Math 6120 Fall 2012 Assignment #1
|
|
|
- Junior Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 6120 Fall 2012 Assignment #1 Choose 10 of the problems below to submit by Weds., Sep. 5. Exercise 1. [Mun, 21, #10]. Show that the following are closed subsets of R 2 : (a) A = { (x, y) xy = 1 }, (b) S 1 = { (x, y) x 2 + y 2 = 1 }, and (c) B 2 = { (x, y) x 2 + y 2 1 }. (Hint: use the fact that the pre-image of a closed set under a continuous map is closed. You don t have to prove that polynomial functions from R n to R are continuous (but you should prove it for yourself if you haven t done a proof before).) Exercise 2. Let X be a topological space and x a point in X. Define a new space X whose underlying set is X and whose open subsets are the empty set and the open subsets of X containing x. Show that X is also a topological space. Exercise 3. Show that every metric on a finite set is always equivalent to the metric d(x, y) = 1. Conclude that a finite metric space has the discrete topology. Exercise 4. (a) Suppose that X is a topological space with the discrete topology and Y is any other topological space. Show that any function X Y is continuous. (b) Suppose that X is a topological space and Y is a topological space with the indiscrete topology. Show that any function X Y is continuous. (c) Let P be a point (with the unique topology on a one-element set) and let X be a topological space. Conclude from the above that any functions P X and X P are continuous. Exercise 5. Let (X, d) be a metric space. (a) Fix a positive number t. Let d (x, y) = min { d(x, y), t }. Show that d is also a metric on X. (b) Let d (x, y) = Show that this is a metric on X. d(x, y) 1 + d(x, y). 1
2 (c) Show that both of the above metrics are equivalent to d. Exercise 6. (a) Show that the following are metrics on R n : (a) The Euclidean metric, d(x, y) = x y. Cf. [Mun, 20, #9] for hints. } (b) The sup metric, d (x, y) = supi=1{ n xi y i. (c) The metric d (x, y) = n x i y i. (b) Show that all of the metrics described above are equivalent. i=1 Exercise 7. Show that if d and d are two equivalent 1 metrics on the same set X then 1 (a) a sequence in X converges in d if and only if it converges in d, and (b) the limits are the same. Exercise 8. Let Q be the set of rational numbers and fix a prime number p. Every non-zero rational number can be written in a unique way as ap n where n is an integer and a is a rational number that is prime to p. 2 Define ap n p = p n 0 p = 0. Show that defines a metric on Q. d(x, y) = x y p Exercise 9. [Mun, 20, #3]. Let X be a metric space with metric d. (a) Show that d : X X R is continuous. (b) Let X be a topological space with the same underlying set as X. Show that if d : X X R is continuous then the topology of X is finer than the topology of X. Exercise 10. Suppose that X is a topological space, x is a point in X, and x 1, x 2,... is a sequence of points in X. Does either of the following statements imply the other? Are they equivalent? (i) The point x is contained in the closure of the set S = { x 1, x 2,... } but not in S itself. (ii) The point x is the limit of the sequence x 1, x 2,.... Give proofs or counterexamples to justify your answer. 1 typo corrected the word equivalent was missing; thanks Shawn 2 This means that a = x where x and y are integers that are not divisible by p. y 2
3 Exercise 11. Let X be a topological space. Call a subset S of X closed in the sequential convergence (sc) topology if, whenever x 1, x 2,... is a sequence in S possessing a limit in X, the limit lies in S. (a) Show that this is a topology on X. (b) Let X be the topological space whose underlying set is X, but given the sc topology. Let f be the map X X 3 whose underlying function is the identity. Show that f is continuous. 3 (c) Demonstrate that the sc topology is not always the same as the original topology. You may want to use the following sequence of steps: (i) Let Y be an uncountable well-ordered set whose ordinality is equal to the first uncountable ordinal. Note that Y has no maximal element. Let X = Y { } be the union of Y and a maximal element. Declare that U X is open if U = or if there is some y Y such that U = { x X x y }. 4 Show that this is a topology on X. (ii) Let U be the complement of in X. Show that U is not closed. (iii) Show that the subset U of the last part is closed in the sc topology. (Hint: use the fact that for any increasing sequence of countable ordinals x 1 < x 2 < x 3 < there is a countable ordinal y such that x i < y for all i; you can prove this fact by observing that a countable union of countable sets is countable.) 4 (d) Show that the sc topology is the same as the original topology if X satisfies the first countability axiom (each point of X has a countable basis of open neighborhoods). Exercise 12. [Mun, 20, #6]. Let x = (x 1, x 2,...) be an element of R ω and ɛ (0, 1) a real number. Define U(x, ɛ) = (x 1 ɛ, x 1 + ɛ) (x 2 ɛ, x 2 + ɛ). (a) Show that U(x, ɛ) B d (x, ɛ) where d is the uniform metric on R ω. (Hint: show that U(x, ɛ) is not even open!) (b) Prove that 5 B d (x, ɛ) = δ<ɛ U(x, δ). 5 Exercise 13. Let X be a metric space. A Cauchy sequence in X is a sequence x 1, x 2,... such that for every ɛ > 0 there is a positive integer N having the property that d(x n, x m ) < ɛ for every n, m N. 3 typo corrected here 4 this was not phrased correctly before; thanks James Van Meter for this observation and clarification suggestions 5 typo corrected in the equation below; thanks Paul Lessard 3
4 (a) Let X be the set of Cauchy sequences in X. Define a relation on X by which x 1, x 2,... is related to y 1, y 2,... if, for any ɛ > 0, there exists a positive integer N such that d(x n, y n ) < ɛ for all n N. Show that this is an equialence relation. (b) Let x 1, x 2,... and y 1, y 2,... be two elements of X. Define d((x 1, x 2,...), (y 1, y 2,...)) = lim n d(x n, y n ). (c) Show that this is a well-defined function on X X. (Show that the limit exists.) (d) Show that this function is actually well-defined on the equivalence classes in X and makes X into a metric space. (e) Show that two sequence x 1, x 2,... and y 1, y 2,... are in the same equivalence class in X if and only if d((x 1, x 2,...), (y 1, y 2,...)) = 0. (f) Let X be the set of equivalence classes in X. Let i : X X that sends x X to the equivalence class of the sequence x, x, x,.... Show that i is injective and that its image is dense in X. X is known as the completion of the metric space X. Exercise 14. A pre-order on a set S is a relation that is reflexive and transitive. That is x x for all x S and if x y z then x z. (a) An element x of a topological space X is said to specialize to y S if y is contained in the closure of the set { x }. We write x y to mean that y is a specialization of x. Show that a closed set contains the specializations of all its elements. A set that contains all the specializations of all its elements is said to be closed under specialization. (b) Show that a subset of a finite topological space is closed if and only if it is closed under specialization. (c) Give an example of an infinite topological space and a subset that is closed under specialization but is not closed. (d) Show that there is a one-to-one correspondence between topologies on a finite set S and pre-orders on S. (Hint: Declare that x y if y is a specialization of x.) (e) Compute the number of topologies on a set with 2 elements, up to reordering of the elements. (f) Compute the number of topologies on a set with 3 elements, up to reordering. 4
5 References [Mun] James R. Munkres. Topology: a first course. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J.,
Problem Set 2: Solutions Math 201A: Fall 2016
 Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
Problem Set 2: s Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. (a) Prove that a closed subset of a complete metric space is complete. (b) Prove that a closed subset of a compact metric space is compact. (c) Prove that
2 Metric Spaces Definitions Exotic Examples... 3
 Contents 1 Vector Spaces and Norms 1 2 Metric Spaces 2 2.1 Definitions.......................................... 2 2.2 Exotic Examples...................................... 3 3 Topologies 4 3.1 Open Sets..........................................
Contents 1 Vector Spaces and Norms 1 2 Metric Spaces 2 2.1 Definitions.......................................... 2 2.2 Exotic Examples...................................... 3 3 Topologies 4 3.1 Open Sets..........................................
MH 7500 THEOREMS. (iii) A = A; (iv) A B = A B. Theorem 5. If {A α : α Λ} is any collection of subsets of a space X, then
 MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
The uniform metric on product spaces
 The uniform metric on product spaces Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto April 3, 2014 1 Metric topology If (X, d) is a metric space, a X, and r > 0, then
The uniform metric on product spaces Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto April 3, 2014 1 Metric topology If (X, d) is a metric space, a X, and r > 0, then
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project
 Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
1 Topology Definition of a topology Basis (Base) of a topology The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3
 Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Introduction to Topology
 Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP Basic Topology
 ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project
 Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Metric Spaces Math 413 Honors Project 1 Metric Spaces Definition 1.1 Let X be a set. A metric on X is a function d : X X R such that for all x, y, z X: i) d(x, y) = d(y, x); ii) d(x, y) = 0 if and only
Math General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions
 Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions Problem 1. Let X be a topological space. a. Show that the following properties of a subset A X are equivalent. 1. The closure of A in X has empty
Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions Problem 1. Let X be a topological space. a. Show that the following properties of a subset A X are equivalent. 1. The closure of A in X has empty
Solve EACH of the exercises 1-3
 Topology Ph.D. Entrance Exam, August 2011 Write a solution of each exercise on a separate page. Solve EACH of the exercises 1-3 Ex. 1. Let X and Y be Hausdorff topological spaces and let f: X Y be continuous.
Topology Ph.D. Entrance Exam, August 2011 Write a solution of each exercise on a separate page. Solve EACH of the exercises 1-3 Ex. 1. Let X and Y be Hausdorff topological spaces and let f: X Y be continuous.
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces
 7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
4 Countability axioms
 4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
Math 190: Fall 2014 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday 11/7/2014
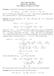 Math 90: Fall 04 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday /7/04 Problem : Recall that S n denotes the n-dimensional unit sphere: S n = {(x 0, x,..., x n ) R n+ : x 0 + x + + x n = }. Let N S n denote
Math 90: Fall 04 Homework 4 Solutions Due 5:00pm on Friday /7/04 Problem : Recall that S n denotes the n-dimensional unit sphere: S n = {(x 0, x,..., x n ) R n+ : x 0 + x + + x n = }. Let N S n denote
Real Analysis Notes. Thomas Goller
 Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Lecture 5 - Hausdorff and Gromov-Hausdorff Distance
 Lecture 5 - Hausdorff and Gromov-Hausdorff Distance August 1, 2011 1 Definition and Basic Properties Given a metric space X, the set of closed sets of X supports a metric, the Hausdorff metric. If A is
Lecture 5 - Hausdorff and Gromov-Hausdorff Distance August 1, 2011 1 Definition and Basic Properties Given a metric space X, the set of closed sets of X supports a metric, the Hausdorff metric. If A is
Sets and Functions. MATH 464/506, Real Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Sets and Functions
 Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination. Answer Key
 NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4
 FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
PROBLEMS. (b) (Polarization Identity) Show that in any inner product space
 1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2.
 MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2. This text is based on the following books: Topology by James Dugundgji Fundamental concepts of topology by Peter O Neil Elements of Mathematics: General Topology
MA651 Topology. Lecture 9. Compactness 2. This text is based on the following books: Topology by James Dugundgji Fundamental concepts of topology by Peter O Neil Elements of Mathematics: General Topology
Real Analysis Math 131AH Rudin, Chapter #1. Dominique Abdi
 Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
POINT SET TOPOLOGY. Definition 2 A set with a topological structure is a topological space (X, O)
 POINT SET TOPOLOGY Definition 1 A topological structure on a set X is a family O P(X) called open sets and satisfying (O 1 ) O is closed for arbitrary unions (O 2 ) O is closed for finite intersections.
POINT SET TOPOLOGY Definition 1 A topological structure on a set X is a family O P(X) called open sets and satisfying (O 1 ) O is closed for arbitrary unions (O 2 ) O is closed for finite intersections.
(1) Consider the space S consisting of all continuous real-valued functions on the closed interval [0, 1]. For f, g S, define
![(1) Consider the space S consisting of all continuous real-valued functions on the closed interval [0, 1]. For f, g S, define (1) Consider the space S consisting of all continuous real-valued functions on the closed interval [0, 1]. For f, g S, define](/thumbs/88/116259117.jpg) Homework, Real Analysis I, Fall, 2010. (1) Consider the space S consisting of all continuous real-valued functions on the closed interval [0, 1]. For f, g S, define ρ(f, g) = 1 0 f(x) g(x) dx. Show that
Homework, Real Analysis I, Fall, 2010. (1) Consider the space S consisting of all continuous real-valued functions on the closed interval [0, 1]. For f, g S, define ρ(f, g) = 1 0 f(x) g(x) dx. Show that
B 1 = {B(x, r) x = (x 1, x 2 ) H, 0 < r < x 2 }. (a) Show that B = B 1 B 2 is a basis for a topology on X.
 Math 6342/7350: Topology and Geometry Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. For each of the following topological spaces X i, determine whether X i and X i X i are homeomorphic. (a) X 1 = [0, 1] (b) X 2
Math 6342/7350: Topology and Geometry Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. For each of the following topological spaces X i, determine whether X i and X i X i are homeomorphic. (a) X 1 = [0, 1] (b) X 2
REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS
 REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS 1. AXIOMATIC STRUCTURE OF R Doğan Çömez The real number system is a complete ordered field, i.e., it is a set R which is endowed with addition and multiplication operations
REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS 1. AXIOMATIC STRUCTURE OF R Doğan Çömez The real number system is a complete ordered field, i.e., it is a set R which is endowed with addition and multiplication operations
MTG 5316/4302 FALL 2018 REVIEW FINAL
 MTG 5316/4302 FALL 2018 REVIEW FINAL JAMES KEESLING Problem 1. Define open set in a metric space X. Define what it means for a set A X to be connected in a metric space X. Problem 2. Show that if a set
MTG 5316/4302 FALL 2018 REVIEW FINAL JAMES KEESLING Problem 1. Define open set in a metric space X. Define what it means for a set A X to be connected in a metric space X. Problem 2. Show that if a set
Functional Analysis Exercise Class
 Functional Analysis Exercise Class Week 2 November 6 November Deadline to hand in the homeworks: your exercise class on week 9 November 13 November Exercises (1) Let X be the following space of piecewise
Functional Analysis Exercise Class Week 2 November 6 November Deadline to hand in the homeworks: your exercise class on week 9 November 13 November Exercises (1) Let X be the following space of piecewise
Metric Spaces and Topology
 Chapter 2 Metric Spaces and Topology From an engineering perspective, the most important way to construct a topology on a set is to define the topology in terms of a metric on the set. This approach underlies
Chapter 2 Metric Spaces and Topology From an engineering perspective, the most important way to construct a topology on a set is to define the topology in terms of a metric on the set. This approach underlies
Introduction to Proofs in Analysis. updated December 5, By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION
 Introduction to Proofs in Analysis updated December 5, 2016 By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION Purpose. These notes intend to introduce four main notions from
Introduction to Proofs in Analysis updated December 5, 2016 By Edoh Y. Amiran Following the outline of notes by Donald Chalice INTRODUCTION Purpose. These notes intend to introduce four main notions from
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR. MATHEMATICS 205A Part 1. I. Foundational material
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 1 Fall 2014 I. Foundational material I.1 : Basic set theory Problems from Munkres, 9, p. 64 2. (a (c For each of the first three parts, choose a 1 1 correspondence
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES FOR MATHEMATICS 205A Part 1 Fall 2014 I. Foundational material I.1 : Basic set theory Problems from Munkres, 9, p. 64 2. (a (c For each of the first three parts, choose a 1 1 correspondence
MAS3706 Topology. Revision Lectures, May I do not answer enquiries as to what material will be in the exam.
 MAS3706 Topology Revision Lectures, May 208 Z.A.Lykova It is essential that you read and try to understand the lecture notes from the beginning to the end. Many questions from the exam paper will be similar
MAS3706 Topology Revision Lectures, May 208 Z.A.Lykova It is essential that you read and try to understand the lecture notes from the beginning to the end. Many questions from the exam paper will be similar
ANALYSIS WORKSHEET II: METRIC SPACES
 ANALYSIS WORKSHEET II: METRIC SPACES Definition 1. A metric space (X, d) is a space X of objects (called points), together with a distance function or metric d : X X [0, ), which associates to each pair
ANALYSIS WORKSHEET II: METRIC SPACES Definition 1. A metric space (X, d) is a space X of objects (called points), together with a distance function or metric d : X X [0, ), which associates to each pair
MATH 426, TOPOLOGY. p 1.
 MATH 426, TOPOLOGY THE p-norms In this document we assume an extended real line, where is an element greater than all real numbers; the interval notation [1, ] will be used to mean [1, ) { }. 1. THE p
MATH 426, TOPOLOGY THE p-norms In this document we assume an extended real line, where is an element greater than all real numbers; the interval notation [1, ] will be used to mean [1, ) { }. 1. THE p
Some Background Material
 Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Contents Ordered Fields... 2 Ordered sets and fields... 2 Construction of the Reals 1: Dedekind Cuts... 2 Metric Spaces... 3
 Analysis Math Notes Study Guide Real Analysis Contents Ordered Fields 2 Ordered sets and fields 2 Construction of the Reals 1: Dedekind Cuts 2 Metric Spaces 3 Metric Spaces 3 Definitions 4 Separability
Analysis Math Notes Study Guide Real Analysis Contents Ordered Fields 2 Ordered sets and fields 2 Construction of the Reals 1: Dedekind Cuts 2 Metric Spaces 3 Metric Spaces 3 Definitions 4 Separability
Math 320-2: Midterm 2 Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 2015
 Math 30-: Midterm Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A metric on R with respect to which R is bounded. (b)
Math 30-: Midterm Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A metric on R with respect to which R is bounded. (b)
Chapter 2 Metric Spaces
 Chapter 2 Metric Spaces The purpose of this chapter is to present a summary of some basic properties of metric and topological spaces that play an important role in the main body of the book. 2.1 Metrics
Chapter 2 Metric Spaces The purpose of this chapter is to present a summary of some basic properties of metric and topological spaces that play an important role in the main body of the book. 2.1 Metrics
Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions
 Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions 1. Give an example of each of the following (and prove that your example indeed works): (a) A complete metric space that is bounded but not compact.
Economics 204 Fall 2012 Problem Set 3 Suggested Solutions 1. Give an example of each of the following (and prove that your example indeed works): (a) A complete metric space that is bounded but not compact.
Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9)
 The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9) MATH3961: Metric Spaces (Advanced) Semester 1, 2018 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/sm/math3961/
The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 8 (Week 9) MATH3961: Metric Spaces (Advanced) Semester 1, 2018 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/sm/math3961/
CARDINALITY OF THE SET OF REAL FUNCTIONS WITH A GIVEN CONTINUITY SET
 CARDINALITY OF THE SET OF REAL FUNCTIONS WITH A GIVEN CONTINUITY SET JIAMING CHEN AND SAM SMITH Abstract. Expanding on an old result of W. H. Young, we determine the cardinality of the set of functions
CARDINALITY OF THE SET OF REAL FUNCTIONS WITH A GIVEN CONTINUITY SET JIAMING CHEN AND SAM SMITH Abstract. Expanding on an old result of W. H. Young, we determine the cardinality of the set of functions
Topology. Xiaolong Han. Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA address:
 Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Definition 2.1. A metric (or distance function) defined on a non-empty set X is a function d: X X R that satisfies: For all x, y, and z in X :
 MATH 337 Metric Spaces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a non-empty set. The elements of X shall be called points. We shall define the general means of determining the distance between two points. Throughout we
MATH 337 Metric Spaces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a non-empty set. The elements of X shall be called points. We shall define the general means of determining the distance between two points. Throughout we
11691 Review Guideline Real Analysis. Real Analysis. - According to Principles of Mathematical Analysis by Walter Rudin (Chapter 1-4)
 Real Analysis - According to Principles of Mathematical Analysis by Walter Rudin (Chapter 1-4) 1 The Real and Complex Number Set: a collection of objects. Proper subset: if A B, then call A a proper subset
Real Analysis - According to Principles of Mathematical Analysis by Walter Rudin (Chapter 1-4) 1 The Real and Complex Number Set: a collection of objects. Proper subset: if A B, then call A a proper subset
Mid Term-1 : Practice problems
 Mid Term-1 : Practice problems These problems are meant only to provide practice; they do not necessarily reflect the difficulty level of the problems in the exam. The actual exam problems are likely to
Mid Term-1 : Practice problems These problems are meant only to provide practice; they do not necessarily reflect the difficulty level of the problems in the exam. The actual exam problems are likely to
CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000
 CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000 Announcement: Section 1.2, Questions 3,5 have been deferred from Assignment 1 to Assignment 2. Section 1.4, Question 5 has been dropped entirely. 1. Review of Wednesday class
CLASS NOTES FOR APRIL 14, 2000 Announcement: Section 1.2, Questions 3,5 have been deferred from Assignment 1 to Assignment 2. Section 1.4, Question 5 has been dropped entirely. 1. Review of Wednesday class
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES. Contents. 1. Sets Functions Countability Axiom of choice Equivalence relations 9
 MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
p-adic Analysis Compared to Real Lecture 1
 p-adic Analysis Compared to Real Lecture 1 Felix Hensel, Waltraud Lederle, Simone Montemezzani October 12, 2011 1 Normed Fields & non-archimedean Norms Definition 1.1. A metric on a non-empty set X is
p-adic Analysis Compared to Real Lecture 1 Felix Hensel, Waltraud Lederle, Simone Montemezzani October 12, 2011 1 Normed Fields & non-archimedean Norms Definition 1.1. A metric on a non-empty set X is
Math 117: Topology of the Real Numbers
 Math 117: Topology of the Real Numbers John Douglas Moore November 10, 2008 The goal of these notes is to highlight the most important topics presented in Chapter 3 of the text [1] and to provide a few
Math 117: Topology of the Real Numbers John Douglas Moore November 10, 2008 The goal of these notes is to highlight the most important topics presented in Chapter 3 of the text [1] and to provide a few
Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 2015.
 Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 015. (1) Let f n : D R be a sequence of functions with domain D R n. Recall that f n f uniformly if and only if for all ɛ > 0, there is an N = N(ɛ) so that if n
Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 015. (1) Let f n : D R be a sequence of functions with domain D R n. Recall that f n f uniformly if and only if for all ɛ > 0, there is an N = N(ɛ) so that if n
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces
 Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
Lecture Notes on Metric Spaces Math 117: Summer 2007 John Douglas Moore Our goal of these notes is to explain a few facts regarding metric spaces not included in the first few chapters of the text [1],
Chapter One. The Real Number System
 Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Problem 1A. Use residues to compute. dx x
 Problem 1A. A non-empty metric space X is said to be connected if it is not the union of two non-empty disjoint open subsets, and is said to be path-connected if for every two points a, b there is a continuous
Problem 1A. A non-empty metric space X is said to be connected if it is not the union of two non-empty disjoint open subsets, and is said to be path-connected if for every two points a, b there is a continuous
We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject
 p. 1 Math 490-01 Notes 5 Topology We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject expands, we will encounter various notions from analysis such as compactness, continuity,
p. 1 Math 490-01 Notes 5 Topology We will begin our study of topology from a set-theoretic point of view. As the subject expands, we will encounter various notions from analysis such as compactness, continuity,
ABSTRACT INTEGRATION CHAPTER ONE
 CHAPTER ONE ABSTRACT INTEGRATION Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means. Suggestions and errors are invited and can be mailed
CHAPTER ONE ABSTRACT INTEGRATION Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means. Suggestions and errors are invited and can be mailed
2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom
 60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
The discrete and indiscrete topologies on any set are zero-dimensional. The Sorgenfrey line
 p. 1 Math 525 Notes on section 17 Isolated points In general, a point x in a topological space (X,τ) is called an isolated point iff the set {x} is τ-open. A topological space is called discrete iff every
p. 1 Math 525 Notes on section 17 Isolated points In general, a point x in a topological space (X,τ) is called an isolated point iff the set {x} is τ-open. A topological space is called discrete iff every
MATH 3300 Test 1. Name: Student Id:
 Name: Student Id: There are nine problems (check that you have 9 pages). Solutions are expected to be short. In the case of proofs, one or two short paragraphs should be the average length. Write your
Name: Student Id: There are nine problems (check that you have 9 pages). Solutions are expected to be short. In the case of proofs, one or two short paragraphs should be the average length. Write your
Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued)
 21. The Metric Topology (cont.) 1 Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued) Note. In this section we give a number of results for metric spaces which are familar from calculus and real analysis. We also
21. The Metric Topology (cont.) 1 Section 21. The Metric Topology (Continued) Note. In this section we give a number of results for metric spaces which are familar from calculus and real analysis. We also
CHAPTER 7. Connectedness
 CHAPTER 7 Connectedness 7.1. Connected topological spaces Definition 7.1. A topological space (X, T X ) is said to be connected if there is no continuous surjection f : X {0, 1} where the two point set
CHAPTER 7 Connectedness 7.1. Connected topological spaces Definition 7.1. A topological space (X, T X ) is said to be connected if there is no continuous surjection f : X {0, 1} where the two point set
TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519
 TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519 The purpose of these notes is to give a mostly self-contained topological background for the study of the representations of locally compact totally disconnected groups, as
TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519 The purpose of these notes is to give a mostly self-contained topological background for the study of the representations of locally compact totally disconnected groups, as
Final Exam Review. 2. Let A = {, { }}. What is the cardinality of A? Is
 1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
Part III. 10 Topological Space Basics. Topological Spaces
 Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
Part III 10 Topological Space Basics Topological Spaces Using the metric space results above as motivation we will axiomatize the notion of being an open set to more general settings. Definition 10.1.
Math 201 Topology I. Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran
 Math 201 Topology I Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran hicham.gebran@yahoo.com Lebanese University, Fanar, Fall 2015-2016 http://fs2.ul.edu.lb/math http://hichamgebran.wordpress.com 2 Introduction and
Math 201 Topology I Lecture notes of Prof. Hicham Gebran hicham.gebran@yahoo.com Lebanese University, Fanar, Fall 2015-2016 http://fs2.ul.edu.lb/math http://hichamgebran.wordpress.com 2 Introduction and
AN EXPLORATION OF THE METRIZABILITY OF TOPOLOGICAL SPACES
 AN EXPLORATION OF THE METRIZABILITY OF TOPOLOGICAL SPACES DUSTIN HEDMARK Abstract. A study of the conditions under which a topological space is metrizable, concluding with a proof of the Nagata Smirnov
AN EXPLORATION OF THE METRIZABILITY OF TOPOLOGICAL SPACES DUSTIN HEDMARK Abstract. A study of the conditions under which a topological space is metrizable, concluding with a proof of the Nagata Smirnov
Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics.
 MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
Math 426 Homework 4 Due 3 November 2017
 Math 46 Homework 4 Due 3 November 017 1. Given a metric space X,d) and two subsets A,B, we define the distance between them, dista,b), as the infimum inf a A, b B da,b). a) Prove that if A is compact and
Math 46 Homework 4 Due 3 November 017 1. Given a metric space X,d) and two subsets A,B, we define the distance between them, dista,b), as the infimum inf a A, b B da,b). a) Prove that if A is compact and
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions
 18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
Math 117: Continuity of Functions
 Math 117: Continuity of Functions John Douglas Moore November 21, 2008 We finally get to the topic of ɛ δ proofs, which in some sense is the goal of the course. It may appear somewhat laborious to use
Math 117: Continuity of Functions John Douglas Moore November 21, 2008 We finally get to the topic of ɛ δ proofs, which in some sense is the goal of the course. It may appear somewhat laborious to use
Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1
 Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1 2.1) By definition, 2 Ω is the set of all subsets of Ω. Therefore, to show that 2 Ω is a σ-algebra we must show that the conditions of the definition σ-algebra are
Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1 2.1) By definition, 2 Ω is the set of all subsets of Ω. Therefore, to show that 2 Ω is a σ-algebra we must show that the conditions of the definition σ-algebra are
HW 4 SOLUTIONS. , x + x x 1 ) 2
 HW 4 SOLUTIONS The Way of Analysis p. 98: 1.) Suppose that A is open. Show that A minus a finite set is still open. This follows by induction as long as A minus one point x is still open. To see that A
HW 4 SOLUTIONS The Way of Analysis p. 98: 1.) Suppose that A is open. Show that A minus a finite set is still open. This follows by induction as long as A minus one point x is still open. To see that A
Profinite Groups. Hendrik Lenstra. 1. Introduction
 Profinite Groups Hendrik Lenstra 1. Introduction We begin informally with a motivation, relating profinite groups to the p-adic numbers. Let p be a prime number, and let Z p denote the ring of p-adic integers,
Profinite Groups Hendrik Lenstra 1. Introduction We begin informally with a motivation, relating profinite groups to the p-adic numbers. Let p be a prime number, and let Z p denote the ring of p-adic integers,
INTRODUCTION TO TOPOLOGY, MATH 141, PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO TOPOLOGY, MATH 141, PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem 1. Give an example of a non-metrizable topological space. Explain. Problem 2. Introduce a topology on N by declaring that open sets are, N,
INTRODUCTION TO TOPOLOGY, MATH 141, PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem 1. Give an example of a non-metrizable topological space. Explain. Problem 2. Introduce a topology on N by declaring that open sets are, N,
In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need to extend N to the integers
 Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1. Some Preliminaries Discussion: The Irrationality of 2. We begin with the natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3, }. In N we can do addition, but in order to do subtraction we need
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE. B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER. (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK 1. Find the number of elements in the power
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK 1. Find the number of elements in the power
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS
 3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
3 COUNTABILITY AND CONNECTEDNESS AXIOMS Definition 3.1 Let X be a topological space. A subset D of X is dense in X iff D = X. X is separable iff it contains a countable dense subset. X satisfies the first
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE
 MAT641- MSC Mathematics, MNIT Jaipur FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR 1. Normed space Norm generalizes the concept of length in an arbitrary
MAT641- MSC Mathematics, MNIT Jaipur FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR 1. Normed space Norm generalizes the concept of length in an arbitrary
STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES
 Undergraduate Research Opportunity Programme in Science STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES Submitted by Dai Bo Supervised by Dr. Wong Yan-loi Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Academic
Undergraduate Research Opportunity Programme in Science STRONGLY CONNECTED SPACES Submitted by Dai Bo Supervised by Dr. Wong Yan-loi Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Academic
Numerical Sequences and Series
 Numerical Sequences and Series Written by Men-Gen Tsai email: b89902089@ntu.edu.tw. Prove that the convergence of {s n } implies convergence of { s n }. Is the converse true? Solution: Since {s n } is
Numerical Sequences and Series Written by Men-Gen Tsai email: b89902089@ntu.edu.tw. Prove that the convergence of {s n } implies convergence of { s n }. Is the converse true? Solution: Since {s n } is
Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets The Real Numbers The Cantor Set
 Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets Definition. An initial segment is {n N n n 0 }. Definition. A finite set can be put into one-to-one correspondence with an initial segment. The empty set is also considered
Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets Definition. An initial segment is {n N n n 0 }. Definition. A finite set can be put into one-to-one correspondence with an initial segment. The empty set is also considered
Set, functions and Euclidean space. Seungjin Han
 Set, functions and Euclidean space Seungjin Han September, 2018 1 Some Basics LOGIC A is necessary for B : If B holds, then A holds. B A A B is the contraposition of B A. A is sufficient for B: If A holds,
Set, functions and Euclidean space Seungjin Han September, 2018 1 Some Basics LOGIC A is necessary for B : If B holds, then A holds. B A A B is the contraposition of B A. A is sufficient for B: If A holds,
MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1
 MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1 1. In R 3, find d 1 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)), d 2 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)) and d ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)). 2. In R 4, show that d 1 ((4, 4, 4, 6), (0, 0, 0, 0)) =
MAS331: Metric Spaces Problems on Chapter 1 1. In R 3, find d 1 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)), d 2 ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)) and d ((3, 1, 4), (2, 7, 1)). 2. In R 4, show that d 1 ((4, 4, 4, 6), (0, 0, 0, 0)) =
Topology Final Exam. Instructor: W. D. Gillam Date: January 15, 2014
 Topology Final Exam Instructor: W. D. Gillam Date: January 15, 2014 Instructions: Print your name and Topology Final Exam in the upper right corner of the first page. Also be sure to put your name in the
Topology Final Exam Instructor: W. D. Gillam Date: January 15, 2014 Instructions: Print your name and Topology Final Exam in the upper right corner of the first page. Also be sure to put your name in the
Metric Spaces. Exercises Fall 2017 Lecturer: Viveka Erlandsson. Written by M.van den Berg
 Metric Spaces Exercises Fall 2017 Lecturer: Viveka Erlandsson Written by M.van den Berg School of Mathematics University of Bristol BS8 1TW Bristol, UK 1 Exercises. 1. Let X be a non-empty set, and suppose
Metric Spaces Exercises Fall 2017 Lecturer: Viveka Erlandsson Written by M.van den Berg School of Mathematics University of Bristol BS8 1TW Bristol, UK 1 Exercises. 1. Let X be a non-empty set, and suppose
The Heine-Borel and Arzela-Ascoli Theorems
 The Heine-Borel and Arzela-Ascoli Theorems David Jekel October 29, 2016 This paper explains two important results about compactness, the Heine- Borel theorem and the Arzela-Ascoli theorem. We prove them
The Heine-Borel and Arzela-Ascoli Theorems David Jekel October 29, 2016 This paper explains two important results about compactness, the Heine- Borel theorem and the Arzela-Ascoli theorem. We prove them
Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem
 56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS
 MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATH OPTION, Spring 018 Full points can be obtained for correct answers to 8 questions. Each numbered question (which may have several parts) is worth 0 points.
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATH OPTION, Spring 018 Full points can be obtained for correct answers to 8 questions. Each numbered question (which may have several parts) is worth 0 points.
2. Metric Spaces. 2.1 Definitions etc.
 2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
2.2 Lowenheim-Skolem-Tarski theorems
 Logic SEP: Day 1 July 15, 2013 1 Some references Syllabus: http://www.math.wisc.edu/graduate/guide-qe Previous years qualifying exams: http://www.math.wisc.edu/ miller/old/qual/index.html Miller s Moore
Logic SEP: Day 1 July 15, 2013 1 Some references Syllabus: http://www.math.wisc.edu/graduate/guide-qe Previous years qualifying exams: http://www.math.wisc.edu/ miller/old/qual/index.html Miller s Moore
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall F(x) = 1 x. f(t)dt. t 1 2. tf 2 (t)dt. and g(t, x) = 2 t. 2 t
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
Course 212: Academic Year Section 1: Metric Spaces
 Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9;
 Math 553 - Topology Todd Riggs Assignment 2 Sept 17, 2014 Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9; 17.2) Show that if A is closed in Y and
Math 553 - Topology Todd Riggs Assignment 2 Sept 17, 2014 Problems - Section 17-2, 4, 6c, 9, 10, 13, 14; Section 18-1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10; Section 19-1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9; 17.2) Show that if A is closed in Y and
Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210)
 Background Material 1 Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210) Note. These notes contain several definitions, theorems, and examples from Analysis I (MATH 4217/5217) which you must know for
Background Material 1 Essential Background for Real Analysis I (MATH 5210) Note. These notes contain several definitions, theorems, and examples from Analysis I (MATH 4217/5217) which you must know for
MAT327 Big List. Ivan Khatchatourian Department of Mathematics University of Toronto. August 20, 2018
 MAT327 Big List Ivan Khatchatourian Department of Mathematics University of Toronto August 20, 2018 This is a large, constantly growing list of problems in basic point set topology. This list will include
MAT327 Big List Ivan Khatchatourian Department of Mathematics University of Toronto August 20, 2018 This is a large, constantly growing list of problems in basic point set topology. This list will include
Existence of a Limit on a Dense Set, and. Construction of Continuous Functions on Special Sets
 Existence of a Limit on a Dense Set, and Construction of Continuous Functions on Special Sets REU 2012 Recap: Definitions Definition Given a real-valued function f, the limit of f exists at a point c R
Existence of a Limit on a Dense Set, and Construction of Continuous Functions on Special Sets REU 2012 Recap: Definitions Definition Given a real-valued function f, the limit of f exists at a point c R
1.4 Cardinality. Tom Lewis. Fall Term Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term / 9
 1.4 Cardinality Tom Lewis Fall Term 2006 Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 1 / 9 Outline 1 Functions 2 Cardinality 3 Cantor s theorem Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 2 / 9 Functions
1.4 Cardinality Tom Lewis Fall Term 2006 Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 1 / 9 Outline 1 Functions 2 Cardinality 3 Cantor s theorem Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 2 / 9 Functions
Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory)
 Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory) VI.1 : Indexed families and set theoretic operations (Halmos, 4, 8 9; Lipschutz, 5.3 5.4) Lipschutz : 5.3 5.6, 5.29 5.32, 9.14 1. Generalize
Exercises for Unit VI (Infinite constructions in set theory) VI.1 : Indexed families and set theoretic operations (Halmos, 4, 8 9; Lipschutz, 5.3 5.4) Lipschutz : 5.3 5.6, 5.29 5.32, 9.14 1. Generalize
Maths 212: Homework Solutions
 Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Maths 212: Homework Solutions 1. The definition of A ensures that x π for all x A, so π is an upper bound of A. To show it is the least upper bound, suppose x < π and consider two cases. If x < 1, then
Solutions to Tutorial 7 (Week 8)
 The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 7 (Week 8) MATH2962: Real and Complex Analysis (Advanced) Semester 1, 2017 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/im/math2962/
The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial 7 (Week 8) MATH2962: Real and Complex Analysis (Advanced) Semester 1, 2017 Web Page: http://www.maths.usyd.edu.au/u/ug/im/math2962/
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009.
 Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
