arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 23 Jul 1996
|
|
|
- Emerald Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The energy dependence of flow in Ni induced collisions from 400 to 1970A MeV J. Chance (1), S. Albergo (2), F. Bieser (4), F. P. Brady (1), Z. Caccia (2), D. Cebra (1,4), A. D. Chacon (6), Y. Choi (5), S. Costa (2), J. B. Elliott (5), M. Gilkes (3), J. A. Hauger (5), A. S. Hirsch (5), E. L. Hjort (5), A. Insolia (2), M. Justice (3), D. Keane (3), J. C. Kintner (1), arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 23 Jul 1996 M. A. Lisa (4), H. S. Matis (4), M. McMahan (4), C. McParland (4), D. L. Olson (4), M. D. Partlan (1), N. T. Porile (5), R. Potenza (2), G. Rai (4), J. Rasmussen (4), H. G. Ritter (4), J. Romanski (2), J. L. Romero (1), G. V. Russo (2), R. Scharenberg (5), A. Scott (3), Y. Shao (3), B. Srivastava (5), T. J. M. Symons (4), M. Tincknell (5), C. Tuvé (2), S. Wang (3), P. Warren (5), H. H. Wieman (4), T. Wienold (4), K. Wolf (6) (1) University of California, Davis, California (2) Universitá di Catania & INFN-Sezione di Catania, Catania, Italy, (3) Kent State University, Kent, Ohio (4) Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California (5) Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana (6) Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas (The EOS Collaboration) Abstract We study the energy dependence of collective (hydrodynamic-like) nuclear matter flow in A MeV Ni+Au and A MeV Ni+Cu reactions. The flow increases with energy, reaches a maximum, and then gradually decreases at higher energies. A way of comparing the energy dependence of flow values for different projectile-target mass combinations is introduced, which demonstrates a common scaling behaviour among flow values from dif- 1
2 fererent systems. PACS numbers: Pq, Ld Typeset using REVTEX 2
3 The study of nuclear matter over a wide range of temperatures and densities and the determination of the Equation of State (EOS) of nuclear matter continue to be of considerable interest [1]. Lacking the possibility of comprehensive studies of nuclear matter in bulk (as in neutron stars), one resorts to the study of transient, finite systems provided by nucleus-nucleus collisions (over a wide range of energy). It is now clear that the extraction of EOS information from nuclear collisions requires a comprehensive set of measurements of collision observables, which can be compared to realistic microscopic calculations involving the nuclear matter variables. At GeV per nucleon energies, where the collision velocity exceeds that of nuclear sound, the collisions produce densities several times higher than ground state densities and exhibit compression-induced flow of nuclear matter [1]. However, it was not until the analysis of events from the 4π Plastic Ball/Wall [2] and Streamer Chamber [3] detector systems at the Bevalac that the matter flow characteristics could be studied and quantified for a range of systems and energies. More recently, at the Bevalac at LBNL, the EOS Collaboration carried out a comprehensive set of measurements over a wide range of energies, and projectiletarget combinations [4]. Similar studies are underway at GSI in Darmstadt and, with lighter projectiles, by the DIOGENE Collaboration at Saclay [5]. EOS Collaboration data has been used to study flow for the Au+Au system at lab energies ranging from 250 to 1150A MeV [6]. Particle flow for protons, deuterons and alpha particles has been determined, using the transverse momentum method [7]. The flow is found to increase with particle mass A, and with energy up to projectile energies of 1150A MeV where it tends to level out at values close to the Plastic Ball data [8]. Here we present analyses of recent EOS Ni + Au data with energies between 400 and 1970A MeV and EOS Ni+Cu data at energies of 1000, 1500 and 1970A MeV. This study with the Ni beam allows the use of higher energy per nucleon projectiles, and so extends the energy of our flow measurements beyond the 1150A MeV limit of the EOS Au + Au data [6]. We also present a comparison of the flow values with predictions of a BUU model from Bauer et al. [9], and introduce a scaled flow which allows the comparison of flow data from a 3
4 variety of projectile-target mass systems. In total, the data (supported by the calculations) provide the strongest evidence yet that, with increasing energy, flow reaches a maximum near 1000A MeV, and then declines. The EOS Collaboration detector systems have been described in Refs. 4 and 6. The data presented here were obtained using the EOS Time Projection Chamber [10], situated in the magnetic field of the HISS Magnet. The TPC provides fairly unambiguous particle identification, as well as a measurement of momentum, for particles of charge up to Z = 6. Particle ID is ambiguous for rigidities above 2.4 GeV/c. Thus, some misidentification will occur and its effect is represented in the uncertainties. The target is just upstream from the TPC and this results in a large and nearly seamless acceptance. Laser beam calibrations provide a check of the corrections for B field inhomogeneities, and measurements of drift velocity. Simulations have been performed to study the geometrical acceptance of the detector and to provide acceptance corrections. In the present experiment, the thickness of the Au target was 730 mg/cm 2 corresponding to about 1% interaction probability. The trigger was provided by a scintillator just downstream from the target. The MUSIC (Multiple Sampling Ionization Chamber) detector, downstream from the TPC, provided an on-line check on the threshold charge of the heaviest fragment allowed by the trigger. For this analysis, data for a wide range of impact parameters were taken. We used charged particle multiplicity as a measure of the collision centrality, and have adopted the Plastic Ball [8] convention by dividing the events into five multiplicity bins with bin M1 corresponding to the most peripheral and bin M5 having the most central events. For the Ni+Au 400, 600, 1000 and 1970A MeV the numbers of events analyzed were 32k, 26k, 33k and 26k respectively. The Ni + Cu 1000, 1500 and 1970 A MeV analyses were done on recently analyzed data sets of respectively, 35k, 19k and 48k events. For each event, the reaction plane was determined using the transverse momenta of the particles, as proposed by Danielewicz and Odyniec [7]. The plane is determined by the vector Q = iw i p t i and the incident beam direction. Here p t i is the transverse momentum of particle i, and w i is a weighting factor defined to maximize the contribution of 4
5 high rapidity particles to the Q vector determination. Normally, for symmetric collisions of equal A, w i is taken to increase linearly with rapidity up to w i = ±1 at y cm = δ and to be constant at ±1 for y cm δ. Using the sub-event method of Ref. 7 we found the optimal reaction plane determination to be made with δ 0.7. We also found that varying δ by 0.1 results in only a 1% change in the flow values. For the asymmetric 58 Ni Au, the nucleon-nucleon and nucleus-nucleus center of mass frames are different. There is therefore some ambiguity as to which reference frame to use for determining the weighting factors. We went through an iterative procedure as follows: We start out in the nucleus-nucleus cm frame, do the Q weighting in that frame, and then project the p t of each particle onto the reaction plane. We refer to this projection as p x for each particle in the event. Plotting the p x /A (henceforth referred to as p x ) vs. rapidity for all events at a given energy then yields the typical S-shaped curves. These S curves do not cross the p x = 0 axis at y c = 0 where y c here refers to the rapidity in the chosen frame, in this case the nucleus-nucleus cm frame. We next look at p x vs. lab rapidity and note where the curve crosses the p x = 0 axis. This crossing rapidity defines the velocity of the new frame in which we do the next weighting. A couple of iterations yields a stable crossing value of y. Finally, we need to correct p x for the fact that we project onto an imperfectly known reaction plane. For this we use the sub-event method of Ref. 7. These corrections increase the p x values from 10% (for the more central Ni+Au events) to 20% (for the more peripheral Ni+Cu events). Figure 1 shows the S-shaped plots of p x vs. y for the four Ni + Au systems and for multiplicity bin M4. Here, for the moment, we include only protons, for which we have unambiguous particle identification. Following the Plastic Ball analysis we define the flow, F, as the slope (d p x /dy ) px=0 at the zero crossing (generally around y = 0.35). The slope is calculated from a linear fit to the data. Similar F values are obtained using a cubic fit. The imperfect asymmetry of the S-curve with respect to the p x = 0 axis is due to both the lower acceptance in the lower rapidities, as well as reflecting transverse momentum conservation in the asymmetric collision: The larger number of (mainly target) particles (both spectator 5
6 and participant) at low rapidity, is balanced at higher rapidity, by fewer particles having larger average p t values. From the geometrical acceptance studies we found that acceptance corrections on the flow values are on the order of 5% for the lower energy Ni + Au 400A and 600A MeV systems. Flow value corrections above 600A MeV are negligible since the detector has full acceptance for the region where the fitting is performed. In Figure 2 the extracted values of the slope, F (for protons), at y (p x = 0) are plotted vs. projectile kinetic energy per nucleon and compared to the flow predicted by a basic BUU model [9]. This model does not include composite particle formation so the comparison is with the experimental proton F values. With the inclusion of bound protons (from d, t, etc.) the trend of the F values, as a function of energy, is similar. It should be noted that the BUU model used here does not include momentum dependent interactions. It is expected that adding these will increase the predicted BUU flow values, bringing them to better agreement with the data. The hard EOS BUU flow values appear to reach their maximum at a lower energy than the soft EOS. In this aspect the hard EOS BUU is closer to the energy dependence of the data. However, neither case gives quantitatively the energy dependence, and work on this aspect continues [11]. The main point here is that the BUU model does predict a rise and fall of flow. The energy dependence in Fig. 2 is consistent with the EOS Au+Au proton flow data of Partlan et al. [6] and the Plastic Ball data [8] which show the flow beginning to plateau above 800A MeV. We have studied other flow observables: the maximum value of p x, the maximum value of F, regardless of the corresponding y value, and the sum p x, summed over all values for y > y ( p x = 0). All of these observables give a flow energy dependence consistent with that for F. We have also analyzed the data using the reaction plane independent flow signal quantity [12] proposed by the FOPI group. In addition we have examined the flow angle dependence on multiplicity for the 4 energies. Both the flow angle and the FOPI signal show an energy dependence (rise and fall) similar to that of F in Fig. 2. It can be argued that flow should be determined from the laboratory rapidity, y, rather than from reduced rapidity, y = y/y beam. Then flow becomes F y = d p x /dy = F/y p where 6
7 y p is the projectile beam rapidity in the lab frame. Plotting F y vs. energy we find that the rise of flow is reduced while the decline becomes more significant. The rise and fall of flow is explicable or at least qualitatively reasonable. As energy increases, the nucleon-nucleon cross sections become more forward peaked. The mean transverse momentum at first rises rapidly with energy and then is almost constant above p z 2 GeV/c. Thus, flow as a manifestation of multiple scattering effects should eventually fall as p z continues to increase. It is of great interest to compare the flow values for a wide range of data. To allow for different projectile-target (A 1,A 2 ) mass combinations, we divide the flow value by (A 1/3 1 + A 1/3 2 ) and call F S = F/(A 1/3 1 +A 1/3 2 ) the scaled flow. In recent calculations of flow [13], the authors use an F/A 1/3 scaling for symmetric systems, and argue that, for a given energy, the flow should scale with collision (compression) time. This suggested the (A 1/3 1 +A 1/3 2 ) 1 scaling used here. Figure 3 shows a plot of F S vs. energy per nucleon of the projectile. We include here data from the EOS experiment (solid points), along with values derived from other experiments [8,14 16] for a variety of energies and mass combinations. As closely as possible the data selected correspond to Plastic Ball multiplicity bins M3 and M4 or to an equivalent range of impact parameters. For the EOS and Plastic Ball data all the isotopes of Z = 1 and 2 are included, except for [16] where the data is for Z=1 and multiplicity bin M3. The Streamer Chamber data [14,15] normally include all protons, whether free or bound in clusters. Generally the flow values using all isotopes of Z = 1 and 2 are 10 20% larger than those for protons. In Fig. 3 the scaled flow values, F S, follow, within the uncertainties, a common trend with an initial steep rise and then an indication of a gradual decline. The Plastic Ball data are quoted with fairly small statistical uncertainties, 4 7%, about twice the size of the data points in Fig. 3. For the Ar + Pb [14] and Ar + KCl [15] Streamer Chamber data, we estimated the flow and statistical uncertainties from the p x vs. y data plots, for the appropriate multiplicity ranges. Our estimated uncertainties for these flow values are in the range of 15-23%. The 1800A MeV Ar +KCl Streamer Chamber data, as analyzed in Ref. 7, produce a very large flow and scaled flow value (F s 93 MeV/c per 7
8 nucleon which is off the plot scale and not included in Fig. 3). In summary, we have determined the nucleon flow for Ni induced collisions over an energy range of 400 to 1970A MeV. For these Ni systems flow, F, as measured by the change with rapidity of the average transverse momentum, rises with energy, and then declines. Comparison of our flow results with flow data from other mass systems is made by introducing a scaled flow, F S = F/(A 1/3 1 + A 1/3 2 ) which exhibits a nearly universal flow energy dependence. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We are pleased to acknowledge the support of the National Science Foundation (Grant No. PHY ), the Department of Energy (Contracts/grants DE-AC03-76SF00098, DE-FG02-89ER40531, DE-FG02-88ER40408, DE-FG02-88ER40412, DE-FG05-88ER40437) and Associated Western Universities; and the assistance of the Bevalac Operations Support Groups. Present address: Sung Kwun Kwan University, Suwon, Rep. of Korea, Present address: State University of New York, Stonybrook, NY Present address: Lawrence University, Appleton, WI Present address: Nuclear Science Division, LBNL, Berkeley, CA Present address: The Svedberg Laboratory, University of Uppsala, S Sweden Present address: Physics Department, College of Wooster, Wooster, OH Present address: Crump Institute for Biological Imaging, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
9 REFERENCES [1] A recent conference on this topic has been held. Please see the Nuclear Equation of State, Vol. 216 of NATO Advanced Study Institute, Series B: Physics, edited by W. Greiner and H. Stöcker (Plenum, New York, 1989). [2] H. Å. Gustafsson et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 1590 (1984). [3] R. E. Renfordt et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 763 (1984); H. Ströbele et al., Phys. Rev. C 27, 1349 (1983). [4] S. Costa (for the EOS Collaboration), Proceedings of the 23rd International Winter Meeting on Nuclear Physics at Bormio, Italy, January (1994). [5] J. Gosset et al., ibid. Ref. 1, p. 87; J. Poitou et al., Nucl. Phys. A 536, 767 (1992). [6] M. Partlan et al. (the EOS Collaboration), Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2100 (1995). [7] P. Danielewicz and G. Odyniec, Phys. Lett. 157B, 146 (1985). [8] H. H. Gutbrod, A. M. Poskanzer and H.-G. Ritter, Reports on Progress in Physics 52, 1267 (1989), and references therein. [9] W. Bauer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2534 (1988); Bao-An Li and W. Bauer, Phys. Rev. C 44, 2095 (1991); W. Bauer, C. K. Gelbke, and S. Pratt, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Sci. 42, 77 (1992). [10] G. Rai et al., IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 37, 56 (1990). [11] J. Chance, Ph.D. Dissertation, UC Davis, [12] T. Wienold et al., GSI-Preprint [13] A. Lang, B. Blättel, W. Cassing, V. Koch, U. Mosel and K. Weber, Zeitschrift für Physik A 340, 287 (1991). [14] D. Beavis et al., Phys. Rev. C 45, 299 (1992). 9
10 [15] D. Beavis, S. Y. Chu, S. Y. Fung, W. Gorn, D. Keane, Y. M. Liu, G.Van Dalen, M. Vient, Phys. Rev. C 33, 1113, (1986). [16] J.W. Harris et al., Nucl. Phys. A 471, 241C (1987); K.G.R. Doss et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2720 (1987). 10
11 FIGURES 150 Ni400 A MeV Ni600 A MeV p x (MeV/c) Ni1000 A MeV Ni1970 A MeV y y FIG. 1. S curves for the four Ni+Au energies, using protons only in multiplicity bin M4. p x is the average of the x component of the momentum (see text). y is the rapidity in the lab frame scaled by the rapidity of the beam Ni+Au Ni+Cu FIG. 2. Proton flow as a function of beam energy per nucleon in multiplicity bin M4. The top panel is for Ni+Au EOS data. The solid symbols are the flow values from the graphs in Fig. 1 while the open symbols are for soft and hard equation of state BUU Ni + Au calculations with an equivalent impact parameter distribution. The bottom panel consists of flow values determined from Ni+Cu EOS data. 11
12 FIG. 3. Scaled flow values vs. beam energy per nucleon for different projectile-target systems for Plastic Ball multiplicity bins 3+4. In the EOS and Plastic Ball data all isotopes of Z=1,2 are included. For the Streamer Chamber all free and bound protons are included. To improve the distinction between data points at the same beam energy, some of the beam energy values have been staggered around by as much as 20 MeV. 12
Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions
 Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions A. Insolia, 1 C. Tuvè, 1 S. Albergo, 1 F. Bieser, 2 F. P. Brady, 5 Z. Caccia, 1 D. Cebra, 2,5 A. D. Chacon, 6 J. L. Chance, 5 Y. Choi, 4,
Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions A. Insolia, 1 C. Tuvè, 1 S. Albergo, 1 F. Bieser, 2 F. P. Brady, 5 Z. Caccia, 1 D. Cebra, 2,5 A. D. Chacon, 6 J. L. Chance, 5 Y. Choi, 4,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 22 Dec 1999
 PROBING BARYON FREEZE-OUT DENSITY AT THE AGS WITH PROTON CORRELATIONS SERGEI Y. PANITKIN 7 for the E895 Collaboration arxiv:nucl-ex/9912009v1 22 Dec 1999 N.N. AJITANAND, 12 J. ALEXANDER, 12 M. ANDERSON,
PROBING BARYON FREEZE-OUT DENSITY AT THE AGS WITH PROTON CORRELATIONS SERGEI Y. PANITKIN 7 for the E895 Collaboration arxiv:nucl-ex/9912009v1 22 Dec 1999 N.N. AJITANAND, 12 J. ALEXANDER, 12 M. ANDERSON,
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 23 May 1999
 DEUTERON PRODUCTION AND SPACE-MOMENTUM CORRELATIONS AT RHIC S.Y. PANITKIN Department of Physics, Kent State University, OH 44242, USA arxiv:nucl-th/990505v 23 May 999 B. MONREAL, N. XU Nuclear Science
DEUTERON PRODUCTION AND SPACE-MOMENTUM CORRELATIONS AT RHIC S.Y. PANITKIN Department of Physics, Kent State University, OH 44242, USA arxiv:nucl-th/990505v 23 May 999 B. MONREAL, N. XU Nuclear Science
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 May 1996
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 7 Mar 2002
 Longitudinal Flow of Protons from 2-8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/0111006v2 7 Mar 2002 J.L. Klay, 1 N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, 1 D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, 1 T. Case,
Longitudinal Flow of Protons from 2-8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/0111006v2 7 Mar 2002 J.L. Klay, 1 N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, 1 D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, 1 T. Case,
p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations
 Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR. Yvonne Leifels GSI
 Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 May 2004
 arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements
 Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum?
 The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum? L. Phair, L.G. Moretto, J.B. Elliott, G.J. Wozniak Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum? L. Phair, L.G. Moretto, J.B. Elliott, G.J. Wozniak Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Noncentral collisions
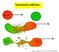 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions
 Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 23 Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions J. L. Klay, N. N. Ajitanand, J. M. Alexander, M. G. Anderson, D. Best,
Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 23 Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions J. L. Klay, N. N. Ajitanand, J. M. Alexander, M. G. Anderson, D. Best,
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear. Fragmentation Experiments. Abstract
 Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 18 Jun 2003
 Ξ and Ξ + production in Pb+Pb collisions at 4 A GeV at CERN SPS arxiv:nucl-ex/352v2 8 Jun 23. Introduction Christine Meurer for the NA49 Collaboration E-mail: Christine.Meurer@cern.ch Gesellschaft für
Ξ and Ξ + production in Pb+Pb collisions at 4 A GeV at CERN SPS arxiv:nucl-ex/352v2 8 Jun 23. Introduction Christine Meurer for the NA49 Collaboration E-mail: Christine.Meurer@cern.ch Gesellschaft für
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast
 Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Measurement of collective flow in heavy-ion collisions using particle-pair correlations
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 44, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1991 Measurement of collective flow in heavy-ion collisions using particle-pair correlations S. Wang, Y. Z. Jiang, and Y. M. Liu Department of Physics, Harbin
PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 44, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1991 Measurement of collective flow in heavy-ion collisions using particle-pair correlations S. Wang, Y. Z. Jiang, and Y. M. Liu Department of Physics, Harbin
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector
 Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39
 VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
Recent Results of NA49
 Recent Results of NA49 M. Gaździcki for the NA49 Collaboration Institut für Kernphysik, Univetsität Frankfurt D 6486 Frankfurt, Germany Abstract Results on the energy dependence of pion and strangeness
Recent Results of NA49 M. Gaździcki for the NA49 Collaboration Institut für Kernphysik, Univetsität Frankfurt D 6486 Frankfurt, Germany Abstract Results on the energy dependence of pion and strangeness
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jul 2003
 K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
Assessment of triangular flow in jet background fluctuations for Au+Au collisions First look at dijet imbalance (A J )
 Assessment of triangular flow in jet background fluctuations for Au+Au collisions First look at dijet imbalance (A J ) Wayne State REU 2012 Research Advisor: Joern Putschke Research Undergraduate: Joshua
Assessment of triangular flow in jet background fluctuations for Au+Au collisions First look at dijet imbalance (A J ) Wayne State REU 2012 Research Advisor: Joern Putschke Research Undergraduate: Joshua
Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department. Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas Abstract
 Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program
 Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
Probing the equation of state with pions
 Probing the equation of state with pions Qingfeng Li 1, Zhuxia Li 2, Sven Soff 3, Marcus Bleicher 3, and Horst Stöcker 1,3 1) Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS), Johann Wolfgang GoetheUniversität,
Probing the equation of state with pions Qingfeng Li 1, Zhuxia Li 2, Sven Soff 3, Marcus Bleicher 3, and Horst Stöcker 1,3 1) Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS), Johann Wolfgang GoetheUniversität,
ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS
 Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC
 Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC (for the STAR Collaboration) University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: lwen@physics.ucla.edu Searches for the chiral effects
Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC (for the STAR Collaboration) University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: lwen@physics.ucla.edu Searches for the chiral effects
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title High pt inclusive charged hadron spectra from Au+Au collisions at Sqrt(s_NN)=00 Gev Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3jp4v8vd
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title High pt inclusive charged hadron spectra from Au+Au collisions at Sqrt(s_NN)=00 Gev Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3jp4v8vd
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR
 Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
PoS(WPCF2011)012. New results on event-by-event fluctuations in A+A collisions at the CERN SPS. Grzegorz Stefanek for the NA49 Collaboration
 New results on eventbyevent fluctuations in AA collisions at the CERN SPS for the NA9 Collaboration Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland Email: grzegorz.stefanek@pu.kielce.pl The study of central
New results on eventbyevent fluctuations in AA collisions at the CERN SPS for the NA9 Collaboration Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland Email: grzegorz.stefanek@pu.kielce.pl The study of central
Papers by Helen Caines
 Papers by Helen Caines 1. rho0 photoproduction in ultraperipheral relativistic heavy ion collisions at snn=200 B. I. Abelev et al. Phys. Rev. C 77, 034910 (2008) 2. Centrality dependence of charged hadron
Papers by Helen Caines 1. rho0 photoproduction in ultraperipheral relativistic heavy ion collisions at snn=200 B. I. Abelev et al. Phys. Rev. C 77, 034910 (2008) 2. Centrality dependence of charged hadron
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 27 Feb 2003
 Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 21 Dec 2004
 φ meson production in d + Au collisions at s NN = 00 GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/041048v1 1 Dec 004 1. Introduction Dipali Pal for the PHENIX collaboration Department of Physics & Astronomy, Vanderbilt University,
φ meson production in d + Au collisions at s NN = 00 GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/041048v1 1 Dec 004 1. Introduction Dipali Pal for the PHENIX collaboration Department of Physics & Astronomy, Vanderbilt University,
The Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS
 The Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS Stephen Bültmann 1 Physics Department, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA 359, USA Abstract. The BoNuS experiment at Jefferson Lab s Hall B measured the structure
The Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS Stephen Bültmann 1 Physics Department, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA 359, USA Abstract. The BoNuS experiment at Jefferson Lab s Hall B measured the structure
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 14 Nov 1999
 Mass dependence of light nucleus production in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/9907002v2 4 Nov 999 T.A. Armstrong, (8, ) K.N. Barish, (3) S. Batsouli, (3) S.J. Bennett, (2) A. Chikanian,
Mass dependence of light nucleus production in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/9907002v2 4 Nov 999 T.A. Armstrong, (8, ) K.N. Barish, (3) S. Batsouli, (3) S.J. Bennett, (2) A. Chikanian,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION. A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal. and. the Kr Collaboration
 AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title SEARCH FOR FLOW IN THE REACTION Ar + Pb Permalink https:escholarship.orgucitem85s8b502 Author Renfordt, R.E. Publication
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title SEARCH FOR FLOW IN THE REACTION Ar + Pb Permalink https:escholarship.orgucitem85s8b502 Author Renfordt, R.E. Publication
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Probing dense baryonic matter with kaons: The nuclear equation-of-state In medium properties of strange mesons
 Kaon production in nucleus-nucleus collisions XI International Conference on Hypernuclear and Strange Particle Physics, October 10 14, Mainz, Germany Peter Senger (GSI) Probing dense baryonic matter with
Kaon production in nucleus-nucleus collisions XI International Conference on Hypernuclear and Strange Particle Physics, October 10 14, Mainz, Germany Peter Senger (GSI) Probing dense baryonic matter with
Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN. = GeV at RHIC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
& Λ Production in ALICE
 Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Jet quenching in PbPb collisions in CMS
 Jet quenching in PbPb collisions in CMS Bolek Wyslouch École Polytechnique Massachusetts Institute of Technology arxiv:1102.1957 Orsay, February 18, 2011 1 Heavy Ions at the LHC Huge energy jump from RHIC:
Jet quenching in PbPb collisions in CMS Bolek Wyslouch École Polytechnique Massachusetts Institute of Technology arxiv:1102.1957 Orsay, February 18, 2011 1 Heavy Ions at the LHC Huge energy jump from RHIC:
Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter
 1 Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter Pawel Danielewicz 1, 2, Roy Lacey 3 & William G. Lynch 1 * Nuclear collisions can compress nuclear matter to densities achieved within neutron stars
1 Determination of the Equation of State of Dense Matter Pawel Danielewicz 1, 2, Roy Lacey 3 & William G. Lynch 1 * Nuclear collisions can compress nuclear matter to densities achieved within neutron stars
Proton radiography with a range telescope and its use in proton therapy
 Proton radiography with a range telescope and its use in proton therapy Juan L. Romero Department of Physics, University of California, Davis, CA Invited talk at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
Proton radiography with a range telescope and its use in proton therapy Juan L. Romero Department of Physics, University of California, Davis, CA Invited talk at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
PoS(Bormio2012)013. K 0 production in pp and pnb reactions. Jia-Chii Berger-Chen
 Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Strangeness photoproduction at the BGO-OD experiment
 Strangeness photoproduction at the BGO-OD experiment Tom Jude On behalf of the BGO-OD Collaboration University of Bonn Supported by the DFG / SFB tr-16 NSTAR 215 Tom Jude (University of Bonn) Strangeness
Strangeness photoproduction at the BGO-OD experiment Tom Jude On behalf of the BGO-OD Collaboration University of Bonn Supported by the DFG / SFB tr-16 NSTAR 215 Tom Jude (University of Bonn) Strangeness
Jet Physics with ALICE
 Jet Physics with ALICE Oliver Busch for the ALICE collaboration Oliver Busch Tsukuba 2014 /03/13 1 Outline introduction results from pp jets in heavy-ion collisions results from Pb-Pb collisions jets in
Jet Physics with ALICE Oliver Busch for the ALICE collaboration Oliver Busch Tsukuba 2014 /03/13 1 Outline introduction results from pp jets in heavy-ion collisions results from Pb-Pb collisions jets in
Neutron emission asymmetries from linearly polarized γ rays on nat Cd, nat Sn, and 181 Ta
 Neutron emission asymmetries from linearly polarized γ rays on nat Cd, nat Sn, and 8 Ta Clarke Smith, Gerald Feldman, and the HIγS Collaboration George Triangle C. Smith, G. Feldman (GWU) Washington University
Neutron emission asymmetries from linearly polarized γ rays on nat Cd, nat Sn, and 8 Ta Clarke Smith, Gerald Feldman, and the HIγS Collaboration George Triangle C. Smith, G. Feldman (GWU) Washington University
The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter,
 4 Antibaryons The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter, 1955 1959 While the existence of antiparticles was established with Anderson s discovery of the positron in 1932, it was not clear in
4 Antibaryons The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter, 1955 1959 While the existence of antiparticles was established with Anderson s discovery of the positron in 1932, it was not clear in
Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions
 Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
Recent results from the NA61/SHINE experiment
 Recent results from the NA6/SHINE experiment Emil Kaptur for the NA6/SHINE collaboration University of Silesia October 7, 5 of 5 Outline NA6/SHINE experiment Selected results from energy scan (,,, 8, 58
Recent results from the NA6/SHINE experiment Emil Kaptur for the NA6/SHINE collaboration University of Silesia October 7, 5 of 5 Outline NA6/SHINE experiment Selected results from energy scan (,,, 8, 58
Cross section measurements of the elastic electron - deuteron scattering
 Cross section measurements of the elastic electron - deuteron scattering for the A1 Collaboration Institut für Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz Johann-Joachim-Becher-Weg 45, 55128 Mainz
Cross section measurements of the elastic electron - deuteron scattering for the A1 Collaboration Institut für Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz Johann-Joachim-Becher-Weg 45, 55128 Mainz
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies
 Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction
 The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction R. Spartà 1, M. La Cognata 1, C. Spitaleri 1,2, S. Cherubini
The 22 Ne(α,n) 25 Mg reaction at astrophysical energies studied via the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2 H( 25 Mg, α 22 Ne) 1 H reaction R. Spartà 1, M. La Cognata 1, C. Spitaleri 1,2, S. Cherubini
Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data
 Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data, for the STAR Collaboration Warsaw University of Technology E-mail: andrew.lipiec@gmail.com The angular correlation function (CF) in this
Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data, for the STAR Collaboration Warsaw University of Technology E-mail: andrew.lipiec@gmail.com The angular correlation function (CF) in this
Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials
 Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials C. Spieles, M. Bleicher, A. Jahns, R. Mattiello, H. Sorge, H. Stöcker, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe Universität,
Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials C. Spieles, M. Bleicher, A. Jahns, R. Mattiello, H. Sorge, H. Stöcker, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe Universität,
Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4
 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 Edited by Wolfgang Bauer Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan and Hans-Georg Ritter Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley,
Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 Edited by Wolfgang Bauer Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan and Hans-Georg Ritter Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley,
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS
 ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
ISOSPIN DIFFUSION IN HEAVY ION REACTIONS M.B. Tsang, T.X. Liu, L. Shi, P. Danielewicz, C.K. Gelbke, X.D. Liu, W.G. Lynch, W.P. Tan a, G. Verde, A.Wagner b, H.S. Xu c National Superconducting Cyclotron
(December 15, 1995) Abstract. We investigate the Equation of State (EOS) of classical systems having 300
 Second Order Phase Transitions : From Innite to Finite Systems P. Finocchiaro 1, M. Belkacem 1, T. Kubo 1, V. Latora 1;2, and A. Bonasera 1 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud Viale Andrea Doria (ang.
Second Order Phase Transitions : From Innite to Finite Systems P. Finocchiaro 1, M. Belkacem 1, T. Kubo 1, V. Latora 1;2, and A. Bonasera 1 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud Viale Andrea Doria (ang.
Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS
 Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS Stephen BültmannB Old Dominion University for the CLAS Collaboration The Structure of the Neutron at Large x The BoNuS Experiment in 005 First Results from the BoNuS
Neutron Structure Function from BoNuS Stephen BültmannB Old Dominion University for the CLAS Collaboration The Structure of the Neutron at Large x The BoNuS Experiment in 005 First Results from the BoNuS
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 26 Feb 2007
 International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:nucl-ex/0702056v1 26 Feb 2007 ENERGY DEPENDENCE OF SHORT AND LONG-RANGE MULTIPLICITY CORRELATIONS IN AU+AU COLLISIONS
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:nucl-ex/0702056v1 26 Feb 2007 ENERGY DEPENDENCE OF SHORT AND LONG-RANGE MULTIPLICITY CORRELATIONS IN AU+AU COLLISIONS
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 11 Jul 2011
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 11 Jul 2011 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 11 Jul 2011](/thumbs/87/96639693.jpg) Bulk Properties of Pb-Pb collisions at snn = 2.76 TeV measured by ALICE arxiv:17.1973v1 [nucl-ex] 11 Jul 2011 Alberica Toia for the ALICE Collaboration CERN Div. PH, 1211 Geneva 23 E-mail: alberica.toia@cern.ch
Bulk Properties of Pb-Pb collisions at snn = 2.76 TeV measured by ALICE arxiv:17.1973v1 [nucl-ex] 11 Jul 2011 Alberica Toia for the ALICE Collaboration CERN Div. PH, 1211 Geneva 23 E-mail: alberica.toia@cern.ch
Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for
 1 Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for 84 Kr 36 - emulsion interaction at around 1 A GeV N. Marimuthu 1, 2, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan 2 1 High Energy Physics laboratory,
1 Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for 84 Kr 36 - emulsion interaction at around 1 A GeV N. Marimuthu 1, 2, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan 2 1 High Energy Physics laboratory,
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model
 High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
FROM LITTLE BANGS TO BIG BANG
 FROM LITTLE BANGS TO BIG BANG C. RISTEA 1, A. JIPA 1, I. LAZANU 1, OANA RISTEA 1, C. BESLIU 1, VALERICA BABAN 1, T. ESANU 1, V. COVLEA 1 1 University of Bucharest, Faculty of Physics E-mail: cat.ristea@gmail.com
FROM LITTLE BANGS TO BIG BANG C. RISTEA 1, A. JIPA 1, I. LAZANU 1, OANA RISTEA 1, C. BESLIU 1, VALERICA BABAN 1, T. ESANU 1, V. COVLEA 1 1 University of Bucharest, Faculty of Physics E-mail: cat.ristea@gmail.com
PoS(BORMIO2010)052. Measurement of the Λ(1405) in proton proton reactions with HADES
 Measurement of the Λ(145) in proton proton reactions with HADES HADES Collaboration Email: johannes.siebenson@ph.tum.de We present an analysis of the Λ(145) resonance in p p reactions at a kinetic beam
Measurement of the Λ(145) in proton proton reactions with HADES HADES Collaboration Email: johannes.siebenson@ph.tum.de We present an analysis of the Λ(145) resonance in p p reactions at a kinetic beam
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, (2004)
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 014307 (2004) Giant resonances in 112 Sn and 124 Sn: Isotopic dependence of monopole resonance energies Y.-W. Lui, D. H. Youngblood, Y. Tokimoto, H. L. Clark, and B. John* Cyclotron
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 014307 (2004) Giant resonances in 112 Sn and 124 Sn: Isotopic dependence of monopole resonance energies Y.-W. Lui, D. H. Youngblood, Y. Tokimoto, H. L. Clark, and B. John* Cyclotron
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 37 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Radioactivity Nuclear reactions http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/ Chapter 29 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Nuclear
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 37 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Radioactivity Nuclear reactions http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/ Chapter 29 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Nuclear
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI
 STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015](/thumbs/94/118739665.jpg) ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
Heavy Ion Interactions. Beginners FLUKA Course
 Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course 1 Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course 1 Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 CMS CR - he Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH- GENEVA 3, Switzerland 8/5/6 Charmonium production measured in and pp collisions by CMS arxiv:7.5v [nucl-ex]
CMS CR - he Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH- GENEVA 3, Switzerland 8/5/6 Charmonium production measured in and pp collisions by CMS arxiv:7.5v [nucl-ex]
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio
 Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Identified charged hadron production in pp, p Pb and Pb Pb collisions at LHC energies with ALICE
 EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04075 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504075 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Identified charged hadron production in pp, p Pb and Pb Pb collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 95, 04075 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20159504075 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 Identified charged hadron production in pp, p Pb and Pb Pb collisions
J/ψ suppression at SPS and RHIC in the comovers approach arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 2 Apr 2001
 1 J/ψ suppression at SPS and RHIC in the comovers approach arxiv:nucl-th/144v1 2 Apr 21 N. Armesto a, A. Capella b MCSD]LPT, Université de Paris XI, Bâtiment 21, 9145 Orsay Cedex, France, E. G. Ferreiro
1 J/ψ suppression at SPS and RHIC in the comovers approach arxiv:nucl-th/144v1 2 Apr 21 N. Armesto a, A. Capella b MCSD]LPT, Université de Paris XI, Bâtiment 21, 9145 Orsay Cedex, France, E. G. Ferreiro
PRODUCTION OF (ANTI-)HYPERNUCLEI WITH ALICE AT THE LHC
 PRODUCTION OF (ANTI-)YPERNUCLEI WIT ALICE AT TE LC Stefano Piano on behalf of ALICE Collaboration INFN sez. Trieste ASTRA: Advances and open problems in low-energy nuclear and hadronic STRAngeness physics
PRODUCTION OF (ANTI-)YPERNUCLEI WIT ALICE AT TE LC Stefano Piano on behalf of ALICE Collaboration INFN sez. Trieste ASTRA: Advances and open problems in low-energy nuclear and hadronic STRAngeness physics
MEASUREMENT OF (ANTI-)HYPERNUCLEI PRODUCTION WITH ALICE AT THE LHC
 MEASUREMENT OF (ANTI-)YPERNUCLEI PRODUCTION WIT ALICE AT TE LC Stefano Piano on behalf of ALICE Collaboration INFN sez. Trieste ALICE EXA217: International Conference on Exotic Atoms and Related Topics
MEASUREMENT OF (ANTI-)YPERNUCLEI PRODUCTION WIT ALICE AT TE LC Stefano Piano on behalf of ALICE Collaboration INFN sez. Trieste ALICE EXA217: International Conference on Exotic Atoms and Related Topics
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse
 1 Hadron yields and spectra in Au+Au collisions at the AGS arxiv:nucl-ex/9609001v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse Foster Radiation Laboratory, McGill University, Montréal, Canada H3A 2B1 For the E877 Collaboration:
1 Hadron yields and spectra in Au+Au collisions at the AGS arxiv:nucl-ex/9609001v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse Foster Radiation Laboratory, McGill University, Montréal, Canada H3A 2B1 For the E877 Collaboration:
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 Dec 1998
 MSUCL-1115 Revisiting lepton pairs at the SPS J. Murray Department of Physics, Linfield College, McMinnville, OR 97128 arxiv:nucl-th/9812024v1 9 Dec 1998 W. Bauer National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
MSUCL-1115 Revisiting lepton pairs at the SPS J. Murray Department of Physics, Linfield College, McMinnville, OR 97128 arxiv:nucl-th/9812024v1 9 Dec 1998 W. Bauer National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 29 Apr 1999
 Observation of Thermodynamical Properties in the 162 Dy, 166 Er and 172 Yb Nuclei E. Melby, L. Bergholt, M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, F. Ingebretsen, S. Messelt, J. Rekstad, A. Schiller, S. Siem, and
Observation of Thermodynamical Properties in the 162 Dy, 166 Er and 172 Yb Nuclei E. Melby, L. Bergholt, M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, F. Ingebretsen, S. Messelt, J. Rekstad, A. Schiller, S. Siem, and
Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS
 986 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS P. Chung and P.
986 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS P. Chung and P.
Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters
 Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters K. Suzuki a,l.fabbietti a,p.kienle a,b, N. Herrmann c, T. Yamazaki d and J. Zmeskal b a Physik Department, TU München, Germany b Stefan Meyer
Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters K. Suzuki a,l.fabbietti a,p.kienle a,b, N. Herrmann c, T. Yamazaki d and J. Zmeskal b a Physik Department, TU München, Germany b Stefan Meyer
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Dec 2005
 The Ratio Σ /Λ at RHIC arxiv:nucl-ex/58v 3 Dec 5 G. Van Buren for the STAR Collaboration Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 973-5 USA E-mail: gene@bnl.gov Abstract While yields
The Ratio Σ /Λ at RHIC arxiv:nucl-ex/58v 3 Dec 5 G. Van Buren for the STAR Collaboration Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 973-5 USA E-mail: gene@bnl.gov Abstract While yields
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 22 Nov 2012](/thumbs/72/67186430.jpg) Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
Correlation and isospin dynamics of participant-spectator matter in neutron-rich colliding nuclei at 50 MeV/nucleon Sanjeev Kumar, Y. G. Ma, and G. Q. Zhang Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions
 The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
S364 Experiment: Resonance in Isobaric Charge-Exchange reactions
 S364 Experiment: Resonance in Isobaric Charge-Exchange reactions Jossitt W. Vargas Cruz GENP,Universidad Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, 15782 Spain May 19, 2011 Motivation The Analysis
S364 Experiment: Resonance in Isobaric Charge-Exchange reactions Jossitt W. Vargas Cruz GENP,Universidad Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, 15782 Spain May 19, 2011 Motivation The Analysis
Outline: Introduction and Motivation
 Heavy ion collisions at lower energies: challenges and opportunities Beam Energy Scan (BES I and II) from RHIC Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Outline: Introduction and Motivation Results
Heavy ion collisions at lower energies: challenges and opportunities Beam Energy Scan (BES I and II) from RHIC Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Outline: Introduction and Motivation Results
Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c
 Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 2003 Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c K. N. Barish, S. Batsouli, S. J. Bennett, M. Bertaina, A.
Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 2003 Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c K. N. Barish, S. Batsouli, S. J. Bennett, M. Bertaina, A.
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC. Abstract
 F,' A RHIC Summer S t u d y 1996: T h e o r y Workshop on RHI Collision, BNL, Upton, NY July 8-19, 1996. THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC FLEMMING VIDEBBK Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory,
F,' A RHIC Summer S t u d y 1996: T h e o r y Workshop on RHI Collision, BNL, Upton, NY July 8-19, 1996. THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC FLEMMING VIDEBBK Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory,
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model
 Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 722 727, 2012 STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES * OANA RISTEA, A. JIPA, C. RISTEA, C. BEŞLIU, ŞTEFANIA VELICA University
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 722 727, 2012 STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES * OANA RISTEA, A. JIPA, C. RISTEA, C. BEŞLIU, ŞTEFANIA VELICA University
