Convergence in Topological Spaces. Nets.
|
|
|
- Emory Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Convergence in Topological Spaces. Nets. Stefano Ferri Abstract Sequences are not always sufficient to describe convergence in topological spaces. In what follows we shall introduce a generalisation to sequence which can satisfactorly describe convergence in any topological space. 1 Preliminaries. It is well-known that many topological properties of metric spaces can be described using sequences (see [Ru, Chapters 3-4]). For istance: Theorem A subset A of a metric space X is open if and only if all sequences x n in X which converge to a point x A are eventually in A. 2. A subset A of a metric space X is closed if and only if, for all sequences x n in A, if lim n x n = x, then x A. 3. If A is a subset of a metric space, then x A if and only if there exists a sequence x n in A which converges to x. 4. A function f : X Y between metric spaces is continuous if and only if, whenever x n is a sequence which converges to x in X, then f(x n ) converges to f(x) in Y. As we shall see, in general topological spaces the above statements are no longer true unless certain conditions are satisfied. We start by extending the definition of convergence (of sequences) to general topological spaces. Definition 1.2. A sequence in a topological space X is a function f : N X. It is common practice to denote a sequence by x n meaning that, for n N, f(n) = x n. Definition 1.3. A sequence x n in a topological space X converges to L X if, for all (basic) neighbourhood U of L, there exists n U N such that, whenever m > n U, we have x m U. Remebering proof of Theorem 1.1 it should be clear that when we can find countably many arbitrarly small neighbourhoods around all points of X, we can still replicate this proof it a topological space. In order to do so we start with a definition which formalises the concept or arbitrarly small neighbourhood to topological spaces. Definition 1.4. A topological space X is first countable if every point has a countable neighbourhood base. 1
2 2 Nets For first countable spaces the four statements of Theorem 1.1 are true. The proofs are very similar to those given for metric spaces. Here we prove only one of the propositions (the other three are left as exercises) in order to illustrate which kind of changes are needed. Theorem 1.5. Let X be a first countable space and A X. Then, x A if and only if there exists a sequence x n in A converging to x. Proof. Let x A and let {U n : n N} be a countable base of neighbourhoods of x. i Let V i := U k. It is not difficult to see that {V n : n N} is also a countable base of k=1 neighbourhoods of x and that: U 1 U 2 U 3... Since x A, for all i ω, V i A. So, for all i N, we can pick x i V i A. The sequence x n obtained this way clearly converges to x. Conversely, if x n converges to x, then, every neighbourhood U of x contains infinitely many points of this sequence. Hence U it has not empty intersection with A, i.e. x A. Thepreviousproof relies on the fact that all points of X have a countable neighbourhood base. If this is not thecase it may happen 1 that sequences arenolonger sufficient to describe the topology of the space. The following examples (which is left as an exercise) illustrate this. Example 1.6. Let X = R R with the product topology. Let us define a subset E of R R as follows: E = {f R R : f(x) = 0 or f(x) = 1 and f(x) = 0 only for finitely many x R}. Let g be the function in R R which is identically 0 and U(g) a basic neighbourhood of g, U(g) = {h R R : h(y) g(y) < ε if y F}, where F is some finite subset of R. The set U(g) E is not empty, since it contains the function which is 0 on E and 1 elsewhere, then g E. However, no sequence in E converges to g. 2 Nets In this section we shall introduce the concept of net and show that this is a valid sobstitute to sequences to describe convergence in topological spaces. Definition 2.1. Let I be a set partially ordered by. We say that I is directed by if, for every, α,β I, there exists γ I such that α γ and β γ. Definition 2.2. A net in a topological space X is a function f from a directed set I to X. Usually, a net is denoted by x α meaning that f(α) = x α. 1 One may think that being first countable is a necessary and sufficient condition in order for sequences to be enough to describe the topology. However, this is not true. Many mathematicians have studied the problem of characterising the topological spaces for which sequences sufficies in order to describe their topology and obtained a somhow wider class than that of first countable spaces.
3 Stefano Ferri 3 Definition 2.3. A net x α in a topological space X, is said to be frequently in a subset A of X if, for all α 0 I, there exists some α α 0 such that x α A. The same net is said to be eventually in A if there exists some α 0 I such that, for all α α 0, x α A. Definition 2.4. A net x α, in a topological space X is said to have a point x of X as a cluster point if the net is frequently in every neighbourhood of x. If the net is eventually in every neighbourhood of x, then it is said to converge to x and x is said to be a limit of the net. In this case we write x limx α. Sometimes, if there is no danger of confusion we simply write x limx α or also x α x. When the limit is unique we write x = limx α α instead of {x} = limx α. Nets are a usefull tool to describe convergence in metric spaces, however to formulate the concept of subnet is rather cumbersome. Definition 2.5. Let I and J bedirected sets. A function f : J I is said to beincreasing and cofinal if: 1. For all α,β J such that α β, f(α) f(β), and; 2. For all δ I, there exists α J such that f(α) δ. Definition 2.6. Let x α be a net in X indexed by I and let f : I X be the function such that f(α) = x α. If g : J I is an increasing cofinal function between the directed sets J and I, then the composition f g : J X is called a subnet of x α. Theorem 2.7. Let x α be a net in a topological space X, and x αβ a subnet of x α (by this notation we mean that the increasing cofinal function which defines the subnet maps β into α β ). Then the following statements hold: 1. If x is a cluster point of x αβ, then it is also a cluster point of x α ; 2. If x is a limit of x α then it is a limit of x αβ ; 3. If x is a cluster point of x α then there exists a subnet x αγ of x α, which admits x as a limit. Proof. 1. Let U be a neighbourhood of x and α 0 I. Since x αβ is a subnet of x α there is β 0 J such that α β0 α 0. Since x is a cluster point of x αβ, there exists β J such that α β α β0 and x αβ U. This means that x is a cluster point of x α. 2. If x is a limit of x α, then, for all neighbourhood U of x, x α is eventually in U. In particular, x αβ is eventually in U. 3. Let x be a cluster point of x α. Consider K = {(β,u) : β I and U is a neighbourhood of x, x β U}. We define a partial order on K as follows: (β 1,U 1 ) (β 2,U 2 ) if β 1 β 2 and U 1 U 2. It is not difficult to check that K is directed by. We define an increasing cofinal map between K and I by (β,u) β and a subnet of x α by x α(α,u) = x α. For all neighbourhood U of x, there exists some β 0 in I such that x β0 U, so for all (β 0,U 0 ) (β,u), x β(β,u) U U 0, i.e. x limx α(α,u), as requested.
4 4 Nets Theorem 2.8. Let A be a subset of a topological space X. A point x of X belongs to A, if and only if there exists a net in A converging to x. Proof. Let S = x α be a net in A converging to x. Then any neighbourhood of x contains points of A, so x is in A. Conversely, let x A and let N x be the set of the neighbourhoods of x. The set N x is directed by the order given by: U V if U V. We construct a net of points of A by choosing for every U N x a point x U U A. It is easy to check that the net x U U Nx, constructed in this way, has x as a limit. The proofs of the following theorems are left as exercises. Theorem 2.9. Let X and Y be topological spaces. A map f : X Y is continuous if and only if, for all net x α in X: f(lim x α ) lim f(x α ). Theorem A topological space X is Hausdorff if and only if every net in X has at most one limit. Nets correspond, for topological spaces, to sequences and, of course, sequences are a particular example of nets in which the directed index set is N. However, when we pass from the definition of subsequence to the definition of subnet we have some differences. For istance, given a sequence there may be subnets which are not subsequences. For this reason, in spite of the fact that by using nets it is possible to extend the concept of convergence to any topological spaces, when dealing with nets we have to be be very careful. Example Consider the sequence ( 1) n n N in the space R with its standard topology. Clearly, this sequence has 1 and 1 as cluster points. We use the construction given in theorem 2.7 to construct a finer net converging to 1. We take as index set: K = {(n,u) : n N and U is a neighbourhood of 1 andx n U} = = {(n,u) : n even and U is a neighbourhood of 1}, directed by the order: (n,u) (m,v) if n m and U V, and construct a net by defining, for (n,u) in K, x (n,u) = ( 1) n = 1. This is a subnet of the net we began with and it converges to 1, but, since Σ > ω, this is not a subsequence. Of course ( 1) 2m m N is a subsequence converging to 1. We conclude this short note with a theorem concerning convergence in product spaces. (This theorem will allow for a fast proof of Tychonoff Theorem.) Theorem A net x α in a product γ IX γ converges to x in the product topology if and only if, for all α I, the net π α (x γ ) converges to π α (x) in X α.
5 Stefano Ferri 5 Proof. If x γ x in γ IX γ, then, since π α is continuous, π α (x γ ) π α (x). In order to show the converse, suppose that, for all α I, π α (x γ ) π α (x) and let π 1 α 1 (U α1 ) π 1 α 2 (U α2 ) π 1 α n (U αn ) be a basic neighbourhood of x. Then, for all i {1,2,...,n}, there exists γ i such that, when γ γ i, then π αi (x γ ) U αi. Hence, if γ 0 is greater than all the γ i s (such a γ exists because the index set of the net is directed) we have that, whenever γ γ 0, for all α I, π αi (x γ ) U αi. This means that, when γ γ 0, x γ π 1 α i (U αi ), i.e. x γ x. References [Ru] Rudin W., Principles of Mathematical Analysis (third edition), Mc Graw Hill, Inc., New York, 1975.
s P = f(ξ n )(x i x i 1 ). i=1
 Compactness and total boundedness via nets The aim of this chapter is to define the notion of a net (generalized sequence) and to characterize compactness and total boundedness by this important topological
Compactness and total boundedness via nets The aim of this chapter is to define the notion of a net (generalized sequence) and to characterize compactness and total boundedness by this important topological
Contents. Index... 15
 Contents Filter Bases and Nets................................................................................ 5 Filter Bases and Ultrafilters: A Brief Overview.........................................................
Contents Filter Bases and Nets................................................................................ 5 Filter Bases and Ultrafilters: A Brief Overview.........................................................
CHAPTER II THE HAHN-BANACH EXTENSION THEOREMS AND EXISTENCE OF LINEAR FUNCTIONALS
 CHAPTER II THE HAHN-BANACH EXTENSION THEOREMS AND EXISTENCE OF LINEAR FUNCTIONALS In this chapter we deal with the problem of extending a linear functional on a subspace Y to a linear functional on the
CHAPTER II THE HAHN-BANACH EXTENSION THEOREMS AND EXISTENCE OF LINEAR FUNCTIONALS In this chapter we deal with the problem of extending a linear functional on a subspace Y to a linear functional on the
2. The Concept of Convergence: Ultrafilters and Nets
 2. The Concept of Convergence: Ultrafilters and Nets NOTE: AS OF 2008, SOME OF THIS STUFF IS A BIT OUT- DATED AND HAS A FEW TYPOS. I WILL REVISE THIS MATE- RIAL SOMETIME. In this lecture we discuss two
2. The Concept of Convergence: Ultrafilters and Nets NOTE: AS OF 2008, SOME OF THIS STUFF IS A BIT OUT- DATED AND HAS A FEW TYPOS. I WILL REVISE THIS MATE- RIAL SOMETIME. In this lecture we discuss two
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS
 3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
Course 212: Academic Year Section 1: Metric Spaces
 Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued)
 21. The Metric Topology (cont.) 1 Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued) Note. In this section we give a number of results for metric spaces which are familar from calculus and real analysis. We also
21. The Metric Topology (cont.) 1 Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued) Note. In this section we give a number of results for metric spaces which are familar from calculus and real analysis. We also
Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping.
 Minimization Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping. 1 Minimization A Topological Result. Let S be a topological
Minimization Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping. 1 Minimization A Topological Result. Let S be a topological
Notes on nets and convergence in topology
 Topology I Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin C. Wendl / F. Schmäschke Summer Semester 2017 Notes on nets and convergence in topology Nets generalize the notion of sequences so that certain familiar results
Topology I Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin C. Wendl / F. Schmäschke Summer Semester 2017 Notes on nets and convergence in topology Nets generalize the notion of sequences so that certain familiar results
Filters in Analysis and Topology
 Filters in Analysis and Topology David MacIver July 1, 2004 Abstract The study of filters is a very natural way to talk about convergence in an arbitrary topological space, and carries over nicely into
Filters in Analysis and Topology David MacIver July 1, 2004 Abstract The study of filters is a very natural way to talk about convergence in an arbitrary topological space, and carries over nicely into
Math General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 8 Solutions
 Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 8 Solutions Problem 1. (Willard Exercise 19B.1) Show that the one-point compactification of R n is homeomorphic to the n-dimensional sphere S n. Note that
Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 8 Solutions Problem 1. (Willard Exercise 19B.1) Show that the one-point compactification of R n is homeomorphic to the n-dimensional sphere S n. Note that
2.31 Definition By an open cover of a set E in a metric space X we mean a collection {G α } of open subsets of X such that E α G α.
 Chapter 2. Basic Topology. 2.3 Compact Sets. 2.31 Definition By an open cover of a set E in a metric space X we mean a collection {G α } of open subsets of X such that E α G α. 2.32 Definition A subset
Chapter 2. Basic Topology. 2.3 Compact Sets. 2.31 Definition By an open cover of a set E in a metric space X we mean a collection {G α } of open subsets of X such that E α G α. 2.32 Definition A subset
1 Topology Definition of a topology Basis (Base) of a topology The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3
 Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
2. Metric Spaces. 2.1 Definitions etc.
 2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
Economics 204 Fall 2011 Problem Set 1 Suggested Solutions
 Economics 204 Fall 2011 Problem Set 1 Suggested Solutions 1. Suppose k is a positive integer. Use induction to prove the following two statements. (a) For all n N 0, the inequality (k 2 + n)! k 2n holds.
Economics 204 Fall 2011 Problem Set 1 Suggested Solutions 1. Suppose k is a positive integer. Use induction to prove the following two statements. (a) For all n N 0, the inequality (k 2 + n)! k 2n holds.
Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators
 Chapter 2 Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators 2.1 Topological vector spaces and locally convex spaces Definition 2.1.1. [Topological Vector Spaces and Locally convex Spaces] Let E be a vector
Chapter 2 Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators 2.1 Topological vector spaces and locally convex spaces Definition 2.1.1. [Topological Vector Spaces and Locally convex Spaces] Let E be a vector
Section 2: Classes of Sets
 Section 2: Classes of Sets Notation: If A, B are subsets of X, then A \ B denotes the set difference, A \ B = {x A : x B}. A B denotes the symmetric difference. A B = (A \ B) (B \ A) = (A B) \ (A B). Remarks
Section 2: Classes of Sets Notation: If A, B are subsets of X, then A \ B denotes the set difference, A \ B = {x A : x B}. A B denotes the symmetric difference. A B = (A \ B) (B \ A) = (A B) \ (A B). Remarks
Characterisation of Accumulation Points. Convergence in Metric Spaces. Characterisation of Closed Sets. Characterisation of Closed Sets
 Convergence in Metric Spaces Functional Analysis Lecture 3: Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces Bengt Ove Turesson September 4, 2016 Suppose that (X, d) is a metric space. A sequence (x n ) X is
Convergence in Metric Spaces Functional Analysis Lecture 3: Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces Bengt Ove Turesson September 4, 2016 Suppose that (X, d) is a metric space. A sequence (x n ) X is
This chapter contains a very bare summary of some basic facts from topology.
 Chapter 2 Topological Spaces This chapter contains a very bare summary of some basic facts from topology. 2.1 Definition of Topology A topology O on a set X is a collection of subsets of X satisfying the
Chapter 2 Topological Spaces This chapter contains a very bare summary of some basic facts from topology. 2.1 Definition of Topology A topology O on a set X is a collection of subsets of X satisfying the
Math General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 1 Solutions
 Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 1 Solutions Definition. Let V be a (real or complex) vector space. A norm on V is a function : V R satisfying: 1. Positivity: x 0 for all x V and moreover
Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 1 Solutions Definition. Let V be a (real or complex) vector space. A norm on V is a function : V R satisfying: 1. Positivity: x 0 for all x V and moreover
Topology. Xiaolong Han. Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA address:
 Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
MH 7500 THEOREMS. (iii) A = A; (iv) A B = A B. Theorem 5. If {A α : α Λ} is any collection of subsets of a space X, then
 MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies
 BS V c Gabriel Nagy Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) In this section we discuss two important, but highly non-trivial,
BS V c Gabriel Nagy Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) In this section we discuss two important, but highly non-trivial,
SOME MEASURABILITY AND CONTINUITY PROPERTIES OF ARBITRARY REAL FUNCTIONS
 LE MATEMATICHE Vol. LVII (2002) Fasc. I, pp. 6382 SOME MEASURABILITY AND CONTINUITY PROPERTIES OF ARBITRARY REAL FUNCTIONS VITTORINO PATA - ALFONSO VILLANI Given an arbitrary real function f, the set D
LE MATEMATICHE Vol. LVII (2002) Fasc. I, pp. 6382 SOME MEASURABILITY AND CONTINUITY PROPERTIES OF ARBITRARY REAL FUNCTIONS VITTORINO PATA - ALFONSO VILLANI Given an arbitrary real function f, the set D
Introduction to Dynamical Systems
 Introduction to Dynamical Systems France-Kosovo Undergraduate Research School of Mathematics March 2017 This introduction to dynamical systems was a course given at the march 2017 edition of the France
Introduction to Dynamical Systems France-Kosovo Undergraduate Research School of Mathematics March 2017 This introduction to dynamical systems was a course given at the march 2017 edition of the France
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP Basic Topology
 ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
i=1 β i,i.e. = β 1 x β x β 1 1 xβ d
 66 2. Every family of seminorms on a vector space containing a norm induces ahausdorff locally convex topology. 3. Given an open subset Ω of R d with the euclidean topology, the space C(Ω) of real valued
66 2. Every family of seminorms on a vector space containing a norm induces ahausdorff locally convex topology. 3. Given an open subset Ω of R d with the euclidean topology, the space C(Ω) of real valued
Topologies, ring norms and algebra norms on some algebras of continuous functions.
 Topologies, ring norms and algebra norms on some algebras of continuous functions. Javier Gómez-Pérez Javier Gómez-Pérez, Departamento de Matemáticas, Universidad de León, 24071 León, Spain. Corresponding
Topologies, ring norms and algebra norms on some algebras of continuous functions. Javier Gómez-Pérez Javier Gómez-Pérez, Departamento de Matemáticas, Universidad de León, 24071 León, Spain. Corresponding
COUNTABLE PRODUCTS ELENA GUREVICH
 COUNTABLE PRODUCTS ELENA GUREVICH Abstract. In this paper, we extend our study to countably infinite products of topological spaces.. The Cantor Set Let us constract a very curios (but usefull) set known
COUNTABLE PRODUCTS ELENA GUREVICH Abstract. In this paper, we extend our study to countably infinite products of topological spaces.. The Cantor Set Let us constract a very curios (but usefull) set known
Changes to the third printing May 18, 2013 Measure, Topology, and Fractal Geometry
 Changes to the third printing May 18, 2013 Measure, Topology, and Fractal Geometry by Gerald A. Edgar Page 34 Line 9. After summer program. add Exercise 1.6.3 and 1.6.4 are stated as either/or. It is possible
Changes to the third printing May 18, 2013 Measure, Topology, and Fractal Geometry by Gerald A. Edgar Page 34 Line 9. After summer program. add Exercise 1.6.3 and 1.6.4 are stated as either/or. It is possible
Notes on the Point-Set Topology of R Northwestern University, Fall 2014
 Notes on the Point-Set Topology of R Northwestern University, Fall 2014 These notes give an introduction to the notions of open and closed subsets of R, which belong to the subject known as point-set topology.
Notes on the Point-Set Topology of R Northwestern University, Fall 2014 These notes give an introduction to the notions of open and closed subsets of R, which belong to the subject known as point-set topology.
Real Analysis Chapter 4 Solutions Jonathan Conder
 2. Let x, y X and suppose that x y. Then {x} c is open in the cofinite topology and contains y but not x. The cofinite topology on X is therefore T 1. Since X is infinite it contains two distinct points
2. Let x, y X and suppose that x y. Then {x} c is open in the cofinite topology and contains y but not x. The cofinite topology on X is therefore T 1. Since X is infinite it contains two distinct points
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces
 7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
MAT3500/ Mandatory assignment 2013 Solutions
 MAT3500/4500 - Mandatory assignment 2013 s Problem 1 Let X be a topological space, A and B be subsets of X. Recall the definition of the boundary Bd A of a set A. Prove that Bd (A B) (Bd A) (Bd B). Discuss
MAT3500/4500 - Mandatory assignment 2013 s Problem 1 Let X be a topological space, A and B be subsets of X. Recall the definition of the boundary Bd A of a set A. Prove that Bd (A B) (Bd A) (Bd B). Discuss
LINDELÖF sn-networks
 Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 43, No. 2, 2013, 201-209 SPACES WITH σ-locally COUNTABLE LINDELÖF sn-networks Luong Quoc Tuyen 1 Abstract. In this paper, we prove that a space X has a σ-locally countable Lindelöf
Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 43, No. 2, 2013, 201-209 SPACES WITH σ-locally COUNTABLE LINDELÖF sn-networks Luong Quoc Tuyen 1 Abstract. In this paper, we prove that a space X has a σ-locally countable Lindelöf
A Note on Generalized Topology
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 6, 2011, no. 1, 19-24 A Note on Generalized Topology Gh. Abbaspour Tabadkan and A. Taghavi Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Sciences Damghan University, Damghan,
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 6, 2011, no. 1, 19-24 A Note on Generalized Topology Gh. Abbaspour Tabadkan and A. Taghavi Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Sciences Damghan University, Damghan,
Axioms of separation
 Axioms of separation These notes discuss the same topic as Sections 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, and also 7, 10 of Munkres book. Some notions (hereditarily normal, perfectly normal, collectionwise normal, monotonically
Axioms of separation These notes discuss the same topic as Sections 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, and also 7, 10 of Munkres book. Some notions (hereditarily normal, perfectly normal, collectionwise normal, monotonically
Extension of continuous functions in digital spaces with the Khalimsky topology
 Extension of continuous functions in digital spaces with the Khalimsky topology Erik Melin Uppsala University, Department of Mathematics Box 480, SE-751 06 Uppsala, Sweden melin@math.uu.se http://www.math.uu.se/~melin
Extension of continuous functions in digital spaces with the Khalimsky topology Erik Melin Uppsala University, Department of Mathematics Box 480, SE-751 06 Uppsala, Sweden melin@math.uu.se http://www.math.uu.se/~melin
4 Countability axioms
 4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
From now on, we will represent a metric space with (X, d). Here are some examples: i=1 (x i y i ) p ) 1 p, p 1.
 Chapter 1 Metric spaces 1.1 Metric and convergence We will begin with some basic concepts. Definition 1.1. (Metric space) Metric space is a set X, with a metric satisfying: 1. d(x, y) 0, d(x, y) = 0 x
Chapter 1 Metric spaces 1.1 Metric and convergence We will begin with some basic concepts. Definition 1.1. (Metric space) Metric space is a set X, with a metric satisfying: 1. d(x, y) 0, d(x, y) = 0 x
Problem Set 2: Solutions Math 201A: Fall 2016
 Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
ABSTRACT INTEGRATION CHAPTER ONE
 CHAPTER ONE ABSTRACT INTEGRATION Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means. Suggestions and errors are invited and can be mailed
CHAPTER ONE ABSTRACT INTEGRATION Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means. Suggestions and errors are invited and can be mailed
Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9)
 The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9) MATH3961: Metric Spaces (Advanced) Semester 1, 2018 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/sm/math3961/
The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9) MATH3961: Metric Spaces (Advanced) Semester 1, 2018 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/sm/math3961/
MAT 530: Topology&Geometry, I Fall 2005
 MAT 530: Topology&Geometry, I Fall 2005 Midterm Solutions Note: These solutions are more detailed than solutions sufficient for full credit. Let X denote the set {a, b, c}. The collections Problem 1 5+5
MAT 530: Topology&Geometry, I Fall 2005 Midterm Solutions Note: These solutions are more detailed than solutions sufficient for full credit. Let X denote the set {a, b, c}. The collections Problem 1 5+5
Handout 2 (Correction of Handout 1 plus continued discussion/hw) Comments and Homework in Chapter 1
 22M:132 Fall 07 J. Simon Handout 2 (Correction of Handout 1 plus continued discussion/hw) Comments and Homework in Chapter 1 Chapter 1 contains material on sets, functions, relations, and cardinality that
22M:132 Fall 07 J. Simon Handout 2 (Correction of Handout 1 plus continued discussion/hw) Comments and Homework in Chapter 1 Chapter 1 contains material on sets, functions, relations, and cardinality that
Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9;
 Math 553 - Topology Todd Riggs Assignment 2 Sept 17, 2014 Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9; 17.2) Show that if A is closed in Y and
Math 553 - Topology Todd Riggs Assignment 2 Sept 17, 2014 Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9; 17.2) Show that if A is closed in Y and
The Lebesgue Integral
 The Lebesgue Integral Brent Nelson In these notes we give an introduction to the Lebesgue integral, assuming only a knowledge of metric spaces and the iemann integral. For more details see [1, Chapters
The Lebesgue Integral Brent Nelson In these notes we give an introduction to the Lebesgue integral, assuming only a knowledge of metric spaces and the iemann integral. For more details see [1, Chapters
A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE. Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim. 1. Introduction
 Comm. Korean Math. Soc. 16 (2001), No. 2, pp. 277 285 A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim Abstract. The purpose of this paper
Comm. Korean Math. Soc. 16 (2001), No. 2, pp. 277 285 A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim Abstract. The purpose of this paper
Mathematics for Economists
 Mathematics for Economists Victor Filipe Sao Paulo School of Economics FGV Metric Spaces: Basic Definitions Victor Filipe (EESP/FGV) Mathematics for Economists Jan.-Feb. 2017 1 / 34 Definitions and Examples
Mathematics for Economists Victor Filipe Sao Paulo School of Economics FGV Metric Spaces: Basic Definitions Victor Filipe (EESP/FGV) Mathematics for Economists Jan.-Feb. 2017 1 / 34 Definitions and Examples
MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2.
 MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2. This text is based on the following books: Topology by James Dugundgji Fundamental concepts of topology by Peter O Neil Elements of Mathematics: General Topology
MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2. This text is based on the following books: Topology by James Dugundgji Fundamental concepts of topology by Peter O Neil Elements of Mathematics: General Topology
3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces
 3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces In this chapter we address the question of when two spaces are homeomorphic. This is done by examining two properties that are shared by any pair of homeomorphic spaces.
3 Hausdorff and Connected Spaces In this chapter we address the question of when two spaces are homeomorphic. This is done by examining two properties that are shared by any pair of homeomorphic spaces.
(U) =, if 0 U, 1 U, (U) = X, if 0 U, and 1 U. (U) = E, if 0 U, but 1 U. (U) = X \ E if 0 U, but 1 U. n=1 A n, then A M.
 1. Abstract Integration The main reference for this section is Rudin s Real and Complex Analysis. The purpose of developing an abstract theory of integration is to emphasize the difference between the
1. Abstract Integration The main reference for this section is Rudin s Real and Complex Analysis. The purpose of developing an abstract theory of integration is to emphasize the difference between the
Math 190: Fall 2014 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday 11/7/2014
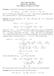 Math 90: Fall 04 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday /7/04 Problem : Recall that S n denotes the n-dimensional unit sphere: S n = {(x 0, x,..., x n ) R n+ : x 0 + x + + x n = }. Let N S n denote
Math 90: Fall 04 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday /7/04 Problem : Recall that S n denotes the n-dimensional unit sphere: S n = {(x 0, x,..., x n ) R n+ : x 0 + x + + x n = }. Let N S n denote
E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem
 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem 359 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem If X is a normed space, then the closed unit ball in X or X is compact if and only if X is finite-dimensional (Problem A.25). Even so, Alaoglu s Theorem
E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem 359 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem If X is a normed space, then the closed unit ball in X or X is compact if and only if X is finite-dimensional (Problem A.25). Even so, Alaoglu s Theorem
Banach-Alaoglu, boundedness, weak-to-strong principles Paul Garrett 1. Banach-Alaoglu theorem
 (April 12, 2004) Banach-Alaoglu, boundedness, weak-to-strong principles Paul Garrett Banach-Alaoglu theorem: compactness of polars A variant Banach-Steinhaus theorem Bipolars Weak
(April 12, 2004) Banach-Alaoglu, boundedness, weak-to-strong principles Paul Garrett Banach-Alaoglu theorem: compactness of polars A variant Banach-Steinhaus theorem Bipolars Weak
Aperiodic Substitution Tilings
 Aperiodic Substitution Tilings Charles Starling January 4, 2011 Charles Starling () Aperiodic Substitution Tilings January 4, 2011 1 / 27 Overview We study tilings of R 2 which are aperiodic, but not completely
Aperiodic Substitution Tilings Charles Starling January 4, 2011 Charles Starling () Aperiodic Substitution Tilings January 4, 2011 1 / 27 Overview We study tilings of R 2 which are aperiodic, but not completely
ADDENDUM B: CONSTRUCTION OF R AND THE COMPLETION OF A METRIC SPACE
 ADDENDUM B: CONSTRUCTION OF R AND THE COMPLETION OF A METRIC SPACE ANDREAS LEOPOLD KNUTSEN Abstract. These notes are written as supplementary notes for the course MAT11- Real Analysis, taught at the University
ADDENDUM B: CONSTRUCTION OF R AND THE COMPLETION OF A METRIC SPACE ANDREAS LEOPOLD KNUTSEN Abstract. These notes are written as supplementary notes for the course MAT11- Real Analysis, taught at the University
CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000
 CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000 Announcement: Section 1.2, Questions 3,5 have been deferred from Assignment 1 to Assignment 2. Section 1.4, Question 5 has been dropped entirely. 1. Review of Wednesday class
CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000 Announcement: Section 1.2, Questions 3,5 have been deferred from Assignment 1 to Assignment 2. Section 1.4, Question 5 has been dropped entirely. 1. Review of Wednesday class
Topological Vector Spaces III: Finite Dimensional Spaces
 TVS III c Gabriel Nagy Topological Vector Spaces III: Finite Dimensional Spaces Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) Convention. Throughout this note K will be one of the fields
TVS III c Gabriel Nagy Topological Vector Spaces III: Finite Dimensional Spaces Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) Convention. Throughout this note K will be one of the fields
The discrete and indiscrete topologies on any set are zero-dimensional. The Sorgenfrey line
 p. 1 Math 525 Notes on section 17 Isolated points In general, a point x in a topological space (X,τ) is called an isolated point iff the set {x} is τ-open. A topological space is called discrete iff every
p. 1 Math 525 Notes on section 17 Isolated points In general, a point x in a topological space (X,τ) is called an isolated point iff the set {x} is τ-open. A topological space is called discrete iff every
Maths 212: Homework Solutions
 Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009.
 Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
Math 6120 Fall 2012 Assignment #1
 Math 6120 Fall 2012 Assignment #1 Choose 10 of the problems below to submit by Weds., Sep. 5. Exercise 1. [Mun, 21, #10]. Show that the following are closed subsets of R 2 : (a) A = { (x, y) xy = 1 },
Math 6120 Fall 2012 Assignment #1 Choose 10 of the problems below to submit by Weds., Sep. 5. Exercise 1. [Mun, 21, #10]. Show that the following are closed subsets of R 2 : (a) A = { (x, y) xy = 1 },
VARIETIES OF ABELIAN TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS AND SCATTERED SPACES
 Bull. Austral. Math. Soc. 78 (2008), 487 495 doi:10.1017/s0004972708000877 VARIETIES OF ABELIAN TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS AND SCATTERED SPACES CAROLYN E. MCPHAIL and SIDNEY A. MORRIS (Received 3 March 2008) Abstract
Bull. Austral. Math. Soc. 78 (2008), 487 495 doi:10.1017/s0004972708000877 VARIETIES OF ABELIAN TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS AND SCATTERED SPACES CAROLYN E. MCPHAIL and SIDNEY A. MORRIS (Received 3 March 2008) Abstract
REAL AND COMPLEX ANALYSIS
 REAL AND COMPLE ANALYSIS Third Edition Walter Rudin Professor of Mathematics University of Wisconsin, Madison Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any
REAL AND COMPLE ANALYSIS Third Edition Walter Rudin Professor of Mathematics University of Wisconsin, Madison Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any
CHAPTER 1. Preliminaries. 1 Set Theory
 CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries 1 et Theory We assume that the reader is familiar with basic set theory. In this paragraph, we want to recall the relevant definitions and fix the notation. Our approach to set
CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries 1 et Theory We assume that the reader is familiar with basic set theory. In this paragraph, we want to recall the relevant definitions and fix the notation. Our approach to set
MA677 Assignment #3 Morgan Schreffler Due 09/19/12 Exercise 1 Using Hölder s inequality, prove Minkowski s inequality for f, g L p (R d ), p 1:
 Exercise 1 Using Hölder s inequality, prove Minkowski s inequality for f, g L p (R d ), p 1: f + g p f p + g p. Proof. If f, g L p (R d ), then since f(x) + g(x) max {f(x), g(x)}, we have f(x) + g(x) p
Exercise 1 Using Hölder s inequality, prove Minkowski s inequality for f, g L p (R d ), p 1: f + g p f p + g p. Proof. If f, g L p (R d ), then since f(x) + g(x) max {f(x), g(x)}, we have f(x) + g(x) p
Preliminary check: are the terms that we are adding up go to zero or not? If not, proceed! If the terms a n are going to zero, pick another test.
 Throughout these templates, let series. be a series. We hope to determine the convergence of this Divergence Test: If lim is not zero or does not exist, then the series diverges. Preliminary check: are
Throughout these templates, let series. be a series. We hope to determine the convergence of this Divergence Test: If lim is not zero or does not exist, then the series diverges. Preliminary check: are
B. Appendix B. Topological vector spaces
 B.1 B. Appendix B. Topological vector spaces B.1. Fréchet spaces. In this appendix we go through the definition of Fréchet spaces and their inductive limits, such as they are used for definitions of function
B.1 B. Appendix B. Topological vector spaces B.1. Fréchet spaces. In this appendix we go through the definition of Fréchet spaces and their inductive limits, such as they are used for definitions of function
Math 201 Topology I. Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran
 Math 201 Topology I Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran hicham.gebran@yahoo.com Lebanese University, Fanar, Fall 2015-2016 http://fs2.ul.edu.lb/math http://hichamgebran.wordpress.com 2 Introduction and
Math 201 Topology I Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran hicham.gebran@yahoo.com Lebanese University, Fanar, Fall 2015-2016 http://fs2.ul.edu.lb/math http://hichamgebran.wordpress.com 2 Introduction and
LIMIT OF APPROXIMATE INVERSE SYSTEM OF TOTALLY REGULAR CONTINUA IS TOTALLY REGULAR. 1. Introduction
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXXIV, 1(2005), pp. 1 13 1 LIMIT OF APPROXIMATE INVERSE SYSTEM OF TOTALLY REGULAR CONTINUA IS TOTALLY REGULAR I. LONČAR Abstract. It is known that the limit of an inverse
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXXIV, 1(2005), pp. 1 13 1 LIMIT OF APPROXIMATE INVERSE SYSTEM OF TOTALLY REGULAR CONTINUA IS TOTALLY REGULAR I. LONČAR Abstract. It is known that the limit of an inverse
Metric Spaces Lecture 17
 Metric Spaces Lecture 17 Homeomorphisms At the end of last lecture an example was given of a bijective continuous function f such that f 1 is not continuous. For another example, consider the sets T =
Metric Spaces Lecture 17 Homeomorphisms At the end of last lecture an example was given of a bijective continuous function f such that f 1 is not continuous. For another example, consider the sets T =
Part III. 10 Topological Space Basics. Topological Spaces
 Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
König s Lemma and Kleene Tree
 König s Lemma and Kleene Tree Andrej Bauer May 3, 2006 Abstract I present a basic result about Cantor space in the context of computability theory: the computable Cantor space is computably non-compact.
König s Lemma and Kleene Tree Andrej Bauer May 3, 2006 Abstract I present a basic result about Cantor space in the context of computability theory: the computable Cantor space is computably non-compact.
Sequence convergence, the weak T-axioms, and first countability
 Sequence convergence, the weak T-axioms, and first countability 1 Motivation Up to now we have been mentioning the notion of sequence convergence without actually defining it. So in this section we will
Sequence convergence, the weak T-axioms, and first countability 1 Motivation Up to now we have been mentioning the notion of sequence convergence without actually defining it. So in this section we will
CHARACTERIZING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS ON COMPACT SPACES
 CHARACTERIZING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS ON COMPACT SPACES C. Good 1 School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK c.good@bham.ac.uk S. Greenwood 2 Department of Mathematics,
CHARACTERIZING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS ON COMPACT SPACES C. Good 1 School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK c.good@bham.ac.uk S. Greenwood 2 Department of Mathematics,
Some Background Material
 Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 7. Metric Spaces December 5, Metric spaces
 Chapter 7 Metric Spaces December 5, 2011 7.1 Metric spaces Note: 1.5 lectures As mentioned in the introduction, the main idea in analysis is to take limits. In chapter 2 we learned to take limits of sequences
Chapter 7 Metric Spaces December 5, 2011 7.1 Metric spaces Note: 1.5 lectures As mentioned in the introduction, the main idea in analysis is to take limits. In chapter 2 we learned to take limits of sequences
THE STONE-WEIERSTRASS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO L 2 SPACES
 THE STONE-WEIERSTRASS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO L 2 SPACES PHILIP GADDY Abstract. Throughout the course of this paper, we will first prove the Stone- Weierstrass Theroem, after providing some initial
THE STONE-WEIERSTRASS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO L 2 SPACES PHILIP GADDY Abstract. Throughout the course of this paper, we will first prove the Stone- Weierstrass Theroem, after providing some initial
A SECOND COURSE IN GENERAL TOPOLOGY
 Heikki Junnila, 2007-8/2014 A SECOND COURSE IN GENERAL TOPOLOGY CHAPTER I COMPLETE REGULARITY 1. Definitions and basic properties..... 3 2. Some examples..... 7 Exercises....9 CHAPTER II CONVERGENCE AND
Heikki Junnila, 2007-8/2014 A SECOND COURSE IN GENERAL TOPOLOGY CHAPTER I COMPLETE REGULARITY 1. Definitions and basic properties..... 3 2. Some examples..... 7 Exercises....9 CHAPTER II CONVERGENCE AND
Analysis III Theorems, Propositions & Lemmas... Oh My!
 Analysis III Theorems, Propositions & Lemmas... Oh My! Rob Gibson October 25, 2010 Proposition 1. If x = (x 1, x 2,...), y = (y 1, y 2,...), then is a distance. ( d(x, y) = x k y k p Proposition 2. In
Analysis III Theorems, Propositions & Lemmas... Oh My! Rob Gibson October 25, 2010 Proposition 1. If x = (x 1, x 2,...), y = (y 1, y 2,...), then is a distance. ( d(x, y) = x k y k p Proposition 2. In
In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend N to the integers
 Chapter The Real Numbers.. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend
Chapter The Real Numbers.. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend
Continuous functions that are nowhere differentiable
 Continuous functions that are nowhere differentiable S. Kesavan The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, CIT Campus, Taramani, Chennai - 600113. e-mail: kesh @imsc.res.in Abstract It is shown that the existence
Continuous functions that are nowhere differentiable S. Kesavan The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, CIT Campus, Taramani, Chennai - 600113. e-mail: kesh @imsc.res.in Abstract It is shown that the existence
Exam 2 extra practice problems
 Exam 2 extra practice problems (1) If (X, d) is connected and f : X R is a continuous function such that f(x) = 1 for all x X, show that f must be constant. Solution: Since f(x) = 1 for every x X, either
Exam 2 extra practice problems (1) If (X, d) is connected and f : X R is a continuous function such that f(x) = 1 for all x X, show that f must be constant. Solution: Since f(x) = 1 for every x X, either
5 Set Operations, Functions, and Counting
 5 Set Operations, Functions, and Counting Let N denote the positive integers, N 0 := N {0} be the non-negative integers and Z = N 0 ( N) the positive and negative integers including 0, Q the rational numbers,
5 Set Operations, Functions, and Counting Let N denote the positive integers, N 0 := N {0} be the non-negative integers and Z = N 0 ( N) the positive and negative integers including 0, Q the rational numbers,
Homework Assignment #2 for Prob-Stats, Fall 2018 Due date: Monday, October 22, 2018
 Homework Assignment #2 for Prob-Stats, Fall 2018 Due date: Monday, October 22, 2018 Topics: consistent estimators; sub-σ-fields and partial observations; Doob s theorem about sub-σ-field measurability;
Homework Assignment #2 for Prob-Stats, Fall 2018 Due date: Monday, October 22, 2018 Topics: consistent estimators; sub-σ-fields and partial observations; Doob s theorem about sub-σ-field measurability;
x 0 + f(x), exist as extended real numbers. Show that f is upper semicontinuous This shows ( ɛ, ɛ) B α. Thus
 Homework 3 Solutions, Real Analysis I, Fall, 2010. (9) Let f : (, ) [, ] be a function whose restriction to (, 0) (0, ) is continuous. Assume the one-sided limits p = lim x 0 f(x), q = lim x 0 + f(x) exist
Homework 3 Solutions, Real Analysis I, Fall, 2010. (9) Let f : (, ) [, ] be a function whose restriction to (, 0) (0, ) is continuous. Assume the one-sided limits p = lim x 0 f(x), q = lim x 0 + f(x) exist
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces
 Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS HAHN-BANACH THEOREM. F (m 2 ) + α m 2 + x 0
 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS HAHN-BANACH THEOREM If M is a linear subspace of a normal linear space X and if F is a bounded linear functional on M then F can be extended to M + [x 0 ] without changing its norm.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS HAHN-BANACH THEOREM If M is a linear subspace of a normal linear space X and if F is a bounded linear functional on M then F can be extended to M + [x 0 ] without changing its norm.
ON PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS POSSESSING A UNIQUE ORDER-COMPATIBLE TOPOLOGY
 ON PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS POSSESSING A UNIQUE ORDER-COMPATIBLE TOPOLOGY E. S. WÖLK1 1. Introduction. Let A" be a partially ordered set (poset) with respect to a relation ^, and possessing least and greatest
ON PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS POSSESSING A UNIQUE ORDER-COMPATIBLE TOPOLOGY E. S. WÖLK1 1. Introduction. Let A" be a partially ordered set (poset) with respect to a relation ^, and possessing least and greatest
Banach-Alaoglu theorems
 Banach-Alaoglu theorems László Erdős Jan 23, 2007 1 Compactness revisited In a topological space a fundamental property is the compactness (Kompaktheit). We recall the definition: Definition 1.1 A subset
Banach-Alaoglu theorems László Erdős Jan 23, 2007 1 Compactness revisited In a topological space a fundamental property is the compactness (Kompaktheit). We recall the definition: Definition 1.1 A subset
We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject
 p. 1 Math 490-01 Notes 5 Topology We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject expands, we will encounter various notions from analysis such as compactness, continuity,
p. 1 Math 490-01 Notes 5 Topology We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject expands, we will encounter various notions from analysis such as compactness, continuity,
The Kolmogorov extension theorem
 The Kolmogorov extension theorem Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto June 21, 2014 1 σ-algebras and semirings If X is a nonempty set, an algebra of sets on
The Kolmogorov extension theorem Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto June 21, 2014 1 σ-algebras and semirings If X is a nonempty set, an algebra of sets on
Math 3T03 - Topology
 Math 3T03 - Topology Sang Woo Park April 5, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction to topology 2 1.1 What is topology?.......................... 2 1.2 Set theory............................... 3 2 Functions 4 3
Math 3T03 - Topology Sang Woo Park April 5, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction to topology 2 1.1 What is topology?.......................... 2 1.2 Set theory............................... 3 2 Functions 4 3
DR.RUPNATHJI( DR.RUPAK NATH )
 Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Convergence Classes and Spaces of Partial Functions
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 10-2001 Convergence Classes and Spaces of Partial Functions Anthony K. Seda Roland
Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 10-2001 Convergence Classes and Spaces of Partial Functions Anthony K. Seda Roland
g 2 (x) (1/3)M 1 = (1/3)(2/3)M.
 COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
Another Riesz Representation Theorem
 Another Riesz Representation Theorem In these notes we prove (one version of) a theorem known as the Riesz Representation Theorem. Some people also call it the Riesz Markov Theorem. It expresses positive
Another Riesz Representation Theorem In these notes we prove (one version of) a theorem known as the Riesz Representation Theorem. Some people also call it the Riesz Markov Theorem. It expresses positive
Classes of Polish spaces under effective Borel isomorphism
 Classes of Polish spaces under effective Borel isomorphism Vassilis Gregoriades TU Darmstadt October 203, Vienna The motivation It is essential for the development of effective descriptive set theory to
Classes of Polish spaces under effective Borel isomorphism Vassilis Gregoriades TU Darmstadt October 203, Vienna The motivation It is essential for the development of effective descriptive set theory to
Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem
 56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
