Magnetic Field Design for a 2.45-GHz ECR Ion Source with Permanent Magnets
|
|
|
- Donald Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 55, No. 2, August 2009, pp Magnetic Field Design for a 2.45-GHz ECR Ion Source with Permanent Magnets J. Y. Park Department of Physics, Pusan National University, Busan and Korea Basic Science Institute, Busan H. S. Lee, M. S. Won, B. S. Lee, J. P. Kim, J. H. Yoon, J. S. Bae and J. K. Bang Korea Basic Science Institute, Busan J. K. Ahn Department of Physics, Pusan National University, Busan (Received 26 December 2008) We optimize the magnetic field configuration for a 2.45 GHz electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) ion source with permanent magnets, which is designed to construct a compact heavy-ion accelerator for intensive studies on nucleosynthesis. The magnetic system consists of two radially magnetized solenoids, a hexapole magnet, and a central ring magnet. We report magnetic field measurements of the permanent-magnet ECR ion source and compare with the results with those obtained using an Opera3D calculation. PACS numbers: n, N, Di Keywords: ECR, Ion Source, Permanent magnet, Plasma I. INTRODUCTION The need for high currents of multiply charged ions led to the development of an electron cyclotron resonance ion source (ECRIS) [1]. The main features of the ECRIS source can be summed up by the following points: highly charged ions produced in continuous and pulsed modes, feasibility to accelerate elements up to uranium, easy adjustment of the electron temperature and density, robustness, and long-life with no wearing parts like filaments. Due to the unique capability of producing highly charged ion beams, the ECRIS has been widely utilized in a variety of research areas ranging from atomic and nuclear physics to material sciences. In an ECR source, highly charged ions are produced stepwise by electron impact ionization. During the bombardment of electrons, the ions or atoms are ionized, leading to charges up to the maximum charge with all electrons stripped off. A highly charged ion generates bremsstrahlung X- ray photons when it is decelerated or stops in materials. The maximum X-ray photon energy can readily reach several hundreds of MeV for highly charged ions. Extreme ultra-violet (EUV) light can also be emitted in atomic transitions of highly charged Xe ions. ahnjk@pusan.ac.kr; Fax: There has been a rapid improvement in the performance, such as achievable charge states and beam intensity, of ECR ion sources. Empirical scaling laws show that the maximum achievable charge state and intensity grow with increasing microwave frequency. At the same time, the magnetic fields should be increased to fulfill the resonance conditions and to have good confinement. That requires superconducting magnets with very high frequencies, for example, 18 GHz, 28 GHz, or even higher. On the other hand, ECR ion sources can be miniaturized with permanent magnets only. This has the advantages of low power consumption and low operating cost [2 7]. In the paper, we report optimization of the magnetic field configuration for a 2.45-GHz ECRIS with permanent magnets. II. DESIGN OF THE ECR MAGNETIC FIELD CONFIGURATION Our 2.45-GHz ECRIS consists of two radially magnetized solenoids, a hexapole magnet, and a central ring magnet. The two solenoid magnets make a mirror field to confine the ECR plasma axially while the hexapole magnet confines it radially. For a solenoid field, the radial magnetization is known to be stronger than the axial one. We have searched for an optimum configuration of -409-
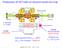
2 -410- Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 55, No. 2, August 2009 Fig. 1. Calculated magnetic field strengths from Eq. (1). Top-right plot (a) shows the axial magnetic field strengths according to the inner radius (R 1) of the solenoid magnet with a fixed thickness of 3 cm. Bottom-left plot (b) indicates the axial magnetic field strengths according to the thickness of the solenoid magnet. Bottom-right figure (c) represents axial magnetic field strengths in terms of the distance between two solenoid magnets. Fig. 2. Profiles of the multicusp field in terms of the numbers of cusp. the solenoid geometry by varying the thickness, the inner and outer radii, and the distance between the two solenoid magnets. The axial magnetic field strength at a given point z along the symmetric axis is given by B z (z) = B r 2 ( 1 a 1 1 a 2 1 b b 2 ) + ln (1 + b 1)(1 + a 2 ) (1 + b 2 )(1 + a 1 ), (1) where B r represents a residual magnetic induction, a 1 = 1 + (z + l)/r 2, a 2 = 1 + (z l)/r 2, b 1 = 1 + (z + l)/r1, and b 2 = 1 + (z l)/r 1. l denotes the half thickness of the solenoid [8]. Calculated magnetic field strengths are shown in Fig. 1. The maximum strength of the axial magnetic field varies with the radial thickness, the axial thickness, and the distance between the two solenoid magnets. The minimum field strength is not very sensitive to the radial thickness of the solenoid, while its depends heavily on the axial thickness and the distance between the two solenoid magnets. The optimized configuration of the
3 Magnetic Field Design for a 2.45-GHz ECR Ion Source J. Y. Park et al Fig. 3. Schematic view of the permanent magnets. mirror magnets is then found to be such that R 1 = 4 cm, 2l = 3 cm, and d = 20 cm. The radial field distribution is proportional to B = B 0 r N/2 1, where N is the number of cusps and r is the radial distance from the center of the device to the tip of the magnet. A high-order multicusp field for confining the plasma in the radial direction can increase the resonant volume in the radial direction. Hexapole-type multicusp magnets (N = 6) are most commonly used for radial confinement in conventional minimum-b ECR ion sources [8 10]. A stick-shaped permant magnet is generally used for the hexapole magnet. However, we have chosen a cylindrical shape due to the space limitation on our design of the whole system. The multicusp magnetic fields obtained by using the OPERA-3D simulator are plotted in Fig. 2 for three different N-pole magnets. A large number of cusps is known to create a more extended center-field region near r = 0. A schematic view of the magnetic structures is displayed in Fig. 3. Two solenoid magnets with an inner radius of 40 mm, an outer radius of 100 mm, and a thicknesses of 30 mm are placed at both ends, are at each end. A hexapole magnet consists of 6 pieces of alternating magnetized cusps. It has an inner radius of 30 mm, an outer radius of 50 mm, and a thicknesses of 150 mm. A movable ring magnet is placed to surround the hexapole magnet in the central region. The ring magnet has an Fig. 4. Calculated axial magnetic field with (solid line) and without (dashed line) a central ring magnet. The horizontal line represents the magnetic field for ECR condition. inner radius of 80 mm, an outer radius of 100 mm, and a thickness of 20 mm, which produces a flat axial magnetic field over the ECR zone for a volume-type ECRIS. Figure 4 illustrates the mirror magnetic field (B z ) strengths with and without a central ring magnet. The
4 -412- Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 55, No. 2, August 2009 Fig. 5. Magnetic field measurement system consisting of a Gauss meter and a movement system to measure the axial and the radial magnetic fields. Table 1. Magnetic design parameters of the permanentmagnet ECR ion source. Binj,ext Bmin Lmirror LECR Plasma chamber ID 0.24 T T 200 mm 50 mm 40 mm Fig. 6. The measured field distribution (triangles) is compared with the OPERA-3D simulation result (solid line). Closed circles indicate the magnetic field distribution measured with a shorter distance between solenoid mirror magnets, which give a better fit to the simulation result. solid line represents the mirror field of a volume-type ECRIS with a central ring magnet while the dashed line represents the surface mirror field without a central ring magnet. The horizontal line shows an ECR magnetic field of T at 2.45 GHz. The features of the magnetic design are given in Table 1. III. MAGNETIC FIELD MEASUREMENT We measured the magnetic field strength (Bz ) every 5 mm along the axial direction, as shown in Fig. 5. A gauss meter (F. W. BELL, Model 6010) was moved along the axial and the radial direction, by using a stepping-motor controller. The measured magnetic field distributions (symbols) are overlaid with the OPERA-3D simulation result (solid line) in Fig. 6. The measured field distribution with the simulation geometry (triangles) is found to be slightly off the simulation result, which could be due to non-uniform magnetization of the permanent magnets. Reducing the distance between the two solenoid magnets makes the field distribution fit the design better, as displayed by the circles. One should note that the ECR zone of Bmin = T is achieved over a length of 50 mm, which is the expected value. The maximum field (Bmax ) was measured to be 0.22 T, with a mirror ratio (Bmax /Bmin ) of 2.5. We also measured the uniformity of the axial magnetic field along the radial direction. Figure 7 shows the axial field distributions measured at r = 0 mm (closed circles), Fig. 7. Axial magnetic field distributions measured along the off-axis direction for small angles and at different azimuthal angles. r = 5 mm (open circles), and r = 10 mm (crosses). The axial field is found to be uniform over the radial volume to a few percent. To understand the systematic uncertainties in measuring the magnetic field strengths, we also calculated the axial magnetic field along the off-axis direction for small angles. The calculation started from the center of one end and moved towards positions 0 mm, 5 mm, 15 mm, and 20 mm away from the center of the other end, which corresponded to polar angle of 0, 1.9, 3.8, and 7.6
5 Magnetic Field Design for a 2.45-GHz ECR Ion Source J. Y. Park et al Fig. 8. Off-axis magnetic field distributions for small angles (left) and the axial field distributions for different azimuthal angles (right). degrees, respectively. The distributions for the off-axis magnetic field with small angles are shown in the bottom left of Fig. 8. A possible shift on the order of 1 mm off the axis was shown to have little effect on the magnetic field distribution. We also studied any possible change in the magnetic field distribution for different azimuthal angles. As shown in the bottom right of Fig. 7, no azimuthal angle dependence was observed. Based on the optimized magnetic structure with all permanent magnets, we constructed and tested a compact ECRIS with a 2.45 GHz microwave generator, as shown in Fig. 9. The maximum 1 kw macrowave passes through the antenna to the plasma chamber. The characteristics of the entire ECRIS will be discussed elsewhere. The permanent-magnet ECRIS will be primarily used for high-energy X-ray generation and for high-intensity heavy-ion production. If this is to be achieved, heavyions from the ECR source should be accelerated up to several hundreds of kev. A single-end van de Graaff accelerator will accelerate the beam before it is replaced with a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) and a drift tube linac (DTL). Intense 12 C beam acceleration is of great interest in studying the 12 C(α, γ) 16 O reaction by using inverse kinematics. We plan to build a superconducting 28 GHz ECRIS that will deliver high-intensity beams of highly-charged heavy ions to the RFQ and DTL accelerator section. Accelerated 7 Li ions will interact with a hydrogen gas jet at an energy of a few MeV/u, Fig. 9. ECR ion source system with a microwave generator and a beam extraction line. which will then generate high-intensity fast neutrons at forward angles, as shown in Fig. 10 [11].
6 -414- Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 55, No. 2, August 2009 Fig. 10. Schematic view of the low-energy heavy ion accelerator with the permanent-magnet 2.45 GHz ECRIS and the superconducting 28 GHz ECRIS. IV. CONCLUSION We optimized the magnetic field configuration for a 2.45 GHz ECRIS with permanent magnets. The configuration was designed to construct a compact heavy-ion accelerator for intensive studies on nucleosynthesis reactions. The optimized design had a 5-cm-long ECR zone with two radially magnetized solenoids, a hexapole magnet, and a central ring magnet. The magnetic field strengths in the axial and the radial directions were measured and were shown to be in a good agreement with the results from OPERA-3D calculations. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by a Korea Research Foundation grant funded by Korean Government (MOEHRD), Basic Research Promotion Fund (KRF C00005), and the authors are grateful to the Korea Basic Science Institute (E28100) for financial support. REFERENCES [1] R. Geller, Electron Cyclotron Resonance Ion Sources and ECR Plasmas (IOP, Bristol, 1996). [2] G. D. Alton and D. N. Smithe, Rev. Sci. Instr (1994) [3] T. Nakagawa et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, L1124 (1996). [4] G. D. Alton, Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 382, 276 (1996). [5] G. D. Alton, F. W. Meyer, Y. Liu, J. R. Beene and D. Tucker, Rev. Sci. Instr. 69 (1998)729 [6] R. Trassl et al., Physica Scripta T 73, 380 (1997). [7] R. Trassl et al., Physica Scripta T 80, 504 (1999). [8] Q. L. Peny et al., J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 268, 165 (2004). [9] Y. Liu and G. D. Alton et al., Rev. Sci. Instr. 69, 1311 (1998). [10] Y. K. Kwon and C. S. Lee, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 39, 604 (2001). [11] J. Y. Park and J. K. Ahn, Sae Mulli 54, 171 (2007).
ECR ION SOURCES : A BRIEF HISTORY AND LOOK INTO THE NEXT GENERATION
 ECR ION SOURCES : A BRIEF HISTORY AND LOOK INTO THE NEXT GENERATION T. Nakagawa, Nishina center for accelerator based science, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan Abstract In the last three
ECR ION SOURCES : A BRIEF HISTORY AND LOOK INTO THE NEXT GENERATION T. Nakagawa, Nishina center for accelerator based science, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan Abstract In the last three
Preliminary Simulation of Beam Extraction for the 28 GHz ECR Ion Source
 Preliminary Simulation of Beam Extraction for the 28 GHz ECR Ion Source Bum-Sik Park*, Yonghwan Kim and Seokjin Choi RISP, Institute for Basic Science, Daejeon 305-811, Korea The 28 GHz ECR(Electron Cyclotron
Preliminary Simulation of Beam Extraction for the 28 GHz ECR Ion Source Bum-Sik Park*, Yonghwan Kim and Seokjin Choi RISP, Institute for Basic Science, Daejeon 305-811, Korea The 28 GHz ECR(Electron Cyclotron
2.Ion sources for pulsed beam production(physics and technology) 2-1. Electron beam ion source 2-2. Laser ion source
 Intense highly charged heavy ion beam production T. NAKAGAWA (RIKEN) 1.Introduction 2.Ion sources for pulsed beam production(physics and technology) 2-1. Electron beam ion source 2-2. Laser ion source
Intense highly charged heavy ion beam production T. NAKAGAWA (RIKEN) 1.Introduction 2.Ion sources for pulsed beam production(physics and technology) 2-1. Electron beam ion source 2-2. Laser ion source
SC-ECR ion source for RIKEN RIBF
 SC-ECR ion source for RIKEN RIBF T. NAKAGAWA (RIKEN) 1. Introduction Requirements for RIKEN RIBF 2. Physics of ECR ion source Effects of the key components on the beam intensity and ECR plasma 3. RIKEN
SC-ECR ion source for RIKEN RIBF T. NAKAGAWA (RIKEN) 1. Introduction Requirements for RIKEN RIBF 2. Physics of ECR ion source Effects of the key components on the beam intensity and ECR plasma 3. RIKEN
Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators. L. Sun
 IMP Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators L. Sun Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000, Lanzhou, China IPAC 18, April 29~May 4, 2018,Vancouver, CA Preface
IMP Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators L. Sun Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000, Lanzhou, China IPAC 18, April 29~May 4, 2018,Vancouver, CA Preface
Plasma Optimization in a Multicusp Ion Source by Using a Monte Carlo Simulation
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 63, No. 7, October 2013, pp. 0 0 Plasma Optimization in a Multicusp Ion Source by Using a Monte Carlo Simulation M. Hosseinzadeh and H. Afarideh Nuclear Engineering
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 63, No. 7, October 2013, pp. 0 0 Plasma Optimization in a Multicusp Ion Source by Using a Monte Carlo Simulation M. Hosseinzadeh and H. Afarideh Nuclear Engineering
Magnetic Field Configuration Dependence of Plasma Production and Parallel Transport in a Linear Plasma Device NUMBER )
 Magnetic Field Configuration Dependence of Plasma Production and Parallel Transport in a Linear Plasma Device NUMBER ) Daichi HAMADA, Atsushi OKAMOTO, Takaaki FUJITA, Hideki ARIMOTO, Katsuya SATOU and
Magnetic Field Configuration Dependence of Plasma Production and Parallel Transport in a Linear Plasma Device NUMBER ) Daichi HAMADA, Atsushi OKAMOTO, Takaaki FUJITA, Hideki ARIMOTO, Katsuya SATOU and
INTENSE HIGHLY CHARGED HEAVY ION BEAM PRODUCTION
 INTENSE HIGHLY CHARGED HEAVY ION BEAM PRODUCTION T. Nakagawa, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan Abstract With the increase in applications of heavy ions in various fields, the production
INTENSE HIGHLY CHARGED HEAVY ION BEAM PRODUCTION T. Nakagawa, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan Abstract With the increase in applications of heavy ions in various fields, the production
Developments of the RCNP cyclotron cascade
 CYCLOTRONS 2007 The 18th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications Developments of the RCNP cyclotron cascade K. Hatanaka,, M. Fukuda, T. Saito, T. Yorita,, H. Tamura, M. Kibayashi,
CYCLOTRONS 2007 The 18th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications Developments of the RCNP cyclotron cascade K. Hatanaka,, M. Fukuda, T. Saito, T. Yorita,, H. Tamura, M. Kibayashi,
Identification of Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating (ECR) Surfaces in the UPPR-Plasma Device Operating in the Cusp and Mirror Mode.
 Identification of Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating (ECR) Surfaces in the UPPR-Plasma Device Operating in the Cusp and Mirror Mode. David Leal Escalante and Franklyn Colmenares Ochoa, Mechanical Engineering,
Identification of Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating (ECR) Surfaces in the UPPR-Plasma Device Operating in the Cusp and Mirror Mode. David Leal Escalante and Franklyn Colmenares Ochoa, Mechanical Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
Dynamics of Drift and Flute Modes in Linear Cylindrical ECR Plasma
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Dynamics of Drift and Flute Modes in Linear Cylindrical ECR Plasma Kunihiro KAMATAKI 1), Sanae I. ITOH 2), Yoshihiko NAGASHIMA 3), Shigeru INAGAKI 2), Shunjiro
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Dynamics of Drift and Flute Modes in Linear Cylindrical ECR Plasma Kunihiro KAMATAKI 1), Sanae I. ITOH 2), Yoshihiko NAGASHIMA 3), Shigeru INAGAKI 2), Shunjiro
CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS
 CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS M. Schlapp'*], R. Trassl[+', P. Hathirammi[*], R. W. McCullough"], J.B Greenwood[#] and E. Salzborn'+] ['I Argonne National
CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS M. Schlapp'*], R. Trassl[+', P. Hathirammi[*], R. W. McCullough"], J.B Greenwood[#] and E. Salzborn'+] ['I Argonne National
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators
 Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Studies of the ECR plasma in the visible light range
 Studies of the ECR plasma in the visible light range S. Biri, R. Rácz, J. Pálinkás* Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary *University of Debrecen, Dept. Exp. Physics, Hungary 1 S. Biri,
Studies of the ECR plasma in the visible light range S. Biri, R. Rácz, J. Pálinkás* Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary *University of Debrecen, Dept. Exp. Physics, Hungary 1 S. Biri,
Nano-ECRIS project: a new ECR ion source at Toyo University to produce endohedral fullerenes
 The Bio-Nano Nano-ECRIS project: a new ECR ion source at Toyo University to produce endohedral fullerenes ECRIS 2008 18th International Workshop on ECR Ion Sources Chicago, Illinois USA - September 15-18,
The Bio-Nano Nano-ECRIS project: a new ECR ion source at Toyo University to produce endohedral fullerenes ECRIS 2008 18th International Workshop on ECR Ion Sources Chicago, Illinois USA - September 15-18,
Helicon Plasma Thruster Experiment Controlling Cross-Field Diffusion within a Magnetic Nozzle
 Helicon Plasma Thruster Experiment Controlling Cross-Field Diffusion within a Magnetic Nozzle IEPC-2013-163 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University
Helicon Plasma Thruster Experiment Controlling Cross-Field Diffusion within a Magnetic Nozzle IEPC-2013-163 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND ELECTRON DENSITY SIMULATIONS AT THE ATOMKI 14.5 GHz ECRIS
 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND ELECTRON DENSITY SIMULATIONS AT THE ATOMKI 14.5 GHz ECRIS S. Biri 1#, R. Rácz 1,, Z. Perduk 1, I. Vajda 1 and J. Pálinkás 2 1 Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Hungary, H-4026
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS AND ELECTRON DENSITY SIMULATIONS AT THE ATOMKI 14.5 GHz ECRIS S. Biri 1#, R. Rácz 1,, Z. Perduk 1, I. Vajda 1 and J. Pálinkás 2 1 Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Hungary, H-4026
2. Acceleration Scheme
 2. Acceleration Scheme Accelerators in the RIBF consist of three existing accelerators and three ring cyclotrons under construction. The existing accelerators are the RIKEN Linear Accelerator (RILAC),
2. Acceleration Scheme Accelerators in the RIBF consist of three existing accelerators and three ring cyclotrons under construction. The existing accelerators are the RIKEN Linear Accelerator (RILAC),
ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE DISCHARGE AS A SOURCE FOR HYDROGEN AND DEUTERIUM IONS PRODUCTION
 ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE DISCHARGE AS A SOURCE FOR HYDROGEN AND DEUTERIUM IONS PRODUCTION Angel.J.Chacon Velasco 1 and V.D.Dougar-Jabon 1 Universidad de Pamplona, Pamplona, Colombia angelch@unipamplona.edu.co
ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE DISCHARGE AS A SOURCE FOR HYDROGEN AND DEUTERIUM IONS PRODUCTION Angel.J.Chacon Velasco 1 and V.D.Dougar-Jabon 1 Universidad de Pamplona, Pamplona, Colombia angelch@unipamplona.edu.co
Ion Beam Cocktail Development and ECR Ion Source Plasma Physics Experiments at JYFL
 Ion Beam Cocktail Development and ECR Ion Source Plasma Physics Experiments at JYFL Olli Tarvainen 11th International Conference on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology Venice, Italy 8-12 June 29 Outline JYFL
Ion Beam Cocktail Development and ECR Ion Source Plasma Physics Experiments at JYFL Olli Tarvainen 11th International Conference on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology Venice, Italy 8-12 June 29 Outline JYFL
Investigation on the spiral inflector and central region of the IsoDAR test-bench cyclotron
 Investigation on the spiral inflector and central region of the IsoDAR test-bench cyclotron Grazia D Agostino, W. Kleeven, E. Forton, V. Nuttens, S. Zaremba, L. Calabretta, A. Calanna for IsoDAR / DAEδALUS
Investigation on the spiral inflector and central region of the IsoDAR test-bench cyclotron Grazia D Agostino, W. Kleeven, E. Forton, V. Nuttens, S. Zaremba, L. Calabretta, A. Calanna for IsoDAR / DAEδALUS
Linac JUAS lecture summary
 Linac JUAS lecture summary Part1: Introduction to Linacs Linac is the acronym for Linear accelerator, a device where charged particles acquire energy moving on a linear path. There are more than 20 000
Linac JUAS lecture summary Part1: Introduction to Linacs Linac is the acronym for Linear accelerator, a device where charged particles acquire energy moving on a linear path. There are more than 20 000
HIGH INTENSITY HIGH CHARGE STATE ECR ION SOURCES*
 HIGH INTENSITY HIGH CHARGE STATE ECR ION SOURCES* D. Leitner and C.M. Lyneis, Lawrence Berkeley Natal Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, U.S.A. Abstract The next-generat heavy beam accelerators such as the proposed
HIGH INTENSITY HIGH CHARGE STATE ECR ION SOURCES* D. Leitner and C.M. Lyneis, Lawrence Berkeley Natal Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, U.S.A. Abstract The next-generat heavy beam accelerators such as the proposed
Monday, 10 th September 2018 (Diocesan Museum) OPENING SESSION: 9:00 9:30 Welcome of INFN-LNS Director: Giacomo Cuttone
 Monday, 10 th September 2018 OPENING SESSION: 9:00 9:30 Welcome of INFN-LNS Director: Giacomo Cuttone MORNING ORAL SESSION: 9:30 10:50 Chair: S. Gammino Status reports and new developments H. Zhao (23'+7')
Monday, 10 th September 2018 OPENING SESSION: 9:00 9:30 Welcome of INFN-LNS Director: Giacomo Cuttone MORNING ORAL SESSION: 9:30 10:50 Chair: S. Gammino Status reports and new developments H. Zhao (23'+7')
Huashun Zhang. Ion Sources. With 187 Figures and 26 Tables Э SCIENCE PRESS. Springer
 Huashun Zhang Ion Sources With 187 Figures and 26 Tables Э SCIENCE PRESS Springer XI Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Major Applications and Requirements 1 1.2 Performances and Research Subjects 1 1.3 Historical
Huashun Zhang Ion Sources With 187 Figures and 26 Tables Э SCIENCE PRESS Springer XI Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Major Applications and Requirements 1 1.2 Performances and Research Subjects 1 1.3 Historical
Destruction of a Magnetic Mirror-Trapped Hot Electron Ring by a shear Alfven Wave
 Destruction of a Magnetic Mirror-Trapped Hot Electron Ring by a shear Alfven Wave Y. Wang 1, W. Gekelman 1, P. Pribyl 1, D. Papadopoulos 2 1 University of California, Los Angeles 2 University of Maryland,
Destruction of a Magnetic Mirror-Trapped Hot Electron Ring by a shear Alfven Wave Y. Wang 1, W. Gekelman 1, P. Pribyl 1, D. Papadopoulos 2 1 University of California, Los Angeles 2 University of Maryland,
Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC )
 Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC ) Hayanori TAKEI, Koichiro HIRANO, Kazuyoshi TSUTSUMI 1) and Shin-ichiro MEIGO J-PARC Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency,
Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC ) Hayanori TAKEI, Koichiro HIRANO, Kazuyoshi TSUTSUMI 1) and Shin-ichiro MEIGO J-PARC Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency,
POLARIZED DEUTERONS AT THE NUCLOTRON 1
 POLARIZED DEUTERONS AT THE NUCLOTRON 1 Yu.K.Pilipenko, S.V.Afanasiev, L.S.Azhgirey, A.Yu.Isupov, V.P.Ershov, V.V.Fimushkin, L.V.Kutuzova, V.F.Peresedov, V.P.Vadeev, V.N.Zhmyrov, L.S.Zolin Joint Institute
POLARIZED DEUTERONS AT THE NUCLOTRON 1 Yu.K.Pilipenko, S.V.Afanasiev, L.S.Azhgirey, A.Yu.Isupov, V.P.Ershov, V.V.Fimushkin, L.V.Kutuzova, V.F.Peresedov, V.P.Vadeev, V.N.Zhmyrov, L.S.Zolin Joint Institute
Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1
 J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
J Fusion Energ (2010) 29:553 557 DOI 10.1007/s10894-010-9327-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Formation of High-b ECH Plasma and Inward Particle Diffusion in RT-1 H. Saitoh Z. Yoshida J. Morikawa Y. Yano T. Mizushima
Available online at Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 266 (2008)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 266 (2008) 820 828 NIM B Beam Interactions with Materials & Atoms www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Field structure
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 266 (2008) 820 828 NIM B Beam Interactions with Materials & Atoms www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Field structure
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 35. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 35 Principle components: Inlet Ion source Mass analyzer Ion transducer Pumps Signal processor Mass analyzers Quadrupole Time of Flight Double Focusing Ion
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 35 Principle components: Inlet Ion source Mass analyzer Ion transducer Pumps Signal processor Mass analyzers Quadrupole Time of Flight Double Focusing Ion
Section 4 : Accelerators
 Section 4 : Accelerators In addition to their critical role in the evolution of nuclear science, nuclear particle accelerators have become an essential tool in both industry and medicine. Table 4.1 summarizes
Section 4 : Accelerators In addition to their critical role in the evolution of nuclear science, nuclear particle accelerators have become an essential tool in both industry and medicine. Table 4.1 summarizes
Physics 663. Particle Physics Phenomenology. April 9, Physics 663, lecture 2 1
 Physics 663 Particle Physics Phenomenology April 9, 2002 Physics 663, lecture 2 1 History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Accelerators Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers
Physics 663 Particle Physics Phenomenology April 9, 2002 Physics 663, lecture 2 1 History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Accelerators Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers
CHAPTER VI RIB SOURCES
 CHAPTER VI RIB SOURCES 6.1 General criteria for target and ion-sources The ion-sources dedicated to the production of Radioactive Ion Beams (RIB) have to be highly efficient, selective (to reduce the isobar
CHAPTER VI RIB SOURCES 6.1 General criteria for target and ion-sources The ion-sources dedicated to the production of Radioactive Ion Beams (RIB) have to be highly efficient, selective (to reduce the isobar
arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 1 Feb 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 1 Feb 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 1 Feb 2008](/thumbs/94/119184832.jpg) Field structure and electron life times in the MEFISTO Electron Cyclotron Resonance Ion Source arxiv:0802.0092v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 1 Feb 2008 Abstract M. Bodendorfer 1,2, K. Altwegg 2, H. Shea 1, P. Wurz
Field structure and electron life times in the MEFISTO Electron Cyclotron Resonance Ion Source arxiv:0802.0092v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 1 Feb 2008 Abstract M. Bodendorfer 1,2, K. Altwegg 2, H. Shea 1, P. Wurz
ADVANCED ECR SOURCES FOR HIGHLY CHARGED IONS
 ADVANCED ECR SOURCES FOR HIGHLY CHARGED IONS S. Gammino, G. Ciavola, L. Celona, L. Andò Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare-Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, Via S. Sofia 44, 95123 Catania, ITALY D. Hitz,
ADVANCED ECR SOURCES FOR HIGHLY CHARGED IONS S. Gammino, G. Ciavola, L. Celona, L. Andò Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare-Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, Via S. Sofia 44, 95123 Catania, ITALY D. Hitz,
Factors Enhancing Production of Multicharged Ion Sources and Their Applications
 Science and Technology 2012, 2(4): 98-108 DOI: 10.5923/j.scit.20120204.07 Factors Enhancing Production of Multicharged Ion Sources and Their Applications M.M. Abdelrahman Accelerators & Ion Sources Department,
Science and Technology 2012, 2(4): 98-108 DOI: 10.5923/j.scit.20120204.07 Factors Enhancing Production of Multicharged Ion Sources and Their Applications M.M. Abdelrahman Accelerators & Ion Sources Department,
A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU
 IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU D. P. Sanderson, NSCL-MSU, 1 Cyclotron Lab, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 1. INTRODUCTION The Rare Isotope Accelerator
IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU D. P. Sanderson, NSCL-MSU, 1 Cyclotron Lab, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 1. INTRODUCTION The Rare Isotope Accelerator
Design of a Sector Magnet for High Temperature Superconducting Injector Cyclotron
 MOA2C01 13th Intl. Conf. on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology Sep. 7, 2015 Design of a Sector Magnet for High Temperature Superconducting Injector Cyclotron Keita Kamakura Research Center for Nuclear Physics
MOA2C01 13th Intl. Conf. on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology Sep. 7, 2015 Design of a Sector Magnet for High Temperature Superconducting Injector Cyclotron Keita Kamakura Research Center for Nuclear Physics
IEPC M. Bodendorfer 1, K. Altwegg 2 and P. Wurz 3 University of Bern, 3012 Bern, Switzerland. and
 Future thruster application: combination of numerical simulation of ECR zone and plasma X-ray Bremsstrahlung measurement of the SWISSCASE ECR ion source IEPC-2009-234 Presented at the 31st International
Future thruster application: combination of numerical simulation of ECR zone and plasma X-ray Bremsstrahlung measurement of the SWISSCASE ECR ion source IEPC-2009-234 Presented at the 31st International
1.4 The Tools of the Trade!
 1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
Regenerative Soot-II: Emission o f carbon clusters from sooting plasma
 Regenerative Soot-II: Emission o f carbon clusters from sooting plasma Shoaib Ahmad National Centre for Physics, Quaid-i-Azam University Campus, Shahdara Valley, Islamabad, 44000, Pakistan Email: sahmad.ncp@gmail.com
Regenerative Soot-II: Emission o f carbon clusters from sooting plasma Shoaib Ahmad National Centre for Physics, Quaid-i-Azam University Campus, Shahdara Valley, Islamabad, 44000, Pakistan Email: sahmad.ncp@gmail.com
Bifurcation-Like Behavior of Electrostatic Potential in LHD )
 Bifurcation-Like Behavior of Electrostatic Potential in LHD ) Akihiro SHIMIZU, Takeshi IDO, Masaki NISHIURA, Ryohei MAKINO 1), Masayuki YOKOYAMA, Hiromi TAKAHASHI, Hiroe IGAMI, Yasuo YOSHIMURA, Shin KUBO,
Bifurcation-Like Behavior of Electrostatic Potential in LHD ) Akihiro SHIMIZU, Takeshi IDO, Masaki NISHIURA, Ryohei MAKINO 1), Masayuki YOKOYAMA, Hiromi TAKAHASHI, Hiroe IGAMI, Yasuo YOSHIMURA, Shin KUBO,
Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
 THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
D- Charge Exchange Ionizer for the JINR Polarized Ion Source POLARIS
 D- Charge Exchange Ionizer for the JINR Polarized Ion Source POLARIS V.P. Ershov, V.V.Fimushkin, G.I.Gai, L.V.Kutuzova, Yu.K.Pilipenko, V.P.Vadeev, A.I.Valevich Λ and A.S. Belov Λ Joint Institute for Nuclear
D- Charge Exchange Ionizer for the JINR Polarized Ion Source POLARIS V.P. Ershov, V.V.Fimushkin, G.I.Gai, L.V.Kutuzova, Yu.K.Pilipenko, V.P.Vadeev, A.I.Valevich Λ and A.S. Belov Λ Joint Institute for Nuclear
Fluctuation Suppression during the ECH Induced Potential Formation in the Tandem Mirror GAMMA 10
 EXC/P8-2 Fluctuation Suppression during the ECH Induced Potential Formation in the Tandem Mirror GAMMA M. Yoshikawa ), Y. Miyata ), M. Mizuguchi ), Y. Oono ), F. Yaguchi ), M. Ichimura ), T. Imai ), T.
EXC/P8-2 Fluctuation Suppression during the ECH Induced Potential Formation in the Tandem Mirror GAMMA M. Yoshikawa ), Y. Miyata ), M. Mizuguchi ), Y. Oono ), F. Yaguchi ), M. Ichimura ), T. Imai ), T.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title A high transmission analyzing magnet for intense high charge state beams Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/25g1x3b4
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title A high transmission analyzing magnet for intense high charge state beams Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/25g1x3b4
Since the beam from the JNC linac is a very high current, low energy beam, energy loss induced in the material irradiated by the beam becomes very lar
 Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on EGS, 8.-12. August 2000, Tsukuba, Japan KEK Proceedings 200-20, pp.255-263 Beam Dump for High Current Electron Beam at JNC H. Takei and Y. Takeda 1 Japan
Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on EGS, 8.-12. August 2000, Tsukuba, Japan KEK Proceedings 200-20, pp.255-263 Beam Dump for High Current Electron Beam at JNC H. Takei and Y. Takeda 1 Japan
CYCLOTRON DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM AT JYVÄSKYLÄ
 CYCLOTRON DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM AT JYVÄSKYLÄ P. Heikkinen, E. Liukkonen, Department of Physics, University of Jyväskylä, Finland Abstract The Jyväskylä K130 cyclotron has been modified to allow also negative
CYCLOTRON DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM AT JYVÄSKYLÄ P. Heikkinen, E. Liukkonen, Department of Physics, University of Jyväskylä, Finland Abstract The Jyväskylä K130 cyclotron has been modified to allow also negative
Introduction to accelerators for teachers (Korean program) Mariusz Sapiński CERN, Beams Department August 9 th, 2012
 Introduction to accelerators for teachers (Korean program) Mariusz Sapiński (mariusz.sapinski@cern.ch) CERN, Beams Department August 9 th, 2012 Definition (Britannica) Particle accelerator: A device producing
Introduction to accelerators for teachers (Korean program) Mariusz Sapiński (mariusz.sapinski@cern.ch) CERN, Beams Department August 9 th, 2012 Definition (Britannica) Particle accelerator: A device producing
Additional Heating Experiments of FRC Plasma
 Additional Heating Experiments of FRC Plasma S. Okada, T. Asai, F. Kodera, K. Kitano, T. Suzuki, K. Yamanaka, T. Kanki, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Okubo, S. Sugimoto, S. Ohi, S. Goto, Plasma Physics
Additional Heating Experiments of FRC Plasma S. Okada, T. Asai, F. Kodera, K. Kitano, T. Suzuki, K. Yamanaka, T. Kanki, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Okubo, S. Sugimoto, S. Ohi, S. Goto, Plasma Physics
Physical Science Research Activities of Korea Basic Science Institute
 institutes in asia PaCiFiC BULLETIN Physical Science Research Activities of Korea Basic Science Institute JouhAhn Lee head ADVAnCeD nano-surface ReSeARCh group, KBSI Fig. 1: Overview of Korea Basic Science
institutes in asia PaCiFiC BULLETIN Physical Science Research Activities of Korea Basic Science Institute JouhAhn Lee head ADVAnCeD nano-surface ReSeARCh group, KBSI Fig. 1: Overview of Korea Basic Science
Physics 610. Adv Particle Physics. April 7, 2014
 Physics 610 Adv Particle Physics April 7, 2014 Accelerators History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers Cyclotron Betatron Linear Induction
Physics 610 Adv Particle Physics April 7, 2014 Accelerators History Two Principles Electrostatic Cockcroft-Walton Van de Graaff and tandem Van de Graaff Transformers Cyclotron Betatron Linear Induction
Direct-Current Accelerator
 Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
Structural Optimization of the AISHa Ion Source
 Structural Optimization of the AISHa Ion Source F. Noto 1*, M. Piscopo 1, L. Celona 1, D. Cittadino 1, S. Gammino 1, G. Cuttone 1, G. Gallo 1, G. Schillaci 1, C. Campisano 2, L. Lo Nigro 3, G. Costa 3,
Structural Optimization of the AISHa Ion Source F. Noto 1*, M. Piscopo 1, L. Celona 1, D. Cittadino 1, S. Gammino 1, G. Cuttone 1, G. Gallo 1, G. Schillaci 1, C. Campisano 2, L. Lo Nigro 3, G. Costa 3,
CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON
 CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON OBJECTIVE: To measure the ratio of the charge of an electron to its mass. METHOD: A stream of electrons is accelerated by having them "fall" through a measured potential
CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON OBJECTIVE: To measure the ratio of the charge of an electron to its mass. METHOD: A stream of electrons is accelerated by having them "fall" through a measured potential
Acceleration of Heavy Ions generated by ECR and EBIS
 Acceleration of Heavy Ions generated by ECR and EBIS R.Becker, Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt, Germany O. Kester, NSCL, MSU, USA OUTLINE Ion production in ECR and EBIS is governed by the same collision
Acceleration of Heavy Ions generated by ECR and EBIS R.Becker, Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt, Germany O. Kester, NSCL, MSU, USA OUTLINE Ion production in ECR and EBIS is governed by the same collision
GANIL STATUS REPORT. B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, Caen Cedex, France.
 GANIL STATUS REPORT B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, 4076 Caen Cedex, France Abstract The GANIL-Spiral facility (Caen, France) is dedicated to the acceleration
GANIL STATUS REPORT B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, 4076 Caen Cedex, France Abstract The GANIL-Spiral facility (Caen, France) is dedicated to the acceleration
Radiation Protection At Synchrotron Radiation Facilities
 3 rd ILSF Advanced School on Synchrotron Radiation and Its Applications September 14-16, 2013 Radiation Protection At Synchrotron Radiation Facilities Ehsan Salimi Shielding and Radiation Safety Group
3 rd ILSF Advanced School on Synchrotron Radiation and Its Applications September 14-16, 2013 Radiation Protection At Synchrotron Radiation Facilities Ehsan Salimi Shielding and Radiation Safety Group
Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J.
 University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
3-D MEASUREMENT OF THE NSCL POSITION-SENSITIVE GAMMA RAY DETECTOR ARRAY
 3-D MEASUREMENT OF THE NSCL POSITION-SENSITIVE GAMMA RAY DETECTOR ARRAY D. P. Sanderson and W. F. Mueller The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI,
3-D MEASUREMENT OF THE NSCL POSITION-SENSITIVE GAMMA RAY DETECTOR ARRAY D. P. Sanderson and W. F. Mueller The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI,
Simulation of Electron Behavior in PIG Ion Source for 9 MeV Cyclotron X. J. Mu 1, M. Ghergherehchi 1a, Y.H. Yeon 1, J.S. Chai 1
 Simulation of Electron Behavior in PIG Ion Source for 9 MeV Cyclotron X. J. Mu 1, M. Ghergherehchi 1a, Y.H. Yeon 1, J.S. Chai 1 1 College of the Electric and Electrical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University,
Simulation of Electron Behavior in PIG Ion Source for 9 MeV Cyclotron X. J. Mu 1, M. Ghergherehchi 1a, Y.H. Yeon 1, J.S. Chai 1 1 College of the Electric and Electrical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University,
Neutralized Drift Compression
 Neutralized Drift Compression D. R. Welch, D. V. Rose Mission Research Corporation Albuquerque, NM 87110 S. S. Yu Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley, CA C. L. Olson Sandia National Laboratories
Neutralized Drift Compression D. R. Welch, D. V. Rose Mission Research Corporation Albuquerque, NM 87110 S. S. Yu Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley, CA C. L. Olson Sandia National Laboratories
ANURIB Advanced National facility for Unstable and Rare Ion Beams
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 505 515 ANURIB Advanced National facility for Unstable and Rare Ion Beams ARUP BANDYOPADHYAY, V NAIK, S DECHOUDHURY,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 505 515 ANURIB Advanced National facility for Unstable and Rare Ion Beams ARUP BANDYOPADHYAY, V NAIK, S DECHOUDHURY,
Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions
 V. P. Ovsyannikov a Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions Hochschulstr. 13, 01069, Dresden, Germany It is proposed to produce the highly charged ions in the local ion
V. P. Ovsyannikov a Main Magnetic Focus Ion Trap, new tool for trapping of highly charged ions Hochschulstr. 13, 01069, Dresden, Germany It is proposed to produce the highly charged ions in the local ion
A Low Energy Beam Transport Design with high SCC for TAC Proton Accelerator
 A Low Energy Beam Transport Design with high SCC for TAC Proton Accelerator * A. Caliskan 1, H. F. Kisoglu 2, S. Sultansoy 3,4, M. Yilmaz 5 1 Department of Engineering Physics, Gumushane University, Gumushane,
A Low Energy Beam Transport Design with high SCC for TAC Proton Accelerator * A. Caliskan 1, H. F. Kisoglu 2, S. Sultansoy 3,4, M. Yilmaz 5 1 Department of Engineering Physics, Gumushane University, Gumushane,
Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia B.Yu. Sharkov*, N.N. Alexeev, M.D. Churazov, A.A. Golubev, D.G. Koshkarev, P.R. Zenkevich
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia B.Yu. Sharkov*, N.N. Alexeev, M.D. Churazov, A.A. Golubev, D.G. Koshkarev, P.R. Zenkevich
solenoid and time projection chamber for neutron lifetime measurement LINA
 solenoid and time projection chamber for neutron lifetime measurement LINA H. Otono a arxiv:1603.06572v1 [physics.ins-det] 21 Mar 2016 a Research Centre for Advanced Particle Physics, Kyushu University,
solenoid and time projection chamber for neutron lifetime measurement LINA H. Otono a arxiv:1603.06572v1 [physics.ins-det] 21 Mar 2016 a Research Centre for Advanced Particle Physics, Kyushu University,
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research
 1) JONG WOON KIM AND YOUNG-OUK LEE: DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE KAERI ntof FACILITY Journal of Radiation Protection and Research pissn 2508-1888 eissn 2466-2461 http://dx.doi.org/10.14407/jrpr.2016.41.2.141
1) JONG WOON KIM AND YOUNG-OUK LEE: DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE KAERI ntof FACILITY Journal of Radiation Protection and Research pissn 2508-1888 eissn 2466-2461 http://dx.doi.org/10.14407/jrpr.2016.41.2.141
MODELING OF AN ECR SOURCE FOR MATERIALS PROCESSING USING A TWO DIMENSIONAL HYBRID PLASMA EQUIPMENT MODEL. Ron L. Kinder and Mark J.
 TECHCON 98 Las Vegas, Nevada September 9-11, 1998 MODELING OF AN ECR SOURCE FOR MATERIALS PROCESSING USING A TWO DIMENSIONAL HYBRID PLASMA EQUIPMENT MODEL Ron L. Kinder and Mark J. Kushner Department of
TECHCON 98 Las Vegas, Nevada September 9-11, 1998 MODELING OF AN ECR SOURCE FOR MATERIALS PROCESSING USING A TWO DIMENSIONAL HYBRID PLASMA EQUIPMENT MODEL Ron L. Kinder and Mark J. Kushner Department of
Progress in the Study of Plasma Heating, Stability, and Confinement on HANBIT Mirror Device
 1 EX/9-6Ra Progress in the Study of Plasma Heating, Stability, and Confinement on HANBIT Mirror Device M. Kwon, J.G. Bak, K.K. Choh, J.H. Choi, J.W. Choi, A.C. England, J.S. Hong, H.G. Jhang, J.Y. Kim,
1 EX/9-6Ra Progress in the Study of Plasma Heating, Stability, and Confinement on HANBIT Mirror Device M. Kwon, J.G. Bak, K.K. Choh, J.H. Choi, J.W. Choi, A.C. England, J.S. Hong, H.G. Jhang, J.Y. Kim,
TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics. P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University
 TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University Outline of the talk Low energy test of Standard Model T =2 Superallowed transition Facility T-REX
TAMU-TRAP facility for Weak Interaction Physics P.D. Shidling Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University Outline of the talk Low energy test of Standard Model T =2 Superallowed transition Facility T-REX
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
This thesis work was carried out in at the Department of Physics in the University of Jyväskylä.
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ RESEARCH REPORT No. 6/2006 MODIFIED MULTIPOLE STRUCTURE FOR ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE ION SOURCES BY PEKKA SUOMINEN Academic Dissertation for the Degree
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ RESEARCH REPORT No. 6/2006 MODIFIED MULTIPOLE STRUCTURE FOR ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE ION SOURCES BY PEKKA SUOMINEN Academic Dissertation for the Degree
INTRODUCTION EBIS. Proceedings of HB2012, Beijing, China
 INTENSE HIGH CHARGE STATE HEAVY ION BEAM PRODUCTION FOR THE ADVANCED ACCELERATORS # L. Sun, Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 509 Nanchang Rd., Lanzhou 730000, China Abstract Modern advanced heavy ion
INTENSE HIGH CHARGE STATE HEAVY ION BEAM PRODUCTION FOR THE ADVANCED ACCELERATORS # L. Sun, Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 509 Nanchang Rd., Lanzhou 730000, China Abstract Modern advanced heavy ion
Introduction to Particle Accelerators & CESR-C
 Introduction to Particle Accelerators & CESR-C Michael Billing June 7, 2006 What Are the Uses for Particle Accelerators? Medical Accelerators Create isotopes tracers for Medical Diagnostics & Biological
Introduction to Particle Accelerators & CESR-C Michael Billing June 7, 2006 What Are the Uses for Particle Accelerators? Medical Accelerators Create isotopes tracers for Medical Diagnostics & Biological
PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses
 Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities
 Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
Beam diagnostics: Alignment of the beam to prevent for activation. Accelerator physics: using these sensitive particle detectors.
 Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
Development of the UNILAC towards a Megawatt Beam Injector
 Development of the UNILAC towards a Megawatt Beam Injector W. Barth, GSI - Darmstadt 1. GSI Accelerator Facility Injector for FAIR 2. Heavy Ion Linear Accelerator UNILAC 3. SIS 18 Intensity Upgrade Program
Development of the UNILAC towards a Megawatt Beam Injector W. Barth, GSI - Darmstadt 1. GSI Accelerator Facility Injector for FAIR 2. Heavy Ion Linear Accelerator UNILAC 3. SIS 18 Intensity Upgrade Program
Microtron for Smog Particles Photo Ionization
 Abstract Microtron for Smog Particles Photo Ionization S. N. Dolya Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Joliot - Curie 6, Dubna, Russia, 141980 The article discusses a possibility of removing smog particles
Abstract Microtron for Smog Particles Photo Ionization S. N. Dolya Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Joliot - Curie 6, Dubna, Russia, 141980 The article discusses a possibility of removing smog particles
PLASMA CONFINEMENT IN THE GAMMA 10 TANDEM MIRROR
 PLASMA CONFINEMENT IN THE GAMMA TANDEM MIRROR K.YATSU, L.G.BRUSKIN, T.CHO, M.HAMADA, M.HIRATA, H.HOJO, M.ICHIMURA, K.ISHII, A.ITAKURA, I.KATANUMA, Y.KIWAMOTO, J.KOHAGURA, S.KUBOTA, A.MASE, Y.NAKASHIMA,
PLASMA CONFINEMENT IN THE GAMMA TANDEM MIRROR K.YATSU, L.G.BRUSKIN, T.CHO, M.HAMADA, M.HIRATA, H.HOJO, M.ICHIMURA, K.ISHII, A.ITAKURA, I.KATANUMA, Y.KIWAMOTO, J.KOHAGURA, S.KUBOTA, A.MASE, Y.NAKASHIMA,
Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter)
 Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields
 Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
llllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllillli
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN LIBRARIES, GENEVA llllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllillli CERN-PS-94-13 CERN/ 94*3 H, / ji GY ELECTRON AND ION CONFINEMENT CONDITIONS IN THE OPEN
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN LIBRARIES, GENEVA llllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllillli CERN-PS-94-13 CERN/ 94*3 H, / ji GY ELECTRON AND ION CONFINEMENT CONDITIONS IN THE OPEN
STUDY ON SPACE CHARGE COMPENSATION OF LOW ENERGY HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAM IN PEKING UNIVERSITY*
 STUDY ON SPACE CHARGE COMPENSATION OF LOW ENERGY HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAM IN PEKING UNIVERSITY* S. X. Peng 1,, A. L. Zhang 1, 2, H. T. Ren 1, T. Zhang 1, J. F. Zhang 1, Y. Xu 1, J. M. Wen 1, W. B. Wu 1,
STUDY ON SPACE CHARGE COMPENSATION OF LOW ENERGY HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAM IN PEKING UNIVERSITY* S. X. Peng 1,, A. L. Zhang 1, 2, H. T. Ren 1, T. Zhang 1, J. F. Zhang 1, Y. Xu 1, J. M. Wen 1, W. B. Wu 1,
University of Groningen. Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh
 University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
arxiv: v2 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v2 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Jun 2017 arxiv: v2 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Jun 2017](/thumbs/96/126775970.jpg) Pulsed Beam Tests at the SANAEM RFQ Beamline arxiv:1705.06462v2 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Jun 2017 G Turemen 1,2, Y Akgun 1, A Alacakir 1, I Kilic 1, B Yasatekin 1,2, E Ergenlik 3, S Ogur 3, E Sunar 3, V Yildiz
Pulsed Beam Tests at the SANAEM RFQ Beamline arxiv:1705.06462v2 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Jun 2017 G Turemen 1,2, Y Akgun 1, A Alacakir 1, I Kilic 1, B Yasatekin 1,2, E Ergenlik 3, S Ogur 3, E Sunar 3, V Yildiz
MAGNETIC PROBLEMS. (d) Sketch B as a function of d clearly showing the value for maximum value of B.
 PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU
 HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU J. W. Xia, Y. F. Wang, Y. N. Rao, Y. J. Yuan, M. T. Song, W. Z. Zhang, P. Yuan, W. Gu, X. T. Yang, X. D. Yang, S. L. Liu, H.W.Zhao, J.Y.Tang, W. L. Zhan, B.
HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU J. W. Xia, Y. F. Wang, Y. N. Rao, Y. J. Yuan, M. T. Song, W. Z. Zhang, P. Yuan, W. Gu, X. T. Yang, X. D. Yang, S. L. Liu, H.W.Zhao, J.Y.Tang, W. L. Zhan, B.
STUDIES OF ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE ION SOURCE PLASMA PHYSICS
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ RESEARCH REPORT No. 8/2005 STUDIES OF ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE ION SOURCE PLASMA PHYSICS BY OLLI TARVAINEN Academic Disser tation for the Degree of Doctor
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ RESEARCH REPORT No. 8/2005 STUDIES OF ELECTRON CYCLOTRON RESONANCE ION SOURCE PLASMA PHYSICS BY OLLI TARVAINEN Academic Disser tation for the Degree of Doctor
RCNP cyclotron facility
 11th International Conference on HEAVY ION ACCELERATOR TECHNOLOGY RCNP cyclotron facility K. Hatanaka hatanaka@rcnp.osaka-u.ac.jp Research Center for Nuclear Physics Osaka University HIAT09 TU9 June 9,
11th International Conference on HEAVY ION ACCELERATOR TECHNOLOGY RCNP cyclotron facility K. Hatanaka hatanaka@rcnp.osaka-u.ac.jp Research Center for Nuclear Physics Osaka University HIAT09 TU9 June 9,
Introduction to accelerators for boron neutron capture therapy
 Review Article Page 1 of 13 Introduction to accelerators for boron neutron capture therapy Fujio Naito High energy accelerator research organization (KEK), Tsukuba, Japan Correspondence to: Fujio Naito.
Review Article Page 1 of 13 Introduction to accelerators for boron neutron capture therapy Fujio Naito High energy accelerator research organization (KEK), Tsukuba, Japan Correspondence to: Fujio Naito.
Performance Studies of the Vibration Wire Monitor on the Test Stand with Low Energy Electron Beam
 Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Science at J-PARC Unlocking the Mysteries of Life, Matter and the Universe http://dx.doi.org/10.7566/jpscp.8.012024 Performance Studies of the Vibration Wire Monitor on the Test Stand
Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Science at J-PARC Unlocking the Mysteries of Life, Matter and the Universe http://dx.doi.org/10.7566/jpscp.8.012024 Performance Studies of the Vibration Wire Monitor on the Test Stand
The Q Machine. 60 cm 198 cm Oven. Plasma. 6 cm 30 cm. 50 cm. Axial. Probe. PUMP End Plate Magnet Coil. Filament Cathode. Radial. Hot Plate.
 1 The Q Machine 60 cm 198 cm Oven 50 cm Axial Probe Plasma 6 cm 30 cm PUMP End Plate Magnet Coil Radial Probe Hot Plate Filament Cathode 2 THE Q MACHINE 1. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF A Q MACHINE A Q machine
1 The Q Machine 60 cm 198 cm Oven 50 cm Axial Probe Plasma 6 cm 30 cm PUMP End Plate Magnet Coil Radial Probe Hot Plate Filament Cathode 2 THE Q MACHINE 1. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF A Q MACHINE A Q machine
Lecture 1: Applications of High Power Electromagnetic Systems
 Lecture 1: Applications of High Power Electromagnetic Systems Low Power (not covered in this class) + EM sensors + Radio communications and broadcast + Cellular communications High Power + High power microwaves
Lecture 1: Applications of High Power Electromagnetic Systems Low Power (not covered in this class) + EM sensors + Radio communications and broadcast + Cellular communications High Power + High power microwaves
Present status of RIBF accelerators at RIKEN
 Present status of RIBF accelerators at RIKEN 1) Introduction to RIBF ( - 2007) 2) Improvements & Present status (2008-2010) 3) Recent results from RIBF (2008-2010) 4) Further developments & Plans (2009-2010)
Present status of RIBF accelerators at RIKEN 1) Introduction to RIBF ( - 2007) 2) Improvements & Present status (2008-2010) 3) Recent results from RIBF (2008-2010) 4) Further developments & Plans (2009-2010)
