Background 1. Cramer-Rao inequality
|
|
|
- Michael Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bro-06, Lecture, D/Stt/Bro-06/tex wwwmstqueesuc/ blevit/ Observtio vector, dt: Bckgroud Crmer-Ro iequlity X (X,, X X R Here dt c be rel- or vector vlued, compoets of the dt c be idepedet or depedet, ideticlly distributed or ot; it c eve be rdom process Deote the desity of the dt by f(x θ, x X, θ Θ (, b R Assume tht f(x θ > 0, x X, f(x θ dx f(x piecewise cotiuosly differetible X Note o termiology: outside Sttistics, better kow kotio of Iformtio is due to C Sho (bout 950 However, The Fisher iformtio itroduced erlier (90-0 is more useful i Sttistics Score fuctio: Expected scores re zero: l(x θ : θ log f(x θ θ f(x θ f(x θ E X θ θ log f(x θ 0 Ideed, 0 d dθ X d f(x θ dx d dθ X dθ 0 f(x θ dx f(x θ dx l(x θf(x θ dx E X θ l(x θ θ X The Fisher iformtio I X (θ, cotied i the dt X bout the prmeter θ, for give θ: X I X (θ Vr X θ θ log f(x θ E X θ θ log f(x θ ( ( log f(x θ f(x θ dx f(x θ θ dx θ f(x θ The Crmer-Ro iequlity: For y ubised estimtor ψ ψ(x of ψ(θ, EX θ ( ψ(x ψ(θ, E X θ ( θ θ (ψ (θ I X (θ Exmple X (X,, X iid, X f(x θ The Fisher Iformtio cotied i y X i idividully:
2 I(θ Vr Xi θ ( θ log f(x i θ ( ( I X (θ Vr X θ θ log f(x θ f ( X θ Vr X θ i Vr Xi θ i ( θ log f(x i θ I(θ θ log f(x i θ Exmple X (X,, X iid, X N (θ, σ f(x i θ (x πσ e i θ σ log f(x i θ log (x i θ, πσ σ θ log f(x i θ X i θ σ ( Xi θ I(θ Vr Xi θ σ σ I X (θ σ Thus for y ubised estimtor θ of θ, The MLE is the best ubised estimtor: E X θ ( θ θ I X (θ σ ˆθ X + + X, E X θ ˆθ θ E X θ (ˆθ θ σ I X (θ A ubised estimtor trets ll θ R fily, or eqully But pose ext tht θ Θ (, b R estimtor θ does ot eed to be ubised We c cosider the mximl risk: d the miimx risk: r( θ, Θ E X θ ( θ θ r(θ if θ Miimx estimtors re oly kow i cse b 0 E X θ ( θ θ Elemets of the Decisio Theory Let λ(θ > 0, θ (, b, be weight fuctio: b λ(θ dθ
3 the verge, or Byes, risk of etimtor θ is R( θ, λ : b E X θ ( θ θ λ(θ dθ E X θ ( θ θ b ie the mximl risk does ot exceed the Byes risk of estimtor Also r( θ, Θ if θ R( θ, λ R(λ λ(θ dθ E X θ ( θ θ r( θ, Θ, d therefore, r(θ if r( θ, Θ R(λ θ Thus, the miimx risk is t lest s lrge s the Byes risk The Wld priciple: typiclly r(θ R(λ λ I the Byesi settig: λ(θ is viewed s the prior desity of θ, f X,θ (x, θ f(x θλ(θ is viewed s the joit desity of X d θ, R( θ, λ E θ ( E X θ ( θ(x θ E X,θ ( θ(x θ, ccordig to the Lw of Totl Expecttio Sice here we re delig simulteously with the coditiol d verge (Byes risk, d sice bove we hve defied the coditiol Fisher iformtio, give θ, it suggests itself turlly to defie the Byes, or verge, Fisher iformtio cotied i X, bout prmeter θ: By the Lw of Totl Expecttio, I X E θ { I X E X,θ θ log f(x θ E X θ θ log f(x θ } E θ (I X (θ b I X (θλ(θ dθ Kowig the prior distributio of θ lso provides some iformtio bout θ Agi the expected scores re zero: E θ ( d dθ log λ(θ 0 We c mesure this iformtio by the Fisher iformtio correspodig to the prior desity: I λ E θ ( d dθ log λ(θ Now we c defie the Totl Fisher iformtio joitly cotied i the dt, X, d i the prior distributio of θ: ( I E Xθ log (f(x θλ(θ θ Fisher iformtio is dditive : I I X + I λ I X (θλ(θ dt + I λ 3
4 Ideed, Corollry I E Xθ θ log (f(x θλ(θ E Xθ θ log f X(X θ + θ log λ(θ ( ( E θx θ log f X(X θ + E θ θ log λ(θ + E Xθ θ log f(x θ θ ( I X + I λ + E θ θ log λ(θe X θ log f(x θ I X + I λ θ X (X,, X iid f(x θ Cosider the mout of iformtio cotied i every sigle observtio idividully: I(θ E Xi θ ( θ log f(x i θ log λ(θ the totl Fisher iformtio I I X + I λ I(θλ(θ dθ + I λ I prticulr, i the cse we hve X (X,, X iid N (θ, σ, I σ + I λ v Trees iequlity: Byesi Crmer-Ro lower boud; see [], [] Assume tht λ(θ is piece-wise cotiuously differetible d λ( λ(b 0 for y estimtor ψ ψ(x of ψ(θ (cf the Crmer-Ro lower boud Corollry Uder the bove ssumptios, R( ψ, λ (E θψ (θ I E X θ ( ψ ψ(θ (E θψ (θ I Proof Let us tke look t the followig itegrl J : ( ψ(x ψ(θ (f(x θλ(θ dθdx θ ( ( ψ(x ψ(θf(x θλ(θ b θ ( ψ(x ψ(θf(x θλ(θ dθ dx ( ψ (θf(x θπ(θ dθ dx ψ (θλ(θ dθ E θ ψ (θ 4
5 O the other hd, E θ ψ (θ J ( ψ(x θ ψ(θ (f(x θλ(θ f(x θλ(θ dθdx f(x θλ(θ [ ( ] E Xθ ( ψ(x ψ(θ log (f(x θλ(θ θ By the Cuchy-Schwrz iequlity: (E θ ψ (θ E Xθ ( ψ(x ψ(θ E Xθ Corollry ( log (f(x θλ(θ IE θ θx ( ψ(x ψ(θ IR( ψ, λ X (X,, X iid f(x θ, θ (, b, for y piece-wise cotiuously differetible prior desity λ(θ > 0, θ (, b, λ( λ(b 0, d y estimtor ψ of ψ(θ, ( b ψ (θλ(θ dθ I prticulr, if mx E X θ( ψ ψ(θ b I(θλ(θ dθ + I λ X (X,, X iid N (θ, σ, θ (, b mx E X θ( θ θ + I σ λ Note Of the two terms pperig i the deomitor of the v Trees iequlity, the first oe is essetilly determied by the Fisher iformtio I(θ, wheres the prior kowledge tht θ (, b is mily cptured by the secod term i the deomitor The followig mkes this depedece more explicit Suppose (, b (ϑ δ, ϑ + δ where ϑ ( + b/ d δ (b / Let (resclig λ(θ ( θ ϑ δ λ 0 δ where λ 0 (θ is desity o (,, with the correspodig Fisher iformtio I λ ϑ+δ ϑ δ (λ (θ λ(θ dθ I λ0 (λ 0(θ λ 0 (θ ϑ+δ ( ( λ θ ϑ δ 0 δ ϑ δ λ ( θ ϑ δ 0 δ dθ < dθ δ (λ 0(θ λ 0 (θ dθ δ I λ0 Corollry X (X,, X iid f(x θ, θ (, b, for y piece-wise cotiuously differetible prior desity λ 0 (θ > 0, θ (,, λ 0 (± 0, d y estimtor ψ of ψ(θ, ( b ψ (θλ(θ dθ mx E X θ( ψ ψ(θ b I(θλ(θ dθ + δ I λ0 5
6 I prticulr, if X (X,, X iid N (θ, σ, θ (, b mx E X θ( θ θ + I λ 0 σ δ Oe c further improve the bove lower boud by miimizig the Fisher iformtio I λ0 Thus cosider the followig miimiztio problem: Deote I λ0 I λ0 mi, λ 0 (θ dθ λ 0 (θ ω (θ, ω(θ > 0, θ (,, ω(± 0 (λ 0(θ λ 0 (θ dθ This is costried miimiztio problem: (ω (θω(θ ω (θ dθ 4 (ω (θ dθ mi (ω (θ dθ mi, ω (θ dθ Euler-Lgrge equtio: ω (θ + cω(θ 0, ω(± 0 where c is the Lgrge multiplier The oly positive solutio of this equtio is ( πθ ω(θ cos Thus the desity λ 0 miimizig I λ0 d (the lest fvorble desity is ( πθ λ 0 (θ cos, θ I λ0 π Corollry 3 X (X,, X iid f(x θ, θ (, b, ssumig λ(θ is the lest fvorble desity o (, b (ϑ δ, ϑ + δ, for y estimtor ψ of ψ(θ, I prticulr, if for y estimtor θ of θ mx E X θ( ψ ψ(θ ( b ψ (θλ(θ dθ b I(θλ(θ dθ + π δ X (X,, X iid N (θ, σ, θ (, b mx E X θ( θ θ 6 + π σ δ
7 Applictios Asymptotic lower boud Let X (X,, X iid f(x θ Let I(θ be the Fisher iformtio cotied i y X i idividully, for y prior desity λ o [, b], d y estimtor θ, Thus E X θ ( θ θ θ (,b lim Also, for y (ϑ δ, ϑ + δ (, b lim θ (,b θ (,b E X θ ( θ θ lim b I(θλ(θ dθ + I λ E X θ ( θ θ θ (ϑ δ,ϑ+δ b I(θλ(θ dθ + I λ b I(θλ(θ dθ E X θ ( θ θ ϑ+δ ϑ δ I(θλ(θ dθ Therefore, ssumig tht I(θ is cotiuous fuctio, d lettig δ 0, we get, for y < ϑ < b, lim E( θ θ lim θ [,b] δ 0 θ [ϑ δ,ϑ+δ] I(θ I(ϑ Filly, for y (, b, d y sequece of estimtors θ, lim θ (,b E X θ ( θ θ θ (,b I(θ I prticulr, if X,, X iid N (θ, σ, the for y y sequece of estimtors θ d y < b, lim E( θ θ σ θ (,b For y (, b, equlity is chieved i this iequlity, for the MLE ˆθ Hece ˆθ is loclly symptoticlly miimx, mog ll possible estimtors (ot oly ubised Thus, we still c write σ ( + o( E( θ θ σ if we gree to iterprete this i the loclly symptoticlly miimx (LAM sese This is the best possible d complete chrcteriztio of the symptotic optimlity, mog ll possible estimtors Note, tht vlid poit-wise lower boud, i the clss of ll estimtors, is impossible becuse for y θ there exists estimtor which, for this prticulr θ, hs zero me squred error However, this result is, i certi sese trivil, becuse it does ot reflect the ifluece of the prior kowledge tht θ (, b o the optiml estimtor This is becuse such prior iformtio effects oly the secod order optiml properties Applictio Secod order miimx estimtio Let X,, X N (θ, σ, I(θ σ θ ( δ, δ for y estimtor θ E X θ ( θ θ θ ( δ,δ σ + π δ σ + π σ δ ( σ π σ δ 7
8 This lower boud is symptoticlly exct (chievble to the order A estimtor chievig this boud is secod order symptoticlly miimx Note tht lettig δ we get E X θ ( θ θ σ θ (, Thus ˆθ X is miimx i R, for y This rises ext questio whether itis lso dmissible Applictio 3 Admissibility Defiitio θ is dmissible if there is o other estimtor θ such tht E X θ ( θ θ E X θ ( θ θ, for ll θ Θ, E X θ ( θ θ < E X θ ( θ θ, for some θ Θ For y the MLE ˆθ X is dmissible Let us proof it i the cse σ, The geerl cse c be either treted quite similrly, or directly reduced to it by sufficiecy E X θ (ˆθ θ Let λ(θ be prior desity o (, Accordig to the v Trees iequlity, for y estimtor θ, Suppose there is estimtor θ such tht for ll θ E X θ ( θ θ ( θ < + I λ E X θ ( θ θ E X θ (ˆθ θ, wheres for some θ 0 E X θ( θ θ 0 < E X θ(ˆθ θ Sice E X θ ( θ θ is cotiuous fuctio of θ (why?, there exist ε > 0 such tht E X θ ( θ θ ε, θ (θ 0 ε, θ + ε, or equivletly, E X θ ( θ θ ε (θ0 ε,θ 0 +ε(θ, θ R (3 Cosider the followig eve o-egtive cotiuous fuctio θ ( θ b g(θ θ + b b 0 θ > + b where is lrge eough so tht Sice (θ 0 ε, θ 0 + ε (, g(θ dθ b (θ b dθ + dθ + 0 b 0 (θ b3 3b 8 g(θ dθ +b ( ( b3 + b, 3b 3
9 we defie prior desity s: λ(θ g(θ ( + b 3 µ ( θ b µ + b b 0 µ > + b We c evlute directly (λ I λ λ dθ +b 0 (λ λ dθ +b (λ λ dθ Sice for θ + b, we fid λ(θ (θ b ( +, b λ (θ λ b 3 b ( + b 3 b (λ (θ λ(θ (θ b (+ b 3 b 4 (θ b (+ b 3 b I λ 4 ( + b 3 b ( + b 3 b Now by (3 E X θ ( θ θ λ(θ dθ ε θ0 +ε [θ 0 ε, θ 0 + ε]λ(µ dµ ε θ 0 ε dµ ( + b 3 ε ( + b 3 O the other hd from ( E X θ ( θ θ λ(θ dθ 4 I λ + I λ ( + b b 3 These two iequlitites re comptible oly if ε ( + b 4 ( + b b ε 4 b 3 3 Choosig b lrge eough, we get cotrdictio! REFERENCES [] R Gill d B Levit, Mth Meth Sttist, v (996 [] v Trees, Detectio, Estimtio d Modultio Theory (968, vol I 9
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
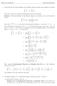 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
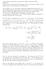 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
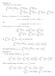 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
8.1 Arc Length. What is the length of a curve? How can we approximate it? We could do it following the pattern we ve used before
 8.1 Arc Legth Wht is the legth of curve? How c we pproximte it? We could do it followig the ptter we ve used efore Use sequece of icresigly short segmets to pproximte the curve: As the segmets get smller
8.1 Arc Legth Wht is the legth of curve? How c we pproximte it? We could do it followig the ptter we ve used efore Use sequece of icresigly short segmets to pproximte the curve: As the segmets get smller
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Lecture 17
 CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Probability for mathematicians INDEPENDENCE TAU
 Probbility for mthemticis INDEPENDENCE TAU 2013 21 Cotets 2 Cetrl limit theorem 21 2 Itroductio............................ 21 2b Covolutio............................ 22 2c The iitil distributio does
Probbility for mthemticis INDEPENDENCE TAU 2013 21 Cotets 2 Cetrl limit theorem 21 2 Itroductio............................ 21 2b Covolutio............................ 22 2c The iitil distributio does
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f m. and. f m = 0. and x i = a + i. a + i. a + n 2. n(n + 1) = a(b a) +
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
Prior distributions. July 29, 2002
 Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
Particle in a Box. and the state function is. In this case, the Hermitian operator. The b.c. restrict us to 0 x a. x A sin for 0 x a, and 0 otherwise
 Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Mathacle. PSet Stats, Concepts In Statistics Level Number Name: Date:
 APPENDEX I. THE RAW ALGEBRA IN STATISTICS A I-1. THE INEQUALITY Exmple A I-1.1. Solve ech iequlity. Write the solutio i the itervl ottio..) 2 p - 6 p -8.) 2x- 3 < 5 Solutio:.). - 4 p -8 p³ 2 or pî[2, +
APPENDEX I. THE RAW ALGEBRA IN STATISTICS A I-1. THE INEQUALITY Exmple A I-1.1. Solve ech iequlity. Write the solutio i the itervl ottio..) 2 p - 6 p -8.) 2x- 3 < 5 Solutio:.). - 4 p -8 p³ 2 or pî[2, +
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
Lecture 19: Convergence
 Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES
 Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
 Kig Fhd Uiversity of Petroleum & Mierls DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL CIENCE Techicl Report eries TR 434 April 04 A Direct Proof of the Joit Momet Geertig Fuctio of mple Me d Vrice Awr H. Jorder d A. Lrdji
Kig Fhd Uiversity of Petroleum & Mierls DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL CIENCE Techicl Report eries TR 434 April 04 A Direct Proof of the Joit Momet Geertig Fuctio of mple Me d Vrice Awr H. Jorder d A. Lrdji
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS
 M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Avd. Matematisk statistik
 Avd. Mtemtisk sttistik TENTAMEN I SF94 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EAM IN SF94 PROBABILITY THE- ORY WEDNESDAY 8th OCTOBER 5, 8-3 hrs Exmitor : Timo Koski, tel. 7 3747, emil: tjtkoski@kth.se Tillåt hjälpmedel Mes
Avd. Mtemtisk sttistik TENTAMEN I SF94 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EAM IN SF94 PROBABILITY THE- ORY WEDNESDAY 8th OCTOBER 5, 8-3 hrs Exmitor : Timo Koski, tel. 7 3747, emil: tjtkoski@kth.se Tillåt hjälpmedel Mes
Introduction to mathematical Statistics
 More ttistics tutoril t wwwdumblittledoctorcom Itroductio to mthemticl ttistics Chpter 7 ypothesis Testig Exmple (ull hypothesis) : the verge height is 5 8 or more ( : μ 5'8" ) (ltertive hypothesis) :
More ttistics tutoril t wwwdumblittledoctorcom Itroductio to mthemticl ttistics Chpter 7 ypothesis Testig Exmple (ull hypothesis) : the verge height is 5 8 or more ( : μ 5'8" ) (ltertive hypothesis) :
Statistical Theory MT 2008 Problems 1: Solution sketches
 Statistical Theory MT 008 Problems : Solutio sketches. Which of the followig desities are withi a expoetial family? Explai your reasoig. a) Let 0 < θ < ad put fx, θ) = θ)θ x ; x = 0,,,... b) c) where α
Statistical Theory MT 008 Problems : Solutio sketches. Which of the followig desities are withi a expoetial family? Explai your reasoig. a) Let 0 < θ < ad put fx, θ) = θ)θ x ; x = 0,,,... b) c) where α
Lecture 38 (Trapped Particles) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 38 (Trpped Prticles) Physics 6-01 Sprig 018 Dougls Fields Free Prticle Solutio Schrödiger s Wve Equtio i 1D If motio is restricted to oe-dimesio, the del opertor just becomes the prtil derivtive
Lecture 38 (Trpped Prticles) Physics 6-01 Sprig 018 Dougls Fields Free Prticle Solutio Schrödiger s Wve Equtio i 1D If motio is restricted to oe-dimesio, the del opertor just becomes the prtil derivtive
Statistical Theory MT 2009 Problems 1: Solution sketches
 Statistical Theory MT 009 Problems : Solutio sketches. Which of the followig desities are withi a expoetial family? Explai your reasoig. (a) Let 0 < θ < ad put f(x, θ) = ( θ)θ x ; x = 0,,,... (b) (c) where
Statistical Theory MT 009 Problems : Solutio sketches. Which of the followig desities are withi a expoetial family? Explai your reasoig. (a) Let 0 < θ < ad put f(x, θ) = ( θ)θ x ; x = 0,,,... (b) (c) where
Remarks: (a) The Dirac delta is the function zero on the domain R {0}.
 Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 1: Linear Algebra Review March 18 th, 2006
 Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Direction: This test is worth 250 points. You are required to complete this test within 50 minutes.
 Term Test October 3, 003 Name Math 56 Studet Number Directio: This test is worth 50 poits. You are required to complete this test withi 50 miutes. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely
Term Test October 3, 003 Name Math 56 Studet Number Directio: This test is worth 50 poits. You are required to complete this test withi 50 miutes. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely
Calculus II Homework: The Integral Test and Estimation of Sums Page 1
 Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Chapter System of Equations
 hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
: : 8.2. Test About a Population Mean. STT 351 Hypotheses Testing Case I: A Normal Population with Known. - null hypothesis states 0
 8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
Stalnaker s Argument
 Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Inference on One Population Mean Hypothesis Testing
 Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
n 2 + 3n + 1 4n = n2 + 3n + 1 n n 2 = n + 1
 Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Why study large deviations? The problem of estimating buer overow frequency The performance of many systems is limited by events which have a small pr
 Why study lrge devitios? The problem of estimtig buer overow frequecy The performce of my systems is ited by evets which hve smll probbility of occurrig, but which hve severe cosequeces whe they occur.
Why study lrge devitios? The problem of estimtig buer overow frequecy The performce of my systems is ited by evets which hve smll probbility of occurrig, but which hve severe cosequeces whe they occur.
( ) k ( ) 1 T n 1 x = xk. Geometric series obtained directly from the definition. = 1 1 x. See also Scalars 9.1 ADV-1: lim n.
 Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
Fig. 1. I a. V ag I c. I n. V cg. Z n Z Y. I b. V bg
 ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
Unbiased Estimation. February 7-12, 2008
 Ubiased Estimatio February 7-2, 2008 We begi with a sample X = (X,..., X ) of radom variables chose accordig to oe of a family of probabilities P θ where θ is elemet from the parameter space Θ. For radom
Ubiased Estimatio February 7-2, 2008 We begi with a sample X = (X,..., X ) of radom variables chose accordig to oe of a family of probabilities P θ where θ is elemet from the parameter space Θ. For radom
Similar idea to multiplication in N, C. Divide and conquer approach provides unexpected improvements. Naïve matrix multiplication
 Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
 ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS DISPERSION, MEAN, MEDIAN, AND MODE VALUES If X, X,, X represet the vlues of rdom smple of items or oservtios, the rithmetic me of these items or oservtios, deoted
ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS DISPERSION, MEAN, MEDIAN, AND MODE VALUES If X, X,, X represet the vlues of rdom smple of items or oservtios, the rithmetic me of these items or oservtios, deoted
INTEGRATION IN THEORY
 CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
Asymptotics. Hypothesis Testing UMP. Asymptotic Tests and p-values
 of the secod half Biostatistics 6 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 6 Fial Exam & Practice Problems for the Fial Hyu Mi Kag Apil 3rd, 3 Hyu Mi Kag Biostatistics 6 - Lecture 6 Apil 3rd, 3 / 3 Rao-Blackwell
of the secod half Biostatistics 6 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 6 Fial Exam & Practice Problems for the Fial Hyu Mi Kag Apil 3rd, 3 Hyu Mi Kag Biostatistics 6 - Lecture 6 Apil 3rd, 3 / 3 Rao-Blackwell
Double Sums of Binomial Coefficients
 Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
This exam contains 19 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided with the exam.
 Probability ad Statistics FS 07 Secod Sessio Exam 09.0.08 Time Limit: 80 Miutes Name: Studet ID: This exam cotais 9 pages (icludig this cover page) ad 0 questios. A Formulae sheet is provided with the
Probability ad Statistics FS 07 Secod Sessio Exam 09.0.08 Time Limit: 80 Miutes Name: Studet ID: This exam cotais 9 pages (icludig this cover page) ad 0 questios. A Formulae sheet is provided with the
7.1 Convergence of sequences of random variables
 Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Certain sufficient conditions on N, p n, q n k summability of orthogonal series
 Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systems Linear Equations
 MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
Last Lecture. Biostatistics Statistical Inference Lecture 16 Evaluation of Bayes Estimator. Recap - Example. Recap - Bayes Estimator
 Last Lecture Biostatistics 60 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 16 Evaluatio of Bayes Estimator Hyu Mi Kag March 14th, 013 What is a Bayes Estimator? Is a Bayes Estimator the best ubiased estimator? Compared
Last Lecture Biostatistics 60 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 16 Evaluatio of Bayes Estimator Hyu Mi Kag March 14th, 013 What is a Bayes Estimator? Is a Bayes Estimator the best ubiased estimator? Compared
EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS
 Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
ALGEBRA. Set of Equations. have no solution 1 b1. Dependent system has infinitely many solutions
 Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
Sequences and Series of Functions
 Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
Chapter 6 Principles of Data Reduction
 Chapter 6 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 0 Chapter 6 Priciples of Data Reductio Sectio 6. Itroductio Goal: To summarize or reduce the data X, X,, X to get iformatio about a
Chapter 6 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 0 Chapter 6 Priciples of Data Reductio Sectio 6. Itroductio Goal: To summarize or reduce the data X, X,, X to get iformatio about a
Math Solutions to homework 6
 Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
1 Convergence in Probability and the Weak Law of Large Numbers
 36-752 Advaced Probability Overview Sprig 2018 8. Covergece Cocepts: i Probability, i L p ad Almost Surely Istructor: Alessadro Rialdo Associated readig: Sec 2.4, 2.5, ad 4.11 of Ash ad Doléas-Dade; Sec
36-752 Advaced Probability Overview Sprig 2018 8. Covergece Cocepts: i Probability, i L p ad Almost Surely Istructor: Alessadro Rialdo Associated readig: Sec 2.4, 2.5, ad 4.11 of Ash ad Doléas-Dade; Sec
