. Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders! Renormalisation in QCD!Asymptotic Freedom and Confinement in QCD! Lepton and Hadron Colliders!R = (e + e!!hadrons)/(e
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 Lecture 10: QCD at Colliders! Renormalisation in QCD!Asymptotic Freedom and Confinement in QCD! Lepton and Hadron Colliders!R = (e + e!!hadrons)/(e
The W-mass Measurement at CDF
 2010-05 - 10 The W-mass Measurement at CDF Ilija Bizjak, University College London 1/33 Outline 1) Motivation for a W mass measurement Implications for the EW constraints on Higgs mass 2) Measurement of
2010-05 - 10 The W-mass Measurement at CDF Ilija Bizjak, University College London 1/33 Outline 1) Motivation for a W mass measurement Implications for the EW constraints on Higgs mass 2) Measurement of
Top quark pair production cross section and properties of the top quark in p p collisions at s = 1.96 TeV
 Top quark pair production cross section and properties of the top quark in p p collisions at s = 1.96 TeV The University of Manchester, School of Physics & Astronomy, United Kingdom E-mail: schwanen@fnal.gov
Top quark pair production cross section and properties of the top quark in p p collisions at s = 1.96 TeV The University of Manchester, School of Physics & Astronomy, United Kingdom E-mail: schwanen@fnal.gov
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO - BICOCCA DIPARTIMENTO DI FISICA G. OCCHIALINI CORSO DI DOTTORATO IN FISICA E ASTRONOMIA CICLO XXVII
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO - BICOCCA DIPARTIMENTO DI FISICA G. OCCHIALINI CORSO DI DOTTORATO IN FISICA E ASTRONOMIA CICLO XXVII Measurement of the branching fraction of B c + J/ψπ + π π + relative
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO - BICOCCA DIPARTIMENTO DI FISICA G. OCCHIALINI CORSO DI DOTTORATO IN FISICA E ASTRONOMIA CICLO XXVII Measurement of the branching fraction of B c + J/ψπ + π π + relative
ATLAS-CONF October 15, 2010
 ATLAS-CONF-2010-096 October 15, 2010 Data-driven background estimation for the H τ + τ τ h search at 7 TeV with the ATLAS detector Ian Howley 7 December 2010 1 Motivation One of the primary LHC physics
ATLAS-CONF-2010-096 October 15, 2010 Data-driven background estimation for the H τ + τ τ h search at 7 TeV with the ATLAS detector Ian Howley 7 December 2010 1 Motivation One of the primary LHC physics
7th International Workshop on Tau Lepton Physics (Tau02), Santa Cruz, CA, September, 2002
 τ physics at LEP Francisco Matorras a a Instituto de Física de Cantabria Santander, Spain This paper gives an overview of some of the more interesting results obtained at LEP in τ physics: precision measurements
τ physics at LEP Francisco Matorras a a Instituto de Física de Cantabria Santander, Spain This paper gives an overview of some of the more interesting results obtained at LEP in τ physics: precision measurements
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 ( )
 Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (9.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 QED Feyman Rules Starting from elm potential exploiting Fermi s gold rule derived QED Feyman
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (9.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 QED Feyman Rules Starting from elm potential exploiting Fermi s gold rule derived QED Feyman
OPEN /12/98
 Precision Electroweak Tests at LEP E. Falk Lund University, Box 118, S-221 00 Lund Sweden Abstract A presentation is given of a selection of the electroweak precision tests that have been carried out at
Precision Electroweak Tests at LEP E. Falk Lund University, Box 118, S-221 00 Lund Sweden Abstract A presentation is given of a selection of the electroweak precision tests that have been carried out at
B-quark discovery. e+ e- PETRA GeV TRISTAN 61.4 GeV LEP Mz Mt > 45.8 GeV
 1970s B-quark discovery e+ e- PETRA 12-47 GeV TRISTAN 61.4 GeV LEP Mz Mt > 45.8 GeV p+p- ISR 60 GeV SppS 630 GeV Tevatron 1800 GeV 1984 UA1 Mt = 40 ± 10 1989 UA1 Mt > 60 GeV UA2 Mt > 69 GeV 1989 CDF Mt
1970s B-quark discovery e+ e- PETRA 12-47 GeV TRISTAN 61.4 GeV LEP Mz Mt > 45.8 GeV p+p- ISR 60 GeV SppS 630 GeV Tevatron 1800 GeV 1984 UA1 Mt = 40 ± 10 1989 UA1 Mt > 60 GeV UA2 Mt > 69 GeV 1989 CDF Mt
Study of Higgs Boson Decaying to Four Muons at s =14 TeV
 Study of Higgs Boson Decaying to Four Muons at s =14 TeV R.M. Aly 1, A.A. Abdelalim 1,2, M.N.El-Bakrey 1 and A. Mahrous 1 1 Department of physics, Faculty of science, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt. 2
Study of Higgs Boson Decaying to Four Muons at s =14 TeV R.M. Aly 1, A.A. Abdelalim 1,2, M.N.El-Bakrey 1 and A. Mahrous 1 1 Department of physics, Faculty of science, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt. 2
Electroweak results. Luca Lista. INFN - Napoli. LHC Physics
 Electroweak results Luca Lista INFN - Napoli EWK processes at LHC p p W and Z production in pp collisions proceeds mainly form the scattering of a valence quark with a sea anti-quark The involved parton
Electroweak results Luca Lista INFN - Napoli EWK processes at LHC p p W and Z production in pp collisions proceeds mainly form the scattering of a valence quark with a sea anti-quark The involved parton
Some fundamental questions
 Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2
 Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2 Theodora D. Papadopoulou NTU Athens DESY Seminar 28/10/03 1 Outline Introduction about LEP Alternatives to the Higgs mechanism Technicolor Contact
Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2 Theodora D. Papadopoulou NTU Athens DESY Seminar 28/10/03 1 Outline Introduction about LEP Alternatives to the Higgs mechanism Technicolor Contact
CDF top quark " $ )(! # % & '
 $% CDF quark 7 3 5 ( "#! Tevatron Run II Started Spring 1. proton-antiproton collider with (Run I :. antiproton recycler commissioning electron cooling operational by Summer 5. increase in luminosity.
$% CDF quark 7 3 5 ( "#! Tevatron Run II Started Spring 1. proton-antiproton collider with (Run I :. antiproton recycler commissioning electron cooling operational by Summer 5. increase in luminosity.
Inclusive top pair production at Tevatron and LHC in electron/muon final states
 Inclusive top pair production at Tevatron and LHC in electron/muon final states Andreas Jung for the ATLAS, CDF, CMS and D Collaboration Fermilab, DAB5 - MS 357, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL, 651, USA DOI:
Inclusive top pair production at Tevatron and LHC in electron/muon final states Andreas Jung for the ATLAS, CDF, CMS and D Collaboration Fermilab, DAB5 - MS 357, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL, 651, USA DOI:
Preparations for the Spin and Parity Measurement of the Higgs Boson in the H ττ Channel
 Preparations for the Spin and Parity Measurement of the Higgs Boson in the H ττ Channel DPG-Frühjahrstagung, Mainz, March 24th - 28th, 24 J. Berger, R. Caspart, F. Frensch, R. Friese, Thomas Müller, G.
Preparations for the Spin and Parity Measurement of the Higgs Boson in the H ττ Channel DPG-Frühjahrstagung, Mainz, March 24th - 28th, 24 J. Berger, R. Caspart, F. Frensch, R. Friese, Thomas Müller, G.
ATLAS Discovery Potential of the Standard Model Higgs Boson
 ATLAS Discovery Potential of the Standard Model Higgs Boson Christian Weiser University of Freiburg (on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration) 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics Moscow,
ATLAS Discovery Potential of the Standard Model Higgs Boson Christian Weiser University of Freiburg (on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration) 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics Moscow,
PoS(EPS-HEP2011)250. Search for Higgs to WW (lνlν, lνqq) with the ATLAS Detector. Jonas Strandberg
 with the ATLAS Detector Royal Institute of Technology, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: jostran@kth.se Higgs boson searches in the H WW ( ) lνlν (l = e, µ) and the H WW ( ) lνqq decay modes, using. fb of
with the ATLAS Detector Royal Institute of Technology, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: jostran@kth.se Higgs boson searches in the H WW ( ) lνlν (l = e, µ) and the H WW ( ) lνqq decay modes, using. fb of
Rare Hadronic B Decays
 XLI st Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High-Energy Hadronic Interactions La Thuile, Italy, March 18-5, 6 Rare Hadronic B Decays Jürgen Kroseberg Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics University of California,
XLI st Rencontres de Moriond QCD and High-Energy Hadronic Interactions La Thuile, Italy, March 18-5, 6 Rare Hadronic B Decays Jürgen Kroseberg Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics University of California,
Higgs Boson Searches at ATLAS
 Higgs Boson Searches at ATLAS Jianming Qian University of Michigan October 5, 2011 Maryland/John Hopkins Joint Seminar, October 5, 2011 Jianming Qian (University of Michigan) 1 Standard Model Standard
Higgs Boson Searches at ATLAS Jianming Qian University of Michigan October 5, 2011 Maryland/John Hopkins Joint Seminar, October 5, 2011 Jianming Qian (University of Michigan) 1 Standard Model Standard
SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM
 SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM USING LEP DATA Elizabeth Locci SPP/DAPNIA Saclay Representing LEP Collaborations 1 Outline LEP performance Theoretical framework Search for neutral Higgs
SEARCHES FOR THE NEUTRAL HIGGS BOSONS OF THE MSSM USING LEP DATA Elizabeth Locci SPP/DAPNIA Saclay Representing LEP Collaborations 1 Outline LEP performance Theoretical framework Search for neutral Higgs
Verifiche del modello standard: stato e prospettive. Gigi Rolandi CERN e Scuola Normale
 Verifiche del modello standard: stato e prospettive Gigi Rolandi CERN e Scuola Normale With the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012 at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) all the input parameters of the SM
Verifiche del modello standard: stato e prospettive Gigi Rolandi CERN e Scuola Normale With the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012 at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) all the input parameters of the SM
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 A047W SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 05 Thursday, 8 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
A047W SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 05 Thursday, 8 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
A b FB status of results
 A b status of results Vitaliano Ciulli Universita di Firenze and INFN XXXVIIth RENCONTRES DE MORIOND ELECTROWEAK INTERACTIONS AND UNIFIED THEORIES Les Arcs, Savoie, France March 9-16,2002 Introduction
A b status of results Vitaliano Ciulli Universita di Firenze and INFN XXXVIIth RENCONTRES DE MORIOND ELECTROWEAK INTERACTIONS AND UNIFIED THEORIES Les Arcs, Savoie, France March 9-16,2002 Introduction
EW Physics at LHC. phi= mu_4: pt=7.9 GeV, eta=-1.13, phi=0.94. Toni Baroncelli:
 EW Physics at LHC Event display of a 2e2mu candidate. EventNumber: 12611816 RunNumber: 205113 m_4l=123.9 GeV. m_12=87.9 GeV, m_34=19.6 GeV. e_1: pt=18.7 GeV, eta=-2.45, phi=1.68,. 15/09/17 e_2: pt=75.96
EW Physics at LHC Event display of a 2e2mu candidate. EventNumber: 12611816 RunNumber: 205113 m_4l=123.9 GeV. m_12=87.9 GeV, m_34=19.6 GeV. e_1: pt=18.7 GeV, eta=-2.45, phi=1.68,. 15/09/17 e_2: pt=75.96
Search for Higgs in H WW lνlν
 Search for Higgs in H WW lνlν John Alison University of Pennsylvania on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration Higgs Physics Standard Model Remarkably Accurate Description Data. One Remaining Piece: Higgs Boson.
Search for Higgs in H WW lνlν John Alison University of Pennsylvania on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration Higgs Physics Standard Model Remarkably Accurate Description Data. One Remaining Piece: Higgs Boson.
Measurement of CP Violation in B s J/ΨΦ Decay at CDF
 Measurement of CP Violation in B s J/ΨΦ Decay at CDF Gavril Giurgiu Johns Hopkins University University of Virginia Seminar April 4, 2012 Introduction - CP violation means that the laws of nature are not
Measurement of CP Violation in B s J/ΨΦ Decay at CDF Gavril Giurgiu Johns Hopkins University University of Virginia Seminar April 4, 2012 Introduction - CP violation means that the laws of nature are not
Measurements of the Higgs Boson at the LHC and Tevatron
 Measurements of the Higgs Boson at the LHC and Tevatron Somnath Choudhury (for the ATLAS, CMS, DØ and CDF collaborations) 44 th International Symposium on Multiparticle Dynamics 8 12 September 2014, Bologna
Measurements of the Higgs Boson at the LHC and Tevatron Somnath Choudhury (for the ATLAS, CMS, DØ and CDF collaborations) 44 th International Symposium on Multiparticle Dynamics 8 12 September 2014, Bologna
Potential Discoveries at the Large Hadron Collider. Chris Quigg
 Potential Discoveries at the Large Hadron Collider Chris Quigg Fermilab quigg@fnal.gov XXIII Taiwan Spring School Tainan 31 March - 3 April 2010 Electroweak theory successes Theoretical Physics Department,
Potential Discoveries at the Large Hadron Collider Chris Quigg Fermilab quigg@fnal.gov XXIII Taiwan Spring School Tainan 31 March - 3 April 2010 Electroweak theory successes Theoretical Physics Department,
Studies of b b gluon and c c vertices Λ. Abstract
 SLAC PUB 8661 October 2000 Studies of b b gluon and c c vertices Λ Toshinori Abe Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94309 Representing the SLD Collaboration Abstract
SLAC PUB 8661 October 2000 Studies of b b gluon and c c vertices Λ Toshinori Abe Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94309 Representing the SLD Collaboration Abstract
Atlas Status and Perspectives
 Atlas Status and Perspectives Bruno Mansoulié (IRFU-Saclay) On behalf of the Topics The hot news: Heavy Ion analysis Data taking in 2010 Luminosity, Data taking & quality, trigger Detector performance
Atlas Status and Perspectives Bruno Mansoulié (IRFU-Saclay) On behalf of the Topics The hot news: Heavy Ion analysis Data taking in 2010 Luminosity, Data taking & quality, trigger Detector performance
Analysis of Electroweak Precision Data and Prospects for Future Improvements
 KEK-TH-512 DESY 96-192 hep-ph/9706331 January 21, 1998 Analysis of Electroweak Precision Data and Prospects for Future Improvements Kaoru Hagiwara 1,2,a, Dieter Haidt 3,b, Seiji Matsumoto 1,c 1 Theory
KEK-TH-512 DESY 96-192 hep-ph/9706331 January 21, 1998 Analysis of Electroweak Precision Data and Prospects for Future Improvements Kaoru Hagiwara 1,2,a, Dieter Haidt 3,b, Seiji Matsumoto 1,c 1 Theory
Hadronic events in e + e -
 Hadronic events in e + e - Hadronic cross-section, asymmetry (Very short on) Accelerators and detectors Events in the continuum; below, above and at the Z Event selection, ISR WW events Selection of heavy-uark
Hadronic events in e + e - Hadronic cross-section, asymmetry (Very short on) Accelerators and detectors Events in the continuum; below, above and at the Z Event selection, ISR WW events Selection of heavy-uark
Events/(10 GeV/c 2 ) Average Weight. -ln L. νwt. Reconstructed Mass (GeV/c 2 ) - log(l) m t
 Electroweak Measurements from Hadron Machines Mark Lancaster Department of Physics and Astronomy University College London London, WC1E 6BT, UK. 1 Introduction The discovery of the W and Z gauge bosons
Electroweak Measurements from Hadron Machines Mark Lancaster Department of Physics and Astronomy University College London London, WC1E 6BT, UK. 1 Introduction The discovery of the W and Z gauge bosons
Higgs searches at L3
 Higgs searches at L3 D. Teyssier To cite this version: D. Teyssier. Higgs searches at L3. High Energy Physics Conference - HEP-MAD 0, Sep 200, Antananariv, Madagascar. World Scientific, pp.67-72, 2002.
Higgs searches at L3 D. Teyssier To cite this version: D. Teyssier. Higgs searches at L3. High Energy Physics Conference - HEP-MAD 0, Sep 200, Antananariv, Madagascar. World Scientific, pp.67-72, 2002.
Search for Physics Beyond the Standard Model at B Factories
 Search for Physics Beyond the Standard Model at B Factories Gautier Hamel de Monchenault CEA-Saclay DAPNIA/SPP on behalf of the BABAR & BELLE Collaborations Moskow, 29 July 2006 New Physics in Flavor Sector
Search for Physics Beyond the Standard Model at B Factories Gautier Hamel de Monchenault CEA-Saclay DAPNIA/SPP on behalf of the BABAR & BELLE Collaborations Moskow, 29 July 2006 New Physics in Flavor Sector
Probing Anomalous WW γ and WWZ Couplings with Polarized Electron Beam at the LHeC and FCC-Ep Collider
 International Journal of Chemical, Molecular, Nuclear, Materials and Metallurgical Engineering Vol:9 No:, 25 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:9, No:, 25 the-scholar.org/publication/99
International Journal of Chemical, Molecular, Nuclear, Materials and Metallurgical Engineering Vol:9 No:, 25 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:9, No:, 25 the-scholar.org/publication/99
Precision Tests of the Standard Model. Yury Kolomensky UC Berkeley Physics in Collision Boston, June 29, 2004
 Precision Tests of the Standard Model Yury Kolomensky UC Berkeley Physics in Collision Boston, June 29, 2004 Motivation Experiments (not covered by previous speakers ) Atomic Parity Violation Neutrino
Precision Tests of the Standard Model Yury Kolomensky UC Berkeley Physics in Collision Boston, June 29, 2004 Motivation Experiments (not covered by previous speakers ) Atomic Parity Violation Neutrino
Single top quark production at CDF
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings 73 75 (16) 74 79 www.elsevier.com/locate/nppp Single top quark production at CDF Sandra Leone, on behalf of the CDF Collaboration
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings 73 75 (16) 74 79 www.elsevier.com/locate/nppp Single top quark production at CDF Sandra Leone, on behalf of the CDF Collaboration
Recent Results from the Tevatron
 Recent Results from the Tevatron Simona Rolli Tufts University (on behalf of the CDF and D0 Collaborations) PPC 2010: IV INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON THE INTERCONNECTION BETWEEN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY
Recent Results from the Tevatron Simona Rolli Tufts University (on behalf of the CDF and D0 Collaborations) PPC 2010: IV INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON THE INTERCONNECTION BETWEEN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY
Top quark pair properties in the production and decays of t t events at ATLAS
 ATL-PHYS-PROC-214-72 11 July 214 Top quark pair properties in the production and decays of t t events at DESY, Hamburg Universität Wuppertal E-mail: ralph.schaefer@cern.ch In proton-proton collisions at
ATL-PHYS-PROC-214-72 11 July 214 Top quark pair properties in the production and decays of t t events at DESY, Hamburg Universität Wuppertal E-mail: ralph.schaefer@cern.ch In proton-proton collisions at
W, Z and top production measurements at LHCb
 1 W, Z and top production measurements at LHCb Lorenzo Sestini, on behalf of the LHCb collaboration. Universitá di Padova e INFN E-mail: lorenzo.sestini@cern.ch The LHCb experiment offers a complementary
1 W, Z and top production measurements at LHCb Lorenzo Sestini, on behalf of the LHCb collaboration. Universitá di Padova e INFN E-mail: lorenzo.sestini@cern.ch The LHCb experiment offers a complementary
