Integers, Fractions, Decimals and Percentages. Equations and Inequations
|
|
|
- Lambert Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integers, Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Round a whole number to a specified number of significant figures Round a decimal number to a specified number of decimal places or significant figures Perform BODMAS calculations with integers Perform simple BODMAS calculations with decimals Perform BODMAS calculations with fractions Given a quantity after a percentage change (increase or decrease), calculate the original amount Equations and Inequations Solve simple equations such as 7x 3 Solve equations where the variable is on both sides of the equation Solve equations with brackets Solve equations with fractions Solve equations with fractions where the variable is in the denominator Solve equations involving any combination of the above Make an equation given a contextual problem and use it to solve problems Solve simple inequations such as 5x < 8 Solve inequations where the variable is on both sides of the inequality Solve inequations with fractions Scientific Notation Express a number written in scientific notation to a stated number of significant figures Multiply or divide a number written in scientific notation by any number and express the answer in scientific notation Multiply or divide numbers written in scientific notation and express the answer in scientific notation M Patel (August 011) 1 St. Machar Academy
2 Functions and Graphs Know that a function is a rule or description that takes an input value and pairs it off with exactly one output value; the set of all input values is called the domain of the function, and the set of all output values is called the range of the function Know the notation for a function f with domain A and range B, namely, f : A B Know that the graph of a function is the picture obtained by plotting points; the domain values (aka x values) are along the x - axis, whereas the range values (aka y values) are along the y - axis Know that a linear function is of the form: f (x) ax + b Know that the graph of a linear function is called a straight line Know that a quadratic function is of the form: f (x) ax + bx + c Know that the graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola Know that a reciprocal function is of the form: a f (x) (x 0) x Know that the graph of a reciprocal function is called a hyperbola; a hyperbola has branches and a hyperbola written as above never crosses the x or y axes Solve problems involving a reciprocal function or its graph, for example, if a point on the graph is known, calculate a Know that the exponential function (with base a) is of the form: f (x) a x Know that the graph of an exponential function is called an exponential curve and that an exponential curve as above always passes through the point (0, 1) Solve problems involving an exponential function or its graph, for example, if a point on the graph is known, calculate the base Know the definitions of the sine, cosine and tangent functions and be familiar with their graphs M Patel (August 011) St. Machar Academy
3 The Straight Line Link the type of a straight line with its gradient: m 0, parallel to x axis, equation: y constant m > 0, positive gradient m < 0, negative gradient m undefined, parallel to y axis, equation: x constant Work out the equation of a straight line when told its gradient and a point lying on the line Given the equation of a straight line, calculate the y intercept by putting x 0 Given the equation of a straight line, calculate the x intercept by putting y 0 Draw or sketch the graph of a straight line when told its equation with specific values for m and c Sketch the graph of a straight line when told its equation with no actual values for m and c, but generic information about m and c such as: m > 0 and c > 0 m > 0 and c < 0 m < 0 and c > 0 m < 0 and c < 0 Solve contextual problems involving straight lines and their graphs M Patel (August 011) 3 St. Machar Academy
4 Factorisation Recognise a difference of squares and factorise according to the rule, a b (a b) (a + b), for example: 9x 1 (3x 1) (3x + 1) 16r 36 (4r 6) (4r + 6) 5a 49b (5a 7b) (5a + 7b) Factorise quadratic trinomials, for example: x + x 3 (x 1) (x + 3) 3p 13p 10 (3p + ) (p 5) 8m + 16m + 6 (4m + ) (m + 3) Factorise more difficult trinomials, for example: 3x 4 + 5x (3x 1) (x + ) Similar Shapes Know that the ratio of areas of similar shapes is the area scale factor (ASF ) and calculated by squaring the length scale factor (k): ASF k Know that the ratio of volumes of similar shapes is the volume scale factor (VSF ) and calculated by cubing the length scale factor: VSF k 3 Calculate the length scale factor when given the ASF by taking the square root of the ASF Given similar shapes and the area of one of them, calculate the area of the other one by finding the area scale factor Calculate the length scale factor when given the VSF by taking the cube root of the VSF Given similar shapes and the volume of one of them, calculate the volume of the other one by finding the volume scale factor M Patel (August 011) 4 St. Machar Academy
5 Quadratic Equations Know that a quadratic expression is one of the form: ax + b x + c Factorise a quadratic expression Know that a quadratic equation is an equation involving a variable x that is squared, and usually an x term and a constant number Know that a quadratic equation in standard form is written as: ax + bx + c 0 Bring a quadratic equation not in standard form to one that is in standard form Know that solving a quadratic equation means finding values of the variable that satisfy the equation Know that a quadratic equation may have 0, 1 or solutions Know that there are 3 techniques for solving a quadratic equation, Factorisation Quadratic Formula Graph Solve a quadratic equation by factorisation Solve a quadratic equation in standard form by using the Quadratic Formula : b ± b 4ac x a Know that every parabola has a maximum or minimum turning point : (a > 0, minimum) (a < 0, maximum) M Patel (August 011) 5 St. Machar Academy
6 Given the graph of y x, sketch the graph of y p (x q) + r Know that a parabola has a line of symmetry (parallel to the y - axis) through the turning point with equation x constant Find the y - intercept of a parabola Find the x - intercept(s) of a parabola by solving the associated quadratic equation in standard form Given a quadratic function y k (x a) (x b), know (i) that a and b are the x - intercepts (ii) how to find the value of k when told the y - intercept and the values of a and b Know that every quadratic expression has either a maximum or minimum value Find the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic expression and know what this means graphically Find the coordinates of the maximum or minimum turning point of a parabola Solve quadratic equation problems in context Make a quadratic equation in contextual problems and solve it, possibly rejecting a solution with justification Areas and Volumes Know that the total surface area of a (closed) cylinder equals the curved surface area (CSA) plus the areas of the identical circles Calculate the total surface area of a cylinder Calculate the volume V of a sphere with radius r using the formula: 4 V 3 πr 3 Given the volume of a sphere, calculate its radius Know that a hemisphere is half a sphere Calculate the volume of a hemisphere Given the volume of a hemisphere, calculate its radius Know that a composite solid is a 3D shape made up of simpler 3D shapes Calculate the volume of a composite solid Given the volume and cross-sectional area, calculate the height of a prism Given the volume and height, calculate the cross-sectional area of a prism M Patel (August 011) 6 St. Machar Academy
7 Trigonometry Know that a positive angle is measured anticlockwise from the positive x axis, whereas a negative angle is measured clockwise from the positive x - axis Know that angles can be bigger than 360 and smaller than 0 Know that the sine function is the function obtained by taking any point P on the circle of radius r and associating to the angle made by the line joining the centre to P the y coordinate of P divided by r Know that the cosine function is the function obtained by taking any point P on the circle of radius r and associating to the angle made by the line joining the centre to P the x coordinate of P divided by r Know that the tangent function is the function obtained by taking any point P on the circle of radius r and associating to the angle made by the line joining the centre to P the y coordinate of P divided by the x coordinate of P Know that the ASTC diagram shows in which quadrants the sine, cosine and tangent functions are positive and negative Know that sine is positive in quadrants I and II and negative in quadrants III and IV Know that cosine is positive in quadrants I and IV and negative in quadrants II and III Know that tangent is positive in quadrants I and III and negative in quadrants II and IV Know that the sine or cosine of any angle can be worked out Know that the tangent of certain angles cannot be worked out, namely those angles which are an odd multiple of 90 Know that: tan x sin x cos x Know the Pythagorean Identity : sin x + cos x 1 Recognise the graph of the sine function, i.e. y sin x Recognise the graph of the cosine function, i.e. y cos x Recognise the graph of the tangent function, i.e. y tan x, and know that it has asymptotes at odd multiples of 90 Know that the sine, cosine and tangent functions are periodic Know that the graphs of y sin x and y cos x each have a period M Patel (August 011) 7 St. Machar Academy
8 of 360, amplitude 1, maximum value 1 and minimum value 1 Know that the graph of y tan x has a period of 180, and no maximum or minimum values Sketch the graphs of y a sin bx + c and y a cos bx + c; b describes how many whole sine or cosine shapes fit into a 0 to 360 range of x values; period 360 ; c shifts up/down the y - axis b Know that a trigonometric equation is an equation involving a trigonometric function Rearrange a trigonometric equation into one of the 3 forms: sin x a ( 1 a 1) cos x a ( 1 a 1) tan x a (a is any number) Solve the above trigonometric equations for a specified range of x - values Solve contextual problems involving trigonometric equations Know that in any triangle with sides a, b, c and opposite angles A, B, C, the Sine Rule holds: a b sin B c sin C sin A Given angles and 1 side in a triangle (say, A, B and a), use the Sine Rule to work out a missing side (b) Given sides and 1 angle in a triangle (say, a, c and C ), use the Sine Rule to work out a missing angle (A ) Know that in any triangle with sides a, b, c and opposite angle C, the Cosine Rule holds: c a + b ab cos C Given sides and the angle between them, use the Cosine Rule to work out the side opposite the angle Given the 3 sides of a triangle, find a missing angle by using the Cosine Rule in the form: a + b c cos C ab Given sides a, b of a triangle and the angle C between them, use the Trigonometric Area Formula to calculate the triangle s area: Area ½ ab sin C M Patel (August 011) 8 St. Machar Academy
9 Indices and Surds Know that any number or variable raised to the power of 0 is, by convention, equal to 1, for example: a 0 1 Know that any number or variable raised to the power of 1 equals that same number or variable. For example: r 1 r Know that the reciprocal of a number or variable equals 1 divided by the number or variable, and is written to the power of 1 : Know that s 1 1 s 1 q a means taking the q th root of a, i.e.: 1 q a q a p q Know that a means raising a to the p th power and then taking the q th root of the result, or equivalently, taking the q th root of a and then raising the result to the p th power : p q p a ( ) 1 q a q p a or p p q 1 q a ( ) q a ( ) p a Simplify numbers with fractional indices, for example: 3 8 ( ) M Patel (August 011) 9 St. Machar Academy
10 or ( ) ( ) Know the rules of indices : 4 a p a q a p + q a p a q a p q p ( a ) q Know that a p q a p q 1 a is often written as a Use the rules of indices to simplify expressions Know that a surd is a root of a natural number that cannot be written as a rational number Know the rules of surds : ab a b a a b b Use the rules of surds to simplify surds, for example: Add and subtract surds of the form a + b c Know that rationalising a denominator in a fraction means writing the denominator without a surd, for example: ( 5 + 1) ( 5 1)( 5 + 1) ( 5 + 1) 4 Solve equations involving surds Solve inequations involving surds M Patel (August 011) 10 St. Machar Academy
11 Money Know that appreciation means an increase in value and depreciation means a decrease in value Calculate percentage appreciation and percentage depreciation using the formulae: % Appreciation % Depreciation New Old Old Old New Old 100 % 100 % where Old refers to the starting value and New refers to the final value Calculate the appreciation or depreciation value when told the starting value, s, the fixed rate of appreciation or depreciation (r %) and the number of years, n, over which the value increases or decreases using the formulae: Appreciation s 1 + n r 100 Depreciation s 1 n r 100 Know that compound interest is an example of appreciation and differs from simple interest in that interest is added to interest Calculate compound interest M Patel (August 011) 11 St. Machar Academy
12 Formulae and Transposition Know that to transpose (aka change the subject) a formula for a specified variable means rearranging an equation in which that variable is the only quantity on the LHS of the equation Transpose the following types of formulae for x : y ¼F (7 x) H tx p N x Deduce the effect on the subject of a formula after changing a specific variable to a constant number times that variable (for example, changing x to 7x in the formula w 3x has the effect of changing w to 49 times its original value) Construct and use a formula in a contextual problem Pythagoras Theorem Use Pythagoras Theorem with surds Solve 3D problems using Pythagoras Theorem Know the Converse of Pythagoras Theorem (aka Converse of Pythagoras), namely that if the square of the longest side of a triangle equals the sum of the squares of the other sides, then the triangle is right-angled (the right angle being opposite the longest side) Use the Converse of Pythagoras to decide whether or not a triangle is right-angled Inductive Number Patterns Given a number pattern for the first several values of the variable n (n 1,, 3, ), write down a formula for (i) a specific value of n and (ii) the n th term Use the formula for the n th term to solve problems M Patel (August 011) 1 St. Machar Academy
13 Geometry of the Circle Know that the following statements are equivalent: the perpendicular bisector of a circle s chord passes through the centre of the circle a perpendicular line from a circle s centre, bisects the chord the line segment through the centre bisecting a chord is perpendicular to the chord Solve problems involving a circle s chord and the perpendicular bisector to the chord Know that the angle fraction of a circle s sector is the angle at the centre (aka sector angle) θ divided by 360 Calculate the arc length L of a sector given its radius r and sector angle θ using the Arc Length Formula : L Angle Fraction πr Calculate a circle s sector angle given its radius and arc length Calculate a circle s radius given its sector angle and arc length Calculate the sector area A of a circle given its radius r and sector angle θ using the Sector Area Formula : A Angle Fraction πr Calculate a circle s sector angle given its radius and sector area Calculate a circle s radius given its sector angle and sector area M Patel (August 011) 13 St. Machar Academy
14 Ratio, Proportion and Variation Solve problems involving ratios where there are more than two segments, such as, if the ratio of parents to teachers to pupils attending a play is 1 : 3 : 15 and 45 pupils attend (i) how many teachers must accompany them (ii) if there are 100 tickets, what is the maximum number of pupils that can attend? Solve more difficult ratio problems such as (i) if copper and pure gold are mixed in the ratio 5 : 7 to produce 14 carat gold, and there are 160 grams of copper and 45 grams of pure gold, what is the maximum weight of 14 carat gold that can be made (ii) if a blend of coffee consisting of Brazilian and Colombian in the ratio : 3 is sold in 1 kilogram tins, and there are 0 kg of Brazilian and 5 kg of Colombian, what is the maximum number of 1 kg tins of this blend that can be made? Know that if two quantities x and y are in inverse proportion, then we say that x varies inversely with (as) y and write, x 1 y and that an equivalent way of writing this is, xy k where k is the proportionality constant Solve problems involving inverse variation, such as, if t varies inversely as the square of d, calculate t when d 4 given that t 50 when d Know that a graph of inverse variation is one branch of a hyperbola Know that joint variation is a combination of direct and inverse variation Solve problems involving joint variation M Patel (August 011) 14 St. Machar Academy
15 Simultaneous Equations Know that simultaneous equations are a pair of equations that can be written in the form: ax + by c dx + ey f Know that simultaneous equations can be solved using 3 techniques: Graph Substitution Elimination Solve simultaneous graphically by knowing that the intersection of two straight lines representing the equations gives the solution Know that solving simultaneous equations by substitution entails: Writing one equation with one variable (say, y) as the subject of the formula Substituting this into the other equation and solving for the other variable (x) Solving for y by substituting x into either one of the equations Know that solving simultaneous equations by elimination entails: Multiplying each equation by a number (usually different) so that the coefficient of x or y in each equation is the same Adding or subtracting the equations so that one variable (say, x) is eliminated and y is solved for Putting this variable back into any of the equations to solve for x After obtaining solutions to simultaneous equations, check that the solutions satisfy the original equations Make simultaneous equations in contextual problems and solve them M Patel (August 011) 15 St. Machar Academy
16 Statistics and Probability Calculate the mean of a data set Know the meaning of cumulative frequency and attach a cumulative frequency column to a frequency table Find the median from a cumulative frequency table Calculate the standard deviation of a data set using the Standard Deviation Formula : s ( x x ) n 1 or s ( x ) n ( x ) n 1 Interpret standard deviation in terms of consistency and spread of data, especially in contextual problems Know that a back-to-back stem-and-leaf diagram compares two data sets and consists of stem-and-leaf diagrams drawn together sharing a common stem Draw a back-to-back stem-and-leaf diagram Know that quartiles split up a data set into 4 equal parts Know that the first and third quartiles are calculated by: Arranging the data set in order from lowest to highest Calculating the median of the whole data set (this is also called the second quartile) Calculating the median of the data set from the lowest value to the second quartile gives the first quartile Calculating the median of the data set from the second quartile to highest value gives the third quartile Know that a 5-figure summary consists of: Lowest value (L) M Patel (August 011) 16 St. Machar Academy
17 1 st quartile (Q 1 ) Median (aka nd quartile) (Q ) 3 rd quartile (Q 3 ) Highest value (H ) Calculate the interquartile range (Q 3 Q 1 ) and the semiinterquartile range (½ the interquartile range) from a data set or a frequency table Know that a 5 figure summary is represented pictorially using a boxplot ; draw a boxplot Interpret a boxplot in terms of consistency of data and compare two data sets in contextual problems Know what a dotplot is and draw one Interpret information from a dotplot Construct a pie chart and interpret information from it Work out the equation of a best-fitting straight line and use it to calculate a y value given an x value Know that the probability P(A) of an event A is a number between 0 and 1 Know that the expectation E(A) of an event A is the number of times A is expected to occur from a sample of items and is calculated using the equation: E(A) P(A) Total number of items in sample Algebraic Expressions and Fractions Expand brackets where there is a variable outside the brackets, for example: p (p + 5q) p + 5pq Use the FOIL (First, Outside, Inside, Last) method to expand and simplify a pair of linear binomial expressions, for example: (a + b) (c + d ) ac + ad + bc + bd (x + 3y) (3x y) 6x + 7xy 3y M Patel (August 011) 17 St. Machar Academy
18 Expand and simplify other bracketed expressions, for example: (3x + 1) (x 5x + 4) 3x 3 14 x + 7x + 4 Know that an algebraic fraction is a fraction where the numerator and denominator are algebraic expressions Add and subtract algebraic fractions such as: 3 m + 4 m + 1 Multiply and divide algebraic fractions, for example: a b a 3b a 3b 3p w p 5w 3 6p 5w Simplify algebraic fractions by cancelling one variable and possibly numbers, for example: 16a 4a 4ab b Simplify algebraic fractions by cancelling variables, for example: 1fr 4r f 3 3f r Simplify algebraic fractions by cancelling a common term (not necessarily a variable), for example: ( x + 1) ( x + 1) 3 Simplify algebraic fractions where the numerator is a difference of two squares, and can be factorised so that one of the factors cancels with the denominator (or a factor of the denominator), for example: x a a t t ( a t )( a + t ) a t a + 1 t a + t p 4q 3 p + 6q ( p q)( p + q) 3( p + q) p q 3 M Patel (August 011) 18 St. Machar Academy
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION
 YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION Autumn Term 1 Powers and roots Spring Term 1 Multiplicative reasoning Summer Term 1 Graphical solutions Quadratics Non-linear graphs Trigonometry Half Term: Assessment
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK - EXTENSION Autumn Term 1 Powers and roots Spring Term 1 Multiplicative reasoning Summer Term 1 Graphical solutions Quadratics Non-linear graphs Trigonometry Half Term: Assessment
Key Facts and Methods
 Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
Intermediate Maths Key Facts and Methods Use this (as well as trying questions) to revise by: 1. Testing yourself. Asking a friend or family member to test you by reading the questions (on the lefthand
Understand the difference between truncating and rounding. Calculate with roots, and with integer and fractional indices.
 The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
The Grade Descriptors below are used to assess work and student progress in Mathematics from Year 7 to
 Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE
 CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE TIER TOPIC HEADING SUB HEADING Both Number Integers Ordering numbers Both Number Integers Rounding numbers Both Number Integers Adding and subtracting whole
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE MATHS EXAMINATION BOARD COVERAGE TIER TOPIC HEADING SUB HEADING Both Number Integers Ordering numbers Both Number Integers Rounding numbers Both Number Integers Adding and subtracting whole
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A)
 Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4
 YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
Free download from not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle.
 Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
Newbattle Community High School National 5 Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Maths Years 9 to 10. Boardworks Maths Years 9 to 10. Presentations: 3-D problems 9 slides. Algebraic fractions 22 slides
 Boardworks Presentations: 3-D problems 9 slides Calculating features of 3-D shapes. Algebraic fractions 22 slides Fractions involving algebraic terms. Angle and chord properties 26 slides Arcs, sectors,
Boardworks Presentations: 3-D problems 9 slides Calculating features of 3-D shapes. Algebraic fractions 22 slides Fractions involving algebraic terms. Angle and chord properties 26 slides Arcs, sectors,
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR
 European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.:010-D-591-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR 6 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.:010-D-591-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR 6 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
2 year GCSE Scheme of Work
 2 year GCSE Scheme of Work Year 10 Pupils follow the 2 year Pearsons/Edexcel Scheme of Work FOUNDATION ROUTE HIGHER ROUTE YEAR 4 YEAR 5 YEAR 4 YEAR 5 GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1)
2 year GCSE Scheme of Work Year 10 Pupils follow the 2 year Pearsons/Edexcel Scheme of Work FOUNDATION ROUTE HIGHER ROUTE YEAR 4 YEAR 5 YEAR 4 YEAR 5 GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1)
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
TeeJay Publishers. SQA - National 5. National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5
 TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5 This Course Planner for National 5, is based on TeeJay s New CfE4 + and N5, comes in two parts :- Part A
TeeJay Publishers SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books CfE4 + and N5 This Course Planner for National 5, is based on TeeJay s New CfE4 + and N5, comes in two parts :- Part A
National 5 Course Notes. Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:-
 National 5 Course Notes Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:- a x 10 n where a is between 1 and 10 and n is an integer
National 5 Course Notes Scientific Notation (or Standard Form) This is a different way of writing very large and very small numbers in the form:- a x 10 n where a is between 1 and 10 and n is an integer
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2
 Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 Number Use standard form, expressed in standard notation and on a calculator display Calculate with standard form Convert between ordinary and standard form representations
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 Number Use standard form, expressed in standard notation and on a calculator display Calculate with standard form Convert between ordinary and standard form representations
Paper 1 Foundation Revision List
 Paper 1 Foundation Revision List Converting units of length 692 Converting units of mass 695 Order of operations 24 Solving one step equations 178 Operations with negative numbers 39, 40 Term to term rules
Paper 1 Foundation Revision List Converting units of length 692 Converting units of mass 695 Order of operations 24 Solving one step equations 178 Operations with negative numbers 39, 40 Term to term rules
MADRAS COLLEGE MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 COURSE NOTES - OCT 2106
 MADRAS COLLEGE MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 COURSE NOTES - OCT 2106 2016-17 NATIONAL 5 OUTLINE S3/4 S3 Oct - Mar (20 weeks) S3 Apr Jun (11 wks) S4 Aug Oct (8 wks) S4 Oct Dec (8 wks) S4 Jan Mar(11 wks) Exp &
MADRAS COLLEGE MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 COURSE NOTES - OCT 2106 2016-17 NATIONAL 5 OUTLINE S3/4 S3 Oct - Mar (20 weeks) S3 Apr Jun (11 wks) S4 Aug Oct (8 wks) S4 Oct Dec (8 wks) S4 Jan Mar(11 wks) Exp &
ZETA MATHS. National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist
 Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist To help you use this personal learning checklist, the target levels for each topic have given to help you decide what to focus on for your tier
Brockington College Mathematics Personal Learning Checklist To help you use this personal learning checklist, the target levels for each topic have given to help you decide what to focus on for your tier
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES
 AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
TeeJay Publishers. SQA - National 5. National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2
 TeeJay Publishers Draft SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2 This Course Planner for National 5, based on TeeJay s Int-2-Credit Books 1 & 2, comes in two parts :-
TeeJay Publishers Draft SQA - National 5 National 5 Course Planner Using TeeJay's Books IC1 and IC2 This Course Planner for National 5, based on TeeJay s Int-2-Credit Books 1 & 2, comes in two parts :-
Applied Mathematics syllabus for Grade 11 and 12 For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman
 Applied Mathematics syllabus for Grade 11 and 12 For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman Commencing Dates: 201/2014 for grade 11 & 2014/2015 for grade 12 Taken from : IB Diploma Syllabus Based on:
Applied Mathematics syllabus for Grade 11 and 12 For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman Commencing Dates: 201/2014 for grade 11 & 2014/2015 for grade 12 Taken from : IB Diploma Syllabus Based on:
GCSE Linear Targeting Grade A*
 GCSE Linear Targeting Grade A* Notes This scheme of work includes all the topics that make up the AQA GCSE Specification 800. It is aimed at classes that will fast-track their GCSE, completing the course
GCSE Linear Targeting Grade A* Notes This scheme of work includes all the topics that make up the AQA GCSE Specification 800. It is aimed at classes that will fast-track their GCSE, completing the course
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics
 King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
YEAR 12 - Mathematics Pure (C1) Term 1 plan
 Week YEAR 12 - Mathematics Pure (C1) Term 1 plan 2016-2017 1-2 Algebra Laws of indices for all rational exponents. Use and manipulation of surds. Quadratic functions and their graphs. The discriminant
Week YEAR 12 - Mathematics Pure (C1) Term 1 plan 2016-2017 1-2 Algebra Laws of indices for all rational exponents. Use and manipulation of surds. Quadratic functions and their graphs. The discriminant
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - The main topics in the Curriculum: NUMBER TOPIC 1 Functions 2 Number patterns, sequences and series 3 Finance, growth and decay 4 Algebra 5 Differential Calculus 6 Probability 7 Euclidian geometry
- 1 - The main topics in the Curriculum: NUMBER TOPIC 1 Functions 2 Number patterns, sequences and series 3 Finance, growth and decay 4 Algebra 5 Differential Calculus 6 Probability 7 Euclidian geometry
Candidates are expected to have available a calculator. Only division by (x + a) or (x a) will be required.
 Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
The Learning Objectives of the Compulsory Part Notes:
 17 The Learning Objectives of the Compulsory Part Notes: 1. Learning units are grouped under three strands ( Number and Algebra, Measures, Shape and Space and Data Handling ) and a Further Learning Unit.
17 The Learning Objectives of the Compulsory Part Notes: 1. Learning units are grouped under three strands ( Number and Algebra, Measures, Shape and Space and Data Handling ) and a Further Learning Unit.
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers
 Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes. Last updated August 2015
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated August 015 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated August 015 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES
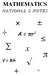 MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document
 Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (1999) Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (2009)
 Use interval notation (A-1) Plot and describe data of quadratic form using appropriate scales (A-) Determine the following characteristics of a graph of a quadratic function: y a x p q Vertex Domain and
Use interval notation (A-1) Plot and describe data of quadratic form using appropriate scales (A-) Determine the following characteristics of a graph of a quadratic function: y a x p q Vertex Domain and
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes. Last updated January 2019
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 019 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 019 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
Mathematics KSHSSA Key Stage 3 Grade Descriptors
 Developing Fluency, reasoning Mathematically and Problem Solving consolidate their numerical and mathematical capability from develop their mathematical knowledge, in part through key stage 2 and extend
Developing Fluency, reasoning Mathematically and Problem Solving consolidate their numerical and mathematical capability from develop their mathematical knowledge, in part through key stage 2 and extend
Evaluate algebraic expressions for given values of the variables.
 Algebra I Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA Variables and Expressions Exponents and Order of Operations Identify a variable expression and its components: variable, coefficient,
Algebra I Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA Variables and Expressions Exponents and Order of Operations Identify a variable expression and its components: variable, coefficient,
Mathematics. GCSE subject content and assessment objectives
 Mathematics GCSE subject content and assessment objectives Contents Introduction 3 Subject aims and learning outcomes 3 Subject content 4 Scope of study 4 Number 4 Algebra 6 Ratio, proportion and rates
Mathematics GCSE subject content and assessment objectives Contents Introduction 3 Subject aims and learning outcomes 3 Subject content 4 Scope of study 4 Number 4 Algebra 6 Ratio, proportion and rates
UNIT 3 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ALGEBRA
 UNIT 3 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ALGEBRA Substitution of Values Rearrangement and Substitution Polynomial Expressions Expanding Expressions Expanding Expressions by Rule Perfect Squares The Difference of Two
UNIT 3 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ALGEBRA Substitution of Values Rearrangement and Substitution Polynomial Expressions Expanding Expressions Expanding Expressions by Rule Perfect Squares The Difference of Two
Algebraic. techniques1
 techniques Algebraic An electrician, a bank worker, a plumber and so on all have tools of their trade. Without these tools, and a good working knowledge of how to use them, it would be impossible for them
techniques Algebraic An electrician, a bank worker, a plumber and so on all have tools of their trade. Without these tools, and a good working knowledge of how to use them, it would be impossible for them
National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions. Alexander Forrest
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions Alexander Forrest Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National
National 5 Mathematics Revision Homework with Worked Solutions Alexander Forrest Contents Mathematics (National 5) Expressions and Formulae... Mathematics (National 5) Relationships...3 Mathematics (National
Algebra III INSTRUCTIONAL PACING GUIDE (Days Based on 90 minutes)
 EA, IA, PC-1. Connect algebra and trigonometry with other branches of mathematics. EA, IA, PC-1.7 G-1. G-1.8 G-1.9 Understand how to represent algebraic and trigonometric relationships by using tools such
EA, IA, PC-1. Connect algebra and trigonometry with other branches of mathematics. EA, IA, PC-1.7 G-1. G-1.8 G-1.9 Understand how to represent algebraic and trigonometric relationships by using tools such
HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST (Grades 9 4)
 HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST 2017+ (s 9 4) Geometry and Measures Circle theorems 8 Vector arguments and proof 8 Area of a triangle 7 Cosine Rule 7 Pythagoras and trig 2D and 3D 7 Sine Rule 7 Combined
HIGHER MATHS REVISION CHECKLIST 2017+ (s 9 4) Geometry and Measures Circle theorems 8 Vector arguments and proof 8 Area of a triangle 7 Cosine Rule 7 Pythagoras and trig 2D and 3D 7 Sine Rule 7 Combined
MATHS S4 Credit Course CHECKLIST
 St Ninian s High School MATHS S Credit Course CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
St Ninian s High School MATHS S Credit Course CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = I do not understand this part of the course = Name Class Teacher
C-1. Snezana Lawrence
 C-1 Snezana Lawrence These materials have been written by Dr. Snezana Lawrence made possible by funding from Gatsby Technical Education projects (GTEP) as part of a Gatsby Teacher Fellowship ad-hoc bursary
C-1 Snezana Lawrence These materials have been written by Dr. Snezana Lawrence made possible by funding from Gatsby Technical Education projects (GTEP) as part of a Gatsby Teacher Fellowship ad-hoc bursary
Method marks are awarded for a correct method which could lead to a correct answer.
 Pre Paper 3F Question Bank Answers November 2017 GCSE Mathematics (AQA style) Foundation Tier This set of answers is not a conventional marking scheme; while it gives a basic allocation of marks, its main
Pre Paper 3F Question Bank Answers November 2017 GCSE Mathematics (AQA style) Foundation Tier This set of answers is not a conventional marking scheme; while it gives a basic allocation of marks, its main
BUILT YOU. ACT Pathway. for
 BUILT for YOU 2016 2017 Think Through Math s is built to equip students with the skills and conceptual understandings of high school level mathematics necessary for success in college. This pathway progresses
BUILT for YOU 2016 2017 Think Through Math s is built to equip students with the skills and conceptual understandings of high school level mathematics necessary for success in college. This pathway progresses
The Australian Curriculum Mathematics
 The Australian Curriculum Mathematics Mathematics Table of Contents ACARA The Australian Curriculum Version 2.0 dated Monday, 17 October 2011 2 Number Algebra Number place value Fractions decimals Real
The Australian Curriculum Mathematics Mathematics Table of Contents ACARA The Australian Curriculum Version 2.0 dated Monday, 17 October 2011 2 Number Algebra Number place value Fractions decimals Real
grasp of the subject while attaining their examination objectives.
 PREFACE SUCCESS IN MATHEMATICS is designed with the purpose of assisting students in their preparation for important school and state examinations. Students requiring revision of the concepts covered in
PREFACE SUCCESS IN MATHEMATICS is designed with the purpose of assisting students in their preparation for important school and state examinations. Students requiring revision of the concepts covered in
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work
 Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Math Prep for College Physics
 Math Prep for College Physics This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (190 topics + 52 additional
Math Prep for College Physics This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (190 topics + 52 additional
2 2xdx. Craigmount High School Mathematics Department
 Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Mapping Australian Curriculum (AC) Mathematics and VELS Mathematics. Australian Curriculum (AC) Year 9 Year 10/10A
 Mapping Australian Curriculum (AC) Mathematics and VELS Mathematics In the following document, the left hand column shows AC content that matches VELS content at the corresponding levels. Teaching programs
Mapping Australian Curriculum (AC) Mathematics and VELS Mathematics In the following document, the left hand column shows AC content that matches VELS content at the corresponding levels. Teaching programs
CC.2.2.HS.D.1 Interpret the structure of expressions to represent a quantity in terms of it. Calculator set builder notation, interval Unit 2:
 Unit/Concepts Unit 1: Number Sets PA Eligible Content PA Common Core CC.2.2.HS.D.1 Interpret the structure of expressions to represent a quantity in terms of it Resources Vocab 1.1 set, number sets (Natural,
Unit/Concepts Unit 1: Number Sets PA Eligible Content PA Common Core CC.2.2.HS.D.1 Interpret the structure of expressions to represent a quantity in terms of it Resources Vocab 1.1 set, number sets (Natural,
Copyright 2018 UC Regents and ALEKS Corporation. ALEKS is a registered trademark of ALEKS Corporation. 2/10
 Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
STAAR STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY
 STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY STANDARDS ALGEBRA I TEKS Snapshot Algebra I (New TEKS 2015-16) Mathematical Process Standards A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes
STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY STANDARDS ALGEBRA I TEKS Snapshot Algebra I (New TEKS 2015-16) Mathematical Process Standards A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes
9-12 Mathematics Vertical Alignment ( )
 Algebra I Algebra II Geometry Pre- Calculus U1: translate between words and algebra -add and subtract real numbers -multiply and divide real numbers -evaluate containing exponents -evaluate containing
Algebra I Algebra II Geometry Pre- Calculus U1: translate between words and algebra -add and subtract real numbers -multiply and divide real numbers -evaluate containing exponents -evaluate containing
Strand 1: Statistics and Probability
 Strand 1: Statistics and Probability Topic 1.1 Counting Listing outcomes of experiments in a systematic way, such as in a table, using sample spaces, tree diagrams. 1.2 C oncepts of The probability of
Strand 1: Statistics and Probability Topic 1.1 Counting Listing outcomes of experiments in a systematic way, such as in a table, using sample spaces, tree diagrams. 1.2 C oncepts of The probability of
Mathematics programmes of study: key stage 3. National curriculum in England
 Mathematics programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England September 2013 Mathematics key stage 3 Purpose of study Mathematics is a creative and highly inter-connected discipline that
Mathematics programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England September 2013 Mathematics key stage 3 Purpose of study Mathematics is a creative and highly inter-connected discipline that
Algebra One Dictionary
 Algebra One Dictionary Page 1 of 17 A Absolute Value - the distance between the number and 0 on a number line Algebraic Expression - An expression that contains numbers, operations and at least one variable.
Algebra One Dictionary Page 1 of 17 A Absolute Value - the distance between the number and 0 on a number line Algebraic Expression - An expression that contains numbers, operations and at least one variable.
Functions and their Graphs
 Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
*X100/201* X100/201. MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE 2 Units 1, 2 and 3 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 2010 FRIDAY, 21 MAY 1.00 PM 1.
 X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 00 FRIDAY, MAY.00 PM.45 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where the
X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 00 FRIDAY, MAY.00 PM.45 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where the
1 You may NOT use a calculator. 2 Full credit will be given only where the solution contains appropriate working. 3 Square-ruled paper is provided.
 X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 008 TUESDAY, 0 MAY.00 PM.5 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where
X00/0 NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS 008 TUESDAY, 0 MAY.00 PM.5 PM MATHEMATICS INTERMEDIATE Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read carefully You may NOT use a calculator. Full credit will be given only where
MATHS Learning Ladder Year 7
 MATHS Learning Ladder Year 7 Key Learning Ladders The Learning Ladders are split into Year 7, 8 and 9 on different pages, and are colour coded to indicate the expected progress the students should be making.
MATHS Learning Ladder Year 7 Key Learning Ladders The Learning Ladders are split into Year 7, 8 and 9 on different pages, and are colour coded to indicate the expected progress the students should be making.
Circle Theorems. Angles at the circumference are equal. The angle in a semi-circle is x The angle at the centre. Cyclic Quadrilateral
 The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
Portable Assisted Study Sequence ALGEBRA IIB
 SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
DESK Secondary Math II
 Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice in Secondary Mathematics I describe mathematical habits of mind that teachers should seek to develop in their students. Students become mathematically
Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice in Secondary Mathematics I describe mathematical habits of mind that teachers should seek to develop in their students. Students become mathematically
MR. YATES. Vocabulary. Quadratic Cubic Monomial Binomial Trinomial Term Leading Term Leading Coefficient
 ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY COURSE OUTLINE SPRING 2009. MR. YATES Vocabulary Unit 1: Polynomials Scientific Notation Exponent Base Polynomial Degree (of a polynomial) Constant Linear Quadratic Cubic Monomial
ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY COURSE OUTLINE SPRING 2009. MR. YATES Vocabulary Unit 1: Polynomials Scientific Notation Exponent Base Polynomial Degree (of a polynomial) Constant Linear Quadratic Cubic Monomial
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1. Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know
 Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
Year 9 Mastery Statements for Assessment 1 Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole Numbers and Decimals Measures, perimeter area and volume Expressions and formulae Indices
Math Review for AP Calculus
 Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier. In any triangle ABC. Sine Rule = = Cosine Rule a 2 = b 2 + c 2 2bccos A
 Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Math Prep for Statics
 Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Wellington College Mathematics Department. Sixth Form Kick Start
 Wellington College Mathematics Department Sith Form Kick Start Wellington College Mathematics Department Sith Form Kick Start Introduction There is a big step up from IGCSE to AS-Level or IB: questions
Wellington College Mathematics Department Sith Form Kick Start Wellington College Mathematics Department Sith Form Kick Start Introduction There is a big step up from IGCSE to AS-Level or IB: questions
Common Core Edition Table of Contents
 Common Core Edition Table of Contents ALGEBRA 1 Chapter 1 Foundations for Algebra 1-1 Variables and Expressions 1-2 Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions 1-3 Real Numbers and the Number Line 1-4
Common Core Edition Table of Contents ALGEBRA 1 Chapter 1 Foundations for Algebra 1-1 Variables and Expressions 1-2 Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions 1-3 Real Numbers and the Number Line 1-4
MATH II CCR MATH STANDARDS
 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITIES M.2HS.1 M.2HS.2 M.2HS.3 M.2HS.4 M.2HS.5 M.2HS.6 Explain how the definition of the meaning of rational exponents follows from extending the properties of integer exponents
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITIES M.2HS.1 M.2HS.2 M.2HS.3 M.2HS.4 M.2HS.5 M.2HS.6 Explain how the definition of the meaning of rational exponents follows from extending the properties of integer exponents
Pre AP Algebra. Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra
 Pre AP Algebra Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra 1 The content of the mathematics standards is intended to support the following five goals for students: becoming
Pre AP Algebra Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra 1 The content of the mathematics standards is intended to support the following five goals for students: becoming
Rearrange m ore complicated formulae where the subject may appear twice or as a power (A*) Rearrange a formula where the subject appears twice (A)
 Moving from A to A* A* Solve a pair of simultaneous equations where one is linear and the other is non-linear (A*) Rearrange m ore complicated formulae may appear twice or as a power (A*) Simplify fractions
Moving from A to A* A* Solve a pair of simultaneous equations where one is linear and the other is non-linear (A*) Rearrange m ore complicated formulae may appear twice or as a power (A*) Simplify fractions
The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II Critical Area 1: Critical Area 2: Critical Area 3: Critical Area 4: Critica l Area 5: Critical Area 6:
 The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II is on quadratic expressions, equations, and functions; comparing their characteristics and behavior to those of linear and exponential relationships from Secondary
The focus of SECONDARY Mathematics II is on quadratic expressions, equations, and functions; comparing their characteristics and behavior to those of linear and exponential relationships from Secondary
Wednesday, 24 May Warm-Up Session. Non-Calculator Paper
 Wednesday, 24 May 2017 Warm-Up Session Non-Calculator Paper Non-Calculator Paper 80 marks in 90 minutes IF YOU FINISH EARLY CHECK EVERYTHING! You have made a silly mistake somewhere. Redo some questions
Wednesday, 24 May 2017 Warm-Up Session Non-Calculator Paper Non-Calculator Paper 80 marks in 90 minutes IF YOU FINISH EARLY CHECK EVERYTHING! You have made a silly mistake somewhere. Redo some questions
PreCalculus. Curriculum (447 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Algebra 1 Math Year at a Glance
 Real Operations Equations/Inequalities Relations/Graphing Systems Exponents/Polynomials Quadratics ISTEP+ Radicals Algebra 1 Math Year at a Glance KEY According to the Indiana Department of Education +
Real Operations Equations/Inequalities Relations/Graphing Systems Exponents/Polynomials Quadratics ISTEP+ Radicals Algebra 1 Math Year at a Glance KEY According to the Indiana Department of Education +
 1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
Π xdx cos 2 x
 Π 5 3 xdx 5 4 6 3 8 cos x Help Your Child with Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Π 5 3 xdx 5 4 6 3 8 cos x Help Your Child with Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
5w 3. 1MA0 Higher Tier Practice Paper 2H (Set D) Question Working Answer Mark Notes 1 (a) 5w 8 = 3(4w + 2) 5w 8 = 12w = 12w 5w 14 = 7w
 (a) 5w 8 = (4w + ) 5w 8 = w + 6 8 6 = w 5w 4 = 7w M for attempting to multiply both sides by as a first step (this can be implied by equations of the form 5w 8 = w +? or 5w 8 =?w + 6 i.e. the LHS must
(a) 5w 8 = (4w + ) 5w 8 = w + 6 8 6 = w 5w 4 = 7w M for attempting to multiply both sides by as a first step (this can be implied by equations of the form 5w 8 = w +? or 5w 8 =?w + 6 i.e. the LHS must
( and 1 degree (1 ) , there are. radians in a full circle. As the circumference of a circle is. radians. Therefore, 1 radian.
 Angles are usually measured in radians ( c ). The radian is defined as the angle that results when the length of the arc of a circle is equal to the radius of that circle. As the circumference of a circle
Angles are usually measured in radians ( c ). The radian is defined as the angle that results when the length of the arc of a circle is equal to the radius of that circle. As the circumference of a circle
MATHS Level 4+ Course Pupil Learning Log
 Success is 99% Perspiration and % Inspiration St Ninian s High School Hard Work beats Talent every time when Talent doesn t Work Hard MATHS Level + Course Pupil Learning Log Expect to get out what you
Success is 99% Perspiration and % Inspiration St Ninian s High School Hard Work beats Talent every time when Talent doesn t Work Hard MATHS Level + Course Pupil Learning Log Expect to get out what you
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1
 Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
MATHEMATICAL SUBJECTS Mathematics should be visualised as the vehicle for aiding a student to think, reason, analyse and articulate logically.
 MATHEMATICAL SUBJECTS Mathematics should be visualised as the vehicle for aiding a student to think, reason, analyse and articulate logically. Apart from being treated as a subject of its own, Mathematics
MATHEMATICAL SUBJECTS Mathematics should be visualised as the vehicle for aiding a student to think, reason, analyse and articulate logically. Apart from being treated as a subject of its own, Mathematics
Global Context Statement of Inquiry MYP subject group objectives/assessment
 Vertical Planner Subject: Mathematics Year level: MYP 1 Unit Title Key Concept Related Concept Global Context Statement of Inquiry MYP subject group objectives/assessment Number Systems and number properties
Vertical Planner Subject: Mathematics Year level: MYP 1 Unit Title Key Concept Related Concept Global Context Statement of Inquiry MYP subject group objectives/assessment Number Systems and number properties
Department Curriculum Map
 Department Curriculum Map 2018-19 Department Mathematics Subject Specific Skills Wider key skills To be able to involving: Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion & Rates of Change Logic skills Problem solving
Department Curriculum Map 2018-19 Department Mathematics Subject Specific Skills Wider key skills To be able to involving: Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion & Rates of Change Logic skills Problem solving
Algebra 2 with Trigonometry Correlation of the ALEKS course Algebra 2 with Trigonometry to the Tennessee Algebra II Standards
 Algebra 2 with Trigonometry Correlation of the ALEKS course Algebra 2 with Trigonometry to the Tennessee Algebra II Standards Standard 2 : Number & Operations CLE 3103.2.1: CLE 3103.2.2: CLE 3103.2.3:
Algebra 2 with Trigonometry Correlation of the ALEKS course Algebra 2 with Trigonometry to the Tennessee Algebra II Standards Standard 2 : Number & Operations CLE 3103.2.1: CLE 3103.2.2: CLE 3103.2.3:
licensed to: St Andrews Academy Page 2
 National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 014 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
National 5 Mathematics Revision Notes Last updated January 014 Use this booklet to practise working independently like you will have to in the exam. Get in the habit of turning to this booklet to refresh
IYGB. Special Paper U. Time: 3 hours 30 minutes. Created by T. Madas. Created by T. Madas
 IYGB Special Paper U Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core Syllabus Booklets of Mathematical
IYGB Special Paper U Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core Syllabus Booklets of Mathematical
Evaluate the expression if x = 2 and y = 5 6x 2y Original problem Substitute the values given into the expression and multiply
 Name EVALUATING ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS Objective: To evaluate an algebraic expression Example Evaluate the expression if and y = 5 6x y Original problem 6() ( 5) Substitute the values given into the expression
Name EVALUATING ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS Objective: To evaluate an algebraic expression Example Evaluate the expression if and y = 5 6x y Original problem 6() ( 5) Substitute the values given into the expression
Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Integrated Math II. A student at this
Limited Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Integrated Math II. A student at this
