Photonic crystal fiber with a hybrid honeycomb cladding
|
|
|
- Shawn Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Photonic crystal fiber with a hybrid honeycomb cladding Niels Asger Mortensen asger@mailaps.org Martin Dybendal Nielsen COM, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kongens Lyngby, Denmark Jacob Riis Folkenberg, Christian Jakobsen, and Harald R. Simonsen Abstract: We consider an air-silica honeycomb lattice and demonstrate a new approach to the formation of a core defect. Typically, a high or low-index core is formed by adding a high-index region or an additional air-hole (or other low-index material) to the lattice, but here we discuss how a core defect can be formed by manipulating the cladding region rather than the core region itself. Germanium-doping of the honeycomb lattice has recently been suggested for the formation of a photonic band-gap guiding silica-core and here we experimentally demonstrate how an index-guiding silica-core can be formed by fluorine-doping of the honeycomb lattice Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Fiber design and fabrication, ( ) Fiber properties, ( ) Fibers, single-mode, ( ) Photonic crystal fiber References and links 1. J. C. Knight, Photonic crystal fibres, Nature 424, (2003). 2. J. C. Knight, T. A. Birks, P. S. J. Russell, and D. M. Atkin, All-silica single-mode optical fiber with photonic crystal cladding, Opt. Lett. 21, (1996). 3. J. C. Knight, J. Broeng, T. A. Birks, and P. S. J. Russell, Photonic Band Gap Guidance in Optical Fibers, Science 282, (1998). 4. J. Lægsgaard and A. Bjarklev, Doped photonic bandgap fibers for short-wavelength nonlinear devices, Opt. Lett. 28, (2003). 5. B. J. Mangan, J. Arriaga, T. A. Birks, J. C. Knight, and P. S. J. Russell, Fundamental-mode cutoff in a photonic crystal fiber with a depressed-index core, Opt. Lett. 26, (2001). 6. J. C. Knight, T. A. Birks, R. F. Cregan, P. S. J. Russell, and J.-P. de Sandro, Large mode area photonic crystal fibre, lectron. Lett. 34, (1998). 7. N. A. Mortensen, M. D. Nielsen, J. R. Folkenberg, A. Petersson, and H. R. Simonsen, Improved large-mode area endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fibers, Opt. Lett. pp (2003). 8. M. D. Nielsen, J. R. Folkenberg, and N. A. Mortensen, Single-mode photonic crystal fiber with an effective area of 600 µm 2 and low bending loss, lectron. Lett. 39, (2003). 9. M. J. Steel, T. P. White, C. M. de Sterke, R. C. McPhedran, and L. C. Botton, Symmetry and degeneracy in microstructured optical fibers, Opt. Lett. 26, (2001). 10. M. D. Nielsen, J. R. Folkenberg, and N. A. Mortensen, Reduced microdeformation attenuation in large-modearea photonic crystal fibers for visible applications, Opt. Lett. 28, (2003).
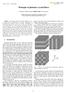
2 11. M. D. Nielsen, G. Vienne, J. R. Folkenberg, and A. Bjarklev, Investigation of micro deformation induced attenuation spectra in a photonic crystal fiber, Opt. Lett. 28, (2003). 12. K. Saitoh and M. Koshiba, Full-vectorial imaginary-distance beam propagation method based on finite element scheme: Application to photonic crystal fibers, I J. Quantum lectron. 38, (2002). 13. T. A. Birks, J. C. Knight, and P. S. J. Russell, ndlessly single mode photonic crystal fibre, Opt. Lett. 22, (1997). 14. S. G. Johnson, M. Ibanescu, M. A. Skorobogatiy, O. Weisberg, J. D. Joannopoulos, and Y. Fink, Perturbation theory for Maxwell s equations with shifting material boundaries, Phys. Rev. 65, 066,611 (2002). 15. B. T. Kuhlmey, R. C. McPhedran, and C. M. de Sterke, Modal cutoff in microstructured optical fibers, Opt. Lett. 27, (2002). 16. N. A. Mortensen, J. R. Folkenberg, M. D. Nielsen, and K. P. Hansen, Modal cut-off and the V parameter in photonic crystal fibers, Opt. Lett. 28, (2003). 17. J. R. Folkenberg, N. A. Mortensen, K. P. Hansen, T. P. Hansen, H. R. Simonsen, and C. Jakobsen, xperimental investigation of cut-off phenomena in non-linear photonic crystal fibers, Opt. Lett. 28, (2003). 18. N. A. Mortensen, M. D. Nielsen, J. R. Folkenberg, K. P. Hansen, and J. Lægsgaard, Small-core photonic crystal fibers with weakly disordered air-hole claddings, J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 6, (2004). 19. T. T. Larsen, A. Bjarklev, D. S. Hermann, and J. Broeng, Optical devices based on liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibres, Opt. xpress 11, (2003). URL 1. Introduction In their basic form photonic crystal fibers (PCF) typically consist of fused silica with an arrangement of air-holes running along the full length of the fiber (for a recent review we refer the reader to Ref. [1] and references therein). Traditionally, triangular [2] or honeycomb [3] cladding arrangements of the air-holes have been considered with the core defect formed by removing or adding an additional air-hole in the lattice, respectively. This is of course the most obvious way to form a defect in a regular lattice. However, for the honeycomb lattice (see Fig. 1) there is at least one alternative approach which involves additional use of indexaltering dopants. Recently, Lægsgaard and Bjarklev [4] suggested how a low-index band-gap guiding core could be formed in a germanium doped honeycomb lattice by absence of doping in the core region. Here, we suggest doping by fluorine which results in an index-guiding core. Fig. 1. Cross-section of the PCF with air-holes indicated by filled circles and the fluorine doped regions indicated by open circles. The perfectly-matched layers employed in finiteelement simulations are also indicated.
3 150 Attenuation [db /km ] Wavelength [nm ] Fig. 2. Spectral loss measured by a standard white-light cut-back technique. OTDR measurements at λ = 1319 nm and 1550 nm are also indicated by red dots. The measurements are performed with 200 m of fiber on a spool with a radius of 8 cm. The left insets show an optical micrograph of the fiber end-facet with the dark circular regions showing the air holes and the light regions showing the fluorine-doping in the silica background. The right inset shows a near-field image of the fundamental mode at λ = 635 nm. Fluorine-doped PCFs have previously been considered by Mangan et al. [5] who fabricated a triangular air-hole cladding PCF with a fluorine-doped silica core region. At sufficiently short wavelengths the core index is lower than the effective index of the cladding and the PCF is anti-guiding, but as the wavelength is increased the effective index of the cladding decreases and eventually becomes lower than the core index so that light is guided in the core region. In the present work we use fluorine doping to form a novel large-mode area PCF and the proposed fiber structure may be an alternative to existing large-mode area designs employing a triangular air-hole arrangement in the cladding [6, 7, 8]. 2. Fiber design and fabrication We consider the structure in Fig. 1 where fluorine doped regions (of diameter d f )areincorporated in a honeycomb lattice of air-holes (of diameter d and nearest-neighbor spacing Λ). The core region is formed by the absence of doping in the central region of the structure. At sufficiently short wavelengths the cladding states will avoid the fluorine-doped regions and the effective cladding index will in some sense resemble that for a triangular arrangement of holes whereas at longer wavelengths the field averages over the fluorine-doped and pure silica regions so that the effective index resembles that of a honeycomb lattice (with a slightly down-shifted background index). The defect region has six-fold rotational symmetry and thus supports a doubly degenerate fundamental mode [9]. We have fabricated the proposed fiber by the stack-and-pull method [2] with hexagonal stack-
4 Fig. 3. Mode-spacing (left axis) derived from periodic micro-deformation spectra (right axis). Red crosses indicate values of n from numerical simulations while the solid curves are the measured attenuation peaks induced by periodic micro-deformations. The number above each peak indicate if the peak is of 1st or 2nd order and the open circles represent the corresponding mode spacing calculated from the measurements. ing of fluorine-doped rods (step-index like doping profile) and fused silica tubes and rods. The inset in Fig. 2 shows an optical micrograph of a typical fiber cross section. The fiber has an outer diameter of 175 µm in order to reduce micro-bending deformations at short wavelengths [10] and it is coated with a standard single layer acrylate coating. The fluorine-doped regions are of diameter d f /Λ 0.7 with an index n f suppressed by δn relative to the index n s of silica. The pitch is Λ 10.1 µm and the relative air-hole diameter is d/λ = Fiber characterization To facilitate coupling of light to the core region a SMF28 was spliced to 200 m of the PCF. The spectral attenuation was measured by the cut-back technique using a white-light source and an optical spectrum analyzer. Fig. 2 shows the spectral attenuation of the PCF. Data from OTDR measurements at λ = 1319nm and 1550 nm are also included and good agreement with the cut-back data is observed. Cut-back transmission experiments on a short length of PCF have revealed no signatures of high-order modes. The fiber has a low loss regime at short wavelengths and a regime with high loss above 1000 nm extending to the O-H absorption peak. In order to further analyze the modal properties we have studied the mode-spacing which can be derived from micro-deformation measurements. For a detailed description of the method and the interpretation of experimental data we refer the reader to Ref. [11] and references therein. Fig. 3 shows loss spectra (right axis) for various periodic micro-deformations and the derived mode-spacings, n are also included (left axis). The figure also includes numerical data calculated with the finite-element method incorporating
5 perfectly matched layers [12], see Fig. 1. In agreement with the experimental observations, our simulations also suggest that the PCF is broad-band single mode [13] in the sense that highorder modes have a negligible spacing ( 10 4 ) to cladding modes. In order to understand the spacing between guided modes and cladding modes we apply firstorder perturbation theory to the guided modes. Treating the absence of fluorine-doping in the core as a perturbation, δε = n 2 s n 2 f 2n sδn, we may estimate the shift n in mode-index with respect to the cladding modes. From standard perturbation theory (see e.g. Ref. [14]) we get n = c 2v g δε ε cn s δn v g ε (1) where c is the velocity of light, is the unperturbed electrical field, and v g is the group velocity. For a high-order mode the field-intensity is strongly suppressed at the center of the core region [15, 16, 17, 18] and since d f /Λ is not too large the mode has a very small overlap with the region where fluorine is absent. This results in a negligible increase in effective index n with respect to the cladding modes. In other words, localization in the core is no big energetic advantage for the high-order modes. For the fundamental mode the situation is opposite since it has a large field-intensity at the center of the core and indeed we find a mode-spacing n comparable to δn. The mode-spacing picture in Fig. 3 suggests that the overall loss has little relation to bendinginduced scattering loss (we have also verified this by changing the bending radius R) and since confinement loss can be excluded (we have verified this numerically) it is likely that the overall high background originates from various contamination added during the stack-and-pull fabrication process. We believe that the background loss level can be lowered similarly to the recent achievements in triangular cladding large-mode area PCFs [8]. 4. Conclusion We have studied a new approach to the formation of a core defect in the honeycomb structure by fluorine-doped regions added to the cladding. At sufficiently short wavelengths the cladding states will avoid the fluorine-doped regions and the effective cladding index will in some sense resemble that for a triangular arrangement and light will be confined to the core region where fluorine-doping is absent. We believe that hybrid cladding designs could be an interesting direction which allows a higher degree of modal/dispersion engineering and the particular structure studied in this paper could also be interesting for photonic band-gap fiber devices employing liquid crystals [19]. Acknowledgments N. A. Mortensen thanks J. Lægsgaard (COM, Technical University of Denmark) for stimulating discussions and L. Gregersen (Comsol A/S) for technical support. M. D. Nielsen acknowledges financial support by the Danish Academy of Technical Sciences.
Effective area of photonic crystal fibers
 Effective area of photonic crystal fibers Niels Asger Mortensen Crystal Fibre A/S, Blokken 84, DK-3460 Birkerød, Denmark nam@crystal-fibre.com http://www.crystal-fibre.com Abstract: We consider the effective
Effective area of photonic crystal fibers Niels Asger Mortensen Crystal Fibre A/S, Blokken 84, DK-3460 Birkerød, Denmark nam@crystal-fibre.com http://www.crystal-fibre.com Abstract: We consider the effective
Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation
 Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation DEBBAL Mohammed 1, CHIKH-BLED Mohammed 2 1 University of Tlemcen, Algeria, Department of electrical
Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation DEBBAL Mohammed 1, CHIKH-BLED Mohammed 2 1 University of Tlemcen, Algeria, Department of electrical
Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers
 Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers W.H. Reeves, J.C. Knight, and P.St.J. Russell Optoelectronics Group, School of Physics, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath,
Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers W.H. Reeves, J.C. Knight, and P.St.J. Russell Optoelectronics Group, School of Physics, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath,
Title. Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 19(4): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Polarization characteristics of photonic crystal fib Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 19(4): 3799-3808 Issue Date 2011-02-14 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/45257
Title Polarization characteristics of photonic crystal fib Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 19(4): 3799-3808 Issue Date 2011-02-14 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/45257
SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 53 64, 2010 SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen, M.-L. V. Tse, and H. Y. Tam Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electrical Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 53 64, 2010 SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen, M.-L. V. Tse, and H. Y. Tam Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electrical Engineering
Single-Polarization Single-Mode Photonic Band Gap Fiber
 Vol. 111 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Single-Polarization Single-Mode Photonic Band Gap Fiber M. Szpulak a,, T. Martynkien a, J. Olszewski a, W. Urbanczyk a, T. Nasilowski b, F. Berghmans b,c and
Vol. 111 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Single-Polarization Single-Mode Photonic Band Gap Fiber M. Szpulak a,, T. Martynkien a, J. Olszewski a, W. Urbanczyk a, T. Nasilowski b, F. Berghmans b,c and
Highly Birefringent Elliptical-Hole Microstructure Fibers With Low Confinement Loss
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 30, NO. 21, NOVEMBER 1, 2012 3381 Highly Birefringent Elliptical-Hole Microstructure Fibers With Low Confinement Loss Wenbin Liang, Ningliang Liu, Zhihua Li, and Peixiang
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 30, NO. 21, NOVEMBER 1, 2012 3381 Highly Birefringent Elliptical-Hole Microstructure Fibers With Low Confinement Loss Wenbin Liang, Ningliang Liu, Zhihua Li, and Peixiang
Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects
 Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects Md. Afzal Hossain*, M. Shah Alam** * Department of Computer Science and Engineering Military Institute
Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects Md. Afzal Hossain*, M. Shah Alam** * Department of Computer Science and Engineering Military Institute
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 9 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 9 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 9 Jul 2007](/thumbs/86/93989347.jpg) Air-clad fibers: pump absorption assisted by chaotic wave dynamics? arxiv:0707.1189v1 [physics.optics] 9 Jul 2007 Niels Asger Mortensen MIC Department of Micro and Nanotechnology, Nano DTU, Technical University
Air-clad fibers: pump absorption assisted by chaotic wave dynamics? arxiv:0707.1189v1 [physics.optics] 9 Jul 2007 Niels Asger Mortensen MIC Department of Micro and Nanotechnology, Nano DTU, Technical University
Dispersion Properties of Photonic Crystal Fiber with Four cusped Hypocycloidal Air Holes in Cladding
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 1, Issue 1, Ver. III (Jan.-Feb. 17), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Dispersion Properties of
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 1, Issue 1, Ver. III (Jan.-Feb. 17), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Dispersion Properties of
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 23 Nov 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 23 Nov 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 23 Nov 2005](/thumbs/96/128051067.jpg) arxiv:physics/0511197v1 [physics.optics] 23 Nov 2005 Non-perturbative approach to high-index-contrast variations in electromagnetic systems Lars Rindorf 1 and Niels Asger Mortensen 2 1 COM DTU, Technical
arxiv:physics/0511197v1 [physics.optics] 23 Nov 2005 Non-perturbative approach to high-index-contrast variations in electromagnetic systems Lars Rindorf 1 and Niels Asger Mortensen 2 1 COM DTU, Technical
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC
 FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
Waveguidance by the photonic bandgap effect in optical fibres
 J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 1 (1999) 477 482. Printed in the UK PII: S1464-4258(99)03575-8 Waveguidance by the photonic bandgap effect in optical fibres Jes Broeng, Thomas Søndergaard, Stig E Barkou, Pablo
J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 1 (1999) 477 482. Printed in the UK PII: S1464-4258(99)03575-8 Waveguidance by the photonic bandgap effect in optical fibres Jes Broeng, Thomas Søndergaard, Stig E Barkou, Pablo
Antiresonant reflecting optical waveguide microstructured fibers revisited: a new analysis based on leaky mode coupling
 Antiresonant reflecting optical waveguide microstructured fibers revisited: a new analysis based on leaky mode coupling Gilles Renversez, Philippe Boyer, and Angelo Sagrini Institut Fresnel (UMR CNRS 6133)
Antiresonant reflecting optical waveguide microstructured fibers revisited: a new analysis based on leaky mode coupling Gilles Renversez, Philippe Boyer, and Angelo Sagrini Institut Fresnel (UMR CNRS 6133)
Principle of photonic crystal fibers
 Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Models for guidance in kagome-structured hollow-core photonic crystal fibres
 Models for guidance in kagome-structured hollow-core photonic crystal fibres G. J. Pearce 1, G. S. Wiederhecker 1, 2, C. G. Poulton 1, S. Burger 3, and P. St. J. Russell 1* 1 Max Planck Research Group
Models for guidance in kagome-structured hollow-core photonic crystal fibres G. J. Pearce 1, G. S. Wiederhecker 1, 2, C. G. Poulton 1, S. Burger 3, and P. St. J. Russell 1* 1 Max Planck Research Group
Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice
 Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice Sharafat Ali, Nasim Ahmed, Monirul Islam, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, H. Jaman, and S. Habib Abstract In this
Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice Sharafat Ali, Nasim Ahmed, Monirul Islam, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, H. Jaman, and S. Habib Abstract In this
All-optical modulation in dye-doped nematic liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibers
 All-optical modulation in dye-doped nematic liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibers Thomas Tanggaard Alkeskjold, Jesper Lægsgaard and Anders Bjarklev COM Center, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800
All-optical modulation in dye-doped nematic liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibers Thomas Tanggaard Alkeskjold, Jesper Lægsgaard and Anders Bjarklev COM Center, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800
Design Optimization of Equiangular Spiral Photonic Crystal Fiber for Large Negative Flat Dispersion and High Birefringence
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 30, NO. 22, NOVEMBER 15, 2012 3545 Design Optimization of Equiangular Spiral Photonic Crystal Fiber for Large Negative Flat Dispersion and High Birefringence Md. Asiful
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 30, NO. 22, NOVEMBER 15, 2012 3545 Design Optimization of Equiangular Spiral Photonic Crystal Fiber for Large Negative Flat Dispersion and High Birefringence Md. Asiful
The Glass Ceiling: Limits of Silica. PCF: Holey Silica Cladding
 The Glass Ceiling: Limits of Silica Loss: amplifiers every 50 100km limited by Rayleigh scattering (molecular entropy) cannot use exotic wavelengths like 10.µm Breaking the Glass Ceiling: Hollow-core Bandgap
The Glass Ceiling: Limits of Silica Loss: amplifiers every 50 100km limited by Rayleigh scattering (molecular entropy) cannot use exotic wavelengths like 10.µm Breaking the Glass Ceiling: Hollow-core Bandgap
Department of Electronic Engineering, Ching Yun University, Jung-Li 320, Taiwan 2
 Advances in Nonlinear Optics Volume 008, Article ID 39037, 6 pages doi:10.1155/008/39037 Research Article Analysis of High Birefringence of Four Types of Photonic Crystal Fiber by Combining Circular and
Advances in Nonlinear Optics Volume 008, Article ID 39037, 6 pages doi:10.1155/008/39037 Research Article Analysis of High Birefringence of Four Types of Photonic Crystal Fiber by Combining Circular and
Bloch method for the analysis of modes in microstructured optical fibers
 Bloch method for the analysis of modes in microstructured optical fibers Boris T. Kuhlmey 1,2, Ross C. McPhedran 1 and C. Martijn de Sterke 1 1: Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems
Bloch method for the analysis of modes in microstructured optical fibers Boris T. Kuhlmey 1,2, Ross C. McPhedran 1 and C. Martijn de Sterke 1 1: Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF HIGH BIREFRINGENCE AND LOW CONFINEMENT LOSS PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER EMPLOYING ELLIPTICAL AIR HOLES IN FIBER CLADDING
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF HIGH BIREFRINGENCE AND LOW CONFINEMENT LOSS PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER EMPLOYING ELLIPTICAL AIR HOLES IN FIBER CLADDING
Surface modes in air-core photonic band-gap fibers
 Surface modes in air-core photonic band-gap fibers James A. West, Charlene M. Smith, Nicholas F. Borrelli, Douglas C. Allan, and Karl W. Koch Sullivan Park, Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY 14831 westja@corning.com
Surface modes in air-core photonic band-gap fibers James A. West, Charlene M. Smith, Nicholas F. Borrelli, Douglas C. Allan, and Karl W. Koch Sullivan Park, Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY 14831 westja@corning.com
Comparative Study of Fundamental Properties of Honey Comb Photonic Crystal Fiber at 1.55µm Wavelength * S.S. Mishra and # Vinod Kumar Singh
 343 Comparative Study of Fundamental Properties of Honey Comb Photonic Crystal Fiber at 1.55µm Wavelength * S.S. Mishra and # Vinod Kumar Singh Department of Applied Physics I. S. M., Dhanbad-826004, India
343 Comparative Study of Fundamental Properties of Honey Comb Photonic Crystal Fiber at 1.55µm Wavelength * S.S. Mishra and # Vinod Kumar Singh Department of Applied Physics I. S. M., Dhanbad-826004, India
NOVEL HYBRID PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH DEFECTED CORE FOR DISPERSION COMPENSATION OVER E TO U BAND TELECOMMUNICATION
 NOVEL HYBRID PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH DEFECTED CORE FOR DISPERSION COMPENSATION OVER E TO U BAND TELECOMMUNICATION Ouadah Mohammed Chamse Eddine and Chikh Bled Mohammed El Kébir Telecommunication Laboratory
NOVEL HYBRID PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH DEFECTED CORE FOR DISPERSION COMPENSATION OVER E TO U BAND TELECOMMUNICATION Ouadah Mohammed Chamse Eddine and Chikh Bled Mohammed El Kébir Telecommunication Laboratory
Negative curvature fibers
 504 Vol. 9, No. 3 / September 2017 / Advances in Optics and Photonics Review Negative curvature fibers CHENGLI WEI, 1 R. JOSEPH WEIBLEN, 2 CURTIS R. MENYUK, 2 AND JONATHAN HU 1,* 1 Department of Electrical
504 Vol. 9, No. 3 / September 2017 / Advances in Optics and Photonics Review Negative curvature fibers CHENGLI WEI, 1 R. JOSEPH WEIBLEN, 2 CURTIS R. MENYUK, 2 AND JONATHAN HU 1,* 1 Department of Electrical
Enhancement of the Sensitivity of Gas Sensor Based on Microstructure Optical Fiber
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol., No. 4, 2: 312 32 Enhancement of the Sensitivity of Gas Sensor Based on Microstructure Optical Fiber Monir MORSHED 1*, Md. Imran HASAN 2, and S. M. Abdur RAZZAK 3 1 Department of
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol., No. 4, 2: 312 32 Enhancement of the Sensitivity of Gas Sensor Based on Microstructure Optical Fiber Monir MORSHED 1*, Md. Imran HASAN 2, and S. M. Abdur RAZZAK 3 1 Department of
Guiding and thermal properties of a hybrid polymer-infused photonic crystal fiber
 Guiding and thermal properties of a hybrid polymer-infused photonic crystal fiber Christos Markos, 1,2,* Kyriakos Vlachos, 1 and George Kakarantzas 2 1 Computer Engineering and Informatics Dept. & Computer
Guiding and thermal properties of a hybrid polymer-infused photonic crystal fiber Christos Markos, 1,2,* Kyriakos Vlachos, 1 and George Kakarantzas 2 1 Computer Engineering and Informatics Dept. & Computer
Guiding and birefringent properties of a hybrid PDMS/Silica photonic crystal fiber
 Guiding and birefringent properties of a hybrid PDMS/Silica photonic crystal fiber Christos Markos*,a,b, Kyriakos Vlachos a, George Kakarantzas b a Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, University
Guiding and birefringent properties of a hybrid PDMS/Silica photonic crystal fiber Christos Markos*,a,b, Kyriakos Vlachos a, George Kakarantzas b a Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, University
Research Article Designing an Ultra-Negative Dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber with Square-Lattice Geometry
 ISRN Optics, Article ID 545961, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/545961 Research Article Designing an Ultra-Negative Dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber with Square-Lattice Geometry Partha Sona Maji
ISRN Optics, Article ID 545961, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/545961 Research Article Designing an Ultra-Negative Dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber with Square-Lattice Geometry Partha Sona Maji
Polarization-mode dispersion of large mode-area photonic crystal fibers
 Optics Communications 226 (2003) 233 239 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization-mode dispersion of large mode-area photonic crystal fibers Tuomo Ritari a, *, Tapio Niemi a, Hanne Ludvigsen a, Mark
Optics Communications 226 (2003) 233 239 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Polarization-mode dispersion of large mode-area photonic crystal fibers Tuomo Ritari a, *, Tapio Niemi a, Hanne Ludvigsen a, Mark
Design of low-loss and highly birefringent hollow-core photonic crystal fiber
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 Design of low-loss and highly birefringent hollow-core photonic crystal fiber Roberts, Peter John; Williams, D.P.; Sabert, H.; Mangan, Brian Joseph; Bird,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 Design of low-loss and highly birefringent hollow-core photonic crystal fiber Roberts, Peter John; Williams, D.P.; Sabert, H.; Mangan, Brian Joseph; Bird,
Confinement loss, including cladding material loss effects, in Bragg fibers
 J. Sakai and N. Nishida Vol. 28, No. 3 / March 2011 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 379 Confinement loss, including cladding material loss effects, in Bragg fibers Jun-ichi Sakai* and Norihiro Nishida Faculty of
J. Sakai and N. Nishida Vol. 28, No. 3 / March 2011 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 379 Confinement loss, including cladding material loss effects, in Bragg fibers Jun-ichi Sakai* and Norihiro Nishida Faculty of
Photonic Crystal Fiber based Network Components: The Future Trend in Optical Network Design
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277 4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Photonic Crystal Fiber based
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277 4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Photonic Crystal Fiber based
Slow-light enhanced absorption in a hollow-core fiber
 Slow-light enhanced absorption in a hollow-core fiber Jure Grgić, 1 Sanshui Xiao, 1 Jesper Mørk, 1 Antti-Pekka Jauho, 2,3 and N. Asger Mortensen 1, 1 DTU Fotonik, Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical
Slow-light enhanced absorption in a hollow-core fiber Jure Grgić, 1 Sanshui Xiao, 1 Jesper Mørk, 1 Antti-Pekka Jauho, 2,3 and N. Asger Mortensen 1, 1 DTU Fotonik, Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical
IN conventional optical fibers, light confinement is achieved
 428 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 3, MARCH 2002 Asymptotic Matrix Theory of Bragg Fibers Yong Xu, George X. Ouyang, Reginald K. Lee, Member, IEEE, and Amnon Yariv, Life Fellow, IEEE Abstract
428 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 3, MARCH 2002 Asymptotic Matrix Theory of Bragg Fibers Yong Xu, George X. Ouyang, Reginald K. Lee, Member, IEEE, and Amnon Yariv, Life Fellow, IEEE Abstract
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers
 Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
Design and Modal Analysis of Photonic Crystal Fiber for Dispersion Compensation over Broadband Range
 365 Design and Modal Analysis of Photonic Crystal Fiber for Dispersion Compensation over Broadband Range Madhavi Waghmare 1, K.T.V.Reddy 2, 1. Research Scholar, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
365 Design and Modal Analysis of Photonic Crystal Fiber for Dispersion Compensation over Broadband Range Madhavi Waghmare 1, K.T.V.Reddy 2, 1. Research Scholar, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
Nikolaos Florous, Kunimasa Saitoh, and Masanori Koshiba
 Title The role of artificial defects for engineering large in photonic crystal fibers: Towards high speed recon Author(s)Florous, Nikolaos; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masano CitationOptics Express, 14(2):
Title The role of artificial defects for engineering large in photonic crystal fibers: Towards high speed recon Author(s)Florous, Nikolaos; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masano CitationOptics Express, 14(2):
Finite Element Method
 Appendix A Finite Element Method A.1 Formulation All the analyses of the PCF properties presented in this book have been performed by using the FEM. The FEM allows the PCF cross-section in the transverse
Appendix A Finite Element Method A.1 Formulation All the analyses of the PCF properties presented in this book have been performed by using the FEM. The FEM allows the PCF cross-section in the transverse
Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals
 Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals Michael James Ventura and Min Gu* Centre for Micro-Photonics and Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems,
Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals Michael James Ventura and Min Gu* Centre for Micro-Photonics and Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems,
DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH HIGH NEGATIVE DISPERSION AND LOW COUPLING LENGTH
 DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH HIGH NEGATIVE DISPERSION AND LOW COUPLING LENGTH Mangesh M. Landge 1, Revathi S. 2, Vinay P. Sigedar 1 and Aditya Chourasia 1 1 Department of Communication Engineering
DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER WITH HIGH NEGATIVE DISPERSION AND LOW COUPLING LENGTH Mangesh M. Landge 1, Revathi S. 2, Vinay P. Sigedar 1 and Aditya Chourasia 1 1 Department of Communication Engineering
Photonic crystal waveguides with semi-slow light and tailored dispersion properties
 Photonic crystal waveguides with semi-slow light and tailored dispersion properties Lars H. Frandsen, Andrei V. Lavrinenko, Jacob Fage-Pedersen, and Peter I. Borel COM DTU, Department of Communications,
Photonic crystal waveguides with semi-slow light and tailored dispersion properties Lars H. Frandsen, Andrei V. Lavrinenko, Jacob Fage-Pedersen, and Peter I. Borel COM DTU, Department of Communications,
PHOTONIC BANDGAP FIBERS
 UMEÅ UNIVERSITY May 11, 2010 Department of Physics Advanced Materials 7.5 ECTS PHOTONIC BANDGAP FIBERS Daba Dieudonne Diba dabadiba@gmail.com Supervisor: Andreas Sandström Abstract The constant pursuit
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY May 11, 2010 Department of Physics Advanced Materials 7.5 ECTS PHOTONIC BANDGAP FIBERS Daba Dieudonne Diba dabadiba@gmail.com Supervisor: Andreas Sandström Abstract The constant pursuit
CHARACTERISTICS ANALYSIS OF DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER (PCF)
 CHARACTERISTICS ANALYSIS OF DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER (PCF) Mali Suraj Suryakant 1, Mali Rameshwar Suryakant 2, Landge Mangesh Manik 3 1 PG Student, Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
CHARACTERISTICS ANALYSIS OF DUAL CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER (PCF) Mali Suraj Suryakant 1, Mali Rameshwar Suryakant 2, Landge Mangesh Manik 3 1 PG Student, Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
Polarization mode dispersion reduction in spun large mode area silica holey fibres
 Polarization mode dispersion reduction in spun large mode area silica holey fibres M. Fuochi 1,, J.R. Hayes 1, K. Furusawa 1, W. Belardi 1, J.C. Baggett 1, T.M. Monro 1,.J. Richardson 1 1 Optoelectronics
Polarization mode dispersion reduction in spun large mode area silica holey fibres M. Fuochi 1,, J.R. Hayes 1, K. Furusawa 1, W. Belardi 1, J.C. Baggett 1, T.M. Monro 1,.J. Richardson 1 1 Optoelectronics
Negative curvature fibers
 Negative curvature fibers presented by Jonathan Hu 1 with Chengli Wei, 1 R. Joseph Weiblen, 2,* and Curtis R. Menyuk 2 1 Baylor University, Waco, Texas 76798, USA 2 University of Maryland Baltimore County,
Negative curvature fibers presented by Jonathan Hu 1 with Chengli Wei, 1 R. Joseph Weiblen, 2,* and Curtis R. Menyuk 2 1 Baylor University, Waco, Texas 76798, USA 2 University of Maryland Baltimore County,
Liquid crystal parameter analysis for tunable photonic bandgap fiber devices
 Liquid crystal parameter analysis for tunable photonic bandgap fiber devices Johannes Weirich, Jesper Lægsgaard, Lei Wei, Thomas Tanggaard Alkeskjold, Thomas X. Wu 3, Shin-Tson Wu 3 and Anders Bjarklev
Liquid crystal parameter analysis for tunable photonic bandgap fiber devices Johannes Weirich, Jesper Lægsgaard, Lei Wei, Thomas Tanggaard Alkeskjold, Thomas X. Wu 3, Shin-Tson Wu 3 and Anders Bjarklev
Group-velocity dispersion in a Bragg fiber
 414 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 5, No. 3/ March 008 J.-I. Sakai and K. Kuramitsu Group-velocity dispersion in a Bragg fiber Jun-Ichi Sakai and Kazuki Kuramitsu Faculty of Science and Engineering, Ritsumeikan
414 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 5, No. 3/ March 008 J.-I. Sakai and K. Kuramitsu Group-velocity dispersion in a Bragg fiber Jun-Ichi Sakai and Kazuki Kuramitsu Faculty of Science and Engineering, Ritsumeikan
Microstructure fibres for optical sensing in gases and liquids
 INSTITUTE OFPHYSICS PUBLISHING Meas. Sci. Technol. 15 (2004) 1120 1128 MEASUREMENTSCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY PII: S0957-0233(04)75385-0 Microstructure fibres for optical sensing in gases and liquids John M
INSTITUTE OFPHYSICS PUBLISHING Meas. Sci. Technol. 15 (2004) 1120 1128 MEASUREMENTSCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY PII: S0957-0233(04)75385-0 Microstructure fibres for optical sensing in gases and liquids John M
Experimental and numerical analysis of the chromatic dispersion dependence upon the actual profile of small core microstructured fibres
 Experimental and numerical analysis of the chromatic dispersion dependence upon the actual profile of small core microstructured fibres L Labonté 1, P Roy 1, D Pagnoux 1, F Louradour 1, C Restoin 1, G
Experimental and numerical analysis of the chromatic dispersion dependence upon the actual profile of small core microstructured fibres L Labonté 1, P Roy 1, D Pagnoux 1, F Louradour 1, C Restoin 1, G
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 08 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Outline: Photonic crystals 2 1. Photonic crystals vs electronic
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 08 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Outline: Photonic crystals 2 1. Photonic crystals vs electronic
Estimating modal instability threshold for photonic crystal rod fiber amplifiers
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Estimating modal instability threshold for photonic crystal rod fiber amplifiers Johansen, Mette Marie; Hansen, Kristian Rymann; Laurila, Marko; Alkeskjold,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Estimating modal instability threshold for photonic crystal rod fiber amplifiers Johansen, Mette Marie; Hansen, Kristian Rymann; Laurila, Marko; Alkeskjold,
Empirical formulae for hollow-core antiresonant fibers: dispersion and effective mode area
 Empirical formulae for hollow-core antiresonant fibers: dispersion and effective mode area MD IMRAN HASAN, * NAIL AKHMEDIEV, AND WONKEUN CHANG Optical Sciences Group, Research School of Physics and Engineering,
Empirical formulae for hollow-core antiresonant fibers: dispersion and effective mode area MD IMRAN HASAN, * NAIL AKHMEDIEV, AND WONKEUN CHANG Optical Sciences Group, Research School of Physics and Engineering,
Highly Nonlinear Fibers and Their Applications
 1/32 Highly Nonlinear Fibers and Their Applications Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Introduction Many nonlinear effects inside optical
1/32 Highly Nonlinear Fibers and Their Applications Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Introduction Many nonlinear effects inside optical
Highly Nonlinear Bending-Insensitive Birefringent Photonic Crystal Fibres
 Engineering, 2010, 2, 608-616 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.28078 Published Online August 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng). Highly Nonlinear Bending-Insensitive Birefringent Photonic Crystal Fibres Abstract
Engineering, 2010, 2, 608-616 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.28078 Published Online August 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng). Highly Nonlinear Bending-Insensitive Birefringent Photonic Crystal Fibres Abstract
Brillouin-zone spectroscopy of nonlinear photonic lattices
 Brillouin-zone spectroscopy of nonlinear photonic lattices Guy Bartal, 1 Oren Cohen, 1 Hrvoje Buljan, 1,2 Jason W. Fleischer, 1,3 Ofer Manela, 1 Mordechai Segev 1 1Physics Department, Technion - Israel
Brillouin-zone spectroscopy of nonlinear photonic lattices Guy Bartal, 1 Oren Cohen, 1 Hrvoje Buljan, 1,2 Jason W. Fleischer, 1,3 Ofer Manela, 1 Mordechai Segev 1 1Physics Department, Technion - Israel
Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in Electromagnetism. You can leave home without them. Complete Band Gaps: Steven G.
 Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in lectromagnetism Steven G. ohnson MIT Complete Band Gaps: You can leave home without them. How else can we confine light? Total Internal Reflection n o n i > n o
Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in lectromagnetism Steven G. ohnson MIT Complete Band Gaps: You can leave home without them. How else can we confine light? Total Internal Reflection n o n i > n o
How long wavelengths can one extract from silica-core fibers?
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 27, 28 How long wavelengths can one extract from silica-core fibers? Lægsgaard, Jesper; Tu, Haohua Published in: Optics Letters Link to article, DOI:.364/OL.38.458
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 27, 28 How long wavelengths can one extract from silica-core fibers? Lægsgaard, Jesper; Tu, Haohua Published in: Optics Letters Link to article, DOI:.364/OL.38.458
Title. Author(s)Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 23(11): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Numerical Modeling of Photonic Crystal Fibers Author(s)Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 23(11): 3580-3590 Issue Date 2005-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1404
Title Numerical Modeling of Photonic Crystal Fibers Author(s)Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 23(11): 3580-3590 Issue Date 2005-11 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1404
Analysis of Power Coupling and Losses at Splice Joints of Dissimilar Optical Fibers
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 014, 4(): 54-61 DOI: 10.593/j.optics.014040.05 Analysis of Power Coupling and Losses at Splice Joints of Dissimilar Optical Fibers Faramarz E. Seraji 1,*,
International Journal of Optics and Applications 014, 4(): 54-61 DOI: 10.593/j.optics.014040.05 Analysis of Power Coupling and Losses at Splice Joints of Dissimilar Optical Fibers Faramarz E. Seraji 1,*,
A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices
 A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices Georgios Veronis, Robert W. Dutton, and Shanhui Fan Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 9435
A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices Georgios Veronis, Robert W. Dutton, and Shanhui Fan Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 9435
QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS
 QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS LASERS. Name some properties, which make laser light different from ordinary light. () {JUN 5. The output power of a given laser is mw and the emitted wavelength is 630nm. Calculate
QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS LASERS. Name some properties, which make laser light different from ordinary light. () {JUN 5. The output power of a given laser is mw and the emitted wavelength is 630nm. Calculate
Tailoring Nonlinearity and Dispersion of Photonic Crystal Fibers Using Hybrid Cladding
 5 Liu Zhao-lun et al. Tailoring Nonlinearity and Dispersion of Photonic Crystal Fibers Using Hybrid Cladding Liu Zhao-lun, Hou Lan-tian, and Wang Wei Institute of Infrared Optical Fibers and Sensors, Yanshan
5 Liu Zhao-lun et al. Tailoring Nonlinearity and Dispersion of Photonic Crystal Fibers Using Hybrid Cladding Liu Zhao-lun, Hou Lan-tian, and Wang Wei Institute of Infrared Optical Fibers and Sensors, Yanshan
Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes
 SMR 189 - Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 1-3 February 007 Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes (second part) K. Thyagarajan Physics Department IIT Delhi New Delhi, India Fundamentals
SMR 189 - Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 1-3 February 007 Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes (second part) K. Thyagarajan Physics Department IIT Delhi New Delhi, India Fundamentals
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Author(s) Citation Control and design of fiber birefringence characteristics based on selective-filled
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Author(s) Citation Control and design of fiber birefringence characteristics based on selective-filled
Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs)
 Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs) FRISNO-9 Dominique Elser 15/02/2007 GAWBS Theory Thermally excited acoustic fiber vibrations at certain resonance frequencies
Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in Photonic Crystal Fibers (PCFs) FRISNO-9 Dominique Elser 15/02/2007 GAWBS Theory Thermally excited acoustic fiber vibrations at certain resonance frequencies
Introducing Defects in Photonic Band-Gap (PBG) Crystals. Elliott C. Johnson
 Introducing Defects in Photonic Band-Gap (PBG) Crystals Elliott C. Johnson Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Dakota State University Stanford Linear Accelerator
Introducing Defects in Photonic Band-Gap (PBG) Crystals Elliott C. Johnson Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Dakota State University Stanford Linear Accelerator
Chalcogenide glass Photonic Crystal Fiber with flattened dispersion and high nonlinearity at telecommunication wavelength
 Chalcogenide glass Photonic Crystal Fiber with flattened dispersion and high nonlinearity at telecommunication wavelength S.REVATHI #, ABHIJITH CHANDRAN #, A. AMIR #3, SRINIVASA RAO INBATHINI #4 # School
Chalcogenide glass Photonic Crystal Fiber with flattened dispersion and high nonlinearity at telecommunication wavelength S.REVATHI #, ABHIJITH CHANDRAN #, A. AMIR #3, SRINIVASA RAO INBATHINI #4 # School
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays. Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković
 Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Geometrical parameters dependence towards ultra-flat dispersion square-lattice PCF with selective liquid infiltration
 Geometrical parameters dependence towards ultra-flat dispersion square-lattice PCF with selective liquid infiltration Partha Sona Maji and Partha Roy Chaudhuri Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian
Geometrical parameters dependence towards ultra-flat dispersion square-lattice PCF with selective liquid infiltration Partha Sona Maji and Partha Roy Chaudhuri Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian
Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 093102 2006 Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs Tai-I Weng and G. Y. Guo a Department of Physics, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 106, Republic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 093102 2006 Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs Tai-I Weng and G. Y. Guo a Department of Physics, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 106, Republic
Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice
 A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice Curtis W. Neff and Christopher J. Summers School of Materials Science and Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0245
A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice Curtis W. Neff and Christopher J. Summers School of Materials Science and Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0245
BENDING ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 293 307, 2011 BENDING ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen 1, 2, *, G. Hu 1, 2, X. A. Liu 1, 2, B. Peng 1, 2, and G. Wu 1, 2 1 Institute
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 293 307, 2011 BENDING ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-CORE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen 1, 2, *, G. Hu 1, 2, X. A. Liu 1, 2, B. Peng 1, 2, and G. Wu 1, 2 1 Institute
Ultra-high Birefringent Photonic Crystal Fiber for Sensing Applications
 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 3 (3) (2017) 121-128 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology journal homepage: www.apjest.com Full length article Ultra-high
Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 3 (3) (2017) 121-128 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology journal homepage: www.apjest.com Full length article Ultra-high
Chapter 5. Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice
 Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal Nanocavity via Unsymmetrical Displacement of Air-Holes
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
A Reflective Photonic Crystal Fiber Temperature Sensor Probe Based on Infiltration with Liquid Mixtures
 Sensors 013, 13, 7916-795; doi:10.3390/s130607916 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors A Reflective Photonic Crystal Fiber Temperature Sensor Probe Based on Infiltration
Sensors 013, 13, 7916-795; doi:10.3390/s130607916 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors A Reflective Photonic Crystal Fiber Temperature Sensor Probe Based on Infiltration
Generation of supercontinuum light in photonic crystal bers
 Generation of supercontinuum light in photonic crystal bers Koji Masuda Nonlinear Optics, Fall 2008 Abstract. I summarize the recent studies on the supercontinuum generation (SC) in photonic crystal fibers
Generation of supercontinuum light in photonic crystal bers Koji Masuda Nonlinear Optics, Fall 2008 Abstract. I summarize the recent studies on the supercontinuum generation (SC) in photonic crystal fibers
Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix O.Kiriyenko,1, W.Hergert 1, S.Wackerow 1, M.Beleites 1 and
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix O.Kiriyenko,1, W.Hergert 1, S.Wackerow 1, M.Beleites 1 and
Cladding defects in hollow core fibers for surface mode suppression and improved birefringence
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 8, 207 Cladding defects in hollow core fibers for surface mode suppression and improved birefringence Michieletto, Mattia; Lyngso, J. K.; Lægsgaard, Jesper; Bang, Ole
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 8, 207 Cladding defects in hollow core fibers for surface mode suppression and improved birefringence Michieletto, Mattia; Lyngso, J. K.; Lægsgaard, Jesper; Bang, Ole
Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations
 July 14, 005 ARDB Note Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations Robert J. Noble Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University 575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo Park, California
July 14, 005 ARDB Note Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations Robert J. Noble Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University 575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo Park, California
Highly Birefringent and Dispersion Compensating Photonic Crystal Fiber Based on Double Line Defect Core
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 20, No. 5, October 2016, pp. 567-574 ISSN: 1226-4776(Print) / ISSN: 2093-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2016.20.5.567 Highly Birefringent
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 20, No. 5, October 2016, pp. 567-574 ISSN: 1226-4776(Print) / ISSN: 2093-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2016.20.5.567 Highly Birefringent
Polarization-maintaining optical microfiber
 Polarization-maintaining optical microfiber Yongmin Jung *, Gilberto Brambilla, and David J. Richardson Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK * Corresponding
Polarization-maintaining optical microfiber Yongmin Jung *, Gilberto Brambilla, and David J. Richardson Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK * Corresponding
Review of Optical Properties of Materials
 Review of Optical Properties of Materials Review of optics Absorption in semiconductors: qualitative discussion Derivation of Optical Absorption Coefficient in Direct Semiconductors Photons When dealing
Review of Optical Properties of Materials Review of optics Absorption in semiconductors: qualitative discussion Derivation of Optical Absorption Coefficient in Direct Semiconductors Photons When dealing
Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer
 Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer Amit Mizrahi and Levi Schächter Electrical Engineering Department, Technion IIT, Haifa 32, ISRAEL amitmiz@tx.technion.ac.il Abstract: It is demonstrated
Bragg reflection waveguides with a matching layer Amit Mizrahi and Levi Schächter Electrical Engineering Department, Technion IIT, Haifa 32, ISRAEL amitmiz@tx.technion.ac.il Abstract: It is demonstrated
Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 23, No. 4, 2005 Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials A. MODINOS 1, N. STEFANOU 2* 1 Department of Physics, National Technical University of Athens, Zografou
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 23, No. 4, 2005 Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials A. MODINOS 1, N. STEFANOU 2* 1 Department of Physics, National Technical University of Athens, Zografou
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information I. Schematic representation of the zero- n superlattices Schematic representation of a superlattice with 3 superperiods is shown in Fig. S1. The superlattice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information I. Schematic representation of the zero- n superlattices Schematic representation of a superlattice with 3 superperiods is shown in Fig. S1. The superlattice
Photonic crystal bers
 UNIVERSITY OF LJUBLJANA FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS Seminar Photonic crystal bers Author: Peter Jakopiµc Mentor: Prof. dr. Irena Drevenšek Olenik May 2008 Abstract Photonic crystal bers (PCF) are
UNIVERSITY OF LJUBLJANA FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS Seminar Photonic crystal bers Author: Peter Jakopiµc Mentor: Prof. dr. Irena Drevenšek Olenik May 2008 Abstract Photonic crystal bers (PCF) are
Photonic Crystals. (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207
 Photonic Crystals (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207 [Based on material made generous made available by S G Johnson, MIT, at http://ab-initio.mit.edu/photons/
Photonic Crystals (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207 [Based on material made generous made available by S G Johnson, MIT, at http://ab-initio.mit.edu/photons/
Photonic Band Gap Crystals. Srivatsan Balasubramanian
 Photonic Band Gap Crystals Srivatsan Balasubramanian Summary Physics of photonic bandgap crystals. Photonic Crystals Classification. Fabrication. Applications. Protoype photonic band gap devices. Current
Photonic Band Gap Crystals Srivatsan Balasubramanian Summary Physics of photonic bandgap crystals. Photonic Crystals Classification. Fabrication. Applications. Protoype photonic band gap devices. Current
Intermodal and cross-polarization four-wave mixing in large-core hybrid photonic crystal fibers
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 12, 2018 Intermodal and cross-polarization four-wave mixing in large-core hybrid photonic crystal fibers Petersen, Sidsel Rübner; Alkeskjold, Thomas Tanggaard; Olausson,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 12, 2018 Intermodal and cross-polarization four-wave mixing in large-core hybrid photonic crystal fibers Petersen, Sidsel Rübner; Alkeskjold, Thomas Tanggaard; Olausson,
Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities
 Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities Kartik Srinivasan, Paul E. Barclay, and Oskar Painter Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities Kartik Srinivasan, Paul E. Barclay, and Oskar Painter Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Decoupling and asymmetric coupling in triplecore photonic crystal fibers
 1488 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 5, No. 9/ September 008 Yan et al. Decoupling and asymmetric coupling in triplecore photonic crystal fibers Yan Yan, 1, * Jean Toulouse, 1 Iavor Velchev, and Slava V. Rotkin
1488 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 5, No. 9/ September 008 Yan et al. Decoupling and asymmetric coupling in triplecore photonic crystal fibers Yan Yan, 1, * Jean Toulouse, 1 Iavor Velchev, and Slava V. Rotkin
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d](/thumbs/92/107830993.jpg) Guiding and reflecting light by boundary material arxiv:physics/0303051v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d a Department of Electrical and Communications
Guiding and reflecting light by boundary material arxiv:physics/0303051v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d a Department of Electrical and Communications
transmission reflection absorption
 Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Photonic crystal-liquid crystal fibers for single-polarization or high-birefringence guidance
 Photonic crystal-liquid crystal fibers for single-polarization or high-birefringence guidance D. C. Zografopoulos, E. E. Kriezis, and T. D. Tsiboukis Applied and Computational Electromagnetics Laboratory,
Photonic crystal-liquid crystal fibers for single-polarization or high-birefringence guidance D. C. Zografopoulos, E. E. Kriezis, and T. D. Tsiboukis Applied and Computational Electromagnetics Laboratory,
