Regression. Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
|
|
|
- Sharlene Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Regression Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
2 Regression: Output a scalar Stock Market Forecast f Self-driving Car = Dow Jones Industrial Average at tomorrow f = 方向盤角度 Recommendation f = 使用者 A 商品 B 購買可能性
3 Example Application Estimating the Combat Power (CP) of a pokemon after evolution x cp f = x s x hp x CP after evolution y x w x h
4 Step 1: Model y = b + w x cp A set of function Model f 1, f 2 w and b are parameters (can be any value) f 1 : y = x cp f 2 : y = x cp f 3 : y = x cp infinite f x = CP after evolution y Linear model: y = b + w i x i x i : x cp, x hp, x w, x h feature w i : weight, b: bias
5 Step 2: Goodness of Function y = b + w x cp A set of function Model f 1, f 2 function input: x 1 function Output (scalar): y 1 x 2 y 2 Training Data
6 Step 2: Goodness of Function Training Data: 10 pokemons x 1, y 1 x 2, y 2 x n cp, y n x 10, y 10 y This is real data. x cp Source:
7 Step 2: Goodness of Function y = b + w x cp A set of function Goodness of function f Training Data Model f 1, f 2 L f Loss function L: 10 = n=1 L w, b 10 = Input: a function, output: how bad it is Sum over examples n=1 Estimation error y n n f x cp 2 Estimated y based on input function y n b + w xn cp 2
8 Step 2: Goodness of Function Loss Function 10 L w, b = n=1 y n b + w xn cp 2 Each point in the figure is a function smallest The color represents L w, b. y = x cp Very large (true example)
9 Step 3: Best Function A set of function Model f 1, f 2 L w, b 10 = n=1 y n b + w xn cp 2 Goodness of function f Training Data Pick the Best Function f = arg min f L f w, b = arg min w,b L w, b 10 = arg min w,b n=1 Gradient Descent y n b + w xn cp 2
10 Step 3: Gradient Descent bum/photo/ w = arg min L w w Consider loss function L(w) with one parameter w: Loss L w (Randomly) Pick an initial value w 0 Compute dl dw w=w 0 Negative Positive Increase w Decrease w w 0 w
11 Step 3: Gradient Descent bum/photo/ w = arg min L w w Consider loss function L(w) with one parameter w: Loss L w (Randomly) Pick an initial value w 0 Compute dl dw w=w 0 w 1 w 0 η dl dw w=w 0 w 0 η dl dw w=w 0 η is called learning rate w
12 Step 3: Gradient Descent w = arg min L w w Consider loss function L(w) with one parameter w: Loss L w (Randomly) Pick an initial value w 0 Compute dl dw w=w 0 Compute dl dw w=w 1 Many iteration w 1 w 0 η dl dw w=w 0 w 2 w 1 η dl dw w=w 1 w 0 Local minima w 1 w 2 w T global minima w
13 L Step 3: Gradient Descent L = w L b gradient How about two parameters? w, b = arg min w,b L w, b (Randomly) Pick an initial value w 0, b 0 Compute L L w w=w 0,b=b0, b w=w 0,b=b 0 w 1 w 0 η L w w=w 0,b=b 0 b 1 b 0 η L b w=w 0,b=b 0 Compute L L w w=w 1,b=b1, b w=w 1,b=b 1 w 2 w 1 η L w w=w 1,b=b 1 b 2 b 1 η L b w=w 1,b=b 1
14 Step 3: Gradient Descent w Color: Value of Loss L(w,b) ( η Compute Τ L b, η Τ L b, Τ L w) Τ L w b
15 Step 3: Gradient Descent When solving: θ = arg max θ L θ by gradient descent Each time we update the parameters, we obtain θ that makes L θ smaller. L θ 0 > L θ 1 > L θ 2 > Is this statement correct?
16 Step 3: Gradient Descent Loss Very slow at L the plateau Stuck at saddle point w 1 w 2 Stuck at local minima L w 0 L w = 0 L w = 0 The value of the parameter w
17 Step 3: Gradient Descent Formulation of Τ L w and Τ L b 10 L w, b = n=1 y n n b + w x cp 2 L w =? 10 n=1 2 y n b + w xn cp xn cp L b =?
18 Step 3: Gradient Descent Formulation of Τ L w and Τ L b 10 L w, b = n=1 y n n b + w x cp 2 L w =? L b =? 10 n=1 10 n=1 2 y n b + w xn cp 2 y n n b + w x cp xn cp 1
19 Step 3: Gradient Descent
20 How s the results? y = b + w x cp b = w = 2.7 Average Error on Training Data Training Data e 2 e 1 10 = 1 10 n=1 e n = 31.9
21 How s the results? - Generalization What we really care about is the error on new data (testing data) y = b + w x cp b = w = 2.7 Average Error on Testing Data Another 10 pokemons as testing data How can we do better? 10 = 1 10 n=1 e n = 35.0 > Average Error on Training Data (31.9)
22 Selecting another Model y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 Best Function b = w 1 = 1.0, w 2 = 2.7 x 10-3 Average Error = 15.4 Testing: Average Error = 18.4 Better! Could it be even better?
23 Selecting another Model y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 Best Function b = 6.4, w 1 = 0.66 w 2 = 4.3 x 10-3 w 3 = -1.8 x 10-6 Average Error = 15.3 Testing: Average Error = 18.1 Slightly better. How about more complex model?
24 Selecting another Model y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 + w 4 (x cp ) 4 Best Function Average Error = 14.9 Testing: Average Error = 28.8 The results become worse...
25 Selecting another Model y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 + w 4 (x cp ) 4 + w 5 (x cp ) 5 Best Function Average Error = 12.8 Testing: Average Error = The results are so bad.
26 Training Data Model Selection y = b + w x cp y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 + w 4 (x cp ) 4 y = b + w 1 x cp + w 2 (x cp ) 2 + w 3 (x cp ) 3 + w 4 (x cp ) 4 + w 5 (x cp ) 5 A more complex model yields lower error on training data. If we can truly find the best function
27 Model Selection Overfitting Training Testing A more complex model does not always lead to better performance on testing data. This is Overfitting. Select suitable model
28 Let s collect more data There is some hidden factors not considered in the previous model
29 What are the hidden factors? Eevee Pidgey Weedle Caterpie
30 Back to step 1: Redesign the Model x s = species of x x y = b + w i x i Linear model? If x s = Pidgey: If x s = Weedle: If x s = Caterpie: If x s = Eevee: y = b 1 + w 1 x cp y = b 2 + w 2 x cp y = b 3 + w 3 x cp y = b 4 + w 4 x cp y
31 Back to step 1: Redesign the Model 1 y = b 1 δ x s = Pidgey 1 +w 1 δ x s = Pidgey x cp 0 +b 2 δ x s = Weedle 0 +w 2 δ x s = Weedle x cp 0 +b 3 δ x s = Caterpie 0 +w 3 δ x s = Caterpie x cp 0 +b 4 δ x s = Eevee 0 x cp +w 4 δ x s = Eevee x cp y = b + w i x i Linear model? δ x s = Pidgey =1 If x s = Pidgey =0 otherwise If x s = Pidgey y = b 1 + w 1 x cp
32 Average error = 3.8 Training Data Average error = 14.3 Testing Data
33 CP after evolution CP after evolution CP after evolution Are there any other hidden factors? weight Height HP
34 Back to step 1: Redesign the Model Again x 2 If x s = Pidgey: y = b 1 + w 1 x cp + w 5 x cp 2 If x s = Weedle: y = b 2 + w 2 x cp + w 6 x cp 2 If x s = Caterpie: y = b 3 + w 3 x cp + w 7 x cp 2 If x s = Eevee: y = b 4 + w 4 x cp + w 8 x cp 2 y = y + w 9 x hp + w 10 x hp +w 11 x h + w 12 x 2 2 h + w 13 x w + w 14 x w Training Error = 1.9 Testing Error = Overfitting! y
35 Back to step 2: Regularization y = b + w i x i 2 The functions with smaller w i are better L = n y n b + w i x i +λ w i 2 Smaller w i means smoother y = b + w i x i y + w i Δx i = b + w i (x i +Δx i ) We believe smoother function is more likely to be correct Do you have to apply regularization on bias?
36 Regularization smoother λ Training Testing How smooth? Select λ obtaining the best model Training error: largerλ, considering the training error less We prefer smooth function, but don t be too smooth.
37 Conclusion Pokémon: Original CP and species almost decide the CP after evolution There are probably other hidden factors Gradient descent More theory and tips in the following lectures We finally get average error = 11.1 on the testing data How about new data? Larger error? Lower error? Next lecture: Where does the error come from? More theory about overfitting and regularization The concept of validation
38 Reference Bishop: Chapter 1.1
39 Acknowledgment 感謝鄭凱文同學發現投影片上的符號錯誤 感謝童寬同學發現投影片上的符號錯誤 感謝黃振綸同學發現課程網頁上影片連結錯誤的符號錯誤
Deep Learning. Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
 Deep Learning Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD 206/Jeff Dean 958: Perceptron
Deep Learning Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD 206/Jeff Dean 958: Perceptron
Classification: Probabilistic Generative Model
 Classification: Probabilistic Generative Model Classification x Function Class n Credit Scoring Input: income, savings, profession, age, past financial history Output: accept or refuse Medical Diagnosis
Classification: Probabilistic Generative Model Classification x Function Class n Credit Scoring Input: income, savings, profession, age, past financial history Output: accept or refuse Medical Diagnosis
Deep Reinforcement Learning. Scratching the surface
 Deep Reinforcement Learning Scratching the surface Deep Reinforcement Learning Scenario of Reinforcement Learning Observation State Agent Action Change the environment Don t do that Reward Environment
Deep Reinforcement Learning Scratching the surface Deep Reinforcement Learning Scenario of Reinforcement Learning Observation State Agent Action Change the environment Don t do that Reward Environment
Deep learning attracts lots of attention.
 Deep Learning Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD/Jeff Dean Ups and downs of Deep Learning
Deep Learning Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD/Jeff Dean Ups and downs of Deep Learning
Unsupervised Learning: Linear Dimension Reduction
 Unsupervised Learning: Linear Dimension Reduction Unsupervised Learning Clustering & Dimension Reduction ( 化繁為簡 ) Generation ( 無中生有 ) only having function input function only having function output function
Unsupervised Learning: Linear Dimension Reduction Unsupervised Learning Clustering & Dimension Reduction ( 化繁為簡 ) Generation ( 無中生有 ) only having function input function only having function output function
Convolutional Neural Network. Hung-yi Lee
 al Neural Network Hung-yi Lee Why CNN for Image? [Zeiler, M. D., ECCV 2014] x 1 x 2 Represented as pixels x N The most basic classifiers Use 1 st layer as module to build classifiers Use 2 nd layer as
al Neural Network Hung-yi Lee Why CNN for Image? [Zeiler, M. D., ECCV 2014] x 1 x 2 Represented as pixels x N The most basic classifiers Use 1 st layer as module to build classifiers Use 2 nd layer as
More Tips for Training Neural Network. Hung-yi Lee
 More Tips for Training Neural Network Hung-yi ee Outline Activation Function Cost Function Data Preprocessing Training Generalization Review: Training Neural Network Neural network: f ; θ : input (vector)
More Tips for Training Neural Network Hung-yi ee Outline Activation Function Cost Function Data Preprocessing Training Generalization Review: Training Neural Network Neural network: f ; θ : input (vector)
Semi-supervised Learning
 Semi-supervised Learning Introduction Supervised learning: x r, y r R r=1 E.g.x r : image, y r : class labels Semi-supervised learning: x r, y r r=1 R, x u R+U u=r A set of unlabeled data, usually U >>
Semi-supervised Learning Introduction Supervised learning: x r, y r R r=1 E.g.x r : image, y r : class labels Semi-supervised learning: x r, y r r=1 R, x u R+U u=r A set of unlabeled data, usually U >>
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Language Modeling. Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
 Language Modeling Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Language modeling Language model: Estimated the probability of word sequence Word sequence: w 1, w 2, w 3,., w n P(w 1, w 2, w 3,., w n ) Application: speech recognition
Language Modeling Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Language modeling Language model: Estimated the probability of word sequence Word sequence: w 1, w 2, w 3,., w n P(w 1, w 2, w 3,., w n ) Application: speech recognition
Optimization and Gradient Descent
 Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
 What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
CSC321 Lecture 2: Linear Regression
 CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression / 26 Overview First learning algorithm of the course: linear regression Task: predict scalar-valued targets,
CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression / 26 Overview First learning algorithm of the course: linear regression Task: predict scalar-valued targets,
Deep Learning Tutorial. 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee
 Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Deep learning attracts lots of attention. Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. The talks in this afternoon This talk will focus on the technical
Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Deep learning attracts lots of attention. Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. The talks in this afternoon This talk will focus on the technical
Tips for Deep Learning
 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
CSC 411: Lecture 04: Logistic Regression
 CSC 411: Lecture 04: Logistic Regression Raquel Urtasun & Rich Zemel University of Toronto Sep 23, 2015 Urtasun & Zemel (UofT) CSC 411: 04-Prob Classif Sep 23, 2015 1 / 16 Today Key Concepts: Logistic
CSC 411: Lecture 04: Logistic Regression Raquel Urtasun & Rich Zemel University of Toronto Sep 23, 2015 Urtasun & Zemel (UofT) CSC 411: 04-Prob Classif Sep 23, 2015 1 / 16 Today Key Concepts: Logistic
Day 3 Lecture 3. Optimizing deep networks
 Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
Tips for Deep Learning
 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Introduction to Natural Computation. Lecture 9. Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation. Peter Lewis
 Introduction to Natural Computation Lecture 9 Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Peter Lewis 1 / 25 Overview of the Lecture Why multilayer perceptrons? Some applications of multilayer perceptrons.
Introduction to Natural Computation Lecture 9 Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Peter Lewis 1 / 25 Overview of the Lecture Why multilayer perceptrons? Some applications of multilayer perceptrons.
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Linear Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574 1
Introduction to Machine Learning Linear Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574 1
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Gradient Descent. Sargur Srihari
 Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018
 Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018 Teacher: Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan A few important informations: In the final exam, no electronic devices are allowed except a calculator. Make sure
Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018 Teacher: Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan A few important informations: In the final exam, no electronic devices are allowed except a calculator. Make sure
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
Advanced Machine Learning
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 4: Deep Learning Essentials Pierre Geurts, Gilles Louppe, Louis Wehenkel 1 / 52 Outline Goal: explain and motivate the basic constructs of neural networks. From linear
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 4: Deep Learning Essentials Pierre Geurts, Gilles Louppe, Louis Wehenkel 1 / 52 Outline Goal: explain and motivate the basic constructs of neural networks. From linear
Beyond Vectors. Hung-yi Lee
 Beyond Vectors Hung-yi Lee Introduction Many things can be considered as vectors. E.g. a function can be regarded as a vector We can apply the concept we learned on those vectors. Linear combination Span
Beyond Vectors Hung-yi Lee Introduction Many things can be considered as vectors. E.g. a function can be regarded as a vector We can apply the concept we learned on those vectors. Linear combination Span
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
CSC 411 Lecture 6: Linear Regression
 CSC 411 Lecture 6: Linear Regression Roger Grosse, Amir-massoud Farahmand, and Juan Carrasquilla University of Toronto UofT CSC 411: 06-Linear Regression 1 / 37 A Timely XKCD UofT CSC 411: 06-Linear Regression
CSC 411 Lecture 6: Linear Regression Roger Grosse, Amir-massoud Farahmand, and Juan Carrasquilla University of Toronto UofT CSC 411: 06-Linear Regression 1 / 37 A Timely XKCD UofT CSC 411: 06-Linear Regression
Neural networks III: The delta learning rule with semilinear activation function
 Neural networks III: The delta learning rule with semilinear activation function The standard delta rule essentially implements gradient descent in sum-squared error for linear activation functions. We
Neural networks III: The delta learning rule with semilinear activation function The standard delta rule essentially implements gradient descent in sum-squared error for linear activation functions. We
CSC 411: Lecture 02: Linear Regression
 CSC 411: Lecture 02: Linear Regression Richard Zemel, Raquel Urtasun and Sanja Fidler University of Toronto (Most plots in this lecture are from Bishop s book) Zemel, Urtasun, Fidler (UofT) CSC 411: 02-Regression
CSC 411: Lecture 02: Linear Regression Richard Zemel, Raquel Urtasun and Sanja Fidler University of Toronto (Most plots in this lecture are from Bishop s book) Zemel, Urtasun, Fidler (UofT) CSC 411: 02-Regression
Introduction of Reinforcement Learning
 Introduction of Reinforcement Learning Deep Reinforcement Learning Reference Textbook: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction http://incompleteideas.net/sutton/book/the-book.html Lectures of David Silver
Introduction of Reinforcement Learning Deep Reinforcement Learning Reference Textbook: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction http://incompleteideas.net/sutton/book/the-book.html Lectures of David Silver
Vasil Khalidov & Miles Hansard. C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks
 C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks Introduction The aim is, as before, to find useful decompositions of the target variable; t(x) = y(x, w) + ɛ(x) (3.7) t(x n ) and x n are the observations,
C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks Introduction The aim is, as before, to find useful decompositions of the target variable; t(x) = y(x, w) + ɛ(x) (3.7) t(x n ) and x n are the observations,
CSC242: Intro to AI. Lecture 21
 CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
Linear Regression. Applied Linear Regression Models (Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li) hsuhl (NUK) SDA Regression 1 / 34
 Linear Regression 許湘伶 Applied Linear Regression Models (Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li) hsuhl (NUK) SDA Regression 1 / 34 Regression analysis is a statistical methodology that utilizes the relation between
Linear Regression 許湘伶 Applied Linear Regression Models (Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li) hsuhl (NUK) SDA Regression 1 / 34 Regression analysis is a statistical methodology that utilizes the relation between
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Logistic Regression. Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Tutorial 8 CPSC 340 Logistic Regression Stochastic Gradient Descent Logistic Regression Model A discriminative probabilistic model for classification e.g. spam filtering Let x R d be input and y { 1, 1}
Tutorial 8 CPSC 340 Logistic Regression Stochastic Gradient Descent Logistic Regression Model A discriminative probabilistic model for classification e.g. spam filtering Let x R d be input and y { 1, 1}
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses about the label (Top-5 error) No Bounding Box
 ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
Deep Learning Tutorial. 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee
 Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Outline Part I: Introduction of Deep Learning Part II: Why Deep? Part III: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network Part IV: Neural Network with Memory Part I: Introduction
Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Outline Part I: Introduction of Deep Learning Part II: Why Deep? Part III: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network Part IV: Neural Network with Memory Part I: Introduction
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks
 Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Week 5: Logistic Regression & Neural Networks
 Week 5: Logistic Regression & Neural Networks Instructor: Sergey Levine 1 Summary: Logistic Regression In the previous lecture, we covered logistic regression. To recap, logistic regression models and
Week 5: Logistic Regression & Neural Networks Instructor: Sergey Levine 1 Summary: Logistic Regression In the previous lecture, we covered logistic regression. To recap, logistic regression models and
Computational statistics
 Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Linear classifiers: Logistic regression
 Linear classifiers: Logistic regression STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 19, 2018 How confident is your prediction? The sushi & everything else were awesome! The
Linear classifiers: Logistic regression STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 19, 2018 How confident is your prediction? The sushi & everything else were awesome! The
More Optimization. Optimization Methods. Methods
 More More Optimization Optimization Methods Methods Yann YannLeCun LeCun Courant CourantInstitute Institute http://yann.lecun.com http://yann.lecun.com (almost) (almost) everything everything you've you've
More More Optimization Optimization Methods Methods Yann YannLeCun LeCun Courant CourantInstitute Institute http://yann.lecun.com http://yann.lecun.com (almost) (almost) everything everything you've you've
Non-Convex Optimization in Machine Learning. Jan Mrkos AIC
 Non-Convex Optimization in Machine Learning Jan Mrkos AIC The Plan 1. Introduction 2. Non convexity 3. (Some) optimization approaches 4. Speed and stuff? Neural net universal approximation Theorem (1989):
Non-Convex Optimization in Machine Learning Jan Mrkos AIC The Plan 1. Introduction 2. Non convexity 3. (Some) optimization approaches 4. Speed and stuff? Neural net universal approximation Theorem (1989):
Overview. Probabilistic Interpretation of Linear Regression Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Estimation MAP Estimation
 Overview Probabilistic Interpretation of Linear Regression Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Estimation MAP Estimation Probabilistic Interpretation: Linear Regression Assume output y is generated
Overview Probabilistic Interpretation of Linear Regression Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Estimation MAP Estimation Probabilistic Interpretation: Linear Regression Assume output y is generated
Machine Learning CS 4900/5900. Lecture 03. Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Machine Learning CS 4900/5900 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Machine Learning is Optimization Parametric ML involves minimizing an objective function
Machine Learning CS 4900/5900 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Machine Learning is Optimization Parametric ML involves minimizing an objective function
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS
 CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
Machine Learning Techniques
 Machine Learning Techniques ( 機器學習技法 ) Lecture 15: Matrix Factorization Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University
Machine Learning Techniques ( 機器學習技法 ) Lecture 15: Matrix Factorization Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University
Introduction to Neural Networks
 CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization
 Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
VBM683 Machine Learning
 VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
Machine Learning Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University. September 20, 2012
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 20, 2012 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 20, 2012 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning. Lecture 04: Logistic and Softmax Regression. Nevin L. Zhang
 Machine Learning Lecture 04: Logistic and Softmax Regression Nevin L. Zhang lzhang@cse.ust.hk Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology This set
Machine Learning Lecture 04: Logistic and Softmax Regression Nevin L. Zhang lzhang@cse.ust.hk Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology This set
Portfolio Optimization
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#12 (Monday October 8) Portfolio Optimization Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Ji Zhang 1 1 Portfolio Optimization - No Regret Portfolio We want to
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#12 (Monday October 8) Portfolio Optimization Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Ji Zhang 1 1 Portfolio Optimization - No Regret Portfolio We want to
Statistical Machine Learning from Data
 January 17, 2006 Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Multi-Layer Perceptrons Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole
January 17, 2006 Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Multi-Layer Perceptrons Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients
 CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING
 Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD. CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017
 Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 2: Linear Classification. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Machine Learning Basics Lecture 2: Linear Classification Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d.
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 2: Linear Classification Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d.
Neural Nets Supervised learning
 6.034 Artificial Intelligence Big idea: Learning as acquiring a function on feature vectors Background Nearest Neighbors Identification Trees Neural Nets Neural Nets Supervised learning y s(z) w w 0 w
6.034 Artificial Intelligence Big idea: Learning as acquiring a function on feature vectors Background Nearest Neighbors Identification Trees Neural Nets Neural Nets Supervised learning y s(z) w w 0 w
CH 5 More on the analysis of consumer behavior
 個體經濟學一 M i c r o e c o n o m i c s (I) CH 5 More on the analysis of consumer behavior Figure74 An increase in the price of X, P x P x1 P x2, P x2 > P x1 Assume = 1 and m are fixed. m =e(p X2,, u 1 ) m=e(p
個體經濟學一 M i c r o e c o n o m i c s (I) CH 5 More on the analysis of consumer behavior Figure74 An increase in the price of X, P x P x1 P x2, P x2 > P x1 Assume = 1 and m are fixed. m =e(p X2,, u 1 ) m=e(p
Nonlinear Models. Numerical Methods for Deep Learning. Lars Ruthotto. Departments of Mathematics and Computer Science, Emory University.
 Nonlinear Models Numerical Methods for Deep Learning Lars Ruthotto Departments of Mathematics and Computer Science, Emory University Intro 1 Course Overview Intro 2 Course Overview Lecture 1: Linear Models
Nonlinear Models Numerical Methods for Deep Learning Lars Ruthotto Departments of Mathematics and Computer Science, Emory University Intro 1 Course Overview Intro 2 Course Overview Lecture 1: Linear Models
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization
 Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Logistic Regression. Professor Ameet Talwalkar. Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms January 25, / 48
 Logistic Regression Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms January 25, 2017 1 / 48 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Logistic regression
Logistic Regression Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms January 25, 2017 1 / 48 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Logistic regression
Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression
 Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting more generally COMP-652 and ECSE-68, Lecture
Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting more generally COMP-652 and ECSE-68, Lecture
Machine Learning. Lecture 2: Linear regression. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2017 Supervised Learning Regression: Predict
Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2017 Supervised Learning Regression: Predict
Logistic Regression Review Fall 2012 Recitation. September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu
 Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Modeling Data with Linear Combinations of Basis Functions. Read Chapter 3 in the text by Bishop
 Modeling Data with Linear Combinations of Basis Functions Read Chapter 3 in the text by Bishop A Type of Supervised Learning Problem We want to model data (x 1, t 1 ),..., (x N, t N ), where x i is a vector
Modeling Data with Linear Combinations of Basis Functions Read Chapter 3 in the text by Bishop A Type of Supervised Learning Problem We want to model data (x 1, t 1 ),..., (x N, t N ), where x i is a vector
Linear Regression. Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington. Oct 5, Kevin Jamieson 1
 Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Neural Networks. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Neural Networks CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Perceptrons x 0 = 1 x 1 x 2 z = h w T x Output: z x D A perceptron
Neural Networks CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Perceptrons x 0 = 1 x 1 x 2 z = h w T x Output: z x D A perceptron
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities. Kakade Announcements: Project Proposals: due this Friday!
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Machine Learning Basics III
 Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
LECTURE # - NEURAL COMPUTATION, Feb 04, Linear Regression. x 1 θ 1 output... θ M x M. Assumes a functional form
 LECTURE # - EURAL COPUTATIO, Feb 4, 4 Linear Regression Assumes a functional form f (, θ) = θ θ θ K θ (Eq) where = (,, ) are the attributes and θ = (θ, θ, θ ) are the function parameters Eample: f (, θ)
LECTURE # - EURAL COPUTATIO, Feb 4, 4 Linear Regression Assumes a functional form f (, θ) = θ θ θ K θ (Eq) where = (,, ) are the attributes and θ = (θ, θ, θ ) are the function parameters Eample: f (, θ)
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS16
 COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS6 Lecture 3: Classification with Logistic Regression Advanced optimization techniques Underfitting & Overfitting Model selection (Training-
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS6 Lecture 3: Classification with Logistic Regression Advanced optimization techniques Underfitting & Overfitting Model selection (Training-
Linear Regression. S. Sumitra
 Linear Regression S Sumitra Notations: x i : ith data point; x T : transpose of x; x ij : ith data point s jth attribute Let {(x 1, y 1 ), (x, y )(x N, y N )} be the given data, x i D and y i Y Here D
Linear Regression S Sumitra Notations: x i : ith data point; x T : transpose of x; x ij : ith data point s jth attribute Let {(x 1, y 1 ), (x, y )(x N, y N )} be the given data, x i D and y i Y Here D
Stochastic gradient descent; Classification
 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 2 28 September 2016 MLP Lecture 2 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification 1 Single Layer Networks MLP
Stochastic gradient descent; Classification Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 2 28 September 2016 MLP Lecture 2 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification 1 Single Layer Networks MLP
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University February 2, 2015 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University February 2, 2015 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms
 CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models I (LFD 3.2, 3.3) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 17, 2018 Linear Regression (LFD 3.2) Regression Classification: Customer record Yes/No Regression: predicting
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models I (LFD 3.2, 3.3) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 17, 2018 Linear Regression (LFD 3.2) Regression Classification: Customer record Yes/No Regression: predicting
An Adaptive Blind Channel Shortening Algorithm for MCM Systems
 Hacettepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering An Adaptive Blind Channel Shortening Algorithm for MCM Systems Blind, Adaptive Channel Shortening Equalizer Algorithm which provides
Hacettepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering An Adaptive Blind Channel Shortening Algorithm for MCM Systems Blind, Adaptive Channel Shortening Equalizer Algorithm which provides
Comments. Assignment 3 code released. Thought questions 3 due this week. Mini-project: hopefully you have started. implement classification algorithms
 Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Statistical Computing (36-350)
 Statistical Computing (36-350) Lecture 19: Optimization III: Constrained and Stochastic Optimization Cosma Shalizi 30 October 2013 Agenda Constraints and Penalties Constraints and penalties Stochastic
Statistical Computing (36-350) Lecture 19: Optimization III: Constrained and Stochastic Optimization Cosma Shalizi 30 October 2013 Agenda Constraints and Penalties Constraints and penalties Stochastic
Machine Learning. Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Non-Convex Optimization. CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017
 Non-Convex Optimization CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017 First some words about grading I sent out a bunch of grades on the course management system Everyone should have all their grades in Not including paper
Non-Convex Optimization CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017 First some words about grading I sent out a bunch of grades on the course management system Everyone should have all their grades in Not including paper
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
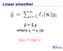 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
CS60021: Scalable Data Mining. Large Scale Machine Learning
 J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
Neural networks and optimization
 Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux INRIA 8 Nov 2011 Nicolas Le Roux (INRIA) Neural networks and optimization 8 Nov 2011 1 / 80 1 Introduction 2 Linear classifier 3 Convolutional neural networks
Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux INRIA 8 Nov 2011 Nicolas Le Roux (INRIA) Neural networks and optimization 8 Nov 2011 1 / 80 1 Introduction 2 Linear classifier 3 Convolutional neural networks
Lecture 2 - Learning Binary & Multi-class Classifiers from Labelled Training Data
 Lecture 2 - Learning Binary & Multi-class Classifiers from Labelled Training Data DD2424 March 23, 2017 Binary classification problem given labelled training data Have labelled training examples? Given
Lecture 2 - Learning Binary & Multi-class Classifiers from Labelled Training Data DD2424 March 23, 2017 Binary classification problem given labelled training data Have labelled training examples? Given
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Binary Classification / Perceptron
 Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Logistic Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning Logistic Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 7
 Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 7 Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Solving Convex Problems using SGD and RLM Shai Shalev-Shwartz (Hebrew
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 7 Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Solving Convex Problems using SGD and RLM Shai Shalev-Shwartz (Hebrew
