Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials
|
|
|
- Kellie Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 23, No. 4, 2005 Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials A. MODINOS 1, N. STEFANOU 2* 1 Department of Physics, National Technical University of Athens, Zografou Campus, GR Athens, Greece 2 University of Athens, Section of Solid State Physics, Panepistimioupolis, GR Athens, Greece Photonic crystals are inhomogeneous materials whose dielectric properties vary periodically in space on a macroscopic scale. These materials have novel and interesting properties concerning both basic physics and technological applications. After a brief description of the main properties of photonic crystals, we present some specific applications related to wave guiding and Anderson localization of light due to stacking faults in these crystals. Key words: photonic crystals; optical wave guide; Anderson localization 1. Introduction Photonic crystals are composite materials whose dielectric properties vary periodically in space on a macroscopic scale [1 3]. For example, a photonic crystal may consist of non-overlapping dielectric or metallic spheres arranged periodically in a host medium with a different dielectric function. When the diameters of the spheres and the lattice constant are of the same order as the wavelength of light, we cannot describe the optical properties of the composite medium using an effective-medium approximation (this approximation holds when the wavelength of light is much larger than the lattice constant). Therefore, for a given photonic crystal (and a given lattice constant) we expect to see qualitatively new phenomena different from those observed in a homogeneous medium at sufficiently high frequencies of the electromagnetic (EM) field and when the wavelength of the EM waves is about the same or smaller than the lattice constant. At these frequencies, one expects to find phenomena that can be derived from the multiple scattering of light (we shall use the term light to stand for any EM wave in what follows) by a multitude of scatterers in the medium. * Corresponding author, nstefan@cc.uoa.gr
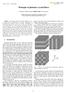
2 878 A. MODINOS, N. STEFANOU Having in mind a photonic crystal of non-overlapping spheres in a host medium, we can state the basic problem related to the modes of propagation of light in the infinite crystal as follows. At a given frequency ω the wave scattered from a particular sphere of the crystal is generated by the wave incident on this sphere, which consists of the waves scattered by all other spheres in the crystal. Naturally, this leads to a homogeneous system of equations (essentially the Maxwell equations in some form), which may or may not have physical solutions at the given frequency, i.e. solutions remaining finite everywhere in the infinite crystal. It turns out, as expected, that these physical solutions are of the Bloch wave type, familiar from solid state physics. There, the Bloch waves are solutions of the Schrödinger field the electron sees in a periodic array of atoms. In the present case, the Bloch waves are EM waves in the composite medium under consideration. It turns out that there are regions of frequency over which propagating modes of the EM field cannot exist in the composite medium (an appropriate photonic crystal), in the same way that electron states cannot have energies in the gaps of the energy band structure of a crystalline solid. 2. A photonic crystal with an absolute gap In Figure 1, we show an example of a frequency band structure of a threedimensional photonic crystal, which exhibits an absolute frequency gap. It consists of non-overlapping spheres with a dielectric constant ε s = in air (ε = 1). The spheres are arranged as in a diamond crystal with a lattice constant a. We view the Fig. 1. Projection of the frequency band structure of a crystal consisting of dielectric spheres (ε s = 12.96, S/a 0 = 0.25), arranged as in the structure of diamond in air (ε = 1), onto the SBZ of the (001) surface (shown in the inset) crystal as a stack of layers parallel to the xy plane. The periodicity of the layers parallel to this plane is described by a two-dimensional square lattice defined by the primitive vectors a 1 = a 0 (1,0,0) and a 2 = a 0 (0,1,0), where a 0 = a 2/2 is the distance between second nearest neighbours in the diamond structure. A basis of two spheres with a radius of S = a 0 /4, centred at (0,0,0) and a 0 (1/2,0, 2/4), defines the two planes of spheres of a layer. The (n+1)th layer along the z axis is obtained from the nth layer by a simple translation, de-
3 Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials 879 scribed by the primitive vector a 3 = a 0 (1/2,1/2, 2/2). What Figure 1 actually shows, is the projection of the frequency band structure onto the surface Brillouin zone (SBZ) of the (001) surface of this crystal, in particular along the symmetry directions of the SBZ. For any value of k (the reduced wave vector parallel to the (001) surface), the figure shows the regions of frequency over which at least one propagating mode of the EM field exists in the crystal (shaded regions) and those regions (gaps) where no such modes exist (blank regions). It is clear that an absolute frequency gap exists between ωa 0 /c = 3.68 and ωa 0 /c = 4.16 (c is the velocity of light in vacuum). We verified that this is indeed true by calculating the band structure at a sufficient number of k points within the SBZ, using a layer multiple-scattering computer code [4, 5]. Over the region of an absolute frequency gap, there can be no propagating wave in the crystal in any direction of propagation, and a slab of the material (sufficiently thick) behaves like a perfect mirror for the light at all incidence angles. The technological applications of this property of photonic band gaps in the construction of useful devices in optoelectronics can be far-reaching. For example, a wave guide with walls made of such a material is an obvious possibility, and a lot of progress has already been made in this direction, especially in relation to two-dimensional wave guides [6]. 3. Coupled resonator optical wave guides A different type of wave guide, intrinsic to photonic crystals, which has come to be known as the coupled cavity wave guide (CCW) or coupled resonator optical wave guide (CROW), was suggested by us in 1998 [7] and, independently, by Yariv et al. a year later [8]. Imagine a photonic crystal with an absolute frequency gap, such as the one described in Figure 1. If we replace one of the spheres by a slightly different one Fig. 2. A diamond structure of spheres. A linear chain of defect spheres (black spheres) is introduced along the [110] direction, which is taken as the x axis (a defect sphere), we obtain a localized state of the EM field within and about this sphere at a frequency within the gap. In reality, one obtains a degenerate state, but for the sake of simplicity we shall assume that we have just one non-degenerate state. If a photon of this frequency is somehow generated within this sphere, it will stay there for ever in the absence of absorption. Now imagine a periodic chain of such spheres along a straight line, as shown in Figure 2. There is bound to be some coupling between these spheres (a hopping interaction). This leads to a one-dimensional narrow band of states, with a width depending on the strength of the coupling between the spheres. Light can now propagate along the chain with a (group) velocity much
4 880 A. MODINOS, N. STEFANOU smaller than that in a homogeneous medium. This velocity can be, to some degree, adjusted to suit a number of purposes. It is also interesting to note that, under certain conditions, the chain can consist of a number of sections joining at angles, and light will still flow through it without being reflected at the corners, which is indeed remarkable and potentially very useful in the design of integrated optoelectronic systems. There is presently a lot of activity related to CCWs [9 16], and hopefully there will be interesting applications, too. 4. Anderson localization of light We would like to close this short review with a brief reference to a quite different problem, which shows the richness of photonic crystals as an area of research. We have established that a random introduction of stacking faults in a slab of an invertedopal photonic crystal leads to Anderson localization of light (localization due to disorder) over certain frequency regions around the absolute frequency gap [17, 18]. We show this by calculating the transmission coefficient of light incident on a slab of the material as a function of the thickness D of the slab. When Anderson localization occurs, the ensemble-averaged logarithm of the transmittance of the slab <lnt> diminishes with thickness as <lnt> = 2D/l, which allows us to determine the localization length l at various frequencies of the incident light. Hopefully such systems can be built in the laboratory [19, 20] in which case the possibility arises to directly compare theory and experiment at a quantitative level, something that is indeed quite rare in studies of Anderson localization phenomena. References [1] JOANNOPOULOS J.D., MEADE R.D., WINN J.N., Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, [2] Photonic Crystals and Light Localization in the 21 st Century, C.M. Soukoulis (Ed.), Kluwer, Dordrecht, [3] SAKODA K., Optical Properties of Photonic Crystals, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, [4] STEFANOU N., YANNOPAPAS V., MODINOS A., Comput. Phys. Commun., 113 (1998), 49. [5] STEFANOU N., YANNOPAPAS V., MODINOS A., Comput. Phys. Commun., 132 (2000), 189. [6] JOHNSON S.G., JOANNOPOULOS J.D., Photonic Crystals: The Road from Theory to Practice, Kluwer, Dordrecht, [7] STEFANOU N., MODINOS A., Phys. Rev. B, 57 (1998), [8] YARIV A., XU Y., LEE R. K., SCHERER A., Opt. Lett., 24 (1999), 711. [9] BAYINDIR M., TEMELKURAN B., OZBAY E., Phys. Rev. Lett., 84 (2000), [10] OLIVIER S., SMITH C., RATTIER M., BENISTY H., WEISBUCH C., KRAUSS T., HOUDRE R., OESTERLE U., Opt. Lett., 26 (2001), [11] MOOKHERJEA S., YARIV A., Phys. Rev. E, 65 (2002), [12] MOOKHERJEA S., YARIV A., Phys. Rev. E, 66 (2002), [13] SOLTANI M., ADIBI A., XU Y., LEE R.K., Opt. Lett., 28 (2003), [14] HAPP T.D., KAMP M., FORCHEL A., GENTNER J.-L., GOLDSTEIN L., Appl. Phys. Lett., 82 (2003), 4.
5 Photonic crystals: a novel class of functional materials 881 [15] MALKOVA N., GOPALAN V., J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 21 (2004), [16] YANIK M.F., FAN S., Phys. Rev. Lett., 92 (2004), [17] YANNOPAPAS V., STEFANOU N., MODINOS A., Phys. Rev. Lett., 86 (2001), [18] YANNOPAPAS V., STEFANOU N., MODINOS A., Phys. Rev. B, 68 (2003), [19] VLASOV YU.A., BO X.Z., STURM J.C., NORRIS D.J., Nature (London), 414 (2001), 289. [20] HOOGENBOOM J.P., VAN LANGEN-SUURLING A.K., ROMIJN H., VAN BLAADEREN A., Phys. Rev. Lett., 90 (2003), Received 10 December 2004 Revised 14 April 2005
Propagation of Photons Through Localized Coupled Cavity Modes in Photonic Band Gap Structures:
 CLEO, May 7-12, 7 2000, San Francisco Propagation of Photons Through Localized Coupled Cavity Modes in Photonic Band Gap Structures: A New Type of Waveguiding Mechanism Mehmet Bayındır Burak Temelkuran
CLEO, May 7-12, 7 2000, San Francisco Propagation of Photons Through Localized Coupled Cavity Modes in Photonic Band Gap Structures: A New Type of Waveguiding Mechanism Mehmet Bayındır Burak Temelkuran
Simulation of two dimensional photonic band gaps
 Available online at www.ilcpa.pl International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy 5 (214) 58-88 ISSN 2299-3843 Simulation of two dimensional photonic band gaps S. E. Dissanayake, K. A. I. L. Wijewardena
Available online at www.ilcpa.pl International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy 5 (214) 58-88 ISSN 2299-3843 Simulation of two dimensional photonic band gaps S. E. Dissanayake, K. A. I. L. Wijewardena
GEOMETRICAL INFLUENCE ON PHOTONIC BANDGAP OF THREE DIMENSIONAL CHALCOGENIDE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
 Journal of Ovonic Research Vol. 6, No. 4, July-August 2010, p. 181 185 GEOMETRICAL INFLUENCE ON PHOTONIC BANDGAP OF THREE DIMENSIONAL CHALCOGENIDE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS B. SUTHAR *, A.K. NAGAR, A. BHARGAVA
Journal of Ovonic Research Vol. 6, No. 4, July-August 2010, p. 181 185 GEOMETRICAL INFLUENCE ON PHOTONIC BANDGAP OF THREE DIMENSIONAL CHALCOGENIDE PHOTONIC CRYSTALS B. SUTHAR *, A.K. NAGAR, A. BHARGAVA
Waveguides in finite-height two-dimensional photonic crystals
 2232 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 19, No. 9/ September 2002 Kafesaki et al. Waveguides in finite-height two-dimensional photonic crystals M. Kafesaki Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser, Foundation
2232 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 19, No. 9/ September 2002 Kafesaki et al. Waveguides in finite-height two-dimensional photonic crystals M. Kafesaki Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser, Foundation
Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 093102 2006 Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs Tai-I Weng and G. Y. Guo a Department of Physics, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 106, Republic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 093102 2006 Band structure of honeycomb photonic crystal slabs Tai-I Weng and G. Y. Guo a Department of Physics, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 106, Republic
Jahn-Teller effect in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW 68, 045105 2003 Jahn-Teller effect in two-dimensional photonic crystals N. Malkova, S. Kim, and V. Gopalan Materials Research Institute, Pennsylvania State University, University Park,
PHYSICAL REVIEW 68, 045105 2003 Jahn-Teller effect in two-dimensional photonic crystals N. Malkova, S. Kim, and V. Gopalan Materials Research Institute, Pennsylvania State University, University Park,
Waveguides in inverted opal photonic crystals
 Waveguides in inverted opal photonic crystals Virginie Lousse 1,2 and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, USA 2 Laboratoire de Physique du Solide, Facultés
Waveguides in inverted opal photonic crystals Virginie Lousse 1,2 and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, USA 2 Laboratoire de Physique du Solide, Facultés
Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 6 journal of December 2006 physics pp. 1155 1164 Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and R K SINHA TIFAC-Center of Relevance
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 6 journal of December 2006 physics pp. 1155 1164 Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and R K SINHA TIFAC-Center of Relevance
Photonic band gaps with layer-by-layer double-etched structures
 Photonic band gaps with layer-by-layer double-etched structures R. Biswas a) Microelectronics Research Center, Ames Laboratory USDOE and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames,
Photonic band gaps with layer-by-layer double-etched structures R. Biswas a) Microelectronics Research Center, Ames Laboratory USDOE and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames,
Sharp bends in photonic crystal waveguides as nonlinear Fano resonators
 Sharp bends in photonic crystal waveguides as nonlinear Fano resonators Andrey E. Miroshnichenko and Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre and Centre for Ultra-high bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems
Sharp bends in photonic crystal waveguides as nonlinear Fano resonators Andrey E. Miroshnichenko and Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre and Centre for Ultra-high bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems
Spontaneous emission rate of an electric dipole in a general microcavity
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 60, NUMBER 7 15 AUGUST 1999-I Spontaneous emission rate of an electric dipole in a general microcavity Jeong-Ki Hwang, Han-Youl Ryu, and Yong-Hee Lee Department of Physics, Korea
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 60, NUMBER 7 15 AUGUST 1999-I Spontaneous emission rate of an electric dipole in a general microcavity Jeong-Ki Hwang, Han-Youl Ryu, and Yong-Hee Lee Department of Physics, Korea
SCATTERING OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ON METAL NANOPARTICLES. Tomáš Váry, Juraj Chlpík, Peter Markoš
 SCATTERING OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ON METAL NANOPARTICLES Tomáš Váry, Juraj Chlpík, Peter Markoš ÚJFI, FEI STU, Bratislava E-mail: tomas.vary@stuba.sk Received xx April 2012; accepted xx May 2012. 1.
SCATTERING OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ON METAL NANOPARTICLES Tomáš Váry, Juraj Chlpík, Peter Markoš ÚJFI, FEI STU, Bratislava E-mail: tomas.vary@stuba.sk Received xx April 2012; accepted xx May 2012. 1.
Photonic band structure in periodic dielectric structures
 Photonic band structure in periodic dielectric structures Mustafa Muhammad Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 December 4, 2001 Abstract Recent experiments have found
Photonic band structure in periodic dielectric structures Mustafa Muhammad Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 December 4, 2001 Abstract Recent experiments have found
Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals
 Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals Michael James Ventura and Min Gu* Centre for Micro-Photonics and Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems,
Polarization control of defect modes in threedimensional woodpile photonic crystals Michael James Ventura and Min Gu* Centre for Micro-Photonics and Centre for Ultrahigh-bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems,
Fano resonances in dielectric, metallic and metamaterial photonic structures
 Fano resonances in dielectric, metallic and metamaterial photonic structures (Invited Paper) Peter Markoš Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University in Bratislava, 842 48 Slovakia
Fano resonances in dielectric, metallic and metamaterial photonic structures (Invited Paper) Peter Markoš Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University in Bratislava, 842 48 Slovakia
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d](/thumbs/92/107830993.jpg) Guiding and reflecting light by boundary material arxiv:physics/0303051v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d a Department of Electrical and Communications
Guiding and reflecting light by boundary material arxiv:physics/0303051v2 [physics.optics] 13 Jan 2005 A. Huttunen a,, K. Varis b K. Kataja c, J. Aikio c, P. Törmä d a Department of Electrical and Communications
Nonlinear optical spectroscopy in one-dimensional photonic crystals. Abstract
 Applied Physics Letters #L03-3261, revised manuscript Nonlinear optical spectroscopy in one-dimensional photonic crystals Garrett J. Schneider and George H. Watson Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Applied Physics Letters #L03-3261, revised manuscript Nonlinear optical spectroscopy in one-dimensional photonic crystals Garrett J. Schneider and George H. Watson Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix O.Kiriyenko,1, W.Hergert 1, S.Wackerow 1, M.Beleites 1 and
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Photonic/Plasmonic Structures from Metallic Nanoparticles in a Glass Matrix O.Kiriyenko,1, W.Hergert 1, S.Wackerow 1, M.Beleites 1 and
Energy flow in photonic crystal waveguides
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Energy flow in photonic crystal waveguides Søndergaard, Thomas; Dridi, Kim Published in: Physical Review B (Condensed Matter and Materials Physics) Link to
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Energy flow in photonic crystal waveguides Søndergaard, Thomas; Dridi, Kim Published in: Physical Review B (Condensed Matter and Materials Physics) Link to
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821981.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies
 Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies Peter Markos and C. M. Soukoulis Outline of Talk What are Metamaterials? An Example: Left-handed Materials Results of the transfer matrix method Negative
Left-handed materials: Transfer matrix method studies Peter Markos and C. M. Soukoulis Outline of Talk What are Metamaterials? An Example: Left-handed Materials Results of the transfer matrix method Negative
Directional emitter and beam splitter based on self-collimation effect
 Directional emitter and beam splitter based on self-collimation effect W. Y. Liang, J. W. Dong, and H. Z. Wang* State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, Zhongshan (Sun Yat-Sen)
Directional emitter and beam splitter based on self-collimation effect W. Y. Liang, J. W. Dong, and H. Z. Wang* State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, Zhongshan (Sun Yat-Sen)
Principle of photonic crystal fibers
 Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Behavior of light at photonic crystal interfaces
 Behavior of light at photonic crystal interfaces Emanuel Istrate, Alexander A. Green, and Edward H. Sargent Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, 10 King s College Road,
Behavior of light at photonic crystal interfaces Emanuel Istrate, Alexander A. Green, and Edward H. Sargent Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, 10 King s College Road,
Ankara, Turkey Published online: 20 Sep 2013.
 This article was downloaded by: [Bilkent University] On: 26 December 2013, At: 12:33 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: [Bilkent University] On: 26 December 2013, At: 12:33 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
Optical properties of metamaterial-based devices modulated by a liquid crystal
 Appl. Phys. A (2014) 117:611 619 DOI 10.1007/s00339-014-8711-x Optical properties of metamaterial-based devices modulated by a liquid crystal Filiz Karaomerlioglu Amirullah M. Mamedov Ekmel Ozbay Received:
Appl. Phys. A (2014) 117:611 619 DOI 10.1007/s00339-014-8711-x Optical properties of metamaterial-based devices modulated by a liquid crystal Filiz Karaomerlioglu Amirullah M. Mamedov Ekmel Ozbay Received:
Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME, NUMBER 16 15 OCTOBER 1996-II Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME, NUMBER 16 15 OCTOBER 1996-II Large omnidirectional band gaps in metallodielectric photonic crystals Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics,
II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles
 II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles We report on the fabrication and optical transmission studies of thin three-dimensional photonic crystals of high-dielectric ZnS-core and low-dielectric
II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles We report on the fabrication and optical transmission studies of thin three-dimensional photonic crystals of high-dielectric ZnS-core and low-dielectric
The photonic band structure of macro- ionic crystal
 21 August 2000 Physics Letters A 273 2000 203 207 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterpla The photonic band structure of macro- ionic crystal Weiyi Zhang ), Zhenlin Wang, An Hu, Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid
21 August 2000 Physics Letters A 273 2000 203 207 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterpla The photonic band structure of macro- ionic crystal Weiyi Zhang ), Zhenlin Wang, An Hu, Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid
Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section Elements
 Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 214, Article ID 78142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1155/214/78142 Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section
Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 214, Article ID 78142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1155/214/78142 Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section
Photonic Bands and Gap Maps in a Photonic Crystal Slab
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 38, NO. 7, JULY 2002 891 Photonic Bands and Gap Maps in a Photonic Crystal Slab Lucio Claudio Andreani and Mario Agio Abstract The photonic bands of a two-dimensional
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 38, NO. 7, JULY 2002 891 Photonic Bands and Gap Maps in a Photonic Crystal Slab Lucio Claudio Andreani and Mario Agio Abstract The photonic bands of a two-dimensional
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization. Yuri S. Kivshar
 Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
Linear waveguides in photonic-crystal slabs
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 12 Linear waveguides in photonic-crystal slabs 15 SEPTEMBER 2000-II Steven G. Johnson, Pierre R. Villeneuve, Shanhui Fan, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 12 Linear waveguides in photonic-crystal slabs 15 SEPTEMBER 2000-II Steven G. Johnson, Pierre R. Villeneuve, Shanhui Fan, and J. D. Joannopoulos Department of Physics
Light Localization in Left-Handed Media
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena Warsaw, Poland, May 25 27, 2007 Light Localization in Left-Handed Media M. Rusek,
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena Warsaw, Poland, May 25 27, 2007 Light Localization in Left-Handed Media M. Rusek,
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 8 Apr 2004
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 8 Apr 2004 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 8 Apr 2004](/thumbs/92/109778850.jpg) Conditions for waveguide decoupling in square-lattice photonic crystals T. Koponen 1, A. Huttunen 2 and P. Törmä 1 arxiv:physics/4445v1 [physics.optics] 8 Apr 24 1 Department of Physics, University of
Conditions for waveguide decoupling in square-lattice photonic crystals T. Koponen 1, A. Huttunen 2 and P. Törmä 1 arxiv:physics/4445v1 [physics.optics] 8 Apr 24 1 Department of Physics, University of
Guided and defect modes in periodic dielectric waveguides
 Fan et al. Vol. 12, No. 7/July 1995/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1267 Guided and defect modes in periodic dielectric waveguides Shanhui Fan, Joshua N. Winn, Adrian Devenyi, J. C. Chen, Robert D. Meade, and J. D.
Fan et al. Vol. 12, No. 7/July 1995/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1267 Guided and defect modes in periodic dielectric waveguides Shanhui Fan, Joshua N. Winn, Adrian Devenyi, J. C. Chen, Robert D. Meade, and J. D.
OMNI-DIRECTION REFLECTION IN ONE DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 7, 133 143, 2008 OMNI-DIRECTION REFLECTION IN ONE DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL R. Srivastava Department of Physics Udai Pratap Autonomous College Varanasi
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 7, 133 143, 2008 OMNI-DIRECTION REFLECTION IN ONE DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL R. Srivastava Department of Physics Udai Pratap Autonomous College Varanasi
Highly Directive Radiation and Negative Refraction Using Photonic Crystals
 Laser Physics, Vol. 5, No., 5, pp. 7 4. Original Text Copyright 5 by Astro, Ltd. Copyright 5 by MAIK Nauka /Interperiodica (Russia). MODERN TRENDS IN LASER PHYSICS Highly Directive Radiation and Negative
Laser Physics, Vol. 5, No., 5, pp. 7 4. Original Text Copyright 5 by Astro, Ltd. Copyright 5 by MAIK Nauka /Interperiodica (Russia). MODERN TRENDS IN LASER PHYSICS Highly Directive Radiation and Negative
Optimizing the Q value in three-dimensional metallic photonic band gap crystals
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 84, NUMBER 8 15 OCTOBER 1998 Optimizing the Q value in three-dimensional metallic photonic band gap crystals W. Y. Leung, G. Tuttle, M. M. Sigalas, R. Biswas, a) K. M.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 84, NUMBER 8 15 OCTOBER 1998 Optimizing the Q value in three-dimensional metallic photonic band gap crystals W. Y. Leung, G. Tuttle, M. M. Sigalas, R. Biswas, a) K. M.
Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror
 Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror Virginie Lousse 1,2, Wonjoo Suh 1, Onur Kilic 1, Sora Kim 1, Olav Solgaard 1, and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror Virginie Lousse 1,2, Wonjoo Suh 1, Onur Kilic 1, Sora Kim 1, Olav Solgaard 1, and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
E. YABLONOVITCH photonic crystals by using level set methods
 Appl. Phys. B 81, 235 244 (2005) DOI: 10.1007/s00340-005-1877-3 Applied Physics B Lasers and Optics C.Y. KAO 1, Maximizing band gaps in two-dimensional S. OSHER 2 E. YABLONOVITCH photonic crystals by using
Appl. Phys. B 81, 235 244 (2005) DOI: 10.1007/s00340-005-1877-3 Applied Physics B Lasers and Optics C.Y. KAO 1, Maximizing band gaps in two-dimensional S. OSHER 2 E. YABLONOVITCH photonic crystals by using
Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles
 Letter to Appl. Phys. Letters June 8, 2001 Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles Krassimir P. Velikov, a, ) Alexander Moroz, a) and Alfons van Blaaderen a,b, ) a Physics and Chemistry of
Letter to Appl. Phys. Letters June 8, 2001 Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles Krassimir P. Velikov, a, ) Alexander Moroz, a) and Alfons van Blaaderen a,b, ) a Physics and Chemistry of
Effects of disorder on superlensing in two dimensional photonic crystal slabs
 Effects of disorder on superlensing in two dimensional photonic crystal slabs X. Wang and K. Kempa Department of Physics, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts 02467 Abstract We demonstrate that
Effects of disorder on superlensing in two dimensional photonic crystal slabs X. Wang and K. Kempa Department of Physics, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts 02467 Abstract We demonstrate that
Canalization of Sub-wavelength Images by Electromagnetic Crystals
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 37 Canalization of Sub-wavelength Images by Electromagnetic Crystals P. A. Belov 1 and C. R. Simovski 2 1 Queen Mary
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 37 Canalization of Sub-wavelength Images by Electromagnetic Crystals P. A. Belov 1 and C. R. Simovski 2 1 Queen Mary
Negative refraction of photonic and polaritonic waves in periodic structures
 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES Vol. 57, No. 1, 2009 Invited paper Negative refraction of photonic and polaritonic waves in periodic structures K. KEMPA and A. ROSE Department
BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES Vol. 57, No. 1, 2009 Invited paper Negative refraction of photonic and polaritonic waves in periodic structures K. KEMPA and A. ROSE Department
Chapter 5. Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice
 Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
Chapter 5 Effects of Photonic Crystal Band Gap on Rotation and Deformation of Hollow Te Rods in Triangular Lattice In chapter 3 and 4, we have demonstrated that the deformed rods, rotational rods and perturbation
Density of modes maps for design of photonic crystal devices
 RESEARCH Revista Mexicana de Física 62 (2016) 193 198 MAY-JUNE 2016 Density of modes maps for design of photonic crystal devices I. Guryev, I. Sukhoivanov, R.I. Mata Chavez, N. Gurieva, J.A. Andrade Lucio,
RESEARCH Revista Mexicana de Física 62 (2016) 193 198 MAY-JUNE 2016 Density of modes maps for design of photonic crystal devices I. Guryev, I. Sukhoivanov, R.I. Mata Chavez, N. Gurieva, J.A. Andrade Lucio,
Analytical Analysis of H Polarized Line-Defect Modes in Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Based on Hermite Expansion of Floquet Orders
 Analytical Analysis of H Polarized Line-Defect Modes in Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Based on Hermite Expansion of Floquet Orders Peyman Sarrafi a, Amir Hossein Atabaki b, Khashayar Mehrany a, Sina
Analytical Analysis of H Polarized Line-Defect Modes in Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Based on Hermite Expansion of Floquet Orders Peyman Sarrafi a, Amir Hossein Atabaki b, Khashayar Mehrany a, Sina
Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal Nanocavity via Unsymmetrical Displacement of Air-Holes
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
transmission reflection absorption
 Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Optical Cages V. Kumar*, J. P. Walker* and H. Grebel The Electronic Imaging Center and the ECE department at NJIT, Newark, NJ 0702. grebel@njit.edu * Contributed equally Faraday Cage [], a hollow structure
Light transmission through a single cylindrical hole in a metallic film
 Light transmission through a single cylindrical hole in a metallic film F. J. García de Abajo Centro Mixto CSIC-UPV/EHU and Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC), Aptdo. 1072, 20080 San Sebastián,
Light transmission through a single cylindrical hole in a metallic film F. J. García de Abajo Centro Mixto CSIC-UPV/EHU and Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC), Aptdo. 1072, 20080 San Sebastián,
Band Gap Simulations of 1-Dimensional Photonic Crystal
 Band Gap Simulations of 1-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Swarnjeet Kaur, Deepak Saini, Amandeep Sappal Abstract one dimensional photonic crystal is the simplest possible type of the photonic crystals. The
Band Gap Simulations of 1-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Swarnjeet Kaur, Deepak Saini, Amandeep Sappal Abstract one dimensional photonic crystal is the simplest possible type of the photonic crystals. The
Surface Plasmon Polariton Assisted Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Passband Filters for Ultraviolet Range
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the International School and Conference on Optics and Optical Materials, ISCOM07, Belgrade, Serbia, September 3 7, 2007 Surface Plasmon Polariton
A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice
 A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice Curtis W. Neff and Christopher J. Summers School of Materials Science and Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0245
A photonic crystal superlattice based on triangular lattice Curtis W. Neff and Christopher J. Summers School of Materials Science and Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0245
Investigation of one-dimensional photonic bandgap structures containing lossy double-negative metamaterials through the Bloch impedance
 Shi et al. Vol. 3, No. 6 / June 23 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 473 Investigation of one-dimensional photonic bandgap structures containing lossy double-negative metamaterials through the Bloch impedance Fenghua
Shi et al. Vol. 3, No. 6 / June 23 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 473 Investigation of one-dimensional photonic bandgap structures containing lossy double-negative metamaterials through the Bloch impedance Fenghua
Theoretical and Experimental Study of Photonic Crystal Based Structures for Optical Communication Applications
 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Photonic Crystal Based Structures for Optical Communication Applications Wei Jiang *a,b, Jizuo Zou a, Linghui Wu b, Yihong Chen b, Chuhua Tian a, Brie Howley a, Xuejun
Theoretical and Experimental Study of Photonic Crystal Based Structures for Optical Communication Applications Wei Jiang *a,b, Jizuo Zou a, Linghui Wu b, Yihong Chen b, Chuhua Tian a, Brie Howley a, Xuejun
Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
 Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Z.A. Pyatakova M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Physics Department zoya.pyatakova@gmail.com Abstract. The paper shows that silicon-based
Acoustooptic Bragg Diffraction in 2-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Z.A. Pyatakova M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Physics Department zoya.pyatakova@gmail.com Abstract. The paper shows that silicon-based
Photonic-crystal slow-light enhancement of nonlinear phase sensitivity
 2052 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 19, No. 9/ September 2002 Soljačíc et al. Photonic-crystal slow-light enhancement of nonlinear phase sensitivity Marin Soljačić and Steven G. Johnson Department of Physics
2052 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 19, No. 9/ September 2002 Soljačíc et al. Photonic-crystal slow-light enhancement of nonlinear phase sensitivity Marin Soljačić and Steven G. Johnson Department of Physics
Defect-based Photonic Crystal Cavity for Silicon Laser
 Defect-based Photonic Crystal Cavity for Silicon Laser Final Term Paper for Nonlinear Optics PHYC/ECE 568 Arezou Khoshakhlagh Instructor: Prof. M. Sheikh-Bahae University of New Mexico karezou@unm.edu
Defect-based Photonic Crystal Cavity for Silicon Laser Final Term Paper for Nonlinear Optics PHYC/ECE 568 Arezou Khoshakhlagh Instructor: Prof. M. Sheikh-Bahae University of New Mexico karezou@unm.edu
Keywords: Bloch-Floquet Theorem, Periodic Media, Photonic Crystals, Plasmonic Crystals, Electronic Crystals, Phononic Crystals
 On the Bloch Theorem and Orthogonality Relations Sina Khorasani School of Electrical Engineering Sharif University of Technology P. O. Box 11365-9363 Tehran, Iran Email: khorasani@sina.sharif.edu Abstract
On the Bloch Theorem and Orthogonality Relations Sina Khorasani School of Electrical Engineering Sharif University of Technology P. O. Box 11365-9363 Tehran, Iran Email: khorasani@sina.sharif.edu Abstract
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information for Biocompatible and Functionalized Silk Opals Sunghwan Kim, Alexander N. Mitropoulos, Joshua D. Spitzberg, Hu Tao, David L. Kaplan, and Fiorenzo G. Omenetto (*) (*) To whom
Supplementary Information for Biocompatible and Functionalized Silk Opals Sunghwan Kim, Alexander N. Mitropoulos, Joshua D. Spitzberg, Hu Tao, David L. Kaplan, and Fiorenzo G. Omenetto (*) (*) To whom
Air-holes radius change effects and structure transitions in the linear photonic crystal nanocavities
 American Journal of Optics and Photonics 2013; 1(3): 11-16 Published online June 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop) doi: 10.11648/j.ajop.20130103.11 Air-holes radius change effects
American Journal of Optics and Photonics 2013; 1(3): 11-16 Published online June 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop) doi: 10.11648/j.ajop.20130103.11 Air-holes radius change effects
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 08 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Outline: Photonic crystals 2 1. Photonic crystals vs electronic
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2012 Lecture 08 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Outline: Photonic crystals 2 1. Photonic crystals vs electronic
Photonic devices for quantum information processing:
 Outline Photonic devices for quantum information processing: coupling to dots, structure design and fabrication Optoelectronics Group, Cavendish Lab Outline Vuckovic s group Noda s group Outline Outline
Outline Photonic devices for quantum information processing: coupling to dots, structure design and fabrication Optoelectronics Group, Cavendish Lab Outline Vuckovic s group Noda s group Outline Outline
Photonic crystal fiber with a hybrid honeycomb cladding
 Photonic crystal fiber with a hybrid honeycomb cladding Niels Asger Mortensen asger@mailaps.org Martin Dybendal Nielsen COM, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kongens Lyngby, Denmark Jacob Riis
Photonic crystal fiber with a hybrid honeycomb cladding Niels Asger Mortensen asger@mailaps.org Martin Dybendal Nielsen COM, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kongens Lyngby, Denmark Jacob Riis
Strongly Localized Photonic Mode in 2D Periodic Structure Without Bandgap
 Strongly Localized Photonic Mode in D Periodic Structure Without Bandgap V. M. APALKOV M. E. RAIKH Physics Department, University of Utah The work was supported by: the Army Research Office under Grant
Strongly Localized Photonic Mode in D Periodic Structure Without Bandgap V. M. APALKOV M. E. RAIKH Physics Department, University of Utah The work was supported by: the Army Research Office under Grant
Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 551 Research on the Wide-angle and Broadband 2D Photonic Crystal Polarization Splitter Y. Y. Li, P. F. Gu, M. Y. Li,
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821987.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 20, 81 94, 2011
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 2, 8 94, 2 PHOTONIC BAND STRUCTURES AND ENHANCE- MENT OF OMNIDIRECTIONAL REFLECTION BANDS BY USING A TERNARY D PHOTONIC CRYSTAL IN- CLUDING LEFT-HANDED MATERIALS
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 2, 8 94, 2 PHOTONIC BAND STRUCTURES AND ENHANCE- MENT OF OMNIDIRECTIONAL REFLECTION BANDS BY USING A TERNARY D PHOTONIC CRYSTAL IN- CLUDING LEFT-HANDED MATERIALS
Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in Electromagnetism. You can leave home without them. Complete Band Gaps: Steven G.
 Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in lectromagnetism Steven G. ohnson MIT Complete Band Gaps: You can leave home without them. How else can we confine light? Total Internal Reflection n o n i > n o
Photonic Crystals: Periodic Surprises in lectromagnetism Steven G. ohnson MIT Complete Band Gaps: You can leave home without them. How else can we confine light? Total Internal Reflection n o n i > n o
A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices
 A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices Georgios Veronis, Robert W. Dutton, and Shanhui Fan Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 9435
A new method for sensitivity analysis of photonic crystal devices Georgios Veronis, Robert W. Dutton, and Shanhui Fan Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 9435
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Observation of unconventional edge states in photonic graphene Yonatan Plotnik 1 *, Mikael C. Rechtsman 1 *, Daohong Song 2 *, Matthias Heinrich 3, Julia M. Zeuner 3, Stefan Nolte 3, Yaakov Lumer 1, Natalia
Observation of unconventional edge states in photonic graphene Yonatan Plotnik 1 *, Mikael C. Rechtsman 1 *, Daohong Song 2 *, Matthias Heinrich 3, Julia M. Zeuner 3, Stefan Nolte 3, Yaakov Lumer 1, Natalia
Transmission resonances on metallic gratings with very narrow slits
 Transmission resonances on metallic gratings with very narrow slits J.A. Porto 1, F.J. García-Vidal 2, and J.B. Pendry 1 1 Condensed Matter Theory Group, The Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London
Transmission resonances on metallic gratings with very narrow slits J.A. Porto 1, F.J. García-Vidal 2, and J.B. Pendry 1 1 Condensed Matter Theory Group, The Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London
Overview. 1. What range of ε eff, µ eff parameter space is accessible to simple metamaterial geometries? ``
 MURI-Transformational Electromagnetics Innovative use of Metamaterials in Confining, Controlling, and Radiating Intense Microwave Pulses University of New Mexico August 21, 2012 Engineering Dispersive
MURI-Transformational Electromagnetics Innovative use of Metamaterials in Confining, Controlling, and Radiating Intense Microwave Pulses University of New Mexico August 21, 2012 Engineering Dispersive
3D analysis of hybrid photonic crystal/ conventional waveguide 90 bend
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2004-07-20 3D analysis of hybrid photonic crystal/ conventional waveguide 90 bend J. Cai S. Kim See next page for additional authors
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2004-07-20 3D analysis of hybrid photonic crystal/ conventional waveguide 90 bend J. Cai S. Kim See next page for additional authors
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 42, 13 22, 2013
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 42, 3 22, 23 OMNIDIRECTIONAL REFLECTION EXTENSION IN A ONE-DIMENSIONAL SUPERCONDUCTING-DIELECTRIC BINARY GRADED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL WITH GRADED GEOMETRIC
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 42, 3 22, 23 OMNIDIRECTIONAL REFLECTION EXTENSION IN A ONE-DIMENSIONAL SUPERCONDUCTING-DIELECTRIC BINARY GRADED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL WITH GRADED GEOMETRIC
Photonic crystal waveguide-mode orthogonality conditions and computation of intrinsic waveguide losses
 Witzens et al. Vol. 20, No. 10/October 2003/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1963 Photonic crystal waveguide-mode orthogonality conditions and computation of intrinsic waveguide losses Jeremy Witzens, Thomas Baehr-Jones,
Witzens et al. Vol. 20, No. 10/October 2003/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1963 Photonic crystal waveguide-mode orthogonality conditions and computation of intrinsic waveguide losses Jeremy Witzens, Thomas Baehr-Jones,
Analysis of waveguides coupling in Photonic Crystal Power-Splitter
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 204 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 225-838X / Vol, 8 (9): 259-264 Science Explorer Publications Analysis of waveguides coupling in
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 204 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 225-838X / Vol, 8 (9): 259-264 Science Explorer Publications Analysis of waveguides coupling in
Appendix. Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices
 91 Appendix Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices 5.1 Introduction The technology of photonic crystals has produced a large variety of new devices. However, photonic crystals have not been
91 Appendix Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices 5.1 Introduction The technology of photonic crystals has produced a large variety of new devices. However, photonic crystals have not been
Theoretical studies on the transmission and reflection properties of metallic planar fractals
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 (2004) 368 373 PII: S0022-3727(04)63919-2 Theoretical studies on the transmission and reflection properties
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D: APPLIED PHYSICS J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 (2004) 368 373 PII: S0022-3727(04)63919-2 Theoretical studies on the transmission and reflection properties
Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media Karim G. Sabra, School of Mechanical Engineering,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Bio-acoustic Scatterers in Complex Media Karim G. Sabra, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Negative refraction and left-handed behavior in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 Negative refraction and left-handed behavior in two-dimensional photonic crystals S. Foteinopoulou and C. M. Soukoulis Ames Laboratory-USDOE and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University,
Negative refraction and left-handed behavior in two-dimensional photonic crystals S. Foteinopoulou and C. M. Soukoulis Ames Laboratory-USDOE and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University,
Frequency bands of negative refraction in finite one-dimensional photonic crystals
 Vol 16 No 1, January 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(01)/0173-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Frequency bands of negative refraction in finite one-dimensional photonic crystals
Vol 16 No 1, January 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(01)/0173-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Frequency bands of negative refraction in finite one-dimensional photonic crystals
Analysis of Photonic Band Structure in 1-D Photonic Crystal using PWE and FDTD Method
 P P IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. Issue 8, August 05. Analysis of Photonic Band Structure in -D Photonic Crystal using PWE and FDTD Method Pooja ChhokerP
P P IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. Issue 8, August 05. Analysis of Photonic Band Structure in -D Photonic Crystal using PWE and FDTD Method Pooja ChhokerP
From optical graphene to topological insulator
 From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
EXISTENCE OF GUIDED MODES ON PERIODIC SLABS
 SUBMITTED FOR: PROCEEDINGS OF THE FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS June 16 19, 2004, Pomona, CA, USA pp. 1 8 EXISTENCE OF GUIDED MODES ON PERIODIC SLABS Stephen
SUBMITTED FOR: PROCEEDINGS OF THE FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS June 16 19, 2004, Pomona, CA, USA pp. 1 8 EXISTENCE OF GUIDED MODES ON PERIODIC SLABS Stephen
Coupling, Scattering, and Perturbation Theory: Semi-analytical Analyses of Photonic-Crystal Waveguides
 Coupling, Scattering, and Perturbation Theory: Semi-analytical Analyses of Photonic-Crystal Waveguides Steven G. Johnson, M. L. Povinelli, P. Bienstman, M. Skorobogatiy,* M. Soljačić, M. Ibanescu, E. Lidorikis,
Coupling, Scattering, and Perturbation Theory: Semi-analytical Analyses of Photonic-Crystal Waveguides Steven G. Johnson, M. L. Povinelli, P. Bienstman, M. Skorobogatiy,* M. Soljačić, M. Ibanescu, E. Lidorikis,
Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by. acoustic metamaterial slabs
 Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by acoustic metamaterial slabs Ke Deng,2, Yiqun Ding, Zhaojian He, Heping Zhao 2, Jing Shi, and Zhengyou Liu,a) Key Lab of Acoustic and Photonic materials and
Theoretical study of subwavelength imaging by acoustic metamaterial slabs Ke Deng,2, Yiqun Ding, Zhaojian He, Heping Zhao 2, Jing Shi, and Zhengyou Liu,a) Key Lab of Acoustic and Photonic materials and
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays. Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković
 Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Electromagnetic Absorption by Metamaterial Grating System
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 2008 91 Electromagnetic Absorption by Metamaterial Grating System Xiaobing Cai and Gengkai Hu School of Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China Abstract
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 2008 91 Electromagnetic Absorption by Metamaterial Grating System Xiaobing Cai and Gengkai Hu School of Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China Abstract
Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements
 Physica E 9 (2001) 384 388 www.elsevier.nl/locate/physe Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements Ulrich Kuhl, Hans-Jurgen Stockmann Fachbereich Physik,
Physica E 9 (2001) 384 388 www.elsevier.nl/locate/physe Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements Ulrich Kuhl, Hans-Jurgen Stockmann Fachbereich Physik,
Theoretical study of left-handed behavior of composite metamaterials
 Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 4 (2006) 12 16 www.elsevier.com/locate/photonics Theoretical study of left-handed behavior of composite metamaterials R.S. Penciu a,b, *, M. Kafesaki
Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 4 (2006) 12 16 www.elsevier.com/locate/photonics Theoretical study of left-handed behavior of composite metamaterials R.S. Penciu a,b, *, M. Kafesaki
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers
 Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
Electromagnetic Wave Guidance Mechanisms in Photonic Crystal Fibers Tushar Biswas 1, Shyamal K. Bhadra 1 1 Fiber optics and Photonics Division, CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute *196, Raja
A PROPOSAL FOR ANTI-UVB FILTER BASED ON ONE-DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 7, No. 1, January - March 2012, p. 367-371 A PROPOSAL FOR ANTI-UVB FILTER BASED ON ONE-DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL STRUCTURE HAMED ALIPOUR-BANAEI
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 7, No. 1, January - March 2012, p. 367-371 A PROPOSAL FOR ANTI-UVB FILTER BASED ON ONE-DIMENSIONAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL STRUCTURE HAMED ALIPOUR-BANAEI
Dynamic group velocity control in a mechanically tunable photonic-crystal coupled-resonator optical waveguide
 Dynamic group velocity control in a mechanically tunable photonic-crystal coupled-resonator optical waveguide The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Dynamic group velocity control in a mechanically tunable photonic-crystal coupled-resonator optical waveguide The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Large Frequency Range of Photonic Band Gaps on Porous Silicon Heterostructures for Infrared Applications
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 7, 327-335 Large Frequency Range of Photonic Band Gaps on Porous Silicon Heterostructures for Infrared Applications J. Manzanares-Martinez, P. Castro-Garay
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 5, 2011, no. 7, 327-335 Large Frequency Range of Photonic Band Gaps on Porous Silicon Heterostructures for Infrared Applications J. Manzanares-Martinez, P. Castro-Garay
Photonic Crystals. (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207
 Photonic Crystals (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207 [Based on material made generous made available by S G Johnson, MIT, at http://ab-initio.mit.edu/photons/
Photonic Crystals (or how to slow, trap, bend, split, and do other funky things to light) Uday Khankhoje, EEL207 [Based on material made generous made available by S G Johnson, MIT, at http://ab-initio.mit.edu/photons/
