Quiz Samples for Chapter 9 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
|
|
|
- Grace Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Department: Student ID #: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer No penalty for an unanswered question Fill the blank ( ) with ( ) if the statement is correct (incorrect) : corrections to an incorrect answer : solution Textbook: Walker, Halliday, Resnick, Principles of Physics, Tenth Edition, John Wiley & Sons (2014) 9-1 Center of Mass 1 ( ) where m i and x i are the mass and the position of the ith particle and M = m i is the total mass of the system If we use the vector notation, then r com = 1 M m i r i, where r i is the position vector of the ith particle 2 ( ) The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though all of the system s mass were concentrated there 3 ( ) The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though all external forces were applied there 4 ( ) The center of mass of a two-body system is r com = m 1r 1 + m 2 r 2 m 1 + m 2 The center of mass of a system of n particles is defined to be the point whose coordinates are given by x com = 1 M y com = 1 M z com = 1 M m i x i, m i y i, m i z i, 5 (a) ( ) The center of mass of an object must lie within the object The center of mass of a C-shaped object does not lie within the object (b) ( ) All the mass of an object is actually concentrated at its center of mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though all of the system s mass were concentrated there and all external forces were applied there (c) ( ) The center of mass of an object cannot move if there is zero net force on the object If there is zero net force on an object, because of the Newton second law, the acceleration of the object is zero, so the object has constant velocity It does not mean that this object cannot move Page 1 of 5
2 (d) (8) The center of mass of a cylinder must lie on its axis!!!the center of mass of a nonuniform cylinder may not lie on its axis Block A, with a mass of m1, is moving with a velocity of v1 while block B, with a mass of m2, is moving with a velocity of v2 The center of mass of the two-block system is moving with the velocity of 6 ( ) vcom = m1 v1 + m2 v2 4 ( ) Two boys with masses of m1 and m2 stand on a horizontal frictionless surface holding the ends of a light road of length L The boys pull themselves together along the rod When they meet the m1 m2 boy will have moved L 9-2 Newton s Second Law for a System of Particles 1 ( ) Newton s Second Law for a System of Particles: The motion of the center of mass of any system of particles is governed by Newton s second law for a system of particles, which is Fnet = M acom Here Fnet is the net force of all the external forces acting on the system, M is the total mass of the system, and acom is the acceleration of the system s center of mass 2 (a) ( ) The center of mass of a system of particles has a constant velocity if the external forces acting on particles of the system sum to zero (b) ( ) The center of mass of a system of particles remains at the same place if it is initially at rest and the external forces sum to zero At the same instant, a ball of mass m1 is dropped from h above Earth, and a second ball, with a mass of m2, is thrown straight upward from Earth s surface with an initial speed of v They move along nearby q lines and pass without colliding After time t( 2h g ) has elapsed, the velocity of the center of mass of the two-ball system is m2 v gt, where the positive direction is upward 5 ( ) 3 ( ) Page 2 of 5
3 A mass m 1 is attached to one end of a spring with a spring constant k and a mass m 2 is attached to the other end The masses are placed on a horizontal surface and the spring is compressed x The spring is then released with the masses at rest and the masses oscillate When the spring has its equilibrium length for the first time, the m 1 mass has a speed of v The mechanical energy that has been lost to this instant is 9-3 Linear Momentum 1 2 kx2 1 2 m 1v 2 1 m 2 1 v 2 = 0 2 m 2 1 ( ) The linear momentum P of a system of particles is P = Mv com, where v com is the velocity of the system s center of mass and M is the total mass of the system 2 (a) ( ) Two bodies, A and B, have equal kinetic energies The mass of A is α times that of B The ratio of the momentum of A to that of B is 1 : α (b) ( ) Two objects, P and Q, have the same momentum Q can have more kinetic energy than P if it is moving faster than P (c) ( ) A m 1 stone is released from rest and falls toward the Earth After time t has elapsed, the magnitude of its momentum is mgt 3 (a) ( ) Force equals the time rate of change of momentum (b) ( ) If the total momentum of a system is changing, a net external force must be acting on the system (c) ( ) The unit of a momentum may be expressed in N s (d) ( ) The momentum of an object at a given instant is in the same direction as its velocity (e) ( ) When you step on the accelerator to increase the speed of your car, the force that accelerates the car is the force of friction of the road on the tires 9-4 Collision and Impulse 1 ( ) The Impulse Linear Momentum Theorem: The change in the body s linear momentum due to an impulse is p = p f p i = J, where p i and p f are the initial and the final momentum, respectively, and the impulse J is defined by J = tf t i F (t)dt = F average t Here, F average is the time average of the force during the collision of time interval [t i, t f = t i + t] 2 ( ) The physical quantity impulse has the same dimensions as that of momentum 3 (a) ( ) A golf ball of mass m is hit by a golf club so that the ball leaves the tee with speed v The club is in contact with the ball for time T The average force on the club on the ball during the time T is mv/t (b) ( ) A box of books with mass m is dropped on the floor from a height of h and comes to rest The floor exerted impulse of m 2gh on the box 9-5 Conservation of Linear Momentum 1 ( ) If a system is isolated so that no net external force acts on it, the linear momentum of the system remains constant: P = constant P f = P i In any two-body collision of an isolated system, the sum of two momenta is invariant: p 1f + p 2f = p 1i + p 2i Here, 1 and 2 are particle IDs and f and i indicate the initial and final states, respectively In terms of the masses and the velocities, the linear momentum conservation can be stated as m 1 v 1f + m 2 v 2f = m 1 v 1i + m 2 v 2i Page 3 of 5
4 2 ( ) The center of mass of a closed, isolated system of two colliding bodies is not affected by a collision In particular, the velocity of the center of mass cannot be changed by the collision 3 ( ) A shell is launched from a cannon and explodes mid-air The explosion exerts only internal forces on the shell, but gravity is an external force Its horizontal momentum is conserved but its vertical momentum is not conserved 9-6 Momentum and Kinetic Energy in Collisions 1 (a) ( ) A puck of mass m1 is traveling at speed v It strikes another puck with mass m2, which is stationary The two pucks stick together Their common final speed is m1 v 2 (a) ( ) An inelastic collision is one in which momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not conserved A block moves at speed v in the positive x direction and hits an identical block, initially at rest A small amount of gunpowder had been placed on one of the blocks The explosion does not harm the blocks but it doubles their total kinetic energy After the explosion, the blocks move along the x axis and the incident block has a speed of 1 3 v 2 4 ( ) Cart A, with a mass of m1, travels on a horizontal air track at a speed of v and hits cart B, which has a mass of m2 and is initially at rest After the collision, the center of mass of the two cart system has a speed of m1 v 5 ( ) A bullet of mass m is fired horizontally into a block of wood with mass M suspended by a rope from the ceiling After the bullet sticks into the block, they swing in an arc, rising h above its lowest position The velocity of the bullet was m+mp 2gh m 6 (a) ( ) For a completely inelastic two-body collision the kinetic energy retained by the 2 where M is objects is the same as 21 M vcom the total mass and vcom is the velocity of the center of mass (b) ( ) (b) ( ) An elastic collision is one in which kinetic energy and momentum are both conserved (c) ( ) A completely inelastic collision is one in which the bodies stick together after the collision 3 ( ) A sack of coal with a mass of m is dropped on a railroad flatcar with mass M which was initially moving at v as shown After the sack rests on the flatcar, the speed of the flatcar is M v m+m Page 4 of 5
5 9-7 Elastic Collisions in One Dimension 1 ( ) In an elastic collision, the total kinetic energy is conserved: K1f + K2f = K1i + K2i In addition, the linear momentum is also conserved: p1f + p2f = p1i + p2i 2 ( ) Blocks A and B are moving toward each other along the x axis A has a mass of ma and a velocity of va, while B has a mass of mb and a velocity of vb They suffer an elastic collision and move off along the x axis The velocity of B after the collision is mb vb + 2mA va ma vb ma + mb 9-8 Collisions in Two Dimensions 1 ( ) 2 ( ) A hockey puck of mass m traveling along the x axis at 45 m/s hits another identical hockey puck at rest If after the collision the second puck travels at a speed of 35 m/s at an angle of 30 above the x axis, this is an inelastic collision since kinetic energy is not conserved 9-9 System with Varying Mass: A Rocket 1 ( ) In the absence of external forces a rocket accelerates at an instantaneous rate given by Rvrelative = M a, where R is the fuel consumption rate, vrelative is the speed of fuel ejected relative to the rocket, Rvrelative is the thrust of the rocket engine, M is the variable mass of the rocket The speed changes from vi to vf when its mass changes from Mi to Mf : Mi vf vi = vrelative ln Mf 2 (a) ( ) A rocket exhausts fuel with a velocity of m/s, relative to the rocket It starts from rest in outer space with fuel comprising 80 percent of the total mass When all the fuel has been exhausted its speed is m/s (b) ( ) A hockey puck of mass m traveling along the x axis at v0 hits another identical hockey puck at rest If after the collision the second puck travels at a speed of v2 at an angle of θ2 above the x axis, the final velocity of the first puck is v1, θ1 below the x axis Then θ1 is 1 v0 v2 cos θ2 tan v2 sin θ2 A space probe of mass M is motionless in space To start moving, its main engine is fired for 5 s during which time it ejects exhaust gases at a speed of v At the end of this process, it is moving at V Note that v and V are not relative speed The mass of the ejected gas is V M v+v Page 5 of 5
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_07 Saturday, October 06, 2007 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_07 Saturday, October 06, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A stream of gas consists of n molecules. Each molecule has mass m and speed v. Each molecule is reflected
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_07 Saturday, October 06, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A stream of gas consists of n molecules. Each molecule has mass m and speed v. Each molecule is reflected
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity of o
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
(D) Based on Ft = m v, doubling the mass would require twice the time for same momentum change
 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
PHYSICS FORMULAS. A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B)
 PHYSICS FORMULAS A = A x i + A y j Φ = tan 1 A y A x A + B = (A x +B x )i + (A y +B y )j A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B) linear motion v = v 0 + at x - x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 2a(x - x
PHYSICS FORMULAS A = A x i + A y j Φ = tan 1 A y A x A + B = (A x +B x )i + (A y +B y )j A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B) linear motion v = v 0 + at x - x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 2a(x - x
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that.
 Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
1 kg. 10,000 kg. 1 Page. Momentum is a vector so it has a magnitude and a velocity. Its magnitude is the product of its mass and velocity, p = mv.
 Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
a) Calculate the height that m 2 moves up the bowl after the collision (measured vertically from the bottom of the bowl).
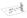 2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
Momentum Conceptual Questions. 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity?
 AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse
 Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
 1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
Momentum and Its Relation to Force
 Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force The linear momentum, or momentum, of an object is defined as the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, p, is a vector and its direction is the
Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force The linear momentum, or momentum, of an object is defined as the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, p, is a vector and its direction is the
Chapter 9. 9 Momentum. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
3. How long must a 100 N net force act to produce a change in momentum of 200 kg m/s? (A) 0.25 s (B) 0.50 s (C) 1.0 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 4.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
Name ID Section. 1. One mile is equal to 1609 m; 1 hour is equal to 3600 s. The highway speed limit of 65 mph is equivalent to the speed of:
 The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
Conservation of Momentum. The total momentum of a closed, isolated system does not change.
 Conservation of Momentum In the 17 th century, Newton and others had measured the momentum of colliding objects before and after collision, and had discovered a strange phenomenon: the total momentum of
Conservation of Momentum In the 17 th century, Newton and others had measured the momentum of colliding objects before and after collision, and had discovered a strange phenomenon: the total momentum of
Chapter 9. Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Momentum Analysis Models Force and acceleration are related by Newton s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated.
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Momentum Analysis Models Force and acceleration are related by Newton s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated.
Chapter 9. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest.
 T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
Impulse,Momentum, CM Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, Mechanics Test
 Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
Practice Problems for Exam 2 Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017
 2017 F = ma Exam 1 AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017 2017 F = ma Contest 25 QUESTIONS - 75 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO BEGIN Use g = 10 N/kg throughout this
2017 F = ma Exam 1 AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017 2017 F = ma Contest 25 QUESTIONS - 75 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO BEGIN Use g = 10 N/kg throughout this
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
PSI AP Physics I Momentum
 PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade
 EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
Physics 231 Lecture 14
 Physics 231 Lecture 14 Impulses: forces that last a short time Momentum: p = mv Impulse-Momentum theorem: FΔt = Δp = mδv = m( v f v i ) Momentum conservation: p tot,f p 1,f + p 2,f = p 1,i + p 2,i p tot,i
Physics 231 Lecture 14 Impulses: forces that last a short time Momentum: p = mv Impulse-Momentum theorem: FΔt = Δp = mδv = m( v f v i ) Momentum conservation: p tot,f p 1,f + p 2,f = p 1,i + p 2,i p tot,i
 1 of 7 4/5/2010 10:25 PM Name Date UNIT 3 TEST 1. In the formula F = Gm m /r, the quantity G: depends on the local value of g is used only when Earth is one of the two masses is greatest at the surface
1 of 7 4/5/2010 10:25 PM Name Date UNIT 3 TEST 1. In the formula F = Gm m /r, the quantity G: depends on the local value of g is used only when Earth is one of the two masses is greatest at the surface
Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum? Newton defined momentum as the quantity of motion
 AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall Answer Key
 Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS
 Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
October 24. Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components
 October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
AP Mechanics Summer Assignment
 2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
AP Physics 1: MIDTERM REVIEW OVER UNITS 2-4: KINEMATICS, DYNAMICS, FORCE & MOTION, WORK & POWER
 MIDTERM REVIEW AP Physics 1 McNutt Name: Date: Period: AP Physics 1: MIDTERM REVIEW OVER UNITS 2-4: KINEMATICS, DYNAMICS, FORCE & MOTION, WORK & POWER 1.) A car starts from rest and uniformly accelerates
MIDTERM REVIEW AP Physics 1 McNutt Name: Date: Period: AP Physics 1: MIDTERM REVIEW OVER UNITS 2-4: KINEMATICS, DYNAMICS, FORCE & MOTION, WORK & POWER 1.) A car starts from rest and uniformly accelerates
St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School
 Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
AAST/AEDT. Center of mass
 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS C: Center of mass Let us run an experiment: We take an object of a random shape and pull it by applying a force as shown on a diagram. The object experiences translational and rotational
AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS C: Center of mass Let us run an experiment: We take an object of a random shape and pull it by applying a force as shown on a diagram. The object experiences translational and rotational
Momentum and Impulse Practice Multiple Choice
 Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions
 Name Date Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the SI unit of momentum? A) N/s B)
Name Date Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the SI unit of momentum? A) N/s B)
PHYSICS 30 MOMENTUM AND IMPULSE ASSIGNMENT 4 VERSION:0 55 MARKS
 Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
(k = force constant of the spring)
 Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Conservation of Momentum. Last modified: 08/05/2018
 Conservation of Momentum Last modified: 08/05/2018 Links Momentum & Impulse Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Example 1: 2 Blocks Initial Momentum is Not Enough Example 2: Blocks Sticking Together
Conservation of Momentum Last modified: 08/05/2018 Links Momentum & Impulse Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Example 1: 2 Blocks Initial Momentum is Not Enough Example 2: Blocks Sticking Together
Energy and Momentum Review Problems
 Energy and Momentum Review Problems NAME 1. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? A) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. B) A physics student stretches a spring. C) A projectile
Energy and Momentum Review Problems NAME 1. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? A) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. B) A physics student stretches a spring. C) A projectile
Solutions to Homework Set #9 Phys2414 Fall 2005
 Solution Set #9 Solutions to Homework Set #9 Phys44 Fall 005 Note: The numbers in the boxes correspond to those that are generated by WebAssign. The numbers on your individual assignment will vary. Any
Solution Set #9 Solutions to Homework Set #9 Phys44 Fall 005 Note: The numbers in the boxes correspond to those that are generated by WebAssign. The numbers on your individual assignment will vary. Any
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum Chaper 6 Review: Work and Energy Forces and Displacements Effect of forces acting over a displacement Work W = (F cos)s Work changes the Kinetic Energy of a mass Kinetic
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum Chaper 6 Review: Work and Energy Forces and Displacements Effect of forces acting over a displacement Work W = (F cos)s Work changes the Kinetic Energy of a mass Kinetic
Impulse and Momentum continued
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
Collision Theory Challenge Problems
 Collision Theory Challenge Problems Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds. Problem 2 You just
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds. Problem 2 You just
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the new concepts of impulse and momentum. Slide 9-2 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-3 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-4 Chapter 9 Preview Slide
Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the new concepts of impulse and momentum. Slide 9-2 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-3 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-4 Chapter 9 Preview Slide
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Slide 1 / 40. Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum
 Slide 1 / 40 Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum Slide 2 / 40 1 A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped
Slide 1 / 40 Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum Slide 2 / 40 1 A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped
Energy in Collisions Problems AP Physics C
 1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1
 Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions
 Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
General Physics I Momentum
 General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions
 Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Elementary Physics October 8, 2007
 INSTRUCTIONS: For for the multiple choice questions 1 8, you will be scored only on the basis of choosing only the one correct answer for full credit. No partial credit will be given. For questions 9 10,
INSTRUCTIONS: For for the multiple choice questions 1 8, you will be scored only on the basis of choosing only the one correct answer for full credit. No partial credit will be given. For questions 9 10,
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper
 NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
z F 3 = = = m 1 F 1 m 2 F 2 m 3 - Linear Momentum dp dt F net = d P net = d p 1 dt d p n dt - Conservation of Linear Momentum Δ P = 0
 F 1 m 2 F 2 x m 1 O z F 3 m 3 y Ma com = F net F F F net, x net, y net, z = = = Ma Ma Ma com, x com, y com, z p = mv - Linear Momentum F net = dp dt F net = d P dt = d p 1 dt +...+ d p n dt Δ P = 0 - Conservation
F 1 m 2 F 2 x m 1 O z F 3 m 3 y Ma com = F net F F F net, x net, y net, z = = = Ma Ma Ma com, x com, y com, z p = mv - Linear Momentum F net = dp dt F net = d P dt = d p 1 dt +...+ d p n dt Δ P = 0 - Conservation
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test. Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b)2.25e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b)2 (c)1.5 (d) (e).
 AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
Wiley Plus. Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm!
 Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
PHYSICS. Chapter 11 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
LINEAR MOMENTUM. Contents. (A. Savas ARAPO GLU) July 16, Introduction 2. 2 Linear Momentum 2
 LINEAR MOMENTUM (A. Savas ARAPO GLU) July 16, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Linear Momentum 2 3 Impulse & Collisions 4 3.1 Collison of Particles................................ 5 3.2 Collison Types...................................
LINEAR MOMENTUM (A. Savas ARAPO GLU) July 16, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Linear Momentum 2 3 Impulse & Collisions 4 3.1 Collison of Particles................................ 5 3.2 Collison Types...................................
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN
 2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
Study Questions/Problems Week 6
 Study Questions/Problems Week 6 Chapters 9 explores further elaborations on Newton s laws that lead to another conservation principle conservation of linear momentum. These problems will help you appreciate
Study Questions/Problems Week 6 Chapters 9 explores further elaborations on Newton s laws that lead to another conservation principle conservation of linear momentum. These problems will help you appreciate
Chapter 9. Collisions. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Linear Momentum Units of Chapter 9 Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Units of Chapter
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Linear Momentum Units of Chapter 9 Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Units of Chapter
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Units of Chapter
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Units of Chapter
CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 69 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW 1. Samantha walks along a horizontal path in the direction shown. The curved
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 69 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW 1. Samantha walks along a horizontal path in the direction shown. The curved
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name:
 Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
(A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III
 1. A solid metal ball and a hollow plastic ball of the same external radius are released from rest in a large vacuum chamber. When each has fallen 1m, they both have the same (A) inertia (B) speed (C)
1. A solid metal ball and a hollow plastic ball of the same external radius are released from rest in a large vacuum chamber. When each has fallen 1m, they both have the same (A) inertia (B) speed (C)
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Impulse and momentum 09-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 10 in textbook Prelecture due next Tuesday HW#8 due this Friday at 5 pm. 09-2 2 9-2.1 A crash
Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Impulse and momentum 09-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 10 in textbook Prelecture due next Tuesday HW#8 due this Friday at 5 pm. 09-2 2 9-2.1 A crash
Momentum. A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball, is... straight up straight down to the right to the left
 Momentum A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball,, is... A: B: C: D: straight up straight down to the right to the left This is also the direction of Momentum A
Momentum A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball,, is... A: B: C: D: straight up straight down to the right to the left This is also the direction of Momentum A
Exam 2: Equation Summary
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Center of Mass and Linear
 PH 221-3A Fall 2010 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum Lecture 15 Chapter 8 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 9 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum In this chapter
PH 221-3A Fall 2010 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum Lecture 15 Chapter 8 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 9 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum In this chapter
Concept Question: Normal Force
 Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
( m/s) 2 4(4.9 m/s 2 )( 52.7 m)
 Version 072 idterm 2 OConnor (05141) 1 This print-out should have 18 questions ultiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering V1:1, V2:1, V3:3, V4:5,
Version 072 idterm 2 OConnor (05141) 1 This print-out should have 18 questions ultiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering V1:1, V2:1, V3:3, V4:5,
( m/s) 2 4(4.9 m/s 2 )( 53.2 m)
 Version 074 idterm 2 OConnor (05141) 1 This print-out should have 18 questions ultiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering V1:1, V2:1, V3:3, V4:5,
Version 074 idterm 2 OConnor (05141) 1 This print-out should have 18 questions ultiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering V1:1, V2:1, V3:3, V4:5,
