Linwood High School S3 CREDIT NOTES
|
|
|
- Amice Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linwood High School S3 CREDIT NOTES
2 INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Calculations and the Calculator page 5 Chapter 2: Similar Shapes page 9 Chapter 3: Going Places page 11 Chapter 4: Money Matters - Saving and Spending page 12 Chapter 5: Positive and Negative Numbers page 14 Chapter 6: Pythagoras Theorem page 16 Chapter 7: Brackets and Equations page 18 Chapter 8: Statistics page 22 Chapter 9: Trigonometry page 24 page 28 page 32 page 36 page 38 page 41 Chapter 10: Simultaneous Equations Chapter 11: Areas and Volumes Chapter 12: Factorisation Chapter 13: Money Matters - Personal Finance Chapter 14: Formulae Chapter 15: Probability
3 CHAPTER 1: CALCULATIONS AND THE CALCULATOR CALCULATORS AND ROUNDING The number of significant figures indicates the accuracy of a measurement. For example, 3400 centimetres = 34 metres = kilometres same measurement, same accuracy, each 2 significant figures. significant figures: count the number of figures used, but do not count zeros at the end of a number without a decimal point do not count zeros at the start of a number with a decimal point. These zeros simply give the place-value 1 of the figures and do not indicate accuracy. rounding: For example, has 5 significant figures 5700 to 2 significant figures (this case, the nearest Hundred) has 5 significant figures to 2 significant figures (this case, the nearest Thousandth) (note would be wrong) Example involving the use of a calculator: Evaluate , giving your answer correct to 2 significant figures. = = evaluate top and bottom by entering in the calculator and write these answers divide top by bottom and write the unrounded answer write the rounded answer 1 place-value meaning Hundreds, Tens, Units, tenths, hundredths etc. page 1
4 CALCULATORS AND SCIENTIFIC NOTATION (STANDARD FORM) Writing numbers in the form a 10 n where 1 a <10 for a, place the decimal point after the first non-zero digit and n is an integer numbers...-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3... For example, = = = = = Notice for numbers starting 0 the power of 10 is negative (same as 10). Examples involving the use of a calculator: (1) One milligram of hydrogen gas contans molecules. Calculate the number of molecules in 5 grams of hydrogen gas, giving you answer correct to 3 significant figures = molecules learn to enter standard form in the calculator using the appropriate button EE or EXP or x10 n eg EXP 20 (2) The total mass of argon in a flask is grams. The mass of a single atom of argon is grams. Find, correct to 3 significant figures, the number of argon atoms in the flask = atoms use the (-) button for a minus eg EXP (-) 2 divide top by bottom and write the unrounded answer write the rounded answer page 2
5 FRACTIONS No calculators! Addition and subtraction requires a common denominator: Example: = = least common multiple of 6 and 9 is 18 for the common denominator = = both fractions now 18ths subtract whole numbers 11-3 = 8 subtract fractions by subtracting the top 15-4 = 11 while the bottom stays the same at 18 Multiplication and division requires no mixed numbers: Examples: (1) 3 of means multiply 10 of no mixed numbers, go top-heavy = = = 11 4 or for the top 4 x 2 +3= 11 bottom stays as 4 = = multiply the top numbers 3 x 11 = 33 multiply the bottom numbers 10 x 4 = 40 (2) = = division becomes multiply by the reciprocal a b becomes b a page 3
6 ORDER OF CALCULATION Rule: x and before + or - to change the order use brackets BRACKETS FIRST Carry out separate calculations: Examples: (1) = 6 36 = 1 6 multiply first fully simplify = = subtraction last common denominator (2) brackets first = = top-heavy first = 2 6 fully simplify = multiply by reciprocal = 1 3 = 4 21 page 4
7 CHAPTER 2: SIMILAR SHAPES Shapes are similar if they are enlargement or reductions of each other. (1) the angles remain unchanged - the shapes are equiangular. and (2) the sides are enlarged or reduced by some scale factor (SF). For example: corresponding angles not equal (wrong order): shapes not equiangular so not similar ratios of corresponding sides not equal (no SF): shapes equiangular but not similar. 4 cm 3 cm 2 cm 1 cm shapes equiangular and ratios of corresponding sides equal (has SF): shapes are similar. 6 cm 8 cm 16 cm cm 9 cm 12 cm 24 cm 9 6 = 12 8 = = 24 16, scale factor = cm 37 Triangles are special: Enlarge or reduce a triangle by some scale factor and the two triangles will be equiangular. Rule: If triangles are equiangular then they are similar and so the sides have been scaled. o x o x page 5
8 SCALING SIDES length scale factor, SF = enlargement if SF > 1 reduction if 0 < SF < 1 image side original side Example: 16 cm x cm 6 cm 9 cm Find the value of x. 16 cm o Original x cm o shape with the unknown side Image x 15 cm x 6 cm triangles are equiangular and so similar SF = image original = 6 15 = < SF < 1 as expected for a reduction x = = 6 4 smaller than 16 as expected for a reduction page 6
9 SCALING AREAS To enlarge a 2D shape both dimensions, length and breadth, must be scaled. For example, original sides doubled sides tripled image contains 4 of image contains 9 of the original rectangles the original rectangles Rule: if the length of the sides are made n times bigger, length SF = n the area of the enlarged shape is n x n bigger. area SF = n 2 Example: 48 cm 2 12 cm A cm 2 15 cm Given that the two shapes shown are similar, find the area of the larger shape. length SF = image original = = 5 4 SF > 1 as expected for an enlargement area SF = = A = = 75 bigger than 48 as expected for an enlargement page 7
10 SCALING VOLUMES To enlarge a 3D solid the dimensions length, breadth and height, must be scaled. For example, original sides doubled sides tripled image contains 8 of image contains 27 of the original cuboids the original cuboids Rule: if the length of the sides are made n times bigger, length SF = n the volume of the enlarged solid is n x n x n bigger. volume SF = n 3 Example: 15 cm 12 cm 250 ml V ml Given that the two solids shown are similar, find the volume of the smaller solid. length SF = image original = = < SF < 1 as expected for a reduction volume SF = = V = = smaller than 250 as expected for a reduction page 8
11 CHAPTER 3: GOING PLACES Speed is a rate, the change of distance with time. It is given as the distance travelled in a unit of time. For example, 20 km/h: 20 kilometres per hour means travelling 20 kilometres in 1 hour. Average speed only considers the change in distance and time between the start and finish of a journey. It does not take into account the varying speed during the journey. total distance travelled average speed = total time taken Example: Travel 23 km in 30 minutes, then 30 km in 45 minutes and finally 13 km in 15 minutes. total distance 66 km, total time 90 minutes (1.5 hours) 66 km average speed = = 44 km / h 1 5 hours NOTE: The speeds at each stage 46 km/h, 40 km/h and 52 km/h average 46 km/h. None of these are involved in calculating the average speed. Distance/Time Graphs The slope of the graph is the speed. The steeper the graph the greater the speed. For example, DISTANCE (km) km/h 15 km/h 10 km/h TIME (hours) page 9
12 FORMULAE WATCH UNITS! The distance and time units must match the speed units. For example, speed km/h requires using time in hours and distance in kilometres cm/s requires using time in seconds and distance in centimetres Examples: (1) Find the speed if: (2) Find the time if: (3) Find the distance if: travel 30 km in 1 hour 12 mins travel 50 km at 12 km/h travel for 2 mins at 8 cm/s units: 12 min = = 0.2 hours 2 min = 2 x 60 = 120 secs so 1 hour 12 mins = 1.2 hours km and hours km matches km/h seconds matches cm/s results in speed in km/h results in time in hours results in distance in cm calculations: D D D S T S T S T S = D T = = 25 km / h T = D S = = hours = 4 hours 10 mins time units: hours = x 60 = 10 min so hours = 4 hour 10 mins D = ST = = 960 cm page 10
13 CHAPTER 4: SAVING AND SPENDING Examples: (1) earnings GROSS PAY = BASIC PAY + OVERTIME, BONUS, COMMISSION etc NET PAY = GROSS PAY - DEDUCTIONS (tax, national insurance etc) (i) 40 hours at basic rate 8.40 per hour. (ii) basic pay a week plus 12.5% 6 hours overtime at time and a half. commission on sales over Weekly sales of 4200 were achieved. overtime rate = 8.40 x 1.5 = extra sales = = 2200 basic pay = 8.40 x 40 = 336 commission = x 12.5 = 275 overtime pay = x 6 = gross pay = = gross pay = = (2) simple interest (3) VAT Invest for 8 months at 6% pa Radio costs 60 excluding VAT at 20%. (pa = per annum, per year) Find the cost inclusive of VAT. for 1 year x 6 = 720 VAT = x 20 = 12 for 8 months x 8 = 480 cost = = 72 (4) HP (5) foreign exchange To purchase a TV requires a 60 deposit Exchange rate is $1.50 to the. and 24 monthly instalments of Change: (i) 30 to $ (ii) $60 to instalments = 24 x = 300 (i) 30 x 1.50 = $45 HP cost = = 360 (ii) $ = 40 page 11
14 CHAPTER 5: POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE NUMBERS (DIRECTED NUMBERS) ADD AND SUBTRACT subtract -4-3 = = -2 add = = add negative = subtract subtract negative = add a + (-b) = a - b a - (-b) = a + b For example, -4 + (-3) 3 + (-5) -7 - (-3) -2 - (-5) = -4-3 = 3-5 = = = -7 = -2 = -4 = 3 MULTIPLY AND DIVIDE Rules: x or For example, 2 x 7 = = +3-2 x (-7) = (-5) = +3 2 x (-7) = (-5) = -3-2 x 7 = = -3 page 12
15 CALCULATIONS Examples: If a = - 3, b = 2 and c = 5, evaluate: (1) 3c ab (2) 2a 2 (3) a b c 3 c a b = 3 5 ( 3) 2 = 15 ( 6) = = 21 2 a a = 2 ( 3) ( 3) = 2 9 = = 5 5 = 1 EQUATIONS Examples: (1) Solve: 5x 4 = 2x 19 5x 4 = 2x 19 3x 4 = 19 subtracted 2 x from each side 3x = 15 added 4 to each side x = 5 divided each side by 3 (2) Solve: 2 5t =10 3t 4 5t = 10 3t 4 = t added 5t to each side 6 = 2t subtracted 10 from each side 3 = t divided each side by 2 t = 3 page 13
16 CHAPTER 6: PYTHAGORAS THEOREM A 1 A 3 Squares sit on the sides of a triangle; the biggest square, area A 1, is opposite the biggest angle. A 2 For right-angled triangles only: A 1 = A 2 + A 3 a c Side length a units is opposite the right angle. It is the longest side, the hypotenuse. b For right-angled triangles: a 2 = b 2 + c 2 FINDING AN UNKNOWN SIDE Examples: (1) finding the longest side: (2) finding a short side: x m 8 m 12 m y m 10 m 9 m x 2 = = x 2 =164 x = 164 = x =12 8 y 2 = (since y =12 2 ) = y 2 = 63 y = 63 = y = 7 9 page 14
17 CONVERSE OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM a b c Side length a units, opposite the biggest angle, is the longest side. If a 2 = b 2 + c 2 then the triangle is right angled Example: Show that triangle ABC is right angled. C 10 m 6 m A 8 m B AB 2 + BC 2 = =100 AC 2 =10 2 = 100 since AB 2 + BC 2 = AC 2 by the Converse of Pyth. Thm. ΔABC is right angled at B (ie. ABC = 90 o ) page 15
18 CHAPTER 7: BRACKETS AND EQUATIONS Examples: SINGLE BRACKETS Each term in the brackets is multiplied by the term outside the brackets. (1) 3x ( 2x y + 7) (2) 2 ( 3t + 5) (3) 3w ( w 2 4) 3x 2x = 6x 2 3x y = 3xy 3x + 7 = +21x 2 3t = 6t = 10 3w w 2 = 3w 3 3w 4 = +12w = 6x 2 3xy + 21x = 6t 10 = 3w w Fully simplify: (4) 2t 3 t ( ) + 5t 2 (5) 5 3 ( n 2) = 6t 2t 2 + 5t 2 = 6t + 3t 2 = 5 3n + 6 = n = 11 3n DOUBLE BRACKETS (1) ( 3x + 2) ( 2x 5) ( 3x + 2) 2x 5 ( ) ( ) + 2 ( 2x 5) = 3x 2x 5 = 6x 2 15x + 4 x 10 = 6x 2 11x 10 or FOIL ( 3x + 2) ( 2 x 5) = 6x 2 15x + 4 x 10 = 6x 2 11x 10 FOIL pairs multiplied between the two brackets. ( 3x + 2) ( 2 x 5) ( 3x + 2) ( 2 x 5) ( 3x + 2) ( 2 x 5) ( 3x + 2) ( 2 x 5) First 6x 2 Outer 15x Inner +4x Last 10 page 16
19 (2) ( 2t 3) 2 or ( 2t 3) 2t 3 ( ) ( ) 3 ( 2t 3) = 2t 2t 3 = 4t 2 6t 6t + 9 = 4t 2 12t + 9 ( 2t 3) ( 2t 3) = 4t 2 6t 6t + 9 = 4t 2 12t + 9 (3) ( w + 2) ( w 2 3w + 5) ( ) ( ) + 2 ( w 2 3w + 5) ( w + 2) w 2 3w + 5 = w w 2 3w + 5 = w 3 3w 2 + 5w + 2w 2 6w +10 = w 3 3w 2 + 2w 2 + 5w 6w + 10 = w 3 w 2 w + 10 EQUATIONS Remove the brackets, fully simplifying, then follow the rules for solving equations. Example: Solve: ( 4 x + 3) ( x 2) = ( 2x 3) 2 4x 2 5x 6 = 4x 2 12x + 9 removed brackets, fully simplifying 5x 6 = 12x + 9 subtracted 4x 2 from each side 7x 6 = + 9 added 12x to each side 7x = 15 added 6 to each side x = 15 7 divided each side by 7 page 17
20 CHAPTER 8: STATISTICS SUPPLEMENT Studying statistical information, it is useful to consider: (1) typical result: average (2) distribution of results: spread AVERAGES: mean = total of all results number of results median = middle result of the ordered results mode = most frequent result SPREAD: Ordered results are split into 4 equal groups so each contains 25% of the results. The 5 figure summary identifies: L, Q 1, Q 2, Q 3, H (lowest result, 1st, 2nd and 3rd quartiles, highest result) A Box Plot is a statistical diagram that displays the 5 figure summary: L Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 H range, R = H L interquartile range, IQR = Q 3 Q 1 semi interquartile range, SIQR = Q 3 Q 1 2 NOTE: If Q 1, Q 2 or Q 3 fall between two results, the mean of the two results is taken. For example, 12 ordered results: split into 4 equal groups of 3 results Q 1 Q 2 Q Q 1 = = 15, Q 2 = = 20, Q 3 = = 25 5 page 18
21 Example: Pulse rates: 66, 64, 71, 56, 60, 79, 77, 75, 69, 73, 75, 62, 66, 71, 66 beats per minute. 15 ordered results: Q 1 Q 2 Q Figure Summary: L = 56, Q 1 = 64, Q 2 = 69, Q 3 = 75, H = 79 Box Plot: pulse rate (beats per minute) Spread: R = H L = = 23 IQR = Q 3 Q 1 = = 11 SIQR = Q 3 Q 1 2 = = 11 2 = 5 5 Averages: (total = =1030) MEAN = = = 68 7 (Q 2 )MEDIAN = 69 MODE = 66 page 19
22 OTHER STATISTICAL DIAGRAMS Examples: ordered stem-and-leaf: Race Times (seconds): 10.4, 10.2, 9.9, 12.1, 11.7, 10.9, 9.9, 11.4, 10.6, 11.5, 10.1, 9.8, 10.2, 11.3, 11.0 unordered first Race Time (seconds) n = = 9.8 dot plot: Car speeds (mph): Speed (mph) FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION TABLES Useful for dealing with a large number of results. In a competition 50 people take part. The table shows the distribution of points scored. Scores (points) result frequency page 20
23 mean: result frequency result x frequency TOTALS MEAN = 652 = cummulative frequency: result frequency cummulative frequency quarter the results: 50 4 = 12 R th 25 / 26th 38th Q 1 = 12, 13th result included here Q 2 =13, 25th / 26th result included here Q 3 =14, 38th result included here cummulative frequency 50 divide the total frequency into 4 quarter intervals to estimate quartiles 50 4 = Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 result page 21
24 CHAPTER 9: TRIGONOMETRY SOH-CAH-TOA H a A O The sides of a right-angled triangle are labelled: Opposite: opposite the angle a. Adjacent: next to the angle a. Hypotenuse: opposite the right angle. The ratios of sides O H, A H and O A have values which depend on the size of angle a. These are called the sine, cosine and tangents of a, written sin a, cos a and tan a. For example, 5 a 4 3 S = O H sin a o = 3 5 C = A H cos a o = 4 5 T = O A tan a o = 3 4 FINDING AN UNKNOWN SIDE Examples: (1) Find x. 10 m x m H 40 A know H, find O O x SOH-CAH-TOA sine ratio uses O and H O S H rearrange for x x sin S = O H sin 40 o = x 10 ensure calculator set to DEGREES x =10 sin 40 o = x = 6 4 page 22
25 (2) Find y. y m 55 4 m A C = A H C H yh 55 4 A know A, find H O SOH-CAH-TOA cosine ratio uses A and H rearrange for y cos55 4 y cos55 o = 4 y 4 y = cos55 o = y = cos 55, calculator set to DEGREES FINDING AN UNKNOWN ANGLE Example: Find x. 9 cm x 7 cm T O A T = O A H x 7A know O, know A O9 SOH-CAH-TOA tangent ratio uses O and A tan x o = x = tan 1 7 = x = 52 1 use brackets for (9 7), calculator set to DEGREES page 23
26 CHAPTER 10: SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS EQUATION OF A LINE The equation gives a rule connecting the x and y coordinates of any point on the line. For example, 2x + y = 6 sample points: 0,6 ( ) x = 0, y = = 6 ( 3,0) x = 3, y = = 6 ( 2,10) x = 2, y = 10 2 ( 2) +10 = 6 ( ) x = 1, y = = 6 2 1, 5 2 Infinite points cannot be listed but can be shown as a graph. SKETCHING STRAIGHT LINES Show where the line meets the axes. Example: Sketch the graph with equation 3x + 2y = 12. Y 3x + 2y = y = 12 substituted for x = 0 2y = 12 ( ) y = 6 plot 0,6 3x + 2y = x + 2y = 12 3x = 12 substituted for y = 0 3x = 12 ( ) x = 4 plot 4,0 0 4 X page 24
27 SOLVE SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS: GRAPHICAL METHOD Sketch the two lines and the point of intersection is the solution. Example: Solve graphically the system of equations: y + 2x = 8 y x = 2 y + 2x = 8 (1) y = 8 substituted for x = 0 ( ) y = 8 plot 0,8 y x = 2 (2 ) y 0 = 2 substituted for x = 0 ( ) y = 2 plot 0,2 y + 2x = 8 (1) 0 + 2x = 8 substituted for y = 0 2x = 8 ( ) x = 4 plot 4,0 y x = 2 (2 ) 0 x = 2 substituted for y = 0 x = 2 ( ) x = 2 plot 2,0 Y y + 2x = 8 8 y x = 2 point of intersection ( 2,4) CHECK: x = 2 and y = 4 substituted in both equations 2 y + 2x = 8 (1) y x = 2 (2 ) = = 2 8 = 8 2 = X SOLUTION: x = 2 and y = 4 page 25
28 SOLVE SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS: SUBSTITUTION METHOD Rearrange both equations to y = and equate the two equations. ( or x = ) Example: Solve algebraically the system of equations: y + 2x = 8 y x = 2 y + 2 x = 8 (1) can choose to rearrange to y = or x = y = 8 2x choosing y = avoids fractions as x = y y x = 2 (2) y = x + 2 rearrange for y = x + 2 = 8 2x 3x + 2 = 8 3x = 6 x = 2 y terms equal y = x + 2 (2) can choose either equation (1) or (2) = substituted for x = 2 y = 4 CHECK: y + 2 x = 8 (1) using the other equation = 8 substituted for x = 2 and y = 4 8 = 8 SOLUTION: x = 2 and y = 4 page 26
29 SOLVE SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS: ELIMINATION METHOD Can add or subtract multiples of the equations to eliminate either the x or y term. Example: Solve algebraically the system of equations: 4x + 3y = 5 5x 2y = 12 4x + 3y = 5 (1) 2 can choose to eliminate x or y term 5x 2y = 12 (2 ) 3 choosing y term, LCM (3y,2y)= 6y (least common multiple) 8x + 6y = 10 (3) multiplied each term of (1) by 2 for + 6y 15x 6y = 36 (4 ) multiplied each term of (2) by 3 for 6y 23x + 0 = 46 (3) + (4 ) added "like" terms, x = 2 + 6y and 6y added to 0 (ie eliminated ) 4x + 3y = 5 (1) can choose either equation (1) or (2) y = 5 substituted for x = y = 5 3y = 3 y = 1 CHECK: 5x 2y = 12 (2 ) using the other equation ( 1)= 12 substituted for x = 2 and y = 1 10 ( 2)= = 12 SOLUTION: x = 2 and y = 1 page 27
30 CHAPTER 11: AREAS AND VOLUMES FORMULAE: triangles A = 1 2 bh kites (incudes the rhombus) A = 1 2 the product of the diagonals h b b b h b h h b h rectangle parallelogram trapezium b b h h l A =lb b A = bh a A = 1h a +b 2 ( ) r circle A = πr 2 C = πd Prism: a solid with the same cross-section throughout its length. Length l is at right-angles to the area A. cylinder V = πr 2 h V = Al A l A l A l page 28
31 AREA AND PERIMETER Example: Calculate: (1) the area (2) the perimeter 10 cm 16 cm Split the shape into known shapes. (1) 10 cm 6 cm A = lb =10 6 = 60 cm 2 A = 1 4 πr 2 = π = cm 2 6 cm r = 16 cm - 10 cm = 6 cm total area = = = 88 3 cm 2 (2) 6 cm 10 cm 16 cm d = 6 cm x 2 = 12 cm 1 4 C = 1 4 πd = π 12 4 = cm perimeter = = = 41 4 cm page 29
32 VOLUMES Examples: (1) Calculate the volume 8 cm 14 cm radius = 8 cm 2 = 4 cm V = πr 2 h = π = = cm 3 (exact answer 224π) (2) Calculate the volume A = 1 2 bh 8 cm = = 40 cm 2 8 cm 10 cm 20 cm 10 cm V = Al = = 800 cm 3 (3) Calculate the volume 12 cm 10 cm 12 cm A = 1 2 h a + b ( ) ( ) 2 = = cm 30 cm 8 cm =100 cm 2 V = Al = cm = 3000 cm 3 page 30
33 SURFACE AREA CYLINDER: π d h curved surface area A = π d h h d total surface area A = π d h + 2 π r 2 Examples: (1) Calculate the total surface area. 10 cm A = πdh + 2πr 2 = π π 6 6 = or 120π + 72π = = 192π cm 2 12 cm = 603 cm 2 (exact answer) triangular prism (2) Calculate the total surface area. 10 cm 8 cm 20 cm triangles A = 1 bh 2 A = l b rectangles A = l b 12 cm = = 48 cm 2 =10 20 = 200 cm 2 =12 20 = 240 cm 2 total area = = 736 cm 2 page 31
34 CHAPTER 12: FACTORSATION COMMON FACTORS Factors: divide into a number without a remainder. Factors of a number come in pairs. For example, 12 = 1 12 = 2 6 = 3 4 factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, = 1 18 = 2 9 = 3 6 factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 4a = 1 4a = 2 2a = 4 a factors of 4a are 1, 2, 4, a, 2a, 4a 2a 2 = 1 2a 2 = 2 a 2 = a 2a factors of 2a 2 are 1, 2, a, 2a, a 2, 2a 2 Highest Common Factor(HCF): the highest factors numbers share. For example, from the above lists of factors: HCF( 12,18) = 6 HCF( 4a,2a 2 ) = 2a Factorisation: HCFs are used to write expressions in fully factorised form. Examples: Factorise fully: (1) 12x + 18y (2) 4a 2a 2 6 2x + 6 3y using HCF( 12,18) = 6 2a 2 2a a using HCF( 4a,2a 2 ) = 2a = 6( 2x + 3y) = 2a( 2 a) NOTE: the following answers are factorised but not fully factorised: ( ) ( ) 2 6x + 9y 3 4 x + 6y ( ) 2 2a a 2 ( ) a 4 2a page 32
35 DIFFERENCE OF TWO SQUARES Rule: a 2 b 2 = ( a +b) ( a b) check: ( a + b) ( a b) = a( a b) + b( a b) = a 2 ab + ab b 2 = a 2 b 2 Examples: Factorise fully: (1) 4x 2 9 (2) t 2 1 (3) n 4 1 ( ) ( )( 2x 3) = 2x = 2x + 3 = t ( )( t 1) = t +1 common factor first (4) 8x 2 18 (5) t 3 t ( ) ( )( n 2 1) ( ) n +1 = n 2 = n = n ( )( n 1) ( ) = 2 4x 2 9 ( )( 2x 3) = 2 2x + 3 ( ) = t t 2 1 ( )( t 1) = t t +1 TRINOMIALS ax 2 +bx+c, a =1 ie. 1x 2 (Quadratic Expressions) ax 2 +bx+c = ( x +? )( x +? ) The missing numbers: are a pair of factors of c sum to b Examples: Factorise fully: (1) x 2 + 5x + 6 (2) x 2 5x + 6 (3) x 2 5x = 2 3 = = 5 use + 2 and + 3 1, 6 or 2, ( ) = 5 use 2 and 3 1,6 or 1, 6 or 2,3 or 2, ( ) = 5 use + 1 and 6 = ( x + 2) ( x + 3) = ( x 2) ( x 3) = ( x + 1) ( x 6) page 33
36 TRINOMIALS ax 2 +bx+c, a 1 Carry out a procedure which is a reversal of bracket breaking. Examples: (1) factorise 2t 2 + 7t =12 pairs of factors 1, or 2 2,6 4 or 44 3, = 7 2t t + 6 = 2t 2 + 4t + 3t + 6 replace + 7t by + 4t + 3t (or + 3t + 4t) ( ) + 3t + 6 ( ) bracket first and last pairs of terms ( ) + 3( t + 2) factorise each bracket using HCF ( )( t + 2) factorise: brackets are common factor = 2t 2 + 4t = 2t t + 2 = 2t + 3 (2) factorise 2t 2 7t + 6 Watch! Take care with negative signs outside brackets. 2 6 =12 pairs of factors 1, or 2 2,6 4 or 44 3, = 7 2t 2 7 t + 6 = 2t 2 4t 3t + 6 replace 7t by 4t 3t (or 3t 4t) ( ) 3t 6 ( ) notice sign change in 2nd bracket, + 6 to 6 ( ) 3( t 2) ( )( t 2) = 2t 2 4t = 2t t 2 = 2t 3 (3) factorise 2t 2 11t ( ) = 12 pairs of factors 1,12 or 2,6 or 3, 4 2t 2 11 t = 11 one factor is negative = 2t 2 12t + 1t 6 replace 11t by 12t +1t (not + 1t 12t) ( ) + 1t 6 ( ) notice no sign change needed in 2nd bracket ( ) + 1 ( t 6) notice 2nd bracket still requires common factor ( )( t 6) = 2t 2 12t = 2t t 6 = 2t +1 page 34
37 ALTERNATIVE METHOD: Try out the possible combinations of the factors which could be in the brackets. Examples: same quadratic expressions as the previous page. (1) factorise 2t 2 + 7t =12 pairs of factors 1, or 2 2,6 4 or 44 3, = 7 2t t + 6 try combinations so that 3t and 4t are obtained factors of 2t 2 : 2t, t factors of 6: 1, 6 or 2, 3 2t 1 2t 6 2t 2 2t 3 t 6 t 1t 12t 2t 2 + 7t + 6 has no common factor. These have so can be ruled out 1 t 3 t 3t 2 4t ( 2t + 3) ( t + 2) (2) factorise 2t 2 7t + 6 exactly as example (1) except -7t requires both negative, so -3, -2 2t 3 ( ) t 2 ( ) (3) factorise 2t 2 11t ( ) = 12 pairs of factors 1,12 or 2,6 or 3, 4 2t 2 11 t one factor is negative = 11 try combinations so that 12t and 1t are obtained 2t +1 2t -6 2t +2 2t +3 t -6 t 1t -12t 2t 2 11t 6 has no common factor. These have so can be ruled out ( 2t +1) ( t 6) +1 t -3 t -2 3t -4t page 35
38 CHAPTER 13: PERSONAL FINANCE PERCENTAGE CHANGE original changed value value INCREASE: growth, appreciation, compound interest 100% +a% ( a)% DECREASE: decay, depreciation 100% a% ( 100 a)% For example, 8% increase: 100% +8% 108% = 1 08 multiply quantity by 1 08 for 8% increase 8% decrease: 100% 8% 92% = 0 92 multiply quantity by 0 92 for 8% decrease Examples: APPRECIATION AND DEPRECIATION (1) A house appreciates in value by 5% in 2007, appreciates 10% in 2008 and depreciates by 15% in Calculate the value of the house at the end of % increase: 100% + 5% = 105% = % increase: 100% +10% = 110% = % decrease: 100% 15% = 085% = = or evaluate year by year year 1 5% = = year 2 10% of = = year 3 15% of = = COMPOUND INTEREST (2) Calculate the compound interest on invested at 5% pa for 3 years ( 1 05) 3 ie or evaluate year by year = compound interest = = page 36
39 INCOME TAX Tax is paid on taxable income, gross annual income less allowances. Example: Tom earns a year and after allowances of he will pay tax at 20%. Calculate his income after tax. 20% tax subtracted 100% 20% 080% = 0 80 taxable income = = = REVERSING PERCENTAGE CHANGE Divide by the factor which produced the increase. Examples: (1) Including VAT of 20%, a radio costs 96. Find the original cost exclusive of VAT. 20% VAT added 100% +20% 120% = 1 20 x 1 20 = 96 x = = 80 (2) A camera costs 120 after a discount of 25% is applied. Find the original cost. 25% discount subtracted 100% 25% 075% = 0 75 x 0 75 = 120 x = = 160 page 37
40 CHAPTER 14: FORMULAE TRANSPOSING FORMULAE (CHANGE OF SUBJECT) Follow the rules for equations to isolate the target term and then the target letter. (has target letter) addition and subtraction x + a = b x a = b subtract a from each side add a to each side x = b a x = b + a multiplication and division x a = b ax = b multiply each side by a divide each side by a x = ab x = b a powers and roots x 2 = a x = a square root each side square each side x = a x = a 2 Examples: Change the subject of the formula to r: (1) F = 3r 2 + p (2) W = r n t subtract p from each side F p = 3r 2 divide each side by 3 F p = r 2 3 square root both sides F p = r 3 subject of formula now r r = F p 3 Wt = Wt + n = ( Wt + n) 2 = r multiply both sides by t r n add n to both side r square both sides subject of formula now r r = ( Wt + n) 2 page 38
41 If the target term is negative, rearrange to the other side so it is positive If the target term is in brackets, break the brackets If there are two target terms, gather the target terms and factorise for the target letter. (3) g = a( v ar) (4) h = πr + t r break the brackets g = av a 2 r g + a 2 r = av add a 2 r to each side subtract g from each side a 2 r = av g divide both sides by a 2 r = av g a 2 multiply both sides by r hr = πr + t hr πr = t r( h π) = t r = subtract πr from each side factorise for r ( ) divide both sides by h π t h π ( ) brackets not needed EFFECT OF CHANGE Examples: (1) The volume of a cylinder is given by (2) The length of a prism is given by V = πr 2 h l = V A Describe the effect on volume of: Describe is the effect on length of: (i) doubling h (ii) trebling r (i) doubling V (ii) trebling A V = πr 2 2h = 2πr 2 h V = π( 3r) 2 h = π 9r 2 h l = V A l = V A 2 times bigger = 9πr 2 h 9 times bigger = 2V A = 2 V A 2 times bigger = V 3A = 1 V 3 A 1 of size 3 page 39
42 CONSTRUCTING FORMULAE An arithmetic process can be generalised using letters to represent quantities. Examples: (1) CAR HIRE CHARGES minimum charge: 20 per day mileage charge: first 200 miles no charge over 200 miles each additional mile 20p (a) Find the cost of hiring a car for 6 days and travelling a distance 500 miles. (b) A car is hired for d days and the mileage is n miles where n > 200. Write a formula for the cost C of hiring the car. (a) The calculations are set out carefully for each stage. minimum charge ( ) : 6 20 = 120 note 20p is 0 20 mileage charge ( ) : = = 60 total cost: C = = 180 (b) The appropriate letters can replace the numbers. minimum charge ( ) : d 20 = 20d mileage charge ( ) : n 200 n 200 total cost ( ), C = 20d n 200 ( ) 0 20 = 0 2( n 200) ( ) (2) Odd numbers starting with 3 are added. Generalise for adding n odd numbers. 4 terms: = terms: = terms: = terms: terms: terms: 6 8 n terms: n n + 2 = n n + 2 ( ) ( ) The first number matches the number of terms. The second number is always 2 more than this. page 40
43 CHAPTER 15: PROBABILITY The probability of an event A occuring is P( A) = number of outcomes involving A total number of outcomes possible Always 0 P 1 and P = 0 impossible to occur, P = 1 certain to occur P( not A) = 1 P( A) number of expected outcomes = number of trials P( A) involving event A For example, In a game, scores from two spinners are added together. The possible totals are shown SPINNER SPINNER ways out of 30 to score a total of 9, P( 9) = 3 30 = ways to score a total which is not 9, P( not 9) = = 9 10 cannot score 12, P( 12) = 0 must score less than 12 P ( < 12) = 1 or P( not 9) =1 P( 9) = = 9 10 spin the pair of spinners 60 times, number of 9s expected = number of trials P( 9) = = 6 page 41
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES
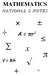 MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
MIA Textbook INTERMEDIATE 1 CHECKLIST
 St Ninian s High School MIA Textbook INTERMEDIATE 1 CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
St Ninian s High School MIA Textbook INTERMEDIATE 1 CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
MATHS S4 Credit Course CHECKLIST
 St Ninian s High School MATHS S Credit Course CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
St Ninian s High School MATHS S Credit Course CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
MATHS Level 4+ Course Pupil Learning Log
 Success is 99% Perspiration and % Inspiration St Ninian s High School Hard Work beats Talent every time when Talent doesn t Work Hard MATHS Level + Course Pupil Learning Log Expect to get out what you
Success is 99% Perspiration and % Inspiration St Ninian s High School Hard Work beats Talent every time when Talent doesn t Work Hard MATHS Level + Course Pupil Learning Log Expect to get out what you
Mathematics Department Level 3 TJ Book 3a Pupil Learning Log. St Ninian s High School. Name Class Teacher. I understand this part of the course =
 St Ninian s High School Mathematics Department Level TJ Book a Pupil Learning Log I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course
St Ninian s High School Mathematics Department Level TJ Book a Pupil Learning Log I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework. Objectives
 Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
12 CSEC Maths Answer Key
 1 CSEC Maths Answer Key 1 Computation No. Answers Further explanations 1 D In order to write a number in standard form it must be written in the form A 10 ±n, where 1 A < 10. B 3 B 4 D Therefore, to write
1 CSEC Maths Answer Key 1 Computation No. Answers Further explanations 1 D In order to write a number in standard form it must be written in the form A 10 ±n, where 1 A < 10. B 3 B 4 D Therefore, to write
MATHEMATICS Standard Grade - General Level
 General Mathematics - Practice Examination G Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
General Mathematics - Practice Examination G Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
Key Facts and Methods
 Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist
 Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist Contents: Page Numeracy Number..2 Measure.4 Statistics...6 Expressions and Formulae Algebra..8 Geometry.....9 Statistics..11 Relationships Linear Equations
Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist Contents: Page Numeracy Number..2 Measure.4 Statistics...6 Expressions and Formulae Algebra..8 Geometry.....9 Statistics..11 Relationships Linear Equations
Integers, Fractions, Decimals and Percentages. Equations and Inequations
 Integers, Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Round a whole number to a specified number of significant figures Round a decimal number to a specified number of decimal places or significant figures Perform
Integers, Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Round a whole number to a specified number of significant figures Round a decimal number to a specified number of decimal places or significant figures Perform
Angles on a Point. Always add up to 360º. a + b + c = 180º.
 Angles on a Point Always add up to 360º a + b + c = 180º a b c Area of a Trapezium Add the parallel sides, multiply by the perpendicular height, then divide by 2. Formula is ½(a+b)h a Perpendicular Height
Angles on a Point Always add up to 360º a + b + c = 180º a b c Area of a Trapezium Add the parallel sides, multiply by the perpendicular height, then divide by 2. Formula is ½(a+b)h a Perpendicular Height
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1. Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know
 Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
The Grade Descriptors below are used to assess work and student progress in Mathematics from Year 7 to
 Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A)
 Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4
 YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION
 YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION Autumn Term 1 Powers and roots Spring Term 1 Multiplicative reasoning Summer Term 1 Graphical solutions Quadratics Non-linear graphs Trigonometry Half Term: Assessment
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION Autumn Term 1 Powers and roots Spring Term 1 Multiplicative reasoning Summer Term 1 Graphical solutions Quadratics Non-linear graphs Trigonometry Half Term: Assessment
National 5 Course Notes. Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:-
 National 5 Course Notes Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:- a x 10 n where a is between 1 and 10 and n is an integer
National 5 Course Notes Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:- a x 10 n where a is between 1 and 10 and n is an integer
Wednesday, 24 May Warm-Up Session. Non-Calculator Paper
 Wednesday, 24 May 2017 Warm-Up Session Non-Calculator Paper Non-Calculator Paper 80 marks in 90 minutes IF YOU FINISH EARLY CHECK EVERYTHING! You have made a silly mistake somewhere. Redo some questions
Wednesday, 24 May 2017 Warm-Up Session Non-Calculator Paper Non-Calculator Paper 80 marks in 90 minutes IF YOU FINISH EARLY CHECK EVERYTHING! You have made a silly mistake somewhere. Redo some questions
The Australian Curriculum Mathematics
 The Australian Curriculum Mathematics Mathematics Table of Contents ACARA The Australian Curriculum Version 2.0 dated Monday, 17 October 2011 2 Number Algebra Number place value Fractions decimals Real
The Australian Curriculum Mathematics Mathematics Table of Contents ACARA The Australian Curriculum Version 2.0 dated Monday, 17 October 2011 2 Number Algebra Number place value Fractions decimals Real
Free download from not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle.
 Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
Middle School Math Course 2
 Middle School Math Course 2 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Middle School Math Course 2 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Answers and Mark Scheme. Holiday Revision Ten minutes a day for ten days
 Answers and Mark Scheme Holiday Revision 10--10 Ten minutes a day for ten days Non-Calculator Answers DAY 1 1. One night at a school concert the audience is made up as follows: 1 are m e n, are w o men,
Answers and Mark Scheme Holiday Revision 10--10 Ten minutes a day for ten days Non-Calculator Answers DAY 1 1. One night at a school concert the audience is made up as follows: 1 are m e n, are w o men,
Mathematics KSHSSA Key Stage 3 Grade Descriptors
 Developing Fluency, reasoning Mathematically and Problem Solving consolidate their numerical and mathematical capability from develop their mathematical knowledge, in part through key stage 2 and extend
Developing Fluency, reasoning Mathematically and Problem Solving consolidate their numerical and mathematical capability from develop their mathematical knowledge, in part through key stage 2 and extend
Pre Algebra. Curriculum (634 topics additional topics)
 Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Algebra Readiness. Curriculum (445 topics additional topics)
 Algebra Readiness This course covers the topics shown below; new topics have been highlighted. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the
Algebra Readiness This course covers the topics shown below; new topics have been highlighted. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the
Revision Notes. Name Class
 M8 Revision Notes Name Class 1 fractions WHEN OR TURN TO TOP HEAVY multiply do both top and bottom 3 1 1 2 = 3 5 3 5 = 10 7 70 15 = 4 10 = 4 2 15 3 divide 2 2 1 1 = 3 4 flip over second number then multiply
M8 Revision Notes Name Class 1 fractions WHEN OR TURN TO TOP HEAVY multiply do both top and bottom 3 1 1 2 = 3 5 3 5 = 10 7 70 15 = 4 10 = 4 2 15 3 divide 2 2 1 1 = 3 4 flip over second number then multiply
CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS)
 CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS) 12 Formulae 13 Time 14 Fractions 17 Percentages 19 Ratio and Proportion 23 Information Handling
CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS) 12 Formulae 13 Time 14 Fractions 17 Percentages 19 Ratio and Proportion 23 Information Handling
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
Course Readiness and Skills Review Handbook (Topics 1-10, 17) (240 topics, due. on 09/11/2015) Course Readiness (55 topics)
 Course Name: Gr. 8 Fall 2015 Course Code: C6HNH-TEK9E ALEKS Course: Middle School Math Course 3 Instructor: Mr. Fernando Course Dates: Begin: 08/31/2015 End: 06/17/2016 Course Content: 642 Topics (637
Course Name: Gr. 8 Fall 2015 Course Code: C6HNH-TEK9E ALEKS Course: Middle School Math Course 3 Instructor: Mr. Fernando Course Dates: Begin: 08/31/2015 End: 06/17/2016 Course Content: 642 Topics (637
Math Literacy. Curriculum (457 topics additional topics)
 Math Literacy This course covers the topics outlined below, and can be used to support a non STEM pathways course. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs.
Math Literacy This course covers the topics outlined below, and can be used to support a non STEM pathways course. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs.
Pre Algebra. Curriculum (634 topics)
 Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Sample : 6 worksheets without solutions
 Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National 5) Applications...4 Arcs & Sectors...5 Brackets...6 Completing the Square...7
Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National 5) Applications...4 Arcs & Sectors...5 Brackets...6 Completing the Square...7
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
Corequisite Support for Liberal Arts Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning
 Corequisite Support for Liberal Arts Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users
Corequisite Support for Liberal Arts Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users
MATHEMATICS Standard Grade - General Level Paper I
 General Mathematics - Practice Examination F Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
General Mathematics - Practice Examination F Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist
 Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist To help you use this personal learning checklist, the target levels for each topic have given to help you decide what to focus on for your tier
Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist To help you use this personal learning checklist, the target levels for each topic have given to help you decide what to focus on for your tier
Math Literacy. Curriculum (457 topics)
 Math Literacy This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Math Literacy This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
TeeJay Publishers. SQA - National 5. National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2
 TeeJay Publishers Draft SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2 This Course Planner for National 5, based on TeeJay s Int-2-Credit Books 1 & 2, comes in two parts :-
TeeJay Publishers Draft SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2 This Course Planner for National 5, based on TeeJay s Int-2-Credit Books 1 & 2, comes in two parts :-
GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 45 minutes ANSWERS. Grade Boundaries A* A B C D E.
 MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 45 minutes ANSWERS Grade Boundaries A* A B C D E 88 71 57 43 22 13 3 Authors Note Every possible effort has been made
MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 45 minutes ANSWERS Grade Boundaries A* A B C D E 88 71 57 43 22 13 3 Authors Note Every possible effort has been made
Maths Revision. Book 2. Name:.
 Maths Revision Book 2 Name:. Number Fractions Calculating with Fractions Addition 6 + 4 2 2 Subtraction 2 Subtract wholes first 0 2 + 9 2 2 2 Change one whole into thirds 9 2 + + 2 7 2 2 Multiplication
Maths Revision Book 2 Name:. Number Fractions Calculating with Fractions Addition 6 + 4 2 2 Subtraction 2 Subtract wholes first 0 2 + 9 2 2 2 Change one whole into thirds 9 2 + + 2 7 2 2 Multiplication
Understand the difference between truncating and rounding. Calculate with roots, and with integer and fractional indices.
 The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
ZETA MATHS. National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions. Alexander Forrest
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions Alexander Forrest Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National
National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions Alexander Forrest Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National
Newbattle Community High School National 5 Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
TeeJay Publishers. SQA - National 4. National 4 Course Planner - Following Outcome Order
 TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 4 * Based on Books 3G and 4G National 4 Course Planner - Following Outcome Order This Course Planner for National 4 based on TeeJay Books 3G & 4G comes in two parts :-
TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 4 * Based on Books 3G and 4G National 4 Course Planner - Following Outcome Order This Course Planner for National 4 based on TeeJay Books 3G & 4G comes in two parts :-
Key Stage 3 Subject: Maths Foundation Year: Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Topic/Module: Geometry
 Subject: Foundation Topic/Module: Geometry Time Geometry 1 234 Metric Units Angles/Polygons Bearings Transformations watch Clips N21 N7 N7 N7 N7 N7, R2, 112 112 G10, 46 G16, 122 G14 G13, G17, 45, 121 G23
Subject: Foundation Topic/Module: Geometry Time Geometry 1 234 Metric Units Angles/Polygons Bearings Transformations watch Clips N21 N7 N7 N7 N7 N7, R2, 112 112 G10, 46 G16, 122 G14 G13, G17, 45, 121 G23
NUMBER. Here are the first 20 prime numbers: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71.
 NUMBER Types of Number Prime Numbers A prime number is a number which can only be divided by 1 or itself. The smallest prime number is 2. 2 can only be divided by 2 or 1. Here are the first 20 prime numbers:
NUMBER Types of Number Prime Numbers A prime number is a number which can only be divided by 1 or itself. The smallest prime number is 2. 2 can only be divided by 2 or 1. Here are the first 20 prime numbers:
QUESTION 1 50 FOR JSS 3
 QUESTION 1 5 FOR JSS 3 1. The knowledge of probability is necessary for the following reasons except A. In predicting B. In deciding C. In selecting D. In drawing table E. In forecasting. Factorise 7a
QUESTION 1 5 FOR JSS 3 1. The knowledge of probability is necessary for the following reasons except A. In predicting B. In deciding C. In selecting D. In drawing table E. In forecasting. Factorise 7a
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
*2500/405* 2500/405. MATHEMATICS STANDARD GRADE Credit Level Paper 1 (Non-calculator) 1 You may NOT use a calculator.
 C 500/405 N A T I O N A L Q U A L I F I C A T I O N S 0 0 8 T H U R S D A Y, 8 M A Y. 0 P M. 5 P M MATHEMATICS STANDARD GRADE Credit Level Paper (Non-calculator) You may NOT use a calculator. Answer as
C 500/405 N A T I O N A L Q U A L I F I C A T I O N S 0 0 8 T H U R S D A Y, 8 M A Y. 0 P M. 5 P M MATHEMATICS STANDARD GRADE Credit Level Paper (Non-calculator) You may NOT use a calculator. Answer as
TeeJay Publishers. SQA - National 5. National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5
 TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5 This Course Planner for National 5, is based on TeeJay s New CfE4 + and N5, comes in two parts :- Part A
TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5 This Course Planner for National 5, is based on TeeJay s New CfE4 + and N5, comes in two parts :- Part A
Middle School Math Course 3
 Middle School Math Course 3 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Middle School Math Course 3 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Paper Reference. Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Monday 2 June 2008 Afternoon Time:
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Monday 2 June 2008 Afternoon Time:
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS
 PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16
 Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
California Algebra 1
 California Algebra 1 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
California Algebra 1 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Method marks are awarded for a correct method which could lead to a correct answer.
 Pre Paper 3F Question Bank Answers November 2017 GCSE Mathematics (AQA style) Foundation Tier This set of answers is not a conventional marking scheme; while it gives a basic allocation of marks, its main
Pre Paper 3F Question Bank Answers November 2017 GCSE Mathematics (AQA style) Foundation Tier This set of answers is not a conventional marking scheme; while it gives a basic allocation of marks, its main
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes. Last updated January 2019
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 019 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 019 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
Markscheme May 2016 Mathematical studies Standard level Paper 2
 M16/5/MATSD/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M Markscheme May 016 Mathematical studies Standard level Paper pages M16/5/MATSD/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M This markscheme is the property of the International Baccalaureate and must not
M16/5/MATSD/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M Markscheme May 016 Mathematical studies Standard level Paper pages M16/5/MATSD/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M This markscheme is the property of the International Baccalaureate and must not
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 11 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 11 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
California 5 th Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 (Activity) L1 L2 L3 Excel Math Objective Recognizing numbers less than a million given in words or place value; recognizing addition and subtraction fact families; subtracting 2 threedigit numbers with
(Activity) L1 L2 L3 Excel Math Objective Recognizing numbers less than a million given in words or place value; recognizing addition and subtraction fact families; subtracting 2 threedigit numbers with
Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator)
 www.themathsprofessor.com Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set Time: 1 hour
www.themathsprofessor.com Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set Time: 1 hour
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. accurately drawn. x + 2. x + 4. x + 2
 1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra
 Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below and is available for use with integrated, interactive ebooks. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to
Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below and is available for use with integrated, interactive ebooks. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A*
 Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
ACT MATH MUST-KNOWS Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions
 Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
1 You may NOT use a calculator. 2 Full credit will be given only where the solution contains appropriate working. 3 Square-ruled paper is provided.
 X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 008 TUESDAY, 0 MAY.00 PM.5 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where
X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 008 TUESDAY, 0 MAY.00 PM.5 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where
PYP Mathematics Continuum
 Counting from One By Imaging to Advanced Counting (-) Y E+ 0- K N O W L E D G E Read,Write, and Count Whole numbers up to 00, forwards and backwards in s, s, 5 s, and 0 s Recall How many tens in a two-digit
Counting from One By Imaging to Advanced Counting (-) Y E+ 0- K N O W L E D G E Read,Write, and Count Whole numbers up to 00, forwards and backwards in s, s, 5 s, and 0 s Recall How many tens in a two-digit
Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 22 1/19/12
 Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 1/19/1 Table of Contents 1. Numbers... 1.1. NAMES FOR NUMBERS... 1.. PLACE VALUES... 3 1.3. INEQUALITIES... 4 1.4. ROUNDING... 4 1.5. DIVISIBILITY TESTS... 5 1.6.
Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 1/19/1 Table of Contents 1. Numbers... 1.1. NAMES FOR NUMBERS... 1.. PLACE VALUES... 3 1.3. INEQUALITIES... 4 1.4. ROUNDING... 4 1.5. DIVISIBILITY TESTS... 5 1.6.
REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Foundation Unit 5. For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011 This Unit Summer 2012
 REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Foundation Unit 5 For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011 This Unit Summer 2012 Version 1: 28 April 10 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit T5
REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Foundation Unit 5 For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011 This Unit Summer 2012 Version 1: 28 April 10 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit T5
Paper 3 Unseen Topics
 Paper 3 Unseen Topics This is a collection of questions based on the topics that are so far UNSEEN or are usually more prominent Make sure you revise all topics as it is very likely topics from Paper 1
Paper 3 Unseen Topics This is a collection of questions based on the topics that are so far UNSEEN or are usually more prominent Make sure you revise all topics as it is very likely topics from Paper 1
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 8 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students know the properties of rational* and irrational* numbers expressed in a variety of forms. They understand and use
8 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students know the properties of rational* and irrational* numbers expressed in a variety of forms. They understand and use
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes. Last updated August 2015
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated August 015 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated August 015 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
Candidate Number. General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Circle Theorems. Angles at the circumference are equal. The angle in a semi-circle is x The angle at the centre. Cyclic Quadrilateral
 The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
Topic I can Complete ( ) Mark Red/Amber/Green Parent s signature. Inverclyde Academy Mathematics Department Page 1
 Fractions, Decimal Fractions and Percentages (MNU 2-07a, MNU 3-07a) I can write fractions by examining shapes cut into even parts. I know percentage is another way of describing a fraction. I can solve
Fractions, Decimal Fractions and Percentages (MNU 2-07a, MNU 3-07a) I can write fractions by examining shapes cut into even parts. I know percentage is another way of describing a fraction. I can solve
Sp Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8
 Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8 Recap: Levels 7 and 8 Core: Higher Levels Hrs Topic Notes Eamples References Page (3). INDICES: STANDARD FORM R: Inde notation Positive integer powers only 5 3 4
Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8 Recap: Levels 7 and 8 Core: Higher Levels Hrs Topic Notes Eamples References Page (3). INDICES: STANDARD FORM R: Inde notation Positive integer powers only 5 3 4
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 9
 INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent schools from 16 to 19 September 2014. During this period all learners
INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent schools from 16 to 19 September 2014. During this period all learners
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE
 CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE TIER TOPIC HEADING SUB HEADING Both Number Integers Ordering numbers Both Number Integers Rounding numbers Both Number Integers Adding and subtracting whole
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE TIER TOPIC HEADING SUB HEADING Both Number Integers Ordering numbers Both Number Integers Rounding numbers Both Number Integers Adding and subtracting whole
The graph of a proportional relation always contains the origin and has a slope equal to the constant of proportionality.
 Chapter 11.1 Ratios and Rates A ratio is a comparison of two numbers, a and b, by division. The numbers a and b are called terms of the ratio. A ratio can be expressed in three different ways. 1. Word
Chapter 11.1 Ratios and Rates A ratio is a comparison of two numbers, a and b, by division. The numbers a and b are called terms of the ratio. A ratio can be expressed in three different ways. 1. Word
Foundations of High School Math
 Foundations of High School Math This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to
Foundations of High School Math This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to
Stage 9 PROMPT Sheet. 9/3 Solve simultaneous equations by an. 9/1 Standard Form. A x 10 n A is between 1 & 10 and n is an integer
 Stage 9 PROMPT Sheet 9/ Standard Form Standard form is a way of expressing numbers that are too big or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form x n is between & and n is an integer Example:
Stage 9 PROMPT Sheet 9/ Standard Form Standard form is a way of expressing numbers that are too big or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form x n is between & and n is an integer Example:
Mathematics A *S37713A0125* Edexcel GCSE S37713A. Paper 2 (Calculator) Higher Tier. Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/2H
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/2H
GCSE 4370/06 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 2 HIGHER TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4370/06 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for this paper.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4370/06 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for this paper.
Fourth Year General Course Outline
 Fourth Year General Course Outline based on TeeJay s General Book 4G Page 0 S3 Revision Work Ch 0 1-15 Could be used in June S3 - Revise 2-3 topics at a time Nil Integers Ch 1 16-18 1 Bank Balance ± 20,
Fourth Year General Course Outline based on TeeJay s General Book 4G Page 0 S3 Revision Work Ch 0 1-15 Could be used in June S3 - Revise 2-3 topics at a time Nil Integers Ch 1 16-18 1 Bank Balance ± 20,
Compound Interest Formula Depreciation Formula. P = principal r = the interest rate n = number of time periods A = final amount. opposite.
 Chapter Finance The simple interest rule I=Prt I = simple interest P = principal r = the interest rate t = the time Compound Interest Formula Depreciation Formula A= P( + 00 A= P( 00 P = principal r =
Chapter Finance The simple interest rule I=Prt I = simple interest P = principal r = the interest rate t = the time Compound Interest Formula Depreciation Formula A= P( + 00 A= P( 00 P = principal r =
GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS. Marks shown in brackets for each question (2)
 MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
QUESTION 1 50 FOR JSS 1
 QUESTION 1 5 FOR JSS 1 1. The LCM of, 3 and 4 is A. 14 B. 1 C. 1 D. 16. Estimate 578.6998 to 3 decimal places. A. 578.7 B. 578.79 C. 578.8 D. 579. 3. Express 111 two as a number in base ten. A. 15 B. 18
QUESTION 1 5 FOR JSS 1 1. The LCM of, 3 and 4 is A. 14 B. 1 C. 1 D. 16. Estimate 578.6998 to 3 decimal places. A. 578.7 B. 578.79 C. 578.8 D. 579. 3. Express 111 two as a number in base ten. A. 15 B. 18
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Tuesday 21 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/4HR
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Tuesday 21 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/4HR
HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST (Grades 9 4)
 HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST 2017+ (s 9 4) Geometry and Measures Circle theorems 8 Vector arguments and proof 8 Area of a triangle 7 Cosine Rule 7 Pythagoras and trig 2D and 3D 7 Sine Rule 7 Combined
HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST 2017+ (s 9 4) Geometry and Measures Circle theorems 8 Vector arguments and proof 8 Area of a triangle 7 Cosine Rule 7 Pythagoras and trig 2D and 3D 7 Sine Rule 7 Combined
Edexcel Mathematics Higher Tier, November 2010 (1380/3H) (Paper 3, non-calculator)
 Link to examining board: www.edexcel.com This question paper is not currently available to download for free from the Edexcel website. You can purchase your own copy by phoning the Edexcel order line on
Link to examining board: www.edexcel.com This question paper is not currently available to download for free from the Edexcel website. You can purchase your own copy by phoning the Edexcel order line on
Mathematics (Linear) 4365/1H
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier November 2014 Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier November 2014 Mathematics
Year 8 Autumn Term Topics Covered Calculations Ratio, Proportion and Compound Measures Manipulating Algebraic Expressions Fractions
 Year 8 Autumn Term Topics Covered Note: grades given are our own internal 'Sprowston' grades used as a guide for the purpose of tracking students' progress Calculations Grade 2 Multiply and divide integers
Year 8 Autumn Term Topics Covered Note: grades given are our own internal 'Sprowston' grades used as a guide for the purpose of tracking students' progress Calculations Grade 2 Multiply and divide integers
You ve likely come to this chapter because you just completed Practice Test 3 in
 Practice Test 3: Answers and Explanations You ve likely come to this chapter because you just completed Practice Test 3 in Chapter 17. I hope you fared well. To find out, spend some time with this chapter
Practice Test 3: Answers and Explanations You ve likely come to this chapter because you just completed Practice Test 3 in Chapter 17. I hope you fared well. To find out, spend some time with this chapter
Paper Reference. Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Wednesday 12 November 2008 Morning
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Wednesday 12 November 2008 Morning
4 th Grade Hinojosa Math Vocabulary Words
 Topic 1 Word Definition Picture Digit A symbol used to make numerals. These are the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Place value The value of where the digit is in the number, such as units(ones),
Topic 1 Word Definition Picture Digit A symbol used to make numerals. These are the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Place value The value of where the digit is in the number, such as units(ones),
GREEN SKILL DRILL 1. Answers Name. Show ALL work! 1) Express as a common fraction: 2) Express
 GREEN SKILL RILL Name Show LL work! ) Express as a common fraction: 7 ) Express as a common fraction in lowest terms. 7 ) Find the number which appears the way from to on the number line. ) Express in
GREEN SKILL RILL Name Show LL work! ) Express as a common fraction: 7 ) Express as a common fraction in lowest terms. 7 ) Find the number which appears the way from to on the number line. ) Express in
