Why study large deviations? The problem of estimating buer overow frequency The performance of many systems is limited by events which have a small pr
|
|
|
- Giles Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why study lrge devitios? The problem of estimtig buer overow frequecy The performce of my systems is ited by evets which hve smll probbility of occurrig, but which hve severe cosequeces whe they occur. The theory dels with rre evets, d is symptotic i ture. It c be viewed s reemet of the lw of lrge umbers. The gure below shows 2 2 switch, where output liks re served t rte c. c B It is useful whe simultio or umericl techiques become icresigly dicult s prmeter teds to its it. It hs my pplictios: queueig d commuictios models, iformtio theory, simultio techiques, prmeter estimtio, hypothesis testig, : : : I order to kow how my virtul circuits my be llowed to use this output lik, for give Qulity of Service costrit, we eed to estimte the probbility tht the cotet of the queue, Q t, eceeds the buer of size B. (Q t B) should be smll. These slides were writte to support iforml discussio of Chpters d 2 of \Lrge Devitios for erformce Alysis", by Shwrtz d Weiss. Richrd Weber, 2 October The overow probbility i MMB queue Elemets of lrge devitio theory Here is other result of lrge devitio theory. Simply to illustrte ides cosider sigle server MMB queue, with ite buer, here beig shred by two trc sources, with combied oisso rrivls t rte We kow Hece B (Q t B) where mes This is typicl. (c) (c) B : (c) B+ (Q t B) e B log(c) for lrge B; B B log (Q t B) log(c): 3 c Suppose ; 2 ; : : : re i.i.d. r.v.s the i i 2 [; b] We hd for the queue: e [if 2[;b] `()+o()] (Q t B) e B log(c) for lrge B: These re typicl. The geerl coclusios re: The symptotic frequecy of occurece of rre evets depeds i epoetil mer o some prmeters of the problem. E.g.,, B. If rre evets occurs the it occurs i the most likely wy. E.g., if 2[;b] `(). Rre evets occur s oisso process. 4
2 Chero's theorem (upper boud) Suppose ; 2 ; : : : is sequece of i.i.d. rdom vribles d E. Let S + +. The for ll >, Hece (S ) E [ + + ] E e [ ++ ] e [ log Ee ] (S ) e sup [ log Ee ] Note tht by Jese's iequlity tht for ll, Ee e E d hece log Ee ( E ). Thus d we coclude Note `(E ). `() def sup sup log Ee log Ee (S ) e `() 5 Observtios Note the key role of momet geertig fuctio, M() Ee d logrithmic momet geertig fuctio, log M() (lso clled the cumult geertig fuctio.) log M() is cove fuctio of. `() : sup [ log M()] is clled the Legedre trsform of log M(). `() is cove fuctio of. `() d log M() re Legedre trsform duls, i.e., sup[ `()] sup[ sup( log M())] sup if[log M() ( )] if log M() : log M() The optimizig, sy, stises M ( )M( ): 6 A typicl rte fuctio Suppose i ; with probbilities q, p. The d `() < : log log M() log(q + pe ); p + ( ) log p ; ; otherwise: : :6 :4 :2 Here E p :6. `() is cove. `() :2 :4 :6 : j`()j s boudry of the set where `() is ite. `(E ). 7 Chero's theorem (lower boud) Suppose F is the distributio of d dee y G(y) M( ) e df () where is s bove. The G is distributio. It is clled tilted distributio. Note tht if ~ G, y E(~) M( ) e df () M ( ) M( ) : Now dg(y) M( ) e y df (y), so (S ) M( ) M( ) y ++y y ++y +y ++y e [ (+) log M ( )] df (y ) : : : df (y ) e (y ++y ) dg(y ) : : : dg(y ) e (y ++y ) dg(y ) : : : dg(y ) +y ++y dg(y ) : : : dg(y ) e `() ( + ~ + + ~ ) e `() ~ + + ~ p
3 Chero's theorem (lower boud), cotiued (S ) e `() Now ~ + + ~ p ~ + + ~ p 2 So sice is rbitrrily smll, if log (S ) `() The upper d lower bouds together imply (S ) e [`()+o()] We eed coditios to esure tht log M() is dieretible t d tht its derivtive is. It is eough to ssume tht M() is ite i some eighborhood of d tht there is i the iterior of this eighborhood such tht `() log M( ). 9 Illustrtio with the orml distributio I the simple cse tht i N(; 2 ), d log M() `() ( ) A more reed estimte c be obtied from y + y e 2 y2 (S ) y e 2 t2 dt y e 2 y2 ) p 2( ) e ( )2 2 2 p 2( ) e `() The pperce of p ( e 2 log ) is typicl. A pplictio of the theory would be to pproimte (S ) by e ( ) Sometimes oe c get reed pproimtios, e.g., s bove, or the Bhdur-Ro pproimtio for the biomil distributio. Geerliztio to i.i.d. vectors Theorem.22. Suppose ; 2 ; : : : 2 R d is sequece of rdom vectors d M() Ee <; > : Dee the rte fuctio `() sup[< ; > log M()]: The for y set C R d log log t t t 2 C t 2 C if 2C o `(); if 2 C `(); where C o d C re respectively the iterior d closure of Note: If you go bck to the proof of Chero's theorem, you will see tht you c esily eted the proof to sttemets bout (S 2 C). You c tke C closed set whe doig the upper boud, but will eed to tke C to be ope set for the lower boud. (You'll wt to let be the miimizer of `() d boud the probbility of beig i C by the probbility of beig i eighbouhood of ; so you'll eed tht if 2 C the eighborhood of is lso i ) Geerl sttemet of lrge devitio priciple Suppose z ; z 2 ; : : : is sequece of rdom vectors i probbility spce (X ; ; F). Here X might be R d, or perhps C[; T ], the spce of cotiuous fuctios. E.g., thik of z ( + + ). Deitio 2.. A rel vlued fuctio I o X is clled \rte fuctio" if (i) I(), (ii) I is lower semi-cotiuous; i.e., if y ; y 2 ; : : : is sequece such tht y y i X the if I(y ) I(y). Deitio 2.2. We sy z ; z 2 ; : : : stisfy lrge devitio priciple with rte fuctio I if for every set C X log (z 2 C) if I(); 2C o log (z 2 C) if I(); 2C where C o d C re respectively the iterior d closure of If if 2C o I() if 2 C the the two bouds coicide d C is sid to be I-cotiuity set for I. 2
4 Vrdh's lemm The cotrctio priciple Theorem 2.2. Suppose tht z ; z 2 ; : : : stisfy lrge devitio priciple with rte fuctio I. The for y bouded cotiuous fuctio g o X, log E e g(z ) The ituitive ide is tht E e g(z ) sup[g() I()]: e g() (z )d e g() e I() d e sup [g() I()] where the lst lie follows from Lplce's rgumet, tht the rte of growth of itegrl (or sum) is obtied by pproimtig it by its lrgest term. E.g., for lrge. 4e 2 + 6e 3 + e 4e 2 Deitio 2.. A rte fuctio is sid to be good rte fuctio if (iii) The set f : I() g is compct for every. Suppose tht z ; z 2 ; : : : stisfy lrge devitio priciple with rte fuctio I. Let f be cotiuous fuctio d let y i f(z i ). Dee I (y) Theorem 2.3. < : iffi() : 2 X ; f() yg ; if y f() for o 2 X (i) If I is good rte fuctio the I is good rte fuctio. (ii) If z ; z 2 ; : : : stisfy lrge devitio priciple with good rte fuctio I the y ; y 2 ; : : : stisfy lrge devitio priciple with good rte fuctio I. Agi, Lplce's rgumet gives the right ituitio why this is true. 3 4 Sov's theorem Deitio A.2. Let ; 2 ; : : : be sequece rdom vribles with distributio F d vlues i some metric spce X. The empiricl distributio of mesurble set A is (A) : i [ i 2 A]: Suppose ; 2 ; : : : re i.i.d. with distributio, i.e., ( y) (( ; y]). Dee I() log d d (y) d(y): I the cse tht of discrete distributio (p ; : : : ; p d ), over discrete set of d poits this would be I(q) q j log j H(q j p): p j Theorem.22. Cosider the sequece ; 2 ; : : :. For every set C cotied i the spce of probbility distributios, log ( 2 C) if I(); 2C o log ( 2 C) if I(); 2C where C o d C re respectively the iterior d closure of 5 Sov's theorem for discrete distributio Suppose X f; : : : ; dg. Give i j, let y i 2 f; g d be vector whose jth compoet is equl to d ll others re equl to. For y z 2 R d, let jzj m jd jz j j. The i y i q if q:jq j q j log A : p j Emple. Suppose we roll die times d the totl is 4. The epected vlue is 3:5. So we hve see rre evet. How did this hppe? For q (:3; :23; :46; :74; :27; :247), we i y i q if q:jq ; j jq j 4 if q: j jq j >4 j j j j j 4A. q j log 6 q j log 6 A A where q is chose s imizer of the deomitor. 6
5 Iformtio theory d lrge devitios Suppose source geertes letters from lphbet of d symbols. Letters re i.i.d. choices mogst the d symbols, with probbilities q ; : : : ; q d. The empiricl distributio of the symbols i strig of symbols will be close to q, so without losig much iformtio, we could igore strigs for which the empiricl distributio is fr from q. There re d possible strigs of legth, but we would be usig oly frctio of these. The umber we would be usig, sy M, is give by m d j where h(q) j q j log 2 q j. Hece 2 q j log A h(q) d d ; m 2 h(q) 2 log 2 d : This shows tht the source hs iformtio rte h(q) log 2 d. 7
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
Students must always use correct mathematical notation, not calculator notation. the set of positive integers and zero, {0,1, 2, 3,...
 Appedices Of the vrious ottios i use, the IB hs chose to dopt system of ottio bsed o the recommedtios of the Itertiol Orgiztio for Stdrdiztio (ISO). This ottio is used i the emitio ppers for this course
Appedices Of the vrious ottios i use, the IB hs chose to dopt system of ottio bsed o the recommedtios of the Itertiol Orgiztio for Stdrdiztio (ISO). This ottio is used i the emitio ppers for this course
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
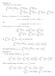 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
Prior distributions. July 29, 2002
 Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
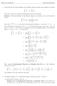 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
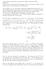 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Probability for mathematicians INDEPENDENCE TAU
 Probbility for mthemticis INDEPENDENCE TAU 2013 21 Cotets 2 Cetrl limit theorem 21 2 Itroductio............................ 21 2b Covolutio............................ 22 2c The iitil distributio does
Probbility for mthemticis INDEPENDENCE TAU 2013 21 Cotets 2 Cetrl limit theorem 21 2 Itroductio............................ 21 2b Covolutio............................ 22 2c The iitil distributio does
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Calculus II Homework: The Integral Test and Estimation of Sums Page 1
 Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
Mathacle. PSet Stats, Concepts In Statistics Level Number Name: Date: Hypothesis Test We assume, calculate and conclude.
 Hypothesis Test We ssume, clculte d coclude. VIII. HYPOTHESIS TEST 8.. P-Vlue, Test Sttistic d Hypothesis Test [MATH] Terms for the mkig hypothesis test. Assume tht the uderlyig distributios re either
Hypothesis Test We ssume, clculte d coclude. VIII. HYPOTHESIS TEST 8.. P-Vlue, Test Sttistic d Hypothesis Test [MATH] Terms for the mkig hypothesis test. Assume tht the uderlyig distributios re either
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Multiplicative Versions of Infinitesimal Calculus
 Multiplictive Versios o Iiitesiml Clculus Wht hppes whe you replce the summtio o stdrd itegrl clculus with multiplictio? Compre the revited deiitio o stdrd itegrl D å ( ) lim ( ) D i With ( ) lim ( ) D
Multiplictive Versios o Iiitesiml Clculus Wht hppes whe you replce the summtio o stdrd itegrl clculus with multiplictio? Compre the revited deiitio o stdrd itegrl D å ( ) lim ( ) D i With ( ) lim ( ) D
Relation of BSTs to Quicksort, Analysis of Random BST. Lecture 9
 Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Background 1. Cramer-Rao inequality
 Bro-06, Lecture, 60506 D/Stt/Bro-06/tex wwwmstqueesuc/ blevit/ Observtio vector, dt: Bckgroud Crmer-Ro iequlity X (X,, X X R Here dt c be rel- or vector vlued, compoets of the dt c be idepedet or depedet,
Bro-06, Lecture, 60506 D/Stt/Bro-06/tex wwwmstqueesuc/ blevit/ Observtio vector, dt: Bckgroud Crmer-Ro iequlity X (X,, X X R Here dt c be rel- or vector vlued, compoets of the dt c be idepedet or depedet,
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
In an algebraic expression of the form (1), like terms are terms with the same power of the variables (in this case
 Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
2. Infinite Series 3. Power Series 4. Taylor Series 5. Review Questions and Exercises 6. Sequences and Series with Maple
 Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
( ) = A n + B ( ) + Bn
 MATH 080 Test 3-SOLUTIONS Fll 04. Determie if the series is coverget or diverget. If it is coverget, fid its sum.. (7 poits) = + 3 + This is coverget geometric series where r = d
MATH 080 Test 3-SOLUTIONS Fll 04. Determie if the series is coverget or diverget. If it is coverget, fid its sum.. (7 poits) = + 3 + This is coverget geometric series where r = d
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
 Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Error-free compression
 Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
 ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS DISPERSION, MEAN, MEDIAN, AND MODE VALUES If X, X,, X represet the vlues of rdom smple of items or oservtios, the rithmetic me of these items or oservtios, deoted
ENGINEERING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS DISPERSION, MEAN, MEDIAN, AND MODE VALUES If X, X,, X represet the vlues of rdom smple of items or oservtios, the rithmetic me of these items or oservtios, deoted
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Particle in a Box. and the state function is. In this case, the Hermitian operator. The b.c. restrict us to 0 x a. x A sin for 0 x a, and 0 otherwise
 Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
SM2H. Unit 2 Polynomials, Exponents, Radicals & Complex Numbers Notes. 3.1 Number Theory
 SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
1 Section 8.1: Sequences. 2 Section 8.2: Innite Series. 1.1 Limit Rules. 1.2 Common Sequence Limits. 2.1 Denition. 2.
 Clculus II d Alytic Geometry Sectio 8.: Sequeces. Limit Rules Give coverget sequeces f g; fb g with lim = A; lim b = B. Sum Rule: lim( + b ) = A + B, Dierece Rule: lim( b ) = A B, roduct Rule: lim b =
Clculus II d Alytic Geometry Sectio 8.: Sequeces. Limit Rules Give coverget sequeces f g; fb g with lim = A; lim b = B. Sum Rule: lim( + b ) = A + B, Dierece Rule: lim( b ) = A B, roduct Rule: lim b =
Chapter 11 Design of State Variable Feedback Systems
 Chpter Desig of Stte Vrible Feedbck Systems This chpter dels with the desig of cotrollers utilizig stte feedbck We will cosider three mjor subjects: Cotrollbility d observbility d the the procedure for
Chpter Desig of Stte Vrible Feedbck Systems This chpter dels with the desig of cotrollers utilizig stte feedbck We will cosider three mjor subjects: Cotrollbility d observbility d the the procedure for
CHAPTER 6: USING MULTIPLE REGRESSION
 CHAPTER 6: USING MULTIPLE REGRESSION There re my situtios i which oe wts to predict the vlue the depedet vrible from the vlue of oe or more idepedet vribles. Typiclly: idepedet vribles re esily mesurble
CHAPTER 6: USING MULTIPLE REGRESSION There re my situtios i which oe wts to predict the vlue the depedet vrible from the vlue of oe or more idepedet vribles. Typiclly: idepedet vribles re esily mesurble
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Avd. Matematisk statistik
 Avd. Mtemtisk sttistik TENTAMEN I SF94 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EAM IN SF94 PROBABILITY THE- ORY WEDNESDAY 8th OCTOBER 5, 8-3 hrs Exmitor : Timo Koski, tel. 7 3747, emil: tjtkoski@kth.se Tillåt hjälpmedel Mes
Avd. Mtemtisk sttistik TENTAMEN I SF94 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EAM IN SF94 PROBABILITY THE- ORY WEDNESDAY 8th OCTOBER 5, 8-3 hrs Exmitor : Timo Koski, tel. 7 3747, emil: tjtkoski@kth.se Tillåt hjälpmedel Mes
( ) k ( ) 1 T n 1 x = xk. Geometric series obtained directly from the definition. = 1 1 x. See also Scalars 9.1 ADV-1: lim n.
 Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burak Kelleci. Spring 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bur Kelleci Sprig 8 OUTLINE The Z-Trsform The Regio of covergece for the Z-trsform The Iverse Z-Trsform Geometric
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bur Kelleci Sprig 8 OUTLINE The Z-Trsform The Regio of covergece for the Z-trsform The Iverse Z-Trsform Geometric
: : 8.2. Test About a Population Mean. STT 351 Hypotheses Testing Case I: A Normal Population with Known. - null hypothesis states 0
 8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Similar idea to multiplication in N, C. Divide and conquer approach provides unexpected improvements. Naïve matrix multiplication
 Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Inference on One Population Mean Hypothesis Testing
 Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
ELG4156 Design of State Variable Feedback Systems
 ELG456 Desig of Stte Vrible Feedbck Systems This chpter dels with the desig of cotrollers utilizig stte feedbck We will cosider three mjor subjects: Cotrollbility d observbility d the the procedure for
ELG456 Desig of Stte Vrible Feedbck Systems This chpter dels with the desig of cotrollers utilizig stte feedbck We will cosider three mjor subjects: Cotrollbility d observbility d the the procedure for
Crushed Notes on MATH132: Calculus
 Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
2017/2018 SEMESTER 1 COMMON TEST
 07/08 SEMESTER COMMON TEST Course : Diplom i Electroics, Computer & Commuictios Egieerig Diplom i Electroic Systems Diplom i Telemtics & Medi Techology Diplom i Electricl Egieerig with Eco-Desig Diplom
07/08 SEMESTER COMMON TEST Course : Diplom i Electroics, Computer & Commuictios Egieerig Diplom i Electroic Systems Diplom i Telemtics & Medi Techology Diplom i Electricl Egieerig with Eco-Desig Diplom
Double Sums of Binomial Coefficients
 Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Surds, Indices, and Logarithms Radical
 MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
National Quali cations SPECIMEN ONLY
 AH Ntiol Quli ctios SPECIMEN ONLY SQ/AH/0 Mthemtics Dte Not pplicble Durtio hours Totl mrks 00 Attempt ALL questios. You my use clcultor. Full credit will be give oly to solutios which coti pproprite workig.
AH Ntiol Quli ctios SPECIMEN ONLY SQ/AH/0 Mthemtics Dte Not pplicble Durtio hours Totl mrks 00 Attempt ALL questios. You my use clcultor. Full credit will be give oly to solutios which coti pproprite workig.
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systems Linear Equations
 MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
THE GAMMA FUNCTION. z w dz.
 THE GAMMA FUNCTION. Some results from lysis Lemm. Suppose f is sequece of fuctios lytic o ope subset D of C. If f coverges uiformly o every compct closed d bouded subset of D to the limit fuctio f the
THE GAMMA FUNCTION. Some results from lysis Lemm. Suppose f is sequece of fuctios lytic o ope subset D of C. If f coverges uiformly o every compct closed d bouded subset of D to the limit fuctio f the
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
Math 2414 Activity 17 (Due with Final Exam) Determine convergence or divergence of the following alternating series: a 3 5 2n 1 2n 1
 Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Riemann Integral Oct 31, such that
 Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
,... are the terms of the sequence. If the domain consists of the first n positive integers only, the sequence is a finite sequence.
 Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
Basic Limit Theorems
 Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
lecture 24: Gaussian quadrature rules: fundamentals
 133 lecture 24: Gussi qudrture rules: fudmetls 3.4 Gussi qudrture It is cler tht the trpezoid rule, b 2 f ()+ f (b), exctly itegrtes lier polyomils, but ot ll qudrtics. I fct, oe c show tht o qudrture
133 lecture 24: Gussi qudrture rules: fudmetls 3.4 Gussi qudrture It is cler tht the trpezoid rule, b 2 f ()+ f (b), exctly itegrtes lier polyomils, but ot ll qudrtics. I fct, oe c show tht o qudrture
Eigenfunction Expansion. For a given function on the internal a x b the eigenfunction expansion of f(x):
 Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Frequency-domain Characteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems
 requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
requecy-domi Chrcteristics of Discrete-time LTI Systems Prof. Siripog Potisuk LTI System descriptio Previous bsis fuctio: uit smple or DT impulse The iput sequece is represeted s lier combitio of shifted
Orthogonal functions - Function Approximation
 Orthogol uctios - Fuctio Approimtio - he Problem - Fourier Series - Chebyshev Polyomils he Problem we re tryig to pproimte uctio by other uctio g which cosists o sum over orthogol uctios Φ weighted by
Orthogol uctios - Fuctio Approimtio - he Problem - Fourier Series - Chebyshev Polyomils he Problem we re tryig to pproimte uctio by other uctio g which cosists o sum over orthogol uctios Φ weighted by
Solutions to Problem Set 7
 8.0 Clculus Jso Strr Due by :00pm shrp Fll 005 Fridy, Dec., 005 Solutios to Problem Set 7 Lte homework policy. Lte work will be ccepted oly with medicl ote or for other Istitute pproved reso. Coopertio
8.0 Clculus Jso Strr Due by :00pm shrp Fll 005 Fridy, Dec., 005 Solutios to Problem Set 7 Lte homework policy. Lte work will be ccepted oly with medicl ote or for other Istitute pproved reso. Coopertio
f(x) is a function of x and it is defined on the set R of real numbers. If then f(x) is continuous at x=x 0, where x 0 R.
 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES Limit Cotiuity Coverget squece Series Dieretible uctios Itegrble uctios Summtio deiitio o itegrl Me vlue theorem Me vlue theorem or itegrls Tylor's theorem Computer represettio
MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES Limit Cotiuity Coverget squece Series Dieretible uctios Itegrble uctios Summtio deiitio o itegrl Me vlue theorem Me vlue theorem or itegrls Tylor's theorem Computer represettio
Discrete Mathematics I Tutorial 12
 Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Two Unknown. Parameter of Beta-Weibull Distribution. under Type II Censored Samples
 Applied Mthemticl Scieces, Vol. 6, 12, o. 48, 2369-2384 Mximum Likelihood Estimtio of Two Ukow Prmeter of Bet-Weibull Distributio uder Type II Cesored Smples M. R. Mhmoud d R. M. Mdouh Istitute of Sttisticl
Applied Mthemticl Scieces, Vol. 6, 12, o. 48, 2369-2384 Mximum Likelihood Estimtio of Two Ukow Prmeter of Bet-Weibull Distributio uder Type II Cesored Smples M. R. Mhmoud d R. M. Mdouh Istitute of Sttisticl
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 5 Elements of Statistics
 Deprtet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 3143 Probbility & Stochstic Process Ch. 5 Eleets of Sttistics Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE Itroductio: wht is sttistics? Sple e d sple vrice Cofidece
Deprtet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 3143 Probbility & Stochstic Process Ch. 5 Eleets of Sttistics Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE Itroductio: wht is sttistics? Sple e d sple vrice Cofidece
SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES
 Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE
 MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5
 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5 Fll K8-5 th Semester Thir Muhmmd tmuhmmd_7@yhoo.com Cotet d Figures re from Discrete-Time Sigl Processig, e by Oppeheim, Shfer, d Buck, 999- Pretice Hll Ic. The -Trsform
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LECTURE 5 Fll K8-5 th Semester Thir Muhmmd tmuhmmd_7@yhoo.com Cotet d Figures re from Discrete-Time Sigl Processig, e by Oppeheim, Shfer, d Buck, 999- Pretice Hll Ic. The -Trsform
