arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 22 Dec 1999
|
|
|
- Ross Darrell Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROBING BARYON FREEZE-OUT DENSITY AT THE AGS WITH PROTON CORRELATIONS SERGEI Y. PANITKIN 7 for the E895 Collaboration arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 22 Dec 1999 N.N. AJITANAND, 12 J. ALEXANDER, 12 M. ANDERSON, 5 D. BEST, 1 F.P. BRADY, 5 T. CASE, 1 W. CASKEY, 5 D. CEBRA, 5 J. CHANCE, 5 P. CHUNG, 12 B. COLE, 4 K. CROWE, 1 A. DAS, 10 J. DRAPER, 5 M. GILKES, 11 S. GUSHUE, 2 M. HEFFNER, 5 A. HIRSCH, 11 E. HJORT, 11 L. HUO, 6 M. JUSTICE, 7 M. KAPLAN, 3 D. KEANE, 7 J. KINTNER, 8 J. KLAY, 5 D. KROFCHECK, 9 R. LACEY, 12 M. LISA, 10 H. LIU, 7 Y. LIU, 6 R. MCGRATH, 12 Z. MILOSEVICH, 3, G. ODYNIEC, 1 D. OLSON, 1 C. PINKENBURG, 12 N. PORILE, 11 G. RAI, 1 H.-G. RITTER, 1 J. ROMERO, 5 R. SCHARENBERG, 11 L. SCHROEDER, 1 B. SRIVASTAVA, 11 N. STONE, 2 T.J.M. SYMONS, 1 S. WANG, 7 J. WHITFIELD, 3 T. WIENOLD, 1 R. WITT, 7 L. WOOD, 5 X. YANG, 4 W. ZHANG, 6 Y. ZHANG 4 1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Columbia University, New York, New York University of California, Davis, California Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin , P. R. China 7 Kent State University, Kent, Ohio St. Mary s College of California, Moraga, California University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand 10 The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana State University of New York, Stony Brook, New York First measurements of the beam energy dependence of the two proton correlation function in central Au+Au collisions are performed by the E895 Collaboration at the BNL AGS. The imaging technique of Brown-Danielewicz is used in order to extract information about the proton source at freeze-out. Measured correlation functions and sources do not exhibit significant changes with beam energy. 1 Introduction The sensitivity of the two-proton correlations to the space-time extent of nuclear reactions was first noted by Koonin 1. A characteristic peak in the proton correlation function is due to the interplay of the attractive strong and repulsive Coulomb interactions along with effects of quantum statistics. paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
2 For simple static chaotic sources, it has been shown 1,2,3,4 that the height of the correlation peak approximately scales inversely with the source volume. Later on it was realized that the height of the peak is also sensitive to various dynamical properties of the emitting sorce such as collective flow 5, space-momentum correlations within the source in general 6, etc. Because of the complex nature of the two-proton final state interactions only modeldependent and/or qualitative statements were possible in proton correlation analysis. Recently, it was shown that one can perform model-independent extractions of the entire source function S(r) from two-proton correlations, not just its radii, using imaging techniques 7,8,9. Furthermore, one can do this without making any a priori assumptions about the source geometry or lifetime, etc. In this paper we present preliminary results of the first measurement of the beam energy dependence of the two-proton correlation function in the central Au+Au collisions at 2,4,6 and 8A GeV performed by the E895 Collaboration at the Brookhaven National Lab (BNL) Alternating Gradient Synchrotron (AGS). 2 Experimental Details and Analysis Procedure The goal of E895 is to study multiparticle correlations and particle production with Au beams incident on a variety of targets, over a range of AGS energies. More information about the E895 experimental setup can be found elsewhere 10,11. Beams of gold ions ( 197 Au) were available at different energies - 2,4,6 and 8A GeV. They were used to bombard targets of different materials- Be, Cu, Ag and Au. Charged particles produced in the collision were detected with time projection chamber (TPC) 10, positioned inside the MPS magnet, and multi-sampling ionization chamber (MUSIC) 11 located downstream from the magnet. For the presented results, only information from the TPC was used. The TPC was capable of detecting and the tracking software of reconstructing up to several hundreds tracks per event. Particle identification was performed via simultaneous measurement of particle momentum and specific ionization in the TPC gas. Momentum resolution within the range of correlation measurements was better than 3%. In order to obtain the two-proton correlation function C 2 experimentally, the mixed event technique was used. We employ the following definition of the correlation function C 2 (q inv ) = N tr(q inv ) N bk (q inv ), (1) paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
3 where q inv = q = 1 2 (p µ 1 pµ 2 )2 (2) is the half relative invariant momentum between the two identical particles with four-momenta p µ 1 and pµ 2. The quantities N tr and N bk are the true and background two-particle distributions obtained by selecting particles from the same and different events, respectively. Before calculating the correlation function, several cuts were applied 12. In order to guarantee a reliable particle identification and high purity of the proton sample, a cut on proton longitudinal momentum P z < 800 MeV/c was used. Contamination of the identified proton sample by other particles, in this momentum interval, was estimated to be less than 2%. For the present analysis events were selected with a multiplicity cut corresponding to the upper 5% of the inelastic cross section for Au+Au collisions. The imaging technique of Brown-Danielewicz 7,8,6 was C GeV 4 GeV 6 GeV 8 GeV Q inv (GeV/c) Figure 1. Measured two-proton correlation functions for Au+Au central collisions at different beam energies. used in order to extract quantitative information from the measured correlation functions. Here we will give just a brief sketch of the method, see Refs 7,8 paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
4 for a more detailed description. The two-particle correlation function may be expressed in the following way: C P (q) dr Φ q ( ) (r) 2 S P (r). (3) S P (r) is the distribution of relative separation of emission points for the two particles, in their center of mass and Φ q ( ) (r) is a relative wave function, which can be calculated numerically given a particular description of the final state interaction. In the present analysis, the proton relative wave functions were calculated by solving the Schrödinger equation with the REID93 13 and Coulomb potentials. The imaging method takes advantage of the fact that the equation relating the source and the correlation function may be inverted to yield a source function S p (r) from a measured correlation function. 3 Results Figure 1 shows the measured two-proton correlation functions for Au+Au central collisions at 2,4,6 and 8A GeV. Within currently available statistical accuracy no significant changes of the measured correlation functions with beam energy were observed. Figure 2 shows the relative distribution of emission points of protons for central Au+Au collisions at 2,4,6 and 8A GeV obtained as a result of the application of the imaging technique described above. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the relative proton source functions have similar shapes at all measured energies. Imaging combined with the measurements of the single particle distribution allows one to obtain freeze-out densities in a rather straightforward way 9 : ρ = S(r 0) N p where ρ is the freeze-out density, S(r 0) is a value of the source finction at zero separation and N p is number of particles(protons). Details of the proton single-particle distribution analysis can be found elsewhere 14. Results of the calculation of proton freeze-out density are shown (as a fraction of normal nuclear density) in Figure 3. Within experimental errors, proton freeze-out density in the measured momentum window is fairly constant with a possible hint of reduction at the highest beam energy. Clearly, better statistical accuracy is desirable to shed more light on the behavior of this important observable. In summary, we reported preliminary results of the analysis of the beam energy dependence of the two-proton correlation function in the target fragmentation region (P z < 800 MeV/c). The correlation functions were measured for the first time for protons in central Au+Au collisions at beam energies 2,4,6 and 8A GeV. Within currently available statistical accuracy no significant changes with beam energy were observed. The source imaging technique paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
5 GeV/A 4 GeV/A 6 GeV/A 8 GeV/A 10 4 S(r) [fm 3 ] r [fm] Figure 2. Relative source functions extracted from the proton correlation data at 2,4,6 and 8A GeV. of Brown-Danielewicz was used to extract information about the space-time extent of the proton source. It was found that the relative proton source functions have similar shapes at all measured energies. Measured freeze-out densities of proton s emmited at target hemisphere (P z < 800 MeV/c) were found to be approximately constant at all available energies. Further investigation of this important observable using high precision measurents is clearly needed. I would like to thank Physics Department of Brown University for warm hospitality during the Conference. Stimulating discussions with Drs. D.Brown and S. Pratt are gratefully acknowledged. This research is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. National Science Foundation and by University of Auckland, New Zealand, Research Committee. References 1. S. Koonin, Phys. Lett. B70, 43 (1977).. 2. R. Lednicky and V.L. Lyuboshitz, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 35, 770 (1982). 3. T. Nakai and H. Yokomi, Prog. Theor. Phys. 66, 1328 (1981). 4. D.J. Ernst, M.R. Strayer and A.S. Umar, Phys. Rev Lett. B 55, 584 (1985). paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
6 E895 Au+Au Central ρ/ρ E Lab (AGeV) Figure 3. Beam energy dependence of the proton freeze-out densities at target rapidity region. 5. W.G. Gong, W. Bauer, C.K. Gelbke, and S. Pratt, Phys. Rev. C 43, 781 (1991). 6. S.Y. Panitkin and D.A. Brown, nucl-th/ D.A. Brown and P. Danielewicz, Phys. Lett. B398, 252 (1997). 8. D.A. Brown and P. Danielewicz, Phys. Rev. C57, 2474 (1998). 9. P. Danielewicz and D.A. Brown, nucl-th/ G. Rai, et al., IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 37, 56 (1990). 11. G. Bauer et al., NIM A386, 249 (1997). 12. S.Y. Panitkin for the E895 Collaboration, nucl-th/ W.G.J. Stoks et al., Phys. Rev. C49, 2950 (1994). 14. R. Witt for the E895 Collaboration, Proc. of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Minisymposium at the Centennial Meeting of the American Physical Society, Atlanta, Georgia, March 1999 (World Scientific, Singapore, in press). paper: submitted to World Scientific on February 8,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 7 Mar 2002
 Longitudinal Flow of Protons from 2-8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/0111006v2 7 Mar 2002 J.L. Klay, 1 N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, 1 D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, 1 T. Case,
Longitudinal Flow of Protons from 2-8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/0111006v2 7 Mar 2002 J.L. Klay, 1 N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, 1 D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, 1 T. Case,
Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions
 Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 23 Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions J. L. Klay, N. N. Ajitanand, J. M. Alexander, M. G. Anderson, D. Best,
Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 23 Charged pion production in 2A to 8A GeV central Au plus Au collisions J. L. Klay, N. N. Ajitanand, J. M. Alexander, M. G. Anderson, D. Best,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 23 Jul 1996
 The energy dependence of flow in Ni induced collisions from 400 to 1970A MeV J. Chance (1), S. Albergo (2), F. Bieser (4), F. P. Brady (1), Z. Caccia (2), D. Cebra (1,4), A. D. Chacon (6), Y. Choi (5),
The energy dependence of flow in Ni induced collisions from 400 to 1970A MeV J. Chance (1), S. Albergo (2), F. Bieser (4), F. P. Brady (1), Z. Caccia (2), D. Cebra (1,4), A. D. Chacon (6), Y. Choi (5),
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 23 May 1999
 DEUTERON PRODUCTION AND SPACE-MOMENTUM CORRELATIONS AT RHIC S.Y. PANITKIN Department of Physics, Kent State University, OH 44242, USA arxiv:nucl-th/990505v 23 May 999 B. MONREAL, N. XU Nuclear Science
DEUTERON PRODUCTION AND SPACE-MOMENTUM CORRELATIONS AT RHIC S.Y. PANITKIN Department of Physics, Kent State University, OH 44242, USA arxiv:nucl-th/990505v 23 May 999 B. MONREAL, N. XU Nuclear Science
Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions
 Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions A. Insolia, 1 C. Tuvè, 1 S. Albergo, 1 F. Bieser, 2 F. P. Brady, 5 Z. Caccia, 1 D. Cebra, 2,5 A. D. Chacon, 6 J. L. Chance, 5 Y. Choi, 4,
Universality in fragment inclusive yields from Au Au collisions A. Insolia, 1 C. Tuvè, 1 S. Albergo, 1 F. Bieser, 2 F. P. Brady, 5 Z. Caccia, 1 D. Cebra, 2,5 A. D. Chacon, 6 J. L. Chance, 5 Y. Choi, 4,
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 May 1996
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS
 986 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS P. Chung and P.
986 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 Recent Femtoscopy Results from NA49: Evidence for a Non-Gaussian Tail in the 3-Dimensional Two-Pion Emission Source at SPS P. Chung and P.
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 18 Jun 2003
 Ξ and Ξ + production in Pb+Pb collisions at 4 A GeV at CERN SPS arxiv:nucl-ex/352v2 8 Jun 23. Introduction Christine Meurer for the NA49 Collaboration E-mail: Christine.Meurer@cern.ch Gesellschaft für
Ξ and Ξ + production in Pb+Pb collisions at 4 A GeV at CERN SPS arxiv:nucl-ex/352v2 8 Jun 23. Introduction Christine Meurer for the NA49 Collaboration E-mail: Christine.Meurer@cern.ch Gesellschaft für
p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Particle correlations to be seen by ALICE
 NUKLEONIKA 2004;49(Supplement 2):S103 S108 PROCEEDINGS Particle correlations to be seen by ALICE Jan Pluta, Zbigniew Chajęcki, Hanna P. Gos, Piotr K. Skowroński Abstract The possibilities of ALICE experiment
NUKLEONIKA 2004;49(Supplement 2):S103 S108 PROCEEDINGS Particle correlations to be seen by ALICE Jan Pluta, Zbigniew Chajęcki, Hanna P. Gos, Piotr K. Skowroński Abstract The possibilities of ALICE experiment
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 26 Sep 2003
 Charged Pion Production in 2 to 8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/3633v2 26 Sep 23 J.L. Klay, N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, T. Case, 3 W. Caskey,
Charged Pion Production in 2 to 8 AGeV Central Au+Au Collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/3633v2 26 Sep 23 J.L. Klay, N.N. Ajitanand, 2 J.M. Alexander, 2 M.G. Anderson, D. Best, 3 F.P. Brady, T. Case, 3 W. Caskey,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 May 2004
 arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
Pion, Kaon, and (Anti-) Proton Production in Au+Au Collisions at s = 62.4 GeV
 Pion, Kaon, and (Anti-) Proton Production in AuAu Collisions at s = 6.4 GeV NN Ming Shao 1, for the STAR Collaboration 1 University of Science & Technology of China, Anhui 3007, China Brookhaven National
Pion, Kaon, and (Anti-) Proton Production in AuAu Collisions at s = 6.4 GeV NN Ming Shao 1, for the STAR Collaboration 1 University of Science & Technology of China, Anhui 3007, China Brookhaven National
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program
 Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV
 Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow
 Physics Letters B 609 (2005) 247 251 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow Piotr Bożek The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
Physics Letters B 609 (2005) 247 251 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow Piotr Bożek The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 21 Dec 2004
 φ meson production in d + Au collisions at s NN = 00 GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/041048v1 1 Dec 004 1. Introduction Dipali Pal for the PHENIX collaboration Department of Physics & Astronomy, Vanderbilt University,
φ meson production in d + Au collisions at s NN = 00 GeV arxiv:nucl-ex/041048v1 1 Dec 004 1. Introduction Dipali Pal for the PHENIX collaboration Department of Physics & Astronomy, Vanderbilt University,
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
Pion Transverse Momentum Spectrum, Elliptic Flow and Interferometry in the Granular Source Model in Ultra-Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions
 Pion Transverse Momentum Spectrum, Elliptic Flow and Interferometry in the Granular Source Model in Ultra-Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Jing Yang 1, Yan-Yu Ren and Wei-Ning Zhang 1, 1 School of Physics
Pion Transverse Momentum Spectrum, Elliptic Flow and Interferometry in the Granular Source Model in Ultra-Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Jing Yang 1, Yan-Yu Ren and Wei-Ning Zhang 1, 1 School of Physics
Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN. = GeV at RHIC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Event anisotropy at RHIC
 Event anisotropy at RHIC Nu Xu - LBNL 1) Introduction 2) Experimental details and 200 GeV results v 2 (m 0, p T, y, b, A) 3) Summary and outlook PHENIX: N. Ajitanand, S. Esumi, R. Lacey, J. Rak PHOBOS:
Event anisotropy at RHIC Nu Xu - LBNL 1) Introduction 2) Experimental details and 200 GeV results v 2 (m 0, p T, y, b, A) 3) Summary and outlook PHENIX: N. Ajitanand, S. Esumi, R. Lacey, J. Rak PHOBOS:
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jan 2003
 Probing Transport Theories via Two-Proton Source Imaging G. Verde a, P. Danielewicz a, W.G. Lynch a, D.A. Brown b, C.K. Gelbke a, M.B. Tsang a a National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department
Probing Transport Theories via Two-Proton Source Imaging G. Verde a, P. Danielewicz a, W.G. Lynch a, D.A. Brown b, C.K. Gelbke a, M.B. Tsang a a National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department
Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials
 Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials C. Spieles, M. Bleicher, A. Jahns, R. Mattiello, H. Sorge, H. Stöcker, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe Universität,
Antibaryons in massive heavy ion reactions: Importance of potentials C. Spieles, M. Bleicher, A. Jahns, R. Mattiello, H. Sorge, H. Stöcker, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe Universität,
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39
 VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector
 Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector Brooke Haag for the STAR Collaboration Hartnell College / University of California, Davis Presented at the Meeting of the California Section of
Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector Brooke Haag for the STAR Collaboration Hartnell College / University of California, Davis Presented at the Meeting of the California Section of
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 14 Nov 1999
 Mass dependence of light nucleus production in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/9907002v2 4 Nov 999 T.A. Armstrong, (8, ) K.N. Barish, (3) S. Batsouli, (3) S.J. Bennett, (2) A. Chikanian,
Mass dependence of light nucleus production in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:nucl-ex/9907002v2 4 Nov 999 T.A. Armstrong, (8, ) K.N. Barish, (3) S. Batsouli, (3) S.J. Bennett, (2) A. Chikanian,
Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data
 Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data, for the STAR Collaboration Warsaw University of Technology E-mail: andrew.lipiec@gmail.com The angular correlation function (CF) in this
Angular correlations of identified particles in the STAR BES data, for the STAR Collaboration Warsaw University of Technology E-mail: andrew.lipiec@gmail.com The angular correlation function (CF) in this
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations
 Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR. Yvonne Leifels GSI
 Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
K 0 sk 0 s correlations in 7 TeV pp collisions from the ALICE experiment at the LHC
 K 0 sk 0 s correlations in 7 TeV pp collisions from the ALICE experiment at the LHC Tom Humanic Ohio State University for the ALICE Collaboration 1 WPCF 2011 Tokyo, Japan Motivation for studying K 0 sk
K 0 sk 0 s correlations in 7 TeV pp collisions from the ALICE experiment at the LHC Tom Humanic Ohio State University for the ALICE Collaboration 1 WPCF 2011 Tokyo, Japan Motivation for studying K 0 sk
Quark-Gluon Plasma Physics
 Quark-Gluon Plasma Physics 7. Hanbury Brown Twiss correlations Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers Heidelberg University SS 017 Momentum correlation of identical bosons emitted from two point sources ~xi : Single-particle
Quark-Gluon Plasma Physics 7. Hanbury Brown Twiss correlations Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers Heidelberg University SS 017 Momentum correlation of identical bosons emitted from two point sources ~xi : Single-particle
Particle correlations in such collision?! N=n(n-1)/2. azimuthal, back-to back, multiplicity... close velocity,
 Future of Nuclear Collisions at High Energies Kielce, Poland, October 14-17 2004 Particle correlations in heavy ion collisions Jan Pluta Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics, Heavy Ion Reactions
Future of Nuclear Collisions at High Energies Kielce, Poland, October 14-17 2004 Particle correlations in heavy ion collisions Jan Pluta Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics, Heavy Ion Reactions
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 26 Feb 2007
 International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:nucl-ex/0702056v1 26 Feb 2007 ENERGY DEPENDENCE OF SHORT AND LONG-RANGE MULTIPLICITY CORRELATIONS IN AU+AU COLLISIONS
International Journal of Modern Physics E c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:nucl-ex/0702056v1 26 Feb 2007 ENERGY DEPENDENCE OF SHORT AND LONG-RANGE MULTIPLICITY CORRELATIONS IN AU+AU COLLISIONS
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse
 1 Hadron yields and spectra in Au+Au collisions at the AGS arxiv:nucl-ex/9609001v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse Foster Radiation Laboratory, McGill University, Montréal, Canada H3A 2B1 For the E877 Collaboration:
1 Hadron yields and spectra in Au+Au collisions at the AGS arxiv:nucl-ex/9609001v1 30 Aug 1996 Roger Lacasse Foster Radiation Laboratory, McGill University, Montréal, Canada H3A 2B1 For the E877 Collaboration:
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 11 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 11 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 11 Jun 2008](/thumbs/82/86259557.jpg) Proc. 4th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (008) 000 000 4th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics South Padre, Texas, USA April 1, 008 arxiv:0806.180v1 [hep-ph] 11 Jun 008 A fully integrated Boltzmann+hydrodynamics
Proc. 4th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (008) 000 000 4th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics South Padre, Texas, USA April 1, 008 arxiv:0806.180v1 [hep-ph] 11 Jun 008 A fully integrated Boltzmann+hydrodynamics
Outline: Introduction and Motivation
 Heavy ion collisions at lower energies: challenges and opportunities Beam Energy Scan (BES I and II) from RHIC Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Outline: Introduction and Motivation Results
Heavy ion collisions at lower energies: challenges and opportunities Beam Energy Scan (BES I and II) from RHIC Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Outline: Introduction and Motivation Results
Probing the QCD phase diagram with dileptons a study using coarse-grained transport dynamics
 Probing the QCD phase diagram with dileptons a study using coarse-grained transport dynamics Stephan Endres, Hendrik van Hees, and Marcus Bleicher Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Ruth-Moufang-Straße
Probing the QCD phase diagram with dileptons a study using coarse-grained transport dynamics Stephan Endres, Hendrik van Hees, and Marcus Bleicher Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Ruth-Moufang-Straße
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 18 Apr 2019
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 18 Apr 2019 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 18 Apr 2019](/thumbs/96/129273857.jpg) Mean-field potential effects in the cumulants of baryons from central Au+Au collision at E lab = 3 GeV/nucleon arxiv:194.82v1 [nucl-th] 18 Apr 19 Yongjia Wang 1,a), Yunxiao Ye 1,2 and Qingfeng Li 1,3 a)
Mean-field potential effects in the cumulants of baryons from central Au+Au collision at E lab = 3 GeV/nucleon arxiv:194.82v1 [nucl-th] 18 Apr 19 Yongjia Wang 1,a), Yunxiao Ye 1,2 and Qingfeng Li 1,3 a)
Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC
 Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC (for the STAR Collaboration) University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: lwen@physics.ucla.edu Searches for the chiral effects
Searches for Chiral Effects and Prospects for Isobaric Collisions at STAR/RHIC (for the STAR Collaboration) University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: lwen@physics.ucla.edu Searches for the chiral effects
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 23 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 23 Mar 2018 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 23 Mar 2018](/thumbs/93/113023633.jpg) Effect of in-medium nucleon-nucleon cross section on proton-proton momentum correlation in intermediate energy heavy-ion collision arxiv:1803.08825v1 [nucl-th] 23 Mar 2018 Ting-Ting Wang, 1, 2 Yu-Gang
Effect of in-medium nucleon-nucleon cross section on proton-proton momentum correlation in intermediate energy heavy-ion collision arxiv:1803.08825v1 [nucl-th] 23 Mar 2018 Ting-Ting Wang, 1, 2 Yu-Gang
Comparison of experimental and theoretical results to define centrality of heavy ion collisions. 1. Introduction.
 Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
arxiv:nucl-th/ v2 8 Jun 2006
 Acta Phys. Hung. A / (2005) 000 000 HEAVY ION PHYSICS Strange quark collectivity of φ meson at RHIC arxiv:nucl-th/0510095v2 8 Jun 2006 J. H. Chen 1,2, Y. G. Ma 1,a, G. L. Ma 1,2, H. Z. Huang 1,3, X. Z.
Acta Phys. Hung. A / (2005) 000 000 HEAVY ION PHYSICS Strange quark collectivity of φ meson at RHIC arxiv:nucl-th/0510095v2 8 Jun 2006 J. H. Chen 1,2, Y. G. Ma 1,a, G. L. Ma 1,2, H. Z. Huang 1,3, X. Z.
Swinburne Research Bank
 Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Holzman, B., Back, B. B., & Baker, M. D., et al. (004). Rapidity and kt dependence of HBT correlations in Au+Au collisions at 00 GeV with PHOBOS.
Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Holzman, B., Back, B. B., & Baker, M. D., et al. (004). Rapidity and kt dependence of HBT correlations in Au+Au collisions at 00 GeV with PHOBOS.
Azimuthally-sensitive pion HBT in STAR
 Azimuthally-sensitive pion HBT in STAR Christopher Anson for the STAR collaboration Ohio State University Outline Reconstructing the Reaction Plane HBT analysis and corrections for effects from v 2 and
Azimuthally-sensitive pion HBT in STAR Christopher Anson for the STAR collaboration Ohio State University Outline Reconstructing the Reaction Plane HBT analysis and corrections for effects from v 2 and
Indications for a critical end point in the phase diagram for hot and dense nuclear matter
 Indications for a critical end point in the phase diagram for hot and dense nuclear matter Roy A. Lacey Stony Brook University Outline Introduction Phase Diagram Search strategy Theoretical guidance Femtoscopic
Indications for a critical end point in the phase diagram for hot and dense nuclear matter Roy A. Lacey Stony Brook University Outline Introduction Phase Diagram Search strategy Theoretical guidance Femtoscopic
Transverse Mass and Rapidity Spectra of Pions and Protons from Au+Au Collisions at the Alternating Gradient Synchrotron
 Transverse Mass and Rapidity Spectra of Pions and Protons from Au+Au Collisions at the Alternating Gradient Synchrotron BY Jennifer Lynn Klay B.S. (University of California, Los Angeles) 1994 M.S. (University
Transverse Mass and Rapidity Spectra of Pions and Protons from Au+Au Collisions at the Alternating Gradient Synchrotron BY Jennifer Lynn Klay B.S. (University of California, Los Angeles) 1994 M.S. (University
Strangeness in Nucleus
 Strangeness in Nucleus L. Fabbietti! Technische Universitaet Muenchen Excellence Cluster Origin and Structure of the Universe https://www.e12.ph.tum.de/groups/kcluster Utrecht University WS214-15 O. Arnold,
Strangeness in Nucleus L. Fabbietti! Technische Universitaet Muenchen Excellence Cluster Origin and Structure of the Universe https://www.e12.ph.tum.de/groups/kcluster Utrecht University WS214-15 O. Arnold,
The measurement of non-photonic electrons in STAR
 The measurement of non-photonic electrons in STAR Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Břehová 7, 11519, Prague 1, Czech Republic E-mail: olga.hajkova@fjfi.cvut.cz
The measurement of non-photonic electrons in STAR Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Břehová 7, 11519, Prague 1, Czech Republic E-mail: olga.hajkova@fjfi.cvut.cz
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION. A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal. and. the Kr Collaboration
 AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies
 Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies Critical Point and Onset of Deconfinement 2016, Wrocław. Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, P. M. Hohler, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
Thermal dileptons as fireball probes at SIS energies Critical Point and Onset of Deconfinement 2016, Wrocław. Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, P. M. Hohler, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jul 2003
 K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
Papers by Helen Caines
 Papers by Helen Caines 1. rho0 photoproduction in ultraperipheral relativistic heavy ion collisions at snn=200 B. I. Abelev et al. Phys. Rev. C 77, 034910 (2008) 2. Centrality dependence of charged hadron
Papers by Helen Caines 1. rho0 photoproduction in ultraperipheral relativistic heavy ion collisions at snn=200 B. I. Abelev et al. Phys. Rev. C 77, 034910 (2008) 2. Centrality dependence of charged hadron
STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 722 727, 2012 STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES * OANA RISTEA, A. JIPA, C. RISTEA, C. BEŞLIU, ŞTEFANIA VELICA University
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 64, No. 3, P. 722 727, 2012 STRANGENESS PRODUCTION IN HEAVY ION COLLISIONS AT RELATIVISTIC ENERGIES * OANA RISTEA, A. JIPA, C. RISTEA, C. BEŞLIU, ŞTEFANIA VELICA University
Event geometrical anisotropy and fluctuation viewed by HBT interferometry
 Event geometrical anisotropy and fluctuation viewed by HB interferometry akafumi Niida University of sukuba -- ennoudai, sukuba, Ibaraki 35-857, Japan Abstract Azimuthal angle dependence of the pion source
Event geometrical anisotropy and fluctuation viewed by HB interferometry akafumi Niida University of sukuba -- ennoudai, sukuba, Ibaraki 35-857, Japan Abstract Azimuthal angle dependence of the pion source
Antiflow of Nucleons at the Softest Point of the EoS
 UFTP 492/1999 Antiflow of Nucleons at the Softest Point of the EoS J. Brachmann, S. Soff, A. Dumitru, H. Stöcker, J.A. Maruhn, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik der J.W. Goethe Universität Postfach
UFTP 492/1999 Antiflow of Nucleons at the Softest Point of the EoS J. Brachmann, S. Soff, A. Dumitru, H. Stöcker, J.A. Maruhn, W. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik der J.W. Goethe Universität Postfach
Beam Energy Scan Program in STAR Experimental Approach to the QCD Phase Diagram
 Beam Energy Scan Program in STAR Experimental Approach to the QCD Phase Diagram Grazyna Odyniec / LBNL, Berkeley for STAR Collaboration Central Au+Au @ 7.7 GeV event in STAR TPC CPOD 2010, Dubna, Russia,
Beam Energy Scan Program in STAR Experimental Approach to the QCD Phase Diagram Grazyna Odyniec / LBNL, Berkeley for STAR Collaboration Central Au+Au @ 7.7 GeV event in STAR TPC CPOD 2010, Dubna, Russia,
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v2 28 May 2005
 Extensive Particle Identification with TPC and TOF at the STAR Experiment arxiv:nucl-ex/556v 8 May 5 Ming Shao a,b, Olga Barannikova d, Xin Dong a,c, Yuri Fisyak b, Lijuan Ruan a,b, Paul Sorensen c, Zhangbu
Extensive Particle Identification with TPC and TOF at the STAR Experiment arxiv:nucl-ex/556v 8 May 5 Ming Shao a,b, Olga Barannikova d, Xin Dong a,c, Yuri Fisyak b, Lijuan Ruan a,b, Paul Sorensen c, Zhangbu
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear. Fragmentation Experiments. Abstract
 Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
Size Matters: Origin of Binomial Scaling in Nuclear Fragmentation Experiments Wolfgang Bauer and Scott Pratt Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan
Vale. Femtoscopy in pp and pa collisions at TeV energies. Andi Bernie Oton Dimitar.
 Femtoscopy in pp and pa collisions at TeV energies Laura Fabbietti, Technische Universität München http://www.denseandstrange.ph.tum.de Vale Andi Bernie Oton Dimitar 1 Outline The Hyperon-Nucleon and Hyperon-Hyperon
Femtoscopy in pp and pa collisions at TeV energies Laura Fabbietti, Technische Universität München http://www.denseandstrange.ph.tum.de Vale Andi Bernie Oton Dimitar 1 Outline The Hyperon-Nucleon and Hyperon-Hyperon
Can hadronic rescattering explain the jet quenching at relativistic energies?
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 71, 3496 (25) Can hadronic rescattering explain the jet quenching at relativistic energies? David Hardtke Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley, California 9472 USA
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 71, 3496 (25) Can hadronic rescattering explain the jet quenching at relativistic energies? David Hardtke Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley, California 9472 USA
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements
 Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department. Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas Abstract
 Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Track Reconstruction and Muon Identification in the Muon Detector of the CBM Experiment at FAIR
 Track Reconstruction and Muon Identification in the Muon Detector of the CBM Experiment at FAIR ab, Claudia Höhne a, Ivan Kisel ac, Anna Kiseleva a and Gennady Ososkov b for the CBM collaboration a GSI
Track Reconstruction and Muon Identification in the Muon Detector of the CBM Experiment at FAIR ab, Claudia Höhne a, Ivan Kisel ac, Anna Kiseleva a and Gennady Ososkov b for the CBM collaboration a GSI
Thermal dileptons from coarse-grained transport as probes of hot and dense QCD matter
 Thermal dileptons from coarse-grained transport as probes of hot and dense QCD matter Lunch Club Seminar, Universität Gießen Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
Thermal dileptons from coarse-grained transport as probes of hot and dense QCD matter Lunch Club Seminar, Universität Gießen Florian Seck TU Darmstadt in collaboration with T. Galatyuk, R. Rapp & J. Stroth
Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Resonance analysis in pp collisions with the ALICE detector
 IL NUOVO CIMENO Vol.?, N.?? Resonance analysis in pp collisions with the ALICE detector A Pulvirenti( 1 )( 2 )( ), for the ALICE Collaboration ( 1 ) INFN, Sezione di Catania ( 2 ) Università di Catania
IL NUOVO CIMENO Vol.?, N.?? Resonance analysis in pp collisions with the ALICE detector A Pulvirenti( 1 )( 2 )( ), for the ALICE Collaboration ( 1 ) INFN, Sezione di Catania ( 2 ) Università di Catania
Probing dense baryonic matter with kaons: The nuclear equation-of-state In medium properties of strange mesons
 Kaon production in nucleus-nucleus collisions XI International Conference on Hypernuclear and Strange Particle Physics, October 10 14, Mainz, Germany Peter Senger (GSI) Probing dense baryonic matter with
Kaon production in nucleus-nucleus collisions XI International Conference on Hypernuclear and Strange Particle Physics, October 10 14, Mainz, Germany Peter Senger (GSI) Probing dense baryonic matter with
& Λ Production in ALICE
 Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title High pt inclusive charged hadron spectra from Au+Au collisions at Sqrt(s_NN)=00 Gev Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3jp4v8vd
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title High pt inclusive charged hadron spectra from Au+Au collisions at Sqrt(s_NN)=00 Gev Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3jp4v8vd
Multiplicity dependence of charged pion, kaon, and (anti)proton production at large transverse momentum in p-pb collisions at 5.
 [1] Multiplicity dependence of charged pion, kaon, and (anti)proton production at large transverse momentum in p-pb collisions at 5.02 ATeV Gyula Bencedi (Wigner RCP, Hungary) on behalf of the ALICE Collaboration
[1] Multiplicity dependence of charged pion, kaon, and (anti)proton production at large transverse momentum in p-pb collisions at 5.02 ATeV Gyula Bencedi (Wigner RCP, Hungary) on behalf of the ALICE Collaboration
New Limits on Heavy Neutrino from NA62
 CERN E-mail: michal.koval@cern.ch The NA6 experiment at CERN collected large samples of charged kaon decays in flight with a minimum bias trigger configuration in 7 and in 15 using a completely new detector
CERN E-mail: michal.koval@cern.ch The NA6 experiment at CERN collected large samples of charged kaon decays in flight with a minimum bias trigger configuration in 7 and in 15 using a completely new detector
Hints of incomplete thermalization in RHIC data
 Hints of incomplete thermalization in RHIC data Nicolas BORGHINI CERN in collaboration with R.S. BHALERAO Mumbai J.-P. BLAIZOT ECT J.-Y. OLLITRAULT Saclay N. BORGHINI p.1/30 RHIC Au Au results: the fashionable
Hints of incomplete thermalization in RHIC data Nicolas BORGHINI CERN in collaboration with R.S. BHALERAO Mumbai J.-P. BLAIZOT ECT J.-Y. OLLITRAULT Saclay N. BORGHINI p.1/30 RHIC Au Au results: the fashionable
arxiv:hep-ph/ v3 5 Dec 2005
 Acta Phys. Hung. A 19/1 (2005) 000 000 HEAVY ION PHYSICS Rapidity equilibration in d + Au and Au + Au systems arxiv:hep-ph/0509108v3 5 Dec 2005 Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität,
Acta Phys. Hung. A 19/1 (2005) 000 000 HEAVY ION PHYSICS Rapidity equilibration in d + Au and Au + Au systems arxiv:hep-ph/0509108v3 5 Dec 2005 Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität,
Review of photon physics results at Quark Matter 2012
 Review of photon physics results at Quark Matter 2012 Jet Gustavo Conesa Balbastre 1/28 Why photons? Direct thermal: Produced by the QGP Measure medium temperature R AA > 1, v 2 > 0 Direct prompt: QCD
Review of photon physics results at Quark Matter 2012 Jet Gustavo Conesa Balbastre 1/28 Why photons? Direct thermal: Produced by the QGP Measure medium temperature R AA > 1, v 2 > 0 Direct prompt: QCD
Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c
 Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 2003 Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c K. N. Barish, S. Batsouli, S. J. Bennett, M. Bertaina, A.
Physics Physics Research Publications Purdue University Year 2003 Measurement of leading Lambda s and Delta(++) s in p+pb collisions at 19 GeV/c K. N. Barish, S. Batsouli, S. J. Bennett, M. Bertaina, A.
Final source eccentricity measured by HBT interferometry with the event shape selection
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Final source eccentricity measured by HB interferometry with the event shape o cite this article: akafumi Niida and PHENIX Collaboration J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Final source eccentricity measured by HB interferometry with the event shape o cite this article: akafumi Niida and PHENIX Collaboration J. Phys.:
Global and Collective Dynamics at PHENIX
 Global and Collective Dynamics at PHENIX Takafumi Niida for the PHENIX Collaboration University of Tsukuba Heavy Ion collisions in the LHC era in Quy Nhon outline n Introduction of v n n Higher harmonic
Global and Collective Dynamics at PHENIX Takafumi Niida for the PHENIX Collaboration University of Tsukuba Heavy Ion collisions in the LHC era in Quy Nhon outline n Introduction of v n n Higher harmonic
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 28 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 28 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 28 Nov 2017](/thumbs/89/98876960.jpg) Initial state and hydrodynamic modeling of heavy-ion collisions at RHIC BES energies arxiv:1711.1544v1 [nucl-th] 28 Nov 217 Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA E-mail:
Initial state and hydrodynamic modeling of heavy-ion collisions at RHIC BES energies arxiv:1711.1544v1 [nucl-th] 28 Nov 217 Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA E-mail:
COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67, No. 3, P. 831 836, 2015 COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67, No. 3, P. 831 836, 2015 COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Analysis of a bubble chamber picture
 PHY 4822L (Advanced Laboratory): Analysis of a bubble chamber picture Introduction In this experiment you will study a reaction between elementary particles by analyzing their tracks in a bubble chamber.
PHY 4822L (Advanced Laboratory): Analysis of a bubble chamber picture Introduction In this experiment you will study a reaction between elementary particles by analyzing their tracks in a bubble chamber.
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 13 Dec 2005
 The Ratio Σ /Λ at RHIC arxiv:nucl-ex/58v 3 Dec 5 G. Van Buren for the STAR Collaboration Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 973-5 USA E-mail: gene@bnl.gov Abstract While yields
The Ratio Σ /Λ at RHIC arxiv:nucl-ex/58v 3 Dec 5 G. Van Buren for the STAR Collaboration Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 973-5 USA E-mail: gene@bnl.gov Abstract While yields
The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum?
 The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum? L. Phair, L.G. Moretto, J.B. Elliott, G.J. Wozniak Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Nuclear Liquid-Vapor Phase Transition: Equilibrium Between Phases Or Free Decay In Vacuum? L. Phair, L.G. Moretto, J.B. Elliott, G.J. Wozniak Nuclear Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Analysis of a bubble chamber picture
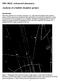 PHY 4822L (Advanced Laboratory): Analysis of a bubble chamber picture Introduction Elementary particles are everywhere around us [1,2]. Apart from the standard matter particles proton, neutron and electron,
PHY 4822L (Advanced Laboratory): Analysis of a bubble chamber picture Introduction Elementary particles are everywhere around us [1,2]. Apart from the standard matter particles proton, neutron and electron,
arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 15 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 15 Jul 2016 arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 15 Jul 2016](/thumbs/82/86957993.jpg) Muon Identification with Muon Telescope Detector at the STAR Experiment T.C. Huang a, R. Ma b, B. Huang d, X. Huang c, L. Ruan b, T. Todoroki b, Z. Xu b, C. Yang e, S. Yang e, Q. Yang e, Y. Yang a,, W.
Muon Identification with Muon Telescope Detector at the STAR Experiment T.C. Huang a, R. Ma b, B. Huang d, X. Huang c, L. Ruan b, T. Todoroki b, Z. Xu b, C. Yang e, S. Yang e, Q. Yang e, Y. Yang a,, W.
Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 CMS CR - he Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH- GENEVA 3, Switzerland 8/5/6 Charmonium production measured in and pp collisions by CMS arxiv:7.5v [nucl-ex]
CMS CR - he Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH- GENEVA 3, Switzerland 8/5/6 Charmonium production measured in and pp collisions by CMS arxiv:7.5v [nucl-ex]
PoS(Bormio2012)013. K 0 production in pp and pnb reactions. Jia-Chii Berger-Chen
 Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Can Momentum Correlations Proof Kinetic Equilibration in. Heavy Ion Collisions at 160 AGeV?
 Can Momentum Correlations Proof Kinetic Equilibration in Heavy Ion Collisions at 160 AGeV? M. Bleicher a, M. Belkacem a, C. Ernst a, H. Weber a, L. Gerland a, C. Spieles a, S. A. Bass b, H. Stöcker a,
Can Momentum Correlations Proof Kinetic Equilibration in Heavy Ion Collisions at 160 AGeV? M. Bleicher a, M. Belkacem a, C. Ernst a, H. Weber a, L. Gerland a, C. Spieles a, S. A. Bass b, H. Stöcker a,
Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions
 Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions Kristen Parzuchowski Research Experience for Undergraduates Wayne State University August 7, 2015 Abstract The study of nuclear matter is
Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions Kristen Parzuchowski Research Experience for Undergraduates Wayne State University August 7, 2015 Abstract The study of nuclear matter is
Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions. Georg Wolschin. Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany
 Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany Heavy-ion collisions at relativistic energy have been investigated for many
Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany Heavy-ion collisions at relativistic energy have been investigated for many
Recent Result on Pentaquark Searches from
 Recent Result on Pentaquark Searches from STAR @RHIC Huan Z. Huang Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California, Los Angeles The STAR Collaboration Pentaquark Workshop @JLab, Oct. 2005
Recent Result on Pentaquark Searches from STAR @RHIC Huan Z. Huang Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California, Los Angeles The STAR Collaboration Pentaquark Workshop @JLab, Oct. 2005
Outline: Introduction
 Electromagnetic radiation in hadronic interactions: from pp to AA collisions Outline: Introduction Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Recent results on dileptons (dielectrons) Recent results
Electromagnetic radiation in hadronic interactions: from pp to AA collisions Outline: Introduction Lijuan Ruan (Brookhaven National Laboratory) Recent results on dileptons (dielectrons) Recent results
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR
 Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 5
 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 5 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 5 Edited by Wolfgang Bauer Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan and Gary D. Westfall Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan
Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 5 Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 5 Edited by Wolfgang Bauer Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan and Gary D. Westfall Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan
THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC. Abstract
 F,' A RHIC Summer S t u d y 1996: T h e o r y Workshop on RHI Collision, BNL, Upton, NY July 8-19, 1996. THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC FLEMMING VIDEBBK Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory,
F,' A RHIC Summer S t u d y 1996: T h e o r y Workshop on RHI Collision, BNL, Upton, NY July 8-19, 1996. THE BRAHMS EXPERIMENT AT RHIC FLEMMING VIDEBBK Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory,
Selected Results on Strong and Coulomb-Induced Correlations from the STAR Experiment
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 95 Selected Results on Strong and oulomb-induced orrelations from the STAR Experiment M. Šumbera for the STAR ollaboration Nuclear Physics Institute,
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 37, no. 3A, September, 7 95 Selected Results on Strong and oulomb-induced orrelations from the STAR Experiment M. Šumbera for the STAR ollaboration Nuclear Physics Institute,
arxiv:hep-ph/ v2 5 Jan 2007
 Chemical Equilibrium in Heavy Ion Collisions: Rapidity Dependence. arxiv:hep-ph/7129v2 5 Jan 27, 1. Introduction F. Becattini 1, J. Cleymans 2 1 1, Università di Firenze and INFN Sezione di Firenze Largo
Chemical Equilibrium in Heavy Ion Collisions: Rapidity Dependence. arxiv:hep-ph/7129v2 5 Jan 27, 1. Introduction F. Becattini 1, J. Cleymans 2 1 1, Università di Firenze and INFN Sezione di Firenze Largo
